The Relationship between p-tau217, p-tau231, and p-tau205 in the Human Brain Is Affected by the Cellular Environment and Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Individuals Included in the Study: Cohort I and Cohort II
2.2. Brain Sample Preparation
2.3. Immunostaining
2.4. Analysis of Co-Localization between p-Tau Variants
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
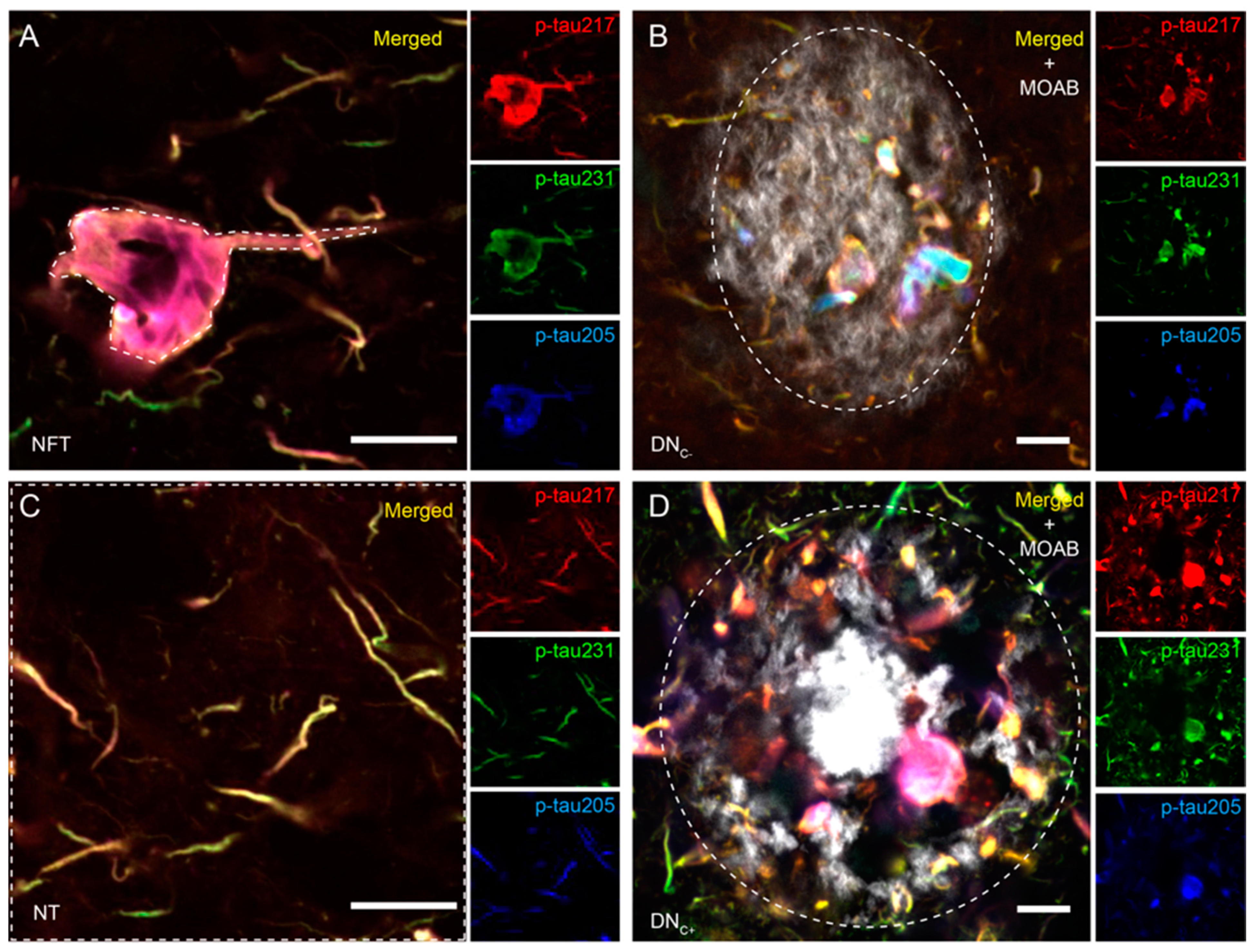
3.1. Co-Localizations between p-Tau Variants Differ between Tau Structures
3.2. Co-Localizations between p-Tau Variants in NTs Are Altered in AD Patients
3.3. AD Pathology Alters the Proportions of the p-Tau Variants
3.4. Analysis of Correlations between p-Tau, Aß, and NFT Scores
4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DeTure, M.A.; Dickson, D.W. The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.S.; Hothersall, J.; Crosby, J.; Simpson, T.J.; Thomas, C.M. Tandemly duplicated acyl carrier proteins, which increase polyketide antibiotic production, can apparently function either in parallel or in series. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 6399–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, C.M.; Lowe, V.J.; Murray, M.E. Visualization of neurofibrillary tangle maturity in Alzheimer’s disease: A clinicopathologic perspective for biomarker research. Alzheimers Dement. 2021, 17, 1554–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.L.; Murray, J.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Continuity of neuropil threads with tangle-bearing and tangle-free neurons in Alzheimer disease cortex. A confocal laser scanning microscopy study. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1993, 18, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, J.C.; Chin, D.; Edwards, A.M.; Sampson, V.; Harper, C.; Morrison, J. Dystrophic neurite formation associated with age-related beta amyloid deposition in the neocortex: Clues to the genesis of neurofibrillary pathology. Exp. Neurol. 1996, 141, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergeant, N.; Delacourte, A.; Buee, L. Tau protein as a differential biomarker of tauopathies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1739, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mandelkow, E. Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Zetterberg, H.; Lopera, F.; Stomrud, E.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Serrano, G.E.; Leuzy, A.; et al. Discriminative Accuracy of Plasma Phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer Disease vs Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. JAMA 2020, 324, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Calvet, M.; Karikari, T.K.; Ashton, N.J.; Lantero Rodriguez, J.; Mila-Aloma, M.; Gispert, J.D.; Salvado, G.; Minguillon, C.; Fauria, K.; Shekari, M.; et al. Novel tau biomarkers phosphorylated at T181, T217 or T231 rise in the initial stages of the preclinical Alzheimer’s continuum when only subtle changes in Abeta pathology are detected. EMBO Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mila-Aloma, M.; Salvado, G.; Gispert, J.D.; Vilor-Tejedor, N.; Grau-Rivera, O.; Sala-Vila, A.; Sanchez-Benavides, G.; Arenaza-Urquijo, E.M.; Crous-Bou, M.; Gonzalez-de-Echavarri, J.M.; et al. Amyloid beta, tau, synaptic, neurodegeneration, and glial biomarkers in the preclinical stage of the Alzheimer’s continuum. Alzheimers Dement. 2020, 16, 1358–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Bali, D.; Ashton, N.J.; Barthelemy, N.R.; Vanbrabant, J.; Stoops, E.; Vanmechelen, E.; He, Y.; Dolado, A.O.; Triana-Baltzer, G.; et al. Head-to-head comparison of 10 plasma phospho-tau assays in prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2023, 146, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, N.J.; Janelidze, S.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Binette, A.P.; Strandberg, O.; Brum, W.S.; Karikari, T.K.; Gonzalez-Ortiz, F.; Di Molfetta, G.; Meda, F.J.; et al. Differential roles of Abeta42/40, p-tau231 and p-tau217 for Alzheimer’s trial selection and disease monitoring. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Janelidze, S.; Bateman, R.J.; Smith, R.; Stomrud, E.; Serrano, G.E.; Reiman, E.M.; Palmqvist, S.; Dage, J.L.; Beach, T.G.; et al. Soluble P-tau217 reflects amyloid and tau pathology and mediates the association of amyloid with tau. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mila-Aloma, M.; Ashton, N.J.; Shekari, M.; Salvado, G.; Ortiz-Romero, P.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Vanmechelen, E.; et al. Plasma p-tau231 and p-tau217 as state markers of amyloid-beta pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1797–1801, Publisher Correction: Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salvado, G.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Ashton, N.J.; Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Reiman, E.M.; Zetterberg, H.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Janelidze, S.; Blennow, K.; et al. Specific associations between plasma biomarkers and postmortem amyloid plaque and tau tangle loads. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e17123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennstrom, M.; Janelidze, S.; Nilsson, K.P.R.; Netherlands Brain, B.; Serrano, G.E.; Beach, T.G.; Dage, J.L.; Hansson, O. Cellular localization of p-tau217 in brain and its association with p-tau217 plasma levels. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2022, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelemy, N.R.; Li, Y.; Joseph-Mathurin, N.; Gordon, B.A.; Hassenstab, J.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Buckles, V.; Fagan, A.M.; Perrin, R.J.; Goate, A.M.; et al. A soluble phosphorylated tau signature links tau, amyloid and the evolution of stages of dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, J.F.; Barthelemy, N.; Horie, K.; Gordon, B.A.; Kilgore, C.; Aschenbrenner, A.; Cruchaga, C.; Xiong, C.; Joseph-Mathurin, N.; Hassenstab, J.; et al. CSF Tau phosphorylation at Thr205 is associated with loss of white matter integrity in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 168, 105714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthelemy, N.R.; Saef, B.; Li, Y.; Gordon, B.A.; He, Y.; Horie, K.; Stomrud, E.; Salvado, G.; Janelidze, S.; Sato, C.; et al. CSF tau phosphorylation occupancies at T217 and T205 represent improved biomarkers of amyloid and tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Montoliu-Gaya, L.; Benedet, A.L.; Vrillon, A.; Dumurgier, J.; Cognat, E.; Brum, W.S.; Rahmouni, N.; Stevenson, J.; Servaes, S.; et al. CSF p-tau205: A biomarker of tau pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2024, 147, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Serrano, G.; Shill, H.A.; Walker, D.G.; Lue, L.; Roher, A.E.; Dugger, B.N.; Maarouf, C.; et al. Arizona Study of Aging and Neurodegenerative Disorders and Brain and Body Donation Program. Neuropathology 2015, 35, 354–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consensus Recommendations for the Postmortem Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18, S1–S2. [Google Scholar]
- Mirra, S.S.; Heyman, A.; McKeel, D.; Sumi, S.M.; Crain, B.J.; Brownlee, L.M.; Vogel, F.S.; Hughes, J.P.; van Belle, G.; Berg, L. The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1991, 41, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical, A. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, K.W.; Kamocka, M.M.; McDonald, J.H. A practical guide to evaluating colocalization in biological microscopy. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, C723–C742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Lendel, C. Extracellular protein components of amyloid plaques and their roles in Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.A. Beta-amyloid plaques: Stages in life history or independent origin? Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 1998, 9, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crary, J.F.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Schneider, J.A.; Abisambra, J.F.; Abner, E.L.; Alafuzoff, I.; Arnold, S.E.; Attems, J.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; et al. Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): A common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 128, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costoya-Sánchez, A.; Moscoso, A.; Silva-Rodríguez, J.; Pontecorvo, M.J.; Devous, M.D.; Aguiar, P.; Schöll, M.; Grothe, M.J.; Weiner, M.W.; Aisen, P.; et al. Increased Medial Temporal Tau Positron Emission Tomography Uptake in the Absence of Amyloid-beta Positivity. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajbanshi, B.; Guruacharya, A.; Mandell, J.W.; Bloom, G.S. Localization, induction, and cellular effects of tau phosphorylated at threonine 217. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 2874–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neddens, J.; Temmel, M.; Flunkert, S.; Kerschbaumer, B.; Hoeller, C.; Loeffler, T.; Niederkofler, V.; Daum, G.; Attems, J.; Hutter-Paier, B. Phosphorylation of different tau sites during progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, N.J.; Pascoal, T.A.; Karikari, T.K.; Benedet, A.L.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Brinkmalm, G.; Snellman, A.; Scholl, M.; Troakes, C.; Hye, A.; et al. Plasma p-tau231: A new biomarker for incipient Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot, C.; Smith, R.; Stomrud, E.; Binette, A.P.; Leuzy, A.; Wuestefeld, A.; Wisse, L.E.M.; Palmqvist, S.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Janelidze, S.; et al. Phospho-tau with subthreshold tau-PET predicts increased tau accumulation rates in amyloid-positive individuals. Brain 2023, 146, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teylan, M.; Mock, C.; Gauthreaux, K.; Chen, Y.C.; Chan, K.C.G.; Hassenstab, J.; Besser, L.M.; Kukull, W.A.; Crary, J.F. Cognitive trajectory in mild cognitive impairment due to primary age-related tauopathy. Brain 2020, 143, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, C.M.; Labuzan, S.A.; Crook, J.E.; Siddiqui, H.; Castanedes-Casey, M.; Lachner, C.; Petersen, R.C.; Duara, R.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; Dickson, D.W.; et al. Phosphorylated tau sites that are elevated in Alzheimer’s disease fluid biomarkers are visualized in early neurofibrillary tangle maturity levels in the post mortem brain. Alzheimers Dement. 2022, 19, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cohort I | Cohort II | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC (n = 5) | AD (n = 11) | PART (n = 12) | ADint (n = 21) | ADhigh (n = 11) | |
| Age (years) | 84 ± 8 | 82 ± 10 | 84 ± 9 | 85 ± 7 | 83 ± 6 |
| Females (%) | 40 | 45 | 67 | 48 | 9 |
| APOE4 (%) | 0 * | 45 † | 17 | 52 | 73 |
| MMSE (scores) | - | - | 25 ± 7 | 25 ± 9 | 17 ± 6 |
| Antibody | Antigen | Clone | Specie | Dilution | Incubation Time | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-tau217 | IBA413-biotin | Rabbit | 1:500 | Overnight | Eli Lilly | |
| p-tau231 | ADx253 | Mouse | 1:200 | Overnight | ADx Neuroscience | |
| p-tau205 | 44-738G | Rabbit | 1:200 | Overnight | Invitrogen | |
| Dye | Target | |||||
| β-sheets | Methoxi-X04 | - | 1:5000 | 1 h | TOCRIS |
| EC | DN (n = 29) | NT (n = 29) | NFT (n = 29) | ||||||
| 217/231 | 217/205 | 231/205 | 217/231 | 217/205 | 231/205 | 217/231 | 217/205 | 231/205 | |
| NFT-Tot | ns | ns | ns | r = −0.649 ***a | r = −0.522 ** | ns | ns | ns | r = −0.444 * |
| NFT-EC | ns | ns | ns | r = −0.420 * | r = −0.436 * | ns | ns | ns | r = −0.536 ** |
| ITG | DN (n = 29) | NT (n = 29) | NFT (n = 29) | ||||||
| 217/231 | 217/205 | 231/205 | 217/231 | 217/205 | 231/205 | 217/231 | 217/205 | 231/205 | |
| Aß-Tot | ns | ns | ns | r = −0.461 * | r = −0.558 *a | r = −0.667 **a | ns | ns | ns |
| Aß-T | ns | ns | ns | r = −0.462 * | r = −0.647 **a | r = −0.721 ***a | r = −0.476 * | ns | r = −0.552 *a |
| NFT-Tot | ns | ns | r = −0.586 * | r = −0.491 *a | r = −0.486 *a | r = −0.624 **a | ns | ns | r = −0.461 *a |
| NFT-T | ns | ns | r = −0.626 * | ns | r = −0.535 *a | r = −0.613 **a | ns | ns | r = −0.484 *a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wennström, M.; Schultz, N.; Gallardo, P.M.; The Netherlands Brain Bank; Serrano, G.E.; Beach, T.G.; Bose, S.; Hansson, O. The Relationship between p-tau217, p-tau231, and p-tau205 in the Human Brain Is Affected by the Cellular Environment and Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. Cells 2024, 13, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13040331
Wennström M, Schultz N, Gallardo PM, The Netherlands Brain Bank, Serrano GE, Beach TG, Bose S, Hansson O. The Relationship between p-tau217, p-tau231, and p-tau205 in the Human Brain Is Affected by the Cellular Environment and Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. Cells. 2024; 13(4):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13040331
Chicago/Turabian StyleWennström, Malin, Nina Schultz, Paula Mille Gallardo, The Netherlands Brain Bank, Geidy E. Serrano, Thomas G. Beach, Suchira Bose, and Oskar Hansson. 2024. "The Relationship between p-tau217, p-tau231, and p-tau205 in the Human Brain Is Affected by the Cellular Environment and Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology" Cells 13, no. 4: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13040331
APA StyleWennström, M., Schultz, N., Gallardo, P. M., The Netherlands Brain Bank, Serrano, G. E., Beach, T. G., Bose, S., & Hansson, O. (2024). The Relationship between p-tau217, p-tau231, and p-tau205 in the Human Brain Is Affected by the Cellular Environment and Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. Cells, 13(4), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13040331







