Protecting Orthopaedic Implants from Infection: Antimicrobial Peptide Mel4 Is Non-Toxic to Bone Cells and Reduces Bacterial Colonisation When Bound to Plasma Ion-Implanted 3D-Printed PAEK Polymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. PIII Treatment
2.3. Contact Angle Measurements
2.4. Peptide Immobilisation
2.5. Antimicrobial Studies
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Cell Adhesion
2.8. Proliferation and Mineralisation
2.9. Cytotoxicity of Unbound Mel4
2.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
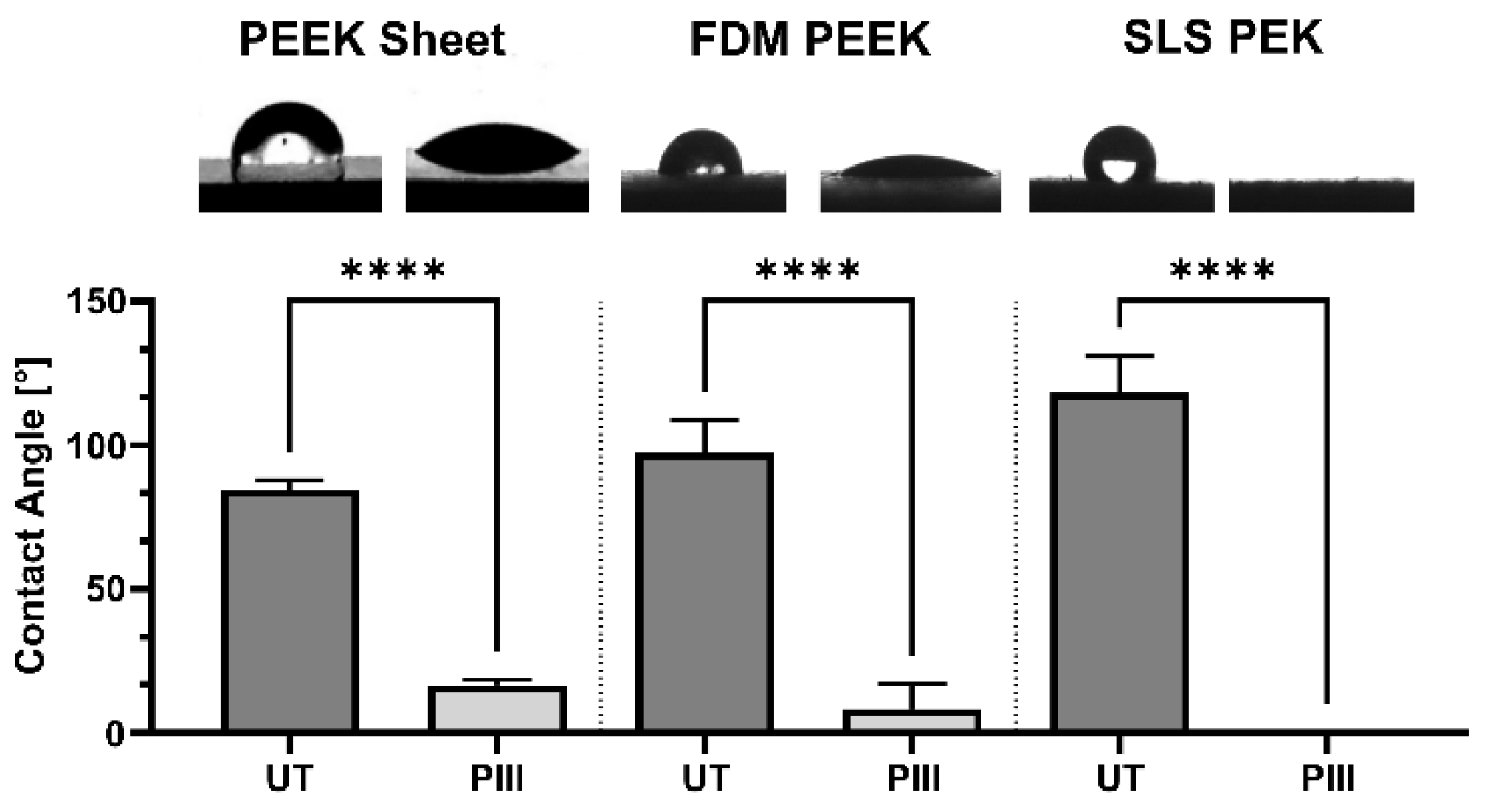
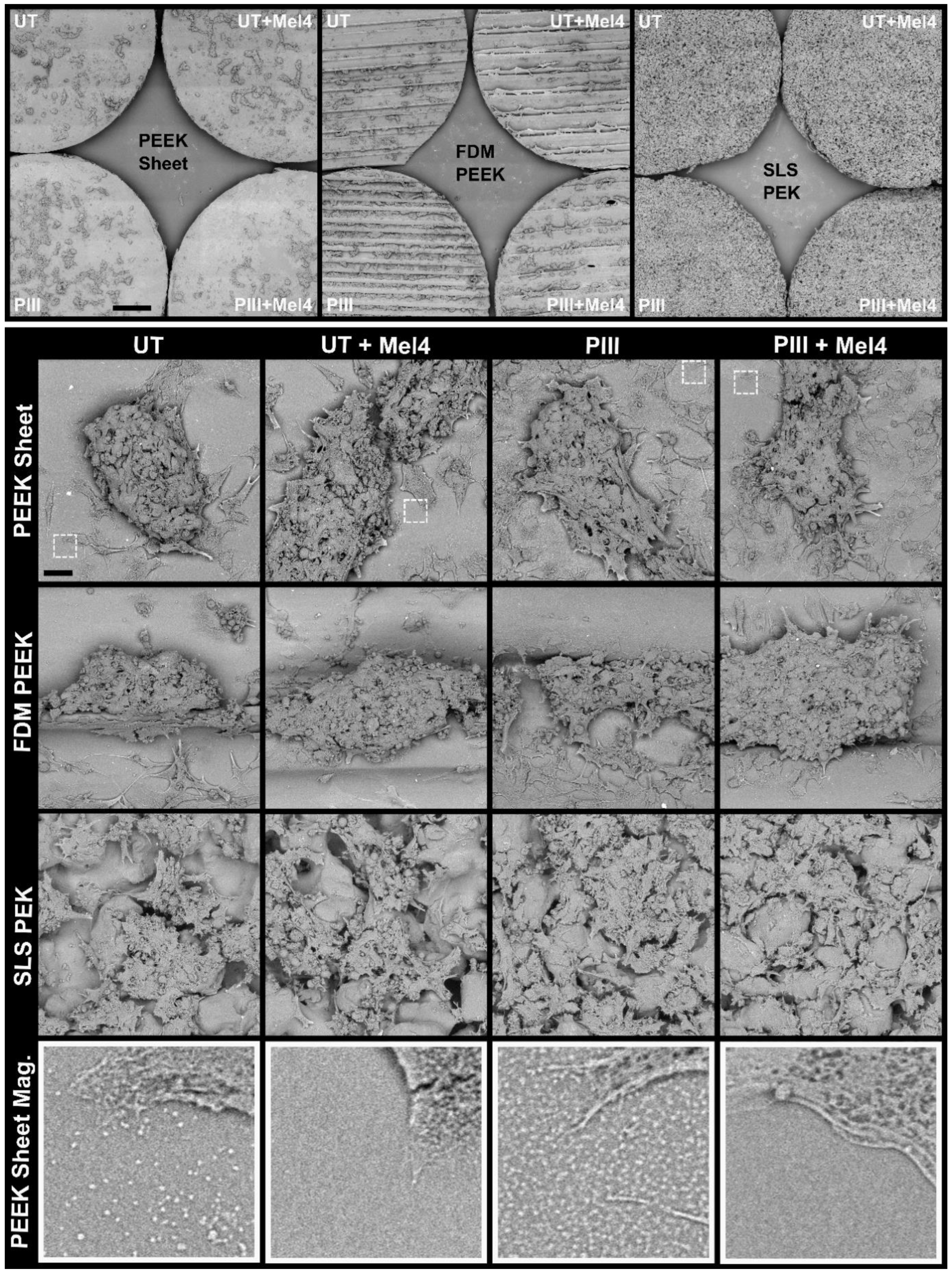
3.1. Surface Characterisation
3.2. Antimicrobial Effect of Mel4
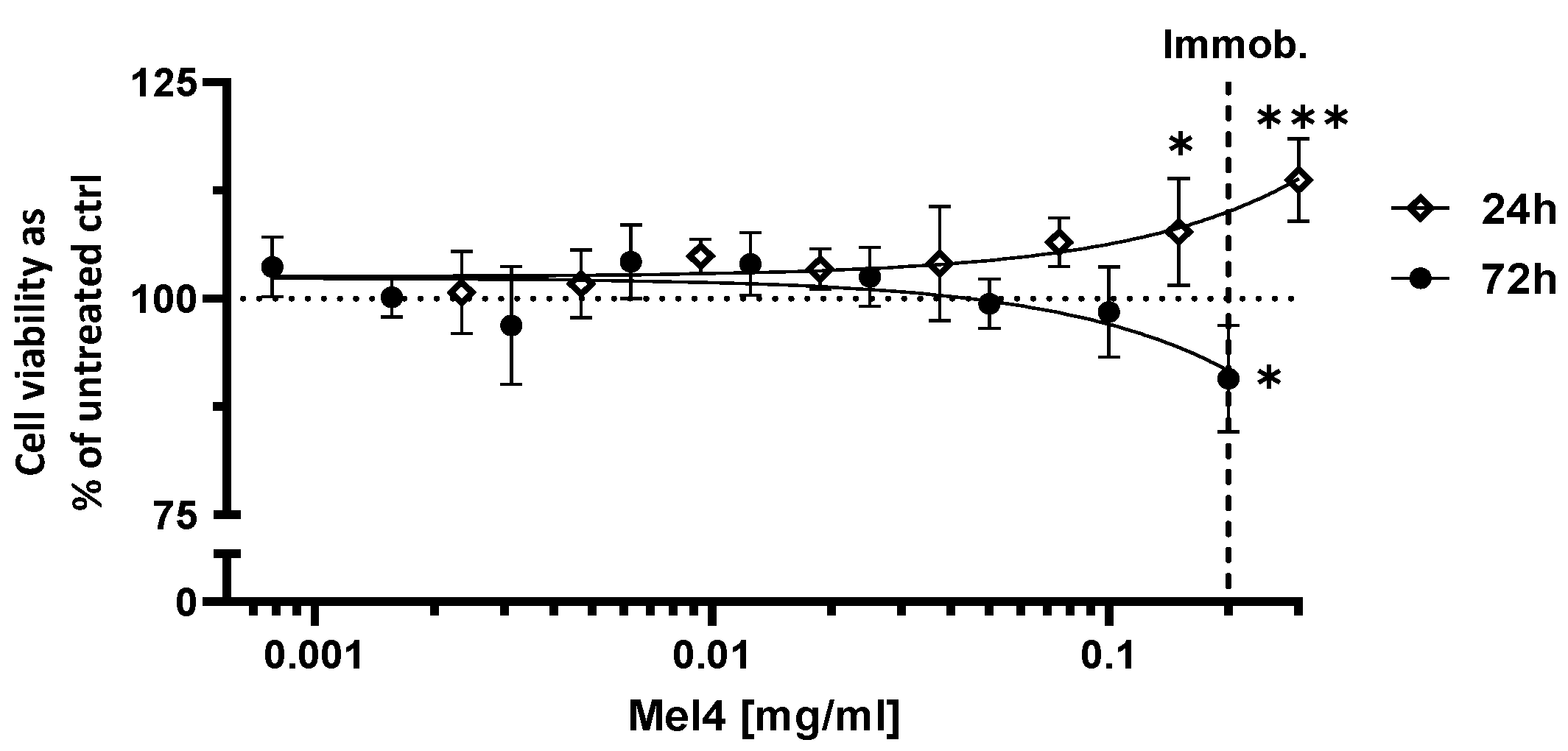
3.3. Cytotoxicity of Mel4
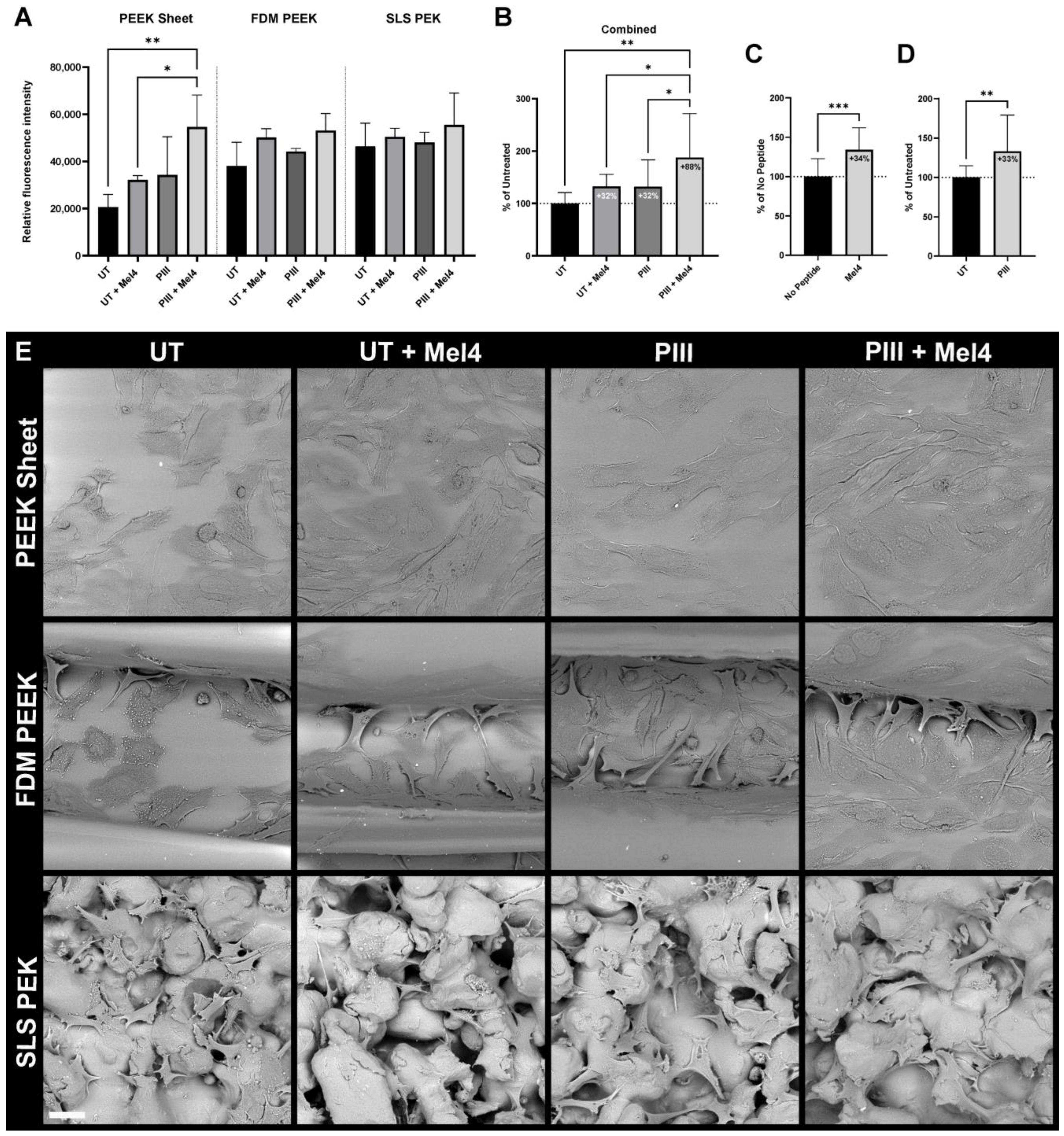
3.4. Bone Cell Adhesion
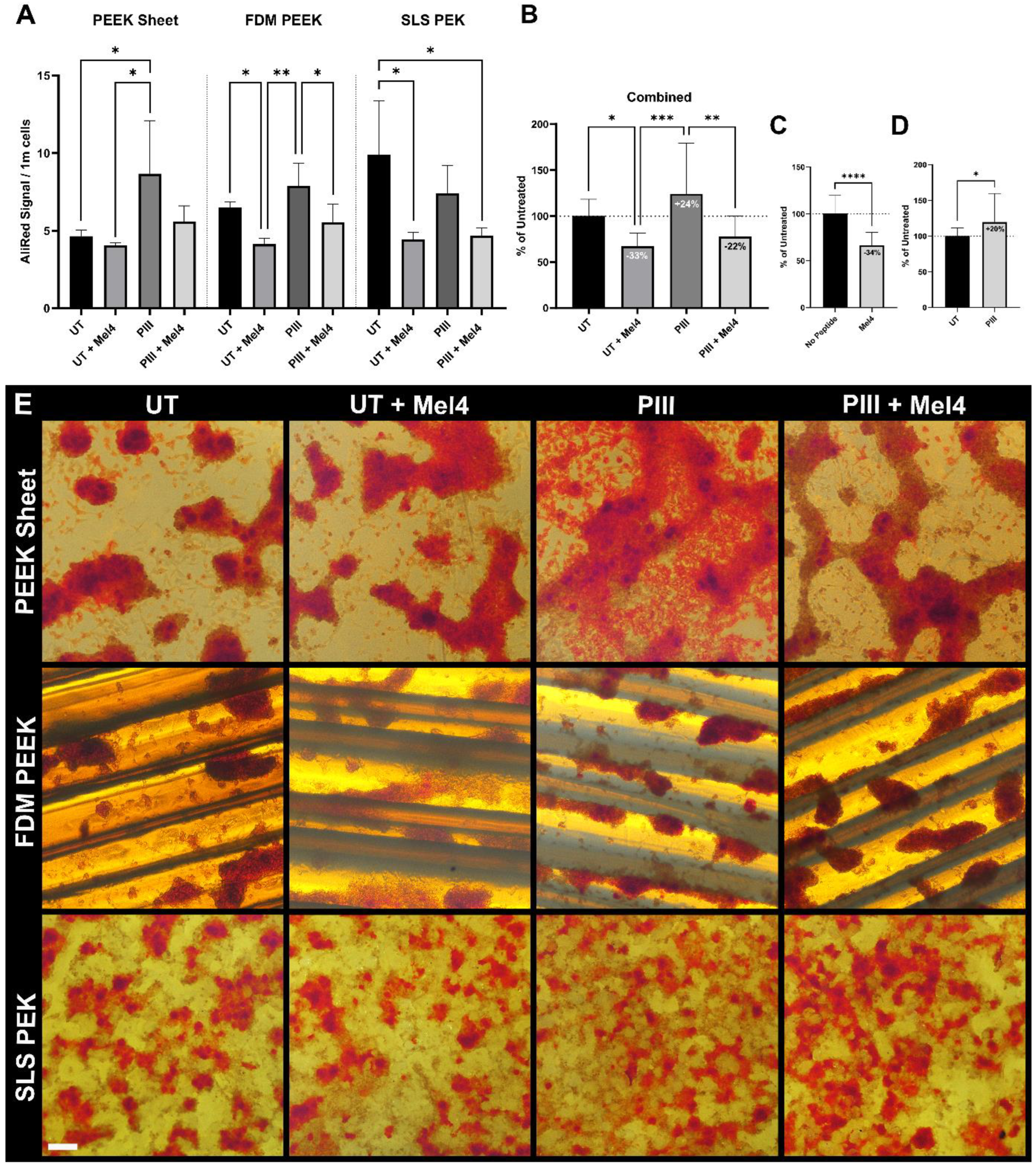
3.5. Proliferation and Mineralisation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribeiro, M.; Monteiro, F.J.; Ferraz, M.P. Infection of orthopedic implants with emphasis on bacterial adhesion process and techniques used in studying bacterial-material interactions. Biomatter 2012, 2, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Fleming, K.E.; Chuang, H.F.; Chau, T.M.; Loose, C.R.; Stephanopoulos, G.N.; Hammond, P.T. Controlling the release of peptide antimicrobial agents from surfaces. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2348–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.D.; Won, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Mishig-Ochir, T.; Lee, B.J. Antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic applications: A review. Molecules 2012, 17, 12276–12286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Chen, R.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Black, D.S.; Walsh, W.R.; Kumar, N. A new era of antibiotics: The clinical potential of antimicrobial peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummanapalli, S.S.; Willcox, M.D. Antimicrobial resistance of ocular microbes and the role of antimicrobial peptides. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2021, 104, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasir, M.; Dutta, D.; Willcox, M.D.P. Mode of action of the antimicrobial peptide Mel4 is independent of Staphylococcus aureus cell membrane permeability. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasir, M.; Dutta, D.; Willcox, M.D.P. Comparative mode of action of the antimicrobial peptide melimine and its derivative Mel4 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondyurin, A.; Nosworthy, N.J.; Bilek, M.M.M. Attachment of horseradish peroxidase to polytetrafluorethylene (teflon) after plasma immersion ion implantation. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosobrodova, E.; Gan, W.J.; Kondyurin, A.; Thorn, P.; Bilek, M.M.M. Improved Multiprotein Microcontact Printing on Plasma Immersion Ion Implanted Polystyrene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.K.Y.; Cheung, I.T.L.; Mei, Y.F.; Shek, C.H.; Siu, G.G.; Chu, P.K.; Yang, W.M.; Leng, Y.X.; Huang, Y.X.; Tian, X.B.; et al. Surface modification of polymeric materials by plasma immersion ion implantation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2005, 237, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilek, M.M.M.; Bax, D.V.; Kondyurin, A.; Yin, Y.; Nosworthy, N.J.; Fisher, K.; Waterhouse, A.; Weiss, A.S.; Dos Remedios, C.G.; McKenzie, D.R. Free radical functionalization of surfaces to prevent adverse responses to biomedical devices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14405–14410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakelin, E.A.; Kondyurin, A.V.; Wise, S.G.; McKenzie, D.R.; Davies, M.J.; Bilek, M.M.M. Bio-activation of polyether ether ketone using plasma immersion ion implantation: A kinetic model. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelin, E.A.; Davies, M.J.; Bilek, M.M.M.; McKenzie, D.R. Temperature Activated Diffusion of Radicals through Ion Implanted Polymers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 26340–26345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosobrodova, E.A.; Kondyurin, A.V.; Fisher, K.; Moeller, W.; McKenzie, D.R.; Bilek, M.M.M. Free radical kinetics in a plasma immersion ion implanted polystyrene: Theory and experiment. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2012, 280, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Bilek, M.M.M.; McKenzie, D.R. Direct evidence of covalent immobilisation of microperoxidase-11 on plasma polymer surfaces. Plasma Process. Polym. 2010, 7, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, H.V.; Lewin, W.T.; Suchowerska, N.; Al Maruf, D.S.A.; Cheng, K.; Clark, J.R.; McKenzie, D.R. Plasma immersion ion-implanted 3D-printed PEEK bone implants: In vivo sheep study shows strong osseointegration. Plasma Process. Polym. 2022, 19, 2100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsifis, G.; Kruse, H.; Lewin, W.; Al Maruf, A.; Clark, J.R.; McKenzie, D.R.; Suchowerska, N. Micro-CT Analysis of Implanted Poly-Ether-Ether-Ketone Scaffolds: Plasma Immersion Ion Implantation Increases Osteoconduction. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ma, L.; Sun, X.; Sloan, A.J.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Li, W. The overview of antimicrobial peptide-coated implants against oral bacterial infections. Aggregate 2023, 4, e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.C.; Kumar, S.R.; Vi, T.T.T.; Huang, Y.T.; Chen, D.W.; Lue, S.J. Facilitating gl13k peptide grafting on polyetheretherketone via 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide: Surface properties and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Bai, J.; Tao, H.; Hao, L.; Yin, W.; Ren, X.; Gao, A.; Li, N.; Wang, M.; Fang, S.; et al. Rational integration of defense and repair synergy on PEEK osteoimplants via biomimetic peptide clicking strategy. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Dutta, D.; Kumar, N.; Willcox, M.D.P. Interaction of the surface bound antimicrobial peptides melimine and Mel4 with Staphylococcus aureus. Biofouling 2020, 36, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Nie, B.; Yue, B.; Zhang, W.; Lyu, Z.; Long, T.; Wang, Y. KR-12 coating of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) surface: Via polydopamine improves osteointegration and antibacterial activity in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10190–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsh, S.L.; Bilek, M.M.M.; Nosworthy, N.J.; Kondyurin, A.; Dos Remedios, C.G.; McKenzie, D.R. A Comparison of covalent immobilization and physical adsorption of a cellulase enzyme mixture. Langmuir 2010, 26, 14380–14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosworthy, N.J.; Ho, J.P.Y.; Kondyurin, A.; McKenzie, D.R.; Bilek, M.M.M. The attachment of catalase and poly-l-lysine to plasma immersion ion implantation-treated polyethylene. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelin, E.A.; Yeo, G.C.; McKenzie, D.R.; Bilek, M.M.M.; Weiss, A.S. Plasma ion implantation enabled bio-functionalization of PEEK improves osteoblastic activity. APL Bioeng. 2018, 2, 026109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, H.V.; Tran, C.T.H.; Zandwijk, N.; Suchowerska, N.; McKenzie, D.R.; Reid, G. Covalent binding of molecules to plasma immersion ion implantation-activated microparticles for delivery into cells. Eng. Rep. 2020, 2, e12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Yasir, M.; Dutta, D.; Eswaramoorthy, N.; Suchowerska, N.; Willcox, M.; McKenzie, D.R. Single Step Plasma Process for Covalent Binding of Antimicrobial Peptides on Catheters to Suppress Bacterial Adhesion. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 5739–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvan, P.; Konda, N.; Pampi, N.; Vaddavalli, P.K.; Sharma, S.; Stapleton, F.; Kumar, N.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Dutta, D. Effect of antimicrobial contact lenses on corneal infiltrative events: A randomized clinical trial. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, M.D.P.; Chen, R.; Kalaiselvan, P.; Yasir, M.; Rasul, R.; Kumar, N.; Dutta, D. The Development of an Antimicrobial Contact Lens—From the Laboratory to the Clinic. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 21, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.; Liu, T.; Huang, Y.; Li, J. The effects of Peptide Mel4-coated titanium plates on infection rabbits after internal fixation of open fractures. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2022, 142, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Cole, N.; Kumar, N.; Willcox, M.D.P.P. Broad spectrum antimicrobial activity of melimine covalently bound to contact lenses. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Zhao, T.; Cheah, K.B.; Holmlund, L.; Willcox, M.D.P. Activity of a melimine derived peptide Mel4 against Stenotrophomonas, Delftia, Elizabethkingia, Burkholderia and biocompatibility as a contact lens coating. Contact Lens Anterior Eye 2017, 40, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Dutta, D.; Hossain, K.R.; Chen, R.; Ho, K.K.K.; Kuppusamy, R.; Clarke, R.J.; Kumar, N.; Willcox, M.D.P. Mechanism of Action of Surface Immobilized Antimicrobial Peptides against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Kumar, N.; Willcox, M.D.P. Antimicrobial activity of four cationic peptides immobilised to poly-hydroxyethylmethacrylate. Biofouling 2016, 32, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi, D.; Iqbal, N.; Sadeghi, M.; Sudin, I.; Abdul Kadir, M.R.; Kamarul, T. Preparation Methods for Improving PEEK’s Bioactivity for Orthopedic and Dental Application: A Review. Int. J. Biomater. 2016, 2016, 8202653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prideaux, M.; Wijenayaka, A.R.; Kumarasinghe, D.D.; Ormsby, R.T.; Evdokiou, A.; Findlay, D.M.; Atkins, G.J. SaOS2 osteosarcoma cells as an in vitro model for studying the transition of human osteoblasts to osteocytes. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2014, 95, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, H.V.; McKenzie, D.R.; Clark, J.R.; Suchowerska, N. Plasma ion implantation of 3D-printed PEEK creates optimal host conditions for bone ongrowth and mineralisation. Plasma Process. Polym. 2021, 18, 2000219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.T.H.; Craggs, M.; Smith, L.M.; Stanley, K.; Bilek, M.M.; McKenzie, D.R. A plasma ion bombardment process enabling reagent-free covalent binding of multiple functional molecules onto magnetic particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolansky, G.; Marmur, A. Apparent Contact Angles on Rough Surfaces: The Wenzel Equation Revisited. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 156, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouverey, C.; Strzelecka-Kiliszek, A.; Balcerzak, M.; Buchet, R.; Pikula, S. Matrix vesicles originate from apical membrane microvilli of mineralizing osteoblast-like saos-2 cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 106, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, D.; Singh, S.; Mehta, A.; Agrawal, P.; Raghava, G.P.S. In silico approaches for predicting the half-life of natural and modified peptides in blood. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalaiselvan, P.; Dutta, D.; Konda, N.V.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, N.; Stapleton, F.; Willcox, M.D.P. Effect of Deposition and Protease Digestion on the Ex Vivo Activity of Antimicrobial Peptide-Coated Contact Lenses. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nozzle temperature | 440 °C |
| Print bed temperature | 200 °C |
| Chamber temperature | 120 °C |
| Layer height | 0.2 mm |
| Nozzle diameter | 0.2 mm |
| Extrusion width | 0.25 mm |
| Print speed | 5 mm/s |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Layer thickness | 0.12 mm |
| Build area configuration | 230 mm × 350 mm |
| Process chamber temperature | 364 °C |
| Building platform temperature | 336 °C |
| Exchangeable frame temperature | 343 °C |
| Post sintering time | 12 s |
| Beam offset | 0.41 mm |
| Laser exposure set | PAEK1304_120_011 |
| Cooldown | Passive ambient |
| UT | UT + Mel4 | PIII | PIII + Mel4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protection from bacterial cell adhesion | 0 | + | 0 | + + |
| Bone cell adhesion | 0 | + | + | + + |
| Bone cell proliferation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bone cell-mediated mineralisation | 0 | − − | + | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kruse, H.V.; Chakraborty, S.; Chen, R.; Kumar, N.; Yasir, M.; Lewin, W.T.; Suchowerska, N.; Willcox, M.D.P.; McKenzie, D.R. Protecting Orthopaedic Implants from Infection: Antimicrobial Peptide Mel4 Is Non-Toxic to Bone Cells and Reduces Bacterial Colonisation When Bound to Plasma Ion-Implanted 3D-Printed PAEK Polymers. Cells 2024, 13, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13080656
Kruse HV, Chakraborty S, Chen R, Kumar N, Yasir M, Lewin WT, Suchowerska N, Willcox MDP, McKenzie DR. Protecting Orthopaedic Implants from Infection: Antimicrobial Peptide Mel4 Is Non-Toxic to Bone Cells and Reduces Bacterial Colonisation When Bound to Plasma Ion-Implanted 3D-Printed PAEK Polymers. Cells. 2024; 13(8):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13080656
Chicago/Turabian StyleKruse, Hedi Verena, Sudip Chakraborty, Renxun Chen, Naresh Kumar, Muhammad Yasir, William T. Lewin, Natalka Suchowerska, Mark D. P. Willcox, and David R. McKenzie. 2024. "Protecting Orthopaedic Implants from Infection: Antimicrobial Peptide Mel4 Is Non-Toxic to Bone Cells and Reduces Bacterial Colonisation When Bound to Plasma Ion-Implanted 3D-Printed PAEK Polymers" Cells 13, no. 8: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13080656
APA StyleKruse, H. V., Chakraborty, S., Chen, R., Kumar, N., Yasir, M., Lewin, W. T., Suchowerska, N., Willcox, M. D. P., & McKenzie, D. R. (2024). Protecting Orthopaedic Implants from Infection: Antimicrobial Peptide Mel4 Is Non-Toxic to Bone Cells and Reduces Bacterial Colonisation When Bound to Plasma Ion-Implanted 3D-Printed PAEK Polymers. Cells, 13(8), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13080656