GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors: Updates on Clinicopathologic and Molecular Genetics Features
Abstract
1. Clinical and Epidemiologic Characteristics of GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors
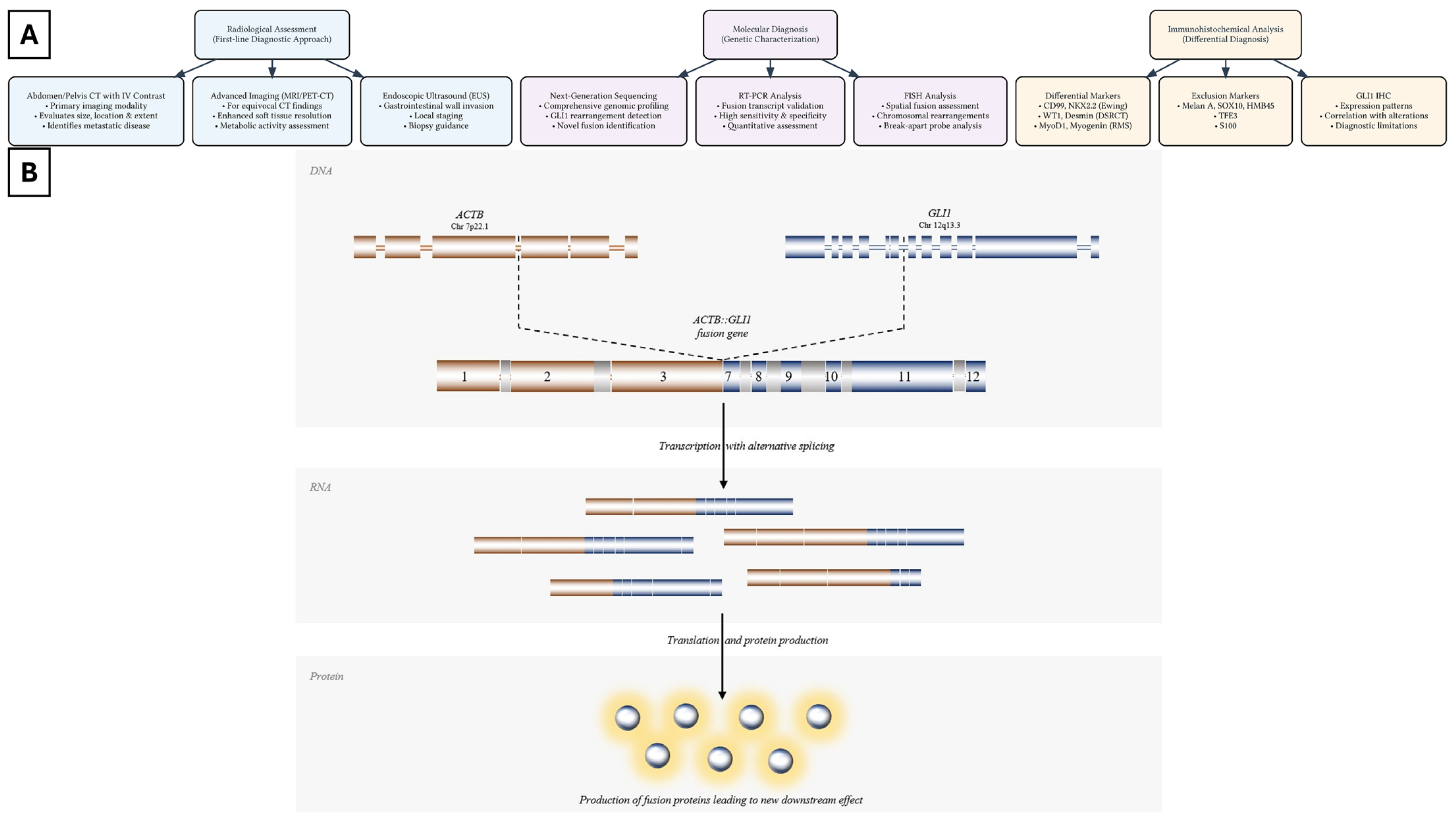
2. Histopathologic and Immunophenotypic Characteristics of GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors
3. Molecular Characteristics of GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors
4. Prognosis and Management of GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jessurun, J.; Orr, C.; McNulty, S.N.; Hagen, C.E.; Alnajar, H.; Wilkes, D.; Kudman, S.; Al Assaad, M.; Dorsaint, P.; Ohara, K.; et al. GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumor: Expanding the Spectrum of Gastrointestinal Neoplasms With GLI1 Gene Fusions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 47, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D.A.; Pinto, A.; Subhawong, T.K.; Wilky, B.A.; Schlumbrecht, M.P.; Antonescu, C.R.; Nielsen, G.P.; Rosenberg, A.E. Pericytoma with t(7;12) and ACTB-GLI1 Fusion: Reevaluation of an Unusual Entity and its Relationship to the Spectrum of GLI1 Fusion-related Neoplasms. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 1682–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.C.F.; Liu, A.P.Y.; Wong, S.I.; Loong, H.H.; Shek, T.W.H. GLI1-Altered Mesenchymal Tumor-Multiomic Characterization of a Case Series and Patient-Level Meta-analysis of One Hundred Sixty-Seven Cases for Risk Stratification. Mod. Pathol. 2024, 38, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, C.; Agaimy, A.; Dermawan, J.K.; Chen, J.F.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Dickson, B.C.; Dashti, N.; Michal, M.; Kosemehmetoglu, K.; Din, N.U.; et al. A Comprehensive Clinicopathologic and Molecular Reappraisal of GLI1-altered Mesenchymal Tumors with Pooled Outcome Analysis Showing Poor Survival in GLI1-amplified Versus GLI1-rearranged Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2024, 48, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonescu, C.R.; Agaram, N.P.; Sung, Y.S.; Zhang, L.; Swanson, D.; Dickson, B.C. A Distinct Malignant Epithelioid Neoplasm With GLI1 Gene Rearrangements, Frequent S100 Protein Expression, and Metastatic Potential: Expanding the Spectrum of Pathologic Entities With ACTB/MALAT1/PTCH1-GLI1 Fusions. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahceci, D.; Kim, G.E.; Kakar, S.; Balitzer, D.J.; Nguyen, E.D.; Ramachandran, R.; Umetsu, S.E.; Joseph, N.M. Expanding the Spectrum of GLI1-rearranged Neoplasms of the Gastrointestinal Tract to Include Monophasic Keratin-positive Epithelial Neoplasms. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2024, 48, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, D.A.; Cloutier, J.M.; Margolis, M.; Mata, D.A.; Rodrigues Simoes, N.J.; Faquin, W.C.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Chopra, S.; Charville, G.W.; Wangsiricharoen, S.; et al. GLI1-Altered Mesenchymal Tumors With ACTB or PTCH1 Fusion: A Molecular and Clinicopathologic Analysis. Mod. Pathol. 2024, 37, 100386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Ota, S.; Yamasaki, M.; Batsaikhan, B.; Furukawa, A.; Watanabe, Y. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A comprehensive radiological review. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 1105–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Lim, C.H.; Lee, B.I. Accuracy of Endoscopic Ultrasonography for Determining the Depth of Invasion in Early Gastric Cancer. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 33, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chang, K.; Folpe, A.L.; Kao, Y.C.; Wey, S.L.; Huang, H.Y.; Gill, A.J.; Rooper, L.; Bishop, J.A.; Dickson, B.C.; et al. Head and Neck Mesenchymal Neoplasms With GLI1 Gene Alterations: A Pathologic Entity With Distinct Histologic Features and Potential for Distant Metastasis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zuo, L.; Tang, L.; Yan, X.; Chen, S. Duodenal Soft Tissue Sarcoma with GLI1 Gene Rearrangement: A Case Report and Literature Review. Am. J. Case Rep. 2024, 25, e943271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, I.; Agaimy, A.; Giner, F.; Navarro, S.; Michal, M.; Bridge, J.; Claramunt, R.; Lopez-Guerrero, J.A.; Alcacer, J.; Linos, K.; et al. The value of GLI1 and p16 immunohistochemistry in the premolecular screening for GLI1-altered mesenchymal neoplasms. Virchows Arch. 2024, 484, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papke, D.J., Jr.; Dickson, B.C.; Sholl, L.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Pseudoendocrine Sarcoma: Clinicopathologic Analysis of 23 Cases of a Distinctive Soft Tissue Neoplasm with Metastatic Potential, Recurrent CTNNB1 Mutations, and a Predilection for Truncal Locations. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, V.Y.; Fletcher, C.D. Myoepithelial neoplasms of soft tissue: An updated review of the clinicopathologic, immunophenotypic, and genetic features. Head. Neck Pathol. 2015, 9, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosquera, J.M.; Sboner, A.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.L.; Sung, Y.S.; Chen, H.W.; Agaram, N.P.; Briskin, D.; Basha, B.M.; Singer, S.; et al. Novel MIR143-NOTCH fusions in benign and malignant glomus tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013, 52, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, E.; Cortes-Santiago, N.; Ferguson, L.M.; Rao, P.H.; Venkatramani, R.; Lopez-Terrada, D. Translocation t(7;12) as the sole chromosomal abnormality resulting in ACTB-GLI1 fusion in pediatric gastric pericytoma. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 53, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.A.; Sanders, K.; Huang, D.; Nelson, M.; Neff, J.R.; Muirhead, D.; Walker, C.; Seemayer, T.A.; Sumegi, J. Pericytoma with t(7;12) and ACTB-GLI1 fusion arising in bone. Hum. Pathol. 2012, 43, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakuchi, N.; Yanagawa, S.; Kushitani, K.; Kodama, S.; Takeshima, Y.; Sumimoto, K. Primary Small Intestinal Sarcomatoid Carcinoma: Report of a Rare Case and Literature Review. Case Rep. Oncol. 2021, 14, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folpe, A.L.; Goldblum, J.R.; Rubin, B.P.; Shehata, B.M.; Liu, W.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Weiss, S.W. Morphologic and immunophenotypic diversity in Ewing family tumors: A study of 66 genetically confirmed cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.P.; Buckley, K.; Iwenofu, O.H.; Singhi, A.; Kahwash, S.B.; Arnold, C.A.; Tan, G.C.; Arnold, M.A. Selective Immunoreactivity for WT1 Carboxy-Terminus Distinguishes Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumor From its Histologic Mimics. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2022, 25, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Siegal, G.P. Small Round Cell Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2022, 146, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Chuaychob, S.; Homme, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Lyu, R.; Yamashita, K.; Ae, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Kumegawa, K.; Maruyama, R.; et al. ASPSCR1::TFE3 orchestrates the angiogenic program of alveolar soft part sarcoma. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, B.; Singh, A.V. Patterns of neural differentiation in melanomas. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrack, P.H.; Marino-Enriquez, A.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Hornick, J.L.; Papke, D.J., Jr. GLI1 Immunohistochemistry Distinguishes Mesenchymal Neoplasms With GLI1 Alterations From Morphologic Mimics. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 47, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Lessnick, S.L. Promiscuous partnerships in Ewing’s sarcoma. Cancer Genet. 2011, 204, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roller, L.A.; Chebib, I.; Bredella, M.A.; Chang, C.Y. Clinical, radiological, and pathological features of extraskeletal osteosarcoma. Skeletal Radiol. 2018, 47, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, J.T.; Zhang, R.; Boohaker, R.J. GLI1: A Therapeutic Target for Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 673154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spans, L.; Fletcher, C.D.; Antonescu, C.R.; Rouquette, A.; Coindre, J.M.; Sciot, R.; Debiec-Rychter, M. Recurrent MALAT1-GLI1 oncogenic fusion and GLI1 up-regulation define a subset of plexiform fibromyxoma. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlen, A.; Fletcher, C.D.; Mertens, F.; Fletcher, J.A.; Perez-Atayde, A.R.; Hicks, M.J.; Debiec-Rychter, M.; Sciot, R.; Wejde, J.; Wedin, R.; et al. Activation of the GLI oncogene through fusion with the beta-actin gene (ACTB) in a group of distinctive pericytic neoplasms: Pericytoma with t(7;12). Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.P.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Myopericytomatosis: Clinicopathologic Analysis of 11 Cases With Molecular Identification of Recurrent PDGFRB Alterations in Myopericytomatosis and Myopericytoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, J.; Nakayama, S.; Koga, K.; Aoki, M. Keratin-Positive Giant Cell-Rich Tumor: A Review and Update. Cancers 2024, 16, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtys, W.; Oron, M. How Driver Oncogenes Shape and Are Shaped by Alternative Splicing Mechanisms in Tumors. Cancers 2023, 15, 2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coucha, M.; Shanab, A.Y.; Sayed, M.; Vazdarjanova, A.; El-Remessy, A.B. Modulating Expression of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Prevents Secondary Damage and Preserves Visual Function in a Mouse Model of Ischemia/Reperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.L.; Lee, K.T.; Chen, P.S.; Cheung, C.H.A.; Chang, C.P.; Phan, N.N.; Shen, M.R.; Hsu, H.P. Mutation of the PTCH1 gene predicts recurrence of breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alwaqfi, R.R.; Samuelson, M.I.; Guseva, N.N.; Ouyang, M.; Bossler, A.D.; Ma, D. PTCH1-GLI1 Fusion-Positive Ovarian Tumor: Report of a Unique Case With Response to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Pazopanib. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cintio, F.; Dal Bo, M.; Baboci, L.; De Mattia, E.; Polano, M.; Toffoli, G. The Molecular and Microenvironmental Landscape of Glioblastomas: Implications for the Novel Treatment Choices. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 603647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, M.; Modlin, I.M.; Bodei, L.; Drozdov, I. Decoding the Molecular and Mutational Ambiguities of Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasm Pathobiology. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q. Protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in malignant tumors: Molecular mechanisms and future perspective. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.; Zhang, C.; Xu, C.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Knockdown of MALAT1 inhibits osteosarcoma progression via regulating the miR-34a/cyclin D1 axis. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.; Rahman, M.F.; Vyatkin, Y.; Azatyan, A.; St Laurent, G.; Kapranov, P.; Zaphiropoulos, P.G. Identification of novel GLI1 target genes and regulatory circuits in human cancer cells. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1718–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Deng, W.; Lobo-Ruppert, S.M.; Ruppert, J.M. Gli1 acts through Snail and E-cadherin to promote nuclear signaling by beta-catenin. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4489–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lama-Sherpa, T.D.; Lin, V.T.G.; Metge, B.J.; Weeks, S.E.; Chen, D.; Samant, R.S.; Shevde, L.A. Hedgehog signaling enables repair of ribosomal DNA double-strand breaks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 10342–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, K.S.; Chang, C.F.; Lin, S.S. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Organogenesis, Tumors, and Tumor Microenvironments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, I.N.; Phi, L.T.H.; Jun, N.; Wijaya, Y.T.; Lee, S.; Kwon, H.Y. Hedgehog Signaling in Cancer: A Prospective Therapeutic Target for Eradicating Cancer Stem Cells. Cells 2018, 7, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, E.K.; Stearns, T. Hedgehog signaling and the primary cilium: Implications for spatial and temporal constraints on signaling. Development 2021, 148, dev195552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohatgi, R.; Milenkovic, L.; Scott, M.P. Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science 2007, 317, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, S.C.; Ocbina, P.J.; Anderson, K.V. The primary cilium as a Hedgehog signal transduction machine. Methods Cell Biol. 2009, 94, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigafoos, A.N.; Paradise, B.D.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Hedgehog/GLI Signaling Pathway: Transduction, Regulation, and Implications for Disease. Cancers 2021, 13, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, D.; Chen, X.; Cheng, L.; Mahoney, M.; Riobo, N.A. Noncanonical Hedgehog signaling. Vitam. Horm. 2012, 88, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doheny, D.; Manore, S.G.; Wong, G.L.; Lo, H.W. Hedgehog Signaling and Truncated GLI1 in Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriana, S.; Asha, K.; Repak, M.; Sharma-Walia, N. Hedgehog Signaling: Implications in Cancers and Viral Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, R.L.; Lo, H.W. Hedgehog pathway and GLI1 isoforms in human cancer. Discov. Med. 2012, 13, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Song, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, G.; Yan, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Song, G. Hedgehog/Gli2 signaling triggers cell proliferation and metastasis via EMT and wnt/beta-catenin pathways in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matissek, S.J.; Elsawa, S.F. GLI3: A mediator of genetic diseases, development and cancer. Cell Commun. Signal 2020, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ciebiera, M.; Bariani, M.V.; Ali, M.; Elkafas, H.; Boyer, T.G.; Al-Hendy, A. Comprehensive Review of Uterine Fibroids: Developmental Origin, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 678–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsgrove, D.N.; Rooper, L.M.; Stevens, T.M.; Shin, C.; Damm, D.D.; Gagan, J.; Bridge, J.A.; Thompson, L.D.R.; Koduru, P.R.; Bishop, J.A. GLI1-Altered Soft Tissue Tumors of the Head and Neck: Frequent Oropharyngeal Involvement, p16 Immunoreactivity, and Detectable Alterations by DDIT3 Break Apart FISH. Head. Neck Pathol. 2022, 16, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prall, O.W.J.; McEvoy, C.R.E.; Byrne, D.J.; Iravani, A.; Browning, J.; Choong, D.Y.; Yellapu, B.; O’Haire, S.; Smith, K.; Luen, S.J.; et al. A Malignant Neoplasm From the Jejunum With a MALAT1-GLI1 Fusion and 26-Year Survival History. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 28, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Wu, M.; Zhao, F.; Fu, W.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Liu, T. Prognostic and clinicopathological value of Gli-1 expression in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 69087–69096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hazan, A.; Selway, J.L.; Herath, D.S.; Harwood, C.A.; Pirzado, M.S.; Atkar, R.; Kelsell, D.P.; Linton, K.J.; Philpott, M.P.; et al. A Novel Mechanism for Activation of GLI1 by Nuclear SMO That Escapes Anti-SMO Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, H.J.; Pau, G.; Dijkgraaf, G.J.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Modrusan, Z.; Januario, T.; Tsui, V.; Durham, A.B.; Dlugosz, A.A.; Haverty, P.M.; et al. Genomic analysis of smoothened inhibitor resistance in basal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Ma, J.; Avery, J.T.; Sambandam, V.; Nguyen, T.H.; Xu, B.; Suto, M.J.; Boohaker, R.J. GLI1 Inhibitor SRI-38832 Attenuates Chemotherapeutic Resistance by Downregulating NBS1 Transcription in BRAF(V600E) Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Sugumar, V.; Alshanon, A.F.; Wong, W.F.; Fung, S.Y.; Looi, C.Y. Defining the Role of GLI/Hedgehog Signaling in Chemoresistance: Implications in Therapeutic Approaches. Cancers 2021, 13, 4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiacchini, G.; Benettini, G.; Trico, D.; Torregrossa, L.; Vianini, M.; Picariello, M.; Dallan, I.; Berrettini, S.; Bruschini, L. Human papillomavirus-related head and neck adenosquamous carcinoma: A systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Oral. Oncol. 2021, 119, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrobono, S.; Gaudio, E.; Gagliardi, S.; Zitani, M.; Carrassa, L.; Migliorini, F.; Petricci, E.; Manetti, F.; Makukhin, N.; Bond, A.G.; et al. Targeting non-canonical activation of GLI1 by the SOX2-BRD4 transcriptional complex improves the efficacy of HEDGEHOG pathway inhibition in melanoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3799–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, H.; Matsuno, Y.; Kusumoto-Matsuo, R.; Kojima, S.; Ueno, T.; Ikegami, M.; Kitada, R.; Sumiyoshi-Okuma, H.; Kojima, Y.; Yonemori, K.; et al. GLI1 confers resistance to PARP inhibitors by activating the DNA damage repair pathway. Oncogene 2024, 43, 3037–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Younes, A.I.; Mejbel, H.A. GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors: Updates on Clinicopathologic and Molecular Genetics Features. Cells 2025, 14, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020118
Younes AI, Mejbel HA. GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors: Updates on Clinicopathologic and Molecular Genetics Features. Cells. 2025; 14(2):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020118
Chicago/Turabian StyleYounes, Ahmed I., and Haider A. Mejbel. 2025. "GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors: Updates on Clinicopathologic and Molecular Genetics Features" Cells 14, no. 2: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020118
APA StyleYounes, A. I., & Mejbel, H. A. (2025). GLI1-Rearranged Enteric Tumors: Updates on Clinicopathologic and Molecular Genetics Features. Cells, 14(2), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020118




