Adiponectin Influences the Behavior of Stem Cells in Hormone-Resistant Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Mammosphere Assay
2.3. Flow Cytometric Detection of CD44, CD24 and ALDH1 Expression
2.4. Total RNA Extraction, RT-PCR, and qRT-PCR Assay
2.5. Proteomic Analysis
2.5.1. Protein Digestion
2.5.2. Nanoscale Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry (nLC-MS/MS)
2.5.3. Data Analysis and Results Reporting
2.6. MetaCoreTM Analysis
2.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Proliferation Assay
2.10. Annexin V/PI Assay
2.11. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Assessment
2.12. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
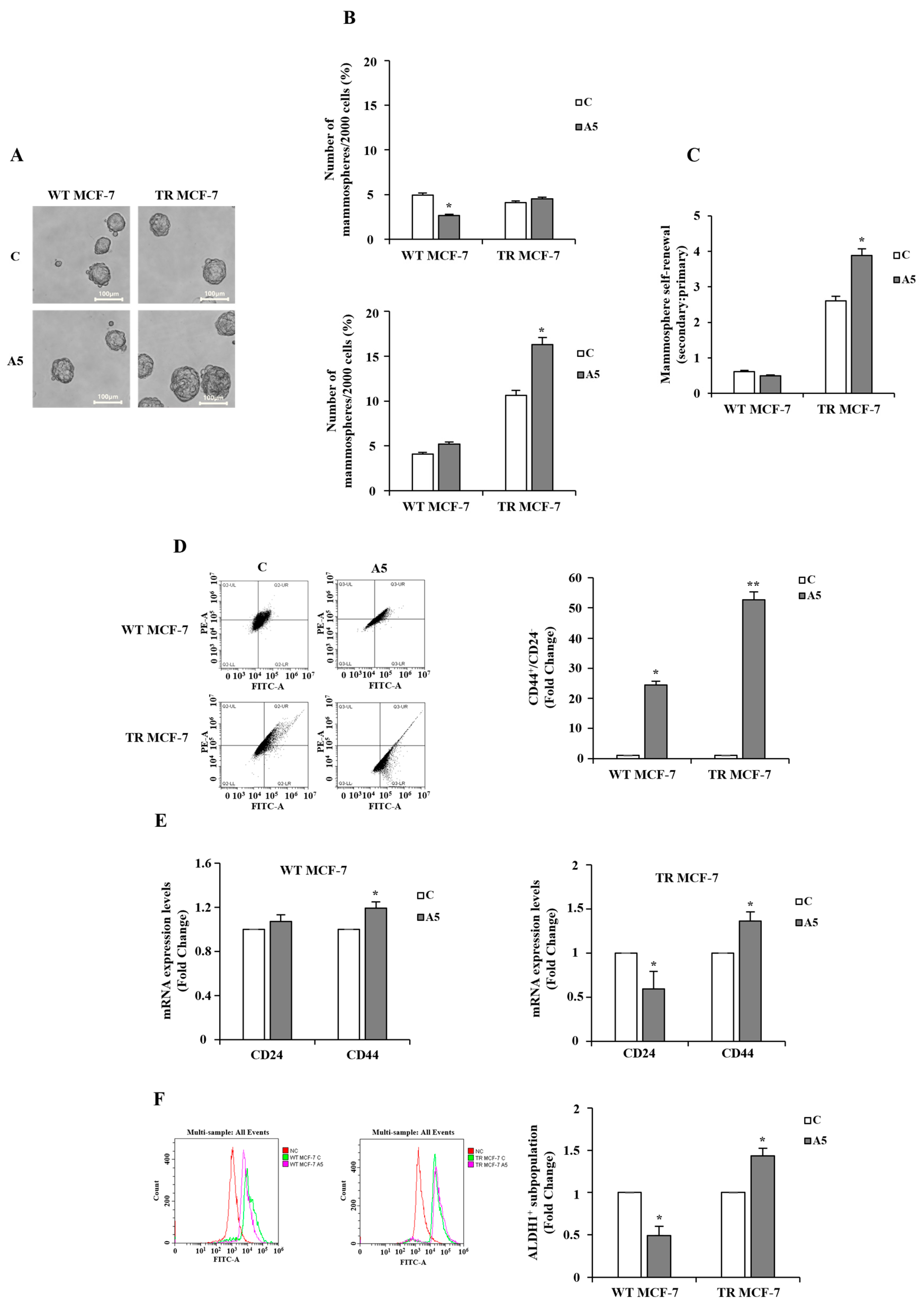
3.1. Effects of Adiponectin on Stem Subpopulation Enrichment in TR MCF-7 Mammospheres
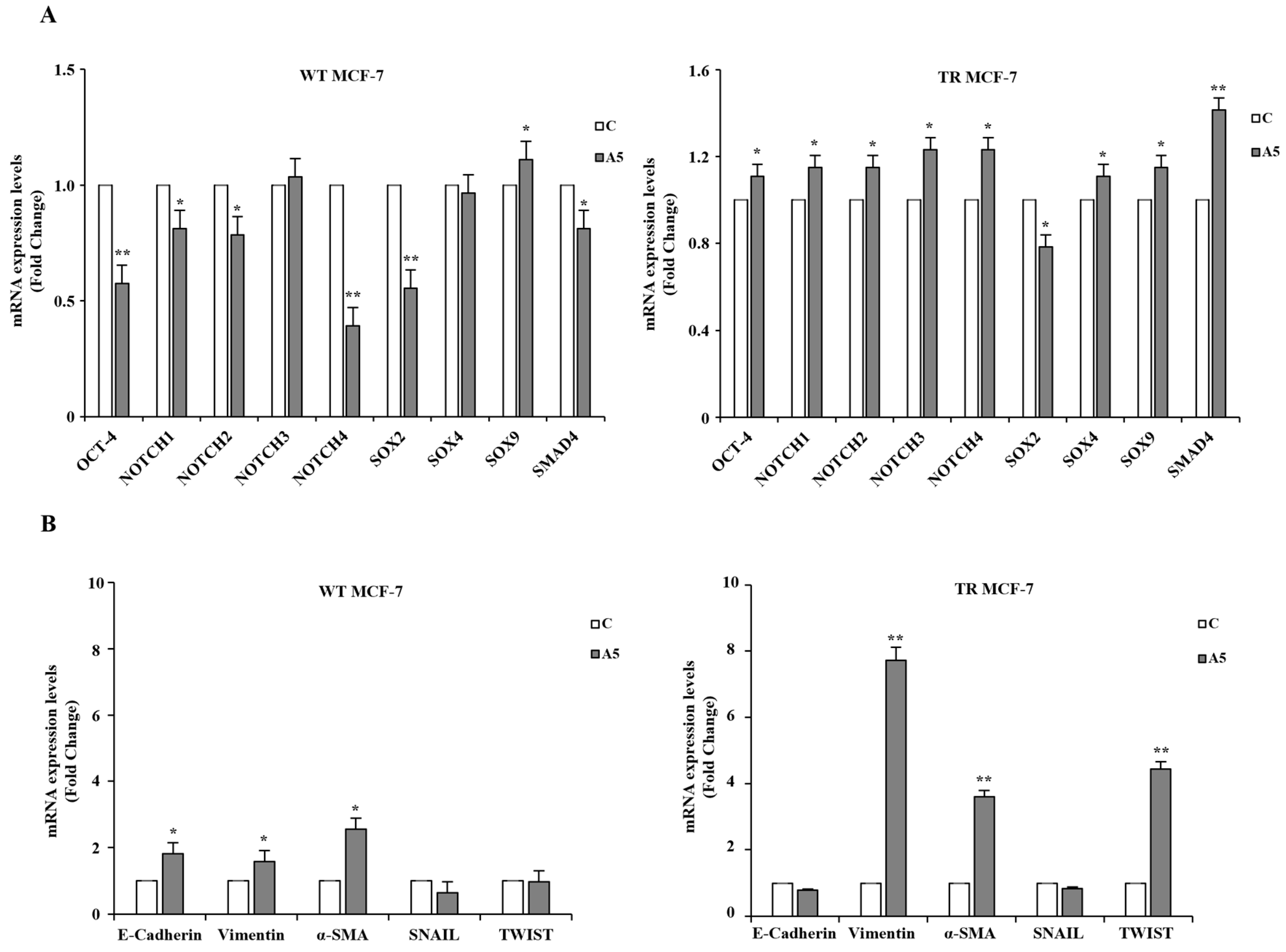
3.2. Proteomic and GO Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins (DEPs) in MCF-7 Mammospheres
3.3. Impact of Low Adiponectin Levels on Cell Cycle Regulation in TR MCF-7 Mammospheres
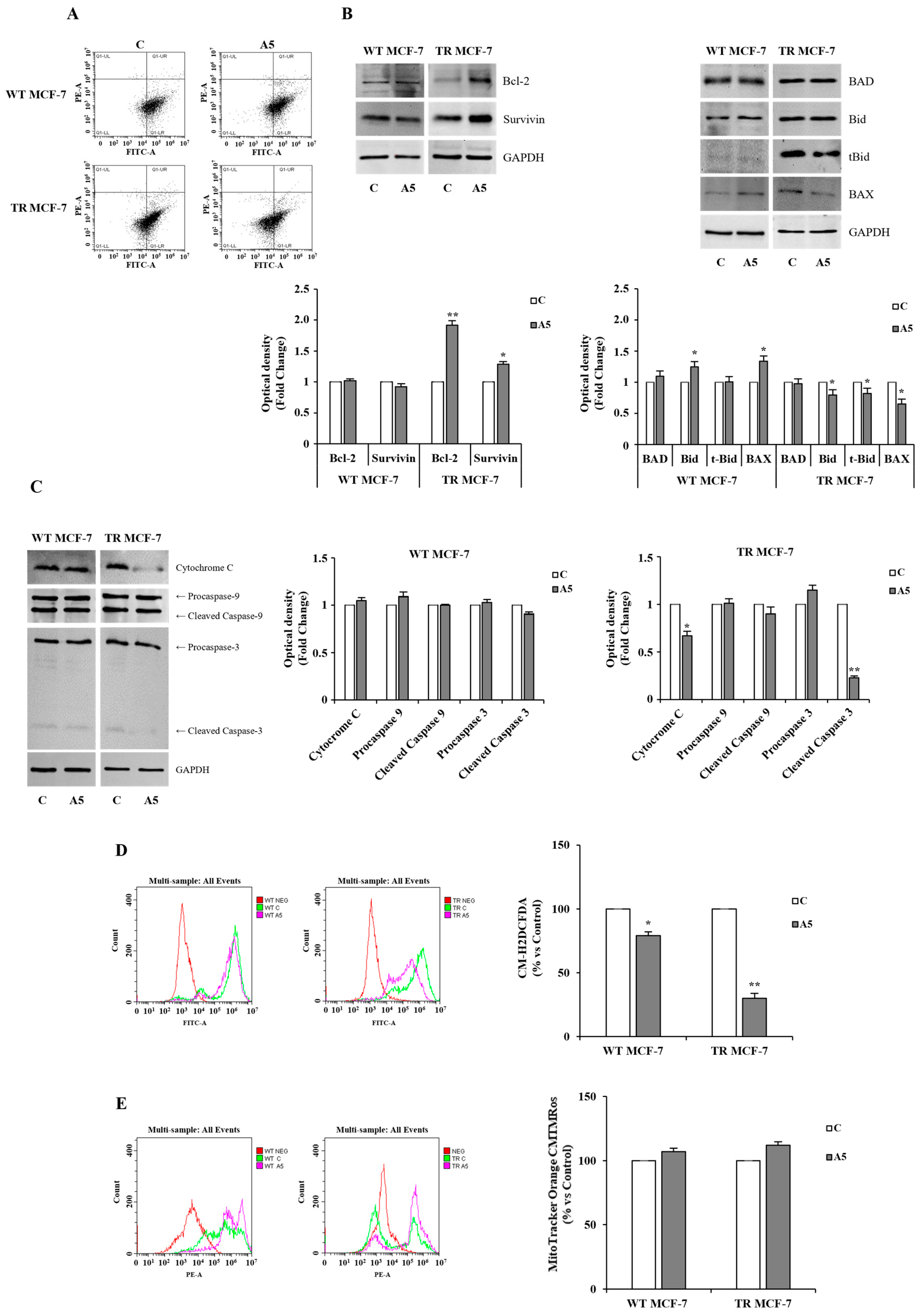
3.4. Events Converging on Apoptosis Inhibition in TR MCF-7 Cells upon Adiponectin Exposure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| TAM | Tamoxifen |
| BCSCs | Breast cancer stem Cells |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| WT MCF-7 | Hormone-responsive MCF-7 breast cancer cells |
| TR MCF-7 | Tamoxifen-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells |
| MFE | Mammosphere-forming efficiency |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| PAC | Protein Aggregation Capture |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| TEAB | Triethylammonium bicarbonate |
| FA | Formic acid |
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| DIA | Data Independent Acquisition |
| CSCs | Cancer stem cells |
| ALDH1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 |
| DEPs | Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, L.; Lin, C.G.; Hu, H.; Zheng, H. Tafazzin mediates tamoxifen resistance by regulating cellular phospholipid composition in ER-positive breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024, 31, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbeck, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Cortes, J.; Gnant, M.; Houssami, N.; Poortmans, P.; Ruddy, K.; Tsang, J.; Cardoso, F. Breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanker, A.B.; Sudhan, D.R.; Arteaga, C.L. Overcoming endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.T.; Anurag, M.; Haricharan, S.; Gou, X.; Ellis, M.J. Endocrine therapy resistance: New insights. Breast 2019, 48, S26–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belachew, E.B.; Sewasew, D.T. Molecular mechanisms of endocrine resistance in estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 599586. [Google Scholar]
- Rondón-Lagos, M.; Villegas, V.E.; Rangel, N.; Sánchez, M.C.; Zaphiropoulos, P.G. Tamoxifen resistance: Emerging molecular targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulos, F.-I.; Kottorou, A.; Tzezou, A. Endocrine resistance and epigenetic reprogramming in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2021, 517, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Stebbing, J.; Giamas, G.; Murphy, J. Endocrine resistance in hormone receptor positive breast cancer–from mechanism to therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasha, F.; Sharma, M.; Pruitt, K. Mechanisms of endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 532, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, J.O.; Spring, L.M.; Bardia, A.; Wander, S.A. ESR1 mutation as an emerging clinical biomarker in metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Tian, W.; Ning, J.; Xiao, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, Z.; Tanzhu, G.; Yang, J.; Zhou, R. Cancer stem cells: Advances in knowledge and implications for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 170. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, L.; Meng, X. The breast cancer stem cells traits and drug resistance. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 599965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romaniuk-Drapała, A.; Totoń, E.; Taube, M.; Idzik, M.; Rubiś, B.; Lisiak, N. Breast Cancer Stem Cells and Tumor Heterogeneity: Characteristics and Therapeutic Strategies. Cancers 2024, 16, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, A.; Goswami, K.K.; Sultana, J.; Ganguly, N.; Choudhury, P.R.; Chakravarti, M.; Bhuniya, A.; Sarkar, A.; Bera, S.; Dhar, S. Cancer stem cell–immune cell crosstalk in breast tumor microenvironment: A determinant of therapeutic facet. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1245421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurin, S.; Alkhalifa, H. Breast cancers, mammary stem cells, and cancer stem cells, characteristics, and hypotheses. Neoplasia 2020, 22, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, C. Targeting breast cancer stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 552–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhao, W.; Xi, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhao, W. Role, molecular mechanism and the potential target of breast cancer stem cells in breast cancer development. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Zhang, C.; Ling, S.; Wei, R.; Wang, J.; Xu, X. The metabolic flexibility of quiescent CSC: Implications for chemotherapy resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Ni, J.; Beretov, J.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Cancer stem cell in breast cancer therapeutic resistance. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 69, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.; Lukong, K.E. Breast cancer stem-like cells in drug resistance: A review of mechanisms and novel therapeutic strategies to overcome drug resistance. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 856974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattabiraman, D.R.; Weinberg, R.A. Tackling the cancer stem cells—What challenges do they pose? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkaya, H.; Liu, S.; Wicha, M.S. Breast cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor microenvironment. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3804–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, J.J.; Wellberg, E.A. The tumor promotional role of adipocytes in the breast cancer microenvironment and macroenvironment. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Dong, S.; Huang, R.; Chen, X. Cancer-associated adipocytes and breast cancer: Intertwining in the tumor microenvironment and challenges for cancer therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaledian, B.; Thibes, L.; Shimono, Y. Adipocyte regulation of cancer stem cells. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 4134–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andò, S.; Naimo, G.D.; Gelsomino, L.; Catalano, S.; Mauro, L. Novel insights into adiponectin action in breast cancer: Evidence of its mechanistic effects mediated by ERα expression. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimo, G.D.; Forestiero, M.; Paolì, A.; Malivindi, R.; Gelsomino, L.; Győrffy, B.; Leonetti, A.E.; Giordano, F.; Panza, S.; Conforti, F.L. ERα/LKB1 complex upregulates E-cadherin expression and stimulates breast cancer growth and progression upon adiponectin exposure. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 153, 1257–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimo, G.D.; Gelsomino, L.; Catalano, S.; Mauro, L.; Andò, S. Interfering role of ERα on adiponectin action in breast cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naimo, G.D.; Paolì, A.; Giordano, F.; Forestiero, M.; Panno, M.L.; Andò, S.; Mauro, L. Unraveling the role of adiponectin receptors in obesity-related breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelsomino, L.; Naimo, G.D.; Catalano, S.; Mauro, L.; Andò, S. The emerging role of adiponectin in female malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, S.; Irfan, W.; Jameel, A.; Ahmed, S.; Shahid, R.K. Obesity and cancer: A current overview of epidemiology, pathogenesis, outcomes, and management. Cancers 2023, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassman, I.; Le, N.; Asif, A.; Goulding, A.; Alcantara, C.A.; Vu, A.; Chorbajian, A.; Mirhosseini, M.; Singh, M.; Venketaraman, V. The role of obesity in breast cancer pathogenesis. Cells 2023, 12, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, S.; Michl, P.; Roth, L. Modeling obesity-driven pancreatic carcinogenesis—A review of current in vivo and in vitro models of obesity and pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cells 2022, 11, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalamaga, M.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Mantzoros, C.S. The role of adiponectin in cancer: A review of current evidence. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 547–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, H.E.; Doğan, L.; Gülçelik, M.A.; Gülçelik, N.E. Adiponectin: A predictor for breast cancer survival? Eur. J. Breast Health 2019, 15, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, L.; Naimo, G.D.; Gelsomino, L.; Malivindi, R.; Bruno, L.; Pellegrino, M.; Tarallo, R.; Memoli, D.; Weisz, A.; Panno, M.L. Uncoupling effects of estrogen receptor α on LKB1/AMPK interaction upon adiponectin exposure in breast cancer. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4343–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, L.; Naimo, G.D.; Ricchio, E.; Panno, M.L.; Andò, S. Cross-talk between adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, L.; Pellegrino, M.; De Amicis, F.; Ricchio, E.; Giordano, F.; Rizza, P.; Catalano, S.; Bonofiglio, D.; Sisci, D.; Panno, M.L. Evidences that estrogen receptor α interferes with adiponectin effects on breast cancer cell growth. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, L.; Pellegrino, M.; Giordano, F.; Ricchio, E.; Rizza, P.; De Amicis, F.; Catalano, S.; Bonofiglio, D.; Panno, M.L.; Andò, S. Estrogen receptor-α drives adiponectin effects on cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer cells. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 2150–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, M.; Rizza, P.; Donà, A.; Nigro, A.; Ricci, E.; Fiorillo, M.; Perrotta, I.; Lanzino, M.; Giordano, C.; Bonofiglio, D. FoxO3a as a positive prognostic marker and a therapeutic target in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, F.L.; Harrison, H.; Spence, K.; Ablett, M.P.; Simões, B.M.; Farnie, G.; Clarke, R.B. A detailed mammosphere assay protocol for the quantification of breast stem cell activity. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2012, 17, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murfuni, M.S.; Prestagiacomo, L.E.; Giuliano, A.; Gabriele, C.; Signoretti, S.; Cuda, G.; Gaspari, M. Evaluation of PAC and FASP Performance: DIA-Based Quantitative Proteomic Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, F.; Paolì, A.; Forastiero, M.; Marsico, S.; De Amicis, F.; Marrelli, M.; Naimo, G.D.; Mauro, L.; Panno, M.L. Valproic acid inhibits cell growth in both MCF-7 and MDA-MB231 cells by triggering different responses in a cell type-specific manner. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dontu, G.; Abdallah, W.M.; Foley, J.M.; Jackson, K.W.; Clarke, M.F.; Kawamura, M.J.; Wicha, M.S. In vitro propagation and transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1253–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, S.; Das, T.; Damodaran, C. Silencing NOTCH signaling causes growth arrest in both breast cancer stem cells and breast cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2587–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Mayea, Y.; Mir, C.; Masson, F.; Paciucci, R.; LLeonart, M.E. Insights into New Mechanisms and Models of Cancer Stem Cell Multidrug Resistance. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 60, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomeras, S.; Ruiz-Martínez, S.; Puig, T. Targeting breast cancer stem cells to overcome treatment resistance. Molecules 2018, 23, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paula, A.D.C.; Marques, O.; Sampaio, R.; Rosa, A.; Garcia, J.; Rema, A.; Faria, M.D.F.; Silva, P.; Vizcaino, R.; Lopes, C. Characterization of CD44+ ALDH1+ Ki-67− cells in non-malignant and neoplastic lesions of the breast. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 4629–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandoti, S. Mechanisms adopted by cancer cells to escape apoptosis—A review. Biocell 2021, 45, 863–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, N.J.; Goldstein, J.C.; Von Ahsen, O.; Schuler, M.; Newmeyer, D.D.; Green, D.R. Cytochrome c maintains mitochondrial transmembrane potential and ATP generation after outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization during the apoptotic process. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, M.R.; Lamberti, A.; Serrano, M.J.; Fiume, G.; Arcucci, A. Tumor microenvironment and cancer cell interactions in solid tumor growth and therapy resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 896194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panno, M.L.; Naimo, G.D.; Spina, E.; Andò, S.; Mauro, L. Different molecular signaling sustaining adiponectin action in breast cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2016, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartkopf, A.D.; Grischke, E.-M.; Brucker, S.Y. Endocrine-resistant breast cancer: Mechanisms and treatment. Breast Care 2020, 15, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szostakowska, M.; Trębińska-Stryjewska, A.; Grzybowska, E.A.; Fabisiewicz, A. Resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: Molecular mechanisms and future goals. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 173, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.-T.; Nguyen Thi Phuong, T.; Tien, N.L.B.; Tran, D.-K.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Thanh, V.V.; Luu Quang, T.; Minh, L.B.; Pham, V.H.; Ngoc, V.T.N. The effects of adipocytes on the regulation of breast cancer in the tumor microenvironment: An update. Cells 2019, 8, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-R.; Fang, Y.; Lyu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L. Exploring the dynamic interplay between cancer stem cells and the tumor microenvironment: Implications for novel therapeutic strategies. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallasamy, P.; Nimmakayala, R.K.; Parte, S.; Are, A.C.; Batra, S.K.; Ponnusamy, M.P. Tumor microenvironment enriches the stemness features: The architectural event of therapy resistance and metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavingire, N.; Campbell, P.; Wooten, J.; Aja, J.; Davis, M.B.; Loaiza-Perez, A.; Brantley, E. Cancer stem cells: Culprits in endocrine resistance and racial disparities in breast cancer outcomes. Cancer Lett. 2021, 500, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoes, B.M.; O’Brien, C.S.; Eyre, R.; Silva, A.; Yu, L.; Sarmiento-Castro, A.; Alférez, D.G.; Spence, K.; Santiago-Gomez, A.; Chemi, F. Anti-estrogen resistance in human breast tumors is driven by JAG1-NOTCH4-dependent cancer stem cell activity. Cell Rep. 2015, 12, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gooding, A.J.; Schiemann, W.P. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition programs and cancer stem cell phenotypes: Mediators of breast cancer therapy resistance. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, S.; Quader, S.; Cabral, H.; Ono, R. Interplay of EMT and CSC in Cancer and the Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, P.; Yoshihara, H.; Hosokawa, K.; Tai, I.; Shinmyozu, K.; Tsukahara, F.; Maru, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Nakayama, K.I.; Suda, T. p57Kip2 and p27Kip1 cooperate to maintain hematopoietic stem cell quiescence through interactions with Hsc70. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 9, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, V.; Giordano, A.; Benedetti, E.; Giansanti, F.; Quintiliani, M.; Cimini, A.; d’Angelo, M. The great escape: The power of cancer stem cells to evade programmed cell death. Cancers 2021, 13, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| OLIGO NAME | SEQUENCE 5′-3′ |
|---|---|
| ALPHA-SMA | Fw-AGACATCAGGGGGTGATGGT |
| Rw-CATGGCTGGGACATTGAAAG | |
| CD24 | Fw-GCTCCTACCCACGCAGATT |
| Rw-GTGAGACCACGAAGAGACTGG | |
| CD44 | Fw-GAAGAAGGTGTGGGCAGAAGA |
| Rw-ACCATTTCCTGAGACTTGCTG | |
| CYCLIN D1 | Fw-GATGCCAACCTCCTCAACGAC |
| Rw-CTCCTCGCACTTCTGTTCCTC | |
| E-CADHERIN | Fw-TGCCCAGAAAATGAAAAAGG |
| Rw-GTGTATGTGGCAATGCGTTC | |
| NOTCH1 | Fw-GTGACTGCTCCCTCAACTTCAAT |
| Rw-CTGTCACAGTGGCCGTCACT | |
| NOTCH2 | Fw-CACCCCAGCTGCTACTCACA |
| Rw-GCCAACCCAGCCTGCAT | |
| NOTCH3 | Fw-CCTGTCTTCCTGGGTTTGAG |
| Rw-CAGAACTGGCCTGTGCACTC | |
| NOTCH4 | Fw-CCAACCCTGCGATAATGCGAG |
| Rw-AGTCATCCGTTGAGACCCTGC | |
| OCT-4 | Fw-AGCGACTATGCACAACGAGA |
| Rw-CCATAGCCTGGGTACCAAA | |
| p21 | Fw-GCATGACAGATTTCTACCACTCC |
| Rw-AAGATGTAGAGCGGGCCTTT | |
| SMAD4 | Fw-GGAGCTCATCCTAGTAAATG |
| Rw-GACGGGCATAGATCACATGA | |
| SNAIL | Fw-CGAGTGGTTCTTCTGCGCTA |
| Rw-GGGCTGCTGGAAGGTAAACT | |
| SOX2 | Fw-CACATGAAGGAGCACCCGGATTAT |
| Rw-GTTCATGTGCGCGTAACTGTCCAT | |
| SOX4 | Fw-GGCCTCGAGCTGGGAATCGC |
| Rw-GCCCACTCGGGGTCTTGCAC | |
| SOX9 | Fw-AACGCCGAGCTCAGCAAGA |
| Rw-TTCTTGTGCTGCACGCGCA | |
| TWIST | Fw-TCCAAATTCAAAGAAACAGGGCG |
| Rw-CAGAATGCAGAGGTGTGAGGA | |
| VIMENTIN | Fw-GAGAACTTTGCCGTTGAAGC |
| Rw-GCTTCCTGTAGGTGGCAATC | |
| Ki67 | Fw-TCCTTTGGTGGGCACCTAAGACCTG |
| Rw-TGATGGTTGAGGTCGTTCCTTGATG | |
| 18S | Fw-CGGCGACGACCCATTCGAAC |
| Rw-GAATCGAACCCTGATTCCCCGTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naimo, G.D.; Forestiero, M.; Giordano, F.; Leonetti, A.E.; Gelsomino, L.; Panno, M.L.; Andò, S.; Mauro, L. Adiponectin Influences the Behavior of Stem Cells in Hormone-Resistant Breast Cancer. Cells 2025, 14, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040286
Naimo GD, Forestiero M, Giordano F, Leonetti AE, Gelsomino L, Panno ML, Andò S, Mauro L. Adiponectin Influences the Behavior of Stem Cells in Hormone-Resistant Breast Cancer. Cells. 2025; 14(4):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040286
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaimo, Giuseppina Daniela, Martina Forestiero, Francesca Giordano, Adele Elisabetta Leonetti, Luca Gelsomino, Maria Luisa Panno, Sebastiano Andò, and Loredana Mauro. 2025. "Adiponectin Influences the Behavior of Stem Cells in Hormone-Resistant Breast Cancer" Cells 14, no. 4: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040286
APA StyleNaimo, G. D., Forestiero, M., Giordano, F., Leonetti, A. E., Gelsomino, L., Panno, M. L., Andò, S., & Mauro, L. (2025). Adiponectin Influences the Behavior of Stem Cells in Hormone-Resistant Breast Cancer. Cells, 14(4), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040286







