MIRO1 Is Required for Dynamic Increases in Mitochondria-ER Contact Sites and Mitochondrial ATP During the Cell Cycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Animals
- Skin wounding
- Cell isolation and culture
- Cell counting
- Cell cycle synchronization
- Flow-cytometry analysis of cell cycle progression
- Construction and transduction of MIRO1 cDNA-expressing adenoviruses
- Construction and transduction of SPLICSL and nucleofection of SPLICSS cDNA
- Confocal microscopy
- Transmission electron microscopy and analysis of the mitochondrial ultrastructure
- Duolink Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
- MAM isolation
- Co-immunoprecipitation
- Transfection with MIRO1 siRNAs
- Cell lysis and fractionation
- Immunoblotting
- Measurement of ER Ca2+ transients
- Measurement of cytosolic Ca2+ transients
- Mitochondrial Ca2+ imaging
- Mitochondrial membrane potential
- Mitochondrial ATP measurement
- Intracellular ATP measurement
- Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. MIRO1 Is Required for Fibroblast Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression
3.2. MIRO1 Deficiency Abolishes Cell Cycle Changes at MERCS
3.3. MIRO1 Associates with MERCS During the Cell Cycle
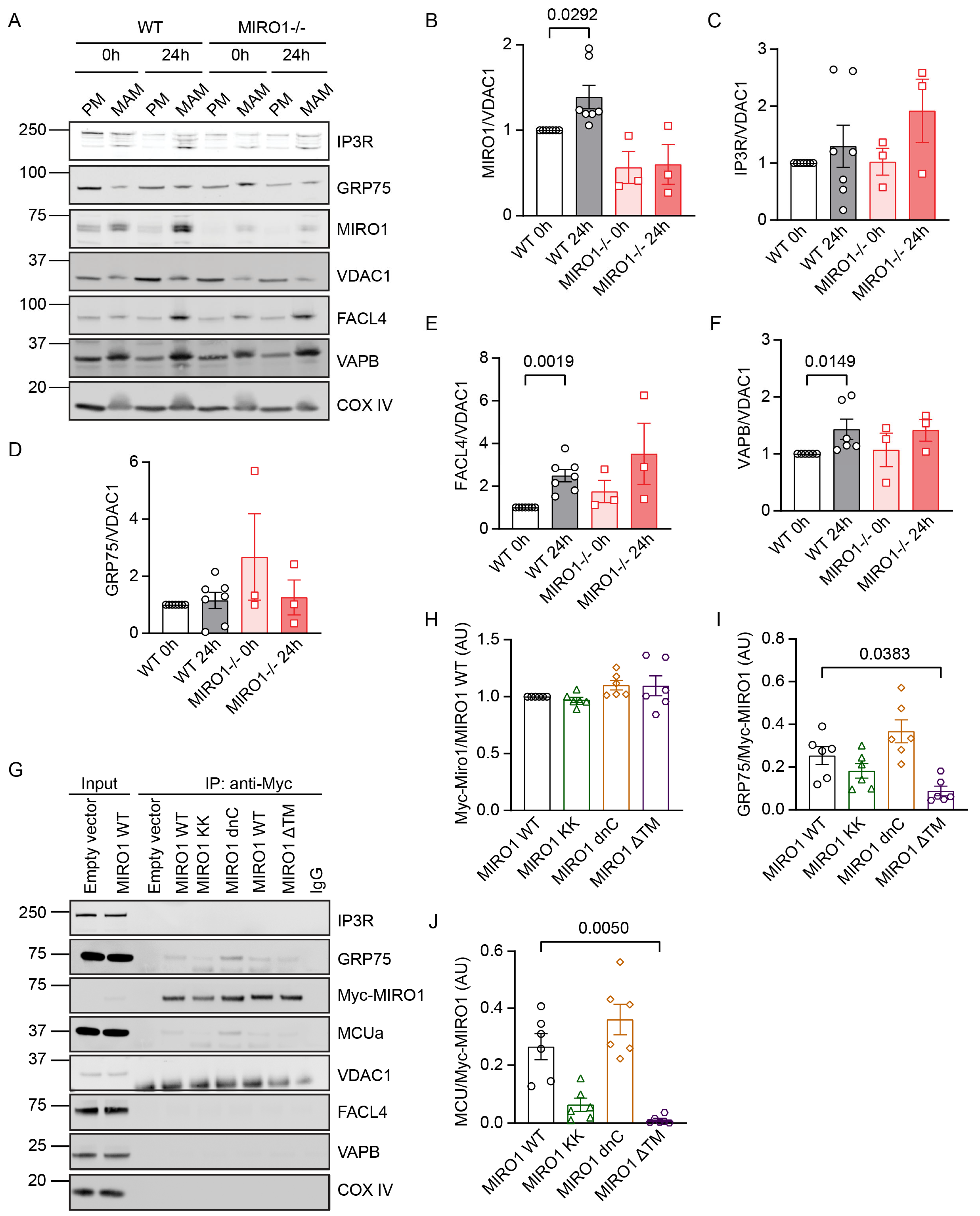
3.4. MIRO1 Abundance Increases in MAMs in G1/S
3.5. MIRO1 EF Hands Are Required for Its Association with GRP75 and MCU
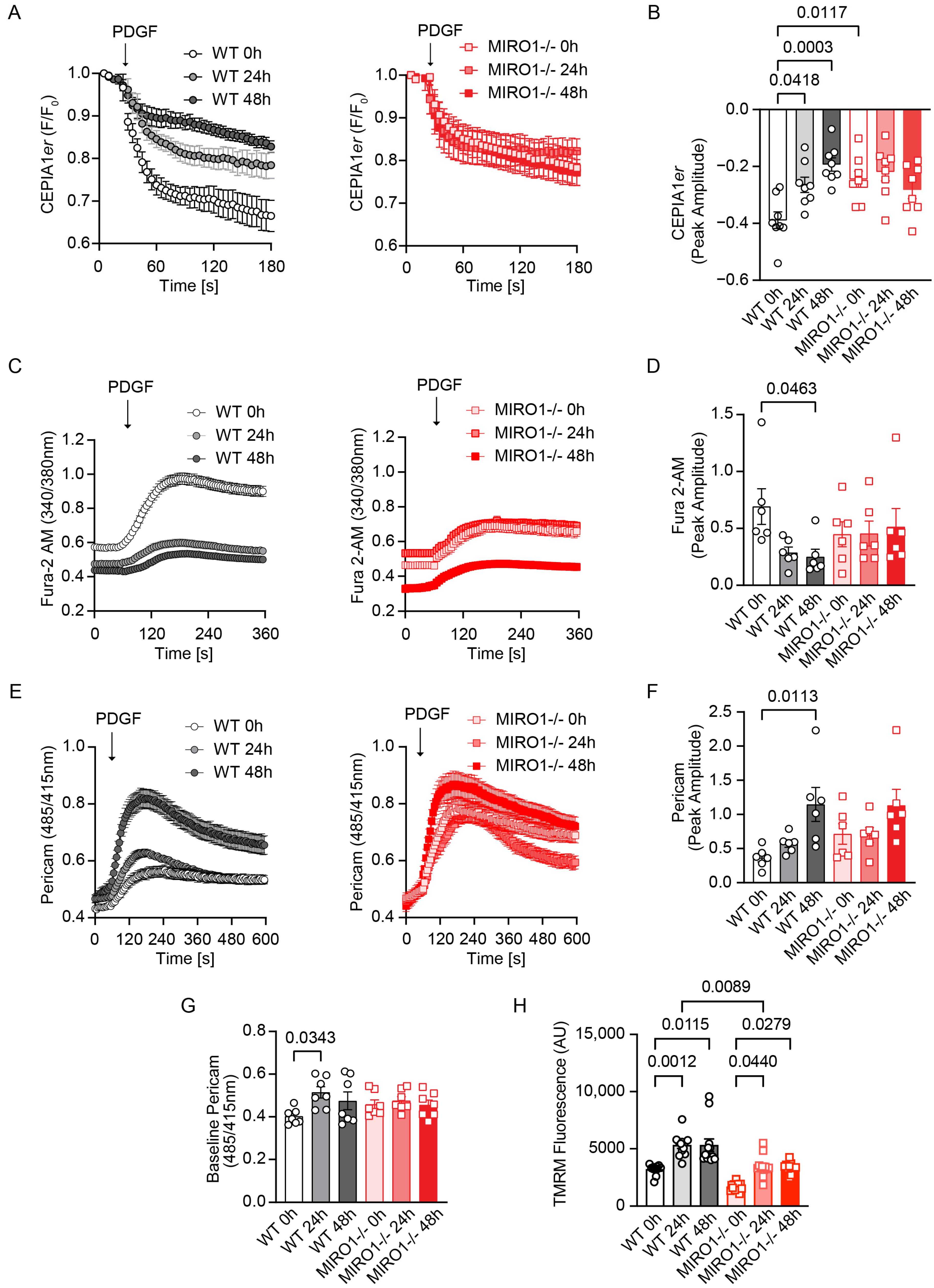
3.6. MIRO1 Promotes ER–Mitochondria Ca2+ Transfer During Cell Cycle Progression
3.7. MIRO1 Is Required to Maintain Intracellular ATP Levels During Cell Cycle Progression
3.8. MIRO1 EF-Hand Domains Are Required for MERCS Formation and Proliferation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kornmann, B.; Currie, E.; Collins, S.R.; Schuldiner, M.; Nunnari, J.; Weissman, J.S.; Walter, P. An ER-mitochondria tethering complex revealed by a synthetic biology screen. Science 2009, 325, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Csordas, G.; Varnai, P.; Golenar, T.; Roy, S.; Purkins, G.; Schneider, T.G.; Balla, T.; Hajnoczky, G. Imaging interorganelle contacts and local calcium dynamics at the ER-mitochondrial interface. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, A.A.; Voeltz, G.K. Endoplasmic reticulum–mitochondria contacts: Function of the junction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kornmann, B.; Walter, P. ERMES-mediated ER-mitochondria contacts: Molecular hubs for the regulation of mitochondrial biology. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardail, D.; Popa, I.; Bodennec, J.; Louisot, P.; Schmitt, D.; Portoukalian, J. The mitochondria-associated endoplasmic-reticulum subcompartment (MAM fraction) of rat liver contains highly active sphingolipid-specific glycosyltransferases. Biochem. J. 2003, 371, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuto, R.; Pinton, P.; Carrington, W.; Fay, F.S.; Fogarty, K.E.; Lifshitz, L.M.; Tuft, R.A.; Pozzan, T. Close contacts with the endoplasmic reticulum as determinants of mitochondrial Ca2+ responses. Science 1998, 280, 1763–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.; Dematteis, G.; Tapella, L.; Genazzani, A.A.; Calì, T.; Brini, M.; Verkhratsky, A. Ca2+ handling at the mitochondria-ER contact sites in neurodegeneration. Cell Calcium 2021, 98, 102453. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto, R.; Brini, M.; Murgia, M.; Pozzan, T. Microdomains with high Ca2+ close to IP3-sensitive channels that are sensed by neighboring mitochondria. Science 1993, 262, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefani, D.; Raffaello, A.; Teardo, E.; Szabo, I.; Rizzuto, R. A forty-kilodalton protein of the inner membrane is the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Nature 2011, 476, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, J.M.; Perocchi, F.; Girgis, H.S.; Plovanich, M.; Belcher-Timme, C.A.; Sancak, Y.; Bao, X.R.; Strittmatter, L.; Goldberger, O.; Bogorad, R.L.; et al. Integrative genomics identifies MCU as an essential component of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Nature 2011, 476, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, R.M. Regulation of mitochondrial dehydrogenases by calcium ions. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2009, 1787, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Machaca, K. Ca2+ signaling, genes and the cell cycle. Cell Calcium 2011, 49, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capiod, T. Cell proliferation, calcium influx and calcium channels. Biochimie 2011, 93, 2075–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Montemurro, C.; Vadrevu, S.; Gurlo, T.; Butler, A.E.; Vongbunyong, K.E.; Petcherski, A.; Shirihai, O.S.; Satin, L.S.; Braas, D.; Butler, P.C.; et al. Cell cycle-related metabolism and mitochondrial dynamics in a replication-competent pancreatic beta-cell line. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 2086–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, T.; Wang, K.; Zhao, F.; Chen, J.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Xia, Q.; et al. AMPK-mediated activation of MCU stimulates mitochondrial Ca. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, O.M.; Nguyen, E.K.; Santhana, V.; Fidler, T.P.; Sebag, S.C.; Rasmussen, T.P.; Mittauer, D.J.; Strack, S.; Goswami, P.C.; Abel, E.D.; et al. Loss of MCU prevents mitochondrial fusion in G1-S phase and blocks cell cycle progression and proliferation. Sci. Signal 2019, 12, eaav1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Courjaret, R.; Assaf, L.; Elmi, A.; Hammad, A.; Fisher, M.; Terasaki, M.; Machaca, K. Mitochondria-ER contact sites expand during mitosis. iScience 2024, 27, 109379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahacka, Z.; Zobalova, R.; Dubisova, M.; Rohlena, J.; Neuzil, J. Miro proteins connect mitochondrial function and intercellular transport. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 56, 401–425. [Google Scholar]
- Fatiga, F.F.; Wang, L.J.; Hsu, T.; Capuno, J.I.; Fu, C.Y. Miro1 functions as an inhibitory regulator of MFN at elevated mitochondrial Ca2+ levels. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 1848–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Fransson, Å.; Ruusala, A.; Aspenström, P. The atypical Rho GTPases Miro-1 and Miro-2 have essential roles in mitochondrial trafficking. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 344, 500–510. [Google Scholar]
- Berenguer-Escuder, C.; Grossmann, D.; Massart, F.; Antony, P.; Burbulla, L.F.; Glaab, E.; Imhoff, S.; Trinh, J.; Seibler, P.; Grünewald, A. Variants in Miro1 cause alterations of ER-mitochondria contact sites in fibroblasts from Parkinson’s disease patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Huh, S.; Lee, S.; Wu, Z.; Kim, A.K.; Kang, H.Y.; Lu, B. Altered ER-mitochondria contact impacts mitochondria calcium homeostasis and contributes to neurodegeneration in vivo in disease models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8844–E8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, K.S.; Huh, S.; Liu, S.; Lee, D.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Yu, K.; Lu, B. Polo Kinase Phosphorylates Miro to Control ER-Mitochondria Contact Sites and Mitochondrial Ca2+ Homeostasis in Neural Stem Cell Development. Dev. Cell 2016, 37, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornmann, B.; Osman, C.; Walter, P. The conserved GTPase Gem1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria connections. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14151–14156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; López-Doménech, G.; Halff, E.F.; Covill-Cooke, C.; Ivankovic, D.; Melandri, D.; Arancibia-Cárcamo, I.L.; Burden, J.J.; Lowe, A.R.; Kittler, J.T. Miro clusters regulate ER-mitochondria contact sites and link cristae organization to the mitochondrial transport machinery. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4399. [Google Scholar]
- Niescier, R.F.; Hong, K.; Park, D.; Min, K.T. MCU Interacts with Miro1 to Modulate Mitochondrial Functions in Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 4666–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamogante, F.; Barazzuol, L.; Poggio, E.; Tromboni, M.; Brini, M.; Calì, T. Stable Integration of Inducible SPLICS Reporters Enables Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Multiple Organelle Contact Sites upon Modulation of Cholesterol Traffic. Cells 2022, 11, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieckowski, M.R.; Giorgi, C.; Lebiedzinska, M.; Duszynski, J.; Pinton, P. Isolation of mitochondria-associated membranes and mitochondria from animal tissues and cells. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieri, D.; Vicario, M.; Giacomello, M.; Vallese, F.; Filadi, R.; Wagner, T.; Pozzan, T.; Pizzo, P.; Scorrano, L.; Brini, M. SPLICS: A split green fluorescent protein-based contact site sensor for narrow and wide heterotypic organelle juxtaposition. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.; Koval, O.M.; Endoni, B.T.; Juhr, D.; Stein, C.C.; Allamargot, C.; Lin, L.-H.; Guo, D.-F.; Rahmouni, K.; Boudreau, R.L. MIRO1 controls energy production and proliferation of smooth muscle cells. Biorxiv 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Atakpa-Adaji, P.; Ivanova, A. IP3R at ER-Mitochondrial Contact Sites: Beyond the IP3R-GRP75-VDAC1 Ca2+ Funnel. Contact 2023, 6, 25152564231181020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, N.; Mignery, G.A.; Banach, K. Cell cycle-dependent calcium oscillations in mouse embryonic stem cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C1510–C1518. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Russa, A.D.; Maesawa, C.; Satoh, Y.-i. Spontaneous Ca2+ i oscillations in G1/S phase-synchronized cells. J. Electron. Microsc. 2009, 58, 321–329. [Google Scholar]
- Glancy, B.; Balaban, R.S. Role of mitochondrial Ca2+ in the regulation of cellular energetics. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 2959–2973. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Jia, M.; Zhu, S.; Ren, H.; Wang, G.; Xin, G.; Sun, M.; Wang, X.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Mitotic ER-mitochondria contact enhances mitochondrial Ca. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saotome, M.; Safiulina, D.; Szabadkai, G.; Das, S.; Fransson, Å.; Aspenstrom, P.; Rizzuto, R.; Hajnóczky, G. Bidirectional Ca2+-dependent control of mitochondrial dynamics by the Miro GTPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 20728–20733. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Schwarz, T.L. The mechanism of Ca2+-dependent regulation of kinesin-mediated mitochondrial motility. Cell 2009, 136, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, E.K.; Koval, O.M.; Noble, P.; Broadhurst, K.; Allamargot, C.; Wu, M.; Strack, S.; Thiel, W.H.; Grumbach, I.M. CaMKII (Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Kinase II) in Mitochondria of Smooth Muscle Cells Controls Mitochondrial Mobility, Migration, and Neointima Formation. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhou, H.; Yu, X.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Meng, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chisholm, A.D.; Xu, S. Wounding triggers MIRO-1 dependent mitochondrial fragmentation that accelerates epidermal wound closure through oxidative signaling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Domenech, G.; Covill-Cooke, C.; Ivankovic, D.; Halff, E.F.; Sheehan, D.F.; Norkett, R.; Birsa, N.; Kittler, J.T. Miro proteins coordinate microtubule- and actin-dependent mitochondrial transport and distribution. EMBO J. 2018, 37, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartok, A.; Weaver, D.; Golenár, T.; Nichtova, Z.; Katona, M.; Bánsághi, S.; Alzayady, K.J.; Thomas, V.K.; Ando, H.; Mikoshiba, K.; et al. IP3 receptor isoforms differently regulate ER-mitochondrial contacts and local calcium transfer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dematteis, G.; Tapella, L.; Casali, C.; Talmon, M.; Tonelli, E.; Reano, S.; Ariotti, A.; Pessolano, E.; Malecka, J.; Chrostek, G. ER-mitochondria distance is a critical parameter for efficient mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and oxidative metabolism. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Ruan, N.; Luo, P.; Wang, Q.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Dai, Y.; Lin, L.; Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Modulation of ER-mitochondria tethering complex VAPB-PTPIP51: Novel therapeutic targets for aging-associated diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 98, 102320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillusson, S.; Gomez-Suaga, P.; Stoica, R.; Little, D.; Gissen, P.; Devine, M.J.; Noble, W.; Hanger, D.P.; Miller, C.C.J. α-Synuclein binds to the ER-mitochondria tethering protein VAPB to disrupt Ca. Acta. Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, K.J.; Mórotz, G.M.; Stoica, R.; Tudor, E.L.; Lau, K.F.; Ackerley, S.; Warley, A.; Shaw, C.E.; Miller, C.C. VAPB interacts with the mitochondrial protein PTPIP51 to regulate calcium homeostasis. Hum Mol Genet. 2012, 21, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, K.; Wunder, C.; Roysam, B.; Lin, G.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. A hyperfused mitochondrial state achieved at G1–S regulates cyclin E buildup and entry into S phase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11960–11965. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.T.; Niescier, R.F.; Min, K.T. Mitochondrial matrix Ca2+ as an intrinsic signal regulating mitochondrial motility in axons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15456–15461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, T.L.; Higgs, N.F.; Sheehan, D.F.; Al Awabdh, S.; López-Doménech, G.; Arancibia-Carcamo, I.L.; Kittler, J.T. Miro1 Regulates Activity-Driven Positioning of Mitochondria within Astrocytic Processes Apposed to Synapses to Regulate Intracellular Calcium Signaling. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 15996–16011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Sheng, Z.-H. Moving or stopping mitochondria: Miro as a traffic cop by sensing calcium. Neuron 2009, 61, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.P.; Focia, P.J.; Chakravarthy, S.; Landahl, E.C.; Klosowiak, J.L.; Rice, S.E.; Freymann, D.M. Insight into human Miro1/2 domain organization based on the structure of its N-terminal GTPase. J. Struct. Biol. 2020, 212, 107656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babic, M.; Russo, G.J.; Wellington, A.J.; Sangston, R.M.; Gonzalez, M.; Zinsmaier, K.E. Miro’s N-terminal GTPase domain is required for transport of mitochondria into axons and dendrites. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5754–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhea, L.; Dunnwald, M. Murine Excisional Wound Healing Model and Histological Morphometric Wound Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 162, e61616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzo, R.; Costa, R.; Bachmann, M.; Leanza, L.; Szabò, I. Mitochondrial Metabolism, Contact Sites and Cellular Calcium Signaling: Implications for Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krols, M.; van Isterdael, G.; Asselbergh, B.; Kremer, A.; Lippens, S.; Timmerman, V.; Janssens, S. Mitochondria-associated membranes as hubs for neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainbinder, A.; Boncompagni, S.; Protasi, F.; Dirksen, R.T. Role of Mitofusin-2 in mitochondrial localization and calcium uptake in skeletal muscle. Cell Calcium 2015, 57, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Kawasaki, K.; Kondo, R.; Imaizumi, Y.; Yamamura, H. Mitofusin 2 positively regulates Ca2+ signaling by tethering the sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C295–C305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Endoni, B.T.; Koval, O.M.; Allamargot, C.; Kortlever, T.; Qian, L.; Sadoski, R.J.; Juhr, D.; Grumbach, I.M. MIRO1 Is Required for Dynamic Increases in Mitochondria-ER Contact Sites and Mitochondrial ATP During the Cell Cycle. Cells 2025, 14, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070482
Endoni BT, Koval OM, Allamargot C, Kortlever T, Qian L, Sadoski RJ, Juhr D, Grumbach IM. MIRO1 Is Required for Dynamic Increases in Mitochondria-ER Contact Sites and Mitochondrial ATP During the Cell Cycle. Cells. 2025; 14(7):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070482
Chicago/Turabian StyleEndoni, Benney T., Olha M. Koval, Chantal Allamargot, Tara Kortlever, Lan Qian, Riley J. Sadoski, Denise Juhr, and Isabella M. Grumbach. 2025. "MIRO1 Is Required for Dynamic Increases in Mitochondria-ER Contact Sites and Mitochondrial ATP During the Cell Cycle" Cells 14, no. 7: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070482
APA StyleEndoni, B. T., Koval, O. M., Allamargot, C., Kortlever, T., Qian, L., Sadoski, R. J., Juhr, D., & Grumbach, I. M. (2025). MIRO1 Is Required for Dynamic Increases in Mitochondria-ER Contact Sites and Mitochondrial ATP During the Cell Cycle. Cells, 14(7), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070482





