Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Composite Nanofibrous Membranes Prepared from Hemp Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Skin Collagen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Nanofibrous Membranes
2.2.2. Cross-Linking of Nanofibre Membranes
2.2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Thermogravimetry Analysis (DSC and TGA)
2.2.6. Determination of Tensile Stress
2.2.7. Cytocompatibility Evaluation
2.2.8. Wound Healing
2.2.9. TGF-β and VEGF Expression Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
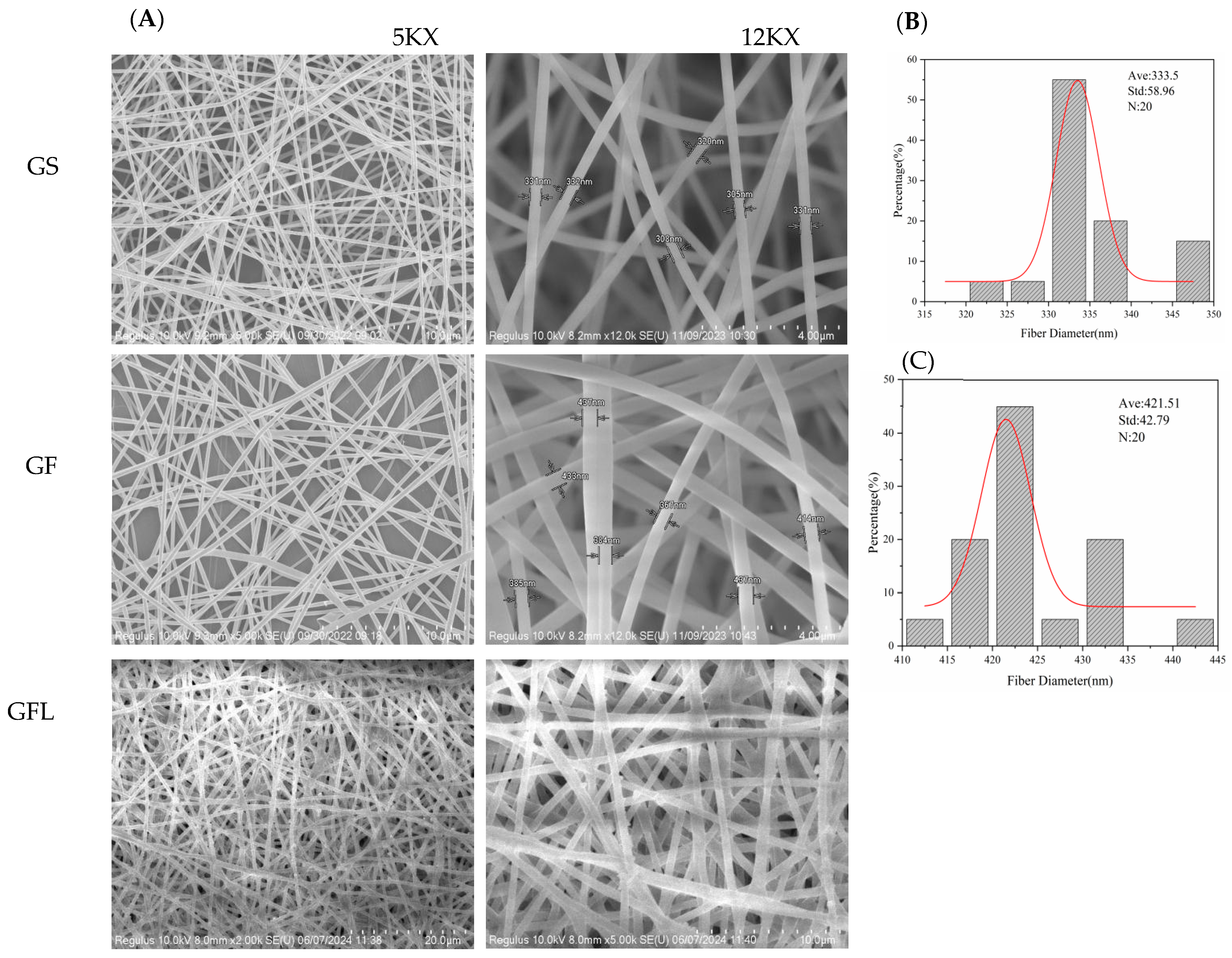
3.1. Morphological Characteristics
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry and Thermogravimetry Analysis (DSC and TGA)
3.4. Determination of Tensile Stress
3.5. Cytocompatibility Evaluation
3.6. Wound Healing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Maitz, P.K. Advances and new technologies in the treatment of burn injury. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 123, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushani, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques: Potential food based applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Liu, J.; Oh, S.H.; Soker, S.; Atala, A.; Yoo, J.J. Development of a composite vascular scaffolding system that withstands physiological vascular conditions. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stitzel, J.; Liu, J.; Lee, S.J.; Komura, M.; Berry, J.; Soker, S.; Lim, G.; Van, D.M.; Czerw, R.; Yoo, J.J.; et al. Controlled fabrication of a biological vascular substitute. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, G.; Wu, J. The structure and property of the electrospinning silk fibroin/gelatin blend nanofibers. e-Polymers 2008, 8, 098. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Li, W.; Luo, X.; Zhang, X.; Di, J.; Wang, G.; Yu, J. Polarity-dominated stable N97 respirators for airborne virus capture based on nanofibrous membranes. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 23949–23955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fang, K. Anti-adhesive and antibacterial chitosan/PEO nanofiber dressings with high breathability for promoting wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-J.; Yu, T.-C.; Huang, B.-H.; Tso, K.-H.; Song, Y.-F.; Yin, G.-Y.; Yang, G.-S.; Wu, P.-W. Synthesis of novel chitosan/sodium hyaluronate/iridium hydrogel nanocomposite for wound healing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdian, N.; Etminanfar, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Sheykholeslami, S.O.R. Incorporating mesoporous SiO2-HA particles into chitosan/hydroxyapatite scaffolds: A comprehensive evaluation of bioactivity and biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Li, Y.; Pan, J.; Liu, F.; Dai, H.; Fu, Y.; Huang, T.; Farooq, S.; Zhang, H. Collagen and gelatin: Structure, properties, and applications in food industry. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 128037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, H. Structural, functional, rheological, and biological properties of the swim bladder collagen extracted from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Lwt 2022, 153, 112518. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, F.-Y.; Hung, Y.-S.; Liou, H.-M.; Shen, C.-H. Electrospun hyaluronate–collagen nanofibrous matrix and the effects of varying the concentration of hyaluronate on the characteristics of foreskin fibroblast cells. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Songchotikunpan, P.; Tattiyakul, J.; Supaphol, P. Extraction and electrospinning of gelatin from fish skin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, F.; Singh, V. Assessment of antibacterial properties of electrospun fish collagen/poly (vinyl) alcohol nanofibers with biosurfactant rhamnolipid. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 67, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, J.; Dasgupta, S.; Das, P.; Gouripriya, D.A.; Barui, A.; Basak, P.; Ghosh, M.; Saha, P. Bilayer regenerated cellulose/quaternized chitosan-hyaluronic acid/collagen electrospun scaffold for potential wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W. Prepartion of Prionace Glauca Type Ii Collagen/Chitosan Based Seawater Proofnanomembranes for Wound Healing. Master’s Thesis, Donghua University, Shanghai, China, 2018. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=lwcs1eIaudikpYhE0YiM-agxKMGdNssVn2P4YlALI0jOcGlf6yxA_DUakdm2ioViJVfOh3tkQ6GzWZEUMPBKAYjhI6-ZtISAUcJM4XLF_2-IMnnneRcNtuMFlpJPLC10wcUFYE-GLJ6YzzqOvrNAO_njvTKMIW9dvgPz3pEACFprB0qqo6o63GB-OQqb7mAErlczd39v2TU=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Arumugam, M.; Murugesan, B.; Chinnalagu, D.K.; Mahalingam, S. Dual therapeutic approach: Biodegradable nanofiber scaffolds of silk fibroin and collagen combined with silver and gold nanoparticles for enhanced bacterial infections treatment and accelerated wound healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2024, 95, 105620. [Google Scholar]
- Action, S. World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2020; Volume 2020, pp. 1–244. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Turnay, J.; Fernández-Dıaz, M.; Ulmo, N.; Lizarbe, M.A.; Montero, P. Structural and physical properties of gelatin extracted from different marine species: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yunoki, S.; Suzuki, T.; Takai, M. Stabilization of low denaturation temperature collagen from fish by physical cross-linking methods. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 575–577. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Pei, X.-R.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Wang, J.-B.; Li, Y. Marine collagen peptides prepared from chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) skin extend the life span and inhibit spontaneous tumor incidence in sprague-dawley rats. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M.; Kang, H.Y.; Min, H.-J.; Choi, D.J.; Lee, R.; Ikram, M.; Subhan, F.; Jin, S.W.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kwak, J.-Y.; et al. Bioactive fish collagen/polycaprolactone composite nanofibrous scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning for 3D cell culture. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 205, 47–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorani, B.; Emadzadeh, B.; Rezaeinia, H.; Russell, S.J. Improvements in gelatin cold water solubility after electrospinning and associated physicochemical, functional and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105740. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Qin, X.; Xu, Z.; Song, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ruan, H.; Chen, J. Comparison of cytotoxicity evaluation of anticancer drugs between real-time cell analysis and CCK-8 method. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12036–12042. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Guo, Z.; He, P.; Chen, T.; Li, L.; Ding, S.; Li, H. Study on structure, mechanical property and cell cytocompatibility of electrospun collagen nanofibers crosslinked by common agents. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 476–486. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Yuan, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Xiang, A.; Ashok, B.; Rajulu, A.V. Electrospinning of polyvinyl alcohol into crosslinked nanofibers: An approach to fabricate functional adsorbent for heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tsukada, M.; Morikawa, H.; Aojima, K.; Zhang, G.; Miura, M. Production of silk sericin/silk fibroin blend nanofibers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 510. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Feng, X. Microporous CA/PVDF membranes based on electrospun nanofibers with controlled crosslinking induced by solvent vapor. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 512, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Mo, X.; He, C.; Wang, H. Intermolecular interactions in electrospun collagen–chitosan complex nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 410–418. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Yi, R.; Xu, N.; Gao, R.; Hong, B. Extraction and characterization of acid-soluble collagen from scales and skin of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Raia, N.R.; Partlow, B.P.; McGill, M.; Kimmerling, E.P.; Ghezzi, C.E.; Kaplan, D.L. Enzymatically crosslinked silk-hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Biomaterials 2017, 131, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Cao, C.; Ma, X.; Lin, J. Electrospinning of silk fibroin and collagen for vascular tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, D.; Shepherd, J.; Ghose, S.; Kew, S.; Cameron, R.; Best, S. The process of EDC-NHS cross-linking of reconstituted collagen fibres increases collagen fibrillar order and alignment. APL Mater. 2015, 3, 014902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C. Enhanced physicochemical properties of collagen by using EDC/NHS-crosslinking. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2012, 35, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisdorf, W.C.; Krimm, S. Infrared amide I ‘band of the coiled coil. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Wang, R.; Sui, X.; Qi, B.; Han, F.; Bi, S.; Jiang, L. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analysis of soybean isolate protein at different heat treatment conditions. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2016, 37, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khirzin, M.; Ton, S.; Fatkhurrohman, F. Ekstraksi dan karakterisasi gelatin tulang itik menggunakan metode ekstraksi asam. J. Sain Peternak. Indones. 2019, 14, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy-Moonshine, A.; Amir, E.-A.D.; Keasar, C. Enhancement of beta-sheet assembly by cooperative hydrogen bonds potential. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2639–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, C.; Dias, C.L. Hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonds in β-sheet formation. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 139, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.; Valluzzi, R.; Kaplan, D. Conformational transitions in model silk peptides. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 2690–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Kaplan, D.; Cebe, P. Determining beta-sheet crystallinity in fibrous proteins by thermal analysis and infrared spectroscopy. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 6161–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Grimsley, G.R.; Razvi, A.; Scholtz, J.M.; Pace, C.N. Increasing protein stability by improving beta-turns. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2009, 77, 491–498. [Google Scholar]
- Narhi, L.O.; Philo, J.S.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Samal, B.; Arakawa, T. Induction of α-helix in the β-sheet protein tumor necrosis factor-α: Thermal-and trifluoroethanol-induced denaturation at neutral pH. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 11447–11453. [Google Scholar]
- Dzwolak, W.; Muraki, T.; Kato, M.; Taniguchi, Y. Chain-length dependence of α-helix to β-sheet transition in polylysine: Model of protein aggregation studied by temperature-tuned FTIR spectroscopy. Biopolym. Orig. Res. Biomol. 2004, 73, 463–469. [Google Scholar]
- Ricaurte, L.; Santagapita, P.R.; Díaz, L.E.; Quintanilla-Carvajal, M.X. Edible gelatin-based nanofibres loaded with oil encapsulating high-oleic palm oil emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 595, 124673. [Google Scholar]
- Caflisch, A.; Karplus, M. Molecular dynamics simulation of protein denaturation: Solvation of the hydrophobic cores and secondary structure of barnase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1746–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, A.M.; Lisboa, C.R.; Costa, J.A.V. High protein ingredients of microalgal origin: Obtainment and functional properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 47, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Mosayebi, V.; Fathi, M.; Shahedi, M.; Soltanizadeh, N.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Fast-dissolving antioxidant nanofibers based on Spirulina protein concentrate and gelatin developed using needleless electrospinning. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101759. [Google Scholar]
- Borsoi, C.; Zimmernnam, M.V.; Zattera, A.J.; Santana, R.M.; Ferreira, C.A. Thermal degradation behavior of cellulose nanofibers and nanowhiskers. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Gimenez, E.; Lagaron, J.M. Characterization of the morphology and thermal properties of zein prolamine nanostructures obtained by electrospinning. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, G.; Woell, S.; Argos, P. Protein thermal stability, hydrogen bonds, and ion pairs. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 269, 631–643. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, C.N.; Horn, G.; Hebert, E.J.; Bechert, J.; Shaw, K.; Urbanikova, L.; Scholtz, J.M.; Sevcik, J. Tyrosine hydrogen bonds make a large contribution to protein stability. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 312, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safandowska, M.; Pietrucha, K. Effect of fish collagen modification on its thermal and rheological properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 53, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olloqui-Sariego, J.L.; Díaz-Quintana, A.; De la Rosa, M.Á.; Calvente, J.J.; Márquez, I.; Díaz-Moreno, I.; Andreu, R. Protein crosslinking improves the thermal resistance of plastocyanin immobilized on a modified gold electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 124, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.N.C.; Marigheto, N.A.; Wellner, N.; Fairhurst, S.A.; Jenkins, J.A.; Mann, R.; Belton, P.S. Thermally induced structural changes in glycinin, the 11S globulin of soya bean (Glycine max)—An in situ spectroscopic study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1648, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badii, F.; MacNaughtan, W.; Mitchell, J.; Farhat, I. The effect of drying temperature on physical properties of thin gelatin films. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Panzavolta, S.; Rubini, K. Relationship between triple-helix content and mechanical properties of gelatin films. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5675–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. Electrospun chitosan/sericin composite nanofibers with antibacterial property as potential wound dressings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 68, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Li, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Ren, G.; Yan, M.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L. The effect of pacific cod (Gadus macrocephalus) skin gelatin polypeptides on UV radiation-induced skin photoaging in ICR mice. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cui, S. Preparation and characterization of biomimetic tussah silk fibroin/chitosan composite nanofibers. Iran. Polym. J. 2013, 22, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoura, N.; Aiba, S.-I.; Higuchi, M.; Gotoh, Y.; Tsukada, M.; Imai, Y. Attachment and growth of fibroblast cells on silk fibroin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 208, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature 1984, 309, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zuo, B.Q.; Zhang, H.X.; Bai, L. Studies of electrospun regenerated SF/TSF nanofibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Takasu, Y.; Yamada, H.; Tsubouchi, K. Isolation of three main sericin components from the cocoon of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2715–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Lee, C.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K. Novel bilayer wound dressing based on electrospun gelatin/keratin nanofibrous mats for skin wound repair. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 533–540. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B. Determination of Amino Acid Content of Collagen in Medical Macromolecules. Hans J. Med. Chem. 2017, 5, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, M.; Mechanic, G.L. Cross-Linking of Collagen. Collagen; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 157–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Y. Collagen-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 1132–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Shan, Y.; Xiong, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J. In vivo study of silk fibroin/gelatin electrospun nanofiber dressing loaded with astragaloside IV on the effect of promoting wound healing and relieving scar. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 272–281. [Google Scholar]
- Hassani, M.S.; Salehi, M.; Ehterami, A.; Mahami, S.; Bitaraf, F.S.; Rahmati, M. Evaluation of collagen type I and III, TGF-β1, and VEGF gene expression in rat skin wound healing treated by alginate/chitosan hydrogel containing crocetin. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 195, 108895. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Dong, W.; Lai, E.; Wang, H. Silk fibroin-based scaffolds for tissue engineering. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1381838. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, T.-W.; Chang, Y.-L. Silk fibroin/chitosan–hyaluronic acid versus silk fibroin scaffolds for tissue engineering: Promoting cell proliferations in vitro. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elson, D.A.; Ryan, H.E.; Snow, J.W.; Johnson, R.; Arbeit, J.M. Coordinate up-regulation of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α and HIF-1 target genes during multi-stage epidermal carcinogenesis and wound healing. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 6189–6195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kisling, A.; Lust, R.M.; Katwa, L.C. What is the role of peptide fragments of collagen I and IV in health and disease? Life Sci. 2019, 228, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.R.; Sultan, M.T.; Park, H.J.; Lee, J.M.; Ju, H.W.; Lee, O.J.; Lee, D.J.; Kaplan, D.L.; Park, C.H. NF-κB signaling is key in the wound healing processes of silk fibroin. Acta Biomater. 2018, 67, 183–195. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, Z.; Li, B.; Wu, L.; Qiu, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Lu, M.; Yang, Y. Probiotic-functionalized silk fibroin/sodium alginate scaffolds with endoplasmic reticulum stress-relieving properties for promoted scarless wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 6297–6311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Suzawa, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Nishida, E.; Fujitaa, T.; Matsumotoa, T. Differentiation and transforming growth factor-β receptor down-regulation by collagen-α2β1 integrin interaction is mediated by focal adhesion kinase and its downstream signals in murine osteoblastic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29309–29316. [Google Scholar]
- Mitola, S.; Brenchio, B.; Piccinini, M.; Tertoolen, L.; Zammataro, L.; Breier, G.; Rinaudo, M.T.; Hertog, J.D.; Arese, M.; Bussolino, F. Type I collagen limits VEGFR-2 signaling by a SHP2 protein-tyrosine phosphatase–dependent mechanism 1. Circ. Res. 2006, 98, 45–54. [Google Scholar]

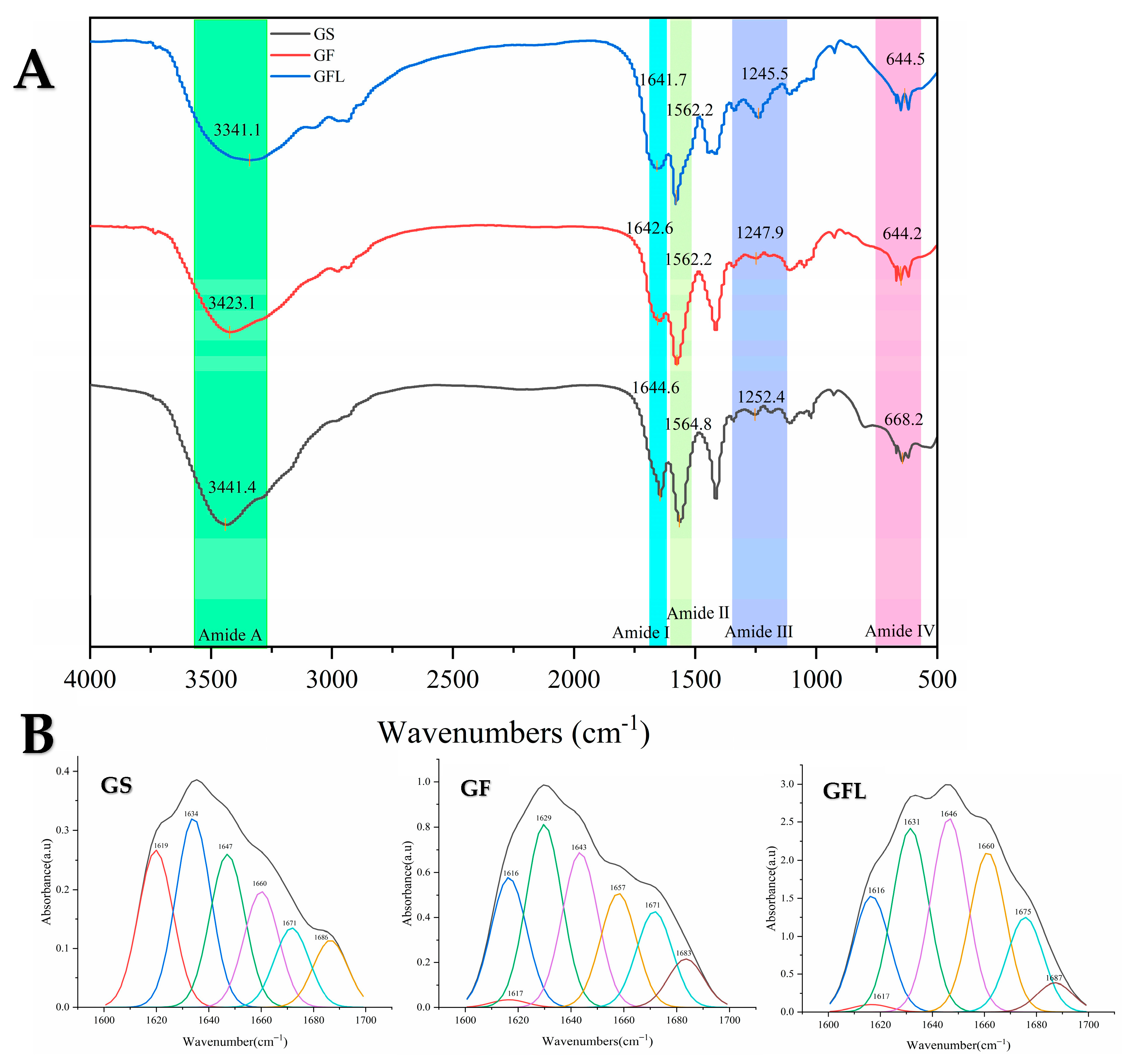




| α-Helix (1650–1660) | β-Turn (1660–1700) | β-Sheet (1600–1640) | Random Coil (1640–1650) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GS | 23.34% | 28.70% | 24.79% | 23.17% |
| GF | 15.58% | 19.69% | 43.63% | 21.10% |
| GFL | 14.38% | 15.81% | 47.16% | 22.64% |
| Sample | Degradation Onset Temperature (Tonset) | Maximum Degradation Temperature (Tmax) |
|---|---|---|
| GS | 38 ± 0.22 °C | 324 ± 0.68 °C |
| GF | 59 ± 0.21 °C | 327 ± 0.31 °C |
| GFL | 63.31 ± 0.51 °C | 331.99 ± 0.14 °C |
| Sample | GS | GF | GSL |
| TS (MPa) | 1.72 ± 0.39 | 2.4 ± 0.62 | 4 ± 0.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Duan, R.; Zhang, J. Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Composite Nanofibrous Membranes Prepared from Hemp Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Skin Collagen. Cells 2025, 14, 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070537
Liu Y, Zhu M, Duan R, Zhang J. Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Composite Nanofibrous Membranes Prepared from Hemp Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Skin Collagen. Cells. 2025; 14(7):537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070537
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yu, Mochi Zhu, Rui Duan, and Junjie Zhang. 2025. "Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Composite Nanofibrous Membranes Prepared from Hemp Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Skin Collagen" Cells 14, no. 7: 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070537
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhu, M., Duan, R., & Zhang, J. (2025). Characterization and Biological Evaluation of Composite Nanofibrous Membranes Prepared from Hemp Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) Skin Collagen. Cells, 14(7), 537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070537






