The Emerging Role of Water Loss in Dog Aging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
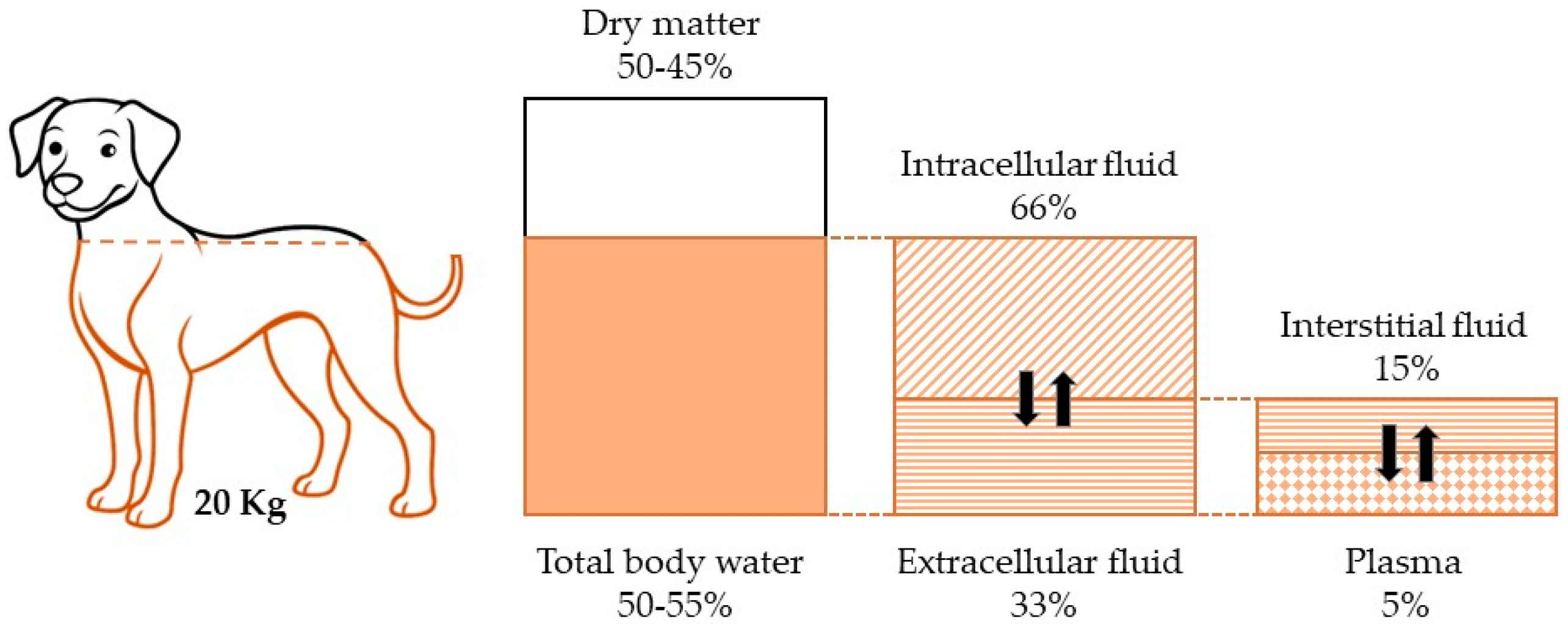
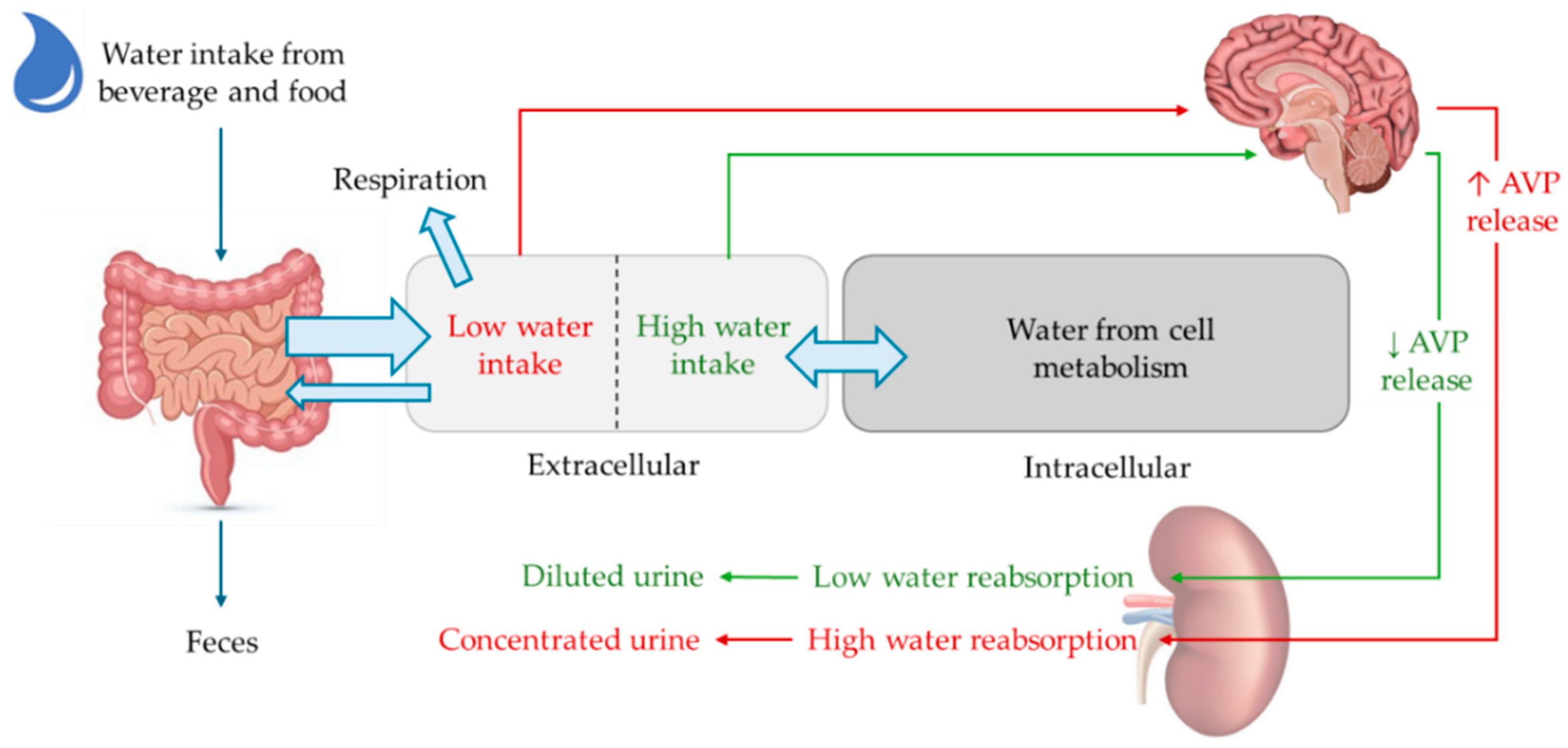
2. Aging and Water Balance
3. Altered Structural Role of Water and Metabolic Efficiency in Key Biological Compartments
4. Osmotic Balance and Cell-Volume Adaptation
5. Membrane Stability and Dynamics
6. Biological Macromolecule Rearrangement: Proteins and DNA
7. Aging-Related Changes in Hydration Impair the Effectiveness of Water as a Solvent and Transport Medium
8. Aging-Related Water Loss and Musculoskeletal Reorganization
9. Neuronal Signaling and Water Aging-Related Loss
10. Water-Balance Valuation in Aged Dogs Via Visual and Instrumental Approaches
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bellows, J.; Colitz, C.M.H.; Daristotle, L.; Ingram, D.K.; Lepine, A.; Marks, S.L.; Sanderson, S.L.; Tomlinson, J.; Zhang, J. Defining Healthy Aging in Older Dogs and Differentiating Healthy Aging from Disease. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Healthy Ageing: A Challenge for Europe; National Institute of Public Health: Stockholm, Sweden, 2007; ISBN 978-91-7257-481-6.
- Ruple, A.; MacLean, E.; Snyder-Mackler, N.; Creevy, K.E.; Promislow, D. Dog Models of Aging. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 10, 419–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermingham, E.N.; Patterson, K.A.; Shoveller, A.K.; Fraser, K.; Butowski, C.F.; Thomas, D.G. Nutritional Needs and Health Outcomes of Ageing Cats and Dogs: Is It Time for Updated Nutrient Guidelines? Anim. Front. 2024, 14, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, A.; Fujiyoshi, Y.; Agre, P. The Importance of Aquaporin Water Channel Protein Structures. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, A.; Ogura, T.; Taiji1, M.; Toyama, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Son, M.; Takayama, K.; Iwamoto, M.; Sato, I.; Yeh, J.Z.; et al. The Atomic-Level Mechanism Underlying the Functionality of Aquaporin-0. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1304.5898. [Google Scholar]
- Adeoye, A.; Odugbemi, A.; Ajewole, T. Structure and Function of Aquaporins: The Membrane Water Channel Proteins. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 12, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J.; Törnroth-Horsefield, S. Aquaporin Protein-Protein Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magouliotis, D.E.; Tasiopoulou, V.S.; Svokos, A.A.; Svokos, K.A. Aquaporins in Health and Disease. In Advances in Clinical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 98, pp. 149–171. ISBN 978-0-12-821558-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jéquier, E.; Constant, F. Water as an Essential Nutrient: The Physiological Basis of Hydration. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, H.J. Dehydration in the Older Adult. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2015, 41, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, A.; Ballard, B.D.; Mohiuddin, S.S. Physiology, Water Balance. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Scallan, J.; Huxley, V.H.; Korthuis, R.J. Fluid Movement Across the Endothelial Barrier. In Capillary Fluid Exchange: Regulation, Functions, and Pathology; Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kavouras, S.A.; Anastasiou, C.A. Water Physiology: Essentiality, Metabolism, and Health Implications. Nutr. Today 2010, 45, S27–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt Creedon, J.M. Sodium Disorders. In Small Animal Critical Care Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 263–268. ISBN 978-1-4557-0306-7. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, D.C. Daily Intravenous Fluid Therapy. In Small Animal Critical Care Medicine; Elsevie: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 271–275. ISBN 978-1-4160-2591-7. [Google Scholar]
- Muir, W.W.; Hughes, D.; Silverstein, D.C. Editorial: Fluid Therapy in Animals: Physiologic Principles and Contemporary Fluid Resuscitation Considerations. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 744080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanghi, B.M. Water Needs and Hydration for Cats and Dogs; 2017. Available online: https://topdogtips.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Zanghi-Water-Needs-and-Hydration-for-Cats-and-Dogs.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Bateman, S.W.; Chew, D.J. Fluid Therapy for Dogs and Cats. In Saunders Manual of Small Animal Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 82–99. ISBN 978-0-7216-0422-0. [Google Scholar]
- World Small Animal Veterinary Association Congress Proceedings, 2018. VIN.com 2017. Available online: https://www.vin.com/apputil/project/defaultadv1.aspx?pId=20539 (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Guelfi, G.; Capaccia, C.; Tedeschi, M.; Bufalari, A.; Leonardi, L.; Cenci-Goga, B.; Maranesi, M. Dog Aging: A Comprehensive Review of Molecular, Cellular, and Physiological Processes. Cells 2024, 13, 2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellows, J.; Colitz, C.M.H.; Daristotle, L.; Ingram, D.K.; Lepine, A.; Marks, S.L.; Sanderson, S.L.; Tomlinson, J.; Zhang, J. Common Physical and Functional Changes Associated with Aging in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 246, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, K.; Carey, S. Dehydration in Geriatrics: Consequences and Practical Guidelines. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2022, 26, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, X. Hydration Status in Older Adults: Current Knowledge and Future Challenges. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneville, R.; Guidoux, C.; Barrett, L.; Viltart, O.; Mattot, V.; Polito, A.; Siami, S.; De La Grandmaison, G.L.; Blanchard, A.; Singer, M.; et al. Vasopressin Synthesis by the Magnocellular Neurons Is Different in the Supraoptic Nucleus and in the Paraventricular Nucleus in Human and Experimental Septic Shock. Brain Pathol. 2009, 20, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrasher, T.N. Baroreceptor Regulation of Vasopressin and Renin Secretion: Low-Pressure versus High-Pressure Receptors. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1994, 15, 157–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, G.; Valenti, G.; Grossini, E.; Donnini, S.; Marino, A.; Marinelli, R.A.; Calamita, G. Aquaporin Membrane Channels in Oxidative Stress, Cell Signaling, and Aging: Recent Advances and Research Trends. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1501847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robben, J.H.; Knoers, N.V.A.M.; Deen, P.M.T. Regulation of the Vasopressin V2 Receptor by Vasopressin in Polarized Renal Collecting Duct Cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 5693–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, W.J. Drinking by Dogs during and after Running. J. Physiol. 1975, 250, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.A.; Adolph, E.F. Pattern of normal water drinking in dogs. Am. J. Physiol. Leg. Content 1943, 139, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizowski, C.; Bourque, C.W. The Neural Basis of Homeostatic and Anticipatory Thirst. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, S.; Prot-Bertoye, C.; Daudon, M.; Courbebaisse, M.; Baron, S. How to Monitor Hydration Status and Urine Dilution in Patients with Nephrolithiasis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, G.; Goswami, N.; Reichmuth, J.; De Santo, N.G.; Valenti, G. Aquaporins, Vasopressin, and Aging: Current Perspectives. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begg, D.P. Disturbances of Thirst and Fluid Balance Associated with Aging. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 178, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, N.I.; Burg, M.B. Increased Insensible Water Loss Contributes to Aging Related Dehydration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.; Bunn, D.; Jimoh, F.O.; Fairweather-Tait, S.J. Water-Loss Dehydration and Aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ayers, E.; Patel, P.; Mattoo, T.K. Body Water Percentage from Childhood to Old Age. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 42, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danziger, J.; Zeidel, M.L. Osmotic Homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpire, E.; Gagnon, K.B. Water Homeostasis and Cell Volume Maintenance and Regulation. Curr. Top. Membr. 2018, 81, 3–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.B.; Stewart, J.M.; Izzo, M.J.; Young, L.E. Age as affecting the osmotic and mechanical fragility of dog erythrocytes tagged with radioactive iron. J. Exp. Med. 1950, 91, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuss, L. Water Transport Across Cell Membranes. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-470-01617-6. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, N.; Ahmadi, V. Aquaporin Channels in Skin Physiology and Aging Pathophysiology: Investigating Their Role in Skin Function and the Hallmarks of Aging. Biology 2024, 13, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Nie, X.; Lu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, Z. Roles and Regulation of Aquaporin-3 in Maintaining the Gut Health: An Updated Review. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1264570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahr, J.Y. Physiology of Aging. Med. Hypotheses 2019, 123, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuper, C.; Beck, F.-X.; Neuhofer, W. Osmoadaptation of Mammalian Cells—An Orchestrated Network of Protective Genes. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burg, M.B.; Ferraris, J.D.; Dmitrieva, N.I. Cellular Response to Hyperosmotic Stresses. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1441–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moronetti Mazzeo, L.E.; Dersh, D.; Boccitto, M.; Kalb, R.G.; Lamitina, T. Stress and Aging Induce Distinct polyQ Protein Aggregation States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10587–10592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocker, C.; Thompson, D.C.; Vasiliou, V. The Role of Hyperosmotic Stress in Inflammation and Disease. Biomol. Concepts 2012, 3, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, I.; Serra-Prat, M.; Yébenes, J.C. The Role of Water Homeostasis in Muscle Function and Frailty: A Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Parini, P.; Giuliani, C.; Santoro, A. Inflammaging: A New Immune–Metabolic Viewpoint for Age-Related Diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Róg, T.; Murzyn, K.; Pasenkiewicz-Gierula, M. The Dynamics of Water at the Phospholipid Bilayer Surface: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 352, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beranová, L.; Humpolíčková, J.; Sýkora, J.; Benda, A.; Cwiklik, L.; Jurkiewicz, P.; Gröbner, G.; Hof, M. Effect of Heavy Water on Phospholipid Membranes: Experimental Confirmation of Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 14516–14522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, M.L.; Vácha, R. Aqueous Solutions at the Interface with Phospholipid Bilayers. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laage, D.; Elsaesser, T.; Hynes, J.T. Water Dynamics in the Hydration Shells of Biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10694–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, M.; Krok, E.; Orlikowska, H.; Schwille, P.; Franquelim, H.G.; Piatkowski, L. Hydration Layer of Only a Few Molecules Controls Lipid Mobility in Biomimetic Membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14551–14562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disalvo, E.A.; Lairion, F.; Martini, F.; Tymczyszyn, E.; Frías, M.; Almaleck, H.; Gordillo, G.J. Structural and Functional Properties of Hydration and Confined Water in Membrane Interfaces. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2008, 1778, 2655–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Water Loss in Aging Erythrocytes Provides a Clue to a General Mechanism of Cellular Senescence. Biophys. J. 2020, 119, 2039–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zs-Nagy, I. Aging of Cell Membranes: Facts and Theories. In Interdisciplinary Topics in Gerontology and Geriatrics; Robert, L., Fulop, T., Eds.; S. Karger AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 39, pp. 62–85. ISBN 978-3-318-02652-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.; Tang, H.; Pang, S. The Crucial Roles of Phospholipids in Aging and Lifespan Regulation. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 775648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.G.; Dotti, C.G. Plasma Membrane and Brain Dysfunction of the Old: Do We Age from Our Membranes? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1031007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, M. Do We Underestimate the Importance of Water in Cell Biology? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, P. Water as an Active Constituent in Cell Biology. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 74–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplin, M.F. Water: Its Importance to Life. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ. 2001, 29, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunyk, L.A.; Neidle, S. On Water Arrangements in Right- and Left-Handed DNA Structures. Molecules 2024, 29, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan-Xuan, T.; Bogdanova, E.; Millqvist Fureby, A.; Fransson, J.; Terry, A.E.; Kocherbitov, V. Hydration-Induced Structural Changes in the Solid State of Protein: A SAXS/WAXS Study on Lysozyme. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 3246–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Luo, J.; Bao, T.; Wang, S.; Wu, X. Molecular Mechanisms of Aging and Anti-Aging Strategies. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshdastidar, D.; Senapati, S. Dehydrated DNA in B-Form: Ionic Liquids in Rescue. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 4344–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargason, J.M.; Henderson, K.; Ho, P.S. A Crystallographic Map of the Transition from B-DNA to A-DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7265–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellissent-Funel, M.-C.; Hassanali, A.; Havenith, M.; Henchman, R.; Pohl, P.; Sterpone, F.; van der Spoel, D.; Xu, Y.; Garcia, A.E. Water Determines the Structure and Dynamics of Proteins. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7673–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raschke, T.M. Water Structure and Interactions with Protein Surfaces. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2006, 16, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Saven, J.G. Statistical and Molecular Dynamics Studies of Buried Waters in Globular Proteins. Proteins 2005, 60, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, M.A.; Biggin, P.C. Quantifying Water-Mediated Protein–Ligand Interactions in a Glutamate Receptor: A DFT Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 7085–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, R.; Romero-Romero, S.; Velázquez-López, I.; Espinoza-Pérez, G.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.; Pulido, N.O.; Sosa-Peinado, A.; Rodríguez-Romero, A.; Fernández-Velasco, D.A. The Interplay of Protein–Ligand and Water-mediated Interactions Shape Affinity and Selectivity in the LAO Binding Protein. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 763–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, P. Water Is an Active Matrix of Life for Cell and Molecular Biology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13327–13335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, S.D.; Randolph, T.W.; Manning, M.C.; Middleton, K.; Davis, A.; Carpenter, J.F. Effects of Drying Methods and Additives on Structure and Function of Actin: Mechanisms of Dehydration-Induced Damage and Its Inhibition. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 358, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riveros-Perez, E.; Riveros, R. Water in the Human Body: An Anesthesiologist’s Perspective on the Connection between Physicochemical Properties of Water and Physiologic Relevance. Ann. Med. Surg. 2018, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, Y. (Ed.) The Hydrogen Bond and the Water Molecule: The Physics and Chemistry of Water, Aqueous and Bio Media, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 978-0-08-046929-4. [Google Scholar]
- Robayo-Amortegui, H.; Quintero-Altare, A.; Florez-Navas, C.; Serna-Palacios, I.; Súarez-Saavedra, A.; Buitrago-Bernal, R.; Casallas-Barrera, J.O. Fluid Dynamics of Life: Exploring the Physiology and Importance of Water in the Critical Illness. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1368502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, M.M.; Alazwari, M.N.; E Alotaibi, M.; Almalki, N.K. Hypernatremia: A Concise Practical Review. Curr. Trends Intern. Med. 2024, 8, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, K.M.; Lunn, K.F. Normal and Abnormal Water Balance: Hyponatremia and Hypernatremia. Compend. Contin. Educ. Pract. Vet. 2007, 29, 589–609. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.K.; Workeneh, B.; Taffet, G.E. Hypernatremia in the Geriatric Population. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1987–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.G.; Hopper, K. Hyponatremia in Dogs and Cats. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2019, 29, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, P.D.; Hinchcliff, K.W.; Done, S.H.; Grünberg, W. (Eds.) 5-Disturbances of Free Water, Electrolytes, Acid-Base Balance, and Oncotic Pressure. In Veterinary Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 113–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewart, S.L. Acid-Base Homeostasis. In Cunningham’s Textbook of Veterinary Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 584–595. ISBN 978-0-323-55227-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, B.A.; Yankin, I.; Perry, S.; Rutter, C.R. Acid-Base and Electrolyte Evaluation in Dogs with Upper GI Obstruction: 115 Dogs (2015–2021). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2023, 64, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel-Pinter, M.; Rajaei, V.; Glass, J.B.; Hud, N.V.; Williams, L.D. Water and Life: The Medium Is the Message. J. Mol. Evol. 2021, 89, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, J.; Sankar, P.; Varacallo, M.A. Physiology, Blood Plasma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Taco-Vasquez, E.D.; Barrera, F.; Serrano-Duenas, M.; Jimenez, E.; Rocuts, A.; Perez, E.R. Association between Blood Viscosity and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Arterial Hypertension in a High Altitude Setting. Cureus 2019, 11, e3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harison, E.; Langston, C.; Palma, D.; Lamb, K. Acute Azotemia as a Predictor of Mortality in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Intern. Medicne 2012, 26, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivers, M.S.; Handel, I.; Gow, A.G.; Lipscomb, V.J.; Jalan, R.; Mellanby, R.J. Hyperammonemia and Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Predicts Presence of Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs with Congenital Portosystemic Shunts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e82303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartges, J.W. Chronic Kidney Disease in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 42, 669–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanghi, B.M.; Robbins, P.J.; Ramos, M.T.; Otto, C.M. Working Dogs Drinking a Nutrient-Enriched Water Maintain Cooler Body Temperature and Improved Pulse Rate Recovery After Exercise. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, C.M.; Hare, E.; Nord, J.L.; Palermo, S.M.; Kelsey, K.M.; Darling, T.A.; Schmidt, K.; Coleman, D. Evaluation of Three Hydration Strategies in Detection Dogs Working in a Hot Environment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawka, M.N.; Wenger, C.B.; Young, A.J.; Pandolf, K.B. Physiological Responses to Exercise in the Heat. In Nutritional Needs in Hot Environments: Applications for Military Personnel in Field Operations; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cederlund, A.A.; Aspden, R.M. Walking on Water: Revisiting the Role of Water in Articular Cartilage Biomechanics in Relation to Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. J. R. Soc. Interface 2022, 19, 20220364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, C.; Reinhardt, D.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J. Regulatory Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations of Musculoskeletal Aging. J. Orthop. Res. 2019, 37, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, S.D. Canine Osteoarthritis and Treatments: A Review. Vet. Sci. Dev. 2015, 5, 669–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeser, R.F., Jr. Aging Cartilage and Osteoarthritis—What’s the Link? Sci. Aging Knowl. Environ. 2004, 2004, pe31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.; Jeong, D. Extracellular Acidosis Accelerates Bone Resorption by Enhancing Osteoclast Survival, Adhesion, and Migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, T.R. Acidosis, Hypoxia and Bone. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 503, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.S.; Loeser, R.F. Why Is Osteoarthritis an Age-Related Disease? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 24, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhou, J.; Wei, L. The Age-Related Changes in Cartilage and Osteoarthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 916530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, M.; Akkus, O.; Sun, J.; Cai, L.; Erol, U.L.; Sabri, L.; Neu, C.P. Raman Spectroscopy-Based Water Content Is a Negative Predictor of Articular Human Cartilage Mechanical Function. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Searleman, A.C.; Ma, Y.; Wong, J.H.; Williams, J.; Murphy, M.E.; Du, J.; Chang, E.Y.; Tang, G. The Effect of Cartilage Dehydration and Rehydration on Quantitative Ultrashort Echo Time Biomarkers. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 6942–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaide-Ruggiero, L.; Cugat, R.; Domínguez, J.M. Proteoglycans in Articular Cartilage and Their Contribution to Chondral Injury and Repair Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung, B.S.; Jung, K.W.; Yeo, W.J.; Seo, H.K.; Lee, Y.-S.; Suh, D.W. Differential Regulation of the Water Channel Protein Aquaporins in Chondrocytes of Human Knee Articular Cartilage by Aging. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapmaz, H.I. Investigation of Age-Related Changes in Expression of Aquaporin-1 and Aquaporin-3 in Rat Bone. Ann. Clin. Anal. Med. 2016, 7, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.-P. P2X7R: A Potential Key Regulator of Acute Gouty Arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 43, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Wu, H. Structural Mechanisms of Inflammasome Assembly. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrettou, C.S.; Issaris, V.; Kokkoris, S.; Poupouzas, G.; Keskinidou, C.; Lotsios, N.S.; Kotanidou, A.; Orfanos, S.E.; Dimopoulou, I.; Vassiliou, A.G. Exploring Aquaporins in Human Studies: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential in Critical Illness. Life 2024, 14, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezuș, E.; Cardoneanu, A.; Burlui, A.; Luca, A.; Codreanu, C.; Tamba, B.I.; Stanciu, G.-D.; Dima, N.; Bădescu, C.; Rezuș, C. The Link Between Inflammaging and Degenerative Joint Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.G.; Núñez-Carro, C.; Blanco-Blanco, M.; Blanco, F.J.; De Andrés, M.C. Inflammaging Contributes to Osteoarthritis Development and Human Microbiota Variations and Vice Versa: A Systematic Review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2025, 33, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuña, E.; Cachán-Vega, C.; Bermejo-Millo, J.C.; Potes, Y.; Caballero, B.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Coto-Montes, A.; Garcia-Gonzalez, C. Inflammaging: Implications in Sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.M.; Hoffman, J.M.; Prescott, J.; Ernst, H.; Promislow, D.E.L.; Dog Aging Project Consortium; Akey, J.M.; Benton, B.; Borenstein, E.; Castelhano, M.G.; et al. The Companion Dog as a Model for Inflammaging: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. GeroScience 2024, 46, 5395–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuggle, N.R.; Laskou, F.; Harvey, N.C.; Dennison, E.M. A Review of Epigenetics and Its Association with Ageing of Muscle and Bone. Maturitas 2022, 165, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A.; Mita, P.; McKerrow, W.; Fenyö, D.; Boeke, J.D.; Linker, S.B.; Gage, F.H.; Kreiling, J.A.; Petrashen, A.P.; et al. The Role of Retrotransposable Elements in Ageing and Age-Associated Diseases. Nature 2021, 596, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menassa, M.; Stronks, K.; Khatami, F.; Díaz, Z.M.R.; Espinola, O.P.; Gamba, M.; Itodo, O.A.; Buttia, C.; Wehrli, F.; Minder, B.; et al. Concepts and definitions of healthy ageing: A systematic review and synthesis of theoretical models. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 56, 101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Wen, W.; Dai, Y.; Qin, L.; Wen, Y.; Duan, D.D.; Xu, S. Drinking Water Temperature Affects Cognitive Function and Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease in a Mouse Model. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauriola, M.; Mangiacotti, A.; D’Onofrio, G.; Cascavilla, L.; Paris, F.; Paroni, G.; Seripa, D.; Greco, A.; Sancarlo, D. Neurocognitive Disorders and Dehydration in Older Patients: Clinical Experience Supports the Hydromolecular Hypothesis of Dementia. Nutrients 2018, 10, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, G.L.; Dayon, L.; Kirkland, R.; Wojcik, J.; Peyratout, G.; Severin, I.C.; Henry, H.; Oikonomidi, A.; Migliavacca, E.; Bacher, M.; et al. Blood-brain Barrier Breakdown, Neuroinflammation, and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, G. Therapeutic Agents for the Treatment of Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome in Senior Dogs. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 29, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, G.; Araujo, J.A. Behavior Problems in Geriatric Pets. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2005, 35, 675–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, G.M.; Nichol, J.; Araujo, J.A. Cognitive Dysfunction Syndrome: A Disease of Canine and Feline Brain Aging. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 42, 749–768, vii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvin, H.E.; McGreevy, P.D.; Sachdev, P.S.; Valenzuela, M.J. The Canine Cognitive Dysfunction Rating Scale (CCDR): A Data-Driven and Ecologically Relevant Assessment Tool. Vet. J. 2011, 188, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, V.M.; Landucci, M.; Lippi, I.; Amat, M.; Manteca, X.; Guidi, G. Epidemiological Study of Behavioral Disorders in Elderly Dogs. J. Vet. Behav. 2010, 5, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, J.C.; Hart, B.L.; Cliff, K.D.; Ruehl, W.W. Prevalence of Behavioral Changes Associated with Age-Related Cognitive Impairment in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 1787–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, M.C.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin Water Channels in the Nervous System. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenza, M.; Facchinetti, R.; Steardo, L.; Scuderi, C. Altered Waste Disposal System in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on Astrocytic Aquaporin-4. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snuggs, J.W.; Day, R.E.; Bach, F.C.; Conner, M.T.; Bunning, R.A.D.; Tryfonidou, M.A.; Le Maitre, C.L. Aquaporin Expression in the Human and Canine Intervertebral Disc during Maturation and Degeneration. JOR Spine 2019, 2, e1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lunde, L.K.; Nuntagij, P.; Oguchi, T.; Camassa, L.M.A.; Nilsson, L.N.G.; Lannfelt, L.; Xu, Y.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; et al. Loss of Astrocyte Polarization in the Tg-ArcSwe Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 27, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, P.; Blasco, E.; Pumarola, M.; Wessmann, A. Aquaporin-4 Protein Expression in Normal Canine Brains. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaut, J.; Brunet, J.F.; Petit, J.-M.; Guérin, C.F.; Magistretti, P.J.; Regli, L. Induction of Brain Aquaporin 9 (AQP9) in Catecholaminergic Neurons in Diabetic Rats. Brain Res. 2008, 1188, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y. Nutrients, Cognitive Function, and Brain Aging: What We Have Learned from Dogs. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K. Multifaceted Roles of Aquaporins in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, R. Emerging Role of Aquaporin in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Novel Target for Drug Development. Learn. Motiv. 2025, 89, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Gao, H.; Fang, X.; Yang, H. Expression and Function of Aquaporins in Peripheral Nervous System. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.; DeFrancesco, T. Relationship between Hydration Estimate and Body Weight Change after Fluid Therapy in Critically Ill Dogs and Cats. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2002, 12, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnati, L.F.; Leo, G.; Zanardi, A.; Genedani, S.; Rivera, A.; Fuxe, K.; Guidolin, D. Volume Transmission and Wiring Transmission from Cellular to Molecular Networks: History and Perspectives. Acta Physiol. 2006, 187, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroto-Escuela, D.O.; Gonzalez-Cristo, E.; Ochoa-Torres, V.; Serra-Rojas, E.M.; Ambrogini, P.; Arroyo-García, L.E.; Fuxe, K. Understanding Electrical and Chemical Transmission in the Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1398862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, C.; Phillips, J.M. Ion Diffusion Modified by Tortuosity and Volume Fraction in the Extracellular Microenvironment of the Rat Cerebellum. J. Physiol. 1981, 321, 225–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, C.; Syková, E. Extracellular Space Structure Revealed by Diffusion Analysis. Trends Neurosci. 1998, 21, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Sweeney, E.M.; Wang, X.H.; Kuceyeski, A.; Chiang, G.C.; Ivanidze, J.; Wang, Y.; Gauthier, S.A.; De Leon, M.J.; et al. Association of Brain Tissue Cerebrospinal Fluid Fraction with Age in Healthy Cognitively Normal Adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1162001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, G.; Pasqualetti, M. Wiring and Volume Transmission: An Overview of the Dual Modality for Serotonin Neurotransmission. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 4093–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnati, L.F.; Guidolin, D.; Guescini, M.; Genedani, S.; Fuxe, K. Understanding Wiring and Volume Transmission. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 64, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attier-Zmudka, J.; Sérot, J.-M.; Valluy, J.; Saffarini, M.; Macaret, A.-S.; Diouf, M.; Dao, S.; Douadi, Y.; Malinowski, K.P.; Balédent, O. Decreased Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow Is Associated With Cognitive Deficit in Elderly Patients. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, T.; Stopa, E.; Morrison, J.; Klinge, P. A New Look at Cerebrospinal Fluid Circulation. Fluids Barriers CNS 2014, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.-J. Normal Aging Induces Changes in the Brain and Neurodegeneration Progress: Review of the Structural, Biochemical, Metabolic, Cellular, and Molecular Changes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 931536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, R.N.; Simsek, Z.D.; Curry, B.; Core, S.L.; Beltz, T.; Xue, B.; Johnson, A.K.; Thunhorst, R.L.; Curtis, K.S. Aging Affects Isoproterenol-Induced Water Drinking, Astrocyte Density, and Central Neuronal Activation in Female Brown Norway Rats. Physiol. Behav. 2018, 192, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusbridge, C.; Salguero, F.J.; David, M.A.; Faller, K.M.E.; Bras, J.T.; Guerreiro, R.J.; Richard-Londt, A.C.; Grainger, D.; Head, E.; Brandner, S.G.P.; et al. An Aged Canid with Behavioral Deficits Exhibits Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid Amyloid Beta Oligomers. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehydration: First Aid. Available online: https://veterinarypartner.vin.com/default.aspx?id=4951322&pid=1923 (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Goucher, T.K.; Hartzell, A.M.; Seales, T.S.; Anmuth, A.S.; Zanghi, B.M.; Otto, C.M. Evaluation of Skin Turgor and Capillary Refill Time as Predictors of Dehydration in Exercising Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 80, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, A.; Guglielmini, C.; Fracassi, F.; Pietra, M.; Balletti, E.; Cipone, M. Use of High-Frequency Ultrasonography for Evaluation of Skin Thickness in Relation to Hydration Status and Fluid Distribution at Various Cutaneous Sites in Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2008, 69, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.; Fray, T.; Clarke, S.; Yates, D.; Markwell, P. Reliable Use of the ServoMed Evaporimeter EP-2TM to Assess Transepidermal Water Loss in the Canine. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 1661S–1664S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisini, N.; Corda, A.; Birettoni, F.; Miglio, A.; Antognoni, M.T. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) Detects Body Resistance Increase in Dogs Undergoing Blood Donation. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 3889–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guelfi, G.; Capaccia, C.; Ratto, V.F.; Bufalari, A.; Leonardi, L.; Mechelli, L.; Cenci, S.; Maranesi, M. The Emerging Role of Water Loss in Dog Aging. Cells 2025, 14, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070545
Guelfi G, Capaccia C, Ratto VF, Bufalari A, Leonardi L, Mechelli L, Cenci S, Maranesi M. The Emerging Role of Water Loss in Dog Aging. Cells. 2025; 14(7):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070545
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuelfi, Gabriella, Camilla Capaccia, Vicente Francisco Ratto, Antonello Bufalari, Leonardo Leonardi, Luca Mechelli, Simone Cenci, and Margherita Maranesi. 2025. "The Emerging Role of Water Loss in Dog Aging" Cells 14, no. 7: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070545
APA StyleGuelfi, G., Capaccia, C., Ratto, V. F., Bufalari, A., Leonardi, L., Mechelli, L., Cenci, S., & Maranesi, M. (2025). The Emerging Role of Water Loss in Dog Aging. Cells, 14(7), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070545









