Pro-Inflammatory Properties of Salivary Gland-Derived Fibroblasts—Implications in Sjögren’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
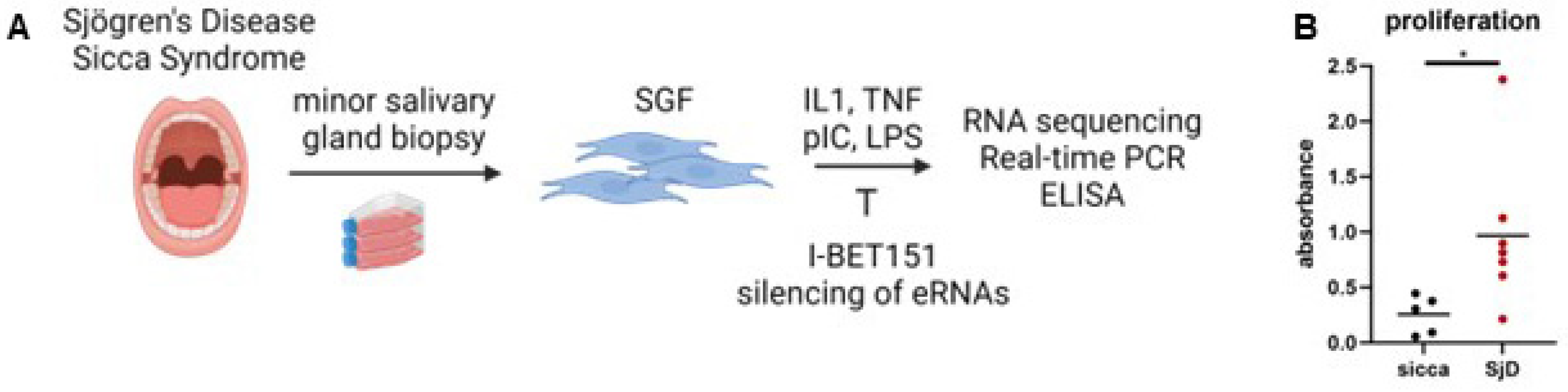
2.1. Patient Samples and Cell Preparation
2.2. FACS Analysis
2.3. Proliferation Assay
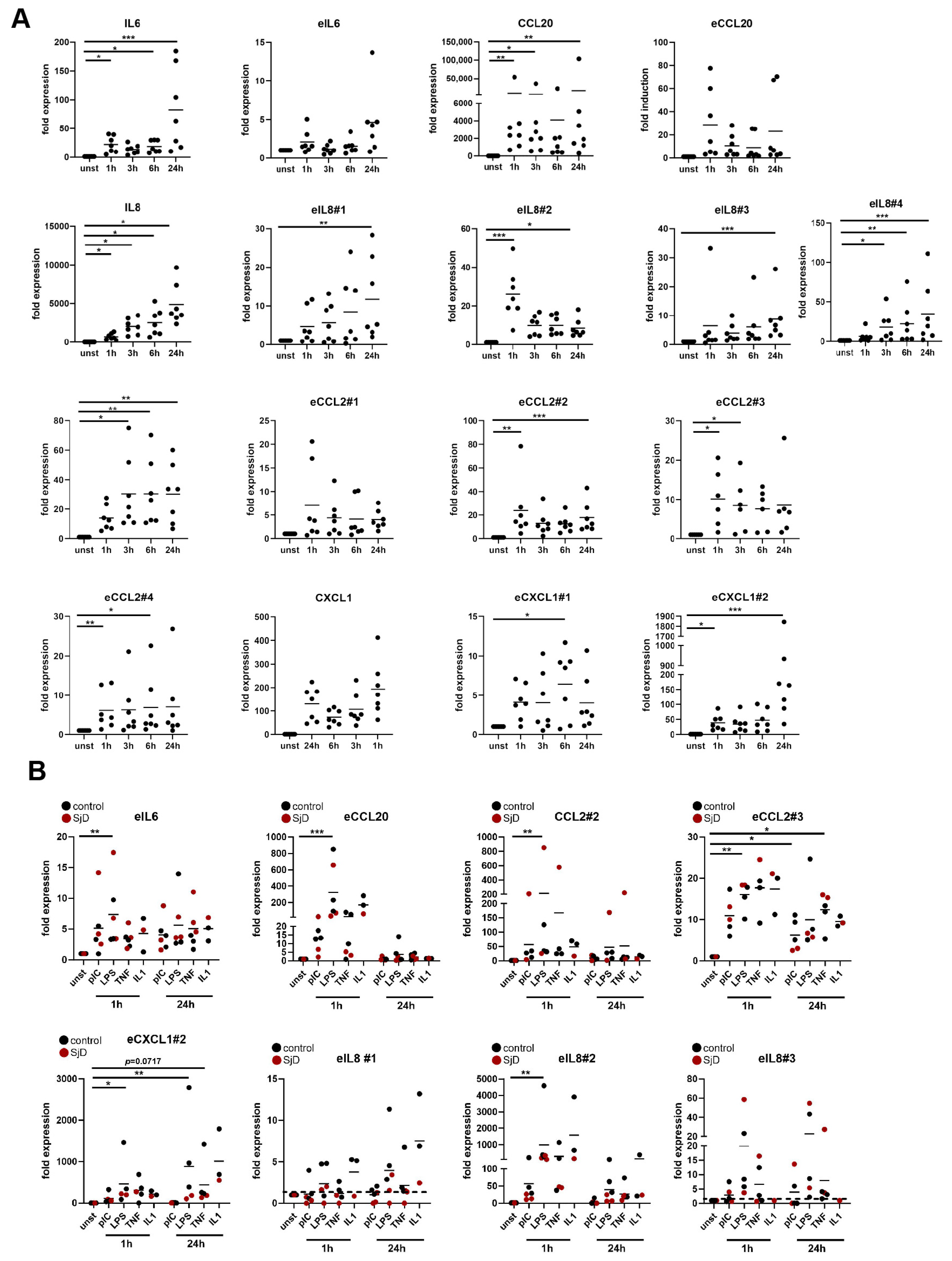
2.4. Treatment of Cells
2.5. RNA Sequencing of SGF
2.6. ELISA
2.7. Cap Analysis of Gene Expression Followed by Sequencing (CAGE-Seq)
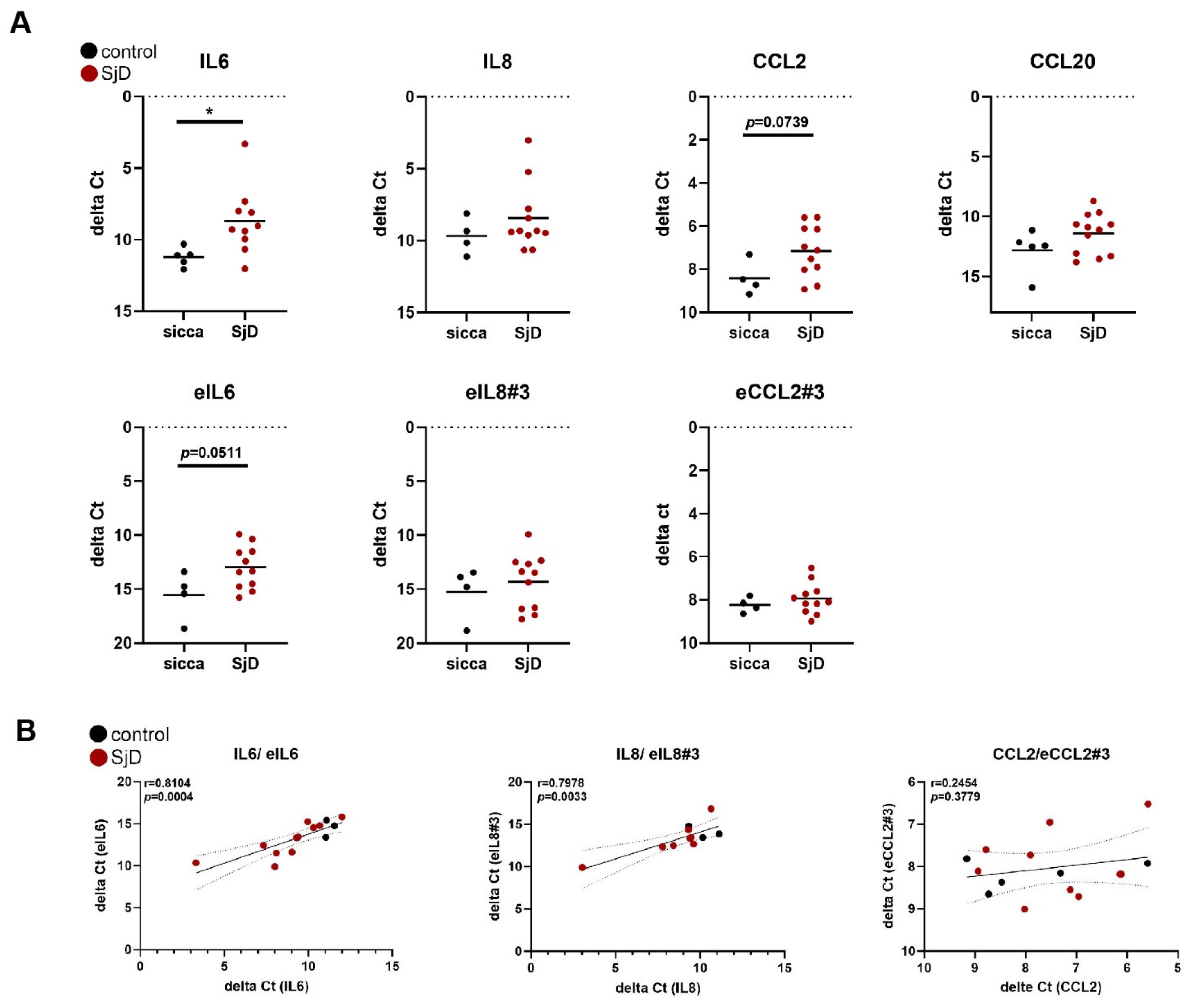
2.8. Real-Time PCR
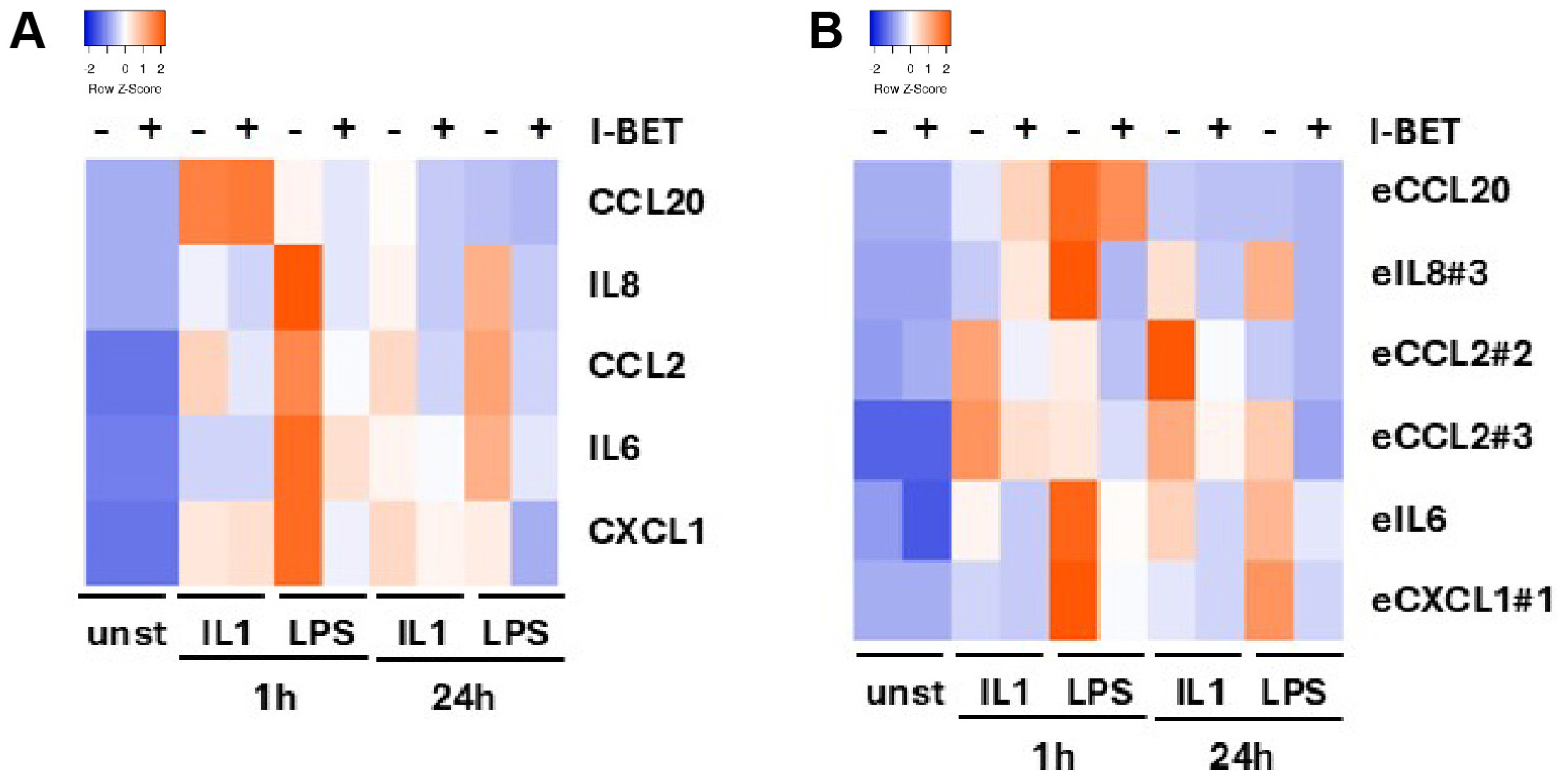
2.9. Silencing of eRNAs in SGF
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Fibroblasts from Patients with Sjögren’s Disease Exhibit Increased Proliferation
3.2. Salivary Gland Fibroblasts Respond to Pro-Inflammatory Stimuli
3.3. Pro-Inflammatory Stimuli Induce Shared Enhancers in Different Types of Fibroblasts
3.4. The Expression of eRNAs Is Detectable in Salivary Gland Tissue Samples
3.5. Bromodomain Protein Inhibition Suppresses eRNA and Coding Gene Expression
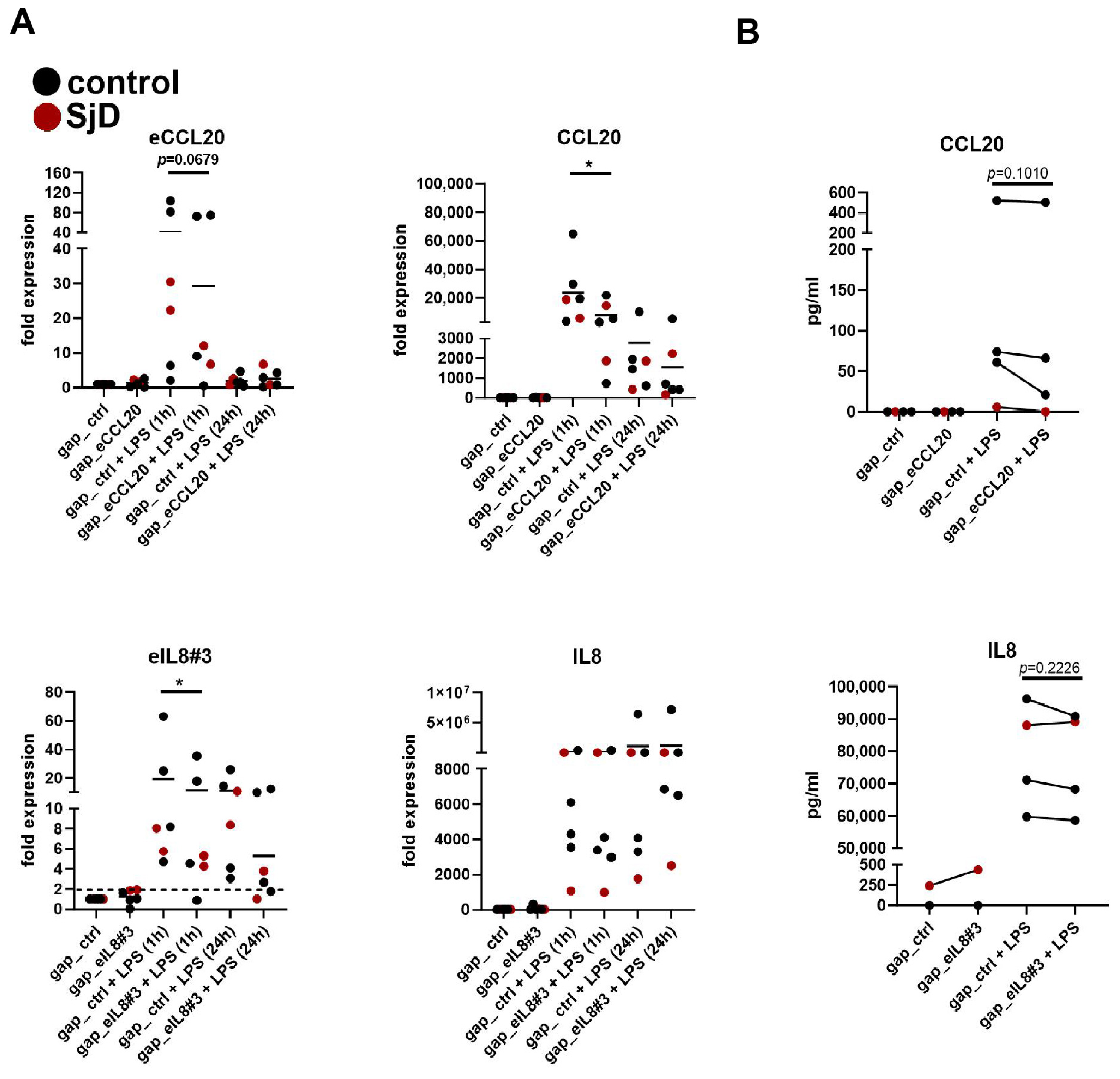
3.6. Silencing of eRNA Expression Suppresses Coding Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mariette, X.; Criswell, L.A. Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Chen, W.; Fan, X.; Zhang, D. Pathogenesis and treatment of Sjogren’s syndrome: Review and update. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1127417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, B.; Tessneer, K.L.; Rasmussen, A.; Aghakhanian, F.; Reksten, T.R.; Adler, A.; Alevizos, I.; Anaya, J.M.; Aqrawi, L.A.; Baecklund, E.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies Sjogren’s risk loci with functional implications in immune and glandular cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, C.; Fulvio, G.; La Rocca, G.; Ferro, F. Update on the pathophysiology and treatment of primary Sjogren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2024, 20, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.; Coles, M.; Thomas, T.; Kollias, G.; Ludewig, B.; Turley, S.; Brenner, M.; Buckley, C.D. Fibroblasts as immune regulators in infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, C.D.; Ospelt, C.; Gay, S.; Midwood, K.S. Location, location, location: How the tissue microenvironment affects inflammation in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, F.; Nayar, S.; Campos, J.; Cloake, T.; Withers, D.R.; Toellner, K.M.; Zhang, Y.; Fouser, L.; Fisher, B.; Bowman, S.; et al. IL-22 regulates lymphoid chemokine production and assembly of tertiary lymphoid organs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11024–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, S.; Campos, J.; Smith, C.G.; Iannizzotto, V.; Gardner, D.H.; Mourcin, F.; Roulois, D.; Turner, J.; Sylvestre, M.; Asam, S.; et al. Immunofibroblasts are pivotal drivers of tertiary lymphoid structure formation and local pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13490–13497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, S.; Pontarini, E.; Campos, J.; Berardicurti, O.; Smith, C.G.; Asam, S.; Gardner, D.H.; Colafrancesco, S.; Lucchesi, D.; Coleby, R.; et al. Immunofibroblasts regulate LTalpha3 expression in tertiary lymphoid structures in a pathway dependent on ICOS/ICOSL interaction. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, I.; Wei, K.; Pohin, M.; Kim, E.Y.; Barone, F.; Major, T.; Taylor, E.; Ravindran, R.; Kemble, S.; Watts, G.F.M.; et al. Cross-tissue, single-cell stromal atlas identifies shared pathological fibroblast phenotypes in four chronic inflammatory diseases. Med 2022, 3, 481–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, T.; O’Neil, J.D.; Adams, H.; Thomas, A.M.; Filer, A.; Buckley, C.D.; Clark, A.R. Priming in response to pro-inflammatory cytokines is a feature of adult synovial but not dermal fibroblasts. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friscic, J.; Bottcher, M.; Reinwald, C.; Bruns, H.; Wirth, B.; Popp, S.J.; Walker, K.I.; Ackermann, J.A.; Chen, X.; Turner, J.; et al. The complement system drives local inflammatory tissue priming by metabolic reprogramming of synovial fibroblasts. Immunity 2021, 54, 1002–1021.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank-Bertoncelj, M.; Klein, K.; Gay, S. Interplay between genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Liu, Y.; Liao, X.; Zhan, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W. Enhancer RNAs (eRNAs): New Insights into Gene Transcription and Disease Treatment. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.Y. Targeting Super-Enhancers for Disease Treatment and Diagnosis. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Seror, R.; Criswell, L.A.; Labetoulle, M.; Lietman, T.M.; Rasmussen, A.; Scofield, H.; Vitali, C.; Bowman, S.J.; et al. 2016 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for primary Sjogren’s syndrome: A consensus and data-driven methodology involving three international patient cohorts. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, F.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Bloch, D.A.; McShane, D.J.; Fries, J.F.; Cooper, N.S.; Healey, L.A.; Kaplan, S.R.; Liang, M.H.; Luthra, H.S.; et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frank-Bertoncelj, M.; Trenkmann, M.; Klein, K.; Karouzakis, E.; Rehrauer, H.; Bratus, A.; Kolling, C.; Armaka, M.; Filer, A.; Michel, B.A.; et al. Epigenetically-driven anatomical diversity of synovial fibroblasts guides joint-specific fibroblast functions. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Frank-Bertoncelj, M.; Klein, K.; McGovern, A.; Kuret, T.; Houtman, M.; Burja, B.; Micheroli, R.; Shi, C.; Marks, M.; et al. Functional genomics atlas of synovial fibroblasts defining rheumatoid arthritis heritability. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noss, E.H.; Nguyen, H.N.; Chang, S.K.; Watts, G.F.; Brenner, M.B. Genetic polymorphism directs IL-6 expression in fibroblasts but not selected other cell types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14948–14953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, K.; Frank-Bertoncelj, M.; Karouzakis, E.; Gay, R.E.; Kolling, C.; Ciurea, A.; Bostanci, N.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Lin, L.L.; Distler, O.; et al. The epigenetic architecture at gene promoters determines cell type-specific LPS tolerance. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 83, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riviere, E.; Pascaud, J.; Tchitchek, N.; Boudaoud, S.; Paoletti, A.; Ly, B.; Dupre, A.; Chen, H.; Thai, A.; Allaire, N.; et al. Salivary gland epithelial cells from patients with Sjogren’s syndrome induce B-lymphocyte survival and activation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviere, E.; Pascaud, J.; Virone, A.; Dupre, A.; Ly, B.; Paoletti, A.; Seror, R.; Tchitchek, N.; Mingueneau, M.; Smith, N.; et al. Interleukin-7/Interferon Axis Drives T Cell and Salivary Gland Epithelial Cell Interactions in Sjogren’s Syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, S.; Turner, J.D.; Asam, S.; Fennell, E.; Pugh, M.; Colafrancesco, S.; Berardicurti, O.; Smith, C.G.; Flint, J.; Teodosio, A.; et al. Molecular and spatial analysis of tertiary lymphoid structures in Sjogren’s syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risselada, A.P.; Kruize, A.A.; Goldschmeding, R.; Lafeber, F.P.; Bijlsma, J.W.; van Roon, J.A. The prognostic value of routinely performed minor salivary gland assessments in primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstappen, G.M.; Kroese, F.G.M. A leading role for interferon as a treatment target in Sjogren syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 468–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farh, K.K.; Marson, A.; Zhu, J.; Kleinewietfeld, M.; Housley, W.J.; Beik, S.; Shoresh, N.; Whitton, H.; Ryan, R.J.; Shishkin, A.A.; et al. Genetic and epigenetic fine mapping of causal autoimmune disease variants. Nature 2015, 518, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K. Bromodomain protein inhibition: A novel therapeutic strategy in rheumatic diseases. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krošel, M.; Moser, L.; Houtman, M.; Friščić, J.; Tomšič, M.; Distler, O.; Hoffmann, M.H.; Ospelt, C.; Klein, K. Bromodomain Protein Inhibitors Reorganize the Chromatin of Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells 2023, 12, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, T.; Kanno, Y.; LeRoy, G.; Campos, E.; Sun, H.W.; Brooks, S.R.; Vahedi, G.; Heightman, T.D.; Garcia, B.A.; Reinberg, D.; et al. BRD4 assists elongation of both coding and enhancer RNAs by interacting with acetylated histones. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Diagnosis | SjD (n = 20) | Sicca (n = 15) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| age (years, mean [range]) | 53.2 (26–83) | 55.2 (37–74) | 0.6638 |
| sex (male/female) | 3/17 | 4/11 | 0.4081 |
| other autoimmune disease (yes/no) | 5/15 | 2/13 | 0.6722 |
| Chisholm-Mason grade (range) | 3.1 (1–4) | 1.27 (0–2) | 0.0001 |
| focus score (range) | 1.81 (0–5) | 0.16 (0–0.8) | 0.0001 |
| anti-SSA/Ro positive (yes/no) | 13/7 | 1/14 | 0.0002 |
| Schirmer test pathological (yes/no/ND) | (14/3 */3 **) | (8/1/6 **) | 0.7558 |
| UWS flow pathological (yes/no/ND) | (3/0/17) | (0/0/15) | - |
| CRP (mg/L range; ND) | 4.3 (0–32; 4) | 1.6 (0.6–5.4; 6) | 0.4308 |
| IgG (g/L range; ND) | 10.4 (4.9–17; 12) | 9.18 (7–12; 10) | 0.4784 |
| treatment | eye drops (2) DMARD (6) | DMARD (1) | - |
| extra-glandular symptoms | articular (4) Raynaud’s phenomenon (3) renal (1) small fiber neuropathy (1) central nervous system (1) cutaneous (1) pulmonary (1) myocardial fibrosis (1) | polyneuropathy (1) | - |
| Coding Gene | eRNA | Location Relative to TSS | Distance to TSS | Location in hg19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL6 | eIL6 | upstream | 0.5 kb | chr7:22766294-22766470 |
| IL8 | eIL8#1 | upstream | 14.1 kb | chr4:74591586-74592042 |
| eIL8#2 | upstream | 4.7 kb | chr4:74600999-74601413 | |
| eIL8#3 | upstream | 18.1 kb | chr4:74587655-74588079 | |
| eIL8#4 | upstream | 35.6 kb | chr4:74570129-74570560 | |
| CCL2 | eCCL2#1 | upstream | 3.1 kb | chr17:32579403-32579877 |
| eCCL2#2 | upstream | 0.3 kb | chr17:32580999-32581402 | |
| eCCL2#3 | downstream | 1.4 kb | chr17:32584373-32584831 | |
| eCCL2#4 | downstream | 3.2 kb | chr17:32586187-32586639 | |
| CCL20 | eCCL20 | intronic | 0.3 kb | chr2:228678859-228679309 |
| CXCL1 | eCXCL1#1 | downstream | 47.8 kb | chr4:74782759-74783271 |
| eCXCL1#2 | upstream | 31.5 kb | chr4:74702960-74703446 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brunner, M.; Guggisberg, D.; Sprecher, M.; Pastva, O.; Bürki, K.; Houtman, M.; Kreuzer, M.; Krättli, S.A.; Jahnke, L.; Roceri, M.; et al. Pro-Inflammatory Properties of Salivary Gland-Derived Fibroblasts—Implications in Sjögren’s Disease. Cells 2025, 14, 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080558
Brunner M, Guggisberg D, Sprecher M, Pastva O, Bürki K, Houtman M, Kreuzer M, Krättli SA, Jahnke L, Roceri M, et al. Pro-Inflammatory Properties of Salivary Gland-Derived Fibroblasts—Implications in Sjögren’s Disease. Cells. 2025; 14(8):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080558
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrunner, Matthias, Daniel Guggisberg, Marco Sprecher, Ondrej Pastva, Kristina Bürki, Miranda Houtman, Marco Kreuzer, Sara Andrea Krättli, Laura Jahnke, Mila Roceri, and et al. 2025. "Pro-Inflammatory Properties of Salivary Gland-Derived Fibroblasts—Implications in Sjögren’s Disease" Cells 14, no. 8: 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080558
APA StyleBrunner, M., Guggisberg, D., Sprecher, M., Pastva, O., Bürki, K., Houtman, M., Kreuzer, M., Krättli, S. A., Jahnke, L., Roceri, M., Bruggmann, R., Elhai, M., Maurer, B., Marti, T. M., Ospelt, C., & Klein, K. (2025). Pro-Inflammatory Properties of Salivary Gland-Derived Fibroblasts—Implications in Sjögren’s Disease. Cells, 14(8), 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080558







