Metformin Inhibits Cell Motility and Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Blocking HMGB1/RAGE Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. MTT Colorimetric Assay
2.3. Preparation of Plasmid Constructs and Purification of Recombinant Hmgb1 Proteins
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Wound-Healing Assay
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. EsiRNA Preparation and RNA Interference
2.8. Colony Formation Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
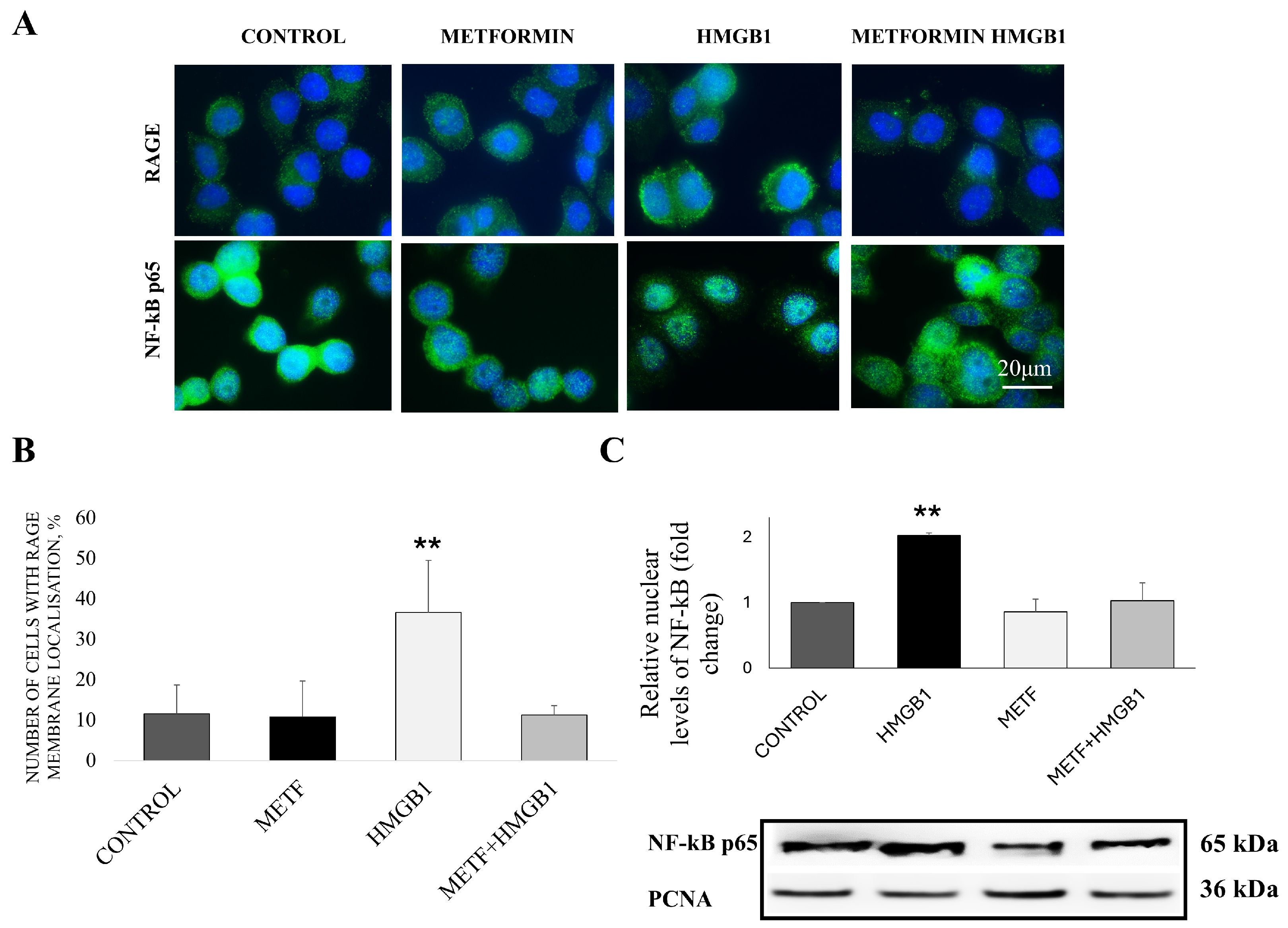
3.1. Metformin Inhibits RAGE Receptor Stabilization on the Cellular Membrane and Downstream HMGB1/RAGE Signaling
3.2. Metformin Prevents HMGB1-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Upregulation as Well as EMT in TNBC
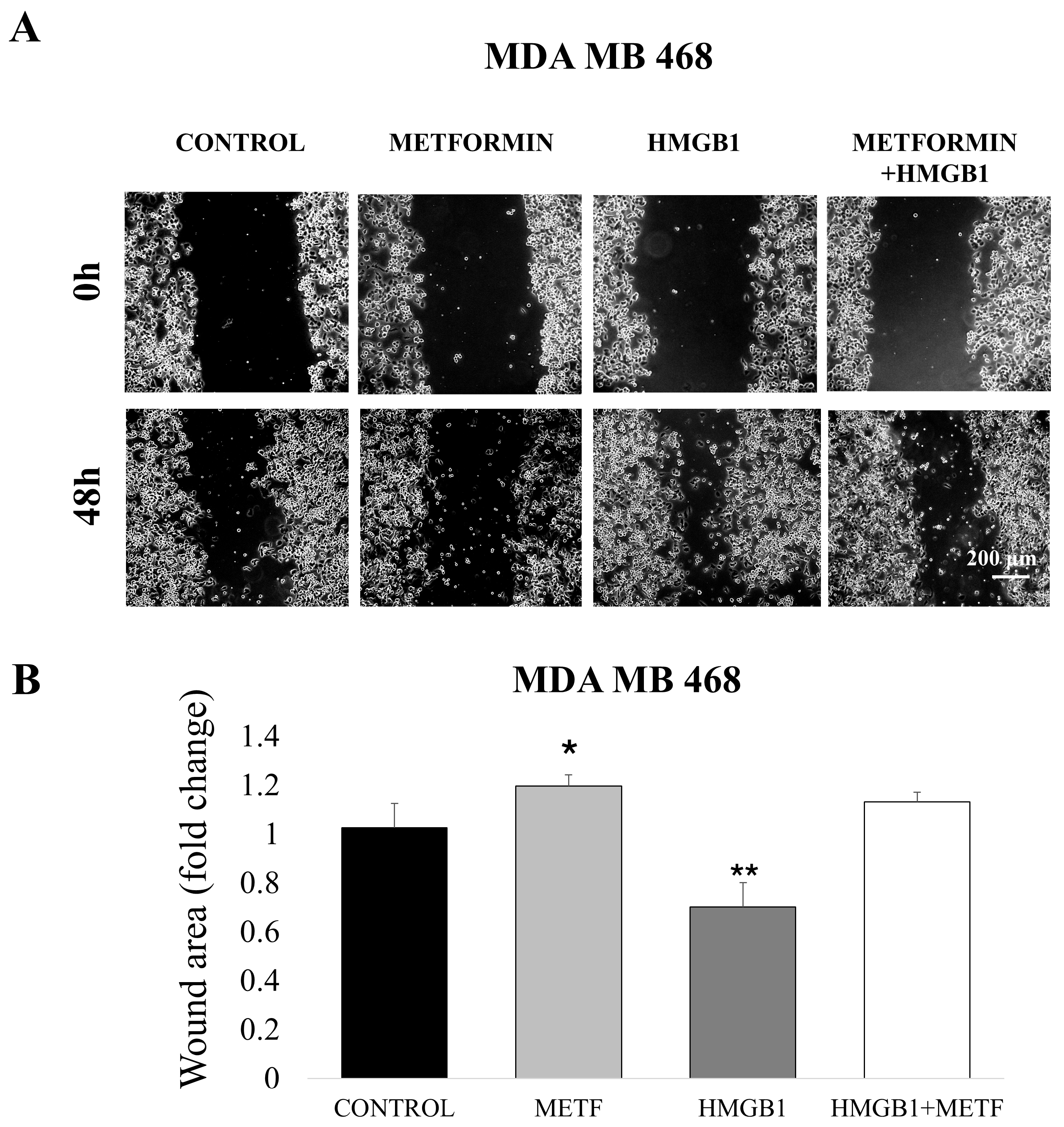
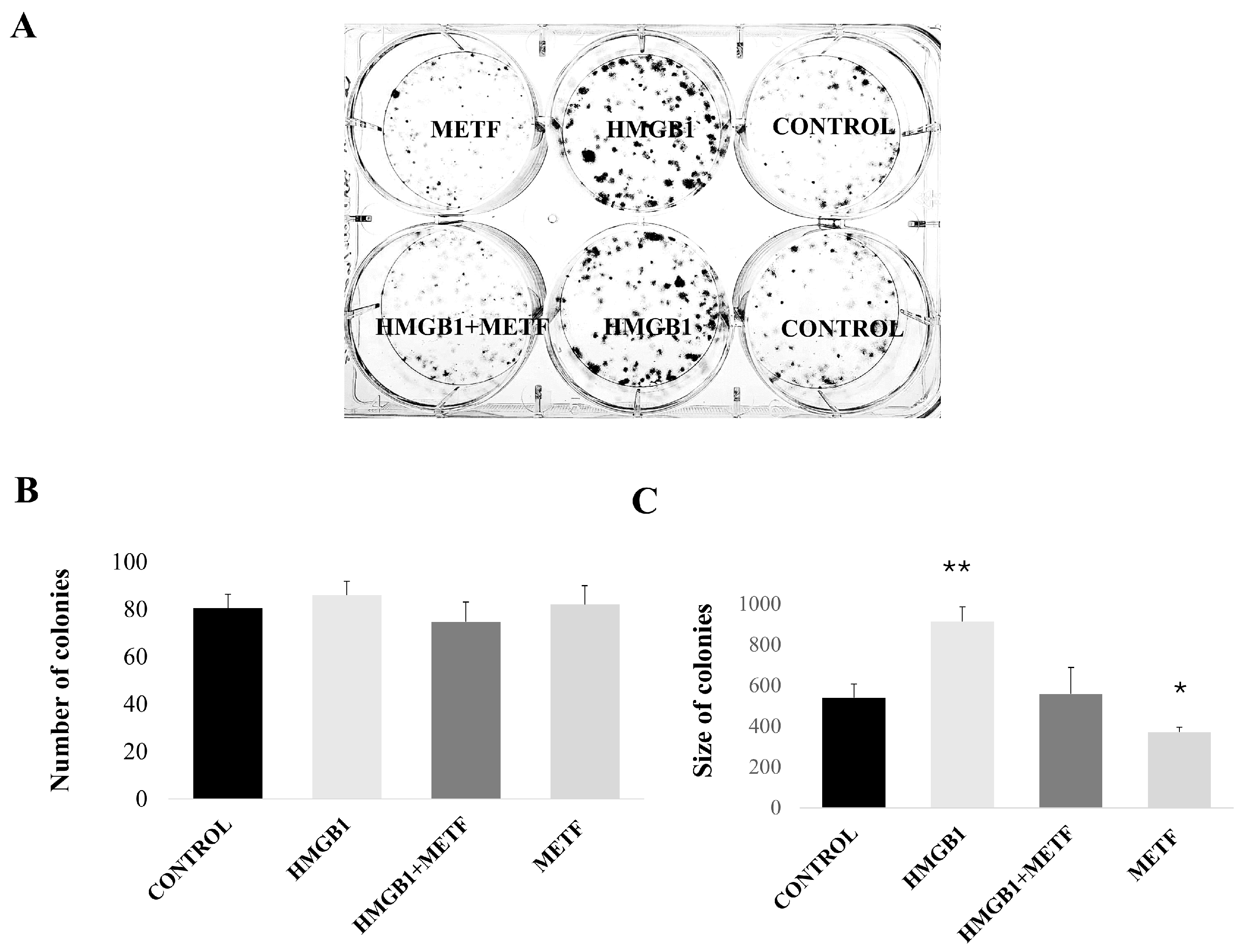
3.3. Metformin Inhibits HMGB1-Induced Cell Motility and Proliferation
3.4. Metformin Decreases HMGB1 and RAGE Protein Levels in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. The Multifunctional Protein HMGB1: 50 Years of Discovery. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 824–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Chiang, S.-F.; Ke, T.-W.; Chen, T.-W.; Lan, Y.-C.; You, Y.-S.; Shiau, A.-C.; Chen, W.T.-L.; Chao, K.S.C. Cytosolic High-Mobility Group Box Protein 1 (HMGB1) and/or PD-1+ TILs in the Tumor Microenvironment May Be Contributing Prognostic Biomarkers for Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Who Have Undergone Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T. High-Mobility Group Box 1 and Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liikanen, I.; Koski, A.; Merisalo-Soikkeli, M.; Hemminki, O.; Oksanen, M.; Kairemo, K.; Joensuu, T.; Kanerva, A.; Hemminki, A. Serum HMGB1 Is a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker for Oncolytic Immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e989771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, O.; Brett, J.; Slattery, T.; Cao, R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.X.; Nagashima, M.; Lundh, E.R.; Vijay, S.; Nitecki, D. The Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) Is a Cellular Binding Site for Amphoterin. Mediation of Neurite Outgrowth and Co-Expression of Rage and Amphoterin in the Developing Nervous System. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25752–25761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Ding, A.; Golenbock, D.T.; Latz, E.; Czura, C.J.; Fenton, M.J.; Tracey, K.J.; Yang, H. HMGB1 Signals through Toll-like Receptor (TLR) 4 and TLR2. Shock 2006, 26, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Dewan, V.; Grace, P.M.; Gunn, R.J.; Tamura, R.; Tzarum, N.; Watkins, L.R.; Wilson, I.A.; Yin, H. HMGB1 Activates Proinflammatory Signaling via TLR5 Leading to Allodynia. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1128–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, H.J.; Fages, C.; Rauvala, H. Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE)-Mediated Neurite Outgrowth and Activation of NF-kappaB Require the Cytoplasmic Domain of the Receptor but Different Downstream Signaling Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19919–19924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-C.; Yi, P.-P.; Zhou, R.-R.; Xiao, M.-F.; Huang, Z.-B.; Tang, D.-L.; Huang, Y.; Fan, X.-G. The Role of HMGB1-RAGE Axis in Migration and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 390, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. High-Mobility Group Box 1 Is Overexpressed in Cervical Carcinoma and Promotes Cell Invasion and Migration in Vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, S.; Han, D.; Xu, Y.; Jiao, D.; Wu, J.; Yang, F.; Ge, Y.; Shi, S.; Li, Y.; et al. High Mobility Group Box 1 Promotes the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Prostate Cancer PC3 Cells via the RAGE/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, P.; O’Connell, K.A.; Thiyagarajan, S.; Crawford, A.; Patil, P.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Shin, S.; Caffrey, T.C.; Grunkemeyer, J.; Neville, T.; et al. Inhibition of the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products Enhances the Cytotoxic Effect of Gemcitabine in Murine Pancreatic Tumors. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Beeraka, N.M.; Xie, L.; Dong, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. Co-Expression of High-Mobility Group Box 1 Protein (HMGB1) and Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) in the Prognosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Discov. Oncol. 2022, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.-B.; Bao, J.-M.; Lu, Y.-J.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, X.-H.; Zheng, D.-Y.; Zhao, S.-C. Co-Expression of RAGE and HMGB1 Is Associated with Cancer Progression and Poor Patient Outcome of Prostate Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wu, C.-Z.; Zheng, J.-J.; Bai, Y.-H.; Xia, P.; Zhang, H.-C.; Guo, Y. HMGB1/RAGE Axis Mediates the Apoptosis, Invasion, Autophagy, and Angiogenesis of the Renal Cell Carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 4501–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Tang, D.; Schapiro, N.E.; Livesey, K.M.; Farkas, A.; Loughran, P.; Bierhaus, A.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J. The Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) Sustains Autophagy and Limits Apoptosis, Promoting Pancreatic Tumor Cell Survival. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, A.; Gao, M.; Tang, X.; Jiao, M.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Gong, Q.; Zhong, J. HMGB1/RAGE Axis in Tumor Development: Unraveling Its Significance. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1336191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Hou, Y.; Deng, T.; Lin, G.; Cao, Y.; Yu, G.; Wei, W.; Zheng, Q.; Huang, L.; Ma, S. A Specific RAGE-Binding Peptide Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer Growth through Blocking of Erk1/2/NF-κB Pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 954, 175861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magna, M.; Hwang, G.H.; McIntosh, A.; Drews-Elger, K.; Takabatake, M.; Ikeda, A.; Mera, B.J.; Kwak, T.; Miller, P.; Lippman, M.E.; et al. RAGE Inhibitor TTP488 (Azeliragon) Suppresses Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2023, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwunonso Obi, B.; Chinwuba Okoye, T.; Okpashi, V.E.; Nonye Igwe, C.; Olisah Alumanah, E. Comparative Study of the Antioxidant Effects of Metformin, Glibenclamide, and Repaglinide in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 1635361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, A.R.; Morrison, V.L.; Levin, D.; Mohan, M.; Forteath, C.; Beall, C.; McNeilly, A.D.; Balfour, D.J.K.; Savinko, T.; Wong, A.K.F.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Metformin Irrespective of Diabetes Status. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Bai, P.; Dai, H.; Deng, Z. Metformin and Risk of Cancer among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Prim. Care Diabetes 2021, 15, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, K.M.; Rambally, B.S.; DiFurio, M.J.; Sampey, B.P.; Gehrig, P.A.; Makowski, L.; Bae-Jump, V.L. Antiproliferative and Metabolic Effects of Metformin in a Preoperative Window Clinical Trial for Endometrial Cancer. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, A.M.; Zannella, V.E.; Downes, M.R.; Bowes, B.; Hersey, K.; Koritzinsky, M.; Schwab, M.; Hofmann, U.; Evans, A.; van der Kwast, T.; et al. A Pilot “window of Opportunity” Neoadjuvant Study of Metformin in Localised Prostate Cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2014, 17, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiuchi, T.; Sakata, N.; Narumi, Y.; Kimura, T.; Hayashi, T.; Nagano, K.; Liu, K.; Nishibori, M.; Tsukita, S.; Yamada, T.; et al. Metformin Directly Binds the Alarmin HMGB1 and Inhibits Its Proinflammatory Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 8436–8446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yuan, F.; Deng, C.; He, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, Z.; Qian, L. Metformin Decreases LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in Rabbit Annulus Fibrosus Stem/Progenitor Cells by Blocking HMGB1 Release. Aging 2019, 11, 10252–10265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoyi, K.; Jang, H.J.; Nizamutdinova, I.T.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Seo, H.G.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, K.C. Metformin Inhibits HMGB1 Release in LPS-Treated RAW 264.7 Cells and Increases Survival Rate of Endotoxaemic Mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1498–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, S.; Fan, Y.; Huang, J.; Xiao, B.; Rao, H.; Huang, L. Effects of Metformin Therapy on HMGB1 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elenkov, I.; Pelovsky, P.; Ugrinova, I.; Takahashi, M.; Pasheva, E. The DNA Binding and Bending Activities of Truncated Tail-Less HMGB1 Protein Are Differentially Affected by Lys-2 and Lys-81 Residues and Their Acetylation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, H.T.; Shcherbinina, E.; Huang, H.-C.; Rezaei, R.; Sarshad, A.A. Biochemical Separation of Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Fraction for Downstream Molecular Analysis. Curr. Protoc. 2024, 4, e1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnette, W.N. “Western Blotting”: Electrophoretic Transfer of Proteins from Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate—Polyacrylamide Gels to Unmodified Nitrocellulose and Radiographic Detection with Antibody and Radioiodinated Protein A. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 112, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, L.G.; Wu, X.; Guan, J.-L. Wound-Healing Assay. In Cell Migration; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; Volume 294, pp. 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Buchholz, F.; Huang, Z.; Goga, A.; Chen, C.-Y.; Brodsky, F.M.; Bishop, J.M. Short RNA Duplexes Produced by Hydrolysis with Escherichia Coli RNase III Mediate Effective RNA Interference in Mammalian Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9942–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittler, R.; Buchholz, F. Functional Genomic Analysis of Cell Division by Endoribonuclease-Prepared siRNAs. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittler, R.; Surendranath, V.; Heninger, A.-K.; Slabicki, M.; Theis, M.; Putz, G.; Franke, K.; Caldarelli, A.; Grabner, H.; Kozak, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Resources of Endoribonuclease-Prepared Short Interfering RNAs for Specific Loss-of-Function Studies. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, N.A.P.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; van Bree, C. Clonogenic Assay of Cells in Vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, G. RAGE: A Single Receptor Fits Multiple Ligands. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcone, R.; Palma, M.; Pagliara, V.; Graziani, G.; Masullo, M.; Nardone, G. Green Tea Polyphenols Affect Invasiveness of Human Gastric MKN-28 Cells by Inhibition of LPS or TNF-α Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9/2. Biochim. Open 2016, 3, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaser, A.-M.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, R.-R.; Hu, G.-S.; Xiao, M.-F.; Huang, Z.-B.; Duan, C.-J.; Tian, W.; Tang, D.-L.; Fan, X.-G. The Role of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) in the Proliferation of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5982–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Chitayat, S.; Dattilo, B.M.; Schiefner, A.; Diez, J.; Chazin, W.J.; Fritz, G. Structural Basis for Ligand Recognition and Activation of RAGE. Structure 2010, 18, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.-M.; Ran, F.; Ni, H.-Z.; Sun, L.-L.; Xiao, L.; Li, X.-Q.; Li, W.-D. Metformin Inhibits High Glucose-Induced Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Migration. Aging 2020, 12, 5352–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Jia, R.; Ge, S.; Zhuang, A. Metformin and Cancer Hallmarks: Shedding New Lights on Therapeutic Repurposing. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavitra, E.; Kancharla, J.; Gupta, V.K.; Prasad, K.; Sung, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Tej, M.B.; Choi, R.; Lee, J.-H.; Han, Y.-K.; et al. The Role of NF-κB in Breast Cancer Initiation, Growth, Metastasis, and Resistance to Chemotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 163, 114822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-F.; Chen, F.-H.; Lu, M.-H.; Hong, J.-H.; Chiang, C.-S. Dual Roles of Tumour Cells-Derived Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 on Brain Tumour Growth and Invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, X.; Yuan, D.; Yu, T.; Chen, G.; Mi, Y.; et al. High Mobility Group Box Protein 1 Serves as a Potential Prognostic Marker of Lung Cancer and Promotes Its Invasion and Metastasis by Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 in a Nuclear Factor-κB-Dependent Manner. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3453706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Da, Q.; Chen, L.; Yu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Weng, Z.; Xin, Z.; Shi, L.; et al. HMGB1-Induced P62 Overexpression Promotes Snail-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Glioblastoma Cells via the Degradation of GSK-3β. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1909–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahdan-Alaswad, R.S.; Salem, H.S.; Edgerton, S.M.; Thor, A.D. Metformin Targets Cholesterol Biosynthesis Pathway, GM1 Lipid Raft Stabilization, EGFR Signaling and Proliferation in Triple Negative Breast Cancers. Cancer Ther. Oncol. Int. J. 2018, 9, 555765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, A.; Manganelli, V.; Riitano, G.; Caissutti, D.; Longo, A.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M.; Misasi, R. Advances in the Pathophysiology of Thrombosis in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Molecular Mechanisms and Signaling through Lipid Rafts. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, A.; Riitano, G.; Recalchi, S.; Manganelli, V.; Costi, R.; Saccoliti, F.; Pulcinelli, F.; Garofalo, T.; Misasi, R.; Longo, A.; et al. Effect of Heparanase Inhibitor on Tissue Factor Overexpression in Platelets and Endothelial Cells Induced by Anti-Β2-GPI Antibodies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 2302–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yusein-Myashkova, S.; Vladimirova, D.; Gospodinov, A.; Ugrinova, I.; Todorova, J. Metformin Inhibits Cell Motility and Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Blocking HMGB1/RAGE Signaling. Cells 2025, 14, 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080590
Yusein-Myashkova S, Vladimirova D, Gospodinov A, Ugrinova I, Todorova J. Metformin Inhibits Cell Motility and Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Blocking HMGB1/RAGE Signaling. Cells. 2025; 14(8):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080590
Chicago/Turabian StyleYusein-Myashkova, Shazie, Desislava Vladimirova, Anastas Gospodinov, Iva Ugrinova, and Jordana Todorova. 2025. "Metformin Inhibits Cell Motility and Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Blocking HMGB1/RAGE Signaling" Cells 14, no. 8: 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080590
APA StyleYusein-Myashkova, S., Vladimirova, D., Gospodinov, A., Ugrinova, I., & Todorova, J. (2025). Metformin Inhibits Cell Motility and Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells by Blocking HMGB1/RAGE Signaling. Cells, 14(8), 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080590





