Regulatory T Cell Mimicry by a Subset of Mesenchymal GBM Stem Cells Suppresses CD4 and CD8 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Cell Culture
2.2. Lentivirus Generation and Cell Transduction
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.5. Cell Viability and Cell Death Assays
2.6. Flow Cytometry and FACS
2.7. RNA Sequencing
2.8. Analysis of Publicly Available GBM Expression Data
2.9. Isolation and Activation of PBMC-Derived T Cells
2.10. Immune Cell Co-Culture Assay
2.11. Immunofluorescence Imaging
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
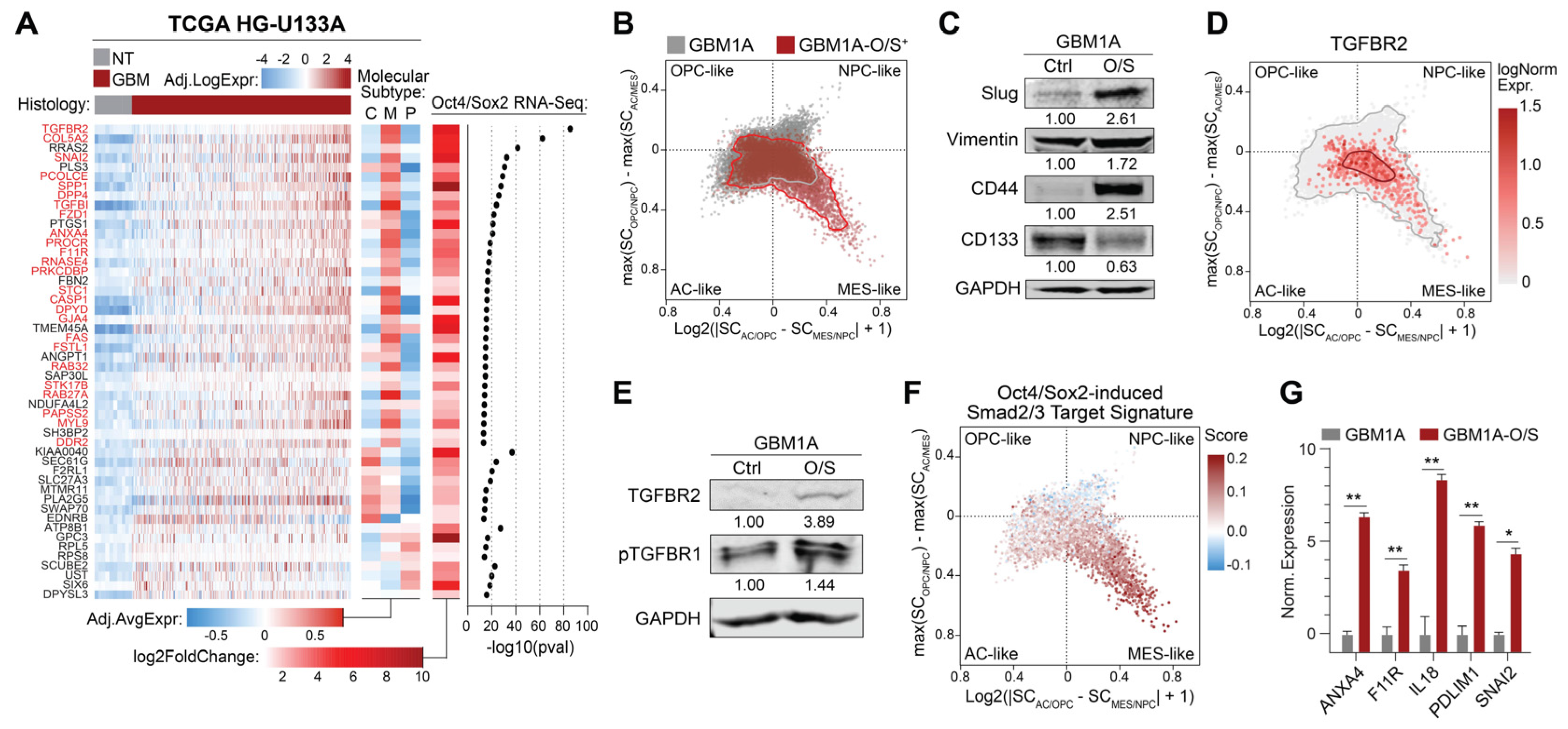
3.1. Oct4 and Sox2 Induce a TGFBR2-Related Mesenchymal Shift in GBM Cells
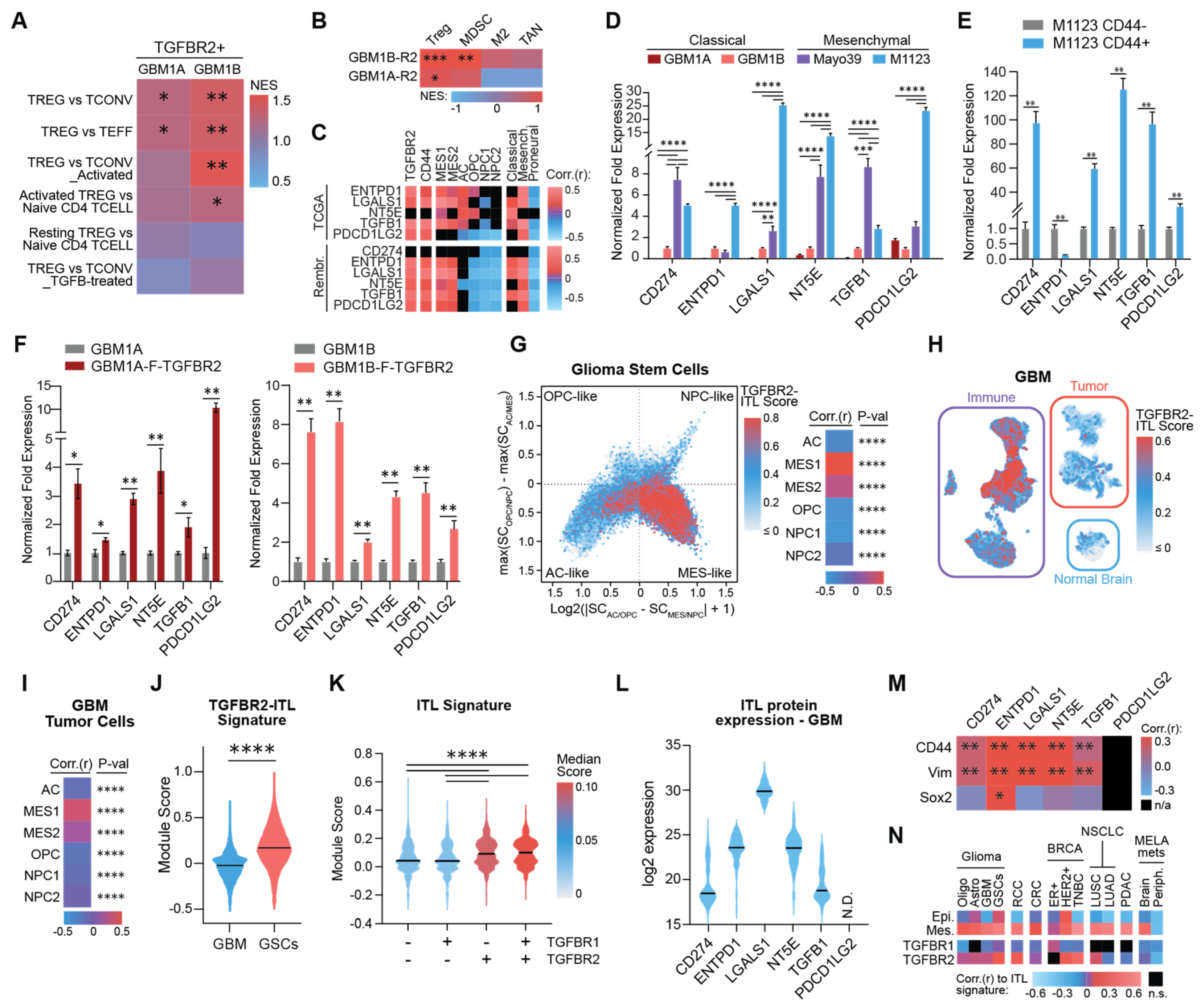
3.2. TGFBR2 Induces an Immunosuppressive ITL Signature in Mesenchymal GSCs
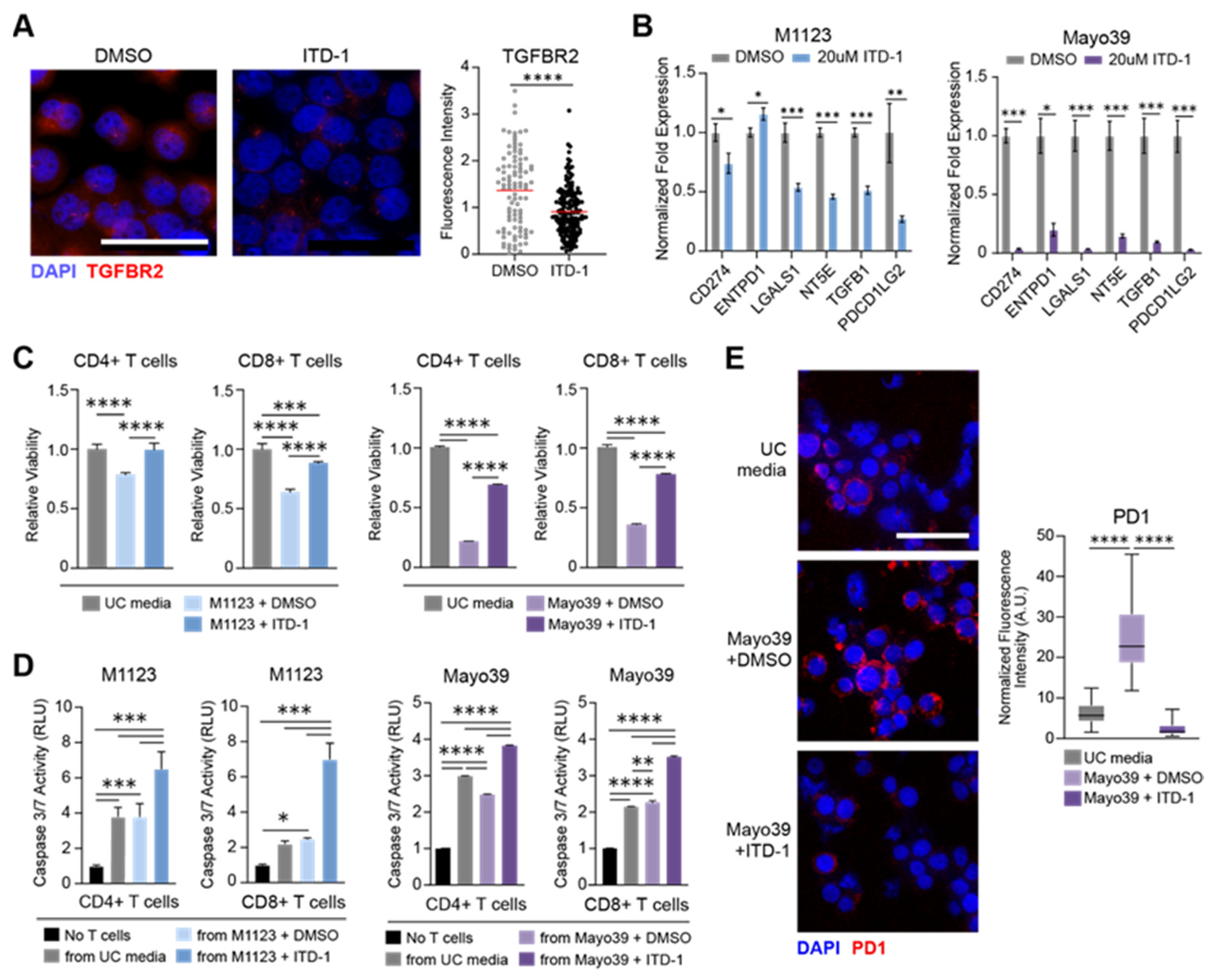
3.3. TGFBR2 Inhibition Blocks the Immunosuppressive GSC Phenotype
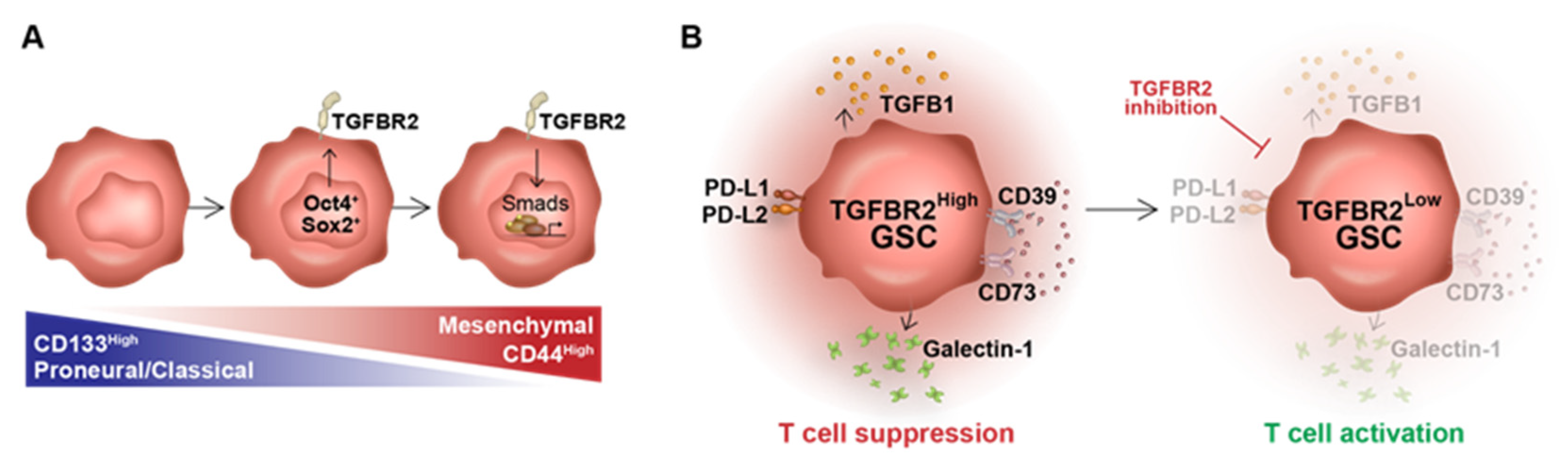
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Q.; Long, W.; Xing, C.; Chu, J.; Luo, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.F. Cancer Stem Cells and Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioma. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikfalvi, A.; da Costa, C.A.; Avril, T.; Barnier, J.V.; Bauchet, L.; Brisson, L.; Cartron, P.F.; Castel, H.; Chevet, E.; Chneiweiss, H.; et al. Challenges in glioblastoma research: Focus on the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Gao, R.; Xiu, Z.; Sun, T. MHC class I dysfunction of glioma stem cells escapes from CTL-mediated immune response via activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene 2020, 39, 1098–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricklefs, F.L.; Alayo, Q.; Krenzlin, H.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Speranza, M.C.; Nakashima, H.; Hayes, J.L.; Lee, K.; Balaj, L.; Passaro, C.; et al. Immune evasion mediated by PD-L1 on glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Hu, C.; Lal, B.; Zhou, W.; Ma, Y.; Ying, M.; Prinos, P.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Lim, M.; Laterra, J.; et al. Reprogramming Transcription Factors Oct4 and Sox2 Induce a BRD-Dependent Immunosuppressive Transcriptome in GBM-Propagating Cells. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2457–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.V.; Filiz, G.; Daniel, P.M.; Hollande, F.; Dworkin, S.; Amiridis, S.; Kountouri, N.; Ng, W.; Morokoff, A.P.; Mantamadiotis, T. Expression of CD133 and CD44 in glioblastoma stem cells correlates with cell proliferation, phenotype stability and intra-tumor heterogeneity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Xin, S.; Li, J.; Pei, G.; Kang, J. Yamanaka factors critically regulate the developmental signaling network in mouse embryonic stem cells. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 1177–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bertoni, H.; Lal, B.; Li, A.; Caplan, M.; Guerrero-Cazares, H.; Eberhart, C.G.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Glas, M.; Scheffler, B.; Laterra, J.; et al. DNMT-dependent suppression of microRNA regulates the induction of GBM tumor-propagating phenotype by Oct4 and Sox2. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3994–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Chanoch-Myers, R.; Mathewson, N.D.; Myskiw, C.; Atta, L.; Bussema, L.; Eichhorn, S.W.; Greenwald, A.C.; Kinker, G.S.; Rodman, C.; et al. Interactions between cancer cells and immune cells drive transitions to mesenchymal-like states in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 779–792.e711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Deng, Y.; Yang, M.; Su, G.; Yang, K.; Qian, C.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Revealed Subtype-Specific Tumor Immune Microenvironments in Human Glioblastomas. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 914236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekarian, T.; Zinner, C.P.; Bartoszek, E.M.; Duchemin, W.; Wachnowicz, A.T.; Hogan, S.; Etter, M.M.; Flammer, J.; Paganetti, C.; Martins, T.A.; et al. Immunotherapy of glioblastoma explants induces interferon-gamma responses and spatial immune cell rearrangements in tumor center, but not periphery. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanoch-Myers, R.; Wider, A.; Suva, M.L.; Tirosh, I. Correction: Elucidating the diversity of malignant mesenchymal states in glioblastoma by integrative analysis. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Pang, Y.; Moses, H.L. TGF-beta and immune cells: An important regulatory axis in the tumor microenvironment and progression. Trends Immunol. 2010, 31, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.L.; Coull, B.J.; Spender, L.C.; Watt, C.; Willison, A.; Syed, N.; Chalmers, A.J.; Hossain-Ibrahim, M.K.; Inman, G.J. Multifaceted transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) signalling in glioblastoma. Cell Signal. 2020, 72, 109638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, R.; Binda, E.; Orfanelli, U.; Cipelletti, B.; Gritti, A.; De Vitis, S.; Fiocco, R.; Foroni, C.; Dimeco, F.; Vescovi, A. Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7011–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandita, A.; Aldape, K.D.; Zadeh, G.; Guha, A.; James, C.D. Contrasting in vivo and in vitro fates of glioblastoma cell subpopulations with amplified EGFR. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2004, 39, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, P.; Joshi, K.; Li, J.; Kim, S.H.; Li, P.; Santana-Santos, L.; Luthra, S.; Chandran, U.R.; Benos, P.V.; Smith, L.; et al. Mesenchymal glioma stem cells are maintained by activated glycolytic metabolism involving aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8644–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, I.; Millard, N.; Fan, J.; Slowikowski, K.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Baglaenko, Y.; Brenner, M.; Loh, P.R.; Raychaudhuri, S. Fast, sensitive and accurate integration of single-cell data with Harmony. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbie, D.A.; Tamayo, P.; Boehm, J.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Moody, S.E.; Dunn, I.F.; Schinzel, A.C.; Sandy, P.; Meylan, E.; Scholl, C.; et al. Systematic RNA interference reveals that oncogenic KRAS-driven cancers require TBK1. Nature 2009, 462, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neftel, C.; Laffy, J.; Filbin, M.G.; Hara, T.; Shore, M.E.; Rahme, G.J.; Richman, A.R.; Silverbush, D.; Shaw, M.L.; Hebert, C.M.; et al. An Integrative Model of Cellular States, Plasticity, and Genetics for Glioblastoma. Cell 2019, 178, 835–849.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatari, N.; Khan, S.; Livingstone, J.; Zhai, K.; McKenna, D.; Ignatchenko, V.; Chokshi, C.; Gwynne, W.D.; Singh, M.; Revill, S.; et al. The proteomic landscape of glioblastoma recurrence reveals novel and targetable immunoregulatory drivers. Acta. Neuropathol. 2022, 144, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, D.; Ma, D.; Wei, S.; Lal, B.; Fu, Y.; Eberhart, C.; Laterra, J.; Ying, M.; Li, Y.; Meeker, A.; et al. Monoallelic IDH1 R132H Mutation Mediates Glioma Cell Response to Anticancer Therapies via Induction of Senescence. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdieri, L.; Jash, A.; Malkova, O.; Mao, D.D.; DeSouza, P.; Chu, Y.E.; Salter, A.; Campian, J.L.; Naegle, K.M.; Brennan, C.W.; et al. Defining phenotypic and functional heterogeneity of glioblastoma stem cells by mass cytometry. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e128456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koinuma, D.; Tsutsumi, S.; Kamimura, N.; Taniguchi, H.; Miyazawa, K.; Sunamura, M.; Imamura, T.; Miyazono, K.; Aburatani, H. Chromatin immunoprecipitation on microarray analysis of Smad2/3 binding sites reveals roles of ETS1 and TFAP2A in transforming growth factor beta signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varn, F.S.; Johnson, K.C.; Martinek, J.; Huse, J.T.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Wesseling, P.; Cooper, L.A.D.; Malta, T.M.; Wade, T.E.; Sabedot, T.S.; et al. Glioma progression is shaped by genetic evolution and microenvironment interactions. Cell 2022, 185, 2184–2199.e2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecci, P.E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Whitesides, J.F.; Xie, W.; Friedman, A.H.; Archer, G.E.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Bigner, D.D.; Dranoff, G.; Sampson, J.H. Increased regulatory T-cell fraction amidst a diminished CD4 compartment explains cellular immune defects in patients with malignant glioma. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3294–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshetaiwi, H.; Pervolarakis, N.; McIntyre, L.L.; Ma, D.; Nguyen, Q.; Rath, J.A.; Nee, K.; Hernandez, G.; Evans, K.; Torosian, L.; et al. Defining the emergence of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in breast cancer using single-cell transcriptomics. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaay6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhairavabhotla, R.; Kim, Y.C.; Glass, D.D.; Escobar, T.M.; Patel, M.C.; Zahr, R.; Nguyen, C.K.; Kilaru, G.K.; Muljo, S.A.; Shevach, E.M. Transcriptome profiling of human FoxP3+ regulatory T cells. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, R.R.; Soukup, K.; Fournier, N.; Massara, M.; Galland, S.; Kornete, M.; Wischnewski, V.; Lourenco, J.; Croci, D.; Alvarez-Prado, A.F.; et al. The local microenvironment drives activation of neutrophils in human brain tumors. Cell 2023, 186, 4546–4566.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaldo, E.; Lusito, E.; Bianchessi, V.; Caronni, N.; Scala, S.; Basso-Ricci, L.; Cantaffa, C.; Masserdotti, A.; Barilaro, M.; Barresi, S.; et al. Cellular and transcriptional dynamics of human neutrophils at steady state and upon stress. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 1470–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshi, M.; Tokumaru, Y.; Asaoka, M.; Yan, L.; Satyananda, V.; Matsuyama, R.; Matsuhashi, N.; Futamura, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Yoshida, K.; et al. M1 Macrophage and M1/M2 ratio defined by transcriptomic signatures resemble only part of their conventional clinical characteristics in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, A.T.; Rawal, S.; Delcuze, B.; Christofides, A.; Atayde, A.; Strauss, L.; Balaj, L.; Rogers, V.A.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Varma, H.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals evolution of immune landscape during glioblastoma progression. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, D.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.M.; Whitley, O.K.N.; MacLeod, G.; Cavalli, F.M.G.; Coutinho, F.J.; Jaramillo, J.E.; Svergun, N.; Riverin, M.; Croucher, D.C.; Kushida, M.; et al. Gradient of Developmental and Injury Response transcriptional states defines functional vulnerabilities underpinning glioblastoma heterogeneity. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, E.; Cabral-Teixeira, J.; Schade, D.; Cai, W.; Reeves, P.; Bushway, P.J.; Lanier, M.; Walsh, C.; Kirchhausen, T.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C.; et al. Small molecule-mediated TGF-beta type II receptor degradation promotes cardiomyogenesis in embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, B.; Hu, X.; Kim, H.; Squatrito, M.; Scarpace, L.; deCarvalho, A.C.; Lyu, S.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; et al. Tumor Evolution of Glioma-Intrinsic Gene Expression Subtypes Associates with Immunological Changes in the Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 42–56.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, K.; Shan, D.; Cui, G.; Yuan, W.; Lin, Q.; Gimple, R.C.; Dixit, D.; Lu, C.; et al. IFI35 regulates non-canonical NF-kappaB signaling to maintain glioblastoma stem cells and recruit tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Death Differ. 2024, 31, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, X.; Han, X.; Li, G.; Hou, A.; Han, S. CCL2 mediated IKZF1 expression promotes M2 polarization of glioma-associated macrophages through CD84-SHP2 pathway. Oncogene 2024, 43, 2737–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Tao, J.; Gou, H.; Liu, S.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Ji, J.; Lin, N.; Wang, Y. FSTL1 sustains glioma stem cell stemness and promotes immunosuppressive macrophage polarization in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2024, 611, 217400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Liu, B.; Cai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, Y. Suberanilohydroxamic acid (SAHA), a HDAC inhibitor, suppresses the effect of Treg cells by targeting the c-Myc/CCL1 pathway in glioma stem cells and improves PD-L1 blockade therapy. J. Neurooncol. 2024, 168, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniotis, A.J.; Folberg, R.; Hess, A.; Seftor, E.A.; Gardner, L.M.; Pe’er, J.; Trent, J.M.; Meltzer, P.S.; Hendrix, M.J. Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: Vasculogenic mimicry. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chadalavada, K.; Wilshire, J.; Kowalik, U.; Hovinga, K.E.; Geber, A.; Fligelman, B.; Leversha, M.; Brennan, C.; Tabar, V. Glioblastoma stem-like cells give rise to tumour endothelium. Nature 2010, 468, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramani, V.; Yang, Y.; Schubert, M.C.; Reyhan, E.; Tetzlaff, S.K.; Wissmann, N.; Botz, M.; Soyka, S.J.; Beretta, C.A.; Pramatarov, R.L.; et al. Glioblastoma hijacks neuronal mechanisms for brain invasion. Cell 2022, 185, 2899–2917.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, H.S.; Morishita, W.; Geraghty, A.C.; Silverbush, D.; Gillespie, S.M.; Arzt, M.; Tam, L.T.; Espenel, C.; Ponnuswami, A.; Ni, L.; et al. Electrical and synaptic integration of glioma into neural circuits. Nature 2019, 573, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangoso, E.; Southgate, B.; Bradley, L.; Rus, S.; Galvez-Cancino, F.; McGivern, N.; Guc, E.; Kapourani, C.A.; Byron, A.; Ferguson, K.M.; et al. Glioblastomas acquire myeloid-affiliated transcriptional programs via epigenetic immunoediting to elicit immune evasion. Cell 2021, 184, 2454–2470.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagiwa, S.; Gray, J.D.; Hashimoto, S.; Horwitz, D.A. A role for TGF-beta in the generation and expansion of CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cells from human peripheral blood. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 7282–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lan, Q.; Lu, L.; Chen, M.; Xia, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Fan, H.; Shen, Y.; Ryffel, B.; et al. Phenotypic and functional characteristic of a newly identified CD8+ Foxp3- CD103+ regulatory T cells. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 6, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deaglio, S.; Dwyer, K.M.; Gao, W.; Friedman, D.; Usheva, A.; Erat, A.; Chen, J.F.; Enjyoji, K.; Linden, J.; Oukka, M.; et al. Adenosine generation catalyzed by CD39 and CD73 expressed on regulatory T cells mediates immune suppression. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin, M.I.; Chu, C.C.; Golshayan, D.; Cernuda-Morollon, E.; Wait, R.; Lechler, R.I. Galectin-1: A key effector of regulation mediated by CD4 + CD25 + T cells. Blood 2007, 109, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strauss, L.; Bergmann, C.; Szczepanski, M.; Gooding, W.; Johnson, J.T.; Whiteside, T.L. A unique subset of CD4 + CD25highFoxp3 + T cells secreting interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta1 mediates suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4345–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotot, J.; Gottschalk, C.; Leopold, S.; Knolle, P.A.; Yagita, H.; Kurts, C.; Ludwig-Portugall, I. Regulatory T cells use programmed death 1 ligands to directly suppress autoreactive B cells in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10468–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.M.; Will, P.; Kueckelhaus, J.; Sun, N.; Joseph, K.; Salie, H.; Vollmer, L.; Kuliesiute, U.; von Ehr, J.; Benotmane, J.K.; et al. Spatially resolved multi-omics deciphers bidirectional tumor-host interdependence in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 639–655.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, A.A.; Carpentier, A.F.; Kesari, S.; Sepulveda-Sanchez, J.M.; Wheeler, H.R.; Chinot, O.; Cher, L.; Steinbach, J.P.; Capper, D.; Specenier, P.; et al. A Phase II randomized study of galunisertib monotherapy or galunisertib plus lomustine compared with lomustine monotherapy in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2016, 18, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khasraw, M.; Weller, M.; Lorente, D.; Kolibaba, K.; Lee, C.K.; Gedye, C.; de La Fuente, M.I.; Vicente, D.; Reardon, D.A.; Gan, H.K.; et al. Bintrafusp alfa (M7824), a bifunctional fusion protein targeting TGF-beta and PD-L1: Results from a phase I expansion cohort in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, A.; Desjardins, A.; Suarez, C.; Forsyth, P.; Gueorguieva, I.; Burkholder, T.; Cleverly, A.L.; Estrem, S.T.; Wang, S.; Lahn, M.M.; et al. Phase 1b/2a study of galunisertib, a small molecule inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta receptor I, in combination with standard temozolomide-based radiochemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed malignant glioma. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 1570–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolcher, A.W.; Berlin, J.D.; Cosaert, J.; Kauh, J.; Chan, E.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Amaya, A.; Tang, S.; Driscoll, K.; Kimbung, R.; et al. A phase 1 study of anti-TGFbeta receptor type-II monoclonal antibody LY3022859 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derynck, R.; Turley, S.J.; Akhurst, R.J. TGFbeta biology in cancer progression and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Johnson, A.L.; Khela, H.S.; Korleski, J.; Sall, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Smith-Connor, K.; Laterra, J.; Lopez-Bertoni, H. Regulatory T Cell Mimicry by a Subset of Mesenchymal GBM Stem Cells Suppresses CD4 and CD8 Cells. Cells 2025, 14, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080592
Johnson AL, Khela HS, Korleski J, Sall S, Li Y, Zhou W, Smith-Connor K, Laterra J, Lopez-Bertoni H. Regulatory T Cell Mimicry by a Subset of Mesenchymal GBM Stem Cells Suppresses CD4 and CD8 Cells. Cells. 2025; 14(8):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080592
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohnson, Amanda L., Harmon S. Khela, Jack Korleski, Sophie Sall, Yunqing Li, Weiqiang Zhou, Karen Smith-Connor, John Laterra, and Hernando Lopez-Bertoni. 2025. "Regulatory T Cell Mimicry by a Subset of Mesenchymal GBM Stem Cells Suppresses CD4 and CD8 Cells" Cells 14, no. 8: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080592
APA StyleJohnson, A. L., Khela, H. S., Korleski, J., Sall, S., Li, Y., Zhou, W., Smith-Connor, K., Laterra, J., & Lopez-Bertoni, H. (2025). Regulatory T Cell Mimicry by a Subset of Mesenchymal GBM Stem Cells Suppresses CD4 and CD8 Cells. Cells, 14(8), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080592






