Psoriasis in Obese Adolescents with Diabetes—From Common Molecular Background to Vicious Circle of Metabolic Syndrome—Case Report and Review of Literature
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
3.1. Prevalence of Psoriasis in Type 1 Diabetes
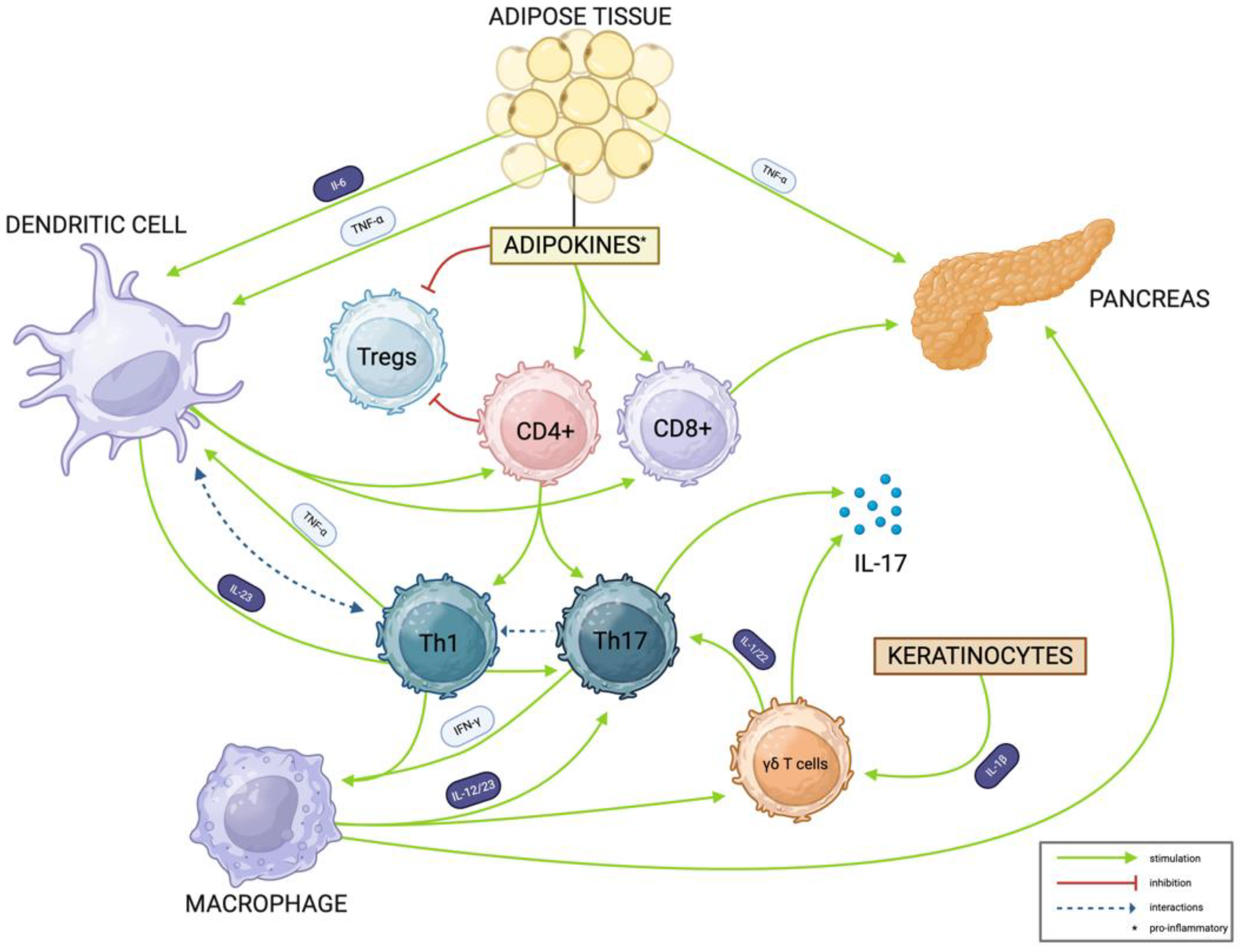
3.2. Shared Disease Mechanisms
3.2.1. The Key Role of Th17, γδ T, and Th1 Cells in Autoimmune Response
3.2.2. Psoriasis Development
3.2.3. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Pathogenesis
3.3. Necrobiosis Lipoidica
3.3.1. The Epidemiology of Necrobiosis Lipoidica
3.3.2. Histological Findings in Necrobiosis Lipoidica
3.3.3. The Immunology of Necrobiosis Lipoidica and Targeted Therapy
3.4. Obesity and Autoimmune Disorders
3.4.1. Leptin
3.4.2. Resistin
3.4.3. Adiponectin
3.4.4. IL-18
3.5. Double Diabetes
3.5.1. Coincidence of Insulin Resistance in Autoimmune-Mediated Diabetes
3.5.2. Genetic Susceptibility and Molecular Mechanisms
3.6. Psoriasis, Obesity, and Insulin Resistance
3.6.1. Bidirectional Interaction Between Adipose Tissue Level and Psoriasis Severity
3.6.2. Psoriasis Increases the Risk for Insulin Resistance
3.6.3. Leptin as a Molecular Link Between Obesity, Psoriasis, and Metabolic Syndrome
3.6.4. The Impact of the Disease Burden on Patient Care Strategy and Treatment Outcomes
3.7. Metabolic Syndrome in Psoriatic Population
3.7.1. Definition of Metabolic Syndrome
3.7.2. Patient Care Strategy to Reduce Metabolic and Cardiovascular Risk
3.7.3. The Rationale for Choosing Anti IL-17A/F Therapy
3.8. The Significance of Interdisciplinary Care for Patients with Multimorbidity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABPM | Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring |
| ADAMTSL | Protein Produced by Melanocytes |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BP | Blood Pressure |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| CXCL10 | C-X-C motif chemokine 10 |
| CXCR3 | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| FABP4 | Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 |
| GLUT-1 | Glucose Transporter 1 |
| HLA | Human Leukocyte Antigen |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| LL37 | Antimicrobial Peptide Derived from Keratinocytes |
| MAP | Mean Arterial Pressure |
| MetS | Metabolic Syndrome |
| NL | Necrobiosis Lipoidica |
| NK cells | Natural Killer Cells |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| PASI | Psoriasis Area and Severity Index |
| T1DM | Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| Th1 | T Helper Type 1 Cells |
| Th17 | T Helper Type 17 Cells |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| Tregs | Regulatory T Cells |
| TRM | Tissue-Resident Memory Cells |
| WHtR | Waist-to-Height Ratio |
| γδ T cells | Gamma Delta T Cells |
References
- Ukegbu, T.E.; Wylie-Rosett, J.; Groisman-Perelstein, A.E.; Diamantis, P.M.; Rieder, J.; Ginsberg, M.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Matthan, N.R.; Shankar, V. Waist-to-Height Ratio Associated Cardiometabolic Risk Phenotype in Children with Overweight/Obesity. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, Y.-B.; Jin, S.-M.; Hur, K.Y.; Kim, G.; Kim, J.H. Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control and Its Derived Metrics in Type 1 Diabetes: A Longitudinal Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1165471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Sierra, A.; Staplin, N.; Ruilope, L.M.; Gorostidi, M.; Vinyoles, E.; Segura, J.; Baigent, C.; Williams, B. A Blunted Nocturnal Blood Pressure Decline Is Associated with All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality. J. Hypertens. 2024, 42, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chang, P.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kizer, J.R.; Best, L.G.; Howard, B.V. Triglyceride and HDL-C Dyslipidemia and Risks of Coronary Heart Disease and Ischemic Stroke by Glycemic Dysregulation Status: The Strong Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, S.; Weitzman, M.; Auinger, P.; Nguyen, M.; Dietz, W.H. Prevalence of a Metabolic Syndrome Phenotype in Adolescents: Findings From the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2003, 157, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ferranti, S.D.; Gauvreau, K.; Ludwig, D.S.; Neufeld, E.J.; Newburger, J.W.; Rifai, N. Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in American Adolescents: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Circulation 2004, 110, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassi, E.; Pervanidou, P.; Kaltsas, G.; Chrousos, G. Metabolic Syndrome: Definitions and Controversies. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samotij, D.; Nedoszytko, B.; Bartosińska, J.; Batycka-Baran, A.; Czajkowski, R.; Dobrucki, I.T.; Dobrucki, L.W.; Górecka-Sokołowska, M.; Janaszak-Jasienicka, A.; Krasowska, D.; et al. Pathogenesis of Psoriasis in the “Omic” Era. Part I. Epidemiology, Clinical Manifestation, Immunological and Neuroendocrine Disturbances. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. Dermatol. Alergol. 2020, 37, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, S.D.; Ladizinski, B.; Lee, K.; Baibergenova, A.; Alavi, A. Update on Necrobiosis Lipoidica: A Review of Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errichetti, E.; Ioannides, D.; Lallas, A. Psoriasis [Łuszczyca]. In Dermoscopy in General Dermatology [Dermatoskopia w dermatologii ogólnej]; Edra Urban & Partner: Wrocław, Poland, 2023; pp. 2–10. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Errichetti, E.; Ioannides, D.; Lallas, A. Necrobiosis lipoidica [Obumieranie tłuszczowate]. In Dermoscopy in General Dermatology [Dermatoskopia w dermatologii ogólnej]; Edra Urban & Partner: Wrocław, Poland, 2023; pp. 61–64. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Parisi, R.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Identification and Management of Psoriasis and Associated ComorbidiTy (IMPACT) project team Global Epidemiology of Psoriasis: A Systematic Review of Incidence and Prevalence. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatema, F.; Ghoshal, L.; Saha, A.; Agarwal, S.; Bandyopadhyay, D. Early-Onset Versus Late-Onset Psoriasis: A Comparative Study of Clinical Variables, Comorbidities, and Association with HLA CW6 in a Tertiary Care Center. Indian J. Dermatol. 2021, 66, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raychaudhuri, S.P.; Gross, J. A Comparative Study of Pediatric Onset Psoriasis with Adult Onset Psoriasis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2000, 17, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, M.; Glaeske, G.; Radtke, M.A.; Christophers, E.; Reich, K.; Schäfer, I. Epidemiology and Comorbidity of Psoriasis in Children. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 162, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Weinstein, R.; Porter, S.B.; Neimann, A.L.; Berlin, J.A.; Margolis, D.J. Prevalence and Treatment of Psoriasis in the United Kingdom: A Population-Based Study. Arch. Dermatol. 2005, 141, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagnani, A.; Tosti, A.; Patrizi, A.; Salardi, S.; Cacciari, E. Diabetes Mellitus and Skin Diseases in Childhood. Dermatologica 1985, 170, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Costanzo, L.; Fattorusso, V.; Mozzillo, E.; Patrì, A.; Di Caprio, R.; De Nitto, E.; Balato, N.; Franzese, A. Psoriasis in Children with Type 1 Diabetes: A New Comorbidity to Be Considered? Acta Diabetol. 2017, 54, 803–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroppo, F.; Galderisi, A.; Moretti, C.; Ventura, L.; Belloni Fortina, A. Prevalence of Psoriasis in a Cohort of Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2021, 35, e589–e591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, J.; Bertilsson, R.; Bülow, E.; Carlsson, S.; Åkesson, S.; Eliasson, B.; Hanas, R.; Åkesson, K. Autoimmune Comorbidity in Type 1 Diabetes and Its Association with Metabolic Control and Mortality Risk in Young People: A Population-Based Study. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeachy, M.J.; Cua, D.J.; Gaffen, S.L. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity 2019, 50, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatya, N.; Garg, A.V.; Gaffen, S.L. IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparber, F.; LeibundGut-Landmann, S. Interleukin-17 in Antifungal Immunity. Pathogens 2019, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanesi, C.; Cavani, A.; Girolomoni, G. IL-17 Is Produced by Nickel-Specific T Lymphocytes and Regulates ICAM-1 Expression and Chemokine Production in Human Keratinocytes: Synergistic or Antagonist Effects with IFN-Gamma and TNF-Alpha. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cua, D.J.; Tato, C.M. Innate IL-17-Producing Cells: The Sentinels of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, E.; Sato, Y.; Minagawa, A.; Okuyama, R. Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Development of Treatment. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, B.S.; Lee, K.; Fanok, M.H.; Mascaraque, C.; Amoury, M.; Cohn, L.; Rogoz, A.; Dallner, O.S.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Domingos, A.I.; et al. Leptin Receptor Signaling in T Cells Is Required for Th17 Differentiation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5253–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehuen, A.; Diana, J.; Zaccone, P.; Cooke, A. Immune Cell Crosstalk in Type 1 Diabetes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrack, A.L.; Martinov, T.; Fife, B.T. T Cell-Mediated Beta Cell Destruction: Autoimmunity and Alloimmunity in the Context of Type 1 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, C.; La Rocca, C.; Carbone, F.; De Rosa, V.; Galgani, M.; Matarese, G. Leptin as Immune Mediator: Interaction between Neuroendocrine and Immune System. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 66, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoura, N.; Nagai, H.; Fujiwara, S.; Jimbo, H.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nishigori, C. Interleukin (IL)-18, Cooperatively with IL-23, Induces Prominent Inflammation and Enhances Psoriasis-like Epidermal Hyperplasia. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccone, P.; Phillips, J.; Conget, I.; Cooke, A.; Nicoletti, F. IL-18 Binding Protein Fusion Construct Delays the Development of Diabetes in Adoptive Transfer and Cyclophosphamide-Induced Diabetes in NOD Mouse. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Shen, X.; Ding, C.; Qi, C.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Jala, V.R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, T.; Zheng, J.; et al. Pivotal Role of Dermal IL-17-Producing Γδ T Cells in Skin Inflammation. Immunity 2011, 35, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, J. Gamma Delta T Cells and Their Pathogenic Role in Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 627139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarczyk Saczonek, A.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Kasprowicz-Furmańczyk, M.; Placek, W. Immunological Memory of Psoriatic Lesions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarczyk-Saczonek, A.; Kasprowicz-Furmańczyk, M.; Czerwińska, J.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Placek, W. The Effect of Therapy on TRM in Psoriatic Lesions. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2022, 39, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuric, E.; Seiron, P.; Krogvold, L.; Edwin, B.; Buanes, T.; Hanssen, K.F.; Skog, O.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; Korsgren, O. Demonstration of Tissue Resident Memory CD8 T Cells in Insulitic Lesions in Adult Patients with Recent-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cheong, L.Y.; Yuan, L.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, A.; Hoo, R.L.; Shu, L. Islet-Resident Memory T Cells Orchestrate the Immunopathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes through the FABP4-CXCL10 Axis. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2308461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, K.; Cooke, A. CD4 T Cells and Their Antigens in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diabetes. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwaha, A.K.; Leung, N.J.; McMurchy, A.N.; Levings, M.K. TH17 Cells in Autoimmunity and Immunodeficiency: Protective or Pathogenic? Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinert-Hartwall, L.; Honkanen, J.; Salo, H.M.; Nieminen, J.K.; Luopajärvi, K.; Härkönen, T.; Veijola, R.; Simell, O.; Ilonen, J.; Peet, A.; et al. Th1/Th17 Plasticity Is a Marker of Advanced β Cell Autoimmunity and Impaired Glucose Tolerance in Humans. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemore, S.M.; Nikoopour, E.; Schwartz, J.A.; Krougly, O.; Lee-Chan, E.; Singh, B. Preventative Role of Interleukin-17 Producing Regulatory T Helper Type 17 (Treg 17) Cells in Type 1 Diabetes in Non-Obese Diabetic Mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Benitez, P.; Ardissone, A.; Wilson, T.D.; Collins, E.L.; Lorca, G.; Li, N.; Sankar, D.; Wasserfall, C.; Neu, J.; et al. Inhibition of Type 1 Diabetes Correlated to a Lactobacillus Johnsonii N6.2-Mediated Th17 Bias. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3538–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, R.L.; Matsuda, J.; Aydintug, M.K.; Jin, N.; Phalke, S.; Born, W.K. A Distinctive Γδ T Cell Repertoire in NOD Mice Weakens Immune Regulation and Favors Diabetic Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körber, A.; Dissemond, J. Necrobiosis Lipoidica Diabeticorum. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2007, 177, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrí, J.; Moreno, A.; Marcoval, J. Necrobiosis Lipoidica. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2007, 26, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibanian, R.S.; Muradian, A.G. Association of psoriasis with sarcoid-like form of necrobiosis lipoidica. Vestn. Dermatol. Venerol. 1982, 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, H.; Imamura, S. Scald-Induced Necrobiosis Lipoidica in a Patient with Diabetes Mellitus and Psoriasis. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2016, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, Z.; Lahat, N.; Kinarty, A.; Feuerman, E.J. Psoriasis, Necrobiosis Lipoidica, Granuloma Annulare, Vitiligo and Skin Infections in the Same Diabetic Patient. J. Dermatol. 1990, 17, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura-Wakatsuki, T.; Yamamoto, T. Palmoplantar Pustulosis Associated with Necrobiosis Lipoidica: A Possible Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin-17. J. Dermatol. 2014, 41, 461–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbald, C.; Reid, S.; Alavi, A. Necrobiosis Lipoidica. Dermatol. Clin. 2015, 33, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ke, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhou, P.; Jiang, H.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. High Glucose Causes Distinct Expression Patterns of Primary Human Skin Cells by RNA Sequencing. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 603645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikarinen, A.; Mörtenhumer, M.; Kallioinen, M.; Savolainen, E.R. Necrobiosis Lipoidica: Ultrastructural and Biochemical Demonstration of a Collagen Defect. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1987, 88, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, C.; Givens, V.; Smoller, B.R. Expression of the Human Erythrocyte Glucose Transporter Glut-1 in Areas of Sclerotic Collagen in Necrobiosis Lipoidica. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2001, 28, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manicone, A.M.; McGuire, J.K. Matrix Metalloproteinases as Modulators of Inflammation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 19, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, D.-I.; Lee, A.-H.; Shin, H.-Y.; Song, H.-R.; Park, J.-H.; Kang, T.-B.; Lee, S.-R.; Yang, S.-H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-α Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O. Regulators of Macrophage Activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakusawa, C.; Fujimura, T.; Kambayashi, Y.; Furudate, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Aiba, S. Pigmented Necrobiosis Lipoidica Accompanied by Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Induces CD163+ Proinflammatory Macrophages and Interleukin-17-Producing Cells. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2013, 93, 475–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, L.A.; Sivamani, R.K.; Sharon, V.R.; Silverstein, M.A.; Burrall, B.A.; Tartar, D.M. Ustekinumab to Target Granulomatous Dermatitis in Recalcitrant Ulcerative Necrobiosis Lipoidica: Case Report and Proposed Mechanism. Dermatol. Online J. 2017, 23, 13030/qt3k32k916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourang, A.; Sivamani, R.K. Treatment-Resistant Ulcerative Necrobiosis Lipoidica in a Diabetic Patient Responsive to Ustekinumab. Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 25, 13030/qt2q05z4rw. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.S.; Salian, P.; Beckles, A.; Stavert, R.; Tahan, S.; Kimball, A.B.; Porter, M.L. Treatment of Necrobiosis Lipoidica with Secukinumab (Cosentyx): A Case Series. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, 1198–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, P.; Killion, L.; Blake, C.; Kelly, G.; Tobin, A. Ulcerating Necrobiosis Lipoidica Successfully Treated with Ustekinumab. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2021, 62, e473–e474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhie, M.L.; Swales, W.C.; Gooderham, M.J. Improvement of Granulomatous Skin Conditions with Tofacitinib in Three Patients: A Case Report. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2021, 9, 2050313X211039477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikonomou, E.K.; Antoniades, C. The Role of Adipose Tissue in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.B. The Complex Role of Adipokines in Obesity, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.M.; Halaas, J.L. Leptin and the Regulation of Body Weight in Mammals. Nature 1998, 395, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. The Weight of Leptin in Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, G.M.; Matarese, G.; Howard, J.K.; Baker, R.J.; Bloom, S.R.; Lechler, R.I. Leptin Modulates the T-Cell Immune Response and Reverses Starvation-Induced Immunosuppression. Nature 1998, 394, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarese, G.; Moschos, S.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin in Immunology. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 3137–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, V.; Procaccini, C.; Calì, G.; Pirozzi, G.; Fontana, S.; Zappacosta, S.; La Cava, A.; Matarese, G. A Key Role of Leptin in the Control of Regulatory T Cell Proliferation. Immunity 2007, 26, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A. Role of the Blood–Brain Barrier in the Evolution of Feeding and Cognition. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1264, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasandani, C.; Clark, G.O.; Adams-Huet, B.; Quittner, C.; Garg, A. Efficacy and Safety of Metreleptin Therapy in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Pilot Study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, C.M.; Lazar, M.A. Resistin and Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2002, 13, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Tsuchiya, H.; Hama, S.; Kajimoto, K.; Kogure, K. Resistin Affects Lipid Metabolism during Adipocyte Maturation of 3T3-L1 Cells. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5884–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codoñer-Franch, P.; Alonso-Iglesias, E. Resistin: Insulin Resistance to Malignancy. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. 2015, 438, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filková, M.; Haluzík, M.; Gay, S.; Šenolt, L. The Role of Resistin as a Regulator of Inflammation: Implications for Various Human Pathologies. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, K.; Torii, K.; Furuhashi, T.; Saito, C.; Nishio, E.; Nishida, E.; Shintani, Y.; Morita, A. Phototherapy Reduces Serum Resistin Levels in Psoriasis Patients. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, S.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Salgo, R.; Garbaraviciene, J.; Beschmann, H.; Diehl, S.; Hardt, K.; Thaçi, D.; Boehncke, W.-H. Systemic Therapy of Plaque-Type Psoriasis Ameliorates Endothelial Cell Function: Results of a Prospective Longitudinal Pilot Trial. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2011, 303, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Shen, E.; Tang, S.; Tan, X.; Guo, X.; Wang, Q.; Ding, H. Increased Serum Resistin Levels Correlate with Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyikli, I.; Keskin, M.; Kör, Y.; Akan, M. Increased Resistin Serum Concentrations in Patientswith Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Res. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2013, 5, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askin, L.; Abus, S.; Tanriverdi, O. Resistin and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review of the Current Literature Regarding Clinical and Pathological Relationships. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2022, 18, e290721195114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.F.; McAinch, A.J.; Poronnik, P.; Hryciw, D.H. Adipokines as a Link between Obesity and Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2013, 305, F1629–F1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, L.G.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic Messengers: Adiponectin. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Zheng, W.; Dong, Y.; Wang, J.; Garstka, M.A.; Li, R.; An, J.; Ma, H. Serum Levels of Adipokines and Cytokines in Psoriasis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 1266–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, S.; Osadtschy, S.; Rostami-Yazdi, M.; Buhles, N.; Weichenthal, M.; Mrowietz, U. Leptin, Adiponectin, Visfatin and Retinol-Binding Protein-4—Mediators of Comorbidities in Patients with Psoriasis? Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, S.; Saeki, H.; Tada, Y.; Karakawa, M.; Komine, M.; Tamaki, K. Serum High Molecular Weight Adiponectin Levels Are Decreased in Psoriasis Patients. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2009, 55, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.-J.; Shi, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Fan, Y.-M. Adiponectin Levels in Patients with Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavoso, N.C.; Pinto, J.M.; Soares, M.M.S.; Diniz, M.d.S.; Teixeira Júnior, A.L. Psoriasis in Obesity: Comparison of Serum Levels of Leptin and Adiponectin in Obese Subjects—Cases and Controls. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2019, 94, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Flisiak, I.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Świderska, M. Effect of Psoriasis Activity on Serum Adiponectin and Leptin Levels. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. Dermatol. Alergol. 2015, 32, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.S.A.; Liew, C.F.; Theng, C.T.S.; Oon, H.H. Serum Adiponectin Levels and Their Association with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Patients with Psoriasis. Cureus 2020, 12, e8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.I.; Snell-Bergeon, J.K.; Erickson, C.; Schauer, I.E.; Bergman, B.C.; Rewers, M.; Maahs, D.M. Adiponectin Dysregulation and Insulin Resistance in Type 1 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E642–E647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.; Choubey, M.; Tirumalasetty, M.B.; Arbee, S.; Mohib, M.M.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Mamun, M.A.; Uddin, M.B.; Mohiuddin, M.S. Adiponectin: A Promising Target for the Treatment of Diabetes and Its Complications. Life 2023, 13, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayur, T.; Banerjee, S.; Hugunin, M.; Butler, D.; Herzog, L.; Carter, A.; Quintal, L.; Sekut, L.; Talanian, R.; Paskind, M.; et al. Caspase-1 Processes IFN-Gamma-Inducing Factor and Regulates LPS-Induced IFN-Gamma Production. Nature 1997, 386, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, S.; Uehara, A.; Nochi, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Ueda, H.; Sugiyama, A.; Hanzawa, K.; Kumagai, K.; Okamura, H.; Takada, H. Neutrophil Proteinase 3-Mediated Induction of Bioactive IL-18 Secretion by Human Oral Epithelial Cells. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 6568–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Román-Domínguez, L.; Salazar-León, J.; Meza-Sosa, K.F.; Pérez-Martínez, L.; Pedraza-Alva, G. Adipose Tissue IL-18 Production Is Independent of Caspase-1 and Caspase-11. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rex, D.; Agarwal, N.; Prasad, T.S.K.; Kandasamy, R.K.; Subbannayya, Y.; Pinto, S.M. A Comprehensive Pathway Map of IL-18-Mediated Signalling. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 14, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailbeig, M.; Ghaderi, A. Interleukin-18: A Regulator of Cancer and Autoimmune Diseases. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2017, 28, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, O.J.; Srinivasan, N.; Pott, J.; Schiering, C.; Krausgruber, T.; Ilott, N.E.; Maloy, K.J. Epithelial-Derived IL-18 Regulates Th17 Cell Differentiation and Foxp3+ Treg Cell Function in the Intestine. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Hamada, Y.; Katsuoka, K. Expression of IL-18 in Psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2001, 293, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Companjen, A.; van der Wel, L.; van der Fits, L.; Laman, J.; Prens, E. Elevated Interleukin-18 Protein Expression in Early Active and Progressive Plaque-Type Psoriatic Lesions. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2004, 15, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Gangemi, S.; Merendino, R.A.; Guarneri, F.; Minciullo, P.L.; DiLorenzo, G.; Pacor, M.; Cannavò, S.P. Serum Levels of Interleukin-18 and s-ICAM-1 in Patients Affected by Psoriasis: Preliminary Considerations. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. JEADV 2003, 17, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arican, O.; Aral, M.; Sasmaz, S.; Ciragil, P. Serum Levels of TNF-Alpha, IFN-Gamma, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17, and IL-18 in Patients with Active Psoriasis and Correlation with Disease Severity. Mediat. Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flisiak, I.; Klepacki, A.; Chodynicka, B. Plasma and Scales Levels of Interleukin 18 in Comparison with Other Possible Clinical and Laboratory Biomarkers of Psoriasis Activity. Biomarkers 2006, 11, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marleau, A.M.; Sarvetnick, N.E. IL-18 Is Required for Self-Reactive T Cell Expansion in NOD Mice. J. Autoimmun. 2011, 36, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretowski, A.; Mironczuk, K.; Karpinska, A.; Bojaryn, U.; Kinalski, M.; Puchalski, Z.; Kinalska, I. Interleukin-18 Promoter Polymorphisms in Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3347–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, R.Z.; Yarde, D.N.; Guinn, Z.; Lorenzo-Arteaga, K.M.; Corley, K.P.; Cabrera, M.S.; Sarvetnick, N.E. Increased Expression of IL-18 in the Serum and Islets of Type 1 Diabetics. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 64, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandanmagsar, B.; Youm, Y.-H.; Ravussin, A.; Galgani, J.E.; Stadler, K.; Mynatt, R.L.; Ravussin, E.; Stephens, J.M.; Dixit, V.D. The NLRP3 Inflammasome Instigates Obesity-Induced Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teupe, B.; Bergis, K. Epidemiological Evidence for “Double Diabetes”. Lancet 1991, 337, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merger, S.R.; Kerner, W.; Stadler, M.; Zeyfang, A.; Jehle, P.; Müller-Korbsch, M.; Holl, R.W.; DPV Initiative; German BMBF Competence Network Diabetes Mellitus. Prevalence and Comorbidities of Double Diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 119, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Twigg, S.M.; Flack, J.R. Metabolic Syndrome in Type 1 Diabetes and Its Association with Diabetes Complications. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2021, 38, e14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørk, F.B.; Madsen, J.O.B.; Pilgaard, K.A.; Jensen, A.K.; Klakk, H.; Tarp, J.; Bugge, A.; Heidemann, M.; Van Hall, G.; Pociot, F.; et al. The Metabolic Syndrome Is Frequent in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Compared to Healthy Controls. Pediatr. Diabetes 2022, 23, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Correia, C.; Santos-Silva, R.; Pinheiro, M.; Costa, C.; Fontoura, M. Metabolic Risk Factors in Adolescent Girls with Type 1 Diabetes. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. JPEM 2018, 31, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolosowicz, M.; Lukaszuk, B.; Chabowski, A. The Causes of Insulin Resistance in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Is There a Place for Quaternary Prevention? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Oh, C.-M.; Kim, H. The Interplay of Adipokines and Pancreatic Beta Cells in Metabolic Regulation and Diabetes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnop, M.; Havel, P.J.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Carr, D.B.; Sinha, M.K.; Boyko, E.J.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Knopp, R.H.; Brunzell, J.D.; Kahn, S.E. Relationship of Adiponectin to Body Fat Distribution, Insulin Sensitivity and Plasma Lipoproteins: Evidence for Independent Roles of Age and Sex. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiao, J.; Li, N.; Qiao, S. AMPK A1 Mediates the Protective Effect of Adiponectin against Insulin Resistance in INS-1 Pancreatic β Cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2019, 37, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhao, D.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, C.; Ji, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, F.; Guo, X. Resistin Induces Rat Insulinoma Cell RINm5F Apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1703–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetboun, M.; Abitbol, G.; Rozenberg, K.; Rozenfeld, H.; Deutsch, A.; Sampson, S.R.; Rosenzweig, T. Maintenance of Redox State and Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function: Role of Leptin and Adiponectin. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 1966–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohallem, R.; Aryal, U.K. Regulators of TNFα Mediated Insulin Resistance Elucidated by Quantitative Proteomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisondi, P.; Del Giglio, M.; Di Francesco, V.; Zamboni, M.; Girolomoni, G. Weight Loss Improves the Response of Obese Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Chronic Plaque Psoriasis to Low-Dose Cyclosporine Therapy: A Randomized, Controlled, Investigator-Blinded Clinical Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.-J.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Shi, G.; Fan, Y.-M. Leptin Levels in Patients with Psoriasis: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 38, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestle, F.O.; Kaplan, D.H.; Barker, J. Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolomoni, G.; Strohal, R.; Puig, L.; Bachelez, H.; Barker, J.; Boehncke, W.; Prinz, J. The Role of IL-23 and the IL-23/T17 Immune Axis in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, M.; Shang, Z.; Teng, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M.; Lv, H.; Zhang, R. The Shared and Specific Mechanism of Four Autoimmune Diseases. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 108355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Harskamp, C.T.; Armstrong, E.J. Psoriasis and Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 68, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, H.; Fukushima, S.; Masuguchi, S.; Yamashita, J.; Miyashita, A.; Nakahara, S.; Aoi, J.; Inoue, Y.; Jinnin, M.; Ihn, H. Serum Levels of Leptin Receptor in Patients with Malignant Melanoma as a New Tumor Marker. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 748–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; Yoo, J.A.; Yoon, H.; Han, T.; Yoon, J.; An, S.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, J. The Role of Leptin in the Association between Obesity and Psoriasis. Biomol. Ther. 2021, 29, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopytalska, K.; Baranowska-Bik, A.; Roszkiewicz, M.; Bik, W.; Walecka, I. The Role of Leptin in Selected Skin Diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Shen, J.-L.; Chu, S.-Y.; Chen, C.-K.; Chang, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-M. Psoriasis Independently Associated with Hyperleptinemia Contributing to Metabolic Syndrome. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, S.M.; Seminara, N.M.; Shin, D.B.; Troxel, A.B.; Kimmel, S.E.; Mehta, N.N.; Margolis, D.J.; Gelfand, J.M. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Psoriasis: A Population-Based Study in the United Kingdom. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyldenløve, M.; Storgaard, H.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K.; Skov, L. Patients with Psoriasis Are Insulin Resistant. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 72, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vata, D.; Tarcau, B.M.; Popescu, I.A.; Halip, I.A.; Patrascu, A.I.; Gheuca Solovastru, D.-F.; Mocanu, M.; Chiriac, P.C.; Gheuca Solovastru, L. Update on Obesity in Psoriasis Patients. Life 2023, 13, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.N.; Yu, Y.; Pinnelas, R.; Krishnamoorthy, P.; Shin, D.B.; Troxel, A.B.; Gelfand, J.M. Attributable Risk Estimate of Severe Psoriasis on Major Cardiovascular Events. Am. J. Med. 2011, 124, 775.e1–775.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisondi, P.; Tessari, G.; Conti, A.; Piaserico, S.; Schianchi, S.; Peserico, A.; Giannetti, A.; Girolomoni, G. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Psoriasis: A Hospital-based Case–Control Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 157, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naldi, L.; Addis, A.; Chimenti, S.; Giannetti, A.; Picardo, M.; Tomino, C.; Maccarone, M.; Chatenoud, L.; Bertuccio, P.; Caggese, E.; et al. Impact of Body Mass Index and Obesity on Clinical Response to Systemic Treatment for Psoriasis. Evidence from the Psocare Project. Dermatology 2008, 217, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herron, M.D.; Hinckley, M.; Hoffman, M.S.; Papenfuss, J.; Hansen, C.B.; Callis, K.P.; Krueger, G.G. Impact of Obesity and Smoking on Psoriasis Presentation and Management. Arch. Dermatol. 2005, 141, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setty, A.R.; Curhan, G.; Choi, H.K. Obesity, Waist Circumference, Weight Change, and the Risk of Psoriasis in Women: Nurses’ Health Study II. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, T.V.; Markina, Y.V.; Bogatyreva, A.I.; Tolstik, T.V.; Varaeva, Y.R.; Starodubova, A.V. The Role of Adipokines in Inflammatory Mechanisms of Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upala, S.; Sanguankeo, A. Effect of Lifestyle Weight Loss Intervention on Disease Severity in Patients with Psoriasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codazzi, V.; Frontino, G.; Galimberti, L.; Giustina, A.; Petrelli, A. Mechanisms and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents. Endocrine 2024, 84, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chait, A.; den Hartigh, L.J. Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, V.S.; Hansell, N.K.; Guo, W.; Carpenter, J.S.; Shou, H.; Strike, L.T.; Crouse, J.J.; McAloney, K.; McMahon, K.L.; Byrne, E.M.; et al. Genetic and Environmental Influences on Sleep-Wake Behaviors in Adolescence. Sleep Adv. J. Sleep Res. Soc. 2021, 2, zpab018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisinger, C.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N.; Fredriksen, P.M.; Goswami, N. The Prevalence of Pediatric Metabolic Syndrome-a Critical Look on the Discrepancies between Definitions and Its Clinical Importance. Int. J. Obes. 2021, 45, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Neimann, A.L.; Shin, D.B.; Wang, X.; Margolis, D.J.; Troxel, A.B. Risk of Myocardial Infarction in Patients with Psoriasis. JAMA 2006, 296, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrzak, A.; Grywalska, E.; Walankiewicz, M.; Lotti, T.; Roliński, J.; Myśliński, W.; Chabros, P.; Piekarska-Myślińska, D.; Reich, K. Psoriasis and Metabolic Syndrome in Children: Current Data. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, H.V.S.; Budamakuntla, L.; Sundar, C.M.S. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome among Children with Psoriasis in Urban Bengaluru. Clin. Dermatol. Rev. 2023, 7, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldminz, A.M.; Buzney, C.D.; Kim, N.; Au, S.-C.; Levine, D.E.; Wang, A.C.; Volf, E.M.; Yaniv, S.S.; Kerensky, T.A.; Bhandarkar, M.; et al. Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome in Children with Psoriatic Disease. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2013, 30, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugh, J.; Voorhees, A.S.V.; Nijhawan, R.I.; Bagel, J.; Lebwohl, M.; Blauvelt, A.; Hsu, S.; Weinberg, J.M. From the Medical Board of the National Psoriasis Foundation: The Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Individuals with Psoriasis and the Potential Impact of Current Therapies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinagra, E.; Perricone, G.; Romano, C.; Cottone, M. Heart Failure and Anti Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in Systemic Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Dong, C. IL-17F: Regulation, Signaling and Function in Inflammation. Cytokine 2009, 46, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, K.; Warren, R.B.; Lebwohl, M.; Gooderham, M.; Strober, B.; Langley, R.G.; Paul, C.; Cuyper, D.D.; Vanvoorden, V.; Madden, C.; et al. Bimekizumab versus Secukinumab in Plaque Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, R.B.; Lebwohl, M.; Thaçi, D.; Gooderham, M.; Pinter, A.; Paul, C.; Gisondi, P.; Szilagyi, B.; White, K.; Deherder, D.; et al. Bimekizumab Efficacy and Safety through 3 Years in Patients with Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis: Long-Term Results from the BE RADIANT Phase 3b Trial Open-Label Extension Period. Br. J. Dermatol. 2025, ljaf032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morey, A.; Loades, M.E. Review: How Has Cognitive Behaviour Therapy Been Adapted for Adolescents with Comorbid Depression and Chronic Illness? A Scoping Review. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2021, 26, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

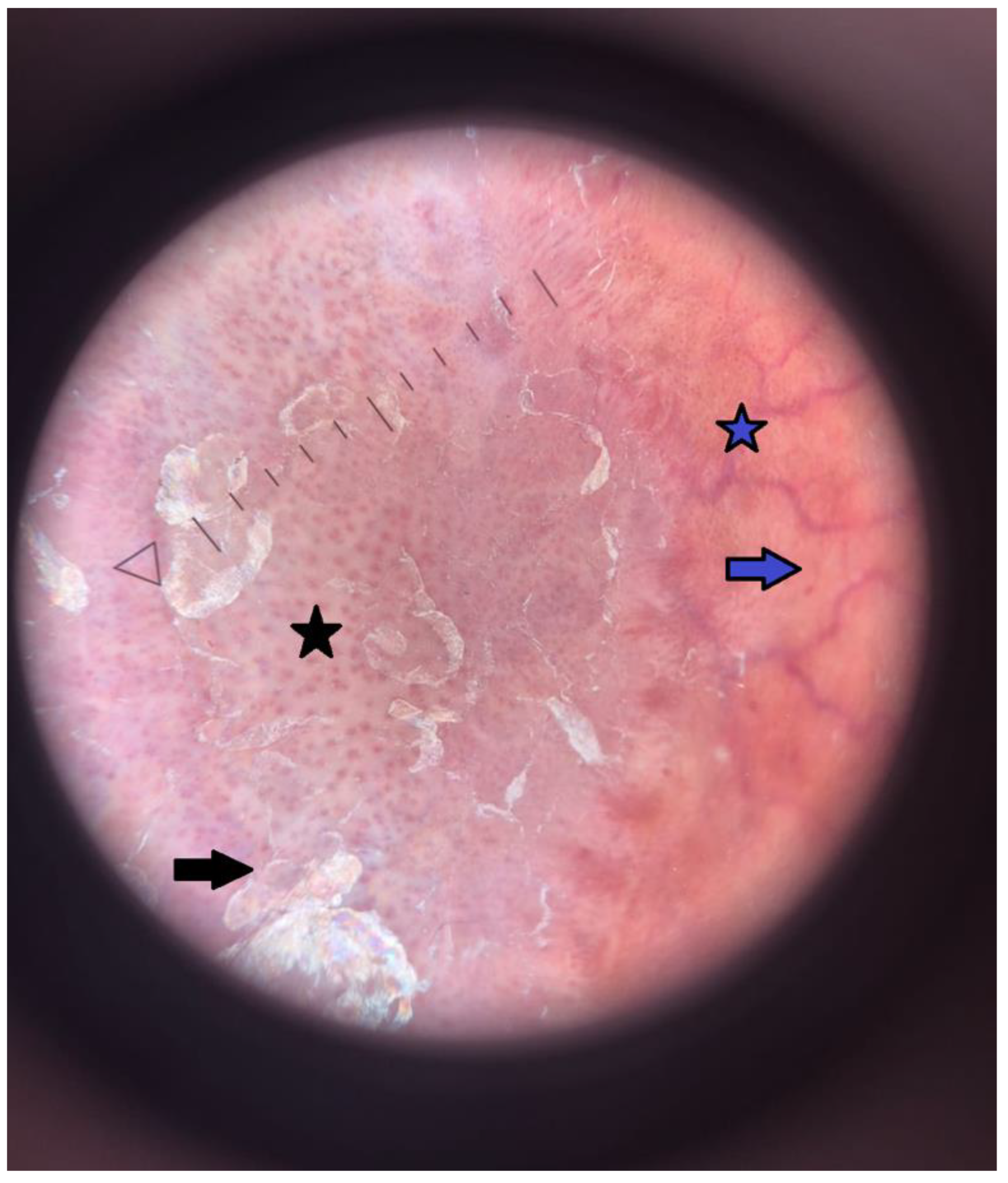
| Criterion | Cook et al. [5] | de Ferranti et al. [6] | IDF Adult Criteria (≥16 Year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Waist Circumference | >90th percentile for age/sex | ≥75th percentile for age/sex | WC ≥ 94 cm (men) |
| Triglycerides | ≥110 mg/dL | ≥100 mg/dL | ≥150 mg/dL |
| HDL Cholesterol | ≤40 mg/dL | <50 mg/dL | <40 mg/dL (men) |
| Blood Pressure | Systolic or diastolic BP ≥ 90th percentile for age, sex, height | ≥90th percentile for age, sex, height | ≥130/85 mmHg |
| Glucose/Insulin | Fasting glucose ≥ 110 mg/dL (some use ≥ 100 mg/dL) | Fasting glucose ≥ 110 mg/dL (some use ≥ 100 mg/dL) | Fasting glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL |
| Number of Abnormal Factors | ≥3 of the above | ≥2 of the above + elevated LDL or total cholesterol can also be considered in some versions | Central obesity and ≥2 of the remaining factors |
| Age Range | Children and adolescents (~8–19 yrs) | Children and adolescents (~8–19 yrs) | Adults ≥ 16 yr (IDF recommends adult thresholds from age 16 onward) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bielach-Bazyluk, A.; Bossowski, F.; Skorupska, M.; Mysliwiec, H.; Bossowski, A.T.; Flisiak, I. Psoriasis in Obese Adolescents with Diabetes—From Common Molecular Background to Vicious Circle of Metabolic Syndrome—Case Report and Review of Literature. Cells 2025, 14, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080610
Bielach-Bazyluk A, Bossowski F, Skorupska M, Mysliwiec H, Bossowski AT, Flisiak I. Psoriasis in Obese Adolescents with Diabetes—From Common Molecular Background to Vicious Circle of Metabolic Syndrome—Case Report and Review of Literature. Cells. 2025; 14(8):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080610
Chicago/Turabian StyleBielach-Bazyluk, Angelika, Filip Bossowski, Magdalena Skorupska, Hanna Mysliwiec, Artur Tadeusz Bossowski, and Iwona Flisiak. 2025. "Psoriasis in Obese Adolescents with Diabetes—From Common Molecular Background to Vicious Circle of Metabolic Syndrome—Case Report and Review of Literature" Cells 14, no. 8: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080610
APA StyleBielach-Bazyluk, A., Bossowski, F., Skorupska, M., Mysliwiec, H., Bossowski, A. T., & Flisiak, I. (2025). Psoriasis in Obese Adolescents with Diabetes—From Common Molecular Background to Vicious Circle of Metabolic Syndrome—Case Report and Review of Literature. Cells, 14(8), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14080610








