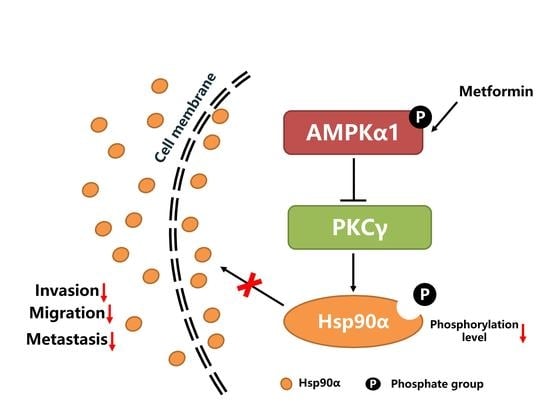
Metformin Inhibits Tumor Metastasis through Suppressing Hsp90α Secretion in an AMPKα1-PKCγ Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Lentivirus Infection
2.5. siRNA Interference
2.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.7. Plasma Membrane Extraction
2.8. Cell Invasion Assay and Cell Migration Assay
2.9. Co-Immunoprecipitation Assay (Co-IP)
2.10. Mass Spectrometry
2.11. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.12. Exosomes Isolation
2.13. Animal Experiments
2.14. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Metformin Inhibits Hsp90α Secretion both In Vitro and In Vivo
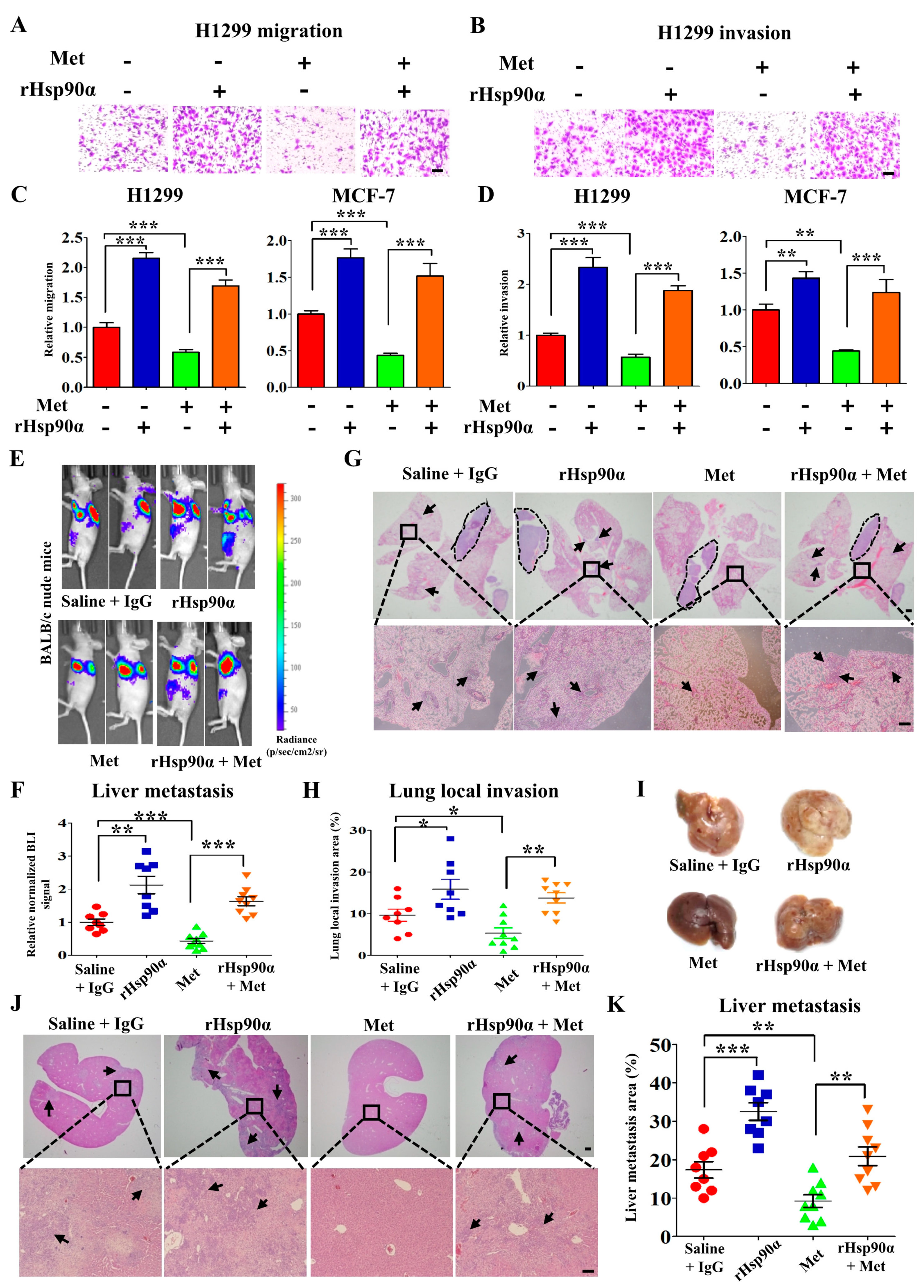
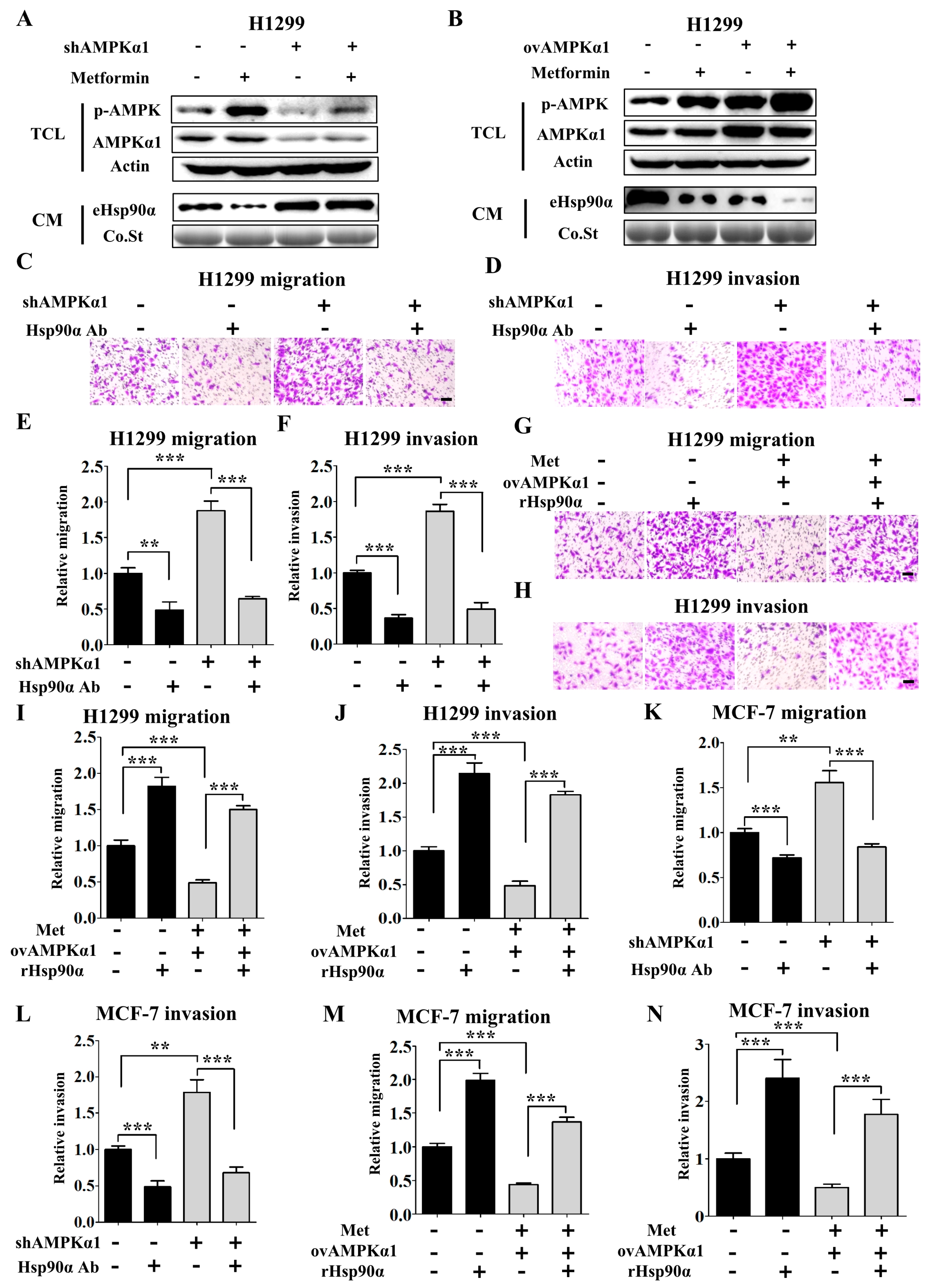
3.2. Metformin Inhibits Tumor Metastasis through Suppressing Hsp90α Secretion
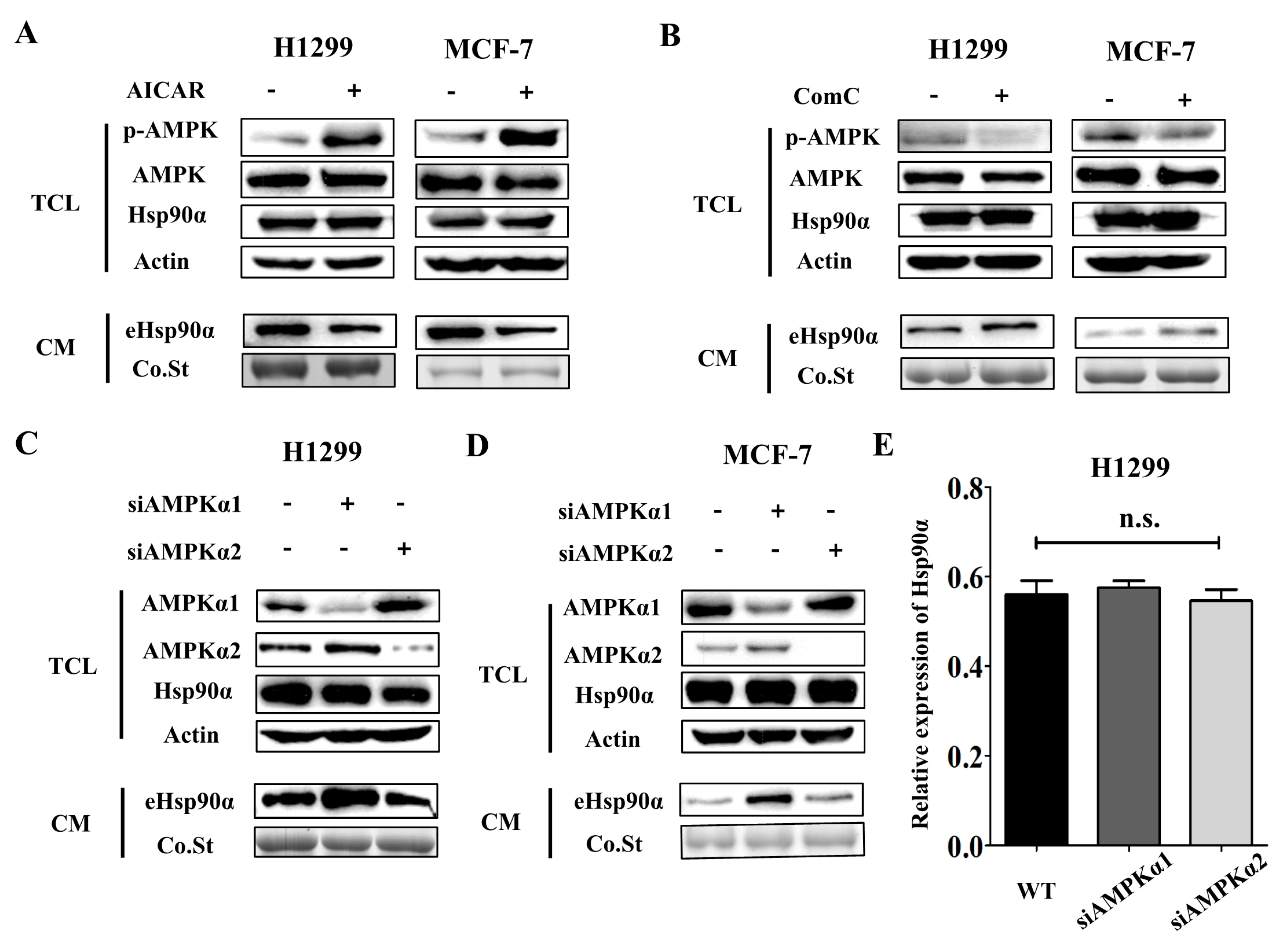
3.3. AMPKα1 but not AMPKα2 Mediates Hsp90α Secretion
3.4. Metformin Inhibits Hsp90α Secretion in an AMPKα1 Dependent Manner
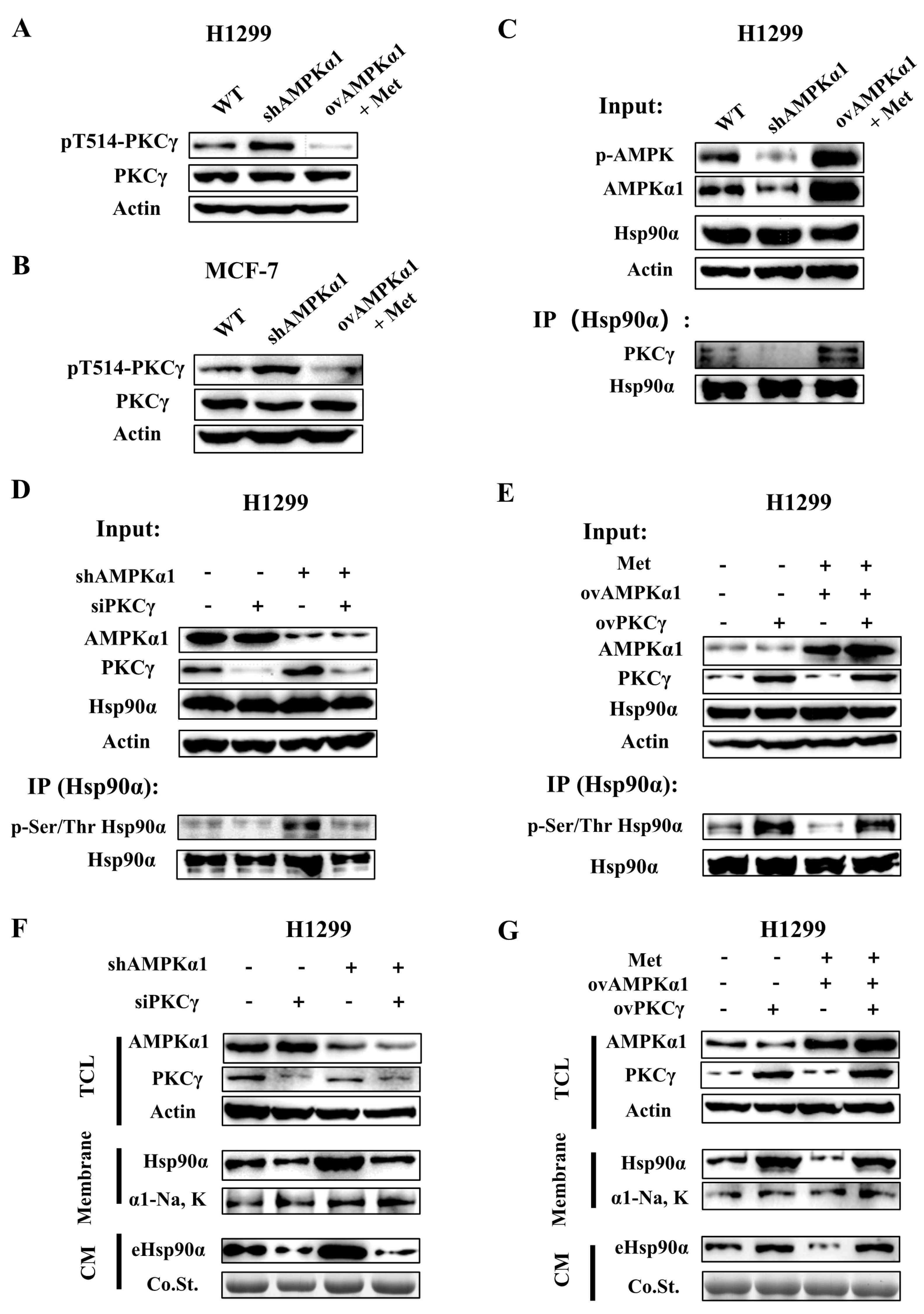
3.5. AMPKα1 Decreases the Phosphorylation Level of Hsp90α and Suppresses Hsp90α Membrane Translocation
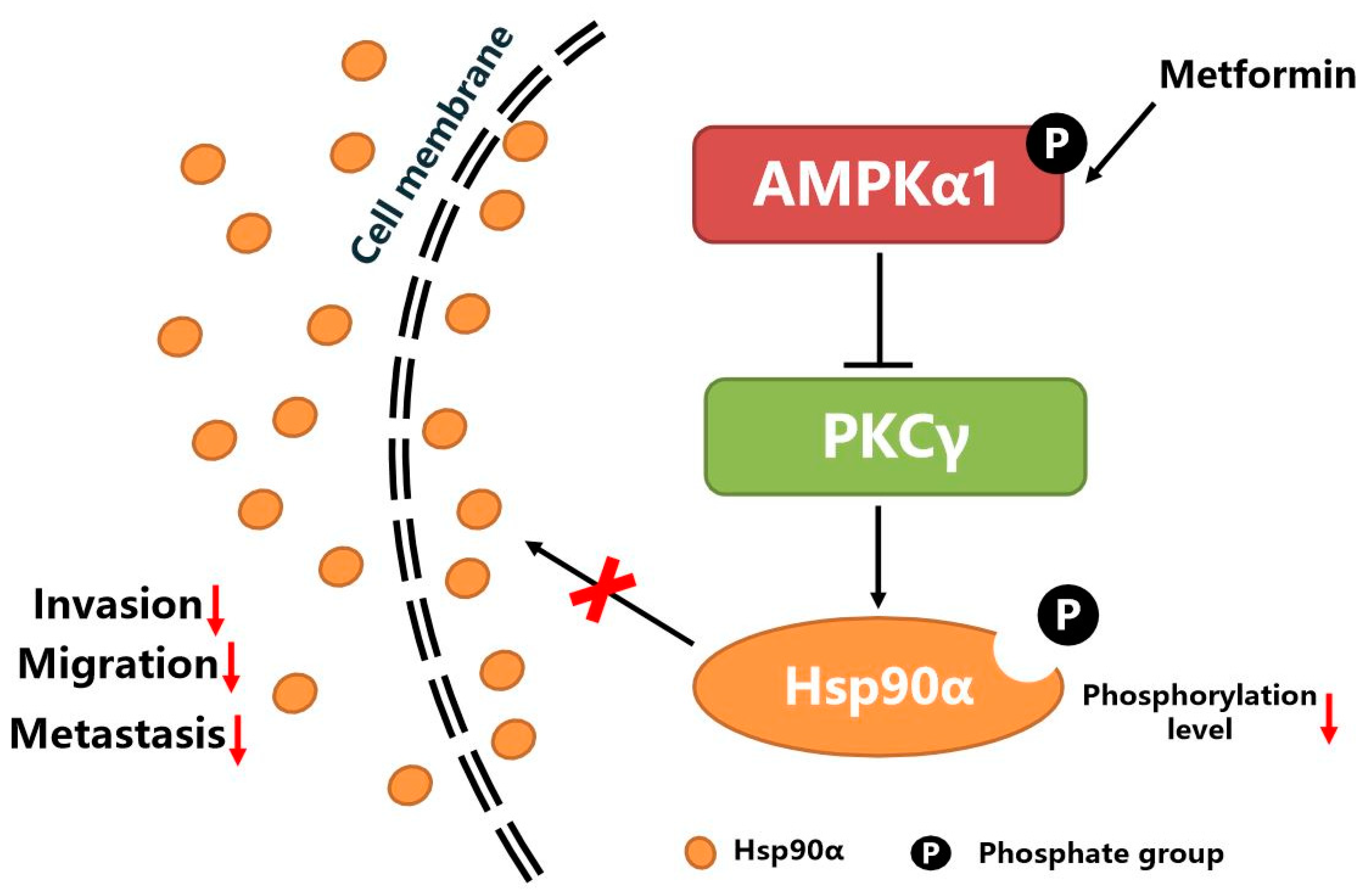
3.6. AMPKα1 Inhibits Hsp90α Phosphorylation, Membrane Translocation and Secretion by Suppressing the Kinase Activity of PKCγ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, J.M.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and Reduced Risk of Cancer in Diabetic Patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimova, I.N.; Liu, B.; Fan, Z.; Edgerton, S.M.; Dillon, T.; Lind, S.E.; Thor, A.D. Metformin Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth, Colony Formation and Induces Cell Cycle Arrest in Vitro. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakikhani, M.; Dowling, R.; Fantus, G.; Sonenberg, N.; Pollak, M. Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10269–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzai, M.; Jones, R.G.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Lum, J.J.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Zhao, F.; Viollet, B.; Thompson, C.B. Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6745–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Yang, L.; Liao, H.; Liang, X.; Xie, B.; Xiong, J.; Tao, X.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Metformin sensitizes endometrial cancer cells to chemotherapy through IDH1-induced Nrf2 expression via an epigenetic mechanism. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5666–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.-W.; Li, S.-C.; Tsai, K.-W. Metformin Treatment Suppresses Melanoma Cell Growth and Motility through Modulation of microRNA Expression. Cancers 2019, 11, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladini, S.; Aventaggiato, M.; Barreca, F.; Morgante, E.; Sansone, L.; Russo, M.A.; Tafani, M. Metformin Impairs Glutamine Metabolism and Autophagy in Tumour Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Kimura, F.; Yamanaka, A.; Takebayashi, A.; Kita, N.; Takahashi, K.; Murakami, T. Metformin impairs growth of endometrial cancer cells via cell cycle arrest and concomitant autophagy and apoptosis. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ke, C.; Tang, Q.; Dong, H.; Zheng, X.; Lin, W.; Ke, J.; Huang, J.; Yeung, S.-C.J.; Zhang, H. Metformin promotes autophagy and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by downregulating Stat3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cufí, S.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Joven, J.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin against TGFβ-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT): From cancer stem cells to aging-associated fibrosis. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 4461–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, R.; Xiao, H.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, K.; Chen, H.; Sun, F.; Yang, Z.; et al. Metformin Sensitizes EGFR-TKI-resistant Human Lung Cancer Cells in Vitro and in Vivo Through Inhibition of IL-6 Signaling and EMT Reversal. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2714–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, D.; Liu, Q.; Liu, G.; Xu, J.; Lan, W.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, J. Metformin Inhibits Castration-Induced EMT in Prostate Cancer by Repressing COX2/PGE2/STAT3 Axis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 389, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, T.; Nagata, Y.; Nishida, M.; Matsuo, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Yoneda, A.; Kanetaka, K.; Udono, H.; Eguchi, S. Metformin Prevents Peritoneal Dissemination via Immune-suppressive Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 4699–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, T.; Eikawa, S.; Nishida, M.; Kunisada, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Fujiwara, T.; Kunisada, T.; Ozaki, T.; Udono, H. Metformin induces CD11b+-cell-mediated growth inhibition of an osteosarcoma: Implications for metabolic reprogramming of myeloid cells and anti-tumor effects. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardie, D.G.; Ross, F.A.; Hawley, S.A. AMPK: A nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Towler, M.C.; Hardie, D.G. AMP-activated protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, D.B.; Shaw, R.J. The LKB1-AMPK pathway: Metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Ginanni, N.; Tota, M.R.; Wu, M.; Bays, N.W.; Richon, V.M.; Kohl, N.E.; Bachman, E.S.; Strack, P.R.; Krauss, S. Control of cell growth and survival by enzymes of the fatty acid synthesis pathway in HCT-116 colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5735–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Miyoshi, H.; Clevers, H.C.; Oshima, M.; Aoki, M.; Taketo, M.M. Suppression of tubulin polymerization by the LKB1-microtubule-associated protein/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase signaling. J. Biol Chem 2007, 282, 23532–23540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Hsu, E.C.; Guh, J.H.; Yang, H.C.; Wang, D.; Kulp, S.K.; Shapiro, C.L.; Chen, C.S. Targeting energy metabolic and oncogenic signaling pathways in triple-negative breast cancer by a novel adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator. J. Biol Chem 2011, 286, 39247–39258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadra, G.; Photopoulos, C.; Tyekucheva, S.; Heidari, P.; Weng, Q.P.; Fedele, G.; Liu, H.; Scaglia, N.; Priolo, C.; Sicinska, E.; et al. A novel direct activator of AMPK inhibits prostate cancer growth by blocking lipogenesis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 519–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Dong, W.; Qu, X.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Q.; Du, J. Metformin Enhances the Therapy Effects of Anti-IGF-1R mAb Figitumumab to NSCLC. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyàs, E.; Martin-Castillo, B.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Menendez, J.A. Metformin inhibits RANKL and sensitizes cancer stem cells to denosumab. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Hotta, K.; Kozuki, T.; Toyooka, S.; Okada, H.; Fujiwara, T.; Udono, H.; Kiura, K. Study Protocol: Phase-Ib Trial of Nivolumab Combined with Metformin for Refractory/Recurrent Solid Tumors. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e861–e864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Roybal, J.; Chaerkady, R.; Zhang, W.; Choi, K.; Alvarez, C.A.; Tran, H.; Creighton, C.J.; Yan, S.; Strieter, R.M.; et al. Identification of secreted proteins that mediate cell-cell interactions in an in vitro model of the lung cancer microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7237–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caccia, D.; Domingues, L.Z.; Miccichè, F.; Bortoli, M.D.; Carniti, C.; Mondellini, P.; Bongarzone, I. Secretome compartment is a valuable source of biomarkers for cancer-relevant pathways. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 4196–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Sahu, D.; Tsen, F. Secreted Heat Shock Protein-90 (Hsp90) in Wound Healing and Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesell, L.; Lindquist, S.L. HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepel, J.; Mollapour, M.; Giaccone, G.; Neckers, L. Targeting the dynamic HSP90 complex in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Piel, W.H.; Gui, L.; Bruford, E.; Monteiro, A. The HSP90 family of genes in the human genome: Insights into their divergence and evolution. Genomics 2005, 86, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard, D. Hsp90 invades the outside. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustace, B.K.; Sakurai, T.; Stewart, J.K.; Yimlamai, D.; Unger, C.; Zehetmeier, C.; Lain, B.; Torella, C.; Henning, S.W.; Beste, G.; et al. Functional proteomic screens reveal an essential extracellular role for hsp90 alpha in cancer cell invasiveness. Nat. Cell Biol 2004, 6, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Hou, Q.; Feng, S.; Liu, L.; Cui, D.; Shi, H.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Y. A novel pan-cancer biomarker plasma heat shock protein 90alpha and its diagnosis determinants in clinic. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2941–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, D.; Cui, D.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; He, Z.; Liu, J.; Zheng, S.; Luo, Y. Plasma Heat Shock Protein 90alpha as a Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Liver Cancer: An Official, Large-scale, and Multicenter Clinical Trial. EBioMedicine 2017, 24, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.S.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, L.L.; Lee, C.C.; Huang, T.S. Secreted heat shock protein 90α (HSP90α) induces nuclear factor-κB-mediated TCF12 protein expression to down-regulate E-cadherin and to enhance colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9001–9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCready, J.; Sims, J.D.; Chan, D.; Jay, D.G. Secretion of extracellular hsp90α via exosomes increases cancer cell motility: A role for plasminogen activation. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.S.; Hsu, Y.M.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, L.L.; Lee, C.C.; Huang, T.S. Secreted heat shock protein 90alpha induces colorectal cancer cell invasion through CD91/LRP-1 and NF-kappaB-mediated integrin alphaV expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 25458–25466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.F.; Fan, J.; Fedesco, M.; Guan, S.; Li, Y.; Bandyopadhyay, B.; Bright, A.M.; Yerushalmi, D.; Liang, M.; Chen, M.; et al. Transforming growth factor alpha (TGF alpha)-stimulated secretion of HSP90 alpha: Using the receptor LRF-1/CD91 to promote human skin cell migration against a TGF beta-rich environment during wound healing. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 3344–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsen, F.; Bhatia, A.; O’Brien, K.; Cheng, C.F.; Chen, M.; Hay, N.; Stiles, B.; Woodley, D.T.; Li, W. Extracellular heat shock protein 90 signals through subdomain II and the NPVY motif of LRP-1 receptor to Akt1 and Akt2: A circuit essential for promoting skin cell migration in vitro and wound healing in vivo. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 4947–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, X.; Zhuo, W.; Shi, H.; Feng, D.; Sun, Y.; Liang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Luo, Y. The regulatory mechanism of extracellular Hsp90{alpha} on matrix metalloproteinase-2 processing and tumor angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 40039–40049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCready, J.; Wong, D.S.; Burlison, J.A.; Ying, W.; Jay, D.G. An Impermeant Ganetespib Analog Inhibits Extracellular Hsp90-Mediated Cancer Cell Migration That Involves Lysyl Oxidase 2-like Protein. Cancers 2014, 6, 1031–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, S.; Scroggins, B.; Koga, F.; Lee, M.J.; Trepel, J.; Felts, S.; Carreras, C.; Neckers, L. A small molecule cell-impermeant Hsp90 antagonist inhibits tumor cell motility and invasion. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2478–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Wondisford, F.E. Metformin action: Concentrations matter. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Rodrigues, G.A. Differential roles of AMPKα1 and AMPKα2 in regulating 4-HNE-induced RPE cell death and permeability. Exp. Eye. Res. 2010, 91, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Zarrinpashneh, E.; Budas, G.R.; Pouleur, A.C.; Dutta, A.; Prescott, A.R.; Vanoverschelde, J.L.; Ashworth, A.; Jovanović, A.; Alessi, D.R. Deficiency of LKB1 in heart prevents ischemia-mediated activation of AMPKalpha2 but not AMPKalpha1. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E780–E788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, X.; Zhuo, W.; Fu, Y.; Shi, H.; Liang, Y.; Tong, M.; Chang, G.; Luo, Y. The regulatory mechanism of Hsp90alpha secretion and its function in tumor malignancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21288–21293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, X.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Y. PLCγ1-PKCγ signaling-mediated Hsp90α plasma membrane translocation facilitates tumor metastasis. Traffic 2014, 15, 861–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhuo, W.; Jia, L.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Y. The regulatory mechanism of a client kinase controlling its own release from Hsp90 chaperone machinery through phosphorylation. Biochem. J. 2014, 457, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.A.; Zohn, I.E. Hectd1 regulates intracellular localization and secretion of Hsp90 to control cellular behavior of the cranial mesenchyme. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.S.; Liu, J.J.; Yu, X.J.; Lu, Y.; Zang, W.J. Protection against ischemia-induced oxidative stress conferred by vagal stimulation in the rat heart: Involvement of the AMPK-PKC pathway. Int J. Mol Sci 2012, 13, 14311–14325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djouder, N.; Tuerk, R.D.; Suter, M.; Salvioni, P.; Thali, R.F.; Scholz, R.; Vaahtomeri, K.; Auchli, Y.; Rechsteiner, H.; Brunisholz, R.A.; et al. PKA phosphorylates and inactivates AMPKalpha to promote efficient lipolysis. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochly-Rosen, D.; Das, K.; Grimes, K.V. Protein kinase C, an elusive therapeutic target? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 937–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Reineke, L.C.; Knutsen, E.; Chen, M.; Pichler, M.; Ling, H.; Calin, G.A. Metformin Blocks MYC Protein Synthesis in Colorectal Cancer via mTOR-4EBP-eIF4E and MNK1-eIF4G-eIF4E Signaling. Mol. Oncol 2018, 12, 1856–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charni-Natan, M.; Solomon, H.; Molchadsky, A.; Jacob-Berger, A.; Goldfinger, N.; Rotter, V. Various Stress Stimuli Rewire the Profile of Liver Secretome in a p53-dependent Manner. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, R.J.O.; Zakikhani, M.; Fantus, I.G.; Pollak, M.; Sonenberg, N. Metformin Inhibits Mammalian Target of Rapamycin-Dependent Translation Initiation in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10804–10812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yi, Y.; Guo, Q.; Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Xiao, S.; Geng, J.; Zheng, Z.; Song, S. Hsp90 Interacts with AMPK and Mediates acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Phosphorylation. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, H.B.; Jin, Y.; Lee, J.K. Ethyl Pyruvate Inhibits HMGB1 Phosphorylation and Secretion in Activated Microglia and in the Postischemic Brain. Neurosci Lett. 2014, 558, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.B.; Gorczynski, R.; Huang, C.K.; Love, J.; Mills, G.B. Tyrosine Phosphorylation Is an Obligatory Event in IL-2 Secretion. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar]
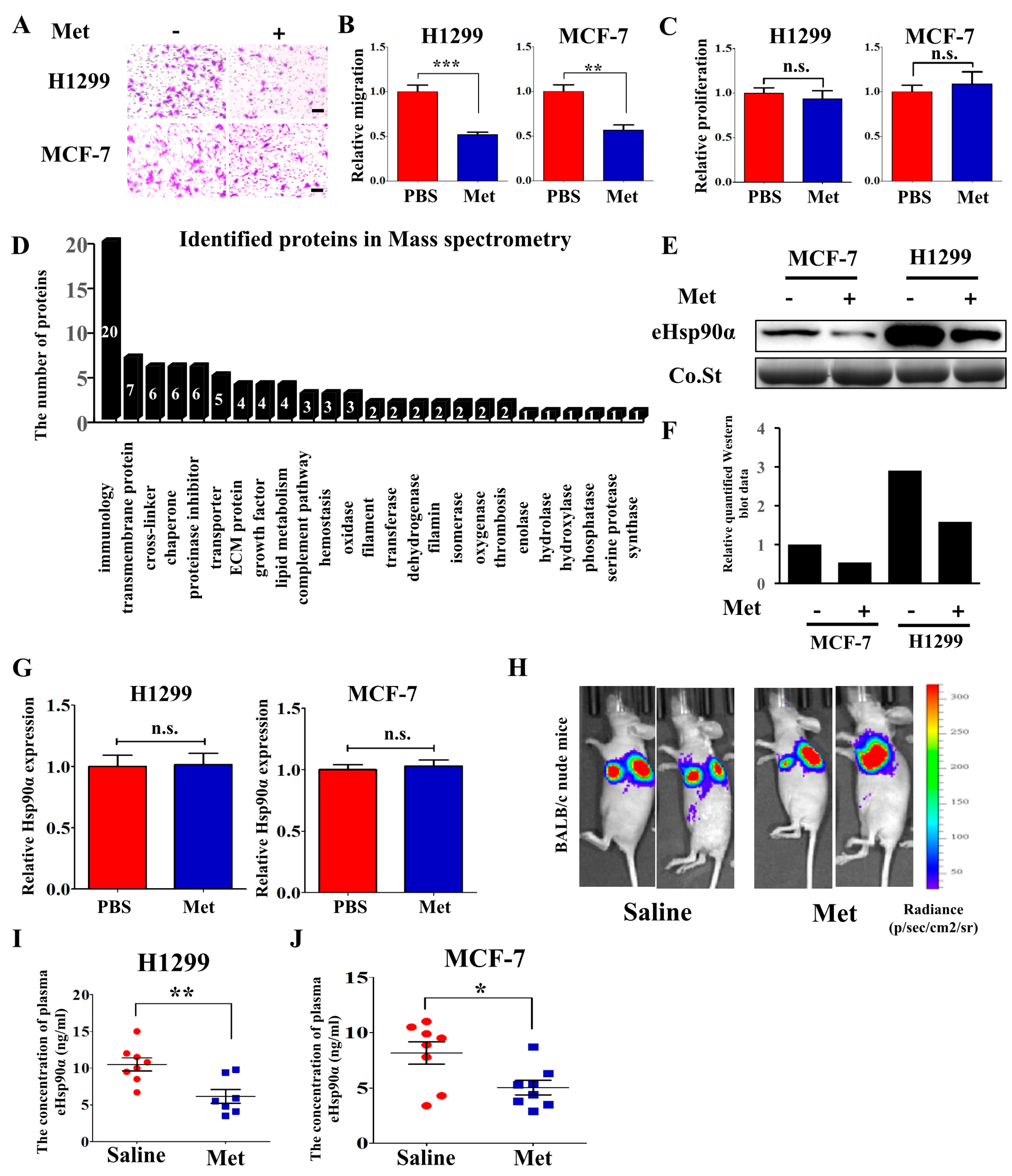

| Protein Name | Score | Coverage | Peptides | Change | Functions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | Met | Ctrl | Met | Ctrl | Met | Ctrl/Met | ||
| THBS1 | 223.84 | 161.90 | 15.04 | 12.65 | 16 | 13 | 3.52 | Promoting platelet aggregation, angiogenesis and tumorigenesis |
| Hsp90α | 875.14 | 908.54 | 39.07 | 38.25 | 43 | 39 | 3.24 | Promoting tumor cells migration, invasion and metastasis |
| CYR61 | 158.90 | 128.75 | 33.07 | 32.81 | 12 | 11 | 2.33 | Extracellular matrix-associated protein, regulating cell adhesion, migration and proliferation |
| TIMP1 | 612.70 | 556.36 | 62.32 | 62.32 | 10 | 10 | 2.28 | An inhibitor of the matrix metalloproteinases, promoting cell proliferation and wound healing |
| 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | 353.79 | 332.20 | 72.65 | 72.65 | 23 | 23 | 2.11 | Promoting lung tumor and breast tumor metastasis |
| LOXL2 | 120.47 | 100.85 | 21.83 | 17.44 | 15 | 11 | 2.08 | Formation of crosslinks in collagens and elastin, promoting tumor metastasis and lymphatic metastasis |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Y.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Feng, S.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Y. Metformin Inhibits Tumor Metastasis through Suppressing Hsp90α Secretion in an AMPKα1-PKCγ Dependent Manner. Cells 2020, 9, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010144
Gong Y, Wang C, Jiang Y, Zhang S, Feng S, Fu Y, Luo Y. Metformin Inhibits Tumor Metastasis through Suppressing Hsp90α Secretion in an AMPKα1-PKCγ Dependent Manner. Cells. 2020; 9(1):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010144
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Yuanchao, Caihong Wang, Yi Jiang, Shaosen Zhang, Shi Feng, Yan Fu, and Yongzhang Luo. 2020. "Metformin Inhibits Tumor Metastasis through Suppressing Hsp90α Secretion in an AMPKα1-PKCγ Dependent Manner" Cells 9, no. 1: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010144
APA StyleGong, Y., Wang, C., Jiang, Y., Zhang, S., Feng, S., Fu, Y., & Luo, Y. (2020). Metformin Inhibits Tumor Metastasis through Suppressing Hsp90α Secretion in an AMPKα1-PKCγ Dependent Manner. Cells, 9(1), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010144