PlexinB1 Promotes Nuclear Translocation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Antibodies
2.3. Plasmids
2.4. Immunocytochemistry: Endogenous GR and AR localization
2.5. GR Localization following Knockdown of PlexinB1 Expression
2.6. GR-GFP Subcellular Localization
2.7. Subcellular Protein Fractionation
2.8. siRNA
2.9. Cell Motility
2.10. Cell Area Measurement
3. Results
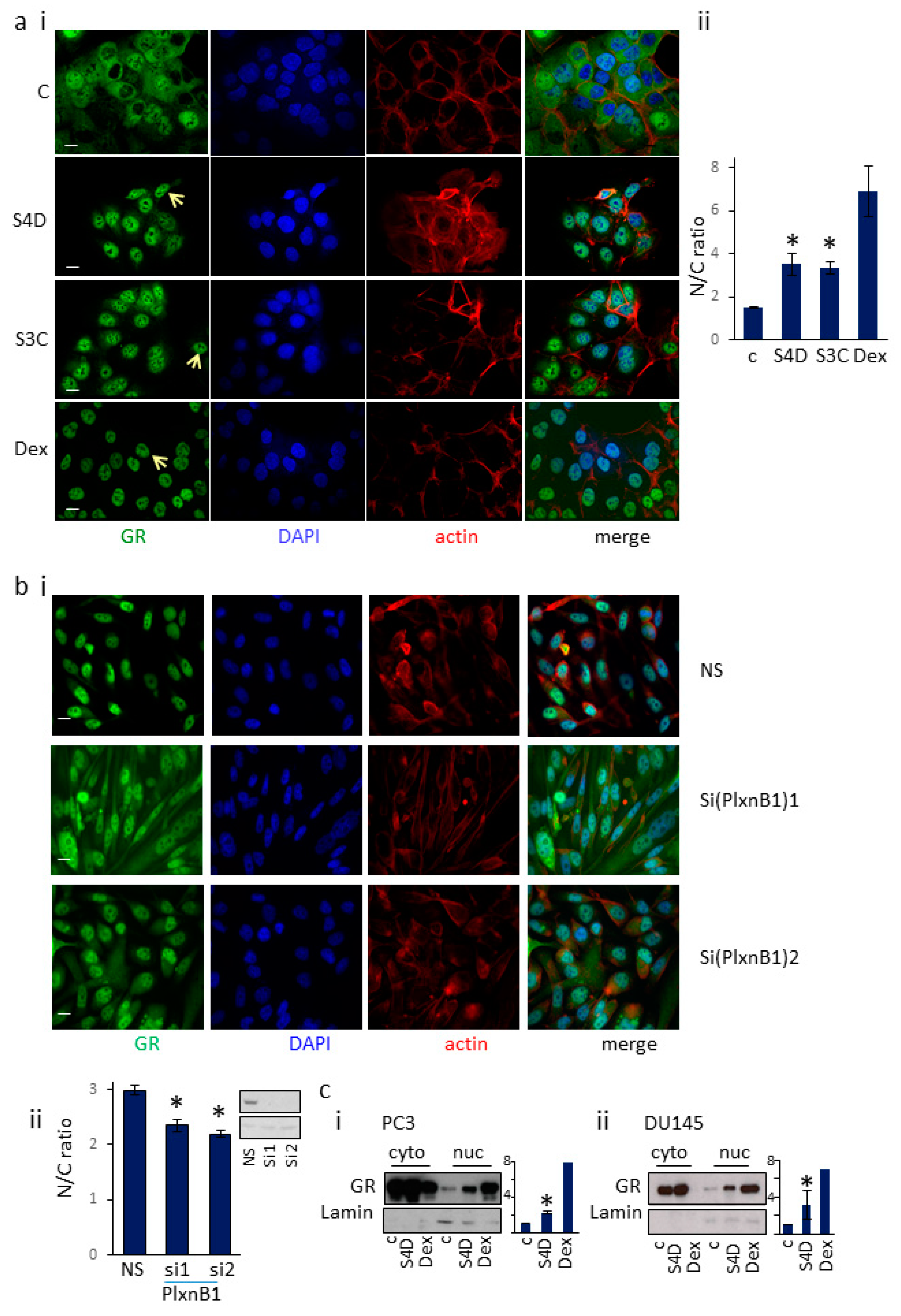
3.1. Sema4D/Sema3C-PlexinB1 Signaling Increases the Levels of Endogenous Glucocorticoid Receptor in the Nucleus
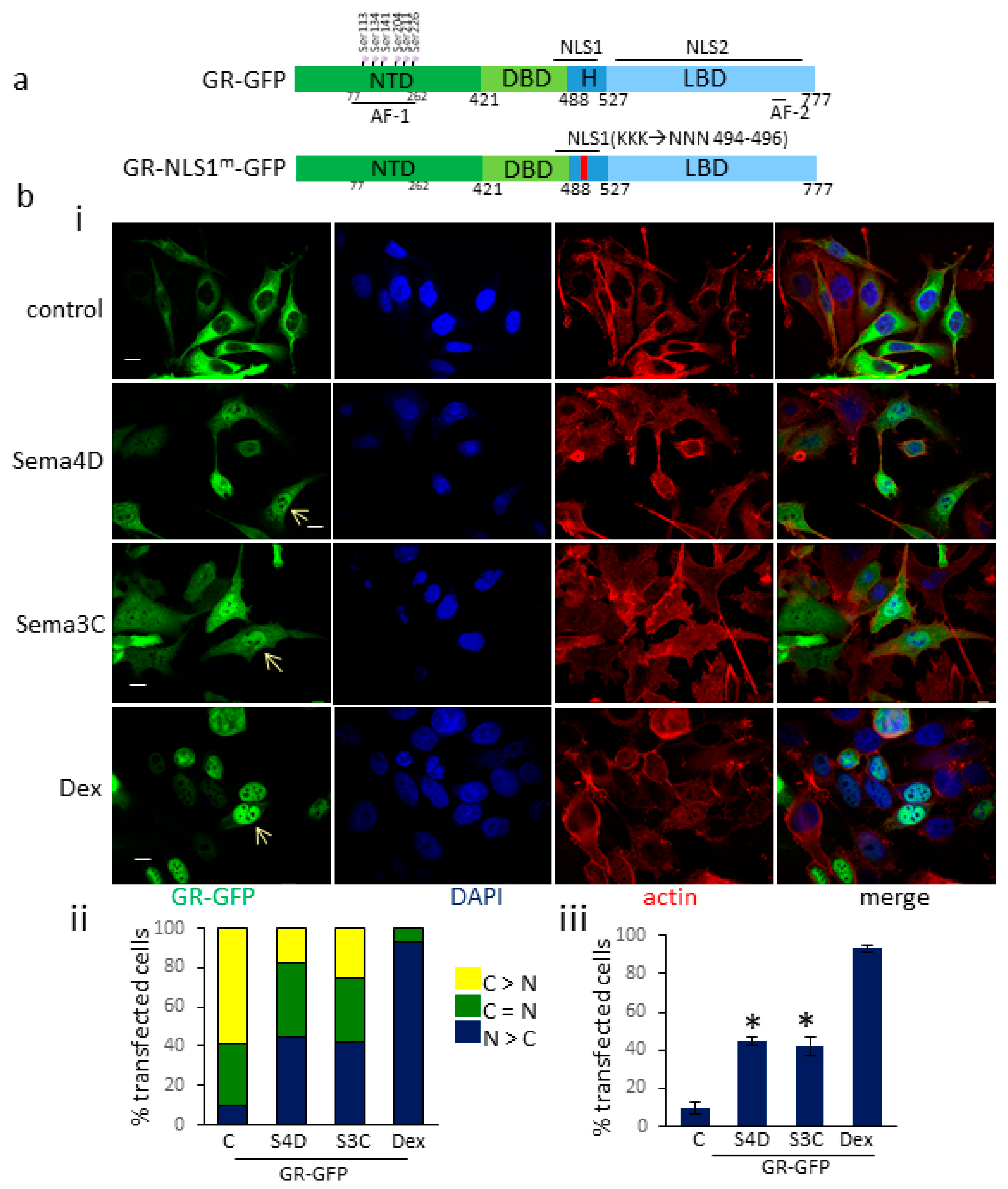
3.2. Sema4D/Sema3C Promotes the Translocation of GR-GFP to the Nucleus
3.3. Sema4D/Sema3C-Induced Translocation of GR-GFP to the Nucleus Requires an Intact NLS1 Site
3.4. PlexinB1 Affects Protein Levels of Glucocorticoid-Responsive Genes
3.5. GR Regulates PlexinB1 Protein Levels
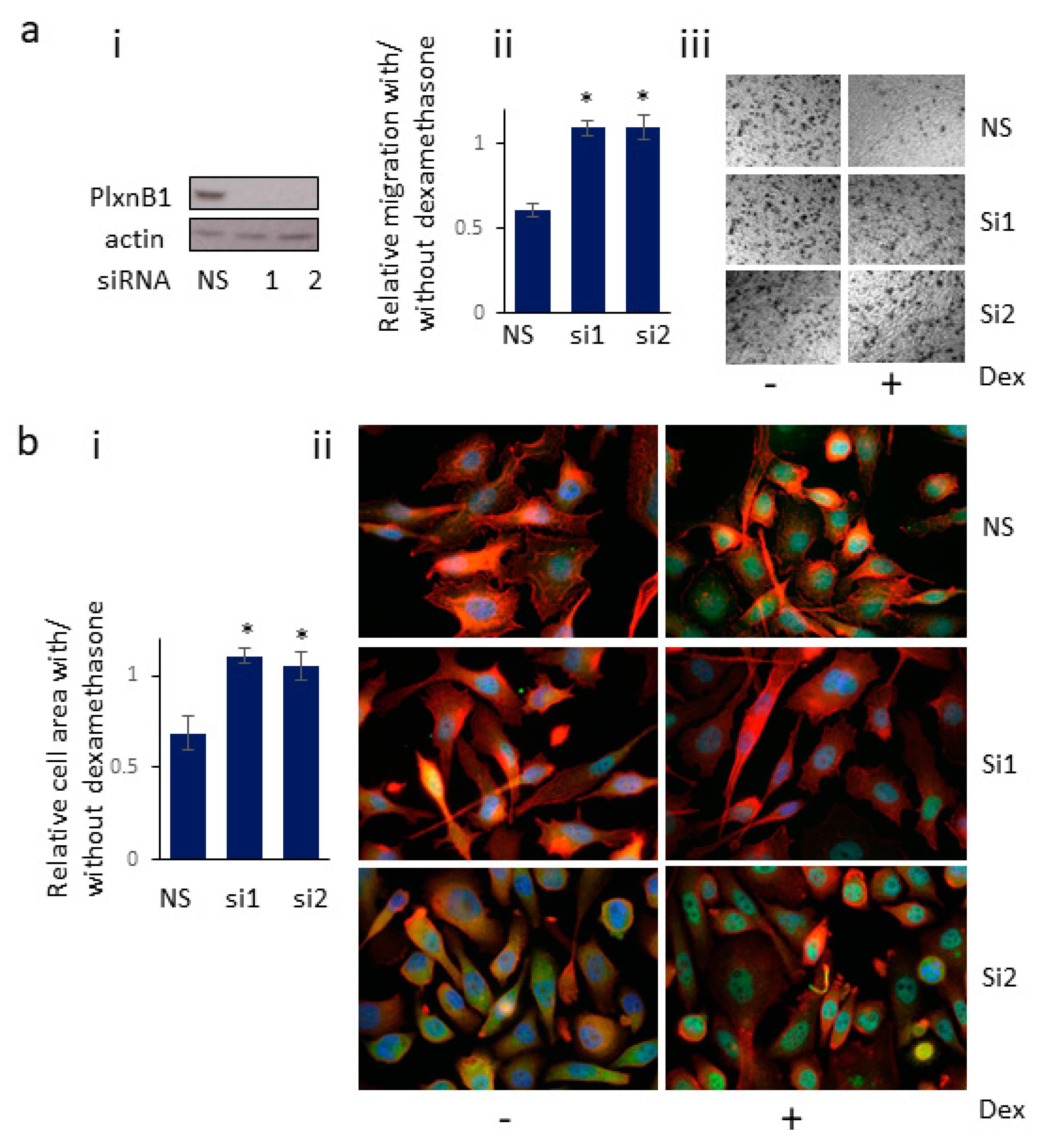
3.6. Knockdown of PlexinB1 Expression Antagonizes the Reduction in Cell Migration Induced by Dexamethasone
3.7. Knockdown of PlexinB1 Expression Antagonizes the Dexamethasone-Induced Reduction in Cell Area
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wadosky, K.M.; Koochekpour, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying resistance to androgen deprivation therapy in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64447–64470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.K.; Sawyers, C.L. Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, V.K.; Schenkein, E.; Murali, R.; Subudhi, S.K.; Wongvipat, J.; Balbas, M.D.; Shah, N.; Cai, L.; Efstathiou, E.; Logothetis, C.; et al. Glucocorticoid receptor confers resistance to antiandrogens by bypassing androgen receptor blockade. Cell 2013, 155, 1309–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puhr, M.; Hoefer, J.; Eigentler, A.; Ploner, C.; Handle, F.; Schaefer, G.; Kroon, J.; Leo, A.; Heidegger, I.; Eder, I.; et al. The Glucocorticoid Receptor Is a Key Player for Prostate Cancer Cell Survival and a Target for Improved Antiandrogen Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isikbay, M.; Otto, K.; Kregel, S.; Kach, J.; Cai, Y.; Vander Griend, D.J.; Conzen, S.D.; Szmulewitz, R.Z. Glucocorticoid receptor activity contributes to resistance to androgen-targeted therapy in prostate cancer. Horm Cancer 2014, 5, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weikum, E.R.; Knuesel, M.T.; Ortlund, E.A.; Yamamoto, K.R. Glucocorticoid receptor control of transcription: Precision and plasticity via allostery. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Ouk, S.; Clegg, N.J.; Chen, Y.; Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.; Wongvipat, J.; Smith-Jones, P.M.; Yoo, D.; Kwon, A.; et al. Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science 2009, 324, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, S.; Srinivas, S.; Feldman, D. Androgen-glucocorticoid interactions in the era of novel prostate cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2016, 13, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiercz, J.M.; Kuner, R.; Offermanns, S. Plexin-B1/RhoGEF-mediated RhoA activation involves the receptor tyrosine kinase ErbB-2. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, J.W.; Takeuchi, A.; Hayashi, N.; Liu, L.; Tam, K.J.; Al Nakouzi, N.; Khazamipour, N.; Tombe, T.; Dejima, T.; Lee, K.C.; et al. SEMA3C drives cancer growth by transactivating multiple receptor tyrosine kinases via Plexin B1. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, S.; Corso, S.; Conrotto, P.; Artigiani, S.; Gilestro, G.; Barberis, D.; Tamagnone, L.; Comoglio, P.M. The semaphorin 4D receptor controls invasive growth by coupling with Met. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, K.J.; Hui, D.H.F.; Lee, W.W.; Dong, M.; Tombe, T.; Jiao, I.Z.F.; Khosravi, S.; Takeuchi, A.; Peacock, J.W.; Ivanova, L.; et al. Semaphorin 3 C drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, invasiveness, and stem-like characteristics in prostate cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damola, A.; Legendre, A.; Ball, S.; Masters, J.R.; Williamson, M. Function of mutant and wild-type plexinb1 in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2013, 73, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiercz, J.M.; Kuner, R.; Behrens, J.; Offermanns, S. Plexin-B1 directly interacts with PDZ-RhoGEF/LARG to regulate RhoA and growth cone morphology. Neuron 2002, 35, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oinuma, I.; Ishikawa, Y.; Katoh, H.; Negishi, M. The Semaphorin 4D receptor Plexin-B1 is a GTPase activating protein for R-Ras. Science 2004, 305, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pascoe, H.G.; Brautigam, C.A.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Structural basis for activation and non-canonical catalysis of the Rap GTPase activating protein domain of plexin. Elife 2013, 2, e01279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worzfeld, T.; Offermanns, S. Semaphorins and plexins as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worzfeld, T.; Swiercz, J.M.; Looso, M.; Straub, B.K.; Sivaraj, K.K.; Offermanns, S. ErbB-2 signals through Plexin-B1 to promote breast cancer metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, G.; Nicotra, G.; Arrondini, M.; Castino, R.; Capparuccia, L.; Prat, M.; Kerim, S.; Tamagnone, L.; Isidoro, C. Co-expression of plexin-B1 and Met in human breast and ovary tumours enhances the risk of progression. Cell. Oncol. 2009, 31, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Hao, X.; Zhou, T.; Wu, M.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, X.; Ji, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Plexin-B1 silencing inhibits ovarian cancer cell migration and invasion. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Man, J.; Shoemake, J.; Zhou, W.; Fang, X.; Wu, Q.; Rizzo, A.; Prayson, R.; Bao, S.; Rich, J.N.; Yu, J.S. Sema3C promotes the survival and tumorigenicity of glioma stem cells through Rac1 activation. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1812–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, L.; McClelland, L.; Fricke, A.; Williamson, M.; Kuo, I.; Scott, G. Plexin B1 suppresses c-Met in melanoma: A role for plexin B1 as a tumor-suppressor protein through regulation of c-Met. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, O.G.; Nitkunan, T.; Oinuma, I.; Zhou, C.; Blanc, V.; Brown, R.S.; Bott, S.R.; Nariculam, J.; Box, G.; Munson, P.; et al. Plexin-B1 mutations in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19040–19045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanc, V.; Nariculam, J.; Munson, P.; Freeman, A.; Klocker, H.; Masters, J.; Williamson, M. A role for class 3 semaphorins in prostate cancer. Prostate 2011, 71, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.A.; Prueitt, R.L.; Yi, M.; Howe, T.M.; Gillespie, J.W.; Yfantis, H.G.; Stephens, R.M.; Caporaso, N.E.; Loffredo, C.A.; Ambs, S. Tumor immunobiological differences in prostate cancer between African-American and European-American men. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapointe, J.; Li, C.; Higgins, J.P.; van de Rijn, M.; Bair, E.; Montgomery, K.; Ferrari, M.; Egevad, L.; Rayford, W.; Bergerheim, U.; et al. Gene expression profiling identifies clinically relevant subtypes of prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magee, J.A.; Araki, T.; Patil, S.; Ehrig, T.; True, L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Catalona, W.J.; Watson, M.A.; Milbrandt, J. Expression profiling reveals hepsin overexpression in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5692–5696. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Chen, M.K.; Li, L.Y.; Lu, M.H.; Shao Ch, K.; Su, Z.L.; He, D.; Pang, J.; Gao, X. The predictive value of semaphorins 3 expression in biopsies for biochemical recurrence of patients with low- and intermediate-risk prostate cancer. Neoplasma 2013, 60, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williamson, M.; de Winter, P.; Masters, J.R. Plexin-B1 signalling promotes androgen receptor translocation to the nucleus. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandevyver, S.; Dejager, L.; Libert, C. On the trail of the glucocorticoid receptor: into the nucleus and back. Traffic 2012, 13, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savory, J.G.; Hsu, B.; Laquian, I.R.; Giffin, W.; Reich, T.; Hache, R.J.; Lefebvre, Y.A. Discrimination between NL1- and NL2-mediated nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermeer, H.; Hendriks-Stegeman, B.I.; van der Burg, B.; van Buul-Offers, S.C.; Jansen, M. Glucocorticoid-induced increase in lymphocytic FKBP51 messenger ribonucleic acid expression: A potential marker for glucocorticoid sensitivity, potency, and bioavailability. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayroldi, E.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper (GILZ): A new important mediator of glucocorticoid action. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3649–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desmet, S.J.; Bougarne, N.; Van Moortel, L.; De Cauwer, L.; Thommis, J.; Vuylsteke, M.; Ratman, D.; Houtman, R.; Tavernier, J.; De Bosscher, K. Compound A influences gene regulation of the Dexamethasone-activated glucocorticoid receptor by alternative cofactor recruitment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Ligand-induced repression of the glucocorticoid receptor gene is mediated by an NCoR1 repression complex formed by long-range chromatin interactions with intragenic glucocorticoid response elements. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Ma, K.; Xia, H.M.; Chen, Q.K.; Li, L.; Deng, J.; Sheng, J.; Hong, Y.Y.; Hu, J.P. Androgen receptor reverts dexamethasoneinduced inhibition of prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5887–5893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.H.; Zhou, H.; Binmadi, N.O.; Proia, P.; Basile, J.R. Plexin-B1 activates NF-kappaB and IL-8 to promote a pro-angiogenic response in endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K.J.; Dalal, K.; Hsing, M.; Cheng, C.W.; Khosravi, S.; Yenki, P.; Tse, C.; Peacock, J.W.; Sharma, A.; Chiang, Y.T.; et al. Androgen receptor transcriptionally regulates semaphorin 3C in a GATA2-dependent manner. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 9617–9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.D.; Welsbie, D.S.; Tran, C.; Baek, S.H.; Chen, R.; Vessella, R.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Sawyers, C.L. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williamson, M.; Garg, R.; Wells, C.M. PlexinB1 Promotes Nuclear Translocation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Cells 2020, 9, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010003
Williamson M, Garg R, Wells CM. PlexinB1 Promotes Nuclear Translocation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Cells. 2020; 9(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliamson, Magali, Ritu Garg, and Claire M. Wells. 2020. "PlexinB1 Promotes Nuclear Translocation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor" Cells 9, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010003
APA StyleWilliamson, M., Garg, R., & Wells, C. M. (2020). PlexinB1 Promotes Nuclear Translocation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Cells, 9(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010003



