Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-1 (p55) Deficiency Attenuates Tumor Growth and Intratumoral Angiogenesis and Stimulates CD8+ T Cell Function in Melanoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Mice
2.4. Mouse Melanoma Model
2.5. Preparation of Conditioned Medium
2.6. Cell Migration
2.7. Histological Procedure
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Indirect Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.11. Measurement of Cellular Melanin Content
2.12. Gelatin Zymography
2.13. Measurements of VEGF, IL-10 and IL-12
2.14. Analysis of Immune Cell Infiltration by Flow Cytometry
2.15. Functional Analysis of CD8+ T Cell Activation
2.16. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
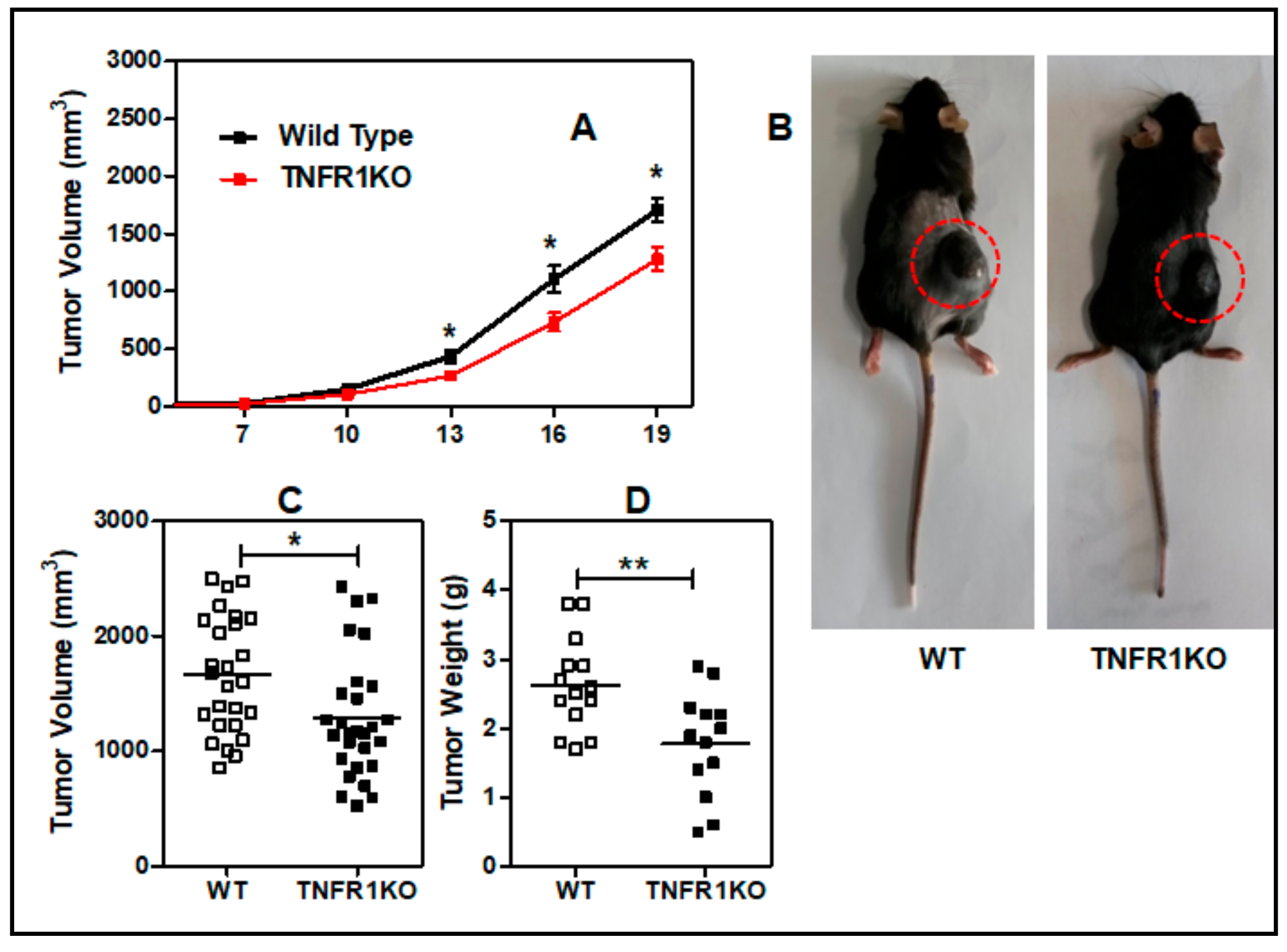
3.1. Lack of TNFR p55 Signaling Delays Tumor Growth
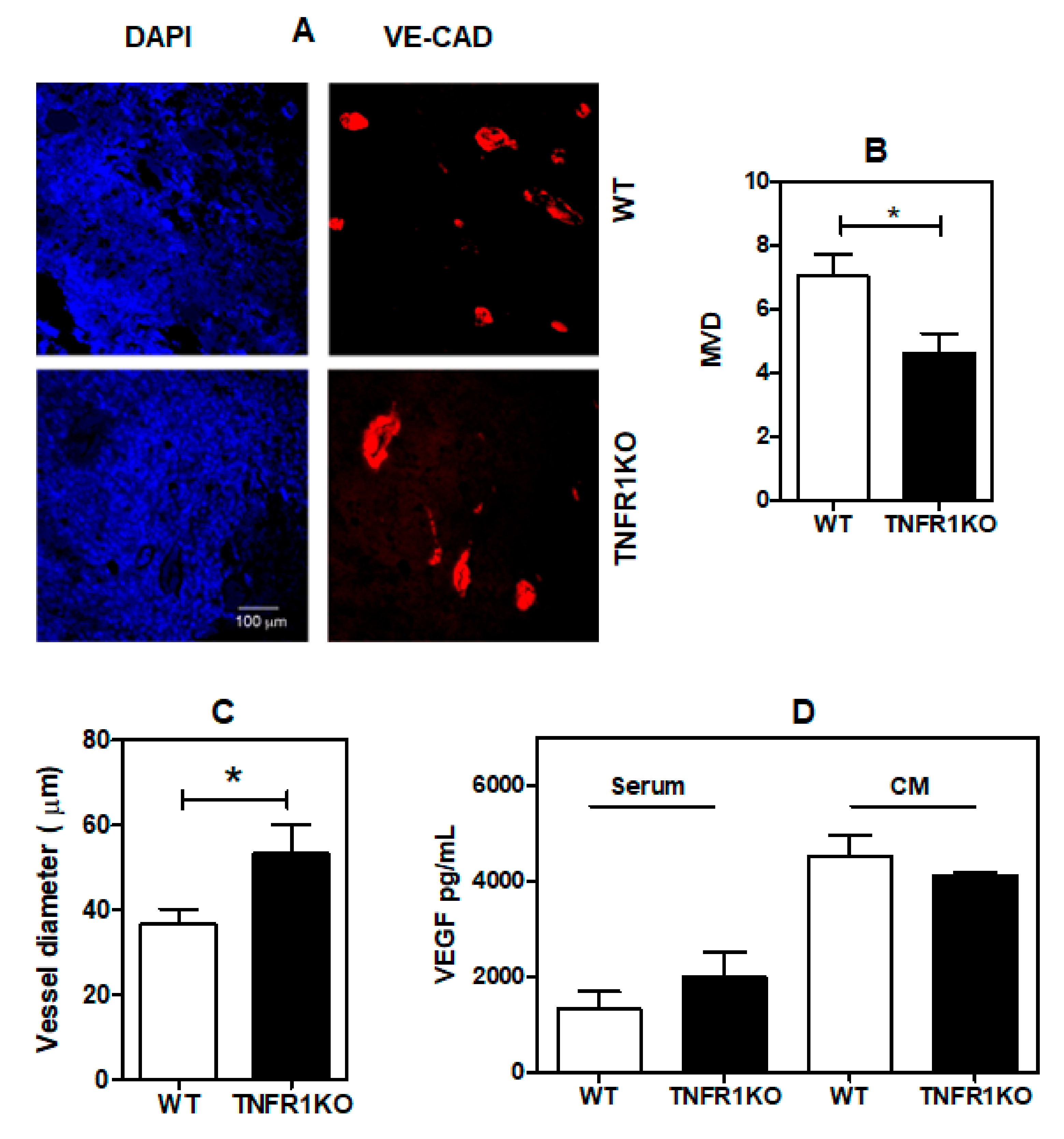
3.2. TNFR1 Deficiency Leads to Impaired Tumor Angiogenesis
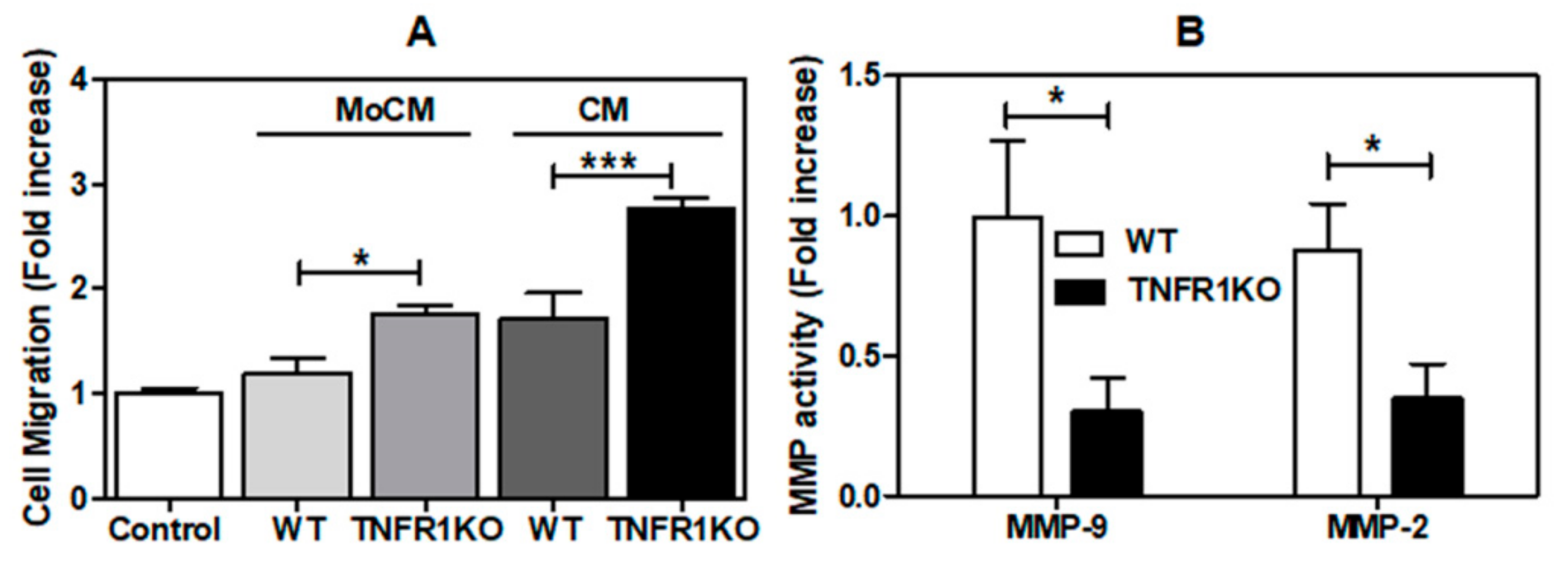
3.3. Impact of Melanoma Conditioned Media from TNFR1 KO Mice in B16.F1 Melanoma Cell Migration
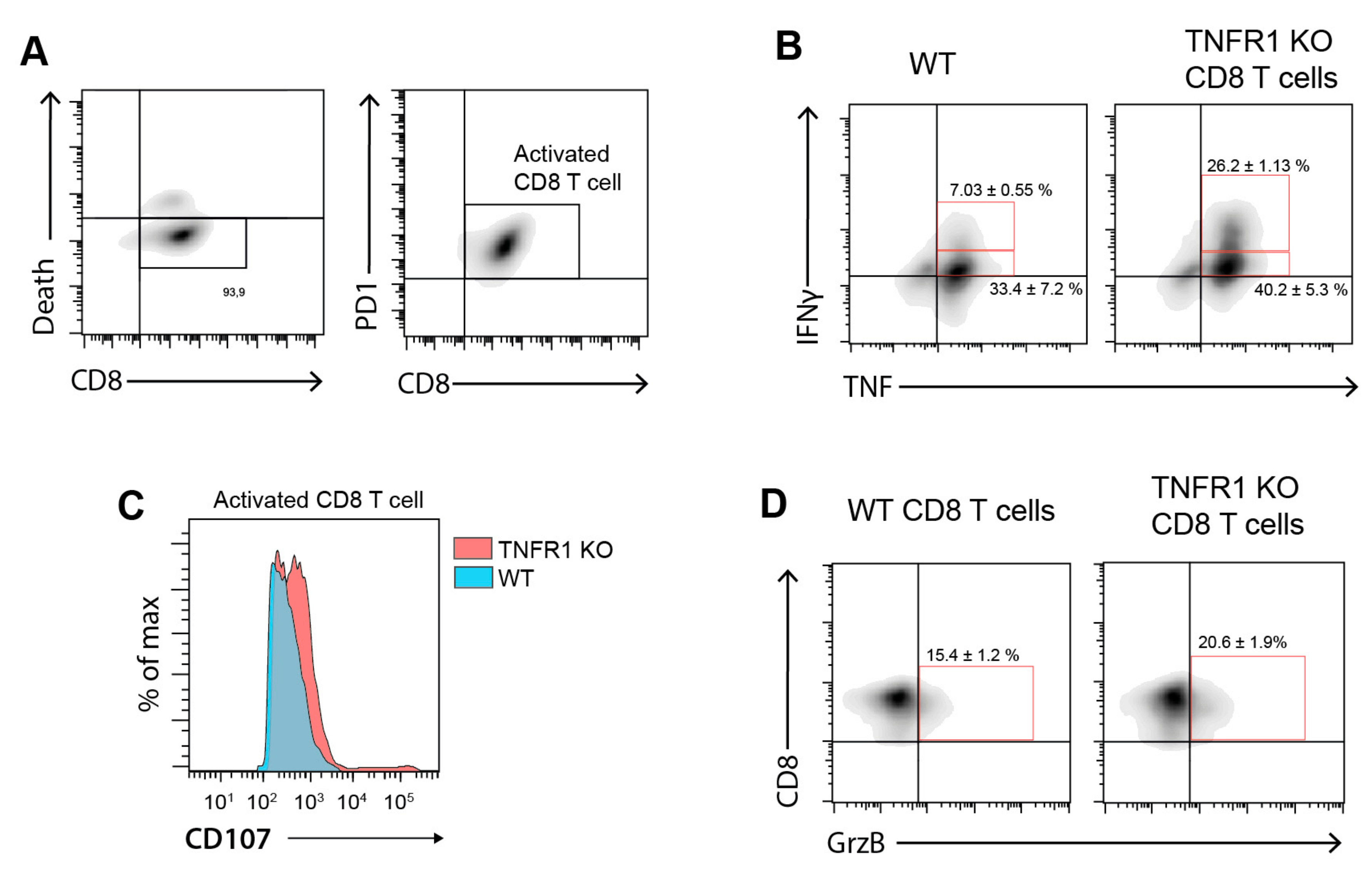
3.4. Tumor-Bearing Mice Lacking TNFR1 KO Display Higher CD8+ T Cell Infiltration
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carswell, E.A.; Old, L.J.; Kassel, R.L.; Green, S.; Fiore, N.; Williamson, B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balkwill, F. Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, B.; Fernandez, M.C.; D’Costa, Z.; Brodt, P. The diverse roles of the TNF axis in cancer progression and metastasis. Trends Cancer Res. 2016, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H. Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood 2012, 119, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brenner, D.; Blaser, H.; Mak, T.W. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor signalling: Live or let die. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 362–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Li, F.; Qin, Z. TNF Receptor 2 Makes Tumor Necrosis Factor a Friend of Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salomon, B.L.; Leclerc, M.; Tosello, J.; Ronin, E.; Piaggio, E.; Cohen, J.L. Tumor Necrosis Factor α and Regulatory T Cells in Oncoimmunology. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, T.; Ishii, N. The TNF–TNFR Family of Co-signal Molecules. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1189, 53–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.K.; Gracias, D.T.; Croft, M. TNF activity and T cells. Cytokine 2018, 101, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.J.; Owens, D.M.; Stamp, G.; Arnott, C.; Burke, F.; East, N.; Holdsworth, H.; Turner, L.; Rollins, B.; Pasparakis, M.; et al. Mice deficient in tumor necrosis factor-α are resistant to skin carcinogenesis. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, C.H.A.; Scott, K.; Moore, R.J.; Robinson, S.C.; Thompson, R.G.; Balkwill, F. Expression of both TNF-α receptor subtypes is essential for optimal skin tumour development. Oncogene 2003, 23, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charles, K.A.; Kulbe, H.; Soper, R.; Escorcio-Correia, M.; Lawrence, T.; Schultheis, A.; Chakravarty, P.; Thompson, R.G.; Kollias, G.; Smyth, J.F.; et al. The tumor-promoting actions of TNF-α involve TNFR1 and IL-17 in ovarian cancer in mice and humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, F.; Lacey, M.R.; Bouljihad, M.; Zu Bentrup, K.H.; Fortgang, I.S. Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 functions as a tumor suppressor. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2011, 302, G195–G206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naito, Y.; Takagi, T.; Handa, O.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakagawa, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Yoshida, N.; Minami, M.; Kita, M.; Imanishi, J.; et al. Enhanced intestinal inflammation induced by dextran sulfate sodium in tumor necrosis factor-alpha deficient mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 18, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, F.; Rochotte, J.; Colacios, C.; Montfort, A.; Tilkin-Mariamé, A.F.; Touriol, C.; Rochaix, P.; Lajoie-Mazenc, I.; Andrieu-Abadie, N.; Levade, T.; et al. Blocking Tumor Necrosis Factor Enhances CD8 T-cell-Dependent Immunity in Experimental Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertrand, F.; Montfort, A.; Marcheteau, E.; Imbert, C.; Gilhodes, J.; Filleron, T.; Rochaix, P.; Andrieu-Abadie, N.; Levade, T.; Meyer, N.; et al. TNFα blockade overcomes resistance to anti-PD-1 in experimental melanoma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monaco, C.; Nanchahal, J.; Taylor, P.; Feldmann, M. Anti-TNF therapy: Past, present and future. Int. Immunol. 2015, 27, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brożyna, A.A.; Jóźwicki, W.; Roszkowski, K.; Filipiak, J.; Slominski, A.T. Melanin content in melanoma metastases affects the outcome of radiotherapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17844–17853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brozyna, A.A.; Jóźwicki, W.; Carlson, J.A.; Slominski, A.T. Melanogenesis affects overall and disease-free survival in patients with stage III and IV melanoma. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2071–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falcone, I.; Conciatori, F.; Bazzichetto, C.; Ferretti, G.; Cognetti, F.; Ciuffreda, L.; Milella, M. Tumor Microenvironment: Implications in Melanoma Resistance to Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elicabe, R.J.; Cargnelutti, E.; Serer, M.I.; Stege, P.W.; Valdez, S.R.; Toscano, M.A.; Rabinovich, G.A.; di Genaro, M.S. Lack of TNFR p55 results in heightened expression of IFN-gamma and IL-17 during the development of reactive arthritis. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 4485–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cargnelutti, E.; Arias, J.L.; Valdez, S.R.; Rabinovich, G.A.; di Genaro, M.S. TNFRp55 controls regulatory T cell responses in Yersinia-induced reactive arthritis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 91, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Research Council Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Croci, D.O.; Cerliani, J.P.; Dalotto-Moreno, T.; Méndez-Huergo, S.P.; Mascanfroni, I.D.; Dergan-Dylon, S.; Toscano, M.A.; Caramelo, J.J.; García-Vallejo, J.J.; Ouyang, J.; et al. Glycosylation-Dependent Lectin-Receptor Interactions Preserve Angiogenesis in Anti-VEGF Refractory Tumors. Cell 2014, 156, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maceyka, M.; Alvarez, S.E.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Filamin A Links Sphingosine Kinase 1 and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 1 at Lamellipodia to Orchestrate Cell Migration. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5687–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, M.G.; Campos, L.E.; Rodriguez, Y.I.; Alvarez, S.E. In Vitro Methods to Study the Modulation of Migration and Invasion by Sphingosine-1-Phosphate. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1697, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, G.J.; Busolini, F.I.; Mohamed, F.H.; Filippa, V.P. Effects of melatonin and gonadal androgens on cell proliferation in the pituitary of viscachas (Lagostomus maximus maximus). Cell Prolif. 2016, 49, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Bronte, V. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, T.I.; Lee, Y.M.; Lim, B.O.; Lim, J.H. Inhibition of NAT10 Suppresses Melanogenesis and Melanoma Growth by Attenuating Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor (MITF) Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.J.; Wu, C.C.; Lee, C.L.; Hsieh, S.L.; Chen, J.B.; Lee, C.I. Antimelanogenic, Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Effects of Antrodia camphorata Fruiting Bodies on B16-F0 Melanoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, A.E.; Colleran, A.; O’Gorman, A.; O’Flynn, L.; Pindjacova, J.; Lohan, P.; O’Malley, G.; Nosov, M.; Mureau, C.; Egan, L.J. Targeting colon cancer cell NF-kappaB promotes an anti-tumour M1-like macrophage phenotype and inhibits peritoneal metastasis. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliger, B.; Wollscheid, U.; Momburg, F.; Blankenstein, T.; Huber, C. Characterization of the major histocompatibility complex class I deficiencies in B16 melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Sasi, S.P.; Yan, X.; Enderling, H.; Park, D.S.; Gilbert, H.Y.; Curry, C.; Coleman, C.; Hlatky, L.; Qin, G.; Kishore, R.; et al. Breaking the ’harmony’ of TNF-α signaling for cancer treatment. Oncogene 2011, 31, 4117–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fortis, S.P.; Mahaira, L.G.; Anastasopoulou, E.A.; Voutsas, I.F.; Perez, S.A.; Baxevanis, C.N. Immune profiling of melanoma tumors reflecting aggressiveness in a preclinical model. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, M.; Lang, I.; Salzmann, S.; Pachel, C.; Kraus, S.; Bäuerlein, C.A.; Brede, C.; Garrote, A.L.J.; Mattenheimer, K.; Ritz, M.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor Induces Tumor Promoting and Anti-Tumoral Effects on Pancreatic Cancer via TNFR1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomita, Y.; Yang, X.; Ishida, Y.; Nemoto-Sasaki, Y.; Kondo, T.; Oda, M.; Watanabe, G.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Fujii, C.; Mukaida, N. Spontaneous regression of lung metastasis in the absence of tumor necrosis factor receptor p55. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlikowska, M.; Piotrowski, J.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Kozak, W.; Slominski, A.T.; Brożyna, A.A. Coriolus versicolor -derived protein-bound polysaccharides trigger the caspase-independent cell death pathway in amelanotic but not melanotic melanoma cells. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.; Zbytek, B.; Slominski, R. Inhibitors of melanogenesis increase toxicity of cyclophosphamide and lymphocytes against melanoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shields, C.L.; Kaliki, S.; Cohen, M.N.; Shields, P.W.; Furuta, M.; Shields, J.A. Prognosis of uveal melanoma based on race in 8100 patients: The 2015 Doyne Lecture. Eye 2015, 29, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Xu, W.; Chen, X.; Han, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, C.; Hao, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Li, D. Icariin induces cell differentiation and cell cycle arrest in mouse melanoma B16 cells via Erk1/2-p38-JNK-dependent pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99504–99513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voronov, E.; Shouval, D.S.; Krelin, Y.; Cagnano, E.; Benharroch, D.; Iwakura, Y.; Dinarello, C.A.; Apte, R.N. IL-1 is required for tumor invasiveness and angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kociok, N.; Radetzky, S.; Krohne, T.U.; Gavranic, C.; Joussen, A.M. Pathological but Not Physiological Retinal Neovascularization Is Altered in TNF-Rp55-Receptor–Deficient Mice. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 5057–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, R.; Kondo, T.; Ohshima, T.; Ishida, Y.; Mukaida, N. Accelerated wound healing in tumor necrosis factor receptor p55-deficient mice with reduced leukocyte infiltration. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the Crime: Functions of Cells Recruited to the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaplanov, I.; Carmi, Y.; Kornetsky, R.; Shemesh, A.; Shurin, G.V.; Shurin, M.R.; Dinarello, C.A.; Voronov, E.; Apte, R.N. Blocking IL-1β reverses the immunosuppression in mouse breast cancer and synergizes with anti–PD-1 for tumor abrogation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 116, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peschon, J.J.; Torrance, D.S.; Stocking, K.L.; Glaccum, M.B.; Otten, C.; Willis, C.R.; Charrier, K.; Morrissey, P.J.; Ware, C.B.; Mohler, K.M. TNF receptor-deficient mice reveal divergent roles for p55 and p75 in several models of inflammation. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 943–952. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, C.F.; Manzoni-De-Almeida, D.; Mello, P.S.; Natale, C.C.; Santiago, H.D.C.; Miranda, L.D.S.; Ferraz, F.O.; Dos Santos, L.M.; Teixeira, M.M.; Arantes, R.M.E.; et al. Characterization of Chronic Cutaneous Lesions from TNF-Receptor-1-Deficient Mice Infected by Leishmania major. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 865708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional 377 affiliations. |



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez, Y.I.; Campos, L.E.; Castro, M.G.; Bannoud, N.; Blidner, A.G.; Filippa, V.P.; Croci, D.O.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Alvarez, S.E. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-1 (p55) Deficiency Attenuates Tumor Growth and Intratumoral Angiogenesis and Stimulates CD8+ T Cell Function in Melanoma. Cells 2020, 9, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112469
Rodriguez YI, Campos LE, Castro MG, Bannoud N, Blidner AG, Filippa VP, Croci DO, Rabinovich GA, Alvarez SE. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-1 (p55) Deficiency Attenuates Tumor Growth and Intratumoral Angiogenesis and Stimulates CD8+ T Cell Function in Melanoma. Cells. 2020; 9(11):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112469
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez, Yamila I., Ludmila E. Campos, Melina G. Castro, Nadia Bannoud, Ada G. Blidner, Verónica P. Filippa, Diego O. Croci, Gabriel A. Rabinovich, and Sergio E. Alvarez. 2020. "Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-1 (p55) Deficiency Attenuates Tumor Growth and Intratumoral Angiogenesis and Stimulates CD8+ T Cell Function in Melanoma" Cells 9, no. 11: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112469
APA StyleRodriguez, Y. I., Campos, L. E., Castro, M. G., Bannoud, N., Blidner, A. G., Filippa, V. P., Croci, D. O., Rabinovich, G. A., & Alvarez, S. E. (2020). Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-1 (p55) Deficiency Attenuates Tumor Growth and Intratumoral Angiogenesis and Stimulates CD8+ T Cell Function in Melanoma. Cells, 9(11), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9112469





