Dynamic Changes in Function and Proteomic Composition of Extracellular Vesicles from Hepatic Stellate Cells during Cellular Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals and Primary Mouse HSC (mHSC) Culture
2.2. Mouse HSC Characterization
2.3. Human LX-2 CELLS
2.4. EV Isolation
2.5. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA)
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Gene Expression in HSC
2.8. EV Protein Extraction and Digestion
2.9. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
2.10. Gene Ontology, Pathway Enrichment, and Protein-Protein Interaction Networks
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Primary mHSC
3.2. Physico-Chemical and Biological Properties of EVs from mHSC or hHSC
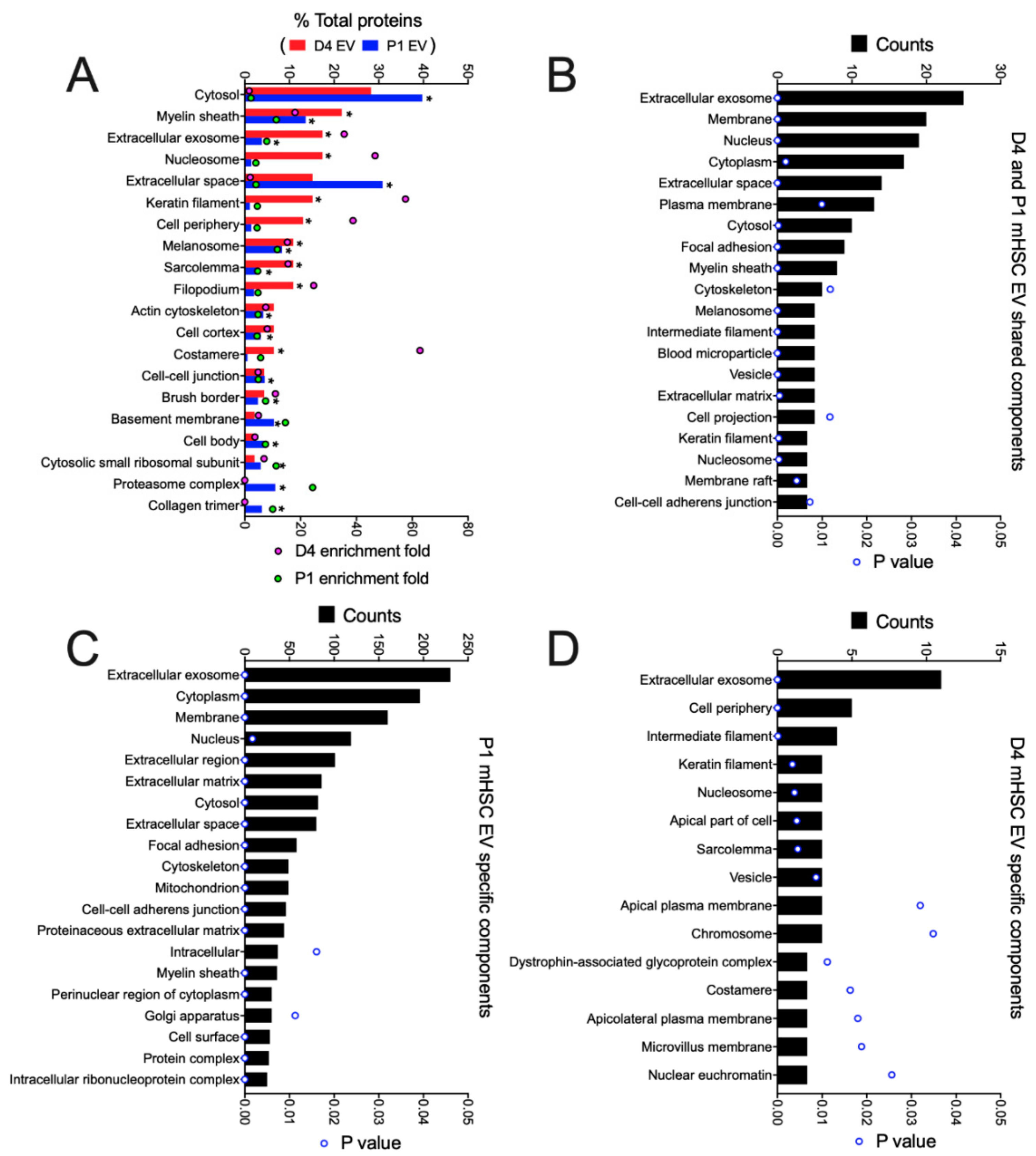
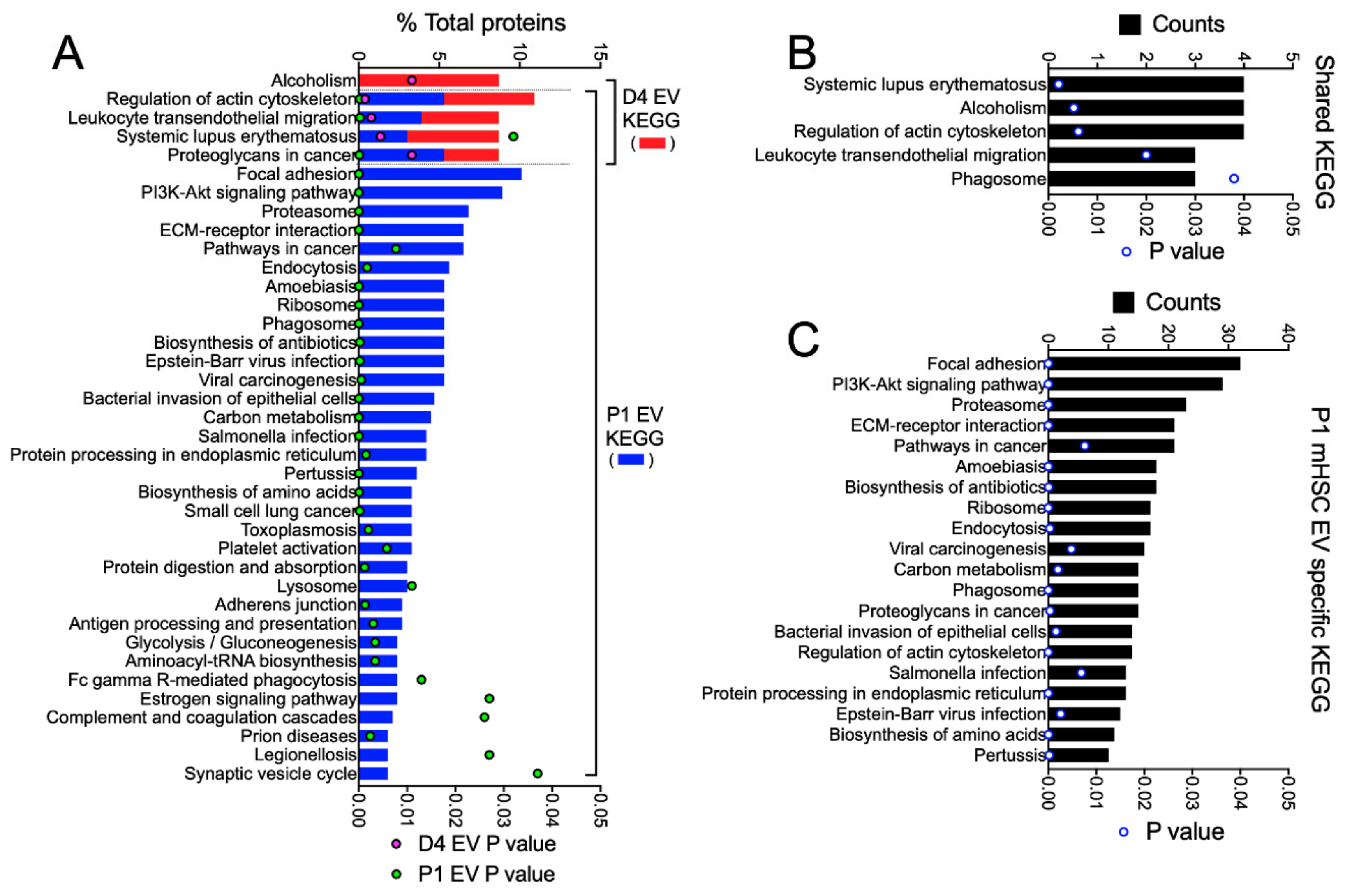
3.3. Proteomic Analysis of EVs from mHSC
3.4. Proteomic Analysis of EVs from hHSC
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hernandez-Gea, V.; Friedman, S.L. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, U.E.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 25, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puche, J.E.; Saiman, Y.; Friedman, S.L. Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1473–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira da Silva, B.; Ramos, L.F.; Moraes, K.C.M. Molecular interplays in hepatic stellate cells: Apoptosis, senescence, and phenotype reversion as cellular connections that modulate liver fibrosis. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T.; Friedman, S.L.; Hoshida, Y. Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilarasan, D.; Sokal, E.; Najimi, M. Hepatic fibrosis: It is time to go with hepatic stellate cell-specific therapeutic targets. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis. Int. 2018, 17, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokdad, A.A.; Lopez, A.D.; Shahraz, S.; Lozano, R.; Mokdad, A.H.; Stanaway, J.; Murray, C.J.; Naghavi, M. Liver cirrhosis mortality in 187 countries between 1980 and 2010: A systematic analysis. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen-Naftaly, M.; Friedman, S.L. Current status of novel antifibrotic therapies in patients with chronic liver disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2011, 4, 391–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiassi-Nejad, Z.; Friedman, S.L. Advances in antifibrotic therapy. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 2, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoinne, S.; Friedman, S.L. New and emerging anti-fibrotic therapeutics entering or already in clinical trials in chronic liver diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharm. 2019, 49, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, R.; Nagorniewicz, B.; Prakash, J. Clinical Advancements in the Targeted Therapies against Liver Fibrosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 7629724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockey, D.C. Translating an understanding of the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis to novel therapies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuppan, D.; Pinzani, M. Anti-fibrotic therapy: Lost in translation? J. Hepatol. 2012, 56 (Suppl. 1), S66–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautwein, C.; Friedman, S.L.; Schuppan, D.; Pinzani, M. Hepatic fibrosis: Concept to treatment. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S15–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, S.L. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 2247–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szabo, G.; Momen-Heravi, F. Extracellular vesicles in liver disease and potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.; Matsuda, A.; Yan, I.K.; Parasramka, M.; Patel, T. Extracellular vesicles in liver diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G194–G200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoinne, S.; Thabut, D.; Housset, C.; Moreau, R.; Valla, D.; Boulanger, C.M.; Rautou, P.E. The emerging roles of microvesicles in liver diseases. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Verma, V.K.; Morton, L.A.; Shah, V.H.; LaRusso, N.F.; Gores, G.J.; Malhi, H. Extracellular vesicles in liver pathobiology: Small particles with big impact. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2219–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, S.; Cheng, X.; Pan, X.; Li, J. Emerging role of exosomes in liver physiology and pathology. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thery, C. Exosomes: Secreted vesicles and intercellular communications. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2011, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charrier, A.; Chen, R.; Chen, L.; Kemper, S.; Hattori, T.; Takigawa, M.; Brigstock, D.R. Exosomes mediate intercellular transfer of pro-fibrogenic connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) between hepatic stellate cells, the principal fibrotic cells in the liver. Surgery 2014, 156, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Charrier, A.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Yu, B.; Agarwal, K.; Tsukamoto, H.; Lee, L.J.; Paulaitis, M.E.; Brigstock, D.R. Epigenetic regulation of connective tissue growth factor by MicroRNA-214 delivery in exosomes from mouse or human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Kemper, S.; Brigstock, D.R. Pathways of production and delivery of hepatocyte exosomes. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Kemper, S.; Charrier, A.; Brigstock, D.R. Suppression of fibrogenic signaling in hepatic stellate cells by Twist1-dependent microRNA-214 expression: Role of exosomes in horizontal transfer of Twist1. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G491–G499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Velazquez, V.M.; Brigstock, D.R. Fibrogenic Signaling Is Suppressed in Hepatic Stellate Cells through Targeting of Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CCN2) by Cellular or Exosomal MicroRNA-199a-5p. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2921–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devhare, P.B.; Sasaki, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Ray, R.; Ray, R.B. Exosome-Mediated Intercellular Communication between Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Hepatocytes and Hepatic Stellate Cells. J. Virol. 2017, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, W.; Eun, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Yi, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, S.H.; Jang, M.J.; Jo, E.; Kim, S.C.; Han, Y.M.; et al. Exosome-mediated activation of toll-like receptor 3 in stellate cells stimulates interleukin-17 production by gammadelta T cells in liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2016, 64, 616–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Povero, D.; Panera, N.; Eguchi, A.; Johnson, C.D.; Papouchado, B.G.; de Araujo Horcel, L.; Pinatel, E.M.; Alisi, A.; Nobili, V.; Feldstein, A.E. Lipid-induced hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles regulate hepatic stellate cell via microRNAs targeting PPAR-gamma. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 646–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, E.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, H.S.; Yoo, Y.J.; Je, J.; Suh, S.J.; Jung, Y.K.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Exosomes derived from palmitic acid-treated hepatocytes induce fibrotic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lua, I.; Li, Y.; Zagory, J.A.; Wang, K.S.; French, S.W.; Sevigny, J.; Asahina, K. Characterization of hepatic stellate cells, portal fibroblasts, and mesothelial cells in normal and fibrotic livers. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Brigstock, D.R. Integrins and heparan sulfate proteoglycans on hepatic stellate cells (HSC) are novel receptors for HSC-derived exosomes. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 4263–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouwaki, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Daito, T.; Sanada, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Mifsud, E.J.; Leong, C.R.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Kohara, M.; Matsumoto, M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Including Exosomes Regulate Innate Immune Responses to Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, V.K.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Hirsova, P.; Mushref, M.; Liu, Y.; Cao, S.; Contreras, P.C.; Malhi, H.; Kamath, P.S.; et al. Alcohol stimulates macrophage activation through caspase-dependent hepatocyte derived release of CD40L containing extracellular vesicles. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Bala, S.; Kodys, K.; Szabo, G. Exosomes derived from alcohol-treated hepatocytes horizontally transfer liver specific miRNA-122 and sensitize monocytes to LPS. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirsova, P.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Krishnan, A.; Verma, V.K.; Bronk, S.F.; Werneburg, N.W.; Charlton, M.R.; Shah, V.H.; Malhi, H.; Gores, G.J. Lipid-induced Signaling Causes Release of Inflammatory Extracellular Vesicles from Hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakazu, E.; Mauer, A.S.; Yin, M.; Malhi, H. Hepatocytes release ceramide-enriched pro-inflammatory extracellular vesicles in an IRE1alpha-dependent manner. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Povero, D.; Eguchi, A.; Niesman, I.R.; Andronikou, N.; de Mollerat du Jeu, X.; Mulya, A.; Berk, M.; Lazic, M.; Thapaliya, S.; Parola, M.; et al. Lipid-induced toxicity stimulates hepatocytes to release angiogenic microparticles that require Vanin-1 for uptake by endothelial cells. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, S.W. Exosomal Transmission of MicroRNA from HCV Replicating Cells Stimulates Transdifferentiation in Hepatic Stellate Cells. Mol. Nucleic Acids 2019, 14, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Ding, Q.; Yaqoob, U.; de Assuncao, T.M.; Verma, V.K.; Hirsova, P.; Cao, S.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Huebert, R.C.; Shah, V.H. Exosome Adherence and Internalization by Hepatic Stellate Cells Triggers Sphingosine 1-Phosphate-dependent Migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 30684–30696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, R.; Kemper, S.; Brigstock, D. Extracellular vesicles from hepatocytes are therapeutic for toxin-mediated fibrosis and gene expression in the liver. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Tan, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhao, T.; Mao, F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Yan, Z.; Qian, H.; Yan, Y. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 6079642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Yan, Y.; Wang, B.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, W.; et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, X.; Li, F.; Ma, Z.; Xu, M.; Lu, L. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardpour, S.; Hassani, S.N.; Mardpour, S.; Sayahpour, F.; Vosough, M.; Ai, J.; Aghdami, N.; Hamidieh, A.A.; Baharvand, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from human embryonic stem cell-MSCs ameliorate cirrhosis in thioacetamide-induced chronic liver injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9330–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, M.; Ohnishi, S.; Hosono, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Yuyama, K.; Nakamura, H.; Fu, Q.; Maehara, O.; Suda, G.; Sakamoto, N. Extracellular Vesicles from Amnion-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 3212643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Povero, D.; Pinatel, E.M.; Leszczynska, A.; Goyal, N.P.; Nishio, T.; Kim, J.; Kneiber, D.; de Araujo Horcel, L.; Eguchi, A.; Ordonez, P.M.; et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles reduce hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis. JCI Insight 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, X.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xie, F. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate liver fibrosis through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruno, S.; Pasquino, C.; Herrera Sanchez, M.B.; Tapparo, M.; Figliolini, F.; Grange, C.; Chiabotto, G.; Cedrino, M.; Deregibus, M.C.; Tetta, C.; et al. HLSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Liver Fibrosis and Inflammation in a Murine Model of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Mol. Ther. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Chen, R.; Kemper, S.; Cong, M.; You, H.; Brigstock, D.R. Therapeutic effects of serum extracellular vesicles in liver fibrosis. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1461505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pranitha, P.; Sudhakaran, P.R. Fibronectin dependent upregulation of matrix metalloproteinases in hepatic stellate cells. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 40, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodig, M.; Ogunwale, B.; Dasarathy, S.; Li, M.; Wang, B.; McCullough, A.J. Differences in regulation of type I collagen synthesis in primary and passaged hepatic stellate cell cultures: The role of alpha5beta1-integrin. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G154–G164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Juan, C.; de la Torre, P.; Garcia-Ruiz, I.; Diaz-Sanjuan, T.; Munoz-Yague, T.; Gomez-Izquierdo, E.; Solis-Munoz, P.; Solis-Herruzo, J.A. Fibronectin increases survival of rat hepatic stellate cells--a novel profibrogenic mechanism of fibronectin. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 24, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milliano, M.T.; Luxon, B.A. Initial signaling of the fibronectin receptor (alpha5beta1 integrin) in hepatic stellate cells is independent of tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Hepatol. 2003, 39, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Brigstock, D.R. Integrin expression and function in the response of primary culture hepatic stellate cells to connective tissue growth factor (CCN2). J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonyak, M.A.; Li, B.; Boroughs, L.K.; Johnson, J.L.; Druso, J.E.; Bryant, K.L.; Holowka, D.A.; Cerione, R.A. Cancer cell-derived microvesicles induce transformation by transferring tissue transglutaminase and fibronectin to recipient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4852–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, O.; Lin, C.; Wagner, J.; Archard, J.A.; Deng, P.; Halmai, J.; Bauer, G.; Fink, K.D.; Fury, B.; Perotti, N.H.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Induce Mitosis and Potentiate Growth Factor Secretion. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gho, Y.S.; Lee, C. Emergent properties of extracellular vesicles: A holistic approach to decode the complexity of intercellular communication networks. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chen, R.; Kemper, S.; Brigstock, D.R. Dynamic Changes in Function and Proteomic Composition of Extracellular Vesicles from Hepatic Stellate Cells during Cellular Activation. Cells 2020, 9, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020290
Li X, Chen R, Kemper S, Brigstock DR. Dynamic Changes in Function and Proteomic Composition of Extracellular Vesicles from Hepatic Stellate Cells during Cellular Activation. Cells. 2020; 9(2):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020290
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xinlei, Ruju Chen, Sherri Kemper, and David R Brigstock. 2020. "Dynamic Changes in Function and Proteomic Composition of Extracellular Vesicles from Hepatic Stellate Cells during Cellular Activation" Cells 9, no. 2: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020290
APA StyleLi, X., Chen, R., Kemper, S., & Brigstock, D. R. (2020). Dynamic Changes in Function and Proteomic Composition of Extracellular Vesicles from Hepatic Stellate Cells during Cellular Activation. Cells, 9(2), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020290





