A Wnt-BMP4 Signaling Axis Induces MSX and NOTCH Proteins and Promotes Growth Suppression and Differentiation in Neuroblastoma
Abstract
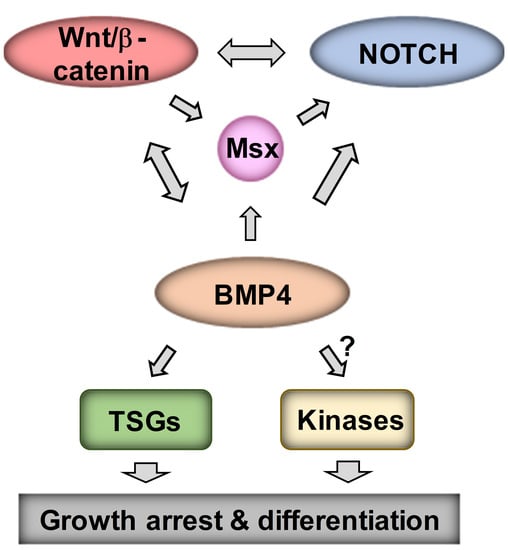
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Neuroblastoma Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.2. Incucyte Live Cell Imaging and Cell Cycle Analysis
2.3. Protein Extraction and Western blot
2.4. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription and qPCR
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. RNA-seq and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cross-Talk between Wnt and BMP Signaling in Neuroblastoma
3.2. BMP4 Signaling Affects Growth and Differentiation of Neuroblastoma Cells
3.3. BMP4 Protein Expression Correlates with Better Prognosis of Neuroblastoma Patients
3.4. Wnt and BMP4 Signaling Have Overlapping but Distinct Effects on the Neuroblastoma Transcriptome
3.5. Notch Signaling Is Downstream of Wnt-BMP Signaling
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADRN | adrenergic |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| ERK | extracellular signal–regulated kinase |
| GRN | gene regulatory network |
| GSEA | Geneset Enrichment Analysis. |
| ICD | Intracellular Domain. |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| LEF | lymphoid enhancer binding factor |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK kinase |
| MNA | MYCN-amplified |
| Rspo | R-spondin |
| TCF | T-cell-factor |
| TGF | Transforming Growth Factor |
References
- Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 2012, 149, 1192–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M. Networking of WNT, FGF, Notch, BMP, and Hedgehog signaling pathways during carcinogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. 2007, 3, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodeur, G.M. Neuroblastoma: Biological insights into a clinical enigma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, J.I.; Dyberg, C.; Wickstrom, M. Neuroblastoma-A Neural Crest Derived Embryonal Malignancy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Castro, M.I.; Marcelle, C.; Bronner-Fraser, M. Ectodermal Wnt function as a neural crest inducer. Science 2002, 297, 848–851. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.W.; Murdoch, B.; Salem, A.F.; Prasad, M.S.; Gomez, G.A.; Garcia-Castro, M.I. WNT/beta-catenin signaling mediates human neural crest induction via a pre-neural border intermediate. Development 2016, 143, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steventon, B.; Araya, C.; Linker, C.; Kuriyama, S.; Mayor, R. Differential requirements of BMP and Wnt signalling during gastrulation and neurulation define two steps in neural crest induction. Development 2009, 136, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brodeur, G.M.; Seeger, R.C.; Schwab, M.; Varmus, H.E.; Bishop, J.M. Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science 1984, 224, 1121–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermark, U.K.; Wilhelm, M.; Frenzel, A.; Henriksson, M.A. The MYCN oncogene and differentiation in neuroblastoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011, 21, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardi, S.; Valli, E.; Erriquez, D.; Perini, G. MYCN-mediated transcriptional repression in neuroblastoma: The other side of the coin. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ten Berge, D.; Brugmann, S.A.; Helms, J.A.; Nusse, R. Wnt and FGF signals interact to coordinate growth with cell fate specification during limb development. Development 2008, 135, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vieira, G.C.; Chockalingam, S.; Melegh, Z.; Greenhough, A.; Malik, S.; Szemes, M.; Park, J.H.; Kaidi, A.; Zhou, L.; Catchpoole, D.; et al. LGR5 regulates pro-survival MEK/ERK and proliferative Wnt/beta-catenin signalling in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40053–40067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Lau, W.; Peng, W.C.; Gros, P.; Clevers, H. The R-spondin/Lgr5/Rnf43 module: Regulator of Wnt signal strength. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Mazanek, P.; Dam, V.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, H.; Guo, R.; Jagannathan, J.; Cnaan, A.; Maris, J.M.; Hogarty, M.D. Deregulated Wnt/beta-catenin program in high-risk neuroblastomas without MYCN amplification. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szemes, M.; Greenhough, A.; Melegh, Z.; Malik, S.; Yuksel, A.; Catchpoole, D.; Gallacher, K.; Kollareddy, M.; Park, J.H.; Malik, K. Wnt Signalling Drives Context-Dependent Differentiation or Proliferation in Neuroblastoma. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerlund, I.; Shi, Y.; Toskas, K.; Fell, S.M.; Li, S.; Surova, O.; Sodersten, E.; Kogner, P.; Nyman, U.; Schlisio, S.; et al. Combined epigenetic and differentiation-based treatment inhibits neuroblastoma tumor growth and links HIF2alpha to tumor suppression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6137–E6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Revet, I.; Huizenga, G.; Chan, A.; Koster, J.; Volckmann, R.; van Sluis, P.; Ora, I.; Versteeg, R.; Geerts, D. The MSX1 homeobox transcription factor is a downstream target of PHOX2B and activates the Delta-Notch pathway in neuroblastoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemes, M.; Greenhough, A.; Malik, K. Wnt Signaling Is a Major Determinant of Neuroblastoma Cell Lineages. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeva, V.; Louis-Brennetot, C.; Peltier, A.; Durand, S.; Pierre-Eugene, C.; Raynal, V.; Etchevers, H.C.; Thomas, S.; Lermine, A.; Daudigeos-Dubus, E.; et al. Heterogeneity of neuroblastoma cell identity defined by transcriptional circuitries. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1408–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Groningen, T.; Koster, J.; Valentijn, L.J.; Zwijnenburg, D.A.; Akogul, N.; Hasselt, N.E.; Broekmans, M.; Haneveld, F.; Nowakowska, N.E.; Bras, J.; et al. Neuroblastoma is composed of two super-enhancer-associated differentiation states. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Yip, H. Effects of bone morphogenetic protein 2 on Id expression and neuroblastoma cell differentiation. Differentiation 2010, 79, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Ozaki, T.; Koseki, H.; Nakagawara, A.; Sakiyama, S. Accumulation of p27 KIP1 is associated with BMP2-induced growth arrest and neuronal differentiation of human neuroblastoma-derived cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 307, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlemann, F.C.; Menon, V.; Condurat, A.L.; Rossler, J.; Pruszak, J. Surface marker profiling of SH-SY5Y cells enables small molecule screens identifying BMP4 as a modulator of neuroblastoma differentiation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhatt, S.; Diaz, R.; Trainor, P.A. Signals and switches in Mammalian neural crest cell differentiation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martik, M.L.; Bronner, M.E. Regulatory Logic Underlying Diversification of the Neural Crest. Trends Genet. 2017, 33, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.F. Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itasaki, N.; Hoppler, S. Crosstalk between Wnt and bone morphogenic protein signaling: A turbulent relationship. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M. Network of WNT and other regulatory signaling cascades in pluripotent stem cells and cancer stem cells. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, D.H.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.K. The Dual Role of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tribulo, C.; Aybar, M.J.; Nguyen, V.H.; Mullins, M.C.; Mayor, R. Regulation of Msx genes by a Bmp gradient is essential for neural crest specification. Development 2003, 130, 6441–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Szemes, M.; Vieira, G.C.; Melegh, Z.; Malik, S.; Heesom, K.J.; Von Wallwitz-Freitas, L.; Greenhough, A.; Brown, K.W.; Zheng, Y.G.; et al. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 is a key regulator of the MYCN oncoprotein in neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, K.; Gerald, W.; LeSauteur, L.; Uri Saragovi, H.; Cheung, N.K. Prognostic value of TrkA protein detection by monoclonal antibody 5C3 in neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 1996, 2, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balamuth, N.J.; Wood, A.; Wang, Q.; Jagannathan, J.; Mayes, P.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Rappaport, E.; Courtright, J.; Pawel, B.; et al. Serial transcriptome analysis and cross-species integration identifies centromere-associated protein E as a novel neuroblastoma target. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2749–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corvetta, D.; Chayka, O.; Gherardi, S.; D’Acunto, C.W.; Cantilena, S.; Valli, E.; Piotrowska, I.; Perini, G.; Sala, A. Physical interaction between MYCN oncogene and polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) in neuroblastoma: Functional and therapeutic implications. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8332–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Woo, C.W.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.S.; Marquez, V.E.; Bates, S.E.; Jin, Q.; Khan, J.; et al. EZH2 Mediates epigenetic silencing of neuroblastoma suppressor genes CASZ1, CLU, RUNX3, and NGFR. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valentijn, L.J.; Koster, J.; Haneveld, F.; Aissa, R.A.; van Sluis, P.; Broekmans, M.E.; Molenaar, J.J.; van Nes, J.; Versteeg, R. Functional MYCN signature predicts outcome of neuroblastoma irrespective of MYCN amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19190–19195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, Y.; Hertwig, F.; Thierry-Mieg, J.; Zhang, W.; Thierry-Mieg, D.; Wang, J.; Furlanello, C.; Devanarayan, V.; Cheng, J.; et al. Comparison of RNA-seq and microarray-based models for clinical endpoint prediction. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Nes, J.; Chan, A.; van Groningen, T.; van Sluis, P.; Koster, J.; Versteeg, R. A NOTCH3 transcriptional module induces cell motility in neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3485–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zins, K.; Schafer, R.; Paulus, P.; Dobler, S.; Fakhari, N.; Sioud, M.; Aharinejad, S.; Abraham, D. Frizzled2 signaling regulates growth of high-risk neuroblastomas by interfering with beta-catenin-dependent and beta-catenin-independent signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46187–46202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, D.J.; Krstic, A.; Schwarzl, T.; Halasz, M.; Iljin, K.; Fey, D.; Haley, B.; Whilde, J.; Haapa-Paananen, S.; Fey, V.; et al. Wnt signalling is a bi-directional vulnerability of cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 60310–60331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Groningen, T.; Akogul, N.; Westerhout, E.M.; Chan, A.; Hasselt, N.E.; Zwijnenburg, D.A.; Broekmans, M.; Stroeken, P.; Haneveld, F.; Hooijer, G.K.J.; et al. A NOTCH feed-forward loop drives reprogramming from adrenergic to mesenchymal state in neuroblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zage, P.E.; Nolo, R.; Fang, W.; Stewart, J.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Zweidler-McKay, P.A. Notch pathway activation induces neuroblastoma tumor cell growth arrest. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 58, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waldeck, K.; Cullinane, C.; Ardley, K.; Shortt, J.; Martin, B.; Tothill, R.W.; Li, J.; Johnstone, R.W.; McArthur, G.A.; Hicks, R.J.; et al. Long term, continuous exposure to panobinostat induces terminal differentiation and long term survival in the TH-MYCN neuroblastoma mouse model. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Kuo, K.K.; Kuo, T.L.; Lee, K.T.; Cheng, K.H. The activation of MEK/ERK signaling pathway by bone morphogenetic protein 4 to increase hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauzon, M.A.; Faucheux, N. A small peptide derived from BMP-9 can increase the effect of bFGF and NGF on SH-SY5Y cells differentiation. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 88, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szemes, M.; Melegh, Z.; Bellamy, J.; Greenhough, A.; Kollareddy, M.; Catchpoole, D.; Malik, K. A Wnt-BMP4 Signaling Axis Induces MSX and NOTCH Proteins and Promotes Growth Suppression and Differentiation in Neuroblastoma. Cells 2020, 9, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030783
Szemes M, Melegh Z, Bellamy J, Greenhough A, Kollareddy M, Catchpoole D, Malik K. A Wnt-BMP4 Signaling Axis Induces MSX and NOTCH Proteins and Promotes Growth Suppression and Differentiation in Neuroblastoma. Cells. 2020; 9(3):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030783
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzemes, Marianna, Zsombor Melegh, Jacob Bellamy, Alexander Greenhough, Madhu Kollareddy, Daniel Catchpoole, and Karim Malik. 2020. "A Wnt-BMP4 Signaling Axis Induces MSX and NOTCH Proteins and Promotes Growth Suppression and Differentiation in Neuroblastoma" Cells 9, no. 3: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030783
APA StyleSzemes, M., Melegh, Z., Bellamy, J., Greenhough, A., Kollareddy, M., Catchpoole, D., & Malik, K. (2020). A Wnt-BMP4 Signaling Axis Induces MSX and NOTCH Proteins and Promotes Growth Suppression and Differentiation in Neuroblastoma. Cells, 9(3), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030783