Role of 2-Arachidonoyl-Glycerol and CB1 Receptors in Orexin-A-Mediated Prevention of Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation-Induced Neuronal Injury
Abstract
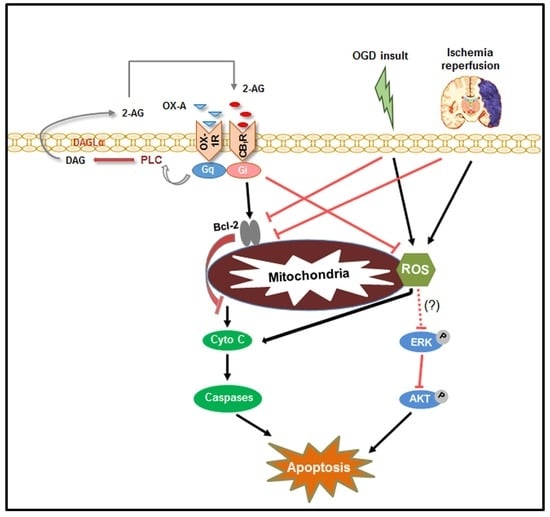
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Cortical Neuron Cultures
2.2. Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation
2.3. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
2.4. Cellular Viability Assay
2.5. Immunocytochemistry
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. EC Measurements
2.8. Animals
2.9. Transient Focal Ischemia in Mice
2.10. Histological Analysis and Assessment of the Infarct Volume
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. OX-A Prevents OGD-Induced ROS Formation in Primary Cultures of Mouse Cortical Neurons
3.2. OX-A Prevents OGD Injury by Inducing 2-AG Biosynthesis and Subsequent Activation of CB1 Receptors
3.3. OX-A Counteracts OGD-Induced Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt Signaling
3.4. Effects of OX-A on Bcl-2 Expression and Cytochrome c Release
3.5. Effects of OX-A in MCAO-Induced Focal Cerebral Ischemia
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kukkonen, J.P.; Holmqvist, T.; Ammoun, S.; Akerman, K.E. Functions of the orexinergic/hypocretinergic system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2002, 283, C1567–C1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, J.P. Recent progress in orexin/hypocretin physiology and pharmacology. Biomol. Concepts 2012, 3, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambu, T.; Sakurai, T.; Mizukami, K.; Hosoya, Y.; Yanagisawa, M.; Goto, K. Distribution of orexin neurons in the adult rat brain. Brain Res. 1999, 827, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, C.; Tighe, D.K.; van den Pol, A.N.; de Lecea, L.; Heller, H.C.; Sutcliffe, J.G.; Kilduff, T.S. Neurons containing hypocretin (orexin) project to multiple neuronal systems. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9996–10015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, T.; Amemiya, A.; Ishii, M.; Matsuzaki, I.; Chemelli, R.M.; Tanaka, H.; Williams, S.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Kozlowski, G.P.; Wilson, S.; et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 1998, 92, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Armitage, R. Sleep and circadian rhythms in mood disorders. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. Suppl. 2007, 433, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, E.; Hamada, J.; Kanazawa, N.; Yonekura, J.; Masuda, R.; Sakai, F.; Mochizuki, H. The effect of orexin-A on the pathological mechanism in the rat focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 68, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, P.; Urbańska, A.; Biegańska, K.; Wagner, W.; Ciszewski, W.; Namiecińska, M.; Zawilska, J.B. Orexins protect neuronal cell cultures against hypoxic stress: An involvement of Akt signaling. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 52, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, T.; Qiu, K.; Liu, M.; Cheng, B.; Pan, Y.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, C. Orexin-A protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced cell damage by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis via the Gi and PI3K signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2019, 62, 109348–109360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yoshioka, H.; Kim, G.S.; Jung, J.E.; Okami, N.; Sakata, H.; Maier, C.M.; Narasimhan, P.; Goeders, C.E.; Chan, P.H. Oxidative Stress in Ischemic Brain Damage: Mechanisms of Cell Death and Potential Molecular Targets for Neuroprotection. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2011, 14, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turunen, P.M.; Jäntti, M.H.; Kukkonen, J.P. OX1 orexin/hypocretin receptor signalling through arachidonic acid and endocannabinoid release. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cristino, L.; Luongo, L.; Imperatore, R.; Boccella, S.; Becker, T.; Morello, G.; Piscitelli, F.; Busetto, G.; Maione, S.; Di Marzo, V. Orexin-A and Endocannabinoid Activation of the Descending Antinociceptive Pathway Underlies Altered Pain Perception in Leptin Signaling Deficiency. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mechoulam, R.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Ligumsky, M.; Kaminski, N.E.; Schatz, A.R.; Gopher, A.; Almog, S.; Martin, B.R.; Compton, D.R. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Sukagawa, A.; Nakane, S.; Shinoda, A.; Itoh, K.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol: A possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 215, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, N.; Schweitzer, P.; Piomelli, D. A second endogenous cannabinoid that modulates long-term potentiation. Nature 1997, 388, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cristino, L.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Chen, S.; Gou, X.; Hu, B.; Du, J.; Lu, Y.; Xiong, L. Pretreatment with electroacupuncture induces rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia through regulation of endocannabinoid system. Stroke 2009, 40, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morello, G.; Imperatore, R.; Palomba, L.; Finelli, C.; Labruna, G.; Pasanisi, F.; Sacchetti, L.; Buono, L.; Piscitelli, F.; Orlando, P.; et al. Orexin-A represses satiety-inducing POMC neurons and contributes to obesity via stimulation of endocannabinoid signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4759–4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palomba, L.; Silvestri, C.; Imperatore, R.; Morello, G.; Piscitelli, F.; Martella, A.; Cristino, L.; Di Marzo, V. Negative regulation of leptin-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation by cannabinoid CB1 receptor activation in hypothalamic neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13669–13677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, H.; Kim, E.; Lee, D.H.; Seo, S.; Ju, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.; Park, S. Ghrelin inhibits apoptosis in hypothalamic neuronal cells during oxygen–glucose deprivation. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, L.; Amadori, A.; Cantoni, O. Early release of arachidonic acid prevents an otherwise immediate formation of toxic levels of peroxynitrite in astrocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide/interferon-gamma. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, O.; Tommasini, I.; Cerioni, L. The arachidonate-dependent survival signaling preventing toxicity in monocytes/macrophages exposed to peroxynitrite. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 441, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bisogno, T.; Mahadevan, A.; Coccurello, R.; Chang, J.W.; Allarà, M.; Chen, Y.; Giacovazzo, G.; Lichtman, A.; Cravatt, B.; Moles, A.; et al. A novel fluorophosphonate inhibitor of the biosynthesis of the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol with potential anti-obesity effects. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 169, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bülbül, M.; Tan, R.; Gemici, B.; Ongüt, G.; Izgüt-Uysal, V.N. Effect of orexin-A on ischemia-reperfusion-induced gastric damage in rats. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterick, T.A.; Nixon, J.P.; Billington, C.J.; Kotz, C.M. Orexin A decreases lipid peroxidation and apoptosis in a novel hypothalamic cell model. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 524, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blankman, J.L.; Simon, G.M.; Cravatt, B.F. A comprehensive profile of brain enzymes that hydrolyze the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanda, P.K.; Gao, Y.; Mark, L.; Btesh, J.; Strassle, B.W.; Lu, P.; Piesla, M.J.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Bingham, B.; Uveges, A.; et al. Monoacylglycerol lipase activity is a critical modulator of the tone and integrity of the endocannabinoid system. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosburg, J.E.; Blankman, J.L.; Long, J.Z.; Nomura, D.K.; Pan, B.; Kinsey, S.G.; Nguyen, P.T.; Ramesh, D.; Booker, L.; Burston, J.J.; et al. Chronic mono-acylglycerol lipase blockade causes functional antagonism of the endocannabinoid system. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malagelada, C.; Xifro, X.; Minano, A.; Sabria, J.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, J. Contribution of caspase-mediated apoptosis to the cell death caused by oxygenglucose deprivation in cortical cell cultures. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 20, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruscher, K.; Freyer, D.; Karsch, M.; Isaev, N.; Megow, D.; Sawitzki, B.; Priller, J.; Dirnagl, U.; Meisel, A. Erythropoietin is a paracrine mediator of ischemic tolerance in the brain: Evidence from an in vitro model. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 10291–10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datta, S.R.; Brunet, A.; Greenberg, M.E. Cellular survival: A play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2905–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers, G.T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lam, P.Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, Q.; Yu, A.C. Activation of Erk1/2 and Akt in astrocytes under ischemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Seo, S.; Moon, M.; Park, S. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and ERK1/2 pathways mediate protective effects of acylated and unacylated ghrelin against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis in primary rat cortical neuronal cells. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 198, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamzami, N.; Susin, S.A.; Marchetti, P.; Hirsch, T.; Gomez-Monterrey, I.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Mitochondrial control of nuclear apoptosis. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Pinzon, M.A.; Xu, G.P.; Born, J.; Lorenzo, J.; Busto, R.; Rosenthal, M.; Sick, T.J. Cytochrome c is released from mitochondria into the cytosol after cerebral anoxia or ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1999, 19, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Guo, L. Effects of orexin A on glucose metabolism in human hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro via PI3K/Akt/mTOR-dependent and -independent mechanism. J. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 420, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasban-Aliabadi, H.; Esmaeili-Mahani, S.; Abbasnejad, M. Orexin-A protects human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity: Involvement of PKC and PI3K signaling pathways. Rejuvenation Res. 2017, 20, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.F.; Xue, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.H.; Diao, H.L.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.P.; Chen, L. Orexin-A exerts neuroprotective effects via OX1R in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Holgado, F.; Pinteaux, E.; Heenan, L.; Moore, J.D.; Rothwell, N.J.; Gibson, R.M. Neuroprotective effects of the synthetic cannabinoid HU-210 in primary cortical neurons are mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2005, 28, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaita, A.; Puighermanal, E.; Maldonado, R. Regulation of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3 pathway by cannabinoids in the brain. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Yankner, B.A. Apoptosis in the nervous system. Nature 2000, 407, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. A structural view of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Nijhawan, D.; Budihardjo, I.; Srinivasula, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Alnemri, E.S.; Wang, X. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 1997, 91, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuida, K.; Haydar, T.F.; Kuan, C.Y.; Gu, Y.; Taya, C.; Karasuyama, H.; Su, M.S.; Rakic, P.; Flavell, R.A. Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell 1998, 94, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, H.; Kong, Y.Y.; Yoshida, R.; Elia, A.J.; Hakem, A.; Hakem, R.; Penninger, J.M.; Mak, T.W. Apaf1 is required for mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and brain development. Cell 1998, 94, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujimura, M.; Morita-Fujimura, Y.; Murakami, K.; Kawase, M.; Chan, P. H, Cytosolic redistribution of cytochrome c after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1998, 18, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, K.; Sugawara, T.; Chan, P.H.; Basus, V.J.; James, T.L.; Litt, L. Cytochrome c associated apoptosis during ATP recovery after hypoxia in neonatal rat cerebrocortical slices. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; Breivogel, C.S.; Tao, Q.; Bridgen, D.T.; Razdan, R.K.; Zimmer, A.M.; Zimmer, A.; Martin, B.R. Levels, Metabolism, and pharmacological activity of anandamide in CB(1) cannabinoid receptor knockout mice: Evidence for non-CB(1), non-CB(2) receptor-mediated actions of anandamide in mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 2434–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cinar, R.; Xiong, K.; Godlewski, G.; Jourdan, T.; Lin, Y.; Ntambi, J.M.; Kunos, G. Monounsaturated fatty acids generated via stearoyl CoA desaturase-1 are endogenous inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18832–18837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| 2-AG (pmol/mL) | AEA (pmol/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| Wild type | ||
| Untreated | 1.30 ± 0.50 | 0.06 ± 0.007 |
| OX-A | 241 ± 66.8 ** | 0.08 ± 0.030 |
| OX-A+ O-7460 | 2.99 ± 2.64 | 0.07 ± 0.010 |
| MAGL−/− | ||
| Untreated | 11.23 ± 0.54 * | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| 2-AG (pmol/g Wet Tissue Weight) | AEA (pmol/g Wet Tissue Weight) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sham | 1.12 ± 0.27 | 0.064 ± 0.015 |
| Transient ischemia | 0.39 ± 0.19 * | 0.058 ± 0.014 |
| Transient ischemia + OX-A | 0.70 ± 0.11 # | 0.088 ± 0.003 *# |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palomba, L.; Motta, A.; Imperatore, R.; Piscitelli, F.; Capasso, R.; Mastroiacovo, F.; Battaglia, G.; Bruno, V.; Cristino, L.; Di Marzo, V. Role of 2-Arachidonoyl-Glycerol and CB1 Receptors in Orexin-A-Mediated Prevention of Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation-Induced Neuronal Injury. Cells 2020, 9, 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061507
Palomba L, Motta A, Imperatore R, Piscitelli F, Capasso R, Mastroiacovo F, Battaglia G, Bruno V, Cristino L, Di Marzo V. Role of 2-Arachidonoyl-Glycerol and CB1 Receptors in Orexin-A-Mediated Prevention of Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation-Induced Neuronal Injury. Cells. 2020; 9(6):1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061507
Chicago/Turabian StylePalomba, Letizia, Andrea Motta, Roberta Imperatore, Fabiana Piscitelli, Raffaele Capasso, Federica Mastroiacovo, Giuseppe Battaglia, Valeria Bruno, Luigia Cristino, and Vincenzo Di Marzo. 2020. "Role of 2-Arachidonoyl-Glycerol and CB1 Receptors in Orexin-A-Mediated Prevention of Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation-Induced Neuronal Injury" Cells 9, no. 6: 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061507
APA StylePalomba, L., Motta, A., Imperatore, R., Piscitelli, F., Capasso, R., Mastroiacovo, F., Battaglia, G., Bruno, V., Cristino, L., & Di Marzo, V. (2020). Role of 2-Arachidonoyl-Glycerol and CB1 Receptors in Orexin-A-Mediated Prevention of Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation-Induced Neuronal Injury. Cells, 9(6), 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061507