Abstract
The pharmacological activation of A3 receptors has shown potential usefulness in the management of bowel inflammation. However, the role of these receptors in the control of visceral hypersensitivity in the presence of intestinal inflammation has not been investigated. The effects of AR170, a potent and selective A3 receptor agonist, and dexamethasone (DEX) were tested in rats with 2,4-dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS)-induced colitis to assess their tissue inflammatory parameters. The animals received AR170, DEX, or a vehicle intraperitoneally for 6 days, starting 1 day before the induction of colitis. Visceral pain was assessed by recording the abdominal responses to colorectal distension in animals with colitis. Colitis was associated with a decrease in body weight and an increase in spleen weight. The macroscopic damage score and tissue tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin 1β (IL-1β), and myeloperoxidase (MPO) levels were also enhanced. AR170, but not DEX, improved body weight. Both drugs counteracted the increase in spleen weight, ameliorated macroscopic colonic damage, and decreased TNF, IL-1β, and MPO tissue levels. The enhanced visceromotor response (VMR) in rats with colitis was decreased via AR170 administration. In rats with colitis, AR170 counteracted colonic inflammatory cell infiltration and decreased pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, thereby relieving visceral hypersensitivity.
1. Introduction
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, are complex multifactorial inflammatory diseases of the gut, driven by genetic, luminal, and environmental factors, leading to an overactive intestinal immune response [1]. Typically, IBDs are characterized by diarrhea or constipation, nausea, weight loss, and rectal bleeding [1].
The visceral pain experienced by 50–70% of IBD patients is one of the most significant problems for subjects suffering from these chronic illnesses [2]. Pain and abdominal discomfort represent a significant burden in these patients that diminishes their quality of life [3]. Indeed, although majority of patients suffering from acute flares of IBD experience pain, which is typically improved by a decrease in disease activity, a significant percentage of IBD patients continue to perceive pain despite resolving their inflammation and achieving clinical remission [2]. Based on these premises, the identification of new therapeutic targets for developing novel pharmacological tools able to manage both the immuno–inflammatory components of IBD and to curb visceral sensitivity represents a significant medical need.
A large body of evidence has highlighted the involvement of adenosine in the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis, which orchestrates the interplay between the intestinal epithelial cells, the neuromuscular compartment, and the enteric immune system [4,5,6,7,8]. In particular, adenosine, via the engagement of four G protein-coupled receptors (named A1, A2A, A2B, and A3 receptors (A1AR, A2AAR, A2BAR, and A3AR, respectively)), plays a key role in driving an immune response [5]. Among them, A3AR has strongly captured the interest of the scientific community, since increasing evidence reveals the complex role of this receptor subtype in the pathophysiology of inflammation, as A3AR participates in the modulation of a broad array of immune cell functions, such as cytokine production, degranulation, chemotaxis, and proliferation [7,9,10].
Over the years, these receptors have also revealed an involvement in the pathophysiology of IBDs [11]. Indeed, preclinical and clinical studies demonstrated a marked alteration of A3AR expression in these conditions, accompanied by increased production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [11,12]. The pharmacological engagement of A3AR determines the inhibition of several cytokine/chemokine/inflammatory genes, thus promoting a marked down-regulation of several pro-inflammatory mediators (i.e., IL-1, IL-6, IL-12, Macrophage Inflammatory Protein 1α (MIP-1α), and MIP-2), as well as the production of oxidative stress, thereby improving experimental colitis. Furthermore, recent work by Ren et al. [12] demonstrated that 2-chloro-N6-(3-iodobenzyl)-adenosine-5′-N-methyluronamide (Cl-IB-MECA, Figure 1), a selective A3AR agonist, can inhibit the NF-κB pathway in the colonic epithelia of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) colitis mice [12].
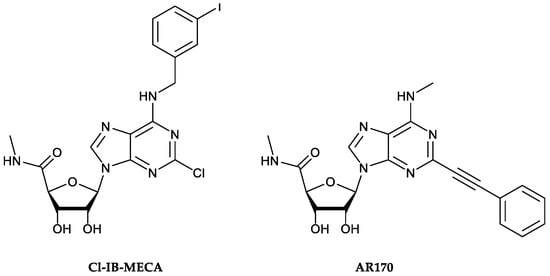
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of the A3AR reference agonist 2-chloro-N6-(3-iodobenzyl)-adenosine-5′-N-methyluronamide (Cl-IB-MECA, left) and the potent and selective A3AR agonist AR170 (right) employed in this study.
Several authors have highlighted the potential anti-nociceptive effects of A3AR activation [13,14]. For instance, Hou et al. [13] described the involvement of A3ARs in the beneficial effects exerted by electroacupuncture on the hypersensitivity induced by colitis in mice [13]. Similarly, Coppi et al. [14] demonstrated an A3AR activation-mediated pain-relieving mechanism involving the N-type Ca2+ channel block and action potential inhibition in the dorsal root ganglion neurons isolated from controls, as well as from animals treated with DNBS. This effect is consistent with the acute visceral pain relief showed by A3AR agonists in rats [15]. However, the potential therapeutic effect of the A3AR agonist on visceral pain development and persistence is an aspect that needs to be further investigated. In parallel, the stimulation of A3AR ameliorated the colonic motor disturbances associated with intestinal inflammation [16], thereby corroborating the relevance of this receptor subtype as an intriguing target for the management of IBDs.
Based on these premises, our study was designed to evaluate the effect of AR170 (Figure 1) [17,18,19], a potent and selective A3AR agonist, in counteracting the inflammatory process and curbing visceral hypersensitivity in a murine model of DNBS-induced intestinal inflammation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Albino male Sprague–Dawley rats, 250–300 g in body weight, were employed throughout the study. The animals were fed standard laboratory chow and tap water ad libitum and were not subjected to experimental procedures for at least one week after their delivery to the laboratory. Animal care and handling were performed in accordance with the provisions of the European Community Council Directive 2010/63/UE, which were recognized and adopted by the Italian Government. All experimental procedures were approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Experimentation of the University of Pisa and by the Italian Ministry of Health (authorization n° 674/2016-PR). In the present study, animal data are presented according to ARRIVE guidelines.
2.2. Induction of Colitis and Drug Treatments
Colitis was induced in accordance with the method previously described by Antonioli et al. [20]. Briefly, during a short period of anesthesia with isoflurane (Abbott, Rome, Italy), 30 mg of DNBS in 0.25 mL of 50% ethanol was administered intrarectally via a polyethylene PE-60 catheter inserted 8 cm proximal to the anus. Control rats received 0.25 mL of 50% ethanol. Animals underwent subsequent experimental procedures 6 days after DNBS administration to allow the full development of evident colonic inflammation. Test drugs were administered intraperitoneally for 6 days, starting 1 day before the induction of colitis. Animals were assigned to the following treatment groups: AR170 (3 mg/kg/day) or DEX (1 mg/kg/day). A group of animals was administered contextually with the A3AR antagonist MRS1523 (8 mg/kg i.p.) and AR170.
The acute effect of AR170 on visceral pain was assessed 14 days after DNBS injection, when pain persisted despite remission from colitis [21]. AR170 (0.5–4.5 mg/kg i.p.) was intraperitoneally administered 15 min before starting the test. The A3AR antagonist MRS1523 (8 mg/kg i.p.) was injected 15 min before AR170. To evaluate its effects on the development and persistence of the visceral hyperalgesia induced by DNBS, AR170 (1.5 mg/kg/day) was intraperitoneally administered for 14 days, starting from the day of DNBS injection, and tests were performed on days 8 and 15, 24 h after the last treatment.
DNBS-untreated animals (control group) and DNBS-treated rats (DNBS group) received only the drug vehicle. Body weight was monitored daily starting from the onset of drug treatments. All the evaluated parameters were not significantly affected in the DNBS-untreated animals administered with AR170 alone in comparison to the control group.
2.3. Assessment of Colitis
At the end of treatments, colonic tissues were excised, rinsed with saline, and scored for macroscopic and histological damage, in accordance with the criteria previously reported by Antonioli et al. [22]. The macroscopic criteria were scored on a 0–6 scale using the scoring system reported in Table 1. The presence of adhesions between colonic tissue and other organs (0 none, 1 minor, and 2 major adhesions) and the consistency of colonic fecal material (0 formed, 1 loose, and 2 liquid stools) were also scored [22]. All parameters of macroscopic damage were recorded and scored for each rat by two observers blinded to the treatment. At the time of experiment, the weight of the spleen was also measured.

Table 1.
Criteria for scoring macroscopic colonic ulceration and inflammation.
2.4. Determination of Tissue Myeloperoxidase
MPO levels in colonic tissues were determined as previously reported by Antonioli et al. [20] and applied as a quantitative index to estimate the degree of mucosal infiltration by polymorphonuclear cells [20]. Briefly, the colonic tissue samples (300 mg) were homogenized 3 times (30 s each) at 4 °C with a polytron homogenizer (Cole Parmer Homogenizer, Vernon Hills, IL, USA) in 1 mL of ice-cold 50 mmol/L phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) containing 0.5% of hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide to prevent the pseudoperoxidase activity of hemoglobin, as well as to solubilize membrane-bound MPO. The homogenate was sonicated for 10 s, frozen–thawed 3 times, and spun by centrifugation for 20 min at 18,000× g. The supernatant was then recovered and used for determination of MPO by means of a kit for an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Bioxytech, Oxis International Inc., Portland, OR, USA). All samples were assayed within 2 days from collection. The results were expressed as the ng of MPO per 100 mg of tissue.
2.5. Cytokine Assays
Tissue TNF and IL-1β levels were measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits (BioSource International, Camarillo, CA, USA) [23,24]. For this purpose, tissue samples, stored previously at 80 °C, were weighed, thawed, and homogenized in 0.3 mL of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.2/100 mg of tissue, at 4 °C and centrifuged at 13,400× g for 20 min. Aliquots (100 µL) of the supernatants were then used for the assay. Tissue TNF and IL-1β levels were expressed as the picogram per milligram of tissue or nanogram per milligram of tissue, respectively.
2.6. Assessment of Visceral Sensitivity
The extent of the abdominal contractions (VMR) due to colorectal distension was measured by performing electromyography (EMG) on the abdominal muscles and used as a quantitative measure of visceral sensitivity in the rats. Two EMG electrodes were sutured into the external oblique abdominal muscles of the animals under anesthesia and exteriorized dorsally [25]. VMR assessment was carried out under light anesthesia (2% isoflurane). A lubricated latex balloon (length: 4.5 cm) was attached on an embolectomy catheter and connected to a water-filled syringe used to perform colorectal distension (CRD). The syringe was used to fill the balloon placed into the colon with increasing volumes of water (0.5, 1, 2, and 3 mL, referred to as the distension volume). After colorectal stimulation, the EMG signal was recorded, amplified and filtered (Animal Bio Amp, ADInstruments, Colorado Springs, CO, USA), digitized (PowerLab 4/35, ADInstruments), analyzed, and quantified using LabChart 8 (ADInstruments). To quantify the VMR magnitude under each distension volume, the area under the curve (AUC) immediately before distension (30 s) was subtracted from the AUC during balloon distension (30 s), and the responses were expressed as a percentage increase from the baseline. The time elapsed between two consecutive distensions was 5 min. The entire measurement process lasted about 25 min.
2.7. Drugs and Reagents
Dimethyl sulfoxide, DNBS, DEX, MRS1523, and methylcellulose were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The synthesis of AR170 was performed as previously reported [17].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The results are presented as the mean ± S.E.M. unless otherwise stated. The significance of differences was evaluated in the raw data by a one-way analysis of variance followed by a post hoc analysis via a Student–Newman–Keuls test or Bonferroni’s test. p-values < 0.05 were considered significantly different. All statistical procedures were performed using commercial software (GraphPad Prism, version 7.0 from GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Visceral sensitivity data were analyzed using the “Origin 9” software (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Body Weight and Spleen Weight
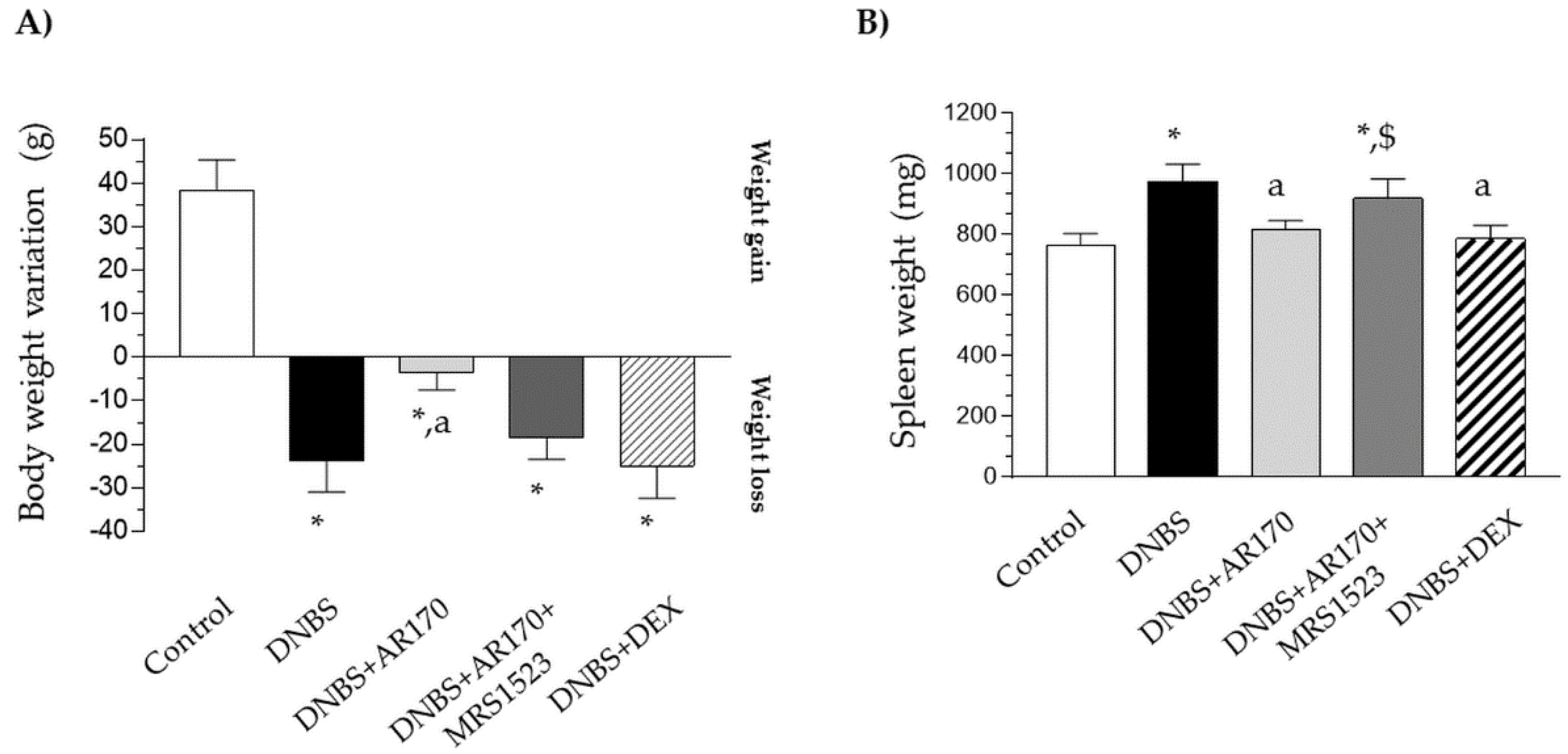
Six days after DNBS administration, the rats displayed a significant decrease in their body weight in comparison with the control animals (Figure 2A). Treatment with AR170 significantly counteracted the body weight decrease observed in the rats with colitis, whereas the animals subjected to dexamethasone administration did not experience this phenomenon (Figure 2A). The induction of colitis was also characterized by a significant increase in spleen weight. This increase was counteracted by AR170 and via dexamethasone administration (Figure 2B).
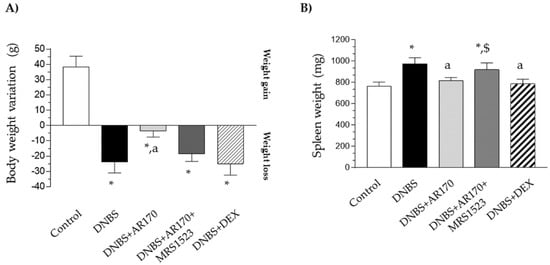
Figure 2.
The effect of AR170 (3 mg/kg/day), alone or in combination with MRS1523 (8 mg/kg/day) or dexamethasone (DEX; 1 mg/kg/day), on body weight (A) and spleen weight; (B) at day 6 after the induction of colitis with 2,4-dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (DNBS). Each column represents the mean ±SEM (n = 8–10). * p < 0.05, significant difference vs. the control group; a p < 0.05, significant difference vs. the DNBS group; $ p <0.05, significant difference vs. the DNBS+AR170 group.
3.2. Colonic Length and Macroscopic Damage Score
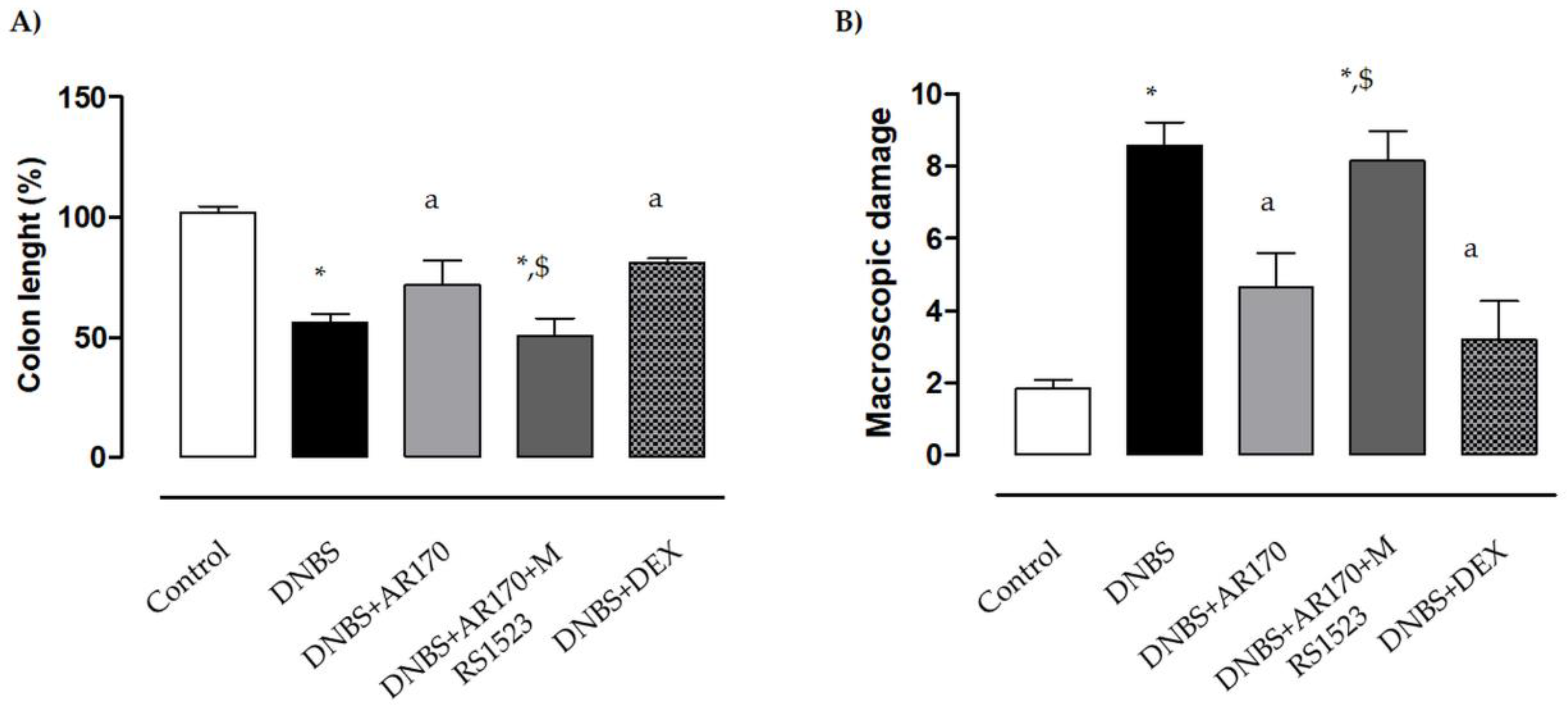
Six days after DNBS administration, the inflamed rats were characterized by a shortening of colonic length (−43.7%) compared to the control animals. Treatment of the inflamed rats with the A3AR agonist AR170 or DEX significantly attenuated the decrease in colonic length (Figure 3A).
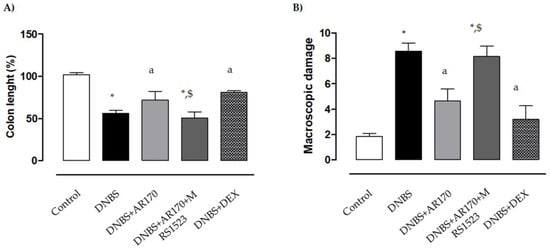
Figure 3.
Effects of AR170 (3 mg/kg/day), alone or in combination with MRS1523 (8 mg/kg/day) or DEX (1 mg/kg/day), on colon length (A) and the macroscopic damage score (B) at day 6 after the induction of colitis with DNBS. Each column represents the mean ±S.E.M. (n = 8–10). * p < 0.05, significant difference vs. control group; a p < 0.05, significant difference vs. DNBS group; $ p < 0.05, significant difference vs. DNBS + AR170 group.
The administration of DNBS was associated with colonic thickening and ulcerations, with marked areas of transmural inflammation. Moreover, adhesions and bowel dilations were detected, with macroscopic damage accounting for 8.6 ± 0.8. In this setting, the macroscopic damage was reduced significantly by AR170 and DEX (Figure 3B). MRS1523 counteracted the effects of AR170 (Figure 3A,B), but not dexamethasone efficacy (not shown).
3.3. MPO Levels in Colonic Tissues
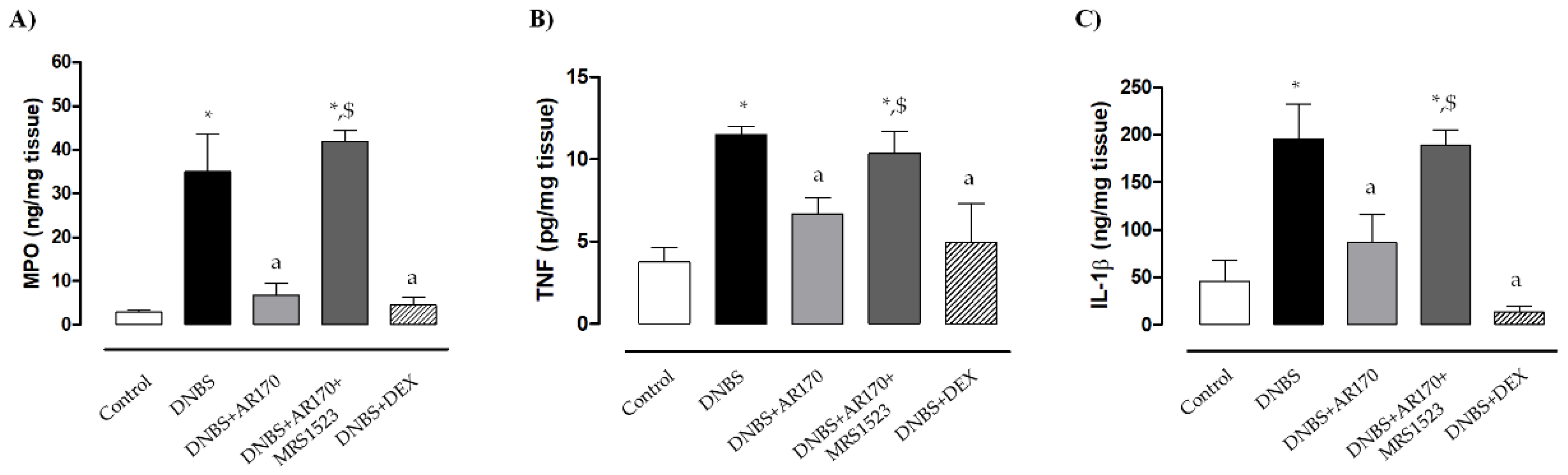
Rats with DNBS-induced colitis showed a marked increase in colonic MPO levels (35 ± 8.6 ng/mg tissue) compared to the control animals (2.8 ± 0.5 ng/mg tissue). Treatment with all test drugs significantly prevented the increase in colonic MPO levels associated with DNBS administration (Figure 4A). MRS1523 significantly counteracted AR170 (Figure 4A) but not the dexamethasone effects (not shown).
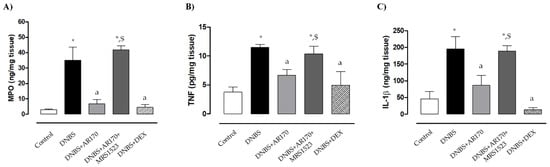
Figure 4.
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) (A), tumor necrosis factor (TNF) (B), and interleukin 1β (IL-1β) levels (C) in colonic tissue in the control rats and in animals treated with DNBS alone or in combination with AR170 (3 mg/kg/day), AR170 plus MRS1523 (8 mg/kg/day), or DEX (1 mg/kg/day). Each column represents the mean ±S.E.M. (n = 8–10). * p < 0.05, significant difference vs. control rats; a p < 0.05, significant difference vs. DNBS group; $ p < 0.05, significant difference vs. the DNBS + AR170 group.
3.4. TNF and IL-1β Levels in Colonic Tissues
Colonic inflammation induced by DNBS was associated with a significant increase in tissue TNF levels (11.5 ± 0.52 pg/mg tissue) compared to the values obtained in the control animals (3.8 ± 0.9 pg/mg tissue). Treatment with AR170 or DEX significantly decreased the concentration of this cytokine in colonic tissues (Figure 4B).
Rats with colitis displayed a significant increase in colonic IL-1β levels (196.1 ± 36.3 ng/mg tissue) compared to the control animals (45.9 ± 21 ng/mg tissue). Treatment with AR170 and DEX was associated with a significant decrease in IL-1β levels (Figure 4C). The effects of AR170 on tissue TNF and IL-1β were counteracted by MRS1523 (Figure 4C). In contrast, the A3AR antagonist did not alter the dexamethasone effect (not shown).
3.5. Effect of the Acute and Repeated Treatment with AR170 on the Visceral Pain Induced by DNBS
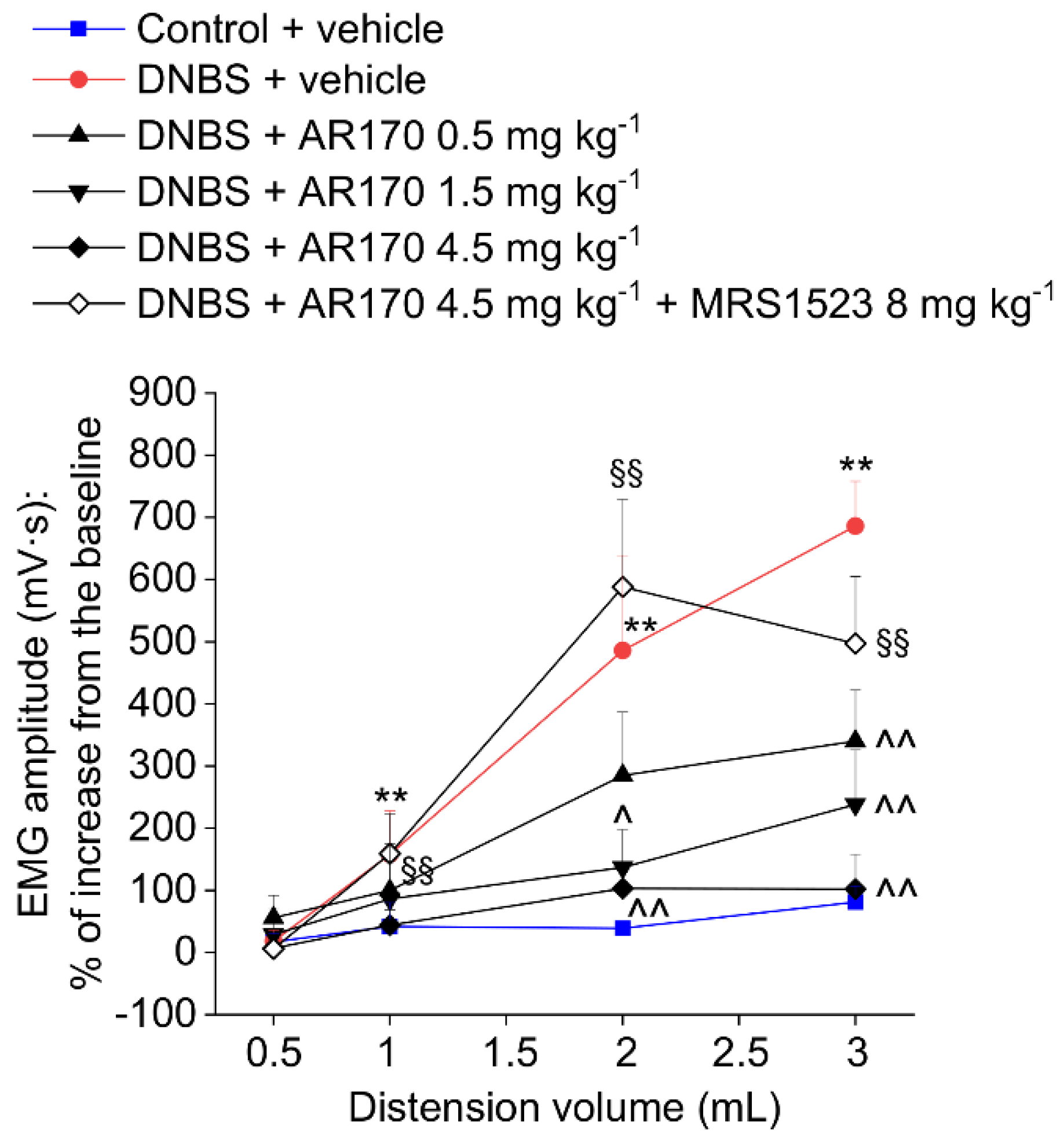
The measurement of the VMR to colorectal distension was used to assess the visceral sensitivity alterations in rats. Colorectal distension was carried out by inflating the balloon positioned in the colon with increasing volumes (0.5–3 mL). After DNBS injection, the VMRs induced by 1, 2, and 3 mL were significantly higher than those of the controls (Figure 5 and Figure 6). This visceral hypersensitivity was established in concomitance with intestinal inflammation (day 8, Figure 6A) and persisted in the remission phase of colitis (day 14, Figure 5 and Figure 6B), as previously reported in the literature [21]. On day 14, the acute administration of AR170 (0.5, 1.5, and 4.5 mg/kg) dose-dependently relieved the visceral hypersensitivity induced by DNBS. The highest dose (4.5 mg/kg) completely reversed the sensitive alterations back to the values of the controls. AR170 1.5 mg/kg significantly reduced the VMR of the animals to CRD (2–3 mL), while the lowest dose (0.5 mg/kg) was only partially effective, significantly lowering the VMR only in response to a 3 mL stimulus. Pre-treatment with the selective A3AR antagonist MRS1523 (8 mg/kg) [26] completely abolished the acute pain-relieving effects of AR170 (4.5 mg/kg).
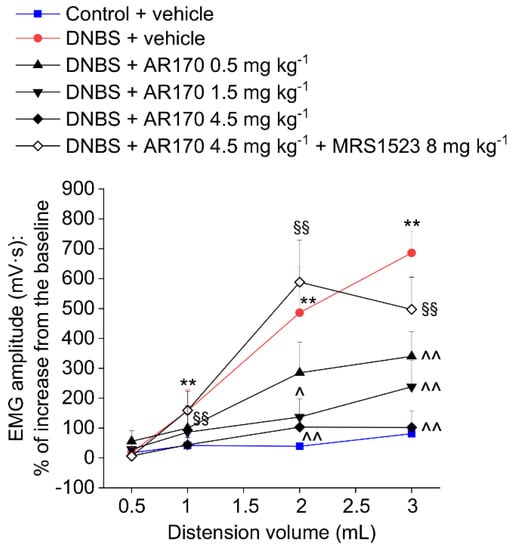
Figure 5.
Visceromotor response (VMR) to the colorectal distension of DNBS treated animals after the acute administration of AR170 (0.5–4.5 mg/kg i.p.) both in the absence and the presence of the selective A3AR antagonist MRS1523 (8 mg/kg i.p., injected 15 min before AR170). Tests were performed 14 days after DNBS injection and 15 min after the acute administration of AR170. Control animals received the vehicle. Each value represents the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. the control + vehicle treated animals. ^ p < 0.05 and ^^ p < 0.01 vs. DNBS + vehicle treated animals. §§ p < 0.01 vs. DNBS + AR170 4.5 mg kg−1 treated animals.
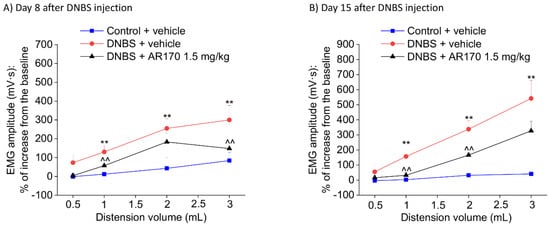
Figure 6.
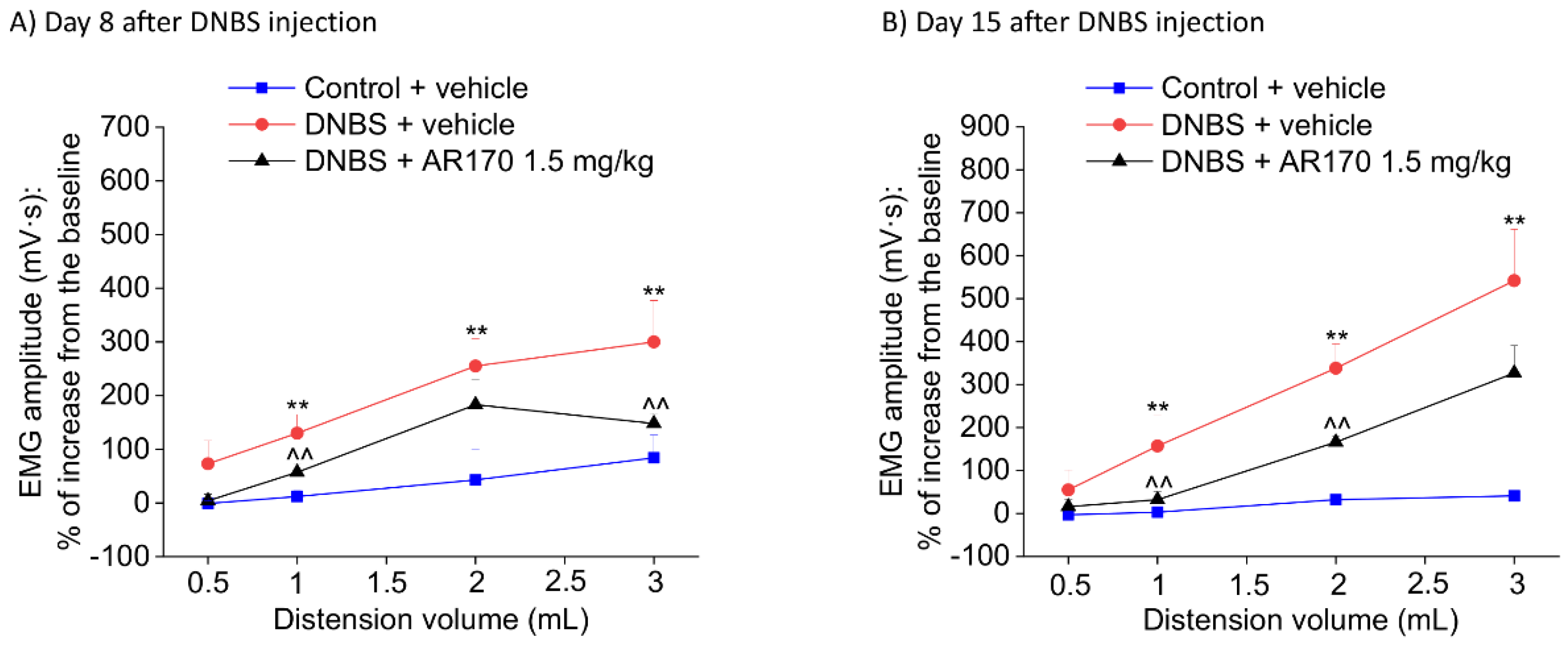
Visceromotor response (VMR) to the colorectal distension of DNBS-treated animals after the repeated administration of AR170 (1.5 mg/kg/day). The test was performed on day 8 (A) and 15 (B) after DNBS injection, 24 h after the last treatment. Control animals received the vehicle. Each value represents the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 4). * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. the control + vehicle treated animals. ^ p < 0.05 and ^^ p < 0.01 vs. DNBS + vehicle treated animals.
Relying on the acute pain-relieving efficacy shown by AR170 1.5 mg/kg in the previous tests, we chose this dose for the following experiment, in which the therapeutic effect of the repeated administration of AR170 on the visceral pain induced by DNBS was examined. Repeated treatment with AR170 (1.5 mg/kg) was able to counteract the development of visceral hypersensitivity induced by colitis in rats. On day 8, during the acute inflammatory phase, DNBS animals treated with the A3AR agonist showed a significant decrease of their abdominal response to both 1 and 3 mL (Figure 6A). This effect was maintained in the remission phase of colitis (day 15, Figure 6B) when the VMR to both 1 and 2 mL significantly decreased in the DNBS animals receiving AR170. Even the response to 3 mL appeared to be reduced on day 15, despite not reaching statistical significance (Figure 6B).
4. Discussion
The pivotal role played by adenosine in regulating the inflammatory responses and counteracting tissue injury through the engagement of specific receptors is widely recognized [7,27,28]. The pharmacological modulation of the adenosine receptor subtype A2A and A3 ARs have demonstrated their beneficial effects in several models of experimental colitis, thereby driving the scientific community to develop novel and selective ligands for these receptor subtypes as promising tools to manage IBDs [16,29,30,31,32,33]. Unfortunately, the great expectations for applying A2AAR agonists in clinical practice are challenged by the severe side effects of such ligands at the cardiovascular level [34]. Hence, increasing attention is being placed on the pharmacology of A3AR.
This receptor subtype is upregulated in activated immune cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, lymphocytes, splenocytes, bone marrow cells, and mast cells [10]. Once pharmacologically activated, A3AR exerts a marked immunosuppressive effect associated with a safe and well tolerated profile, as reported in preclinical studies and in Phase I and II human clinical studies [10].
For these reasons, today, A3AR is considered a novel and very promising therapeutic target, from which new agonists characterized by improved dynamic and kinetic properties are being designed. In this regard, AR170 is of great interest due to its high A3AR affinity (Ki A3AR = 0.44 nM in the radioligand binding assay) and remarkable selectivity versus other AR subtypes (i.e., about 97,000-fold selectivity versus A2AAR) [17,18], making it among the most potent and selective A3AR agonists reported to date.
Presently, the pharmacological management of IBD patients is far from satisfactory. Usually, the targeted treatments for the inflammatory aspect of these diseases are unsatisfactory, and the modulation of visceral hypersensitivity is ineffective.
Visceral pain is a critical component of IBD, which often persists even after complete resolution of the inflammation, significantly impacting the well-being of the patients [35,36,37]. Based on these findings, we developed the present study to investigate the putative anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects of AR170 in a rat model of colitis. To pursue the above aims, the effects of AR170 were assayed in a rat model of colitis elicited by DNBS. DEX was used as a glucocorticoid drug with known anti-inflammatory activity to assess the relative anti-inflammatory potency of the A3AR ligand.
DNBS-induced colitis is a murine model reminiscent of human Crohn’s disease, which is characterized by body weight loss, diarrhea, ulceration and bleeding, the depletion of goblet cells, and the formation of granulomas within the gut wall [20]. In parallel, it has been reported that DNBS-induced colitis represents a useful model for studying visceral hypersensitivity in response to colorectal distension [21]. The suitability of this preclinical model to assay both the anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties of novel drugs increases the translational potential of this research.
In the present study, AR170 administration was associated with significant improvements in all tissue inflammatory parameters, including colon length macroscopic scores, tissue cytokines (TNF and IL-1β), and tissue polymorphonuclear neutrophils and macrophage infiltration (MPO). Consistent with the data presented here, A3AR agonists were previously evaluated and shown to be effective in experimental models of inflammatory intestinal disorders [12,29,31]. In particular, it was reported in murine DSS colitis that the activation of A3AR, expressed in colonic epithelia, exerts anti-inflammatory activity through the inhibition of the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF and IL-1β via the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathways [12]. Recently, these preclinical data have been substantiated by Ren et al. [11]. In this study, the pharmacological stimulation of A3AR, via Cl-IB-MECA, decreased TNF and IL-1β production and attenuated NF-κB p65 activation in colonic tissues in patients with ulcerative colitis, thus corroborating the use of A3AR agonists as an efficacious treatment for IBD patients [11].
Although abdominal pain is an important patient-reported outcome for the evaluation of therapeutic efficacy [38,39], most treatments for Crohn’s disease are primarily focused on inflammation control and only marginally address the problem of chronic abdominal pain [40]. Moreover, opioid treatment, the current frontline therapy for abdominal pain, has serious complications and produces a condition called narcotic bowel syndrome, which leads to an exacerbation of pain rather than relief [41,42].
Over the years, increasing interest has been focused on characterizing the molecular mechanisms involved in visceral hypersensitivity to identify novel targets for managing abdominal pain [43,44,45,46,47]. The adenosine system was also previously demonstrated to have an important role in pain signaling [48,49]. As a result, A3AR modulation emerged as an effective strategy for the treatment of chronic pain with different etiologies, as attested by several preclinical studies [15,50,51,52,53].
In addition to its anti-inflammatory properties, the present work demonstrated the protective effects of AR170 on the development of visceral pain induced by DNBS in animals, as observed during both the acute phase of colitis and remission. The protective efficacy of AR170 on the development of visceral pain after DNBS injection was comparable to that shown by DEX in a previous study conducted by our research group using the same preclinical model of colitis [21]. However, while the pain-relieving effect of DEX is likely attributable to its anti-inflammatory activity and the resulting prevention of intestinal damage, AR170 seems to directly modulate visceral pain signaling. Notably, the mediation of pain by AR170 was detected after the repeated administration of a lower dose (1.5 mg/kg) compared to that used for obtaining protection from intestinal damage (4.5 mg/kg), suggesting the involvement of A3AR in the regulation of visceral sensitivity. A3AR activation mediated by AR170 may limit excitatory neurotransmission, which is altered in visceral pain [54,55,56]. Numerous results in the literature demonstrate neuroprotective effects related to A3AR activation and the resulting decrease in neuronal excitability [15,57,58,59,60]. This mechanism could be adjuvant to the anti-inflammatory properties, actively contributing to the therapeutic effects of AR170 on visceral pain. Notably, previous evidence [15] demonstrating the modulatory role of adenosine A3 receptors in the regulation of colonic neuromuscular functions in the presence of bowel inflammation led researchers to hypothesize the potential application of the A3AR agonist as a suitable tool for the management of IBD patients characterized by enhanced bowel motor activity and diarrhea.
AR170 has also proven effective in the acute relief of visceral pain, showing additional advantages over the use of steroidal and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [61]. These data agree with the anti-hyperalgesic effects previously reported for other A3AR agonists [14,15], supporting the hypothetical direct modulation of visceral pain transmission, which may represent a further benefit of AR170 in the therapy of bowel diseases.
5. Conclusions
Overall, the present results suggest that the pharmacological modulation of A3AR represents a novel and appealing therapeutical strategy for the management of inflammatory bowel disorders, as this method is contextually able to dampen the inflammatory process and mitigate the visceral hypersensitivity associated with colitis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.A., E.L., L.D.C.M., R.V. and D.D.B.; methodology, L.A., E.L., L.D.C.M., R.V. and D.D.B.; investigation, L.A., E.L., L.D.C.M., R.V. and D.D.B.; writing—original draft preparation, L.A., E.L., L.D.C.M. and D.D.B.; writing—review and editing, L.A., E.L., C.L., M.F., C.P., L.B., L.D.C.M., A.S., G.M., C.B., C.G., R.V. and D.D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the contributions of University of Camerino (Fondo di ricerca di Ateneo and Progetto FAR FPI000042).
Acknowledgments
We thank the Italian Ministry of Instruction, University and Research and the University of Pisa, Florence and Camerino for the support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- de Souza, H.S.; Fiocchi, C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current state of the art. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielefeldt, K.; Davis, B.; Binion, D.G. Pain and inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2009, 15, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeitz, J.; Ak, M.; Muller-Mottet, S.; Scharl, S.; Biedermann, L.; Fournier, N.; Frei, P.; Pittet, V.; Scharl, M.; Fried, M.; et al. Pain in IBD Patients: Very Frequent and Frequently Insufficiently Taken into Account. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Del Tacca, M.; Blandizzi, C. Regulation of enteric functions by adenosine: Pathophysiological and pharmacological implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 120, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Csoka, B.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Kokai, E.; Blandizzi, C.; Hasko, G. Adenosine and inflammation: What’s new on the horizon? Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1051–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Colucci, R.; Pellegrini, C.; Giustarini, G.; Tuccori, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Fornai, M. The role of purinergic pathways in the pathophysiology of gut diseases: Pharmacological modulation and potential therapeutic applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 157–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Ben, D.; Antonioli, L.; Lambertucci, C.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Volpini, R. Purinergic Ligands as Potential Therapeutic Tools for the Treatment of Inflammation-Related Intestinal Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Ben, D.; Antonioli, L.; Lambertucci, C.; Spinaci, A.; Fornai, M.; D’Antongiovanni, V.; Pellegrini, C.; Blandizzi, C.; Volpini, R. Approaches for designing and discovering purinergic drugs for gastrointestinal diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2020, 15, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, S.L.; Federico, S.; Venkatesan, G.; Mandel, A.L.; Shao, Y.M.; Moro, S.; Spalluto, G.; Pastorin, G. The A3 adenosine receptor as multifaceted therapeutic target: Pharmacology, medicinal chemistry, and in silico approaches. Med. Res. Rev. 2013, 33, 235–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Merighi, S.; Varani, K.; Borea, P.A.; Baraldi, S.; Aghazadeh Tabrizi, M.; Romagnoli, R.; Baraldi, P.G.; Ciancetta, A.; Tosh, D.K.; et al. A3 Adenosine Receptors as Modulators of Inflammation: From Medicinal Chemistry to Therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 38, 1031–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.H.; Lv, M.M.; An, X.M.; Leung, W.K.; Seto, W.K. Activation of adenosine A3 receptor inhibits inflammatory cytokine production in colonic mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis by down-regulating the nuclear factor-kappa B signaling. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, T.; Tian, T.; Feng, X.; Ye, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, W.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, C.; He, Y.; Zeng, J.; et al. An adenosine A3 receptor agonist inhibits DSS-induced colitis in mice through modulation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Xiang, H.; Yu, L.; Su, W.; Shu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Lin, L.; Hu, X.; Liang, S.; et al. Electroacupuncture inhibits visceral pain via adenosine receptors in mice with inflammatory bowel disease. Purinergic Signal. 2019, 15, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppi, E.; Cherchi, F.; Fusco, I.; Failli, P.; Vona, A.; Dettori, I.; Gaviano, L.; Lucarini, E.; Jacobson, K.A.; Tosh, D.K.; et al. Adenosine A3 receptor activation inhibits pronociceptive N-type Ca2+ currents and cell excitability in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Pain 2019, 160, 1103–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucarini, E.; Coppi, E.; Micheli, L.; Parisio, C.; Vona, A.; Cherchi, F.; Pugliese, A.M.; Pedata, F.; Failli, P.; Palomino, S.; et al. Acute visceral pain relief mediated by A3AR agonists in rats: Involvement of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels. Pain 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Awwad, O.; Bin, A.; Zoppellaro, C.; Castagliuolo, I.; Gaion, R.M.; et al. Control of enteric neuromuscular functions by purinergic A3 receptors in normal rat distal colon and experimental bowel inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 856–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpini, R.; Buccioni, M.; Dal Ben, D.; Lambertucci, C.; Lammi, C.; Marucci, G.; Ramadori, A.T.; Klotz, K.-N.; Cristalli, G. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-alkynyl-N6-methyl-5’-N-methylcarboxamidoadenosine derivatives as potent and highly selective agonists for the human adenosine A3 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7897–7900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Ben, D.; Buccioni, M.; Lambertucci, C.; Marucci, G.; Thomas, A.; Volpini, R.; Cristalli, G. Molecular modeling study on potent and selective adenosine A3 receptor agonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7923–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccioni, M.; Dal Ben, D.; Lambertucci, C.; Marti Navia, A.; Ricciutelli, M.; Spinaci, A.; Volpini, R.; Marucci, G. New sensible method to quantize the intestinal absorption of receptor ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3328–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Ghisu, N.; Da Settimo, F.; Natale, G.; Kastsiuchenka, O.; Duranti, E.; Virdis, A.; Vassalle, C.; et al. Inhibition of adenosine deaminase attenuates inflammation in experimental colitis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisio, C.; Lucarini, E.; Micheli, L.; Toti, A.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Antonini, G.; Panizzi, E.; Maidecchi, A.; Giovagnoni, E.; Lucci, J.; et al. Researching New Therapeutic Approaches for Abdominal Visceral Pain Treatment: Preclinical Effects of an Assembled System of Molecules of Vegetal Origin. Nutrients 2019, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Awwad, O.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Del Tacca, M.; Blandizzi, C. Differential recruitment of high affinity A1 and A2A adenosine receptors in the control of colonic neuromuscular function in experimental colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Awwad, O.; Ghisu, N.; Tuccori, M.; Da Settimo, F.; La Motta, C.; Natale, G.; Duranti, E.; et al. The blockade of adenosine deaminase ameliorates chronic experimental colitis through the recruitment of adenosine A2A and A3 receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, C.; Fornai, M.; Colucci, R.; Benvenuti, L.; D’Antongiovanni, V.; Natale, G.; Fulceri, F.; Giorgis, M.; Marini, E.; Gastaldi, S.; et al. A Comparative Study on the Efficacy of NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Inhibitors in a Pre-clinical Model of Bowel Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, J.A.; Gebhart, G.F. Assessment of colon sensitivity by luminal distension in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2624–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.H.; Moro, S.; Melman, N.; Ji, X.D.; Jacobson, K.A. Structure-activity relationships and molecular modeling of 3, 5-diacyl-2,4-dialkylpyridine derivatives as selective A3 adenosine receptor antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3186–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekic, C.; Linden, J. Purinergic regulation of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonioli, L.; Blandizzi, C.; Pacher, P.; Hasko, G. The Purinergic System as a Pharmacological Target for the Treatment of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 345–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabley, J.; Soriano, F.; Pacher, P.; Hasko, G.; Marton, A.; Wallace, R.; Salzman, A.; Szabo, C. The adenosine A3 receptor agonist, N6-(3-iodobenzyl)-adenosine-5’-N-methyluronamide, is protective in two murine models of colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 466, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, I.C.; Castro, M.V.; Barreto, A.R.; Sullivan, G.W.; Vale, M.; Almeida, P.R.; Linden, J.; Rieger, J.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; Guerrant, R.L.; et al. Effect of novel A2A adenosine receptor agonist ATL 313 on Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced murine ileal enteritis. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 2606–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, J.; Yu, J.G.; Suntres, Z.; Bozarov, A.; Cooke, H.; Javed, N.; Auer, H.; Palatini, J.; Hassanain, H.H.; Cardounel, A.J.; et al. ADOA3R as a therapeutic target in experimental colitis: Proof by validated high-density oligonucleotide microarray analysis. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2006, 12, 766–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odashima, M.; Bamias, G.; Rivera-Nieves, J.; Linden, J.; Nast, C.C.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Marini, M.; Sugawara, K.; Kozaiwa, K.; Otaka, M.; et al. Activation of A2A Adenosine Receptor Attenuates Intestinal Inflammation in Animal Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.; Sanmugalingam, D.; Burton, V.J.; Wilson, T.; Pearson, R.; Watson, R.P.; Smith, P.; Parkinson, S.J. Impairment of adenosine A3 receptor activity disrupts neutrophil migratory capacity and impacts innate immune function in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 3358–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasko, G.; Xu, D.Z.; Lu, Q.; Nemeth, Z.H.; Jabush, J.; Berezina, T.L.; Zaets, S.B.; Csoka, B.; Deitch, E.A. Adenosine A2A receptor activation reduces lung injury in trauma/hemorrhagic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 34, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minderhoud, I.M.; Oldenburg, B.; Wismeijer, J.A.; van Berge Henegouwen, G.P.; Smout, A.J. IBS-like symptoms in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in remission; relationships with quality of life and coping behavior. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keohane, J.; O’Mahony, C.; O’Mahony, L.; O’Mahony, S.; Quigley, E.M.; Shanahan, F. Irritable bowel syndrome-type symptoms in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A real association or reflection of occult inflammation? Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpin, S.J.; Ford, A.C. Prevalence of symptoms meeting criteria for irritable bowel syndrome in inflammatory bowel disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 107, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, B.G.; Sandborn, W.J.; Ruel, J.; Feagan, B.G.; Sands, B.E.; Colombel, J.F. Converging goals of treatment of inflammatory bowel disease from clinical trials and practice. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 37–51.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, M.; Greer, J.B.; Szigethy, E. Etiology and Treatment of Pain and Psychosocial Issues in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 430–439.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombel, J.F.; Narula, N.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Management Strategies to Improve Outcomes of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 351–361.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunkemeier, D.M.; Cassara, J.E.; Dalton, C.B.; Drossman, D.A. The narcotic bowel syndrome: Clinical features, pathophysiology, and management. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilleri, M.; Lembo, A.; Katzka, D.A. Opioids in Gastroenterology: Treating Adverse Effects and Creating Therapeutic Benefits. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinath, A.; Young, E.; Szigethy, E. Pain management in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Translational approaches from bench to bedside. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 2433–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, S.M.; Linden, D.R. Neuroplasticity and dysfunction after gastrointestinal inflammation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiller, R.; Major, G. IBS and IBD—Separate entities or on a spectrum? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Soto, W.; Gulbransen, B.D. Enteric Glia: A New Player in Abdominal Pain. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Chen, L.H.; Xing, C.; Liu, T. Pain regulation by gut microbiota: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zylka, M.J. Pain-relieving prospects for adenosine receptors and ectonucleotidases. Trends Mol. Med. 2011, 17, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawynok, J. Adenosine receptor targets for pain. Neuroscience 2016, 338, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, K.; Vincenzi, F.; Targa, M.; Paradiso, B.; Parrilli, A.; Fini, M.; Lanza, G.; Borea, P.A. The stimulation of A3 adenosine receptors reduces bone-residing breast cancer in a rat preclinical model. Eur. J. Cancer. 2013, 49, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, J.W.; Ford, A.; Symons-Liguori, A.M.; Chen, Z.; Janes, K.; Doyle, T.; Xie, J.; Luongo, L.; Tosh, D.K.; Maione, S.; et al. Endogenous adenosine A3 receptor activation selectively alleviates persistent pain states. Brain 2015, 138, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, K.; Symons-Liguori, A.M.; Jacobson, K.A.; Salvemini, D. Identification of A3 adenosine receptor agonists as novel non-narcotic analgesics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 1253–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, E.; Feng, C.; Zhao, X. Role of A3 adenosine receptor in diabetic neuropathy. J. Neurosci. Res. 2016, 94, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willert, R.P.; Woolf, C.J.; Hobson, A.R.; Delaney, C.; Thompson, D.G.; Aziz, Q. The development and maintenance of human visceral pain hypersensitivity is dependent on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, T.K.; Basso, L.; Iftinca, M.C.; Flynn, R.; Chapman, K.; Dietrich, G.; Vergnolle, N.; Altier, C. TRPV1 sensitization mediates postinflammatory visceral pain following acute colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G87–G99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhart, G.F.; Bielefeldt, K. Physiology of Visceral Pain. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1609–1633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, A.M.; Coppi, E.; Spalluto, G.; Corradetti, R.; Pedata, F. A3 adenosine receptor antagonists delay irreversible synaptic failure caused by oxygen and glucose deprivation in the rat CA1 hippocampus in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Laties, A.M.; Mitchell, C.H. Balance of purines may determine life or death of retinal ganglion cells as A3 adenosine receptors prevent loss following P2X7 receptor stimulation. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X.; Lu, W.; Lim, J.; Eysteinsson, T.; Jacobson, K.A.; Laties, A.M.; Mitchell, C.H. The A3 adenosine receptor attenuates the calcium rise triggered by NMDA receptors in retinal ganglion cells. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Oliver, M.; Diaz-Rios, M. Using caffeine and other adenosine receptor antagonists and agonists as therapeutic tools against neurodegenerative diseases: A review. Life Sci. 2014, 101, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucarini, E.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Micheli, L.; Trallori, E.; Antonioli, L.; Fornai, M.; Blandizzi, C.; Ghelardini, C. P060 Post-inflammatory visceral pain induced by DNBS: Preclinical features for novel therapeutics. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).