Does Siponimod Exert Direct Effects in the Central Nervous System?
Abstract
1. Introduction
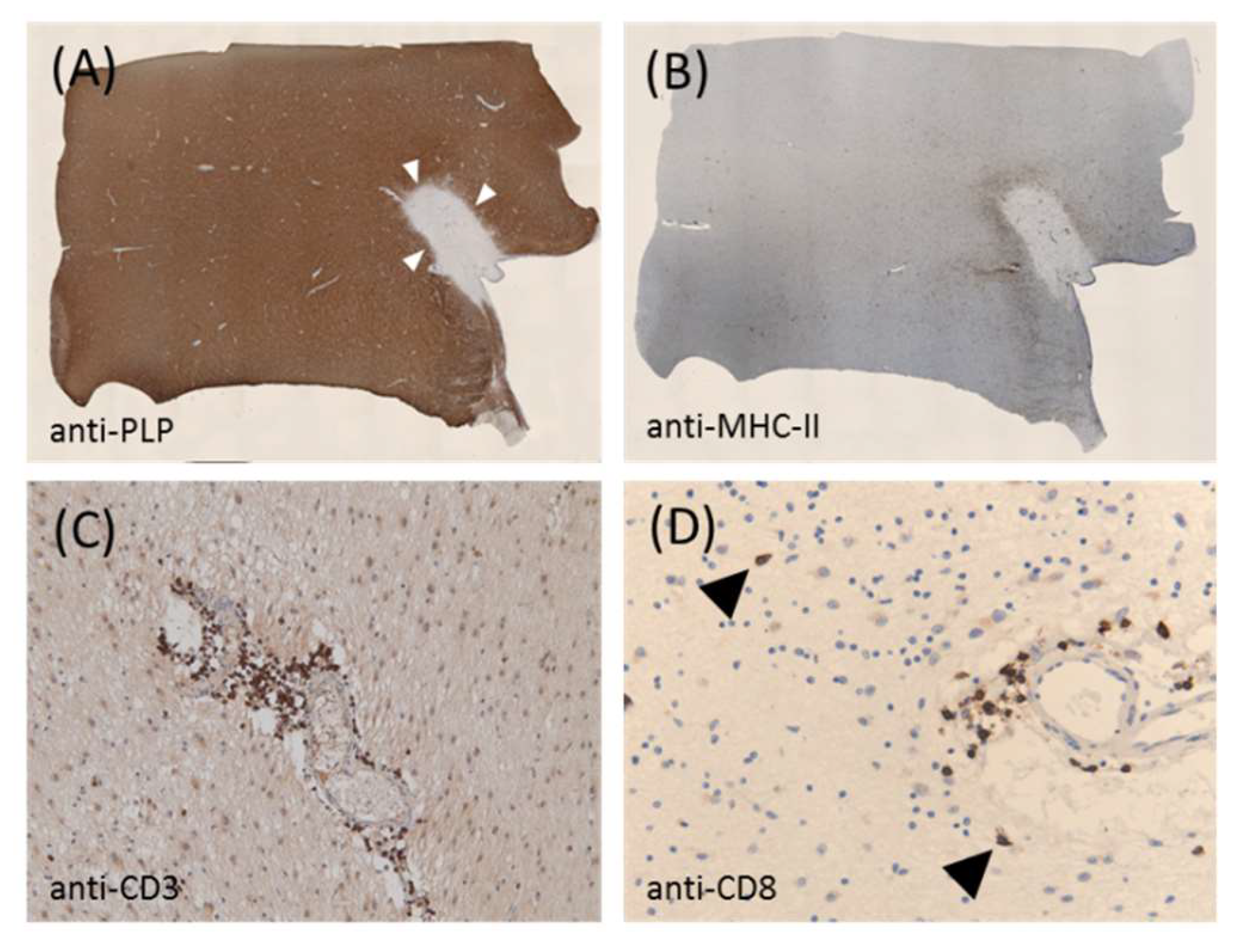
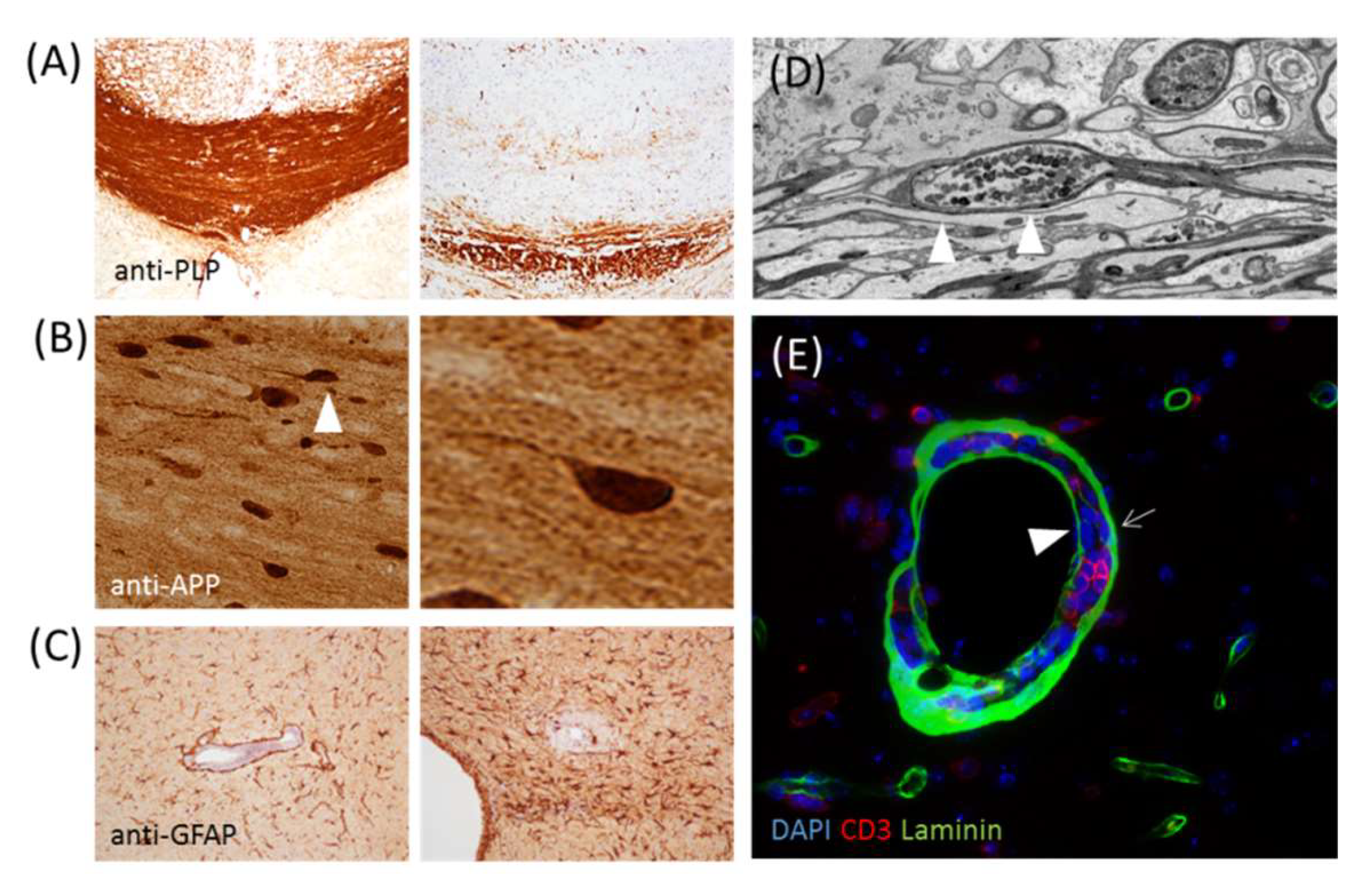
2. General Aspects of MS Pathology and the Relevance of Glial Cells
3. Sphingosine-1 Phosphate Signaling
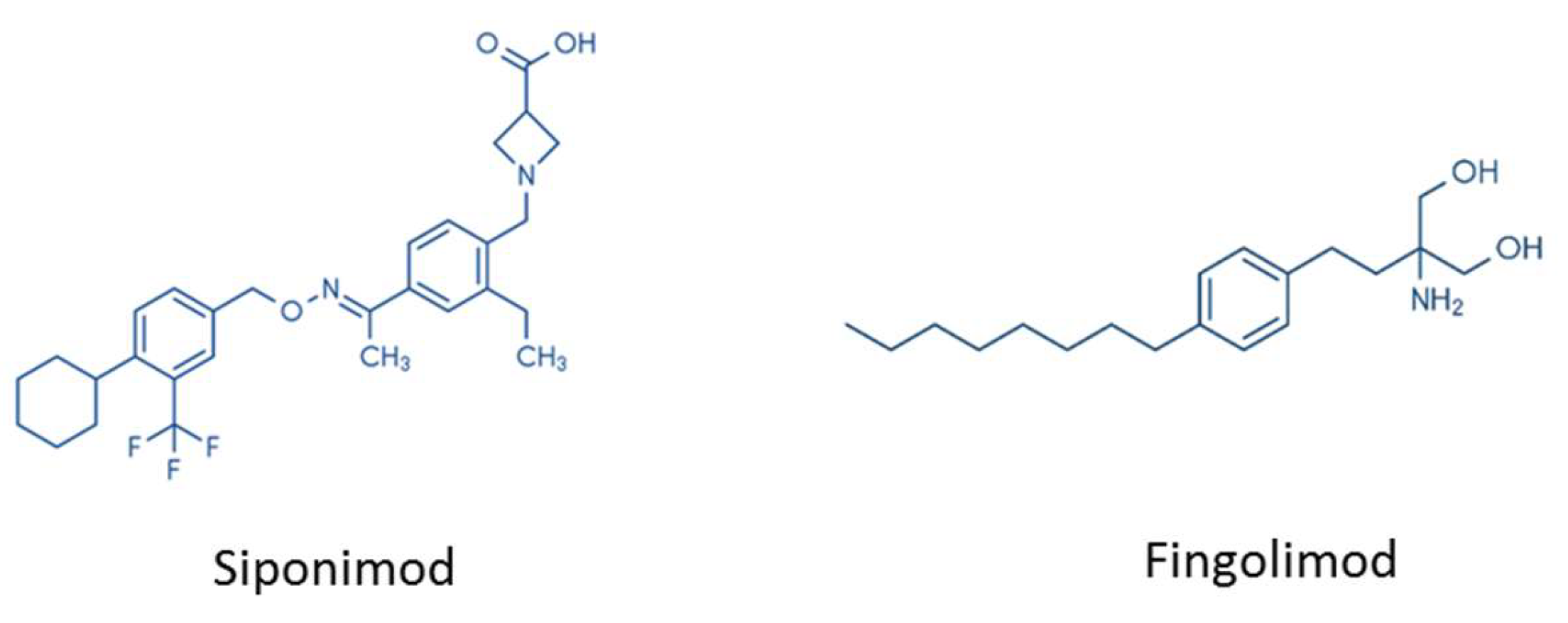
4. From FTY720 to Siponimod
5. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kappos, L.; Bar-Or, A.; Cree, B.A.C.; Fox, R.J.; Giovannoni, G.; Gold, R.; Vermersch, P.; Arnold, D.L.; Arnould, S.; Scherz, T.; et al. Siponimod versus placebo in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis (EXPAND): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalban, X.; Hauser, S.L.; Kappos, L.; Arnold, D.L.; Bar-Or, A.; Comi, G.; de Seze, J.; Giovannoni, G.; Hartung, H.P.; Hemmer, B.; et al. Ocrelizumab versus Placebo in Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idzko, M.; Panther, E.; Corinti, S.; Morelli, A.; Ferrari, D.; Herouy, Y.; Dichmann, S.; Mockenhaupt, M.; Gebicke-Haerter, P.; Di Virgilio, F.; et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces chemotaxis of immature and modulates cytokine-release in mature human dendritic cells for emergence of Th2 immune responses. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2002, 16, 625–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durafourt, B.A.; Lambert, C.; Johnson, T.A.; Blain, M.; Bar-Or, A.; Antel, J.P. Differential responses of human microglia and blood-derived myeloid cells to FTY720. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 230, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brana, C.; Frossard, M.J.; Pescini Gobert, R.; Martinier, N.; Boschert, U.; Seabrook, T.J. Immunohistochemical detection of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and 5 in human multiple sclerosis lesions. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2014, 40, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, H.; Akiyama, T.; Irei, I.; Hamazaki, S.; Sadahira, Y. Cellular localization of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 expression in the human central nervous system. J. Histochem. Cytochem. J. Histochem. Soc. 2010, 58, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tham, C.S.; Lin, F.F.; Rao, T.S.; Yu, N.; Webb, M. Microglial activation state and lysophospholipid acid receptor expression. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. J. Int. Soc. Dev. Neurosci. 2003, 21, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Mizuno, T.; Suzumura, A. Fingolimod phosphate promotes the neuroprotective effects of microglia. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 256, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, R.P.; Payne, S.G.; Bittman, R.; Spiegel, S.; Sato-Bigbee, C. The immunomodulator FTY720 has a direct cytoprotective effect in oligodendrocyte progenitors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, L.; Zrzavy, T.; Hametner, S.; Höftberger, R.; Bagnato, F.; Grabner, G.; Trattnig, S.; Pfeifenbring, S.; Brück, W.; Lassmann, H. The topograpy of demyelination and neurodegeneration in the multiple sclerosis brain. Brain J. Neurol. 2016, 139, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, D.S.; Zackowski, K.M.; Gordon-Lipkin, E.M.; Smith, S.A.; Chodkowski, B.A.; Cutter, G.R.; Calabresi, P.A. Corticospinal tract abnormalities are associated with weakness in multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirko, I.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Sriram, S.; Bakshi, R. Gray matter involvement in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2007, 68, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchinetti, C.F.; Popescu, B.F.; Bunyan, R.F.; Moll, N.M.; Roemer, S.F.; Lassmann, H.; Brück, W.; Parisi, J.E.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Giannini, C.; et al. Inflammatory cortical demyelination in early multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2188–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiljan, S.; Preziosa, P.; Jonkman, L.E.; van de Berg, W.D.; Twisk, J.; Pouwels, P.J.; Schenk, G.J.; Rocca, M.A.; Filippi, M.; Geurts, J.J.; et al. Cortical axonal loss is associated with both gray matter demyelination and white matter tract pathology in progressive multiple sclerosis: Evidence from a combined MRI-histopathology study. Mult. Scler. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, L.; Velmeshev, D.; Holmqvist, S.; Kaufmann, M.; Werneburg, S.; Jung, D.; Vistnes, S.; Stockley, J.H.; Young, A.; Steindel, M.; et al. Neuronal vulnerability and multilineage diversity in multiple sclerosis. Nature 2019, 573, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, W.J.; Solanky, B.; Prados, F.; Yiannakas, M.; Da Mota, P.; Riemer, F.; Cardoso, M.J.; Ourselin, S.; Golay, X.; Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott, C.; et al. Cortical grey matter sodium accumulation is associated with disability and secondary progressive disease course in relapse-onset multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, D.; Gruchot, J.; Weyers, V.; Oldemeier, L.; Göttle, P.; Healy, L.; Ho Jang, J.; Kang, T.X.Y.; Volsko, C.; Dutta, R.; et al. pHERV-W envelope protein fuels microglial cell-dependent damage of myelinated axons in multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 15216–15225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, K.R.; Nakamura, K.; Cohen, J.A.; Trapp, B.D.; Ontaneda, D. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Mechanisms of Thalamic Pathology in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reali, C.; Magliozzi, R.; Roncaroli, F.; Nicholas, R.; Howell, O.W.; Reynolds, R. B cell rich meningeal inflammation associates with increased spinal cord pathology in multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lorenzo, S.; Konings, J.; van der Pol, S.; Kamermans, A.; Amor, S.; van Horssen, J.; Witte, M.E.; Kooij, G.; de Vries, H.E. Inflammation of the choroid plexus in progressive multiple sclerosis: Accumulation of granulocytes and T cells. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, C.; Belachew, S.; Wolinsky, J.S.; Hauser, S.L.; Kappos, L.; Barkhof, F.; Bernasconi, C.; Fecker, J.; Model, F.; Wei, W.; et al. Chronic white matter lesion activity predicts clinical progression in primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain J. Neurol. 2019, 142, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krysko, K.M.; Henry, R.G.; Cree, B.A.C.; Lin, J.; Caillier, S.; Santaniello, A.; Zhao, C.; Gomez, R.; Bevan, C.; Smith, D.L.; et al. Telomere Length Is Associated with Disability Progression in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.C.; Kim, K.; Smith, M.D.; Aston, S.A.; Fioravante, N.; Rothman, A.M.; Krieger, S.; Cofield, S.S.; Kimbrough, D.J.; Bhargava, P.; et al. Early complement genes are associated with visual system degeneration in multiple sclerosis. Brain J. Neurol. 2019, 142, 2722–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, F.; Gauthier, S.A.; Laule, C.; Moore, G.R.W.; Bove, R.; Cai, Z.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Harrison, D.M.; Klawiter, E.C.; Morrow, S.A.; et al. Imaging Mechanisms of Disease Progression in Multiple Sclerosis: Beyond Brain Atrophy. J. Neuroimaging Off. J. Am. Soc. Neuroimaging 2020, 30, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambe, J.; Saidha, S.; Bermel, R.A. Optical coherence tomography and multiple sclerosis: Update on clinical application and role in clinical trials. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, A.V.; Ljungberg, E.; Vavasour, I.M.; Liu, H.; Johnson, P.; Rauscher, A.; Kramer, J.L.K.; Tam, R.; Li, D.K.B.; Laule, C.; et al. Rapid myelin water imaging for the assessment of cervical spinal cord myelin damage. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 23, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, V.T.; Herranz, E.; Treaba, C.A.; Ouellette, R.; Mehndiratta, A.; Loggia, M.L.; Klawiter, E.C.; Ionete, C.; Jacob, S.A.; Mainero, C. Evidence of diffuse cerebellar neuroinflammation in multiple sclerosis by (11)C-PBR28 MR-PET. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra Corral, M.A.; Govindarajan, S.T.; Stefancin, P.; Bangiyev, L.; Coyle, P.K.; Duong, T.Q. Characterization of gray-matter multiple sclerosis lesions using double inversion recovery, diffusion, contrast-enhanced, and volumetric MRI. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2019, 31, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsig, J.; Porzgen, P.; Lund, S.; Schrattenholz, A.; Leist, M. The inflammatory transcriptome of reactive murine astrocytes and implications for their innate immune function. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 893–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Ciric, B.; Curtis, M.T.; Chen, W.J.; Rostami, A.; Zhang, G.X. A dual effect of ursolic acid to the treatment of multiple sclerosis through both immunomodulation and direct remyelination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9082–9093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, E.; Janssens, K.; Hermans, D.; Vandooren, J.; Van den Haute, C.; Schepers, M.; Vanmierlo, T.; Lambrichts, I.; van Horssen, J.; Baekelandt, V.; et al. Oncostatin M-induced astrocytic tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 drives remyelination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5028–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Gonzalez, I.; Miron, V.E. Astrocytes in myelination and remyelination. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 713, 134532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, S.; Meares, G.P.; Lin, S.X.; Pietruczyk, E.A.; Saher, G.; Spieth, L.; Nave, K.A.; Boullerne, A.I.; Lutz, S.E.; Benveniste, E.N.; et al. Liver kinase B1 depletion from astrocytes worsens disease in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Glia 2020, 68, 600–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allnoch, L.; Baumgärtner, W.; Hansmann, F. Impact of Astrocyte Depletion upon Inflammation and Demyelination in a Murine Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Bassani, C.; De Angelis, A.; Ruffini, F.; Ottoboni, L.; Comi, G.; Martino, G.; Farina, C. Siponimod (BAF312) Activates Nrf2 While Hampering NFκB in Human Astrocytes, and Protects From Astrocyte-Induced Neurodegeneration. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, M.A.; Clark, I.C.; Tjon, E.C.; Li, Z.; Zandee, S.E.J.; Couturier, C.P.; Watson, B.R.; Scalisi, G.; Alkwai, S.; Rothhammer, V.; et al. MAFG-driven astrocytes promote CNS inflammation. Nature 2020, 578, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Rothhammer, V.; Mayo, L.; Wheeler, M.A.; Tjon, E.C.; Zandee, S.E.J.; Blain, M.; de Lima, K.A.; Takenaka, M.C.; et al. Metabolic Control of Astrocyte Pathogenic Activity via cPLA2-MAVS. Cell 2019, 179, 1483–1498.e1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, M.; Clarner, T.; Dang, J.; Copray, S.; Beyer, C. The cuprizone animal model: New insights into an old story. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellessen, A.; Nyamoya, S.; Zendedel, A.; Slowik, A.; Wruck, C.; Beyer, C.; Fragoulis, A.; Clarner, T. Nrf2 deficiency increases oligodendrocyte loss, demyelination, neuroinflammation and axonal damage in an MS animal model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2020, 35, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draheim, T.; Liessem, A.; Scheld, M.; Wilms, F.; Weißflog, M.; Denecke, B.; Kensler, T.W.; Zendedel, A.; Beyer, C.; Kipp, M.; et al. Activation of the astrocytic Nrf2/ARE system ameliorates the formation of demyelinating lesions in a multiple sclerosis animal model. Glia 2016, 64, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzanowski, U.; Bhattarai, S.; Scheld, M.; Clarner, T.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Beyer, C.; Rohr, S.O.; Schmitz, C.; Hochstrasser, T.; Schweiger, F.; et al. Oligodendrocyte degeneration and concomitant microglia activation directs peripheral immune cells into the forebrain. Neurochem. Int. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, B.; Sorokin, L. The blood-brain and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers: Function and dysfunction. Semin. Immunopathol. 2009, 31, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsauer, M.; Krause, D.; Dermietzel, R. Angiogenesis of the blood-brain barrier in vitro and the function of cerebral pericytes. Faseb J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2002, 16, 1274–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.; Ling, A.K.; Hamm, S.; Voigt, K.; Oschmann, P.; Engelhardt, B. Interferon-beta stabilizes barrier characteristics of brain endothelial cells in vitro. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, M.A.; Sim, J.E.; Russell, J.H. TNFR1-dependent VCAM-1 expression by astrocytes exposes the CNS to destructive inflammation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 151, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolburg-Buchholz, K.; Mack, A.F.; Steiner, E.; Pfeiffer, F.; Engelhardt, B.; Wolburg, H. Loss of astrocyte polarity marks blood-brain barrier impairment during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, R.; Persaud, T.; Hu, X.; Karmally, S.; Shestopalov, V.I.; Dvoriantchikova, G.; Ivanov, D.; Nathanson, L.; Barnum, S.R.; Bethea, J.R. Transgenic inhibition of astroglial NF-kappa B improves functional outcome in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by suppressing chronic central nervous system inflammation. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 2628–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.L.; Manivasagam, S.; Smith, B.C.; Sim, J.; Vollmer, L.L.; Daniels, B.P.; Russell, J.H.; Klein, R.S. Astrocyte-T cell crosstalk regulates region-specific neuroinflammation. Glia 2020, 68, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, L.; Paolicelli, R.C. Microglia-Mediated Synapse Loss in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 2911–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangenberg, E.E.; Lee, R.J.; Najafi, A.R.; Rice, R.A.; Elmore, M.R.; Blurton-Jones, M.; West, B.L.; Green, K.N. Eliminating microglia in Alzheimer’s mice prevents neuronal loss without modulating amyloid-β pathology. Brain J. Neurol. 2016, 139, 1265–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, F.; Chu, X.; Zhang, B.; Liang, L.; Lu, G.; Ding, J.; Chen, S. EriB targeted inhibition of microglia activity attenuates MPP(+) induced DA neuron injury through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Brain 2018, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tröscher, A.R.; Wimmer, I.; Quemada-Garrido, L.; Köck, U.; Gessl, D.; Verberk, S.G.S.; Martin, B.; Lassmann, H.; Bien, C.G.; Bauer, J. Microglial nodules provide the environment for pathogenic T cells in human encephalitis. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szalay, G.; Martinecz, B.; Lénárt, N.; Környei, Z.; Orsolits, B.; Judák, L.; Császár, E.; Fekete, R.; West, B.L.; Katona, G.; et al. Microglia protect against brain injury and their selective elimination dysregulates neuronal network activity after stroke. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otxoa-de-Amezaga, A.; Miró-Mur, F.; Pedragosa, J.; Gallizioli, M.; Justicia, C.; Gaja-Capdevila, N.; Ruíz-Jaen, F.; Salas-Perdomo, A.; Bosch, A.; Calvo, M.; et al. Microglial cell loss after ischemic stroke favors brain neutrophil accumulation. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, M.; Eyo, U.B.; Xie, M.; Peng, J.; Bosco, D.B.; Umpierre, A.D.; Zhu, X.; Tian, D.S.; Xu, P.; Wu, L.J. Microglial P2Y12 Receptor Regulates Seizure-Induced Neurogenesis and Immature Neuronal Projections. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 9453–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.K.; Milner, R. A critical role for microglia in maintaining vascular integrity in the hypoxic spinal cord. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 26029–26037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamita, M.; Barnum, C.; Möbius, W.; Tansey, M.G.; Szymkowski, D.E.; Lassmann, H.; Probert, L. Therapeutic inhibition of soluble brain TNF promotes remyelination by increasing myelin phagocytosis by microglia. JCI Insight 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotter, M.R.; Li, W.W.; Zhao, C.; Franklin, R.J. Myelin impairs CNS remyelination by inhibiting oligodendrocyte precursor cell differentiation. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiola, A.S.; Ryu, J.K.; Bardehle, S.; Meyer-Franke, A.; Ang, K.K.; Wilson, C.; Baeten, K.M.; Hanspers, K.; Merlini, M.; Thomas, S.; et al. Transcriptional profiling and therapeutic targeting of oxidative stress in neuroinflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, M.; Parolisi, R.; Scaroni, F.; Bonfanti, E.; Gualerzi, A.; Gabrielli, M.; Kerlero de Rosbo, N.; Uccelli, A.; Giussani, P.; Viani, P.; et al. Detrimental and protective action of microglial extracellular vesicles on myelin lesions: Astrocyte involvement in remyelination failure. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 987–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.P.; Kam, T.I.; Panicker, N.; Kim, S.; Oh, Y.; Park, J.S.; Kwon, S.H.; Park, Y.J.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Park, H.; et al. Block of A1 astrocyte conversion by microglia is neuroprotective in models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skripuletz, T.; Hackstette, D.; Bauer, K.; Gudi, V.; Pul, R.; Voss, E.; Berger, K.; Kipp, M.; Baumgartner, W.; Stangel, M. Astrocytes regulate myelin clearance through recruitment of microglia during cuprizone-induced demyelination. Brain J. Neurol. 2013, 136, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawji, K.S.; Young, A.M.H.; Ghosh, T.; Michaels, N.J.; Mirzaei, R.; Kappen, J.; Kolehmainen, K.L.; Alaeiilkhchi, N.; Lozinski, B.; Mishra, M.K.; et al. Niacin-mediated rejuvenation of macrophage/microglia enhances remyelination of the aging central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhong, J.; Zhao, T.; Xie, Q.; Zhu, T.; Ma, F.; Tang, Q.; Zhou, B.; et al. Mfsd2a and Spns2 are essential for sphingosine-1-phosphate transport in the formation and maintenance of the blood-brain barrier. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Bleu, T.; Huang, W.; Hallmark, O.G.; Coughlin, S.R.; Goetzl, E.J. Identification of cDNAs encoding two G protein-coupled receptors for lysosphingolipids. FEBS Lett. 1997, 417, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeler, M.; Goetzl, E.J. Activation-regulated expression and chemotactic function of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors in mouse splenic T cells. Faseb J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2002, 16, 1874–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende, M.L.; Dreier, J.L.; Mandala, S.; Proia, R.L. Expression of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor, S1P1, on T-cells controls thymic emigration. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 15396–15401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, C.K.; Xiao, C.Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Omens, J.H.; Ishii, I.; Chun, J.; Brown, J.H. Sphingosine 1-phosphate S1P2 and S1P3 receptor-mediated Akt activation protects against in vivo myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H2944–H2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, C.K.; Brown, J.H. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signalling in the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 82, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupperman, E.; An, S.; Osborne, N.; Waldron, S.; Stainier, D.Y. A sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor regulates cell migration during vertebrate heart development. Nature 2000, 406, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, N.; Stainier, D.Y. Lipid receptors in cardiovascular development. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2003, 65, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, A.; Nishi, T.; Hisano, Y.; Fukui, H.; Yamaguchi, A.; Mochizuki, N. The sphingolipid transporter spns2 functions in migration of zebrafish myocardial precursors. Science 2009, 323, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wada, R.; Yamashita, T.; Mi, Y.; Deng, C.X.; Hobson, J.P.; Rosenfeldt, H.M.; Nava, V.E.; Chae, S.S.; Lee, M.J.; et al. Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandala, S.; Hajdu, R.; Bergstrom, J.; Quackenbush, E.; Xie, J.; Milligan, J.; Thornton, R.; Shei, G.J.; Card, D.; Keohane, C.; et al. Alteration of lymphocyte trafficking by sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonists. Science 2002, 296, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matloubian, M.; Lo, C.G.; Cinamon, G.; Lesneski, M.J.; Xu, Y.; Brinkmann, V.; Allende, M.L.; Proia, R.L.; Cyster, J.G. Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature 2004, 427, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.H.; Nomura, N.; Koprak, S.L.; Quackenbush, E.J.; Forrest, M.J.; Rosen, H. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonism impairs the efficiency of the local immune response by altering trafficking of naive and antigen-activated CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3662–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Sachs, T.; Asavaroengchai, W.; Bronson, R.; Sykes, M. Graft-versus-host disease can be separated from graft-versus-lymphoma effects by control of lymphocyte trafficking with FTY720. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawicka, E.; Zuany-Amorim, C.; Manlius, C.; Trifilieff, A.; Brinkmann, V.; Kemeny, D.M.; Walker, C. Inhibition of Th1- and Th2-mediated airway inflammation by the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonist FTY720. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 6206–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fairchild, R.L.; Heeger, P.S.; Valujskikh, A. Lymphoid sequestration of alloreactive memory CD4 T cells promotes cardiac allograft survival. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhler, T.; Schütz, M.; Budde, K.; Neumayer, H.H.; Waiser, J. Differential effects of single dose FTY720 on CD62L+ B-cells in stable renal allograft recipients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Mi, Y.; Pally, C.; Beerli, C.; Chen, A.; Guerini, D.; Hinterding, K.; Nuesslein-Hildesheim, B.; Tuntland, T.; Lefebvre, S.; et al. A monoselective sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 agonist prevents allograft rejection in a stringent rat heart transplantation model. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguchi, Y.; Andoh, A.; Yagi, Y.; Bamba, S.; Inatomi, O.; Tsujikawa, T.; Fujiyama, Y. The S1P receptor modulator FTY720 prevents the development of experimental colitis in mice. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 16, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maki, T.; Gottschalk, R.; Ogawa, N.; Monaco, A.P. Prevention and cure of autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice by continuous administration of FTY720. Transplantation 2005, 79, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, M.; Imayoshi, T.; Okumoto, T. Effect of FTY720, a novel immunosuppressant, on adjuvant- and collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 2000, 22, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, H.; Hirata, D.; Kamimura, T.; Sato, H.; Iwamoto, M.; Yoshio, T.; Masuyama, J.; Fujimura, A.; Kobayashi, E.; Kano, S.; et al. Effects of FTY720 in MRL-lpr/lpr mice: Therapeutic potential in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 707–716. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, M.; Tham, C.S.; Lin, F.F.; Lariosa-Willingham, K.; Yu, N.; Hale, J.; Mandala, S.; Chun, J.; Rao, T.S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonists attenuate relapsing-remitting experimental autoimmune encephalitis in SJL mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 153, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Sugahara, K.; Shimano, K.; Teshima, K.; Koyama, M.; Fukunari, A.; Chiba, K. FTY720, sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator, ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibition of T cell infiltration. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 2, 439–448. [Google Scholar]
- Mullershausen, F.; Craveiro, L.M.; Shin, Y.; Cortes-Cros, M.; Bassilana, F.; Osinde, M.; Wishart, W.L.; Guerini, D.; Thallmair, M.; Schwab, M.E.; et al. Phosphorylated FTY720 promotes astrocyte migration through sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappos, L.; Antel, J.; Comi, G.; Montalban, X.; O’Connor, P.; Polman, C.H.; Haas, T.; Korn, A.A.; Karlsson, G.; Radue, E.W. Oral fingolimod (FTY720) for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1124–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräler, M.H.; Goetzl, E.J. The immunosuppressant FTY720 down-regulates sphingosine 1-phosphate G-protein-coupled receptors. Faseb J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2004, 18, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinamon, G.; Matloubian, M.; Lesneski, M.J.; Xu, Y.; Low, C.; Lu, T.; Proia, R.L.; Cyster, J.G. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 promotes B cell localization in the splenic marginal zone. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, K.A.; Nichols, E.; Porter, G.; Cui, Y.; Keohane, C.A.; Hajdu, R.; Hale, J.; Neway, W.; Zaller, D.; Mandala, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonist FTY720-phosphate causes marginal zone B cell displacement. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 78, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magliozzi, R.; Howell, O.; Vora, A.; Serafini, B.; Nicholas, R.; Puopolo, M.; Reynolds, R.; Aloisi, F. Meningeal B-cell follicles in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis associate with early onset of disease and severe cortical pathology. Brain J. Neurol. 2007, 130, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magliozzi, R.; Howell, O.W.; Reeves, C.; Roncaroli, F.; Nicholas, R.; Serafini, B.; Aloisi, F.; Reynolds, R. A Gradient of neuronal loss and meningeal inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, N.; Lai, Y.; Tyndall, S.; Popolo, M.; Topalkara, K.; Pru, J.K.; Zhang, L.; Kim, H.; Liao, J.K.; Ding, K.; et al. Distribution of sphingosine kinase activity and mRNA in rodent brain. J. Neurochem. 2007, 103, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeilschifter, W.; Czech-Zechmeister, B.; Sujak, M.; Mirceska, A.; Koch, A.; Rami, A.; Steinmetz, H.; Foerch, C.; Huwiler, A.; Pfeilschifter, J. Activation of sphingosine kinase 2 is an endogenous protective mechanism in cerebral ischemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 413, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, N.C.; Wise, L.E.; Allegood, J.C.; O’Brien, M.; Avni, D.; Reeves, T.M.; Knapp, P.E.; Lu, J.; Luo, C.; Miles, M.F.; et al. Active, phosphorylated fingolimod inhibits histone deacetylases and facilitates fear extinction memory. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemann, B.; Kinzel, B.; Müller, M.; Reuschel, R.; Mechtcheriakova, D.; Urtz, N.; Bornancin, F.; Baumruker, T.; Billich, A. Sphingosine kinase type 2 is essential for lymphopenia induced by the immunomodulatory drug FTY720. Blood 2006, 107, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharel, Y.; Lee, S.; Snyder, A.H.; Sheasley-O’neill, S.L.; Morris, M.A.; Setiady, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zigler, M.A.; Burcin, T.L.; Ley, K.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 2 is required for modulation of lymphocyte traffic by FTY720. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36865–36872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechtcheriakova, D.; Wlachos, A.; Sobanov, J.; Bornancin, F.; Zlabinger, G.; Baumruker, T.; Billich, A. FTY720-phosphate is dephosphorylated by lipid phosphate phosphatase 3. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3063–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, G.; Maddelein, M.L.; Pucelle, M.; Nicaise, Y.; Maurage, C.A.; Duyckaerts, C.; Cuvillier, O.; Delisle, M.B. Neuronal sphingosine kinase 2 subcellular localization is altered in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bien-Möller, S.; Lange, S.; Holm, T.; Böhm, A.; Paland, H.; Küpper, J.; Herzog, S.; Weitmann, K.; Havemann, C.; Vogelgesang, S.; et al. Expression of S1P metabolizing enzymes and receptors correlate with survival time and regulate cell migration in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13031–13046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, I.; Alliod, C.; Martinier, N.; Newcombe, J.; Brana, C.; Pouly, S. Sphingosine kinase 1 and sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 are functionally upregulated on astrocytes under pro-inflammatory conditions. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doorn, R.; Van Horssen, J.; Verzijl, D.; Witte, M.; Ronken, E.; Van Het Hof, B.; Lakeman, K.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Van Der Valk, P.; Reijerkerk, A.; et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 and 3 are upregulated in multiple sclerosis lesions. Glia 2010, 58, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Jin, H.; Yue, X.; Luo, Z.; Liu, C.; Rosenberg, A.J.; Tu, Z. PET Imaging Study of S1PR1 Expression in a Rat Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Orengo, L.; Daniels, B.P.; Dorsey, D.; Basak, S.A.; Grajales-Reyes, J.G.; McCandless, E.E.; Piccio, L.; Schmidt, R.E.; Cross, A.H.; Crosby, S.D.; et al. Enhanced sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 expression underlies female CNS autoimmunity susceptibility. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2571–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Luo, Z.; Gu, J.; Jiang, H.; Joshi, S.; Shoghi, K.I.; Zhou, Y.; Gropler, R.J.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Tu, Z. In vivo Characterization of Four (18)F-Labeled S1PR1 Tracers for Neuroinflammation. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordana, M.T.; Cavalla, P.; Uccelli, A.; Laroni, A.; Bandini, F.; Vercellino, M.; Mancardi, G. Overexpression of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors on reactive astrocytes drives neuropathology of multiple sclerosis rebound after fingolimod discontinuation. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 24, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmaj, K.; Li, D.K.; Hartung, H.P.; Hemmer, B.; Kappos, L.; Freedman, M.S.; Stuve, O.; Rieckmann, P.; Montalban, X.; Ziemssen, T.; et al. Siponimod for patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (BOLD): An adaptive, dose-ranging, randomised, phase 2 study. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samjoo, I.A.; Worthington, E.; Haltner, A.; Cameron, C.; Nicholas, R.; Rouyrre, N.; Dahlke, F.; Adlard, N. Matching-adjusted indirect treatment comparison of siponimod and other disease modifying treatments in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lublin, F.; Miller, D.H.; Freedman, M.S.; Cree, B.A.C.; Wolinsky, J.S.; Weiner, H.; Lubetzki, C.; Hartung, H.P.; Montalban, X.; Uitdehaag, B.M.J.; et al. Oral fingolimod in primary progressive multiple sclerosis (INFORMS): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Gray, N.S.; Gao, W.; Mi, Y.; Fan, Y.; Wang, X.; Tuntland, T.; Che, J.; Lefebvre, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Discovery of BAF312 (Siponimod), a Potent and Selective S1P Receptor Modulator. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappos, L.; Radue, E.W.; O’Connor, P.; Polman, C.; Hohlfeld, R.; Calabresi, P.; Selmaj, K.; Agoropoulou, C.; Leyk, M.; Zhang-Auberson, L.; et al. A placebo-controlled trial of oral fingolimod in relapsing multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.A.; Barkhof, F.; Comi, G.; Hartung, H.P.; Khatri, B.O.; Montalban, X.; Pelletier, J.; Capra, R.; Gallo, P.; Izquierdo, G.; et al. Oral fingolimod or intramuscular interferon for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulak, R.O.; Rosenkranz, S.C.; Schaeffer, B.N.; Pinnschmidt, H.O.; Willems, S.; Heesen, C.; Hoffmann, B.A. Acute and long-term effects of fingolimod on heart rhythm and heart rate variability in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 19, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergely, P.; Nuesslein-Hildesheim, B.; Guerini, D.; Brinkmann, V.; Traebert, M.; Bruns, C.; Pan, S.; Gray, N.S.; Hinterding, K.; Cooke, N.G.; et al. The selective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator BAF312 redirects lymphocyte distribution and has species-specific effects on heart rate. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, A.; Colon-Moran, W.; Bhattarai, N. Characterization of the effects of immunomodulatory drug fingolimod (FTY720) on human T cell receptor signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundehege, P.; Cerina, M.; Eichler, S.; Thomas, C.; Herrmann, A.M.; Gobel, K.; Muntefering, T.; Fernandez-Orth, J.; Bock, S.; Narayanan, V.; et al. The next-generation sphingosine-1 receptor modulator BAF312 (siponimod) improves cortical network functionality in focal autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neural. Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1950–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.A.; Lee, D.S.; Sharma, A.; Wang, A.; Naouar, I.; Ma, X.I.; Pikor, N.; Nuesslein-Hildesheim, B.; Ramaglia, V.; Gommerman, J.L. Siponimod therapy implicates Th17 cells in a preclinical model of subpial cortical injury. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Mills, E.A.; Wang, Q.; Dowling, C.A.; Fisher, C.; Kirch, B.; Lundy, S.K.; Fox, D.A.; Mao-Draayer, Y. Siponimod enriches regulatory T and B lymphocytes in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. JCI Insight 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novgorodov, A.S.; El-Alwani, M.; Bielawski, J.; Obeid, L.M.; Gudz, T.I. Activation of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor S1P5 inhibits oligodendrocyte progenitor migration. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2007, 21, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terai, K.; Soga, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kamohara, M.; Ohno, K.; Yatsugi, S.; Okada, M.; Yamaguchi, T. Edg-8 receptors are preferentially expressed in oligodendrocyte lineage cells of the rat CNS. Neuroscience 2003, 116, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, A.; Kihara, Y.; Chun, J. Fingolimod: Direct CNS effects of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulation and implications in multiple sclerosis therapy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 328, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, A.; Musella, A.; Bullitta, S.; Fresegna, D.; De Vito, F.; Fantozzi, R.; Piras, E.; Gargano, F.; Borsellino, G.; Battistini, L.; et al. Siponimod (BAF312) prevents synaptic neurodegeneration in experimental multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobinger, T.; Manaenko, A.; Burkardt, P.; Beuscher, V.; Sprugel, M.I.; Roeder, S.S.; Bauerle, T.; Seyler, L.; Nagel, A.M.; Linker, R.A.; et al. Siponimod (BAF-312) Attenuates Perihemorrhagic Edema And Improves Survival in Experimental Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2019, 50, 3246–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelgesang, A.; Domanska, G.; Ruhnau, J.; Dressel, A.; Kirsch, M.; Schulze, J. Siponimod (BAF312) Treatment Reduces Brain Infiltration but Not Lesion Volume in Middle-Aged Mice in Experimental Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupino, L.; Perry, T.; Margielewska, S.; Hollows, R.; Ibrahim, M.; Care, M.; Allegood, J.; Tooze, R.; Sabbadini, R.; Reynolds, G.; et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signalling drives an angiogenic transcriptional programme in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2884–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Weaver, J.; Proudfoot, A.E.; Wujek, J.R.; Wei, T.; Richer, E.; Trapp, B.D.; Rao, A.; Ransohoff, R.M. Treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with the chemokine receptor antagonist Met-RANTES. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 128, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serizawa, K.; Tomizawa-Shinohara, H.; Magi, M.; Yogo, K.; Matsumoto, Y. Anti-IL-6 receptor antibody improves pain symptoms in mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018, 319, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaillard, C.; Harrison, S.; Stankoff, B.; Aigrot, M.S.; Calver, A.R.; Duddy, G.; Walsh, F.S.; Pangalos, M.N.; Arimura, N.; Kaibuchi, K.; et al. Edg8/S1P5: An oligodendroglial receptor with dual function on process retraction and cell survival. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.G.; Kim, H.J.; Miron, V.E.; Cook, S.; Kennedy, T.E.; Foster, C.A.; Antel, J.P.; Soliven, B. Functional consequences of S1P receptor modulation in rat oligodendroglial lineage cells. Glia 2007, 55, 1656–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipp, M.; Amor, S. FTY720 on the way from the base camp to the summit of the mountain: Relevance for remyelination. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannioui, A.; Vauzanges, Q.; Fini, J.B.; Henriet, E.; Sekizar, S.; Azoyan, L.; Thomas, J.L.; Pasquier, D.D.; Giovannangeli, C.; Demeneix, B.; et al. The Xenopus tadpole: An in vivo model to screen drugs favoring remyelination. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 24, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kipp, M. Does Siponimod Exert Direct Effects in the Central Nervous System? Cells 2020, 9, 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081771
Kipp M. Does Siponimod Exert Direct Effects in the Central Nervous System? Cells. 2020; 9(8):1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081771
Chicago/Turabian StyleKipp, Markus. 2020. "Does Siponimod Exert Direct Effects in the Central Nervous System?" Cells 9, no. 8: 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081771
APA StyleKipp, M. (2020). Does Siponimod Exert Direct Effects in the Central Nervous System? Cells, 9(8), 1771. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081771




