Genetic Variation in CNS Myelination and Functional Brain Connectivity in Recombinant Inbred Mice
Abstract
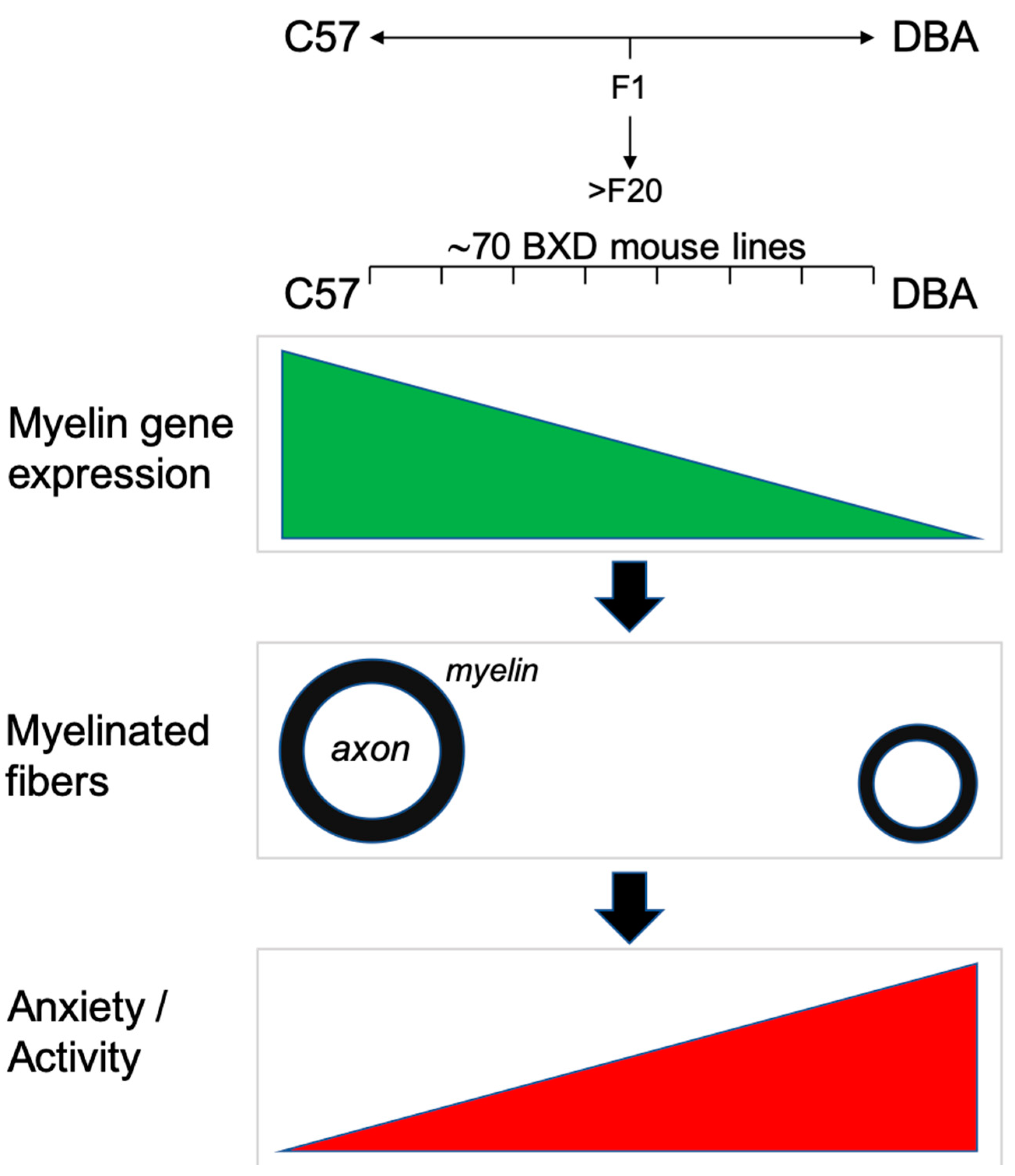
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clustering of BXD Gene Expression Data
2.2. Animals
2.3. Preparation of Brain Extracts
2.4. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and Quantitative PCR
2.5. Immunoblotting on Brain Extracts
2.6. Conduction Velocity Measurements
2.7. Electron Microscopy (EM) and Morphometric Analysis
2.8. Behavioral Measurements and Correlations with Myelin Expression Data from Hippocampus
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
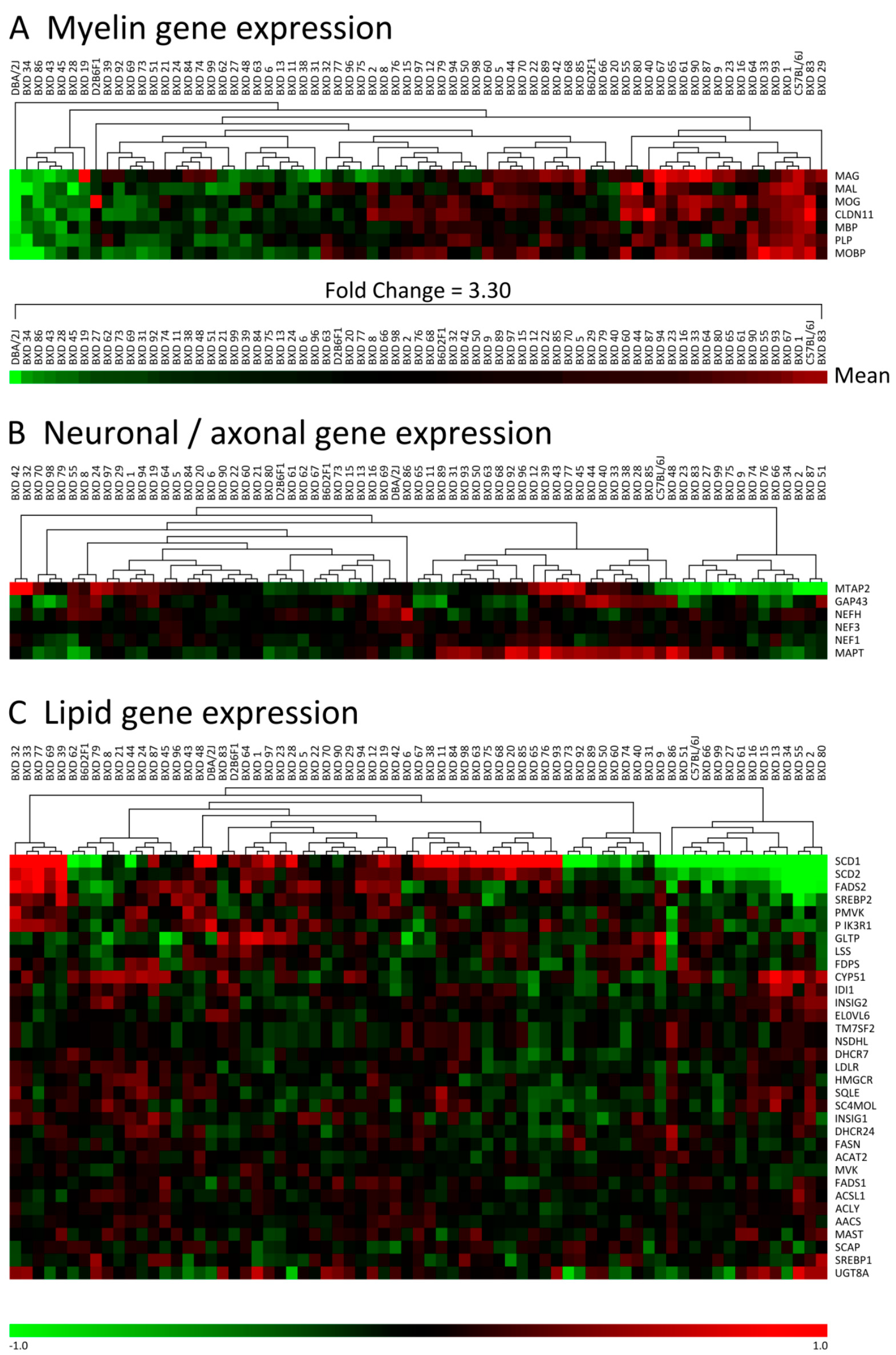
3.1. Myelin Gene Expression Shows Large Differences between C57, DBA and Their BXD Progeny
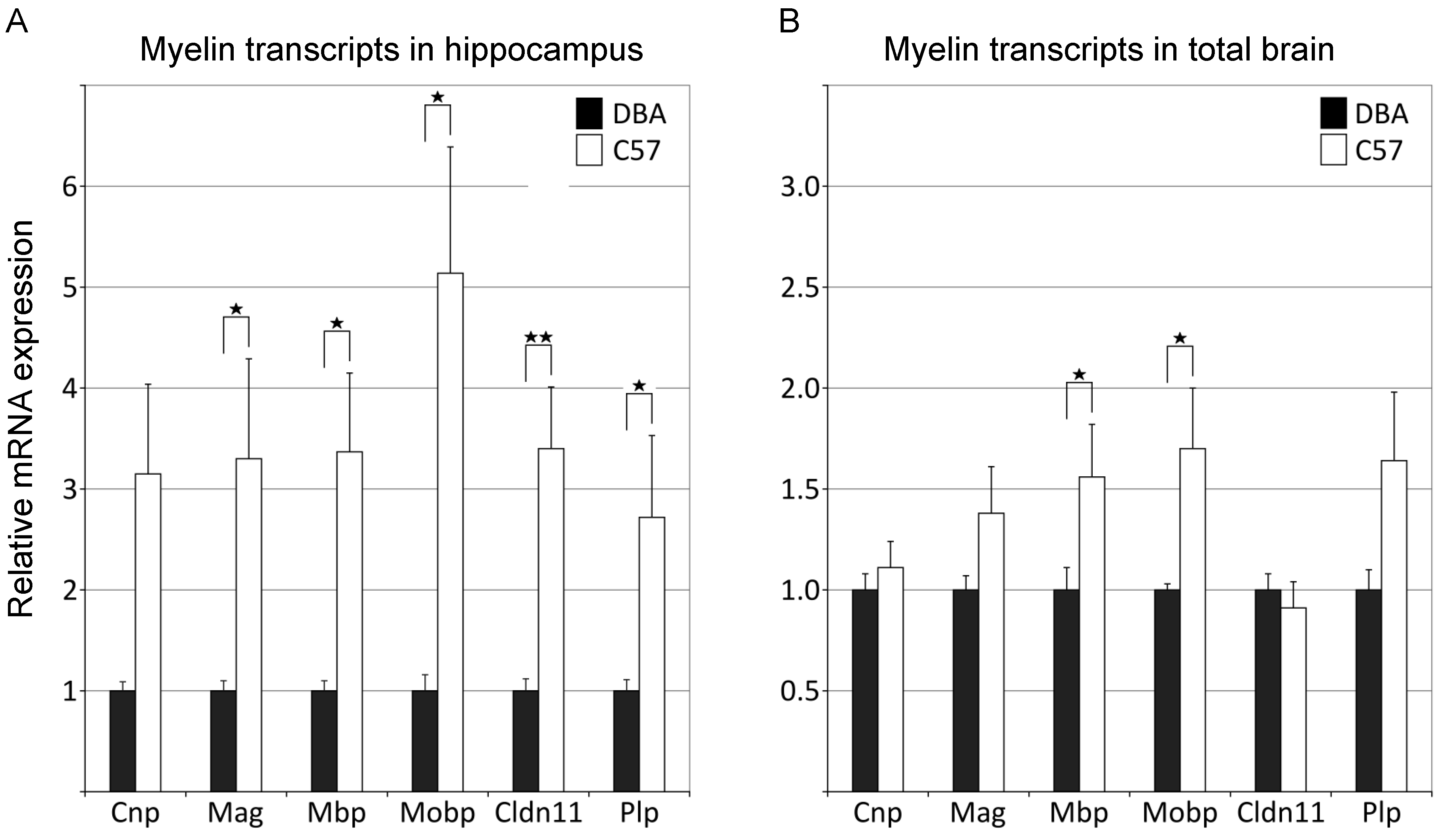
3.2. qPCR Analysis Independently Confirms Significant Differences in Myelin Gene Expression between C57 and DBA Mice
3.3. Protein Analysis Reveals Differences in Myelin Protein Expression between C57 and DBA Strains
3.4. Electron Microscopy (EM) Reveals Smaller Myelinated Fibers in DBA Mice
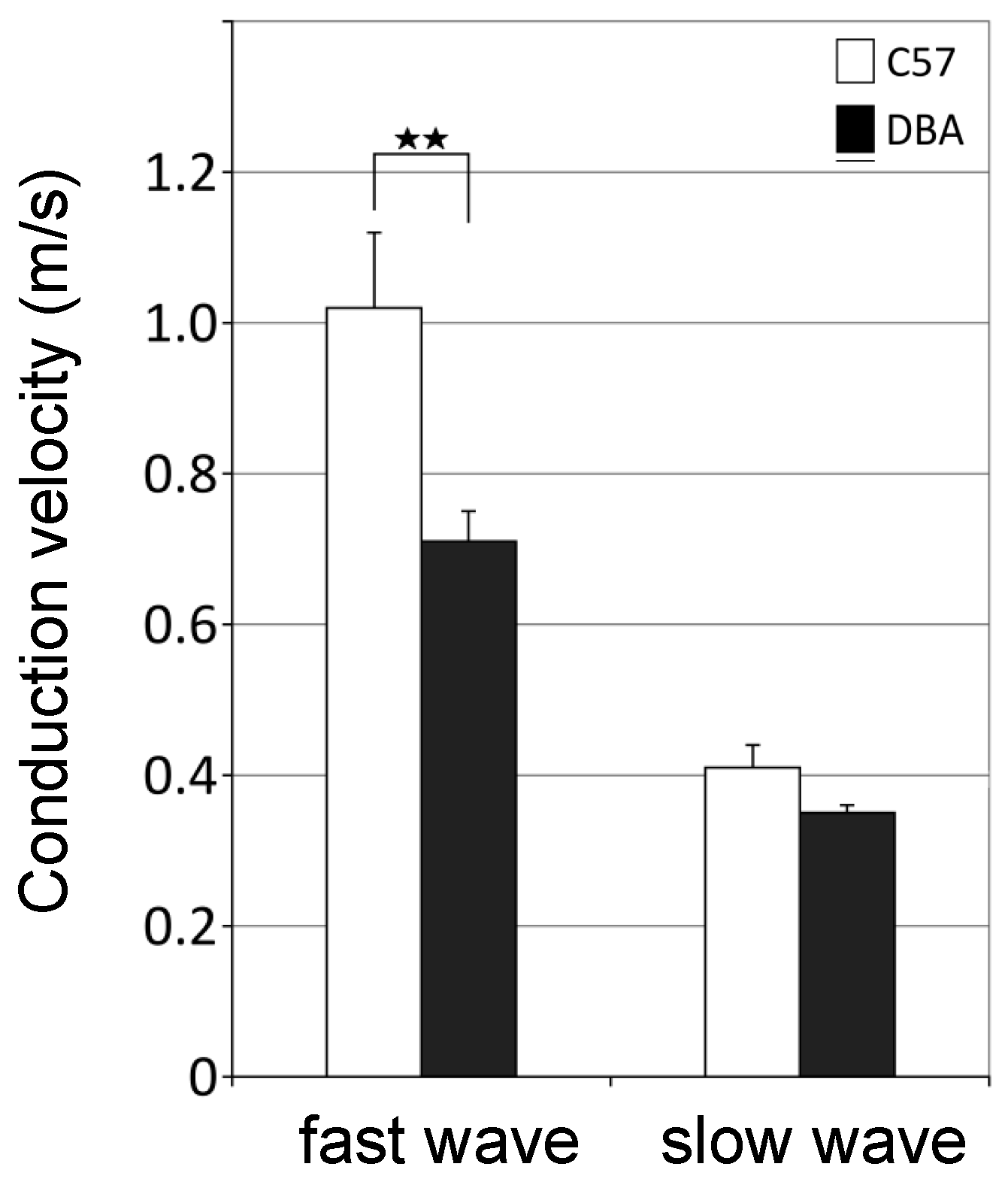
3.5. Higher Axonal Conduction Velocities in Myelinated Axons of C57 Mice
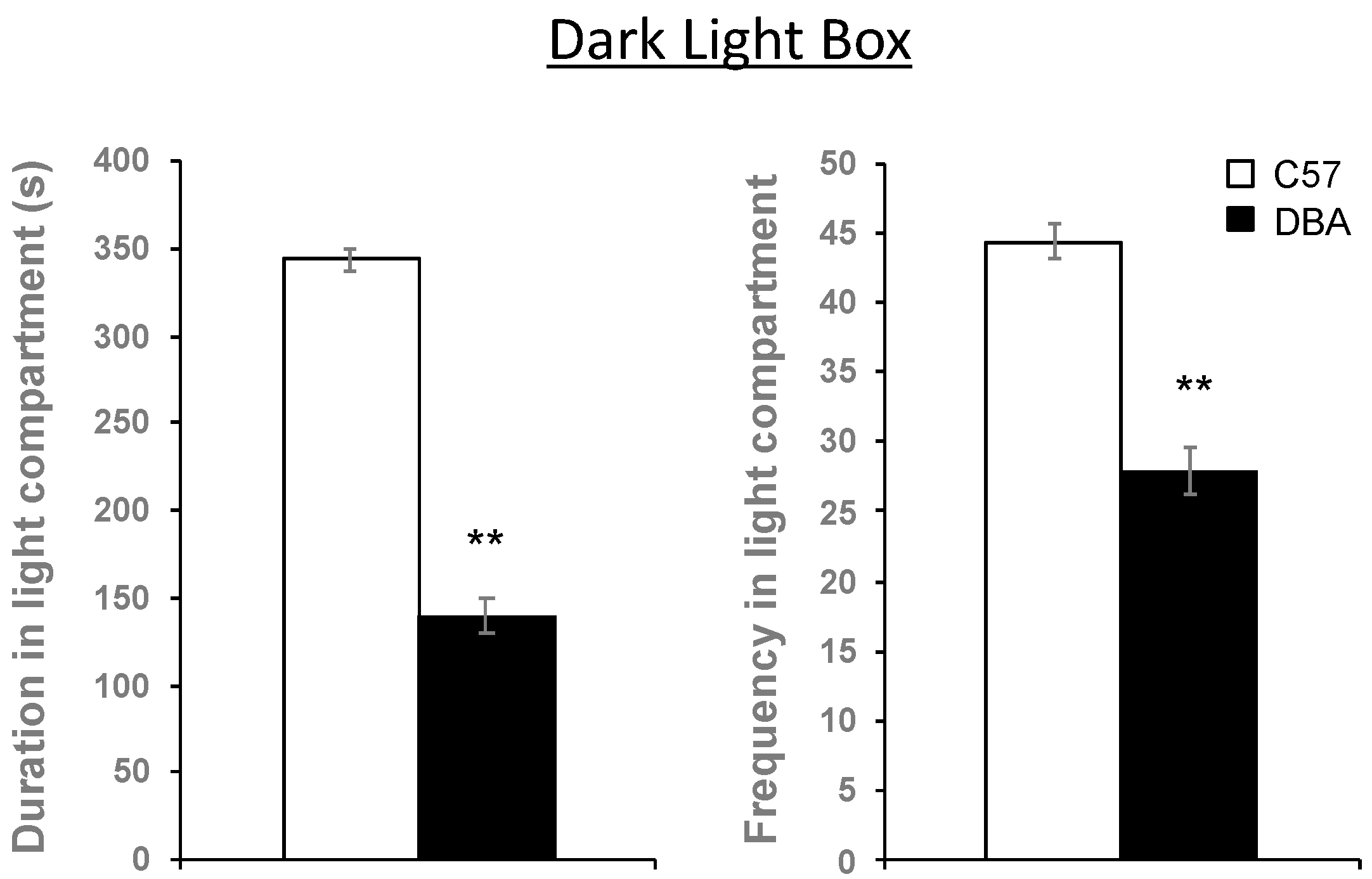
3.6. Hippocampal Myelin Gene Expression Correlates with Behavioral Traits in C57, DBA and Their BXD Progeny
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stadelmann, C.; Timmler, S.; Barrantes-Freer, A.; Simons, M. Myelin in the Central Nervous System: Structure, Function, and Pathology. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1381–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nave, K.A.; Werner, H.B. Myelination of the nervous system: Mechanisms and functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechler, M.E.; Swire, M.; Ffrench-Constant, C. Intrinsic and adaptive myelination-A sequential mechanism for smart wiring in the brain. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, C.W.; Monje, M. Wrapped to Adapt: Experience-Dependent Myelination. Neuron 2017, 95, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, R.D. A new mechanism of nervous system plasticity: Activity-dependent myelination. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, I.A.; Ohayon, D.; Li, H.; de Faria, J.P.; Emery, B.; Tohyama, K.; Richardson, W.D. Motor skill learning requires active central myelination. Science 2014, 346, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, R.D. White matter in learning, cognition and psychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci. 2008, 31, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.A.; Li, A.M.; Grutzendler, J. Lifelong cortical myelin plasticity and age-related degeneration in the live mammalian brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, E.G.; Orthmann-Murphy, J.L.; Langseth, A.J.; Bergles, D.E. Myelin remodeling through experience-dependent oligodendrogenesis in the adult somatosensory cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancucci, A. Neural correlates of cognitive ability. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.; Dicke, U. Evolution of the brain and intelligence in primates. Prog. Brain Res. 2012, 195, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filley, C.M.; Fields, R.D. White matter and cognition: Making the connection. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 116, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolov, B.P. Oligodendroglial abnormalities in schizophrenia, mood disorders and substance abuse. Comorbidity, shared traits, or molecular phenocopies? Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007, 10, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chou, K.H.; Chen, I.Y.; Fan, Y.T.; Decety, J.; Lin, C.P. Atypical development of white matter microstructure in adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Neurolmage 2010, 50, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y. Convergence and divergence in the etiology of myelin impairment in psychiatric disorders and drug addiction. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachev, D.; Mimmack, M.L.; Ryan, M.M.; Wayland, M.; Freeman, T.; Jones, P.B.; Starkey, M.; Webster, M.J.; Yolken, R.H.; Bahn, S. Oligodendrocyte dysfunction in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Lancet 2003, 362, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aston, C.; Jiang, L.; Sokolov, B.P. Transcriptional profiling reveals evidence for signaling and oligodendroglial abnormalities in the temporal cortex from patients with major depressive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarria-Siles, I.; White, T.; de Leeuw, C.; Goudriaan, A.; Lips, E.; Ehrlich, S.; Turner, J.A.; Calhoun, V.D.; Gollub, R.L.; Magnotta, V.A.; et al. Myelination-related genes are associated with decreased white matter integrity in schizophrenia. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 24, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goudriaan, A.; de Leeuw, C.; Ripke, S.; Hultman, C.M.; Sklar, P.; Sullivan, P.F.; Smit, A.B.; Posthuma, D.; Verheijen, M.H. Specific glial functions contribute to schizophrenia susceptibility. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, G.; Hauser, T.U.; Moutoussis, M.; Bullmore, E.T.; Goodyer, I.M.; Fonagy, P.; Jones, P.B.; Consortium, N.; Lindenberger, U.; Dolan, R.J. Compulsivity and impulsivity traits linked to attenuated developmental frontostriatal myelination trajectories. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Agrawal, A.; Bulik, C.M.; Andreassen, O.A.; Borglum, A.D.; Breen, G.; Cichon, S.; Edenberg, H.J.; Faraone, S.V.; Gelernter, J.; et al. Psychiatric genomics: An update and an agenda. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polderman, T.J.; Benyamin, B.; de Leeuw, C.A.; Sullivan, P.F.; van Bochoven, A.; Visscher, P.M.; Posthuma, D. Meta-analysis of the heritability of human traits based on fifty years of twin studies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreux, P.A.; Williams, E.G.; Koutnikova, H.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Champy, M.F.; Henry, H.; Schoonjans, K.; Williams, R.W.; Auwerx, J. Systems genetics of metabolism: The use of the BXD murine reference panel for multiscalar integration of traits. Cell 2012, 150, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, J.B.; Hill, A.E.; Burrage, L.C.; Olszens, K.R.; Song, J.; Justice, M.; O’Brien, W.E.; Conti, D.V.; Witte, J.S.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Genetic dissection of complex traits with chromosome substitution strains of mice. Science 2004, 304, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.W.; Gu, J.; Qi, S.; Lu, L. The genetic structure of recombinant inbred mice: High-resolution consensus maps for complex trait analysis. Genome. Biol. 2001, 2, RESEARCH0046. [Google Scholar]
- Peirce, J.L.; Lu, L.; Gu, J.; Silver, L.M.; Williams, R.W. A new set of BXD recombinant inbred lines from advanced intercross populations in mice. BMC Genet. 2004, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; Staal, J.; Schoffelmeer, A.N.; Smit, A.B.; Spijker, S.; Pattij, T. Inhibitory control and response latency differences between C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice in a Go/No-Go and 5-choice serial reaction time task and strain-specific responsivity to amphetamine. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 214, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.N.; Belknap, J.K.; Collins, A.; Crabbe, J.C.; Frankel, W.; Henderson, N.; Hitzemann, R.J.; Maxson, S.C.; Miner, L.L.; Silva, A.J.; et al. Behavioral phenotypes of inbred mouse strains: Implications and recommendations for molecular studies. Psychopharmacol. Berl 1997, 132, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.; Ellenbroek, B.A.; van Eck, I.; Roubos, S.; Verhage, M.; Stiedl, O. Finding the right motivation: Genotype-dependent differences in effective reinforcements for spatial learning. Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 226, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upchurch, M.; Wehner, J.M. Differences between inbred strains of mice in Morris water maze performance. Behav. Genet. 1988, 18, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.; Wrenn, C.C.; Harris, A.P.; Thayer, K.E.; Crawley, J.N. Behavioral profiles of inbred strains on novel olfactory, spatial and emotional tests for reference memory in mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2002, 1, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andre, J.M.; Cordero, K.A.; Gould, T.J. Comparison of the performance of DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice in transitive inference and foreground and background contextual fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 126, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.V.; Duffy, S.N.; Young, J.Z. Differential maintenance and frequency-dependent tuning of LTP at hippocampal synapses of specific strains of inbred mice. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 84, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimanski, L.A.; Nguyen, P.V. Multidisciplinary approaches for investigating the mechanisms of hippocampus-dependent memory: A focus on inbred mouse strains. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 28, 463–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenselink, A.M.; Rotaru, D.C.; Li, K.W.; van Nierop, P.; Rao-Ruiz, P.; Loos, M.; van der Schors, R.; Gouwenberg, Y.; Wortel, J.; Mansvelder, H.D.; et al. Strain differences in presynaptic function: Proteomics, ultrastructure and physiology of hippocampal synapses in DBA/2J and C57Bl/6J mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15635–15645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, K.; Pandey, S.C. Differences in basal levels of CREB and NPY in nucleus accumbens regions between C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice differing in inborn alcohol drinking behavior. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 74, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; van der Sluis, S.; Bochdanovits, Z.; van Zutphen, I.J.; Pattij, T.; Stiedl, O.; Smit, A.B.; Spijker, S. Activity and impulsive action are controlled by different genetic and environmental factors. Genes Brain Behav. 2009, 8, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, A.T.; Jiang, K.; Levitt, P. Quantitative trait locus mapping and analysis of heritable variation in affiliative social behavior and co-occurring traits. Genes Brain Behav. 2018, 17, e12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoll, A.T.; Halladay, L.R.; Holmes, A.J.; Levitt, P. Quantitative trait loci and a novel genetic candidate for fear learning. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 6258–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delprato, A.; Bonheur, B.; Algeo, M.P.; Rosay, P.; Lu, L.; Williams, R.W.; Crusio, W.E. Systems genetic analysis of hippocampal neuroanatomy and spatial learning in mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2015, 14, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; Mueller, T.; Gouwenberg, Y.; Wijnands, R.; van der Loo, R.J.; Birchmeier, C.; Smit, A.B.; Spijker, S. Neuregulin-3 in the mouse medial prefrontal cortex regulates impulsive action. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, R.E.; Grant, T.L.; Williams, R.W.; Jentsch, J.D. Genetic dissection of behavioral flexibility: Reversal learning in mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, M.; Staal, J.; Pattij, T.; Smit, A.B.; Spijker, S. Independent genetic loci for sensorimotor gating and attentional performance in BXD recombinant inbred strains. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.; Timmerman, J.; Loos, M.; Spijker, S.; van Ooyen, A.; Brussaard, A.B.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Smit, A.B.; de Gunst, M.; Linkenkaer-Hansen, K. Novel candidate genes associated with hippocampal oscillations. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nagtegaal, A.P.; Spijker, S.; Crins, T.T.; Borst, J.G. A novel QTL underlying early-onset, low-frequency hearing loss in BXD recombinant inbred strains. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overall, R.W.; Kempermann, G.; Peirce, J.; Lu, L.; Goldowitz, D.; Gage, F.H.; Goodwin, S.; Smit, A.B.; Airey, D.C.; Rosen, G.D.; et al. Genetics of the hippocampal transcriptome in mouse: A systematic survey and online neurogenomics resource. Front. Neurosci. 2009, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spijker, S. Dissection of Rodent Brain Regions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen, M.H.; Camargo, N.; Verdier, V.; Nadra, K.; de Preux Charles, A.S.; Medard, J.J.; Luoma, A.; Crowther, M.; Inouye, H.; Shimano, H.; et al. SCAP is required for timely and proper myelin membrane synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21383–21388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome. Biol. 2002, 3, RESEARCH0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, N.; Goudriaan, A.; van Deijk, A.F.; Otte, W.M.; Brouwers, J.F.; Lodder, H.; Gutmann, D.H.; Nave, K.A.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Mansvelder, H.D.; et al. Oligodendroglial myelination requires astrocyte-derived lipids. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e1002605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, N.; Brouwers, J.F.; Loos, M.; Gutmann, D.H.; Smit, A.B.; Verheijen, M.H. High-fat diet ameliorates neurological deficits caused by defective astrocyte lipid metabolism. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 4302–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, J.M.; McLaughlin, M.; Werner, H.B.; McCulloch, M.C.; Barrie, J.A.; Brown, A.; Faichney, A.B.; Snaidero, N.; Nave, K.A.; Griffiths, I.R. Early ultrastructural defects of axons and axon-glia junctions in mice lacking expression of Cnp. Glia 2009, 57, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, B.; Agalliu, D.; Cahoy, J.D.; Watkins, T.A.; Dugas, J.C.; Mulinyawe, S.B.; Ibrahim, A.; Ligon, K.L.; Rowitch, D.H.; Barres, B.A. Myelin gene regulatory factor is a critical transcriptional regulator required for CNS myelination. Cell 2009, 138, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suminaite, D.; Lyons, D.A.; Livesey, M.R. Myelinated axon physiology and regulation of neural circuit function. Glia 2019, 11, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vana, A.C.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Le, T.Q.; Armstrong, R.C. Myelin transcription factor 1 (Myt1) expression in demyelinated lesions of rodent and human CNS. Glia 2007, 55, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, D.L.; Denarier, E.; Friedman, H.C.; Wasserman, W.W.; Peterson, A.C. Towards resolving the transcription factor network controlling myelin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 7974–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolay, D.J.; Doucette, J.R.; Nazarali, A.J. Transcriptional control of oligodendrogenesis. Glia 2007, 55, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, M. A matter of identity: Transcriptional control in oligodendrocytes. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2008, 35, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H. Myelin-associated oligodendrocytic basic protein modulates the arrangement of radial growth of the axon and the radial component of myelin. Med. Electron. Microsc. 2001, 34, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.; Fromholt, S.E.; Hess, E.J.; Crawford, T.O.; Griffin, J.W.; Sheikh, K.A.; Schnaar, R.L. Myelin-associated glycoprotein and complementary axonal ligands, gangliosides, mediate axon stability in the CNS and PNS: Neuropathology and behavioral deficits in single- and double-null mice. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 195, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Crawford, T.O.; Griffin, J.W.; Tu, P.; Lee, V.M.; Li, C.; Roder, J.; Trapp, B.D. Myelin-associated glycoprotein is a myelin signal that modulates the caliber of myelinated axons. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, A.; Zhu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, B. Genetic influences on cortical myelination in the human brain. Genes Brain Behav. 2019, 18, e12537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crish, S.D.; Sappington, R.M.; Inman, D.M.; Horner, P.J.; Calkins, D.J. Distal axonopathy with structural persistence in glaucomatous neurodegeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5196–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLin, J.P.; Steward, O. Comparison of seizure phenotype and neurodegeneration induced by systemic kainic acid in inbred, outbred, and hybrid mouse strains. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 2191–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Este, L.; Casini, A.; Puglisi-Allegra, S.; Cabib, S.; Renda, T.G. Comparative immunohistochemical study of the dopaminergic systems in two inbred mouse strains (C57BL/6J and DBA/2J). J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2007, 33, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middei, S.; Vetere, G.; Sgobio, C.; Ammassari-Teule, M. Landmark-based but not vestibular-based orientation elicits mossy fiber synaptogenesis in the mouse hippocampus. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2007, 87, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanat, M.J.; Sparta, D.R.; Hopf, F.W.; Bowers, M.S.; Melis, M.; Bonci, A. Strain specific synaptic modifications on ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons after ethanol exposure. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restivo, L.; Roman, F.S.; Ammassari-Teule, M.; Marchetti, E. Simultaneous olfactory discrimination elicits a strain-specific increase in dendritic spines in the hippocampus of inbred mice. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Task | Parameter | p-Value | r | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dark light box | Duration in light compartment | 0.040 * | 0.31 | 38 |
| Frequency in light compartment | 0.024 * | 0.37 | 37 | |
| Open Field | Total distance travelled | 0.023 * | 0.37 | 38 |
| Frequency in center | 0.021 * | 0.38 | 38 | |
| Duration in center | 0.168 | 0.23 | 37 | |
| 5-choice serial | Number of premature pokes | 0.455 | −0.12 | 40 |
| Reaction time task | RT-correct | 0.092 | −0.27 | 40 |
| Accuracy | 0.695 | 0.07 | 39 | |
| Omissions | 0.567 | 0.09 | 40 | |
| Pre-pulse inhibition | PPI65 | 0.274 | 0.20 | 33 |
| (PPI) | PPI70 | 0.496 | 0.12 | 34 |
| PPI175 | 0.605 | 0.09 | 33 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goudriaan, A.; Loos, M.; Spijker, S.; Smit, A.B.; Verheijen, M.H.G. Genetic Variation in CNS Myelination and Functional Brain Connectivity in Recombinant Inbred Mice. Cells 2020, 9, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092119
Goudriaan A, Loos M, Spijker S, Smit AB, Verheijen MHG. Genetic Variation in CNS Myelination and Functional Brain Connectivity in Recombinant Inbred Mice. Cells. 2020; 9(9):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092119
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoudriaan, Andrea, Maarten Loos, Sabine Spijker, August B. Smit, and Mark H. G. Verheijen. 2020. "Genetic Variation in CNS Myelination and Functional Brain Connectivity in Recombinant Inbred Mice" Cells 9, no. 9: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092119
APA StyleGoudriaan, A., Loos, M., Spijker, S., Smit, A. B., & Verheijen, M. H. G. (2020). Genetic Variation in CNS Myelination and Functional Brain Connectivity in Recombinant Inbred Mice. Cells, 9(9), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9092119





