Identification of Essential Proteins Based on Improved HITS Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Hypertext Induced Topic Search Algorithm
2.2. Constructing Weighted Protein-Protein Interaction Network
2.3. Identifying Essential Proteins Based on HSEP Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 HSEP essential proteins identification. |
| Require: A PPI network , Gene expression data, Subcellular location data Gene Ontology GO. Ensure: Essential protein set. Step 1
|
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Data
3.2. Comparison with Other Identification Measures
3.3. Validation Using Six Statistical Measures
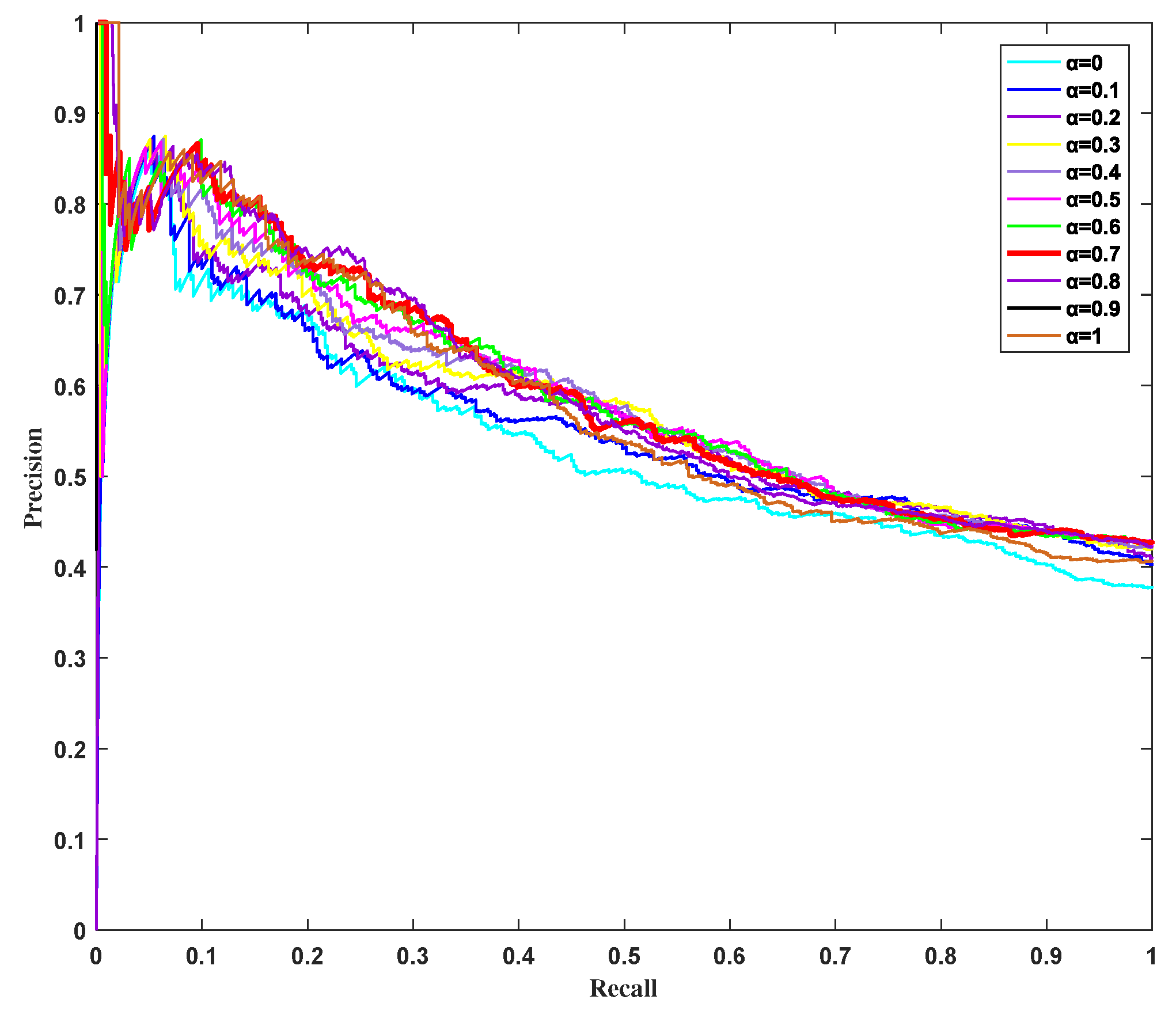
3.4. Influence of Parameter on HSEP Based on Precision–Recall Curves
3.5. The Analysis of Essential Proteins
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winzeler, E.A.; Shoemaker, D.D.; Astromoff, A.; Liang, H.; Anderson, K.; Andre, B.; Bangham, R.; Benito, R.; Boeke, J.D.; Bussey, H. Functional characterization of the S. cerevisiae genome by gene deletion and parallel analysis. Science 1999, 285, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furney, S.J.; Albà, M.M.; López-Bigas, N. Differences in the evolutionary history of disease genes affected by dominant or recessive mutations. BMC Genomics 2006, 7, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Deng, J.; Rhodes, J.C.; Lu, H.; Lu, L.J. Predicting essential genes for identifying potential drug targets in Aspergillus fumigatus. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2014, 50, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaever, G.; Chu, A.M.; Ni, L.; Connelly, C.; Riles, L.; Véronneau, S.; Dow, S.; Lucaudanila, A.; Anderson, K.; André, B. Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 2002, 418, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, L.M.; Arndt, G.M. Genome-wide screening for gene function using RNAi in mammalian cells. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2005, 83, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roemer, T.; Jiang, B.; Davison, J.; Ketela, T.; Veillette, K.; Breton, A.; Tandia, F.; Linteau, A.; Sillaots, S.; Marta, C. Large-scale essential gene identification in Candida albicans and applications to antifungal drug discovery. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fields, S.; Song, O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature 1989, 340, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.; Gruhler, A.; Heilbut, A.; Bader, G.D.; Moore, L.; Adams, S.L.; Millar, A.; Taylor, P.; Bennett, K.; Boutilier, K. Systematic identification of protein complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by mass spectrometry. Nature 2002, 415, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigaut, G.; Shevchenko, A.; Rutz, B.; Wilm, M.; Mann, M.; Séraphin, B. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1030–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Mason, S.P.; Barabási, A.L.; Oltvai, Z.N. Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature 2001, 411, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, M.E.J. A measure of betweenness centrality based on random walks. Soc. Netw. 2003, 27, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuchty, S.; Stadler, P.F. Centers of complex networks. J. Theor. Biol. 2003, 223, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, E.; Rodríguez-Velázquez, J.A. Subgraph centrality in complex networks. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2005, 71, 056103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonacich, P. Power and centrality: A family of measures. Am. J. Sociol. 1987, 92, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, K.; Zelen, M. Rethinking centrality: Methods and examples. Soc. Netw. 1989, 11, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y. Identification of essential proteins based on edge clustering coefficient. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2012, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y. A local average connectivity-based method for identifying essential proteins from the network level. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2011, 35, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.X.; Pan, Y. A new essential protein discovery method based on the integration of protein-protein interaction and gene expression data. BMC Syst. Biol. 2012, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Pan, Y. Predicting essential proteins based on weighted degree centrality. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2014, 11, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, G.T.; Lee, I.; Marcotte, E.M. A high-accuracy consensus map of yeast protein complexes reveals modular nature of gene essentiality. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Wu, F.X. United complex centrality for identification of essential proteins from PPI networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2017, 14, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.W. Predicting essential proteins using a new method. In Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, F.X.; Pan, Y. Predicting essential proteins based on subcellular localization, orthology and PPI networks. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Guan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Essential protein detection by random walk on weighted protein-protein interaction networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wu, F.; Pan, Y. UDoNC: An algorithm for identifying essential proteins based on protein domains and protein-protein interaction networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2015, 12, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinberg, J.M. Authoritative sources in a hyperlinked environment. J. ACM 1999, 46, 604–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, S.; Oyama, S.; Hayamizu, T.; Ishida, T. Analysis and improvement of HITS algorithm for detecting web communities. Syst. Comput. Jpn. 2004, 35, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radicchi, F.; Castellano, C.; Cecconi, F.; Loreto, V.; Parisi, D. Defining and identifying communities in networks. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 101, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherlock, G. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Can. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. J. 2009, 22, 415. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.Z.; Du, Z.; Payattakool, R.; Yu, P.S.; Chen, C.F. A new method to measure the semantic similarity of GO terms. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Agarwal, S.; Heyman, J.A.; Matson, S.; Heidtman, M.; Piccirillo, S.; Umansky, L.; Drawid, A.; Jansen, R.; Liu, Y. Subcellular localization of the yeast proteome. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, W.; Hu, X. Predicting essential proteins by integrating orthology, gene expressions, and PPI networks. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Wu, F.X.; Pan, Y. Detecting protein complexes based on uncertain graph model. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2014, 11, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anne-Claude, G.; Patrick, A.; Paola, G.; Roland, K.; Markus, B.; Martina, M.; Christina, R.; Lars Juhl, J.; Sonja, B.; Birgit, D. Proteome survey reveals modularity of the yeast cell machinery. Nature 2006, 440, 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Das, J.; Yu, H. HINT: High-quality protein interactomes and their applications in understanding human disease. BMC Syst. Biol. 2012, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, J.X.; Pletscherfrankild, S.; Tsafou, K.; Stolte, C.; O’Donoghue, S.I.; Schneider, R.; Jensen, L.J. COMPARTMENTS: Unification and visualization of protein subcellular localization evidence. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2014, 2014, bau012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, B.P.; Kudlicki, A.; Rowicka, M.; Mcknight, S.L. Logic of the yeast metabolic cycle: Temporal compartmentalization of cellular processes. Science 2005, 310, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintapalli, V.; Wang, J.; Dow, J. Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila models of human disease. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, G.O. Gene ontology consortium: Going forward. Nucl. Acids Res. 2015, 43, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Müller, H.G.; Wang, J.L. MIPS: Analysis and annotation of proteins from whole genomes. Nucl. Acids Res. 2004, 34, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Cherry, J.M.; Adler, C.; Ball, C.; Chervitz, S.A.; Dwight, S.S.; Hester, E.T.; Jia, Y.; Juvik, G.; Roe, T.; Schroeder, M. SGD: Saccharomyces genome database. Nucl. Acids Res. 1998, 26, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Lin, Y. DEG 5.0, a database of essential genes in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Nucl. Acids Res. 2009, 37, D455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Database | Proteins | Interactions | Density | GO Annotation | Gene Expression | Essential Proteins |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIP | 5093 | 24,743 | 0.0019 | 5061 | 4981 | 1167 |
| Gavin | 1430 | 6531 | 0.0064 | 1430 | 1418 | 617 |
| HINT | 7285 | 24,436 | 0.0009 | 4878 | 6999 | 216 |
| Database | Method | SN | SP | PPV | NPV | F-Measure | ACC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC | 0.4302 | 0.8033 | 0.3940 | 0.8258 | 0.4113 | 0.7178 | |
| IC | 0.4319 | 0.8038 | 0.3956 | 0.8263 | 0.4129 | 0.7186 | |
| SC | 0.4002 | 0.7944 | 0.3666 | 0.8167 | 0.3826 | 0.7040 | |
| EC | 0.4002 | 0.7944 | 0.3666 | 0.8167 | 0.3826 | 0.7040 | |
| NC | 0.4670 | 0.8143 | 0.4278 | 0.8371 | 0.4465 | 0.7347 | |
| DIP | LAC | 0.4730 | 0.8161 | 0.4333 | 0.8389 | 0.4523 | 0.7374 |
| WDC | 0.4567 | 0.8112 | 0.4184 | 0.8339 | 0.4367 | 0.7300 | |
| PeC | 0.4225 | 0.8010 | 0.3870 | 0.8235 | 0.4039 | 0.7143 | |
| HSP | 0.4567 | 0.8112 | 0.4184 | 0.8339 | 0.4367 | 0.7300 | |
| UDoNC | 0.4910 | 0.8214 | 0.4498 | 0.8444 | 0.4695 | 0.7457 | |
| HSEP | 0.5116 | l0.8275 | 0.4686 | 0.8507 | 0.4891 | 0.7551 | |
| DC | 0.3582 | 0.8313 | 0.6173 | 0.6303 | 0.4533 | 0.6270 | |
| IC | 0.3501 | 0.8251 | 0.6034 | 0.6256 | 0.4431 | 0.6200 | |
| SC | 0.3047 | 0.7906 | 0.5251 | 0.5994 | 0.3856 | 0.5808 | |
| EC | 0.2026 | 0.7131 | 0.3492 | 0.5406 | 0.2564 | 0.4927 | |
| Gavin | NC | 0.4084 | 0.8695 | 0.7039 | 0.6592 | 0.5169 | 0.6704 |
| LAC | 0.4117 | 0.8719 | 0.7095 | 0.6611 | 0.5210 | 0.6732 | |
| WDC | 0.3809 | 0.8485 | 0.6564 | 0.6433 | 0.4821 | 0.6466 | |
| PeC | 0.3744 | 0.8103 | 0.6000 | 0.6303 | 0.4611 | 0.6211 | |
| HSP | 0.3890 | 0.8547 | 0.674 | 0.6480 | 0.4923 | 0.6536 | |
| HSEP | 0.4182 | 0.8768 | 0.7207 | 0.6648 | 0.5292 | 0.6788 | |
| DC | 0.4306 | 0.7555 | 0.0511 | 0.9775 | 0.0913 | 0.7459 | |
| IC | 0.4213 | 0.7552 | 0.0500 | 0.9771 | 0.0893 | 0.7453 | |
| SC | 0.3796 | 0.7540 | 0.0450 | 0.9755 | 0.0805 | 0.7429 | |
| EC | 0.3796 | 0.7540 | 0.0450 | 0.9755 | 0.0805 | 0.7429 | |
| HINT | NC | 0.3565 | 0.7533 | 0.0423 | 0.9746 | 0.0756 | 0.7415 |
| LAC | 0.3148 | 0.7520 | 0.0373 | 0.9729 | 0.0668 | 0.7390 | |
| WDC | 0.2361 | 0.7496 | 0.0280 | 0.9698 | 0.0501 | 0.7343 | |
| PeC | 0.2315 | 0.7494 | 0.0275 | 0.9696 | 0.0491 | 0.7341 | |
| HSP | 0.3519 | 0.7531 | 0.0417 | 0.9744 | 0.0746 | 0.7412 | |
| HSEP | 0.5046 | 0.7578 | 0.0599 | 0.9804 | 0.1070 | 0.7503 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, F. Identification of Essential Proteins Based on Improved HITS Algorithm. Genes 2019, 10, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020177
Lei X, Wang S, Wu F. Identification of Essential Proteins Based on Improved HITS Algorithm. Genes. 2019; 10(2):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020177
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Xiujuan, Siguo Wang, and Fangxiang Wu. 2019. "Identification of Essential Proteins Based on Improved HITS Algorithm" Genes 10, no. 2: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020177
APA StyleLei, X., Wang, S., & Wu, F. (2019). Identification of Essential Proteins Based on Improved HITS Algorithm. Genes, 10(2), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020177




