Evaluation of the Abundance of DNA-Binding Transcription Factors in Prokaryotes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial and Archaeal Genomes Analyzed
2.2. Identification of DNA-Binding Domains Associated with TFs
2.3. Protein Domain Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Repertoires of TF Families Correlate with Genome Sizes
3.2. The Abundance of Families is Not Homogeneous Across the Genomes
3.3. Correlation of TF Families among Bacteria and Archaeal Genomes
3.4. Distributions of Families among All the Genomes
3.5. Structural Domains Associated with Families
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Browning, D.F.; Busby, S.J. The regulation of bacterial transcription initiation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, D.F.; Busby, S.J. Local and global regulation of transcription initiation in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rivera-Gomez, N.; Martinez-Nunez, M.A.; Pastor, N.; Rodriguez-Vazquez, K.; Perez-Rueda, E. Dissecting the protein architecture of DNA-binding transcription factors in bacteria and archaea. Microbiology 2017, 163, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Gomez, N.; Segovia, L.; Perez-Rueda, E. Diversity and distribution of transcription factors: Their partner domains play an important role in regulatory plasticity in bacteria. Microbiology 2011, 157, 2308–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemmens, L.; Maklad, H.R.; Bervoets, I.; Peeters, E. Transcription Regulators in Archaea: Homologies and Differences with Bacterial Regulators. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 4132–4146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Rueda, E.; Janga, S.C. Identification and genomic analysis of transcription factors in archaeal genomes exemplifies their functional architecture and evolutionary origin. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Nunez, M.A.; Poot-Hernandez, A.C.; Rodriguez-Vazquez, K.; Perez-Rueda, E. Increments and duplication events of enzymes and transcription factors influence metabolic and regulatory diversity in prokaryotes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Rueda, E.; Hernandez-Guerrero, R.; Martinez-Nunez, M.A.; Armenta-Medina, D.; Sanchez, I.; Ibarra, J.A. Abundance, diversity and domain architecture variability in prokaryotic DNA-binding transcription factors. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tenorio-Salgado, S.; Huerta-Saquero, A.; Perez-Rueda, E. New insights on gene regulation in archaea. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2011, 35, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haft, D.H.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Brover, V.; Chetvernin, V.; O’Neill, K.; Li, W.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. RefSeq: An update on prokaryotic genome annotation and curation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D851–D860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Hagelsieb, G.; Wang, Z.; Walsh, S.; ElSherbiny, A. Phylogenomic clustering for selecting non-redundant genomes for comparative genomics. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 947–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- R-programming: Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ranea, J.A.; Buchan, D.W.; Thornton, J.M.; Orengo, C.A. Evolution of protein superfamilies and bacterial genome size. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 336, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, E.; Charlier, D. The Lrp family of transcription regulators in archaea. Archaea 2010, 2010, 750457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, A.I.; Sharov, V.; White, J.; Li, J.; Liang, W.; Bhagabati, N.; Braisted, J.; Klapa, M.; Currier, T.; Thiagarajan, M.; et al. TM4: A free, open-source system for microarray data management and analysis. BioTechniques 2003, 34, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anantharaman, V.; Aravind, L. New connections in the prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin network: Relationship with the eukaryotic nonsense-mediated RNA decay system. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, R81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engelberg-Kulka, H.; Amitai, S.; Kolodkin-Gal, I.; Hazan, R. Bacterial programmed cell death and multicellular behavior in bacteria. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruss, B.M.; Liu, X.; Hendrickson, W.; Matsumura, P. FlhD/FlhC-regulated promoters analyzed by gene array and lacZ gene fusions. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 197, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.N.; Dressaire, C.; Barahona, S.; Galego, L.; Kaever, V.; Jenal, U.; Arraiano, C.M. BolA Is Required for the Accurate Regulation of c-di-GMP, a Central Player in Biofilm Formation. MBio 2017, 8, e00443-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinote, I.B.; Matos, R.G.; Freire, P.; Arraiano, C.M. BolA affects cell growth, and binds to the promoters of penicillin-binding proteins 5 and 6 and regulates their expression. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, S.W.; Kim, D.; Latif, H.; O’Brien, E.J.; Szubin, R.; Palsson, B.O. Deciphering Fur transcriptional regulatory network highlights its complex role beyond iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, A.; Angarica, V.E.; Sancho, J.; Fillat, M.F. The FurA regulon in Anabaena sp. PCC 7120: In silico prediction and experimental validation of novel target genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4833–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quatrini, R.; Lefimil, C.; Veloso, F.A.; Pedroso, I.; Holmes, D.S.; Jedlicki, E. Bioinformatic prediction and experimental verification of Fur-regulated genes in the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 2153–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grifantini, R.; Sebastian, S.; Frigimelica, E.; Draghi, M.; Bartolini, E.; Muzzi, A.; Rappuoli, R.; Grandi, G.; Genco, C.A. Identification of iron-activated and -repressed Fur-dependent genes by transcriptome analysis of Neisseria meningitidis group B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9542–9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zawilak-Pawlik, A.; Nowaczyk, M.; Zakrzewska-Czerwinska, J. The Role of the N-Terminal Domains of Bacterial Initiator DnaA in the Assembly and Regulation of the Bacterial Replication Initiation Complex. Genes (Basel) 2017, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, M.F.; Peterson, K.R.; Love, P.E. Regulation of the SOS response in Bacillus subtilis: Evidence for a LexA repressor homolog. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 6489–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Alberola, N.; Campoy, S.; Emerson, D.; Barbe, J.; Erill, I. An SOS Regulon under Control of a Noncanonical LexA-Binding Motif in the Betaproteobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 2622–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Nunez, M.A.; Perez-Rueda, E.; Gutierrez-Rios, R.M.; Merino, E. New insights into the regulatory networks of paralogous genes in bacteria. Microbiology 2010, 156, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. 4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korner, H.; Sofia, H.J.; Zumft, W.G. Phylogeny of the bacterial superfamily of Crp-Fnr transcription regulators: Exploiting the metabolic spectrum by controlling alternative gene programs. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 559–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balderas-Martinez, Y.I.; Savageau, M.; Salgado, H.; Perez-Rueda, E.; Morett, E.; Collado-Vides, J. Transcription factors in Escherichia coli prefer the holo conformation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
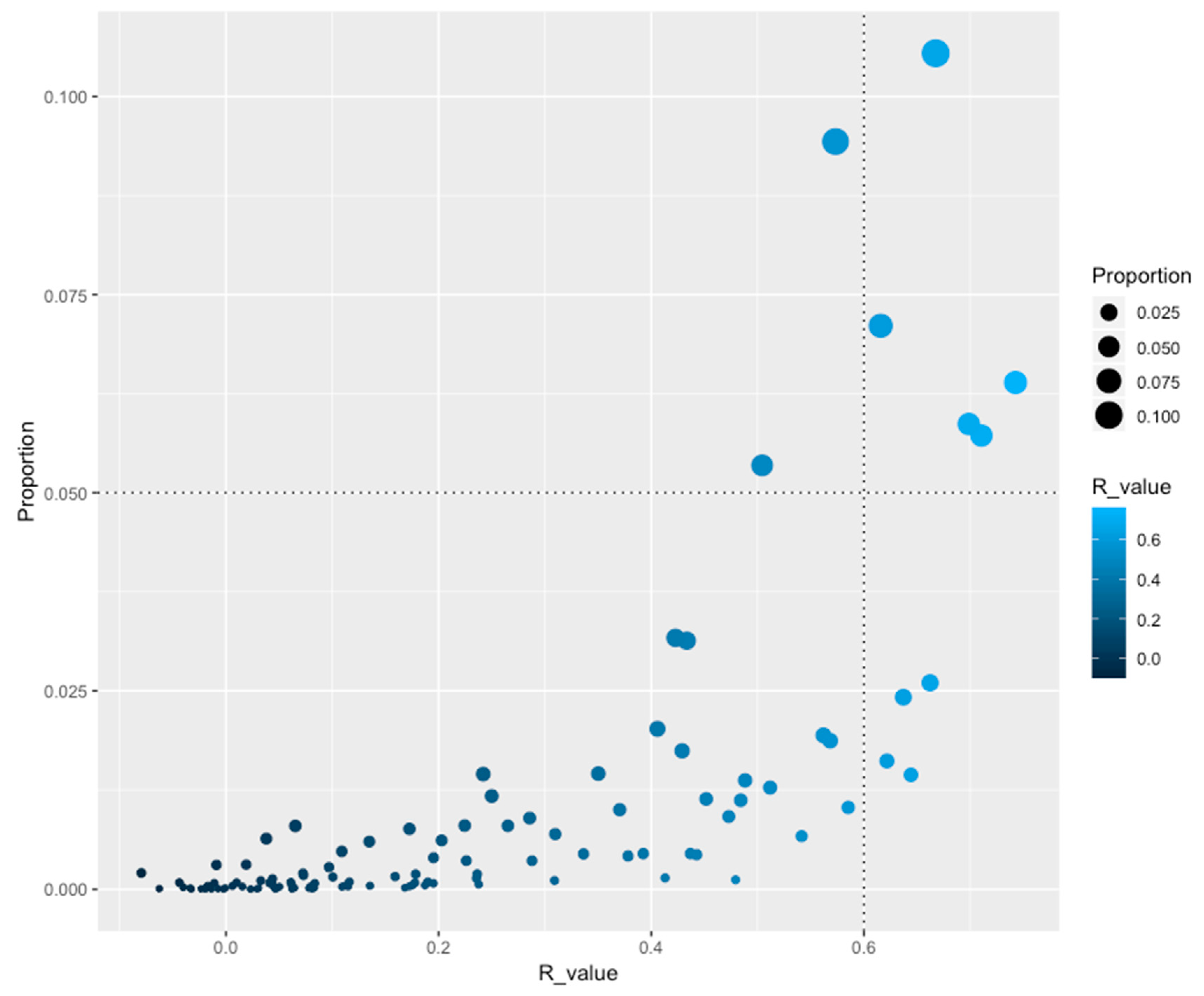




| PFAM ID | PFAM Name | PFAM Description | Correlation (R value) | Total No. of Proteins | Proportion | CV | Domains (Total) | Domains (NR) | Genomic Distribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PF00096 | zf-C2H2 | Zinc finger, C2H2 type | −0.04 | 59 | 0.00 | 6.82 | 105 | 24 | 0.03 |
| PF00126 | HTH_1 | Bacterial regulatory helix-turn-helix protein, lysR family | 0.57 | 21320 | 0.09 | 1.70 | 42400 | 98 | 0.87 |
| PF00165 | HTH_AraC | Bacterial regulatory helix-turn-helix proteins, AraC family | 0.05 | 47 | 0.00 | 6.85 | 86 | 27 | 0.03 |
| PF00170 | bZIP_1 | bZIP transcription factor | 0.03 | 248 | 0.00 | 3.11 | 4587 | 341 | 0.12 |
| PF00196 | GerE | Bacterial regulatory proteins, luxR family | 0.71 | 12932 | 0.06 | 1.53 | 25020 | 290 | 0.79 |
| PF00216 | Bac_DNA_binding | Bacterial DNA-binding protein | 0.24 | 3276 | 0.01 | 0.95 | 4731 | 40 | 0.88 |
| PF00313 | CSD | ’Cold-shock’ DNA-binding domain | 0.62 | 3651 | 0.02 | 0.91 | 3866 | 39 | 0.79 |
| PF00325 | Crp | Bacterial regulatory proteins, crp family | 0.18 | 186 | 0.00 | 2.70 | 377 | 24 | 0.13 |
| PF00356 | LacI | Bacterial regulatory proteins, lacI family | 0.43 | 7083 | 0.03 | 1.71 | 14525 | 108 | 0.61 |
| PF00376 | MerR | MerR family regulatory protein | 0.54 | 1506 | 0.01 | 1.65 | 2885 | 66 | 0.43 |
| PF00392 | GntR | Bacterial regulatory proteins, gntR family | 0.70 | 13263 | 0.06 | 1.33 | 25478 | 205 | 0.79 |
| PF00440 | TetR_N | Bacterial regulatory proteins, tetR family | 0.67 | 23839 | 0.11 | 2.62 | 33009 | 197 | 0.87 |
| PF00486 | Trans_reg_C | Transcriptional regulatory protein, C terminal | 0.74 | 14446 | 0.06 | 1.01 | 31282 | 163 | 0.87 |
| PF00816 | Histone_HNS | H-NS histone family | 0.24 | 434 | 0.00 | 3.68 | 537 | 37 | 0.16 |
| PF00847 | AP2 | AP2 domain | 0.08 | 77 | 0.00 | 5.50 | 105 | 13 | 0.04 |
| PF01022 | HTH_5 | Bacterial regulatory protein, arsR family | 0.43 | 3940 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 4683 | 138 | 0.84 |
| PF01047 | MarR | MarR family | 0.66 | 5880 | 0.03 | 1.15 | 6384 | 142 | 0.81 |
| PF01258 | zf-dskA_traR | Prokaryotic dksA/traR C4-type zinc finger | 0.31 | 1564 | 0.01 | 1.02 | 1744 | 25 | 0.67 |
| PF01316 | Arg_repressor | Arginine repressor, DNA binding domain | 0.10 | 631 | 0.00 | 1.33 | 1287 | 26 | 0.41 |
| PF01325 | Fe_dep_repress | Iron dependent repressor, N-terminal DNA binding domain | 0.11 | 1076 | 0.00 | 1.23 | 2675 | 43 | 0.53 |
| PF01340 | MetJ | Met Apo-repressor, MetJ | 0.05 | 72 | 0.00 | 4.27 | 73 | 2 | 0.05 |
| PF01371 | Trp_repressor | Trp repressor protein | 0.04 | 299 | 0.00 | 2.00 | 330 | 20 | 0.21 |
| PF01381 | HTH_3 | Helix-turn-helix | 0.50 | 12084 | 0.05 | 0.82 | 16741 | 394 | 0.94 |
| PF01402 | RHH_1 | Ribbon-helix-helix protein, copG family | 0.17 | 1714 | 0.01 | 1.56 | 2228 | 93 | 0.52 |
| PF01418 | HTH_6 | Helix-turn-helix domain, rpiR family | 0.27 | 1802 | 0.01 | 1.74 | 3574 | 48 | 0.43 |
| PF01475 | FUR | Ferric uptake regulator family | 0.51 | 2891 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 2992 | 45 | 0.87 |
| PF01638 | HxlR | HxlR-like helix-turn-helix | 0.64 | 3255 | 0.01 | 1.65 | 3389 | 37 | 0.64 |
| PF01722 | BolA | BolA-like protein | 0.20 | 898 | 0.00 | 1.36 | 905 | 5 | 0.37 |
| PF01726 | LexA_DNA_bind | LexA DNA binding domain | 0.44 | 1015 | 0.00 | 0.91 | 1988 | 33 | 0.64 |
| PF01978 | TrmB | Sugar-specific transcriptional regulator TrmB | 0.04 | 1436 | 0.01 | 2.47 | 2475 | 164 | 0.38 |
| PF02082 | Rrf2 | Transcriptional regulator | 0.48 | 2531 | 0.01 | 0.85 | 2644 | 51 | 0.78 |
| PF02257 | RFX_DNA_binding | RFX DNA-binding domain | 0.03 | 12 | 0.00 | 13.56 | 28 | 7 | 0.01 |
| PF02467 | Whib | Transcription factor WhiB | 0.38 | 947 | 0.00 | 2.92 | 1000 | 18 | 0.14 |
| PF02604 | PhdYeFM_antitox | Antitoxin Phd_YefM, type II toxin-antitoxin system | 0.29 | 2020 | 0.01 | 1.58 | 2104 | 30 | 0.52 |
| PF02892 | zf-BED | BED zinc finger | −0.01 | 17 | 0.00 | 11.11 | 30 | 11 | 0.01 |
| PF02954 | HTH_8 | Bacterial regulatory protein, Fis family | 0.42 | 7162 | 0.03 | 1.51 | 20550 | 157 | 0.61 |
| PF03333 | PapB | Adhesin biosynthesis transcription regulatory protein | 0.05 | 14 | 0.00 | 11.01 | 22 | 5 | 0.01 |
| PF03551 | PadR | Transcriptional regulator PadR-like family | 0.49 | 3098 | 0.01 | 1.62 | 3782 | 52 | 0.62 |
| PF03749 | SfsA | Sugar fermentation stimulation protein | 0.07 | 458 | 0.00 | 1.46 | 475 | 7 | 0.33 |
| PF03869 | Arc | Arc-like DNA binding domain | 0.20 | 171 | 0.00 | 3.50 | 174 | 3 | 0.10 |
| PF03965 | Penicillinase_R | Penicillinase repressor | 0.39 | 1013 | 0.00 | 1.88 | 1081 | 39 | 0.37 |
| PF04014 | MazE_antitoxin | Antidote-toxin recognition MazE, bacterial antitoxin | 0.07 | 1798 | 0.01 | 1.72 | 2321 | 59 | 0.46 |
| PF04024 | PspC | PspC domain | 0.34 | 1004 | 0.00 | 1.47 | 1300 | 34 | 0.41 |
| PF04221 | RelB | RelB antitoxin | -0.08 | 466 | 0.00 | 2.96 | 499 | 18 | 0.17 |
| PF04247 | SirB | Invasion gene expression up-regulator, SirB | 0.12 | 213 | 0.00 | 2.56 | 291 | 26 | 0.14 |
| PF04299 | FMN_bind_2 | Putative FMN-binding domain | 0.41 | 325 | 0.00 | 2.04 | 325 | 1 | 0.22 |
| PF04353 | Rsd_AlgQ | Regulator of RNA polymerase sigma(70) subunit, Rsd/AlgQ | 0.11 | 98 | 0.00 | 3.74 | 112 | 4 | 0.07 |
| PF04383 | KilA-N | KilA-N domain | 0.06 | 136 | 0.00 | 4.19 | 160 | 14 | 0.08 |
| PF04397 | LytTR | LytTr DNA-binding domain | 0.25 | 2649 | 0.01 | 2.13 | 4836 | 47 | 0.53 |
| PF04606 | Ogr_Delta | Ogr/Delta-like zinc finger | 0.11 | 80 | 0.00 | 4.94 | 94 | 10 | 0.05 |
| PF04761 | Phage_Treg | Lactococcus bacteriophage putative transcription regulator | −0.01 | 1 | 0.00 | 36.47 | 1 | 1 | 0.00 |
| PF04947 | Pox_VLTF3 | Poxvirus Late Transcription Factor VLTF3 like | −0.02 | 14 | 0.00 | 12.86 | 25 | 12 | 0.01 |
| PF04967 | HTH_10 | HTH DNA binding domain | 0.02 | 704 | 0.00 | 7.47 | 1610 | 61 | 0.07 |
| PF05016 | ParE_toxin | ParE toxin of type II toxin-antitoxin system, parDE | 0.22 | 1808 | 0.01 | 1.63 | 1839 | 10 | 0.48 |
| PF05043 | Mga | Mga helix-turn-helix domain | −0.01 | 695 | 0.00 | 5.32 | 2544 | 41 | 0.13 |
| PF05068 | MtlR | Mannitol repressor | 0.06 | 37 | 0.00 | 6.54 | 38 | 2 | 0.02 |
| PF05225 | HTH_psq | helix-turn-helix, Psq domain | 0.08 | 50 | 0.00 | 6.45 | 139 | 45 | 0.03 |
| PF05247 | FlhD | Flagellar transcriptional activator (FlhD) | 0.18 | 114 | 0.00 | 4.44 | 167 | 2 | 0.06 |
| PF05280 | FlhC | Flagellar transcriptional activator (FlhC) | 0.19 | 116 | 0.00 | 4.12 | 118 | 3 | 0.07 |
| PF05321 | HHA | Haemolysin expression modulating protein | 0.03 | 33 | 0.00 | 8.72 | 34 | 2 | 0.02 |
| PF05443 | ROS_MUCR | ROS/MUCR transcriptional regulator protein | 0.16 | 362 | 0.00 | 6.11 | 416 | 20 | 0.10 |
| PF05764 | YL1 | YL1 nuclear protein | 0.08 | 12 | 0.00 | 10.48 | 41 | 20 | 0.01 |
| PF05848 | CtsR | Firmicute transcriptional repressor of class III stress genes (CtsR) | −0.04 | 191 | 0.00 | 2.50 | 202 | 8 | 0.14 |
| PF05930 | Phage_AlpA | Prophage CP4-57 regulatory protein (AlpA) | 0.18 | 431 | 0.00 | 2.74 | 482 | 11 | 0.18 |
| PF06018 | CodY | CodY GAF-like domain | 0.01 | 188 | 0.00 | 2.85 | 398 | 17 | 0.12 |
| PF06054 | CoiA | Competence protein CoiA-like family | 0.04 | 182 | 0.00 | 2.81 | 198 | 9 | 0.12 |
| PF06069 | PerC | PerC transcriptional activator | 0.02 | 7 | 0.00 | 14.86 | 9 | 3 | 0.01 |
| PF06116 | RinB | Transcriptional activator RinB | −0.02 | 9 | 0.00 | 19.41 | 9 | 1 | 0.00 |
| PF06320 | GCN5L1 | GCN5-like protein 1 (GCN5L1) | −0.03 | 34 | 0.00 | 8.39 | 214 | 71 | 0.02 |
| PF06338 | ComK | ComK protein | 0.01 | 93 | 0.00 | 4.85 | 96 | 4 | 0.05 |
| PF06769 | YoeB_toxin | YoeB-like toxin of bacterial type II toxin-antitoxin system | 0.10 | 350 | 0.00 | 2.49 | 356 | 4 | 0.18 |
| PF06818 | Fez1 | Fez1 | 0.07 | 399 | 0.00 | 2.77 | 8316 | 400 | 0.16 |
| PF06839 | zf-GRF | GRF zinc finger | 0.05 | 4 | 0.00 | 28.82 | 7 | 4 | 0.00 |
| PF06923 | GutM | Glucitol operon activator protein (GutM) | 0.02 | 76 | 0.00 | 4.71 | 81 | 6 | 0.05 |
| PF06943 | zf-LSD1 | LSD1 zinc finger | 0.02 | 5 | 0.00 | 16.28 | 16 | 6 | 0.00 |
| PF07180 | CaiF_GrlA | CaiF/GrlA transcriptional regulator | 0.00 | 6 | 0.00 | 17.17 | 9 | 3 | 0.00 |
| PF07417 | Crl | Transcriptional regulator Crl | 0.08 | 31 | 0.00 | 6.48 | 31 | 1 | 0.02 |
| PF07704 | PSK_trans_fac | Rv0623-like transcription factor | 0.24 | 142 | 0.00 | 4.38 | 293 | 16 | 0.07 |
| PF07716 | bZIP_2 | Basic region leucine zipper | 0.00 | 35 | 0.00 | 7.38 | 901 | 152 | 0.02 |
| PF07750 | GcrA | GcrA cell cycle regulator | 0.19 | 211 | 0.00 | 3.58 | 232 | 12 | 0.10 |
| PF07764 | Omega_Repress | Omega Transcriptional Repressor | -0.03 | 4 | 0.00 | 18.21 | 4 | 1 | 0.00 |
| PF07804 | HipA_C | HipA-like C-terminal domain | 0.29 | 814 | 0.00 | 1.85 | 1436 | 10 | 0.32 |
| PF07848 | PaaX | PaaX-like protein | 0.48 | 272 | 0.00 | 2.68 | 530 | 19 | 0.15 |
| PF07879 | PHB_acc_N | PHB/PHA accumulation regulator DNA-binding domain | 0.31 | 251 | 0.00 | 2.13 | 553 | 17 | 0.18 |
| PF08220 | HTH_DeoR | DeoR-like helix-turn-helix domain | 0.45 | 2567 | 0.01 | 1.35 | 5238 | 87 | 0.60 |
| PF08222 | HTH_CodY | CodY helix-turn-helix domain | −0.01 | 173 | 0.00 | 2.76 | 340 | 3 | 0.12 |
| PF08270 | PRD_Mga | M protein trans-acting positive regulator (MGA) PRD domain | −0.06 | 20 | 0.00 | 10.59 | 57 | 5 | 0.01 |
| PF08279 | HTH_11 | HTH domain | 0.35 | 3290 | 0.01 | 1.36 | 8331 | 183 | 0.72 |
| PF08280 | HTH_Mga | M protein trans-acting positive regulator (MGA) HTH domain | −0.02 | 98 | 0.00 | 7.17 | 325 | 13 | 0.04 |
| PF08299 | Bac_DnaA_C | Bacterial dnaA protein helix-turn-helix | 0.20 | 1385 | 0.01 | 0.56 | 3716 | 23 | 0.90 |
| PF09278 | MerR-DNA-bind | MerR, DNA binding | 0.44 | 981 | 0.00 | 1.75 | 1988 | 39 | 0.35 |
| PF09339 | HTH_IclR | IclR helix-turn-helix domain | 0.56 | 4383 | 0.02 | 1.85 | 8834 | 158 | 0.58 |
| PF11046 | HycA_repressor | Transcriptional repressor of hyc and hyp operons | 0.06 | 5 | 0.00 | 16.28 | 5 | 1 | 0.00 |
| PF12324 | HTH_15 | Helix-turn-helix domain of alkylmercury lyase | 0.17 | 42 | 0.00 | 7.61 | 83 | 20 | 0.03 |
| PF12431 | CitT | Transcriptional regulator | 0.17 | 82 | 0.00 | 5.06 | 186 | 8 | 0.05 |
| PF12793 | SgrR_N | Sugar transport-related sRNA regulator N-term | 0.14 | 102 | 0.00 | 5.68 | 215 | 5 | 0.04 |
| PF12833 | HTH_18 | Helix-turn-helix domain | 0.62 | 16065 | 0.07 | 1.63 | 32766 | 236 | 0.75 |
| PF13384 | HTH_23 | Homeodomain-like domain | 0.37 | 2261 | 0.01 | 1.55 | 4836 | 274 | 0.63 |
| PF13404 | HTH_AsnC-type | AsnC-type helix-turn-helix domain | 0.59 | 2324 | 0.01 | 1.68 | 4460 | 88 | 0.52 |
| PF13411 | MerR_1 | MerR HTH family regulatory protein | 0.64 | 5468 | 0.02 | 1.23 | 7255 | 206 | 0.82 |
| PF13412 | HTH_24 | Winged helix-turn-helix DNA-binding | 0.41 | 4567 | 0.02 | 1.12 | 8874 | 260 | 0.81 |
| PF13413 | HTH_25 | Helix-turn-helix domain | 0.23 | 817 | 0.00 | 1.05 | 1559 | 60 | 0.54 |
| PF13545 | HTH_Crp_2 | Crp-like helix-turn-helix domain | 0.57 | 4228 | 0.02 | 1.02 | 8248 | 122 | 0.82 |
| PF13556 | HTH_30 | PucR C-terminal helix-turn-helix domain | 0.47 | 2065 | 0.01 | 2.50 | 3180 | 69 | 0.36 |
| PF13693 | HTH_35 | Winged helix-turn-helix DNA-binding | 0.04 | 111 | 0.00 | 6.64 | 135 | 17 | 0.05 |
| PF13936 | HTH_38 | Helix-turn-helix domain | 0.13 | 1350 | 0.01 | 2.40 | 2872 | 165 | 0.40 |
| PF14549 | P22_Cro | DNA-binding transcriptional regulator Cro | 0.06 | 41 | 0.00 | 6.64 | 51 | 10 | 0.03 |
| PF14850 | Pro_dh-DNA_bdg | DNA-binding domain of Proline dehydrogenase | 0.24 | 315 | 0.00 | 1.87 | 967 | 4 | 0.23 |
| PF15723 | MqsR_toxin | Motility quorum-sensing regulator, toxin of MqsA | 0.11 | 72 | 0.00 | 4.54 | 103 | 7 | 0.05 |
| PF15731 | MqsA_antitoxin | Antitoxin component of bacterial toxin-antitoxin system, MqsA | 0.06 | 199 | 0.00 | 3.13 | 271 | 20 | 0.12 |
| PF15943 | YdaS_antitoxin | Putative antitoxin of bacterial toxin-antitoxin system, YdaS/YdaT | 0.08 | 171 | 0.00 | 3.87 | 231 | 29 | 0.09 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchez, I.; Hernandez-Guerrero, R.; Mendez-Monroy, P.E.; Martinez-Nuñez, M.A.; Ibarra, J.A.; Pérez-Rueda, E. Evaluation of the Abundance of DNA-Binding Transcription Factors in Prokaryotes. Genes 2020, 11, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010052
Sanchez I, Hernandez-Guerrero R, Mendez-Monroy PE, Martinez-Nuñez MA, Ibarra JA, Pérez-Rueda E. Evaluation of the Abundance of DNA-Binding Transcription Factors in Prokaryotes. Genes. 2020; 11(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchez, Israel, Rafael Hernandez-Guerrero, Paul Erick Mendez-Monroy, Mario Alberto Martinez-Nuñez, Jose Antonio Ibarra, and Ernesto Pérez-Rueda. 2020. "Evaluation of the Abundance of DNA-Binding Transcription Factors in Prokaryotes" Genes 11, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010052
APA StyleSanchez, I., Hernandez-Guerrero, R., Mendez-Monroy, P. E., Martinez-Nuñez, M. A., Ibarra, J. A., & Pérez-Rueda, E. (2020). Evaluation of the Abundance of DNA-Binding Transcription Factors in Prokaryotes. Genes, 11(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010052





