Transcriptomic Analysis of Spleen Revealed Mechanism of Dexamethasone-Induced Immune Suppression in Chicks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
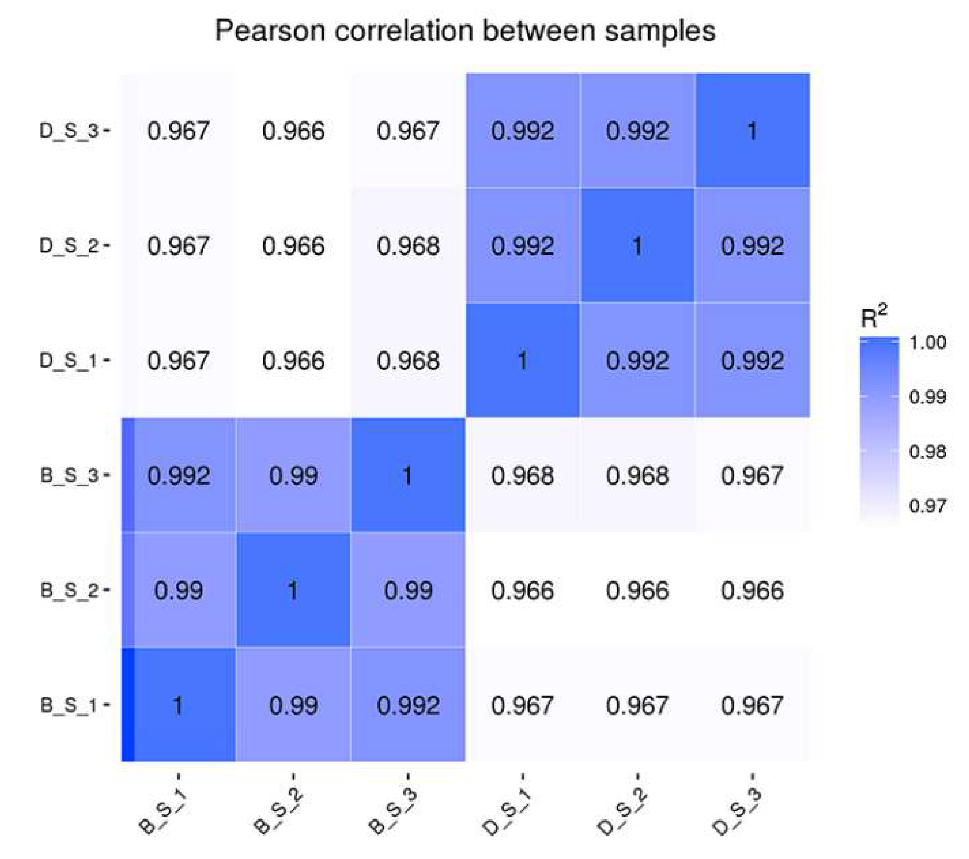
2.2. Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
2.3. RNA-Seq Library Construction and Sequencing
2.4. Differential Expression Analysis
2.5. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis
2.6. qRT-PCR Analysis of SDEGs
2.7. Protein Protein Interaction Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RNA Deep Sequencing Information
3.2. Differential Gene Expression in Spleen Tissue
3.3. Gene Ontology (GO) Analysis
3.4. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
3.5. Corroboration of RNA-Seq Results by qRT-PCR
3.6. Protein Protein Interaction Analysis of SDEGs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shini, S.; Huff, G.R.; Shini, A.; Kaiser, P. Understanding stress-induced immunosuppression: Exploration of cytokine and chemokine gene profiles in chicken peripheral leukocytes. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanian, R.; Rasouli, E. Dietary chromium methionine supplementation could alleviate immunosuppressive effects of heat stress in broiler chicks. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 3355–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cidlowski, J.A.; King, K.L.; Evans-Storms, R.B.; Montague, J.W.; Bortner, C.D.; Hughes, F.M., Jr. The biochemistry and molecular biology of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in the immune system. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 1996, 51, 457–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jing, D.; Bhadri, V.A.; Beck, D.; Thoms, J.A.; Yakob, N.A.; Wong, J.W.; Knezevic, K.; Pimanda, J.E.; Lock, R.B. Opposing regulation of BIM and BCL2 controls glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Blood 2014, 125, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Lethey, H.; Huber-Eicher, B.; Jungi, T.W. Exploration of stress-induced immunosuppression in chickens reveals both stress-resistant and stress-susceptible antigen responses. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2003, 95, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, A.J.; Hutchinson MN, D.; Sonnemann, H.M.; Jung, J.; Fecci, P.E.; Ratnam, N.M.; Zhang, W.; Song, H.; Bailey, R.; Davis, D.; et al. Dexamethasone-induced immunosuppression: Mechanisms and implications for immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, F.; Ji, L.; Shao, X.; Wu, B.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, C.; Min, Z.; Ke, Y.; et al. The abnormal function of CD39+ regulatory T cells could be corrected by high-dose dexamethasone in patients with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff, G.R.; Huff, W.E.; Balog, J.M.; Rath, N.C. The effects of dexamethasone immunosuppression on turkey osteomyelitis complex in an experimental Escherichia coli respiratory infection. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lin, H.; Wang, X.J.; Song, Z.G.; Jiao, H.C. Vitamin E supplementation alleviates the oxidative stress induced by dexamethasone treatment and improves meat quality in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Model Annotation Files. Available online: ftp://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-83/fasta/gallus_gallus/dna/ (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Gene Model Annotation Files. Available online: ftp://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-83/gtf/gallus_gallus (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) PATHWAY. Available online: http://www.genome.jp/kegg (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Chapman, J.R.; Waldenström, J. With Reference to Reference Genes: A Systematic Review of Endogenous Controls in Gene Expression Studies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, G.; Li, K.; Li, Z.; Su, A.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Jiang, R.; Han, R. Transcriptome profile in bursa of Fabricius reveals potential mode for stress-influenced immune function in chicken stress model. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The STRING Database. Organism: Chicken. Available online: http://string-db.org (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Zeng, F.F.; Fan, F.; Xue, W.Q.; Xie, H.L.; Wu, B.H.; Tu, S.L.; Ouyang, W.F.; Chen, Y.M. The association of red meat, poultry, and egg consumption with risk of hip fractures in elderly Chinese: A case–control study. Bone 2013, 56, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.Z. Red meat, poultry, and egg consumption with the risk of hypertension: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2018, 32, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Chi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.H. Ginsenoside Rg1 enhanced immune responses to infectious bursal disease vaccine in chickens with oxidative stress induced by cyclophosphamide. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2698–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, P.A.; Yang, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, S. Selenoproteins and heat shock proteins play important roles in immunosuppression in the bursa of Fabricius of chickens with selenium deficiency. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, A.V.; Quinteiro-Filho, W.M.; Ribeiro, A.; Ferraz-de-Paula, V.; Pinheiro, M.L.; Baskeville, E.; Akamine, A.T.; Astolfi-Ferreira, C.S.; Ferreira, A.J.; Palermo-Neto, J. Overcrowding stress decreases macrophage activity and increases Salmonella Enteritidis invasion in broiler chickens. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Kassas, S.; Abdo, S.E.; El-Naggar, K.; Abdo, W.; Kirrella, A.A.K.; Nashar, T.O. Ameliorative effect of dietary supplementation of copper oxide nanoparticles on inflammatory and immune reponses in commercial broiler under normal and heat-stress housing conditions. J. Biol. 2018, 78, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, T.; Lillehoj, H.S. Dexamethasone suppresses T cell-mediated immunity and enhances disease susceptibility to Eimeria mivati infection. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1994, 39, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchini, S.; Rossetti, M.; Tomaso, F.D.; Caputo, A.R. Evaluation of the effects of dexamethasone-induced stress on levels of natural antibodies in immunized laying hens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2016, 177, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwas, D.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Haldar, C. Melatonin improves humoral and cell-mediated immune responses of male golden hamster following stress induced by dexamethasone. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 259, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebishima, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Soma, G.I.; Kohchi, C.; Watanabe, G.; Taya, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Hirota, Y. Immune Recovery Effects of Immunopotentiator from Pantoea agglomerans 1 (IP-PA1) on Low Antibody Productions in Response to Salmonella Enteritidis Vaccine and Sheep Red Blood Cells in Dexamethasone-Treated Stressed Chicken Models. J. Vet. Med Sci. 2010, 72, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potts, N.D.; Bichet, C.; Merat, L.; Guitton, E.; Krupa, A.P.; Burke, T.A.; Kennedy, L.J.; Sorci, G.; Kaufman, J. Development and optimization of a hybridization technique to type the classical class I and class II B genes of the chicken MHC. Immunogenetics 2019, 71, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chazara, O.; Tixier-Boichard, M.; Morin, V.; Zoorob, R.; Bed’hom, B. Organisation and diversity of the class II DM region of the chicken MHC. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Qu, L.J.; Zheng, J.X.; Liu, C.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Chen, Y.M.; Xu, G.Y.; Yang, N. Expression profiles of genes within a subregion of chicken major histocompatibility complex B in spleen after Marek’s disease virus infection. Poult. Sci. 2010, 89, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Kaufman, J. What chickens might tell us about the MHC class II system. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 46, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoso, P.A.; Pan, T.; Wan, N.; Yang, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, S. Selenium Deficiency Induces Autophagy in Immune Organs of Chickens. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 177, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, B.; Zhao, X.; Gao, P.; Dai, X.; Liao, M.; Ren, T. Newcastle disease virus-induced autophagy mediates antiapoptotic signaling responses in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73981–73993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Gu, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Gao, F. Induction of nuclear factor-κB signal-mediated apoptosis and autophagy by reactive oxygen species is associated with hydrogen peroxide-impaired growth performance of broilers. Animal 2018, 12, 2561–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osuka, A.; Ogura, H.; Ueyama, M.; Shimazu, T.; Lederer, J.A. Immune response to traumatic injury: Harmony and discordance of immune system homeostasis. Acute Med. Surg. 2014, 1, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzone, S.; Cassinotti, A.; Trabattoni, D.; Manzionna, G.; Rainone, V.; Bevilacqua, M.; Massari, A.; Manes, G.; Maconi, G.; Clerici, M.; et al. Immunomodulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on TH1/TH2 cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease: An in vitro study. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharm. 2009, 22, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffer, U.; Wade, R.G.; Gourlay, T. Cytokines in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome: A review. HSR Proc. Intensive Care Cardiovasc. Anesth. 2010, 2, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, D.; Speranza, F.; Martegani, R. Role of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the immune response to Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2002, 2, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Topete, D.; Cidlowski, J.A. One Hormone, Two Actions: Anti- and Pro-Inflammatory Effects of Glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 2015, 22, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. Anti-inflammatory Actions of Glucocorticoids: Molecular Mechanisms. Clin. Sci. 1998, 94, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Pomar, N.; Detková, D.; Arostegui, J.I.; Alvarez, A.; Soler-Palacín, P.; Vidaller, A.; Espanol, T.; Sampalo, A.; de Gracia, J.; Hernandez, M.; et al. Role of TNFRSF13B variants in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Blood 2009, 114, 2846–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzi, M.; Melén, E.; Kull, I.; Wickman, M.; Hammarström, L. Rare mutations in TNFRSF13B increase the risk of asthma symptoms in Swedish children. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yao, Q.M.; Liu, Y.X.; Shan, N.N.; Wang, D.; Peng, J.; Xu, J.; Hou, M. Reduced tumour necrosis factor receptor superfamily 13C inversely correlated with tumour necrosis factor superfamily 13B in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Ohno, K.; Fujiwara-Igarashi, A.; Tomiyasu, H.; Fujino, Y.; Tsujimoto, H. Methylation of TNFRSF13B and TNFRSF13C in duodenal mucosa in canine inflammatory bowel disease and its association with decreased mucosal IgA expression. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 160, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutukculer, N.; Gulez, N.; Karaca, N.E.; Aksu, G.; Berdeli, A. Three Different Classifications, B Lymphocyte Subpopulations, TNFRSF13. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, G.; Bosch, R.; Hodgson, K.; Tejero, R.; Roué, G.; Colomer, D.; Montserrat, E.; Moreno, C. B cell activation through CD40 and IL4R ligation modulates the response of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells to BAFF and APRIL. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexaki, V.I.; Pelekanou, V.; Notas, G.; Venihaki, M.; Kampa, M.; Dessirier, V.; Sabour-Alaoui, S.; Stathopoulos, E.N.; Tsapis, A.; Castanas, E. B-Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA) Activation Exerts Specific Proinflammatory Effects in Normal Human Keratinocytes and Is Preferentially Expressed in Inflammatory Skin Pathologies. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.A.; Petri, M.A.; Wallace, D.J.; Ginzler, E.M.; Merrill, J.T.; Stohl, W.; Chatham, W.W.; Strand, V.; Weinstein, A.; Chevrier, M.R.; et al. Novel evidence-based systemic lupus erythematosus responder index. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Isa, F.; Ahmed Al-Haj, N.; Mat Isa, N.; Ideris, A.; Powers, C.; Oladapo, O.; Nair, V.; Omar, A.R. Differential expression of immune-related genes in the bursa of Fabricius of two inbred chicken lines following infection with very virulent infectious bursal disease virus. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 68, 101399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulwich, K.L.; Giotis, E.S.; Gray, A.; Nair, V.; Skinner, M.A.; Broadbent, A.J. Differential gene expression in chicken primary B cells infected ex vivo with attenuated and very virulent strains of infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV). J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2918–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample Name | Raw Reads | Clean Reads | Total Mapped | Multiple Mapped 1 | Uniquely Mapped 2 | Exon% | Intergenic% | Intron% | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B_S_1 | 49,138,008 | 44,665,444 | 37,779,488 (84.58%) | 888,893 (1.99%) | 36,890,595 (82.59%) | 67.5 | 23.5 | 9.0 | 49.55 |
| B_S_2 | 50,924,048 | 48,075,590 | 39,116,591 (81.36%) | 943,790 (1.96%) | 38,172,801 (79.40%) | 67.8 | 23.4 | 8.8 | 50.41 |
| B_S_3 | 57,824,730 | 55,293,336 | 45,753,593 (82.75%) | 1,112,575 (2.01%) | 44,641,018 (80.73%) | 67.7 | 23.1 | 9.2 | 49.31 |
| D_S_1 | 58,751,020 | 52,244,762 | 44,495,796 (85.17%) | 1,004,681 (1.92%) | 43,491,115 (83.24%) | 64.1 | 25.8 | 10.1 | 48.54 |
| D_S_2 | 59,055,618 | 56,786,086 | 47,986,552 (84.5%) | 1,109,279 (1.95%) | 46,877,273 (82.55%) | 65.7 | 24.6 | 9.7 | 48.76 |
| D_S_3 | 58,552,874 | 57,292,842 | 48,792,672 (85.16%) | 1,116,745 (1.95%) | 47,675,927 (83.21%) | 65.0 | 24.9 | 10.2 | 49.08 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Su, A.; Tian, H.; Zhai, M.; Li, W.; Tian, Y.; Li, K.; Sun, G.; Jiang, R.; Han, R.; et al. Transcriptomic Analysis of Spleen Revealed Mechanism of Dexamethasone-Induced Immune Suppression in Chicks. Genes 2020, 11, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050513
Guo Y, Su A, Tian H, Zhai M, Li W, Tian Y, Li K, Sun G, Jiang R, Han R, et al. Transcriptomic Analysis of Spleen Revealed Mechanism of Dexamethasone-Induced Immune Suppression in Chicks. Genes. 2020; 11(5):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050513
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yujie, Aru Su, Huihui Tian, Minxi Zhai, Wenting Li, Yadong Tian, Kui Li, Guirong Sun, Ruirui Jiang, Ruili Han, and et al. 2020. "Transcriptomic Analysis of Spleen Revealed Mechanism of Dexamethasone-Induced Immune Suppression in Chicks" Genes 11, no. 5: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050513
APA StyleGuo, Y., Su, A., Tian, H., Zhai, M., Li, W., Tian, Y., Li, K., Sun, G., Jiang, R., Han, R., Yan, F., & Kang, X. (2020). Transcriptomic Analysis of Spleen Revealed Mechanism of Dexamethasone-Induced Immune Suppression in Chicks. Genes, 11(5), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050513






