MiR-146a Regulates Migration and Invasion by Targeting NRP2 in Circulating-Tumor Cell Mimicking Suspension Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Analysis of Small-RNA and mRNA Sequencing
2.3. Transfection
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Trans-Well Invasion Assay
2.7. Cell Migration Assay
2.8. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.9. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.10. Insilico Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
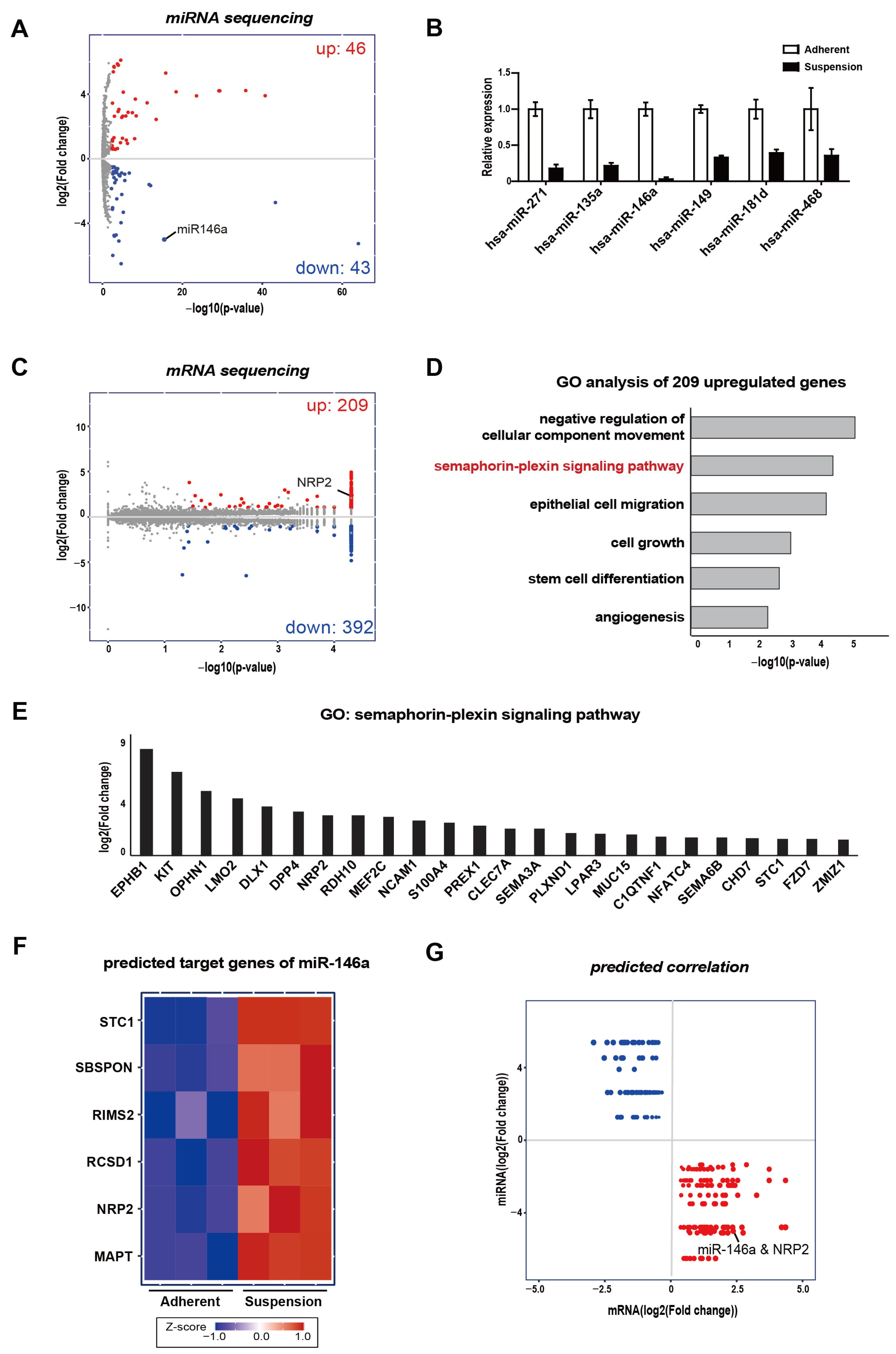
3.1. Integrative Analysis of mRNA and Small–RNA Sequencings
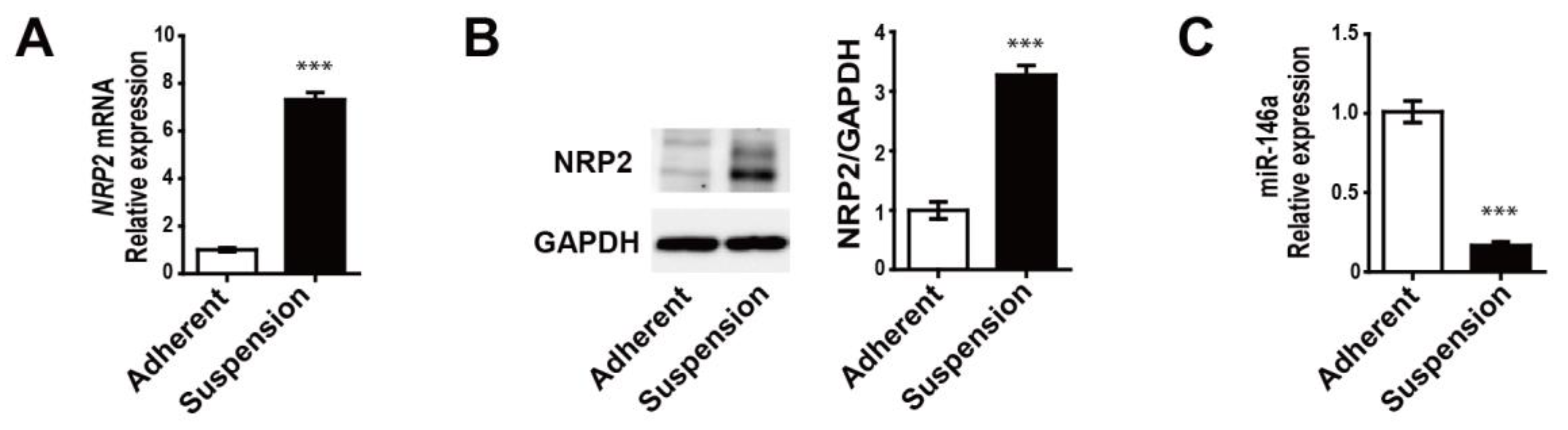
3.2. MDA-MB-468 Suspension Cells Show Upregulated NRP2 and Downregulated miR-146a Expressions Compared to Adherent Cells
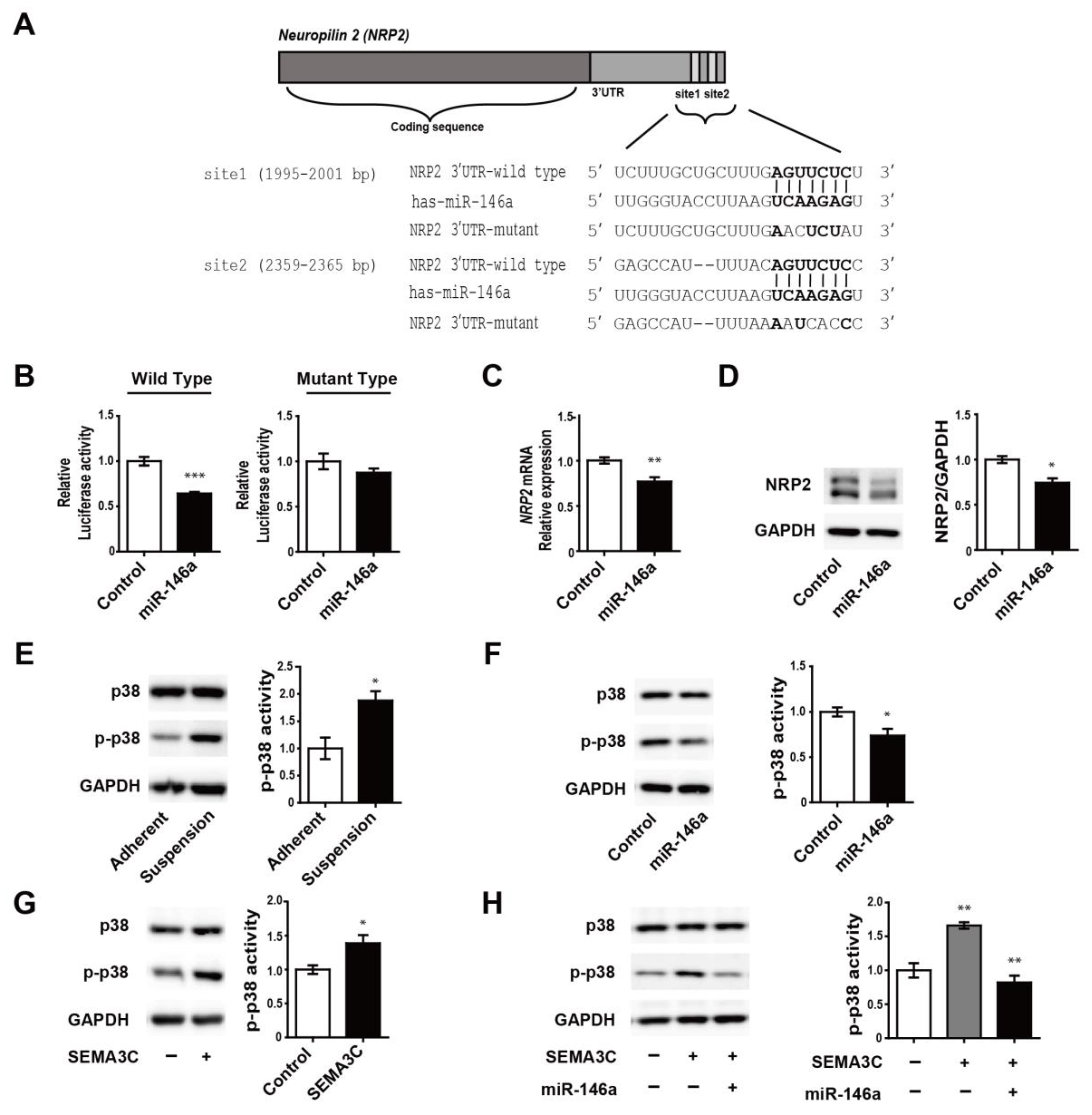
3.3. MiR-146a Directly Targets NRP2 and Regulates SEMA3C-Induced Phosphorylation of p38
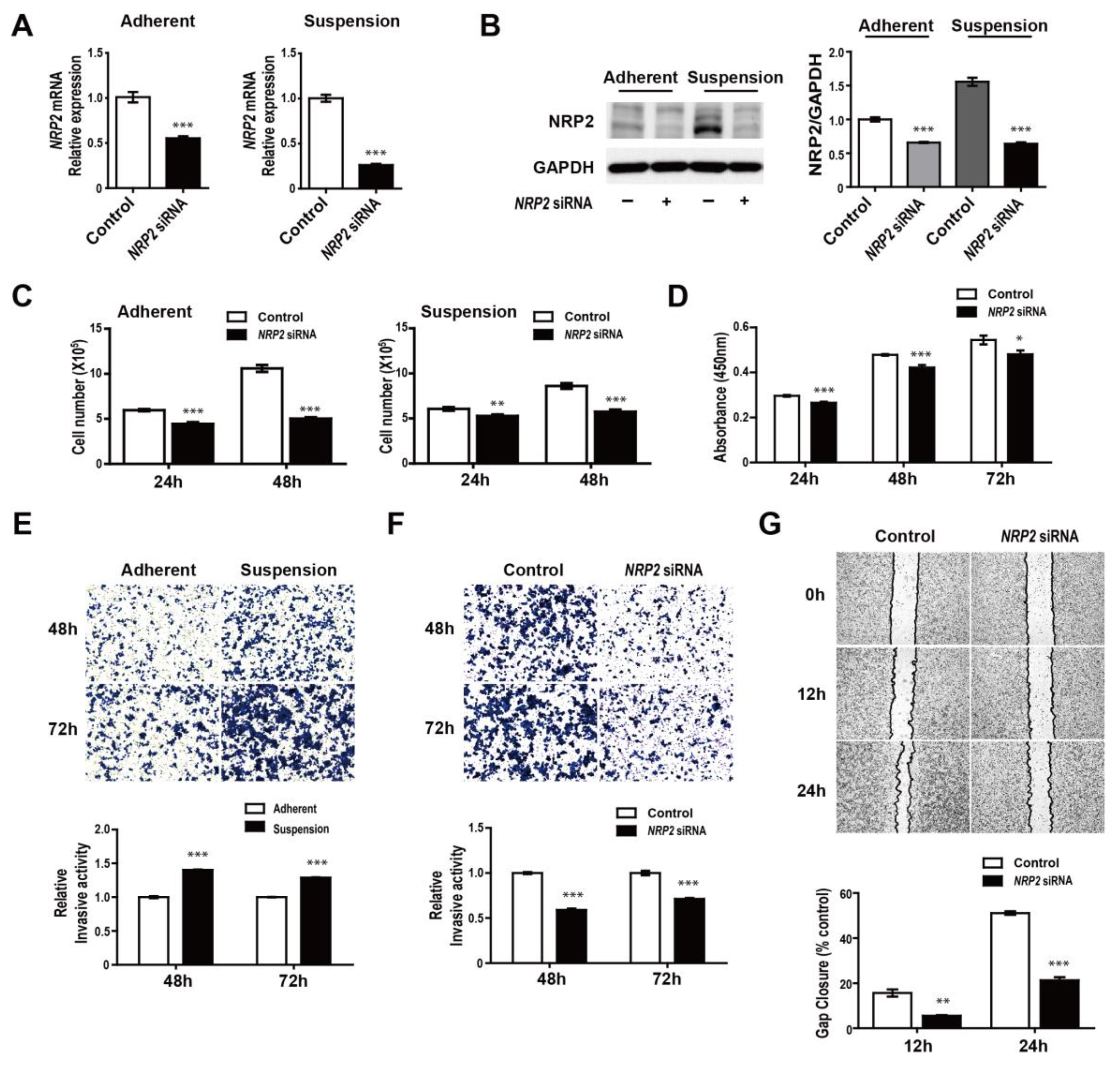
3.4. NRP2 Inhibition Attenuates Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of MDA-MB-468 Cells
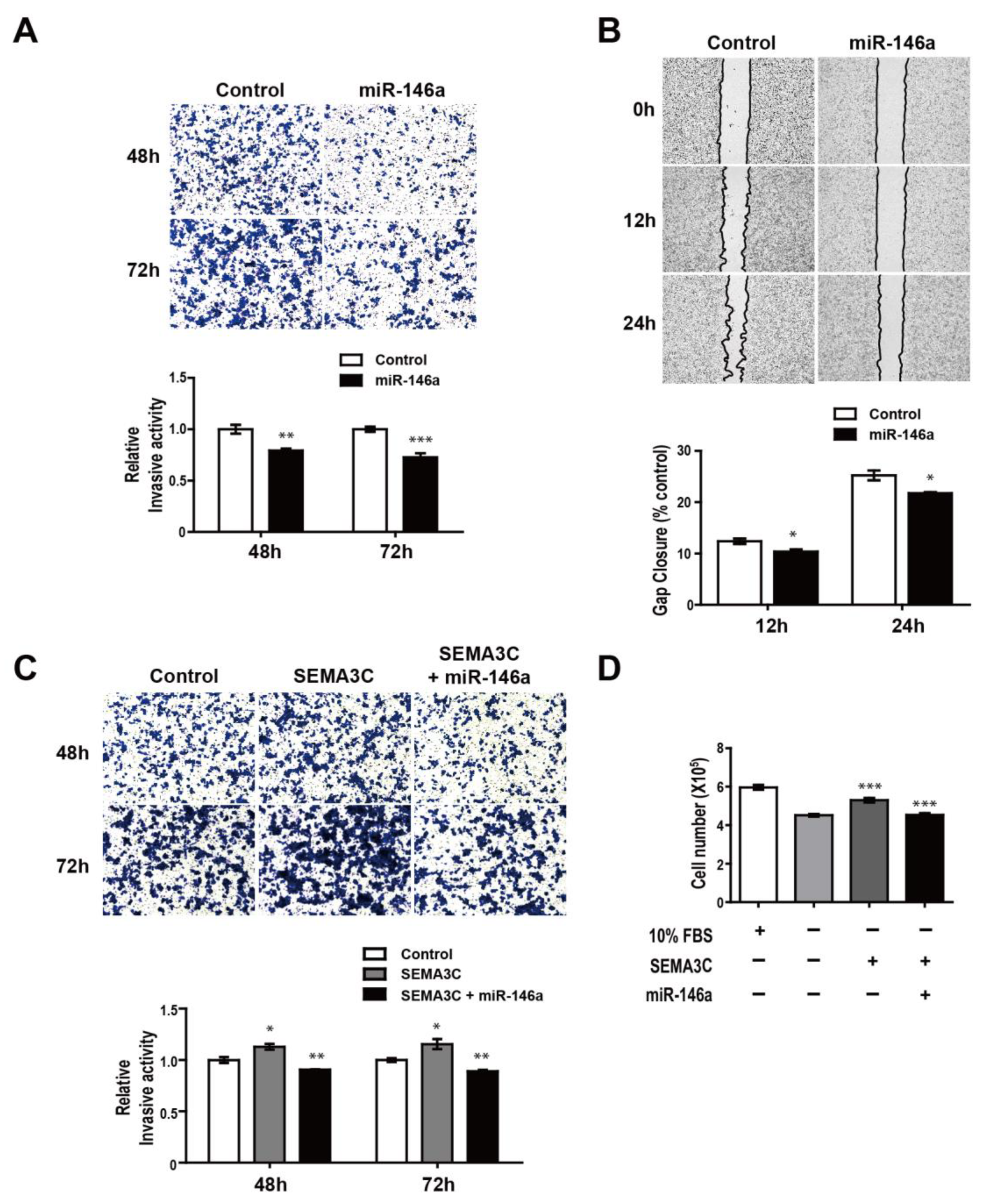
3.5. MiR-146a Impairs SEMA3C-induced Prometastatic Phenotypes in MDA-MB-468 Suspension Cells
3.6. Breast Cancer Patients with Increased NRP2 Are Associated with Poor Clinical Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smerage, J.B.; Barlow, W.E.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Winer, E.P.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Srkalovic, G.; Tejwani, S.; Schott, A.F.; O’Rourke, M.A.; Lew, D.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells and Response to Chemotherapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer: SWOG S0500. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3483–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Proudhon, C.; Pierga, J.-Y. Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabriel, M.T.; Calleja, L.R.; Chalopin, A.; Ory, B.; Heymann, D. Circulating Tumor Cells: A Review of Non-EpCAM-Based Approaches for Cell Enrichment and Isolation. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.Y.; Jeong, A.L.; Joo, H.J.; Han, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Lim, J.-S.; Lee, M.-S.; Choi, H.-K.; Yang, Y. Development of suspension cell culture model to mimic circulating tumor cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dasgupta, A.; Lim, A.R.; Ghajar, C.M. Circulating and disseminated tumor cells: Harbingers or initiators of metastasis? Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Praharaj, P.P.; Bhutia, S.K.; Nagrath, S.; Bitting, R.L.; Deep, G. Circulating tumor cell-derived organoids: Current challenges and promises in medical research and precision medicine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2018, 1869, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katchy, A.; Williams, C. Expression Profiles of Estrogen-Regulated MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 373–393. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.J.; Poliseno, L.; Song, M.S.; Ala, U.; Webster, K.; Ng, C.; Beringer, G.; Brikbak, N.J.; Yuan, X.; Cantley, L.C. MicroRNA-antagonism regulates breast cancer stemness and metastasis via TET-family-dependent chromatin remodeling. Cell 2013, 154, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.-X.; Ma, X.; Chen, Z.-N. microRNA-146a inhibits cancer metastasis by downregulating VEGF through dual pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hurst, D.R.; Edmonds, M.D.; Scott, G.K.; Benz, C.C.; Vaidya, K.S.; Welch, D.R. Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor 1 Up-regulates miR-146, Which Suppresses Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, J.P.; Dong, L.F.; Chen, F.F.; Fan, Y.F. miR-146a-5p targets interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 to inhibit the growth, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geretti, E.; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilins: Novel targets for anti-angiogenesis therapies. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2007, 1, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wittmann, P.; Grubinger, M.; Gröger, C.; Huber, H.; Sieghart, W.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Mikulits, W. Neuropilin-2 induced by transforming growth factor-beta augments migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gemmill, R.M.; Nasarre, P.; Nair-Menon, J.; Cappuzzo, F.; Landi, L.; D’Incecco, A.; Uramoto, H.; Yoshida, T.; Haura, E.B.; Armeson, K.; et al. The neuropilin 2 isoform NRP2b uniquely supports TGFbeta-mediated progression in lung cancer. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaag0528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuoka, H.; Kodama, R.; Tsujimoto, M.; Yoshidome, K.; Akamatsu, H.; Nakahara, M.; Inagaki, M.; Sanke, T.; Nakamura, Y. Neuropilin-2 expression in breast cancer: Correlation with lymph node metastasis, poor prognosis, and regulation of CXCR4 expression. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lv, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H. Silencing of semaphorin 3C suppresses cell proliferation and migration in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5913–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, K.; Minato, H.; Murayama, T.; Sasahara, A.; Nishimura, T.; Kiyokawa, E.; Kanauchi, H.; Shimizu, S.; Sato, A.; Nishioka, K.; et al. Semaphorin signaling via MICAL3 induces symmetric cell division to expand breast cancer stem-like cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 116, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, D.-G.; Chang, W.-W.; Jan, M.-S.; Tu, C.-W.; Lu, Y.-C.; Tai, C.-K. Promotion of metastasis of thyroid cancer cells via NRP-2-mediated induction. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4224–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wada, M.; Canals, D.; Adada, M.; Coant, N.; Salama, M.; Helke, K.; Arthur, J.S.C.; Shroyer, K.R.; Kitatani, K.; Obeid, L.M.; et al. P38 delta MAPK promotes breast cancer progression and lung metastasis by enhancing cell proliferation and cell detachment. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6649–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murali, B.; Ren, Q.; Luo, X.; Faget, D.V.; Wang, C.; Johnson, R.M.; Gruosso, T.; Flanagan, K.C.; Fu, Y.; Leahy, K.; et al. Inhibition of the Stromal p38MAPK/MK2 Pathway Limits Breast Cancer Metastases and Chemotherapy-Induced Bone Loss. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5618–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Si, C.; Yu, Q.; Yao, Y. Effect of miR-146a-5p on proliferation and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer via regulation of SOX5. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4515–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Shen, Y.-Q.; Wang, H.-M.; Ding, L.; Gu, Y.-C.; Lou, J.-T.; Zhao, X.-T.; Ma, Z.; et al. MiR-146a-5p inhibits cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in NSCLC cell lines by targeting CCND1 and CCND2. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59287–59298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.-W.; Gao, L.; Dang, Y.-W.; Li, P.; Li, Z.-Y.; Chen, G.; Luo, D.-Z. Protective potential of miR-146a-5p and its underlying molecular mechanism in diverse cancers: A comprehensive meta-analysis and bioinformatics analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, T.; Sun, Z.; Yan, S.; Zheng, S. Elevated expression of neuropilin-2 associated with unfavorable prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 3827–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, T.; Shimada, K.; Asano, A.; Tatsumi, Y.; Yamaguchi, N.; Yamazaki, M.; Konishi, N. MicroRNA-331-3p Suppresses Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation and E6/E7 Expression by Targeting NRP2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mercurio, A.M. VEGF/Neuropilin Signaling in Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Comer, A.; Frank, J.A.; Ke, Z.J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, X.; Wang, S.; et al. ErbB2 and p38gamma MAPK mediate alcohol-induced increase in breast cancer stem cells and metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, H.M.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Toy, K.A.; Cimino-Mathews, A.; Argani, P.; Kleer, C.G. EZH2 inhibition decreases p38 signaling and suppresses breast cancer motility and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 138, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coma, S.; Shimizu, A.; Klagsbrun, M. Hypoxia induces tumor and endothelial cell migration in a Semaphorin 3F- and VEGF-dependent manner via transcriptional repression of their common receptor Neuropilin 2. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Micalizzi, D.S.; Maheswaran, S.; Haber, D.A. A conduit to metastasis: Circulating tumor cell biology. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 1827–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, A.A.; Talasaz, A.H.; Zhang, H.; Coram, M.A.; Reddy, A.; Deng, G.; Telli, M.L.; Advani, R.H.; Carlson, R.W.; Mollick, J.A.; et al. Single Cell Profiling of Circulating Tumor Cells: Transcriptional Heterogeneity and Diversity from Breast Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pestrin, M.; Salvianti, F.; Galardi, F.; De Luca, F.; Turner, N.; Malorni, L.; Pazzagli, M.; Di Leo, A.; Pinzani, P. Heterogeneity of PIK3CA mutational status at the single cell level in circulating tumor cells from metastatic breast cancer patients. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 9, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heitzer, E.; Auer, M.; Gasch, C.; Pichler, M.; Ulz, P.; Hoffmann, E.M.; Lax, S.; Waldispuehl-Geigl, J.; Mauermann, O.; Lackner, C.; et al. Complex Tumor Genomes Inferred from Single Circulating Tumor Cells by Array-CGH and Next-Generation Sequencing. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2965–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebright, R.Y.; Lee, S.; Wittner, B.S.; Niederhoffer, K.L.; Nicholson, B.T.; Bardia, A.; Truesdell, S.; Wiley, D.F.; Wesley, B.; Li, S.; et al. Deregulation of ribosomal protein expression and translation promotes breast cancer metastasis. Science 2020, 367, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieuwerts, A.M.; Mostert, B.; Vries, J.B.-D.; Peeters, D.; De Jongh, F.E.; Stouthard, J.M.; Dirix, L.Y.; Van Dam, P.; Van Galen, A.; De Weerd, V.; et al. mRNA and microRNA Expression Profiles in Circulating Tumor Cells and Primary Tumors of Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3600–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, W.; Liang, G.; Xie, X.; Jiang, W.; Tan, L.; Sanders, A.J.; Liu, Z.; Ling, Y.; Zhong, W.; Tian, Z.; et al. Incorporating MicroRNA into Molecular Phenotypes of Circulating Tumor Cells Enhances the Prognostic Accuracy for Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2019, 24, e1044–e1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.-H.; Imrali, A.; Heeschen, C. Circulating cancer stem cells: The importance to select. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 27, 437–449. [Google Scholar]
- Elaimy, A.L.; Guru, S.; Chang, C.; Ou, J.; Amante, J.J.; Zhu, L.J.; Goel, H.L.; Mercurio, A.M. VEGF-neuropilin-2 signaling promotes stem-like traits in breast cancer cells by TAZ-mediated repression of the Rac GAP beta2-chimaerin. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaao6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goel, H.L.; Pursell, B.; Chang, C.; Shaw, L.M.; Mao, J.; Simin, K.; Kumar, P.; Kooi, C.W.V.; Shultz, L.D.; Greiner, D.L.; et al. GLI1 regulates a novel neuropilin-2/alpha6beta1 integrin based autocrine pathway that contributes to breast cancer initiation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 488–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, D.; Scott, G.K.; Schokrpur, S.; Patil, C.K.; Campisi, J.; Benz, C.C. Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5643–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhao, D.; Li, F.; Wang, H. MicroRNA-146a inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting RhoA in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Chi, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiu, B.; Su, Y.; Guo, R.; Guo, L.; Sun, H.; Zeng, C.; et al. CAPG enhances breast cancer metastasis by competing with PRMT5 to modulate STC-1 transcription. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2549–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrone, M.A.; Whipple, R.A.; Thompson, K.; Cho, E.H.; Vitolo, M.I.; Balzer, E.M.; Yoon, J.R.; Ioffe, O.B.; Tuttle, K.C.; Tan, M.; et al. Metastatic breast tumors express increased tau, which promotes microtentacle formation and the reattachment of detached breast tumor cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3217–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| miRNA | Log 2-Fold Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Upregulated miRNA | ||
| miR-187 | 3.90 | |
| miR-224 | 1.27 | |
| miR-488 | 5.38 | |
| miR-582 | 2.63 | |
| miR-1298 | 4.53 | |
| Downregulated miRNA | ||
| miR-135a | −2.21 | |
| miR-146a | −5.00 | |
| miR-149 | −1.60 | |
| miR-181d | −1.35 | |
| miR-486 | −1.49 | |
| miR-1271 | −2.48 |
| Symbol | Gene Name | Log 2-Fold Change |
|---|---|---|
| STC1 | Stanniocalcin 1 | 1.20 |
| SBSPON | Somatomedin B and thrombospondin type 1 domain containing | 2.20 |
| RIMS2 | Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 2 | 1.54 |
| RCSD1 | RCSD domain containing 1 | 1.98 |
| NRP2 | Neuropilin 2 | 3.02 |
| MAPT | Microtubule associated protein tau | 3.30 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Do, Y.; Cho, J.G.; Park, J.Y.; Oh, S.; Park, D.; Yoo, K.H.; Lee, M.-S.; Kwon, B.S.; Kim, J.; Yang, Y. MiR-146a Regulates Migration and Invasion by Targeting NRP2 in Circulating-Tumor Cell Mimicking Suspension Cells. Genes 2021, 12, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010045
Do Y, Cho JG, Park JY, Oh S, Park D, Yoo KH, Lee M-S, Kwon BS, Kim J, Yang Y. MiR-146a Regulates Migration and Invasion by Targeting NRP2 in Circulating-Tumor Cell Mimicking Suspension Cells. Genes. 2021; 12(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleDo, Yeojin, Jin Gu Cho, Ji Young Park, Sumin Oh, Doyeon Park, Kyung Hyun Yoo, Myeong-Sok Lee, Byung Su Kwon, Jongmin Kim, and Young Yang. 2021. "MiR-146a Regulates Migration and Invasion by Targeting NRP2 in Circulating-Tumor Cell Mimicking Suspension Cells" Genes 12, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010045
APA StyleDo, Y., Cho, J. G., Park, J. Y., Oh, S., Park, D., Yoo, K. H., Lee, M.-S., Kwon, B. S., Kim, J., & Yang, Y. (2021). MiR-146a Regulates Migration and Invasion by Targeting NRP2 in Circulating-Tumor Cell Mimicking Suspension Cells. Genes, 12(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010045






