Identification of Circular RNAs in Hypothalamus of Gilts during the Onset of Puberty
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals
2.3. RNA Sequencing and the Transcriptome Assembly
2.4. circRNA Identification and Data Analysis
2.5. Pathway Analysis and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Construction
2.6. circRNA Validation by RT-qPCR
3. Results
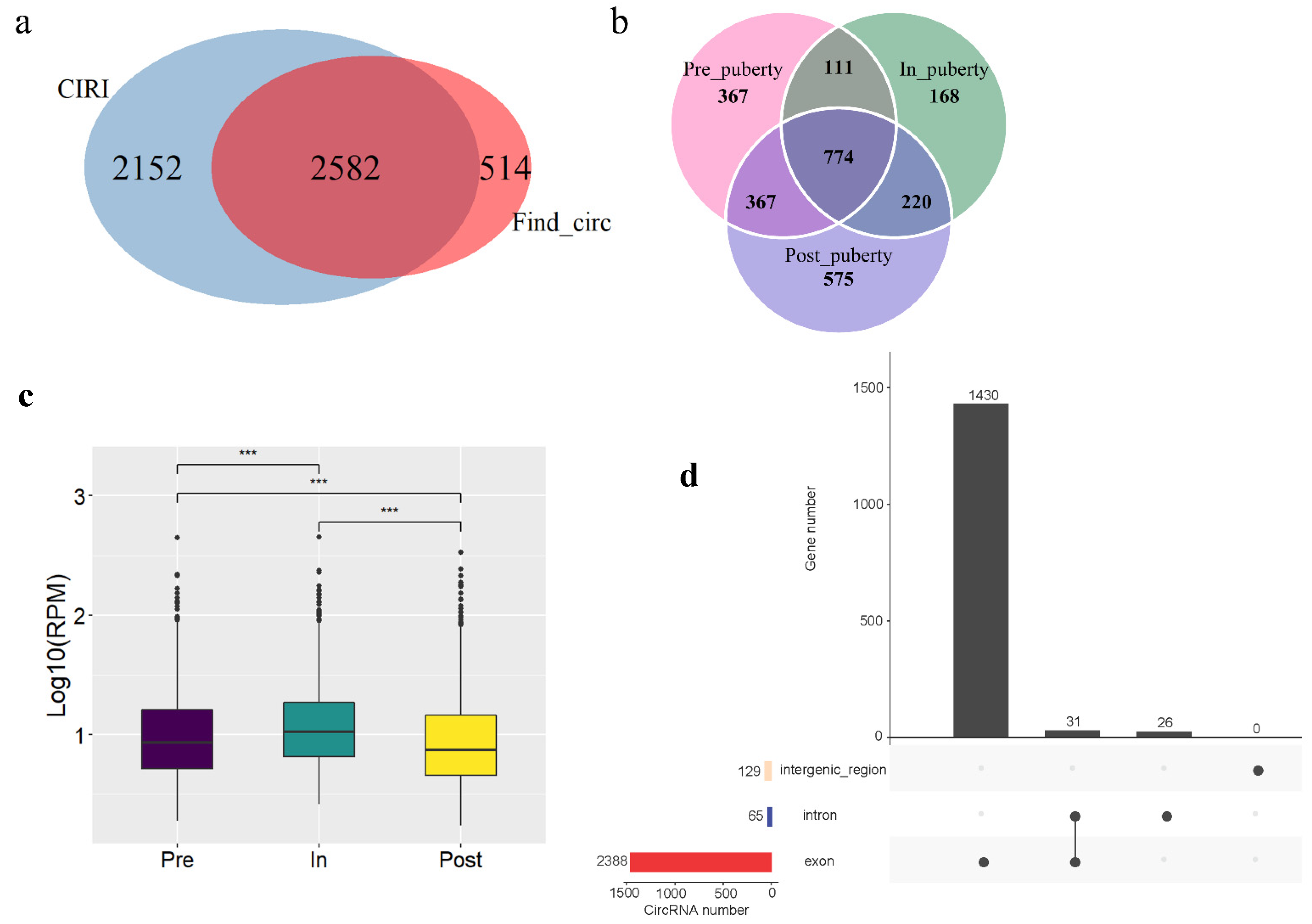
3.1. Identification of Hypothalamus-Derivced circRNAs during the Onset of Puberty
3.2. Key Pathways of cirRNAs in Pubertal Transition
3.3. The Stage-Specific circRNAs in the Pubertal Transition
3.4. Potentially Regulated Network of Differentially Expressed circRNAs
3.5. The Hypothalamus-Specific circRNAs in Puberty
3.6. circRNAs in Pubertal Genes
3.7. Validation of circRNAs by RT-qPCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinat-Botte, F.; Royer, E.; Venturi, E.; Boisseau, C.; Guillouet, P.; Furstoss, V.; Terqui, M. Determination by echography of uterine changes around puberty in gilts and evaluation of a diagnosis of puberty. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 2003, 43, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.; Yao, Z.; Ye, J.; Tian, Y.; Yang, C.; Gao, X.; Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Identification of differential genomic DNA Methylation in the hypothalamus of pubertal rat using reduced representation Bisulfite sequencing. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2017, 15, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonneman, D.J.; Schneider, J.F.; Lents, C.A.; Wiedmann, R.T.; Vallet, J.L.; Rohrer, G.A. Genome-wide association and identification of candidate genes for age at puberty in swine. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tummaruk, P.; Tantasuparuk, W.; Techakumphu, M.; Kunavongkrit, A. Age, body weight and backfat thickness at first observed oestrus in crossbred Landrace x Yorkshire gilts, seasonal variations and their influence on subsequence reproductive performance. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2007, 99, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, A.W. Hormonal changes in puberty. Pediatr. Ann. 1980, 9, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Mark-Kappeler, C.J.; Hoyer, P.B.; Pepling, M.E. The steroid hormone environment during primordial follicle formation in perinatal mouse ovaries. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomniczi, A.; Wright, H.; Ojeda, S.R. Epigenetic regulation of female puberty. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 36, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandolfi, E.C.; Tonsfeldt, K.J.; Hoffmann, H.M.; Mellon, P.L. Deletion of the Homeodomain Protein Six6 From GnRH Neurons Decreases GnRH Gene Expression, Resulting in Infertility. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Chen, R.E.; Olsen, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Brown, P.O. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.O.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Diverse alternative back-splicing and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.U.; Agarwal, V.; Guo, H.; Bartel, D.P. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Feng, J.; Lei, L.; Hu, J.; Xia, L.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhong, S.; Han, L.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of tissue-specific circular RNAs in the human and mouse genomes. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 18, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, G.; Yan, X.; Lv, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhang, S.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Du, Z.; et al. A novel FLI1 exonic circular RNA promotes metastasis in breast cancer by coordinately regulating TET1 and DNMT1. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, I.F.; Climent, M.; Quintavalle, M.; Farina, F.M.; Schorn, T.; Zani, S.; Carullo, P.; Kunderfranco, P.; Civilini, E.; Condorelli, G.; et al. Circ_Lrp6, a Circular RNA Enriched in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells, Acts as a Sponge Regulating miRNA-145 Function. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, I.; Shalamova, L.A.; Gerresheim, G.K.; Niepmann, M.; Bindereif, A.; Rossbach, O. Functional sequestration of microRNA-122 from Hepatitis C Virus by circular RNA sponges. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Vlatkovic, I.; Babic, A.; Will, T.; Epstein, I.; Tushev, G.; Akbalik, G.; Wang, M.; Glock, C.; Quedenau, C.; et al. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, T.; Xie, X.; Li, M.; Shi, J.; Zhou, J.J.; Knox, K.S.; Wang, T.; Chen, Q.; Gu, W. Rat BodyMap transcriptomes reveal unique circular RNA features across tissue types and developmental stages. RNA 2018, 24, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veno, M.T.; Hansen, T.B.; Veno, S.T.; Clausen, B.H.; Grebing, M.; Finsen, B.; Holm, I.E.; Kjems, J. Spatio-temporal regulation of circular RNA expression during porcine embryonic brain development. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, W. Identification and characterization of circular RNAs in zebrafish. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Khaleel, S.S.; Huang, H.; Wu, C.H. Software for pre-processing Illumina next-generation sequencing short read sequences. Source Code Biol. Med. 2014, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F. CIRI: An efficient and unbiased algorithm for de novo circular RNA identification. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, T.B.; Veno, M.T.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Comparison of circular RNA prediction tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, N.; Dawson, J.A.; Thomson, J.A.; Ruotti, V.; Rissman, A.I.; Smits, B.M.; Haag, J.D.; Gould, M.N.; Stewart, R.M.; Kendziorski, C. EBSeq: An empirical Bayes hierarchical model for inference in RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Luo, J.; Wei, L. KOBAS server: A web-based platform for automated annotation and pathway identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W720–W724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, B.; Enright, A.J.; Aravin, A.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, G.; Morris, J.H.; Demchak, B.; Bader, G.D. Biological network exploration with Cytoscape 3. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2014, 47, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Lu, M.; Mu, Y.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Zhan, X. TMT-based quantitative proteomics revealed follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)-related molecular characterizations for potentially prognostic assessment and personalized treatment of FSH-positive non-functional pituitary adenomas. EPMA J. 2019, 10, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marx, S.J. Hyperplasia in glands with hormone excess. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R1–R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braun, B.C.; Okuyama, M.W.; Muller, K.; Dehnhard, M.; Jewgenow, K. Steroidogenic enzymes, their products and sex steroid receptors during testis development and spermatogenesis in the domestic cat (Felis catus). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 178, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorson, J.F.; Heidorn, N.L.; Ryu, V.; Czaja, K.; Nonneman, D.J.; Barb, C.R.; Hausman, G.J.; Rohrer, G.A.; Prezotto, L.D.; McCosh, R.B.; et al. Relationship of neuropeptide FF receptors with pubertal maturation of gilts. Biol. Reprod. 2017, 96, 617–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowicki, A.; Skupin-Mrugalska, P.; Jozkowiak, M.; Wierzchowski, M.; Rucinski, M.; Ramlau, P.; Krajka-Kuzniak, V.; Jodynis-Liebert, J.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H. The Effect of 3′-Hydroxy-3,4,5,4′-Tetramethoxy -stilbene, the Metabolite of the Resveratrol Analogue DMU-212, on the Motility and Proliferation of Ovarian Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, J.S.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, I.; Gonzalez-Robayna, I.; Teuling, E.; Lo, Y.; Boerboom, D.; Falender, A.E.; Doyle, K.H.; LeBaron, R.G.; Thompson, V.; et al. Regulated expression of ADAMTS family members in follicles and cumulus oocyte complexes: Evidence for specific and redundant patterns during ovulation. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Ji, P.; Zhao, F. CircAtlas: An integrated resource of one million highly accurate circular RNAs from 1070 vertebrate transcriptomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbon, A.; Vallini, I.; Barlati, S. Genomic organization of the human GRIK2 gene and evidence for multiple splicing variants. Gene 2001, 274, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, W.E.; Diekman, M.A.; Parfet, J.R.; Moss, G.E. Pituitary responsiveness to GnRH, hypothalamic content of GnRH and pituitary LH and FSH concentrations immediately preceding puberty in gilts. J. Anim. Sci. 1984, 58, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stancic, I.; Stancic, B.; Bozic, A.; Anderson, R.; Harvey, R.; Gvozdic, D. Ovarian activity and uterus organometry in delayed puberty gilts. Theriogenology 2011, 76, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, K.; Colgan, L.A.; Dao, M.T.; Muntean, B.S.; Sutton, L.P.; Orlandi, C.; Boye, S.L.; Boye, S.E.; Shih, C.C.; Li, Y.; et al. NF1 Is a Direct G Protein Effector Essential for Opioid Signaling to Ras in the Striatum. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2992–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, L.; Wu, Y.; Hu, S.; Chen, Q.; Tan, J.; Yan, Y.; Liang, B.; Tang, N. Analysis of Association between MAP2K4 Gene Polymorphism rs3826392 and IL-1b Serum Level in Southern Chinese Han Ischemic Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiddle, S.J.; Steves, C.J.; Mehta, M.; Simmons, A.; Xu, X.; Newhouse, S.; Sattlecker, M.; Ashton, N.J.; Bazenet, C.; Killick, R.; et al. Plasma protein biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease endophenotypes in asymptomatic older twins: Early cognitive decline and regional brain volumes. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogueiras, R.; Sabio, G. Brain JNK and metabolic disease. Diabetologia 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, F.; Richetto, J.; Racagni, G.; Feldon, J.; Meyer, U.; Riva, M.A. Effects of withdrawal from repeated amphetamine exposure in peri-puberty on neuroplasticity-related genes in mice. Neuroscience 2013, 250, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, S.R.; Lomniczi, A.; Sandau, U. Contribution of glial-neuronal interactions to the neuroendocrine control of female puberty. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dziedzic, B.; Prevot, V.; Lomniczi, A.; Jung, H.; Cornea, A.; Ojeda, S.R. Neuron-to-glia signaling mediated by excitatory amino acid receptors regulates ErbB receptor function in astroglial cells of the neuroendocrine brain. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleari, R.; Caramello, A.; Campinoti, S.; Lettieri, A.; Ioannou, E.; Paganoni, A.; Fantin, A.; Cariboni, A.; Ruhrberg, C. PLXNA1 and PLXNA3 cooperate to pattern the nasal axons that guide gonadotropin-releasing hormone neurons. Development 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.; Dao, H.; Wang, M.; Heston, A.; Garcia, K.M.; Sangal, A.; Dowling, A.R.; Faulkner, L.D.; Molitor, S.C.; Elias, C.F.; et al. Insulin and Leptin Signaling Interact in the Mouse Kiss1 Neuron during the Peripubertal Period. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e121974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, J.; Yao, Z.; Si, W.; Gao, X.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Huang, W.; Fang, F.; Zhou, J. Identification and characterization of microRNAs in the pituitary of pubescent goats. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; He, Y.; Kong, Y.; Ye, S.; Gao, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, J. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis of Hypothalamus During the Onset of Puberty in Gilts. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naule, L.; Maione, L.; Kaiser, U.B. Puberty, a sensitive window of hypothalamic development and plasticity. Endocrinology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossler, M.R.; Yao, H.; York, R.D.; Pan, M.G.; Rim, C.S.; Stork, P.J. cAMP activates MAP kinase and Elk-1 through a B-Raf- and Rap1-dependent pathway. Cell 1997, 89, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coronel, R.; Lachgar, M.; Bernabeu-Zornoza, A.; Palmer, C.; Dominguez-Alvaro, M.; Revilla, A.; Ocana, I.; Fernandez, A.; Martinez-Serrano, A.; Cano, E.; et al. Neuronal and Glial Differentiation of Human Neural Stem Cells Is Regulated by Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) Levels. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1248–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugelberg, E. Reproductive endocrinology: ESR1 mutation causes estrogen resistance and puberty delay in women. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Luense, L.J.; McGinnis, L.K.; Nothnick, W.B.; Christenson, L.K. Dicer1 is essential for female fertility and normal development of the female reproductive system. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 6207–6212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| circRNA ID | Position | Strand | circRNA Type | Parental Gene | Top 3 miRNA Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:102571848-102574753 | Chr1:102571848-102574753 | + | exon | DCC | ssc-miR-9814-3p, ssc-miR-15b, ssc-miR-144 |
| 1:11656690-11658867 | Chr1:11656690-11658867 | − | exon | TIAM2 | ssc-miR-383, ssc-miR-7857-3p, ssc-miR-185 |
| 1:14416335-14457143 | Chr1:14416335-14457143 | − | exon | ESR1 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-16, ssc-miR-7143-3p |
| 1:50832070-50838859 | Chr1:50832070-50838859 | + | exon | SMAP1 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-9825-5p, ssc-miR-383 |
| 1:52123108-52152735 | Chr1:52123108-52152735 | + | exon | RIMS1 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-574-5p, ssc-miR-34a |
| 1:593018-598149 | Chr1:593018-598149 | + | exon | WDR27 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-7135-3p, ssc-miR-181b |
| 1:73564812-73595164 | Chr1:73564812-73595164 | + | exon | SOBP | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-27b-5p, ssc-miR-491 |
| 1:80078290-80136352 | Chr1:80078290-80136352 | − | exon | HS3ST5 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-9820-5p, ssc-miR-9-1 |
| 1:87134227-87153004 | Chr1:87134227-87153004 | + | exon | PHIP | ssc-miR-545-3p, ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-148b-5p |
| 11:4104218-4118265 | Chr11:4104218-4118265 | + | exon | CDK8 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-9822-3p, ssc-miR-424-5p |
| 13:68611370-68611602 | Chr13:68611370-68611602 | − | exon | RAF1 | ssc-miR-208b |
| 14:20221955-20238937 | Chr14:20221955-20238937 | + | exon | NEK1 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-505, ssc-miR-2483 |
| 15:109436411-109441836 | Chr15:109436411-109441836 | − | exon | NDUFS1 | ssc-miR-30a-3p, ssc-miR-30e-3p, ssc-miR-676-5p |
| 18:40140465-40161356 | Chr18:40140465-40161356 | − | exon | BBS9 | ssc-miR-199b-5p, ssc-miR-186-5p, ssc-miR-186-3p |
| 2:113442089-113466481 | Chr2:113442089-113466481 | − | exon | FBXL17 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-145-5p, ssc-miR-320 |
| 2:141219340-141222143 | Chr2:141219340-141222143 | + | exon | MATR3 | ssc-miR-10390, ssc-miR-186-5p, ssc-miR-421-5p |
| 3:103726106-103773127 | Chr3:103726106-103773127 | − | exon | CRIM1 | ssc-miR-574-5p, ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-146a-3p |
| 3:131272241-131272989 | Chr3:131272241-131272989 | + | exon | RNASEH1 | ssc-miR-149 |
| 3:26701499-26703165 | Chr3:26701499-26703165 | + | exon | SMG1 | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-106a, ssc-miR-20a-5p |
| 4:46806844-46817760 | Chr4:46806844-46817760 | + | exon | NBN | ssc-miR-4331-3p, ssc-miR-9820-5p, ssc-miR-7140-3p |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Pan, X.; Li, N.; Gong, W.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, X. Identification of Circular RNAs in Hypothalamus of Gilts during the Onset of Puberty. Genes 2021, 12, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010084
Li Q, Pan X, Li N, Gong W, Chen Y, Yuan X. Identification of Circular RNAs in Hypothalamus of Gilts during the Onset of Puberty. Genes. 2021; 12(1):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010084
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qingnan, Xiangchun Pan, Nian Li, Wentao Gong, Yaosheng Chen, and Xiaolong Yuan. 2021. "Identification of Circular RNAs in Hypothalamus of Gilts during the Onset of Puberty" Genes 12, no. 1: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010084
APA StyleLi, Q., Pan, X., Li, N., Gong, W., Chen, Y., & Yuan, X. (2021). Identification of Circular RNAs in Hypothalamus of Gilts during the Onset of Puberty. Genes, 12(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010084




