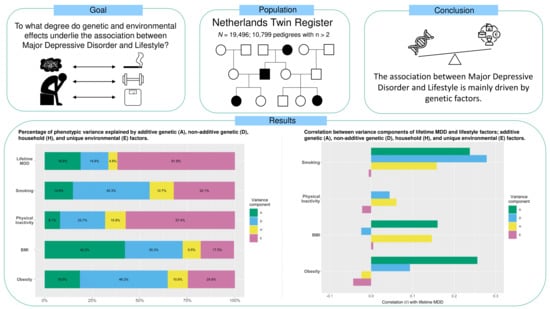
Major Depressive Disorder and Lifestyle: Correlated Genetic Effects in Extended Twin Pedigrees
Abstract
Share and Cite
Huider, F.; Milaneschi, Y.; van der Zee, M.D.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Helmer, Q.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Boomsma, D.I. Major Depressive Disorder and Lifestyle: Correlated Genetic Effects in Extended Twin Pedigrees. Genes 2021, 12, 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101509
Huider F, Milaneschi Y, van der Zee MD, de Geus EJC, Helmer Q, Penninx BWJH, Boomsma DI. Major Depressive Disorder and Lifestyle: Correlated Genetic Effects in Extended Twin Pedigrees. Genes. 2021; 12(10):1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101509
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuider, Floris, Yuri Milaneschi, Matthijs D. van der Zee, Eco J. C. de Geus, Quinta Helmer, Brenda W. J. H. Penninx, and Dorret I. Boomsma. 2021. "Major Depressive Disorder and Lifestyle: Correlated Genetic Effects in Extended Twin Pedigrees" Genes 12, no. 10: 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101509
APA StyleHuider, F., Milaneschi, Y., van der Zee, M. D., de Geus, E. J. C., Helmer, Q., Penninx, B. W. J. H., & Boomsma, D. I. (2021). Major Depressive Disorder and Lifestyle: Correlated Genetic Effects in Extended Twin Pedigrees. Genes, 12(10), 1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12101509