Spectrum of Genetic Diseases in Tunisia: Current Situation and Main Milestones Achieved
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review of Literature Related to Genetic Diseases Spectrum in Tunisia
2.2. Systematic Review of Literature Focusing on Newborn and/or Carrier Screening for Genetic Diseases among Tunisians
3. Results
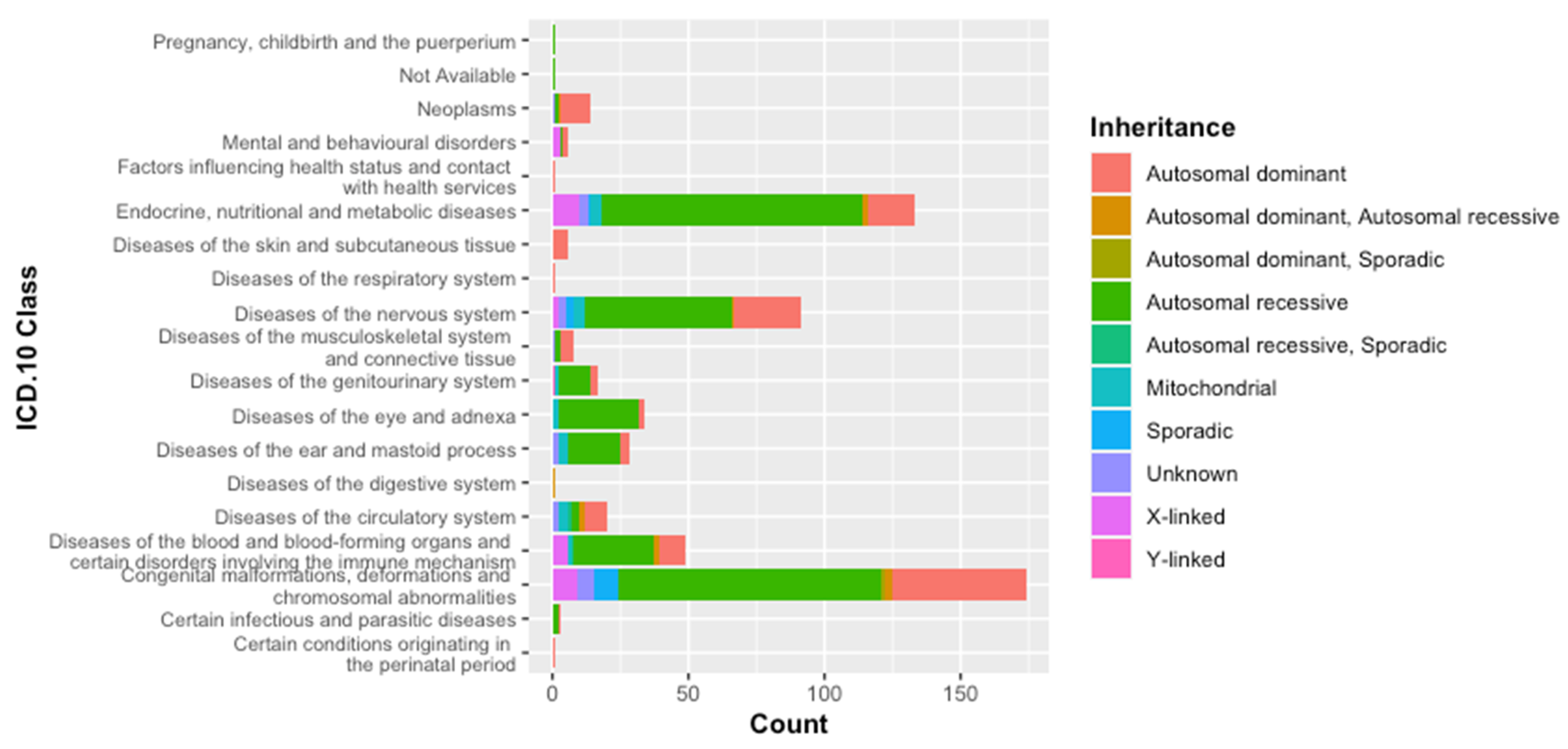
3.1. Classification of Genetic Diseases According to WHO-ICD 10
3.2. Classification According to the Inheritance Mode
3.3. Molecular Etiology of the Genetic Diseases in the Tunisian Population
3.4. Comorbidity among Tunisians
3.5. Phenotypic Features of Genetic Diseases in Tunisia
3.6. Epidemiology of Genetic Diseases in Tunisia
3.7. Current Situation of Newborn and/or Carrier Screening for Genetic Diseases in Tunisia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, C.R. The burden of rare diseases. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2018, 179, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Caplan, A. The Orphan Drug Act Revisited. JAMA 2019, 321, 833–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, T.; Nestler-Parr, S.; Babela, R.; Khan, Z.M.; Tesoro, T.; Molsen, E.; Hughes, D.A. Rare Disease Terminology and Definitions-A Systematic Global Review: Report of the ISPOR Rare Disease Special Interest Group. Value Health 2015, 18, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sara Cannizzo, V.L.; Palla, I.; Pirri, S.; Trieste, L.; Triulzi, I.; Turchetti, G. Rare diseases under different levels of economic analysis: Current activities, challenges and perspectives. RMD Open 2018, 4 (Suppl. 1), e000794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, E.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Shi, B.; Chen, Q. Dental-craniofacial manifestation and treatment of rare diseases. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2019, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lihadh Al-Gazali, H.H.; Al-Arrayad, S. Genetic disorders in the Arab world. Br. Med. J. 2006, 333, 831–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romdhane, L.; Mezzi, N.; Hamdi, Y.; El-Kamah, G.; Barakat, A.; Abdelhak, S. Consanguinity and inbreeding in health and disease in North African populations. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2019, 20, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, H. The Arab genome: Health and wealth. Gene 2016, 592, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadmouri, G.O.; Nair, P.; Obeid, T.; Al Ali, M.T.; Al Khaja, N.; Hamamy, H.A. Consanguinity and reproductive health among Arabs. J. Reprod. Health 2009, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romdhane, L.; Kefi, R.; Azaiez, H.; Ben Halim, N.; Dellagi, K.; Abdelhak, S. Founder mutations in Tunisia: Implications for diagnosis in North Africa and Middle East. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frigi, S.; Cherni, L.; Fadhlaoui-Zid, K.; Benammar-Elgaaied, A. Ancient local evolution of African mtDNA haplogroups in Tunisian Berber populations. Hum. Biol. 2010, 82, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefi, R.; Hsouna, S.; Ben Halim, N.; Lasram, K.; Romdhane, L.; Messai, H.; Abdelhak, S. Phylogeny and genetic structure of Tunisians and their position within Mediterranean populations. Mitochondrial DNA 2015, 26, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughal, M. In Tunisia, in Native Peoples of the World: An Encyclopedia of Groups, Cultures, and Contemporary Issues; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 688–689. [Google Scholar]
- Hajjej, A.; Almawi, W.Y.; Hattab, L.; El-Gaaied, A.; Hmida, S. HLA Class I and Class II Alleles and Haplotypes Confirm the Berber Origin of the Present Day Tunisian Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben Romdhane, H.; Tlili, F.; Skhiri, A.; Zaman, S.; Phillimore, P. Health system challenges of NCDs in Tunisia. Int. J. Public Health 2015, 60, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfa, C.; Achouri, H. Tunisia: “Good Practice” in expanding health care coverage: Lessons from reforms in a country in transition. In Good Practices in Health Financing Lessons from Reforms in Low-and Middle-Income Countries; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; Volume 20, pp. 335–438. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Romdhane, H.; Husseini, A.; Jabbour, S. Non-Communicable Diseases—II: Focus on Cardiovascular Diseases; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 164–177. [Google Scholar]
- Atek, M.; Traissac, P.; El Ati, J.; Laid, Y.; Aounallah-Skhiri, H.; Eymard-Duvernay, S.; Mézimèche, N.; Bougatef, S.; Béji, C.; Boutekdjiret, L. Obesity and association with area of residence, gender and socio-economic factors in Algerian and Tunisian adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben Halim, N.; Bouafif, N.B.A.; Romdhane, L.; Atig, R.K.B.; Chouchane, I.; Bouyacoub, Y.; Arfa, I.; Cherif, W.; Nouira, S.; Talmoudi, F. Consanguinity, endogamy, and genetic disorders in Tunisia. J. Community Genet. 2013, 4, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romdhane, L.; Halim, N.B.; Rejeb, I.; Kefi, R.; Bouyacoub, Y.; Rekaya, M.B.; Messai, H.; Messaoud, O.; Riahi, Z.; Bonnet, C. Specific aspects of consanguinity: Some examples from the Tunisian population. J. Human Hered. 2014, 77, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zakaria, D. Etude de L’endogamie D’origine Régionale, de la Distribution de la Consanguinité Apparente et du Comportement Intergénérationnel Dans le Choix Matrimonial en Tunisie. Intérêt des Noms de Famille et de L’isonymie Maritale. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Science, University of Tunis, Tunis, Tunisia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Halim, N.; Hsouna, S.; Lasram, K.; Rejeb, I.; Walha, A.; Talmoudi, F.; Messai, H.; Sabrine Ben Brick, A.; Ouragini, H.; Cherif, W.; et al. Differential impact of consanguineous marriages on autosomal recessive diseases in Tunisia. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2016, 28, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, L.; Abdelhak, S.; Research Unit on Molecular Investigation of Genetic Orphan Diseases and Collaborators. Genetic diseases in the Tunisian population. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2011, 155, 238–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharrat, M.; Trabelsi, S.; Chaabouni, M.; Maazoul, F.; Kraoua, L.; Ben Jemaa, L.; Gandoura, N.; Barsaoui, S.; Morel, Y.; M’Rad, R.; et al. Only two mutations detected in 15 Tunisian patients with 11beta-hydroxylase deficiency: The p.Q356X and the novel p.G379V. Clin. Genet. 2010, 78, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallabi, F.; Hadj Salem, I.; Ben Salah, G.; Ben Turkia, H.; Ben Chehida, A.; Tebib, N.; Fakhfakh, F.; Kamoun, H. Molecular characterization of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in a Tunisian family: Identification of a novel missense mutation in the ABCD1 gene. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 12, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakroun, A.; Ben Said, M.; Ennouri, A.; Achour, I.; Mnif, M.; Abid, M.; Fakhfakh, F.; Kamoun, H. Long-term clinical follow-up and molecular testing for diagnosis of the first Tunisian family with Alstrom syndrome. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salah, G.B.; Salem, I.H.; Masmoudi, A.; Rhouma, B.B.; Turki, H.; Fakhfakh, F.; Ayadi, H.; Kamoun, H. Chromosomal instability associated with a novel BLM frameshift mutation (c. 1980-1982delAA) in two unrelated Tunisian families with Bloom syndrome. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 28, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kek, H.E.H.; Wigren, E.; Jlizi, A.; Zahra, K.; Pellechia, D.; Vinciguerra, C.; Meddeb, B.; Elggaaied, A.B.A.; Gouider, E. First report of molecular diagnosis of Tunisian. hemophiliacs A: Identification of 8 novel. causative mutations. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 7, 93. [Google Scholar]
- Cherif, W.; Turkia, B.; Rhouma, B.; Riahi, I.; Chemli, J.; Amaral, O.; Miranda, S.; Caillaud, C.; Kaabachi, N.; Tebib, N. Molecular diagnosis of Gaucher disease in Tunisia. Pathol. Biol. 2012, 61, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzucchelli, I.; Garofoli, F.; Decembrino, L.; Castiglia, D.; Tadini, G.; Bellingeri, A.; Borghesi, A.; Tzialla, C.; Manzoni, P.; Stronati, M. A novel LAMA3 mutation in a newborn with junctional epidermolysis bullosa herlitz type. Neonatology 2011, 99, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khiari, H.M.; Lesca, G.; Malafosse, A.; Mrabet, A. A novel exon 3 mutation in a Tunisian patient with Lafora’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 304, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tinsa, F.; Ben Romdhane, M.; Boudabous, H.; Bel Hadj, I.; Brini, I.; Tebib, N.; Louati, H.; Bekri, S.; Boussetta, K. A Novel Mutation c.153 C > A in a Tunisian Girl with Wolman Disease and Unusual Presentation: Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 41, e193–e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaafar, N.; Moleirinho, A.; Kerkeni, E.; Monastiri, K.; Seboui, H.; Amorim, A.; Prata, M.J.; Quental, S. Molecular characterization of maple syrup urine disease patients from Tunisia. Gene 2013, 517, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, E.M.; Logan, C.V.; Mougou-Zerelli, S.; Lee, J.H.; Silhavy, J.L.; Brancati, F.; Iannicelli, M.; Travaglini, L.; Romani, S.; Illi, B.; et al. Mutations in TMEM216 perturb ciliogenesis and cause Joubert, Meckel and related syndromes. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkaouar-Rebai, E.; Chamkha, I.; Mezghani, N.; Ben Ayed, I.; Fakhfakh, F. Screening of mitochondrial mutations in Tunisian patients with mitochondrial disorders: An overview study. Mitochondrial DNA 2013, 24, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.B.; Chouchène, E.; Salem, S.B.; Daoud, K.; Largueche, L.; Bouassida, W.; Benzina, Z.; Ayadi, H.; Söderkvist, P.; Matri, L.; et al. Posterior microphthalmia and nanophthalmia in Tunisia caused by a founder c.1059_1066insC mutation of the PRSS56 gene. Gene 2013, 528, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, S.; Sakka, S.; Romdhane, S.B.; Amer, Y.B.; Lehkim, L.; Farhat, N.; Mahfoudh, K.B.; Authier, F.J.; Dammak, M.; Mhiri, C. Novel splicing dysferlin mutation causing myopathy with intra-familial heterogeneity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 5755–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chkioua, L.; Grissa, O.; Leban, N.; Gribaa, M.; Boudabous, H.; Turkia, H.B.; Ferchichi, S.; Tebib, N.; Laradi, S. The mutational spectrum of hunter syndrome reveals correlation between biochemical and clinical profiles in Tunisian patients. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouesleti, S.; Brunel, V.; Ben Turkia, H.; Dranguet, H.; Miled, A.; Miladi, N.; Ben Dridi, M.F.; Lavoinne, A.; Saugier-Veber, P.; Bekri, S. Molecular characterization of MPS IIIA, MPS IIIB and MPS IIIC in Tunisian patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chkioua, L.; Khedhiri, S.; Grissa, O.; Aloui, C.; Turkia, H.B.; Ferchichi, S.; Miled, A.; Froissart, R.; Acquaviva, C.; Laradi, S. Genetic basis of cystinosis in Tunisian patients: Identification of novel mutation in CTNS gene. Meta Gene 2015, 5, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohler, E.; Mamai, O.; Hirst, J.; Zamiri, M.; Horn, H.; Nomura, T.; Irvine, A.D.; Moran, B.; Wilson, N.J.; Smith, F.J.; et al. Haploinsufficiency for AAGAB causes clinically heterogeneous forms of punctate palmoplantar keratoderma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romdhane, L.; Messaoud, O.; Bouyacoub, Y.; Kerkeni, E.; Naouali, C.; Cherif Ben Abdallah, L.; Tiar, A.; Charfeddine, C.; Monastiri, K.; Chabchoub, I.; et al. Comorbidity in the Tunisian population. Clin. Genet. 2016, 89, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrabet, H.; Borhani-Haghighi, A.; Koseoglu, E.; Mutlu, M.; Baydemir, R.; Nafissi, S.; Eschebbi, S.; Delibas, E.; Samangooie, S.; Yetkin, F.; et al. Association of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Behcet’s disease: Is there a relationship? A multi-national case series. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayeb, M.R.Z.; Laroussi, N.; Bonnet, C.; Romdhane, L.; Mkaouar, R.; Zaouak, A.; Marrakchi, J.; Abdessalem, G.; Messaoud, O.; Bouchniba, O.; et al. A Tunisian family with a novel mutation in the gene CYP4F22 for lamellar ichthyosis and co-occurrence of hearing loss in a child due to mutation in the SLC26A4 gene. Int. Soc. Dermatol. 2019, 58, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghedira, N.; Lagarde, A.; Ben Ameur, K.; Elouej, S.; Sakka, R.; Kerkeni, E.; Chioukh, F.Z.; Olschwang, S.; Desvignes, J.P.; Abdelhak, S.; et al. Clinical profile of comorbidity of rare diseases in a Tunisian patient: A case report associating incontinentia pigmenti and Noonan syndrome. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabebi, M.; Charfi, N.; Kallabi, F.; Alila-Fersi, O.; Ben Mahmoud, A.; Tlili, A.; Keskes-Ammar, L.; Kamoun, H.; Abid, M.; Mnif, M.; et al. Whole mitochondrial genome screening of a family with maternally inherited diabetes and deafness (MIDD) associated with retinopathy: A putative haplotype associated to MIDD and a novel MT-CO2 m.8241T>G mutation. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baya, W.; Fredj, F.B.; Hassine, I.B.; Anoun, J.; Mzabi, A.; Karmani, M.; Rezgui, A.; Laatiri, M.A.; Kechrid, C.L. Systemic lupus erythematosus, antiphospholipid syndrome and Hashimoto thyroiditis occurring in a patient with Niemann-Pick disease: A second case. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 36, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louhichi, N.; Bahloul, E.; Marrakchi, S.; Othman, H.B.; Triki, C.; Aloulou, K.; Trabelsi, L.; Mahfouth, N.; Ayadi-Mnif, Z.; Keskes, L.; et al. Thyroid involvement in Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome in adults in the largest series of patients carrying the same founder mutation in ABHD5 gene. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charfeddine, C.; Dallali, H.; Abdessalem, G.; Ghedira, K.; Hamdi, Y.; Elouej, S.; Landoulsi, Z.; Delague, V.; Lagarde, A.; Levy, N.; et al. Identification of a CDH12 potential candidate genetic variant. for an autosomal dominant form of transgrediens and progrediens palmoplantar keratoderma in a Tunisian family. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Romdhan, S.; Sakka, S.; Farhat, N.; Triki, S.; Dammak, M.; Mhiri, C. A Novel SYNJ1 Mutation in a Tunisian Family with Juvenile Parkinson’s Disease Associated with Epilepsy. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 66, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blibech, R.; Gharbi, Y.; Mrad, A.; Zahra, H.; Mahjoub, T.; Belhaj, A.; Laatiri, Z.; Kastally, R.; Rosa, R. Incidence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in Tunisian populations. Nouv. Rev. Fr. d’Hématol. 1989, 31, 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Fattoum, S. Evolution of hemoglobinopathy prevention in Africa: Results, problems and prospect. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 1, e2009005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilber Nelly, K.E.; Miriam, A. The Libyan Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease focus in Israel: An epidemiologic evaluation. Neurology 1991, 41, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussetta, K.; Khalsi, F.; Bahri, Y.; Belhadj, I.; Tinsa, F.; Messaoud, T.B.; Hamouda, S. Cystic fibrosis in Tunisian children: A review of 32 children. Afr. Health Sci. 2018, 18, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kharfi, M.; Khaled, A.; Mokhtar, I.; Kamoun, M. Atopic dermatitis in Tunisia: Epidemiological and clinical aspects. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2001, 128, 623–625. [Google Scholar]
- Brick, A.S.B.; Laroussi, N.; Mesrati, H.; Kefi, R.; Bchetnia, M.; Lasram, K.; Halim, N.B.; Romdhane, L.; Ouragini, H.; Marrakchi, S. Mutational founder effect in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa families from Southern Tunisia. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2014, 306, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, S.; Ghorbel, M.; Nacef, L.; Daghfous, F.; Osman, N.B.; Reguig, R.; Lachhab, M.J.L.T.m. The exfoliation syndrome in Tunisia. Tunis. Med. 1990, 68, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Abdallah, M.; Zehani, S. Registre des Cancers Nord.-Tunisie 1995–1998; Institut Salah Azaiez: Tunis, Tunisia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Frikha, M.; Mseddi, S.; Elloumi, M.; Bouaziz, M.; Khanfir, A.; Mnif, J.; Saad, A.; Souissi, T. Fanconi disease: Study of 43 cases in Southern Tunisia. Arch. Pediatr. Organe Off. Soc. Fr. Pediatr. 1998, 5, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimane, M.; Pousse, H.; Maatoug, F.; Hammami, M.; Farhat, M.B. Phenotypic expression of familial hypercholesterolaemia in central and southern Tunisia. Atherosclerosis 1993, 104, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkia, B.; Tebib, N.; Azzouz, H.; Abdelmoula, M.S.; Chehida, B.; Chemli, J.; Monastiri, K.; Chaabouni, M.; Sanhagi, H.; Zouari, B. Incidence of mucopolysaccharidoses in Tunisia. Tunis. Med. 2009, 87, 782–785. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrallah, F.; Hadj-Taieb, S.; Chehida, A.B.; Jelassi, A.; Massoued, S.B.; Charfi, M.; Zidi, W.; Amri, F.; Helel, K.B.; Mejaoual, H. Nonketotic hyperglycinemia in tunisia. Report upon a series of 69 patients. Neuropediatrics 2020, 51, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehida, A.B.; Messaoud, S.B.; Abdelaziz, R.B.; Mansouri, H.; Boudabous, H.; Hakim, K.; Ali, N.B.; Ameur, Z.B.; Sassi, Y.; Kaabachi, N. A lower energetic, protein and uncooked cornstarch intake is associated with a more severe outcome in glycogen storage disease type III: An observational study of 50 patients. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 31, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laradi, S.; Monastiri, K.; Ferchichi, S.; Nabli, N.; Rea, P.A.; Limam, H.B.; Mansour, R.B.; Bousoffara, R.; Yacoub, M.; Froissart, R. Les mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) sont des maladies de surcharge lysosomiale. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2001, 59, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- McNally, E.M.; Passos-Bueno, M.R.; Bönnemann, C.G.; Vainzof, M.; de Sa Moreira, E.; Lidov, H.; Othmane, K.B.; Denton, P.H.; Vance, J.M.; Zatz, M. Mild and severe muscular dystrophy caused by a single gamma-sarcoglycan mutation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 59, 1040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moussa, S.A.-B.; Moussa, A.; Lovecchio, T.; Kourda, N.; Najjar, T.; Jilani, S.B.; El Gaaied, A.; Porchet, N.; Manai, M.; Buisine, M.-P. Identification and characterization of a novel MLH1 genomic rearrangement as the cause of HNPCC in a Tunisian family: Evidence for a homologous Alu-mediated recombination. Fam. Cancer 2009, 8, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Bassat, I.; Feinstein, A.; Ramot, B. Selective vitamin B12 malabsorption with proteinuria in Israel. Clinical and genetic aspects. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 1969, 5, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Dridi, M.-F.B.; Turkia, H.B.; Azzouz, H.; Chehida, A.B.; Abdelaziz, R.B.; Tebib, N. Les maladies héréditaires du métabolisme en Tunisie: Défis, acquis, espoirs. Arch. Pediatr. Organe Off. Soc. Fr. Pediatr. 2015, 5, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Rekaya, M.; Jerbi, M.; Messaoud, O.; Ben Brick, A.S.; Zghal, M.; Mbarek, C.; Chadli-Debbiche, A.; Jones, M.; Mokni, M.; Boussen, H.; et al. Further evidence of mutational heterogeneity of the XPC gene in Tunisian families: A spectrum of private and ethnic specific mutations. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 316286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ouali, F.; Siala, H.; Bibi, A.; Hadj Fredj, S.; Dakhlaoui, B.; Othmani, R.; Ouenniche, F.; Zouari, F.; Bouguerra, B.; Rezigua, H.; et al. Prenatal diagnosis of hemoglobinopathies in Tunisia: An 18 years of experience. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2016, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oueslati, S.; Hadj Fredj, S.; Belhaj, R.; Siala, H.; Bibi, A.; Messaoud, T. Preliminary study of haplotypes linked to the rare cystic fibrosis E1104X mutation. Acta Physiol. Hung. 2015, 102, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abed, A.B.; Saad, H.; Mustpha, R.; Chiha, M.; Gamra, B. Early hearning screening by otoacoustic emissions and auditory brain stem response in Nabeul. Tunis. Med. 2013, 91, 643–647. [Google Scholar]
- Guellouz, N.; Mansour, B.; Ouederni, M.; Jabnoun, S.; Kacem, S.; Ch, M.; Kastally, R.; Chahed, M.; Khrouf, N. Neonatal screening of G6PD deficiency in Tunisia. Arch. L’Inst. Pasteur Tunis 2010, 87, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hajer, S.; Neila, T.; Sondess, H.F.; Fekria, O.; Nabila, A.; Mahbouba, K.; Melika, D.; Faida, O.; Amina, B.; Raja, B. A lower-cost protocol for sickle cell disease neonatal screening in Tunisia. Ann. Saudi Med. 2012, 32, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, I.C.; Puri, R.D. Global burden of genetic disease and the role of genetic screening. Semin. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2015, 20, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotogora, J. Autosomal recessive diseases among the Israeli Arabs. Hum. Genet. 2019, 138, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoud, O.; Rekaya, M.B.; Ouragini, H.; Benfadhel, S.; Azaiez, H.; Kefi, R.; Gouider-Khouja, N.; Mokhtar, I.; Amouri, A.; Boubaker, M.S.; et al. Severe phenotypes in two Tunisian families with novel XPA mutations: Evidence for a correlation between mutation location and disease severity. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2012, 304, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, T.; Shen, H.; Chen, X.; Tian, Q. Genome-wide copy number variation study and gene expression analysis identify ABI3BP as a susceptibility gene for Kashin–Beck disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 133, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monies, D.; Abouelhoda, M.; AlSayed, M.; Alhassnan, Z.; Alotaibi, M.; Kayyali, H.; Al-Owain, M.; Shah, A.; Rahbeeni, Z.; Al-Muhaizea, M.A.J.H.g. The landscape of genetic diseases in Saudi Arabia based on the first 1000 diagnostic panels and exomes. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richmond, C.M.; Campbell, S.; Foo, H.W.; Lunke, S.; Stark, Z.; Moody, A.; Bannister, E.; Greenway, A.; Brown, N. Rapid Identification of Biallelic SPTB Mutation in a Neonate with Severe Congenital Hemolytic Anemia and Liver Failure. Mol. Syndr. 2020, 11, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyacoub, Y.; Falfoul, Y.; Ouederni, M.; Sayeb, M.; Chedli, A.; Chargui, M.; Sassi, H.; Chakroun Chenguel, I.; Munier, F.L.; El Matri, L.; et al. Granular type I corneal dystrophy in a large consanguineous Tunisian family with homozygous p.R124S mutation in the TGFBI gene. Ophthalmic Genet. 2019, 40, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfar, S.; Bzéouich, A.A.; Kerkeni, E.; Bouaziz, S.; Najjar, M.F.; Chouchane, L.; Monastiri, K. A novel CASR mutation in a Tunisian FHH/NSHPT family associated with a mental retardation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 2395–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.N.; Sid, E.; Zhu, Q. Recurrent Neural Networks to Automatically Identify Rare Disease Epidemiologic Studies from PubMed. In Proceedings of the AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings, San Diego, CA, USA, 30 October–3 November 2021; p. 325. [Google Scholar]
- De Antonio, M.; Dogan, C.; Daidj, F.; Eymard, B.; Puymirat, J.; Mathieu, J.; Gagnon, C.; Katsahian, S.; Filnemus Myotonic Dystrophy Study Group; Hamroun, D.; et al. The DM-scope registry: A rare disease innovative framework bridging the gap between research and medical care. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, H.; Ouhtit, A.; El Bekay, R. An Arab registry for type 1 diabetes: Global benefits for type 1 diabetes patients. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 1681–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahmoudi, H.; Chalbi, A.; Ben-Lakhal, F.; Borji, W.; Zahra, K.; Zorgan, M.; Meddeb, B.; Gouider, E. Regional registry of bleeding disorders in Tunisia. J. Haemoph. 2012, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iourov, I.Y.; Vorsanova, S.G.; Yurov, Y.B.; Bertrand, T. VIII World Rett Syndrome Congress & Symposium of rare diseases, Kazan, Russia. Mol. Cytogenet. 2018, 11, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Ayed, F.F.-B.; Douira-Khomsi, W.; Rhayem, S.; Jelassi, M.; Zribi, H.; Chaabouni, M.; Khemiri, M.; Bellagha, I.; Barsaoui, S. Burkitt lymphoma in a child with Bloom syndrome. Arch. Pédiatr. 2016, 23, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, Z.; Chahed, H.; Jaafoura, H.; Zainine, R.; Messaoud, O.; Naili, M.; Nagara, M.; Hammami, H.; Laroussi, N.; Bouyacoub, Y. A novel frameshift mutation (c. 405delC) in the GJB2 gene associated with autosomal recessive hearing loss in two Tunisian families. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 1485–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riahi, Z.; Hammami, H.; Ouragini, H.; Messai, H.; Zainine, R.; Bouyacoub, Y.; Romdhane, L.; Essaid, D.; Kefi, R.; Rhimi, M. Update of the spectrum of GJB2 gene mutations in Tunisian families with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Gene 2013, 525, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, M. Novel personalized therapies for cystic fibrosis: Treating the basic defect in all patients. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 277, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connett, G. Lumacaftor-ivacaftor in the treatment of cystic fibrosis: Design, development and place in therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 2405–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, K.; Yarlagadda, S.; Zhang, W.; Moon, C.; Bouquet, E.; Srinivasan, S.; Li, C.; Stokes, D.C.; Naren, A. Personalized medicine in cystic fibrosis: Genistein supplementation as a treatment option for patients with a rare S1045Y-CFTR mutation. Am. J. Physiol.–Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 311, L364–L374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Messaoud, T.; Bibi, A.; Elion, J.; Férec, C.; Fattoum, S. Molecular epidemiology of cystic fibrosis in Tunisia. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2005, 63, 627–630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Hothi, J.S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Srinivasan, S.; Stokes, D.C.; Zhang, W. c. 3623G> A mutation encodes a CFTR protein with impaired channel function. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Kerch, F.; Ratbi, I.; Sbiti, A.; Laarabi, F.Z.; Barkat, A.; Sefiani, A. Carrier frequency of the c.525delT mutation in the SGCG gene and estimated prevalence of limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2C among the Moroccan population. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2014, 18, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siala, O.; Kammoun Feki, F.; Louhichi, N.; Hadj Salem, I.; Gribaa, M.; Elghzel, H.; Saad, A.; Triki, C.; Fakhfakh, F. Molecular prenatal diagnosis of muscular dystrophies in Tunisia and postnatal follow-up role. Genet. Test. 2008, 12, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herson, S.; Hentati, F.; Rigolet, A.; Behin, A.; Romero, N.B.; Leturcq, F.; Laforêt, P.; Maisonobe, T.; Amouri, R.; Haddad, H.J.B. A phase I trial of adeno-associated virus serotype 1-γ-sarcoglycan gene therapy for limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2C. Brain 2012, 135, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamdi, Y.; Mighri, N.; Boujemaa, M.; Mejri, N.; Ben Nasr, S.; Ben Rekaya, M.; Messaoud, O.; Bouaziz, H.; Berrazega, Y.; Rachdi, H.; et al. Identification of Eleven Novel BRCA Mutations in Tunisia: Impact on the Clinical Management of BRCA Related Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 674965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosco, J.P.; Grosse, S.D.; Ross, L.F. Universal state newborn screening programs can reduce health disparities. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeju Sohna, S.T. Inequities in newborn screening: Race and the role of medicaid. SSM—Popul. Health 2019, 9, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, C.F.; Mai, C.T.; Nabukera, S.K.; Botto, L.D.; Feuchtbaum, L.; Romitti, P.A.; Wang, Y.; Piper, K.N.; Olney, R.S. Developing a public health-tracking system for follow-up of newborn screening metabolic conditions: A four-state pilot project structure and initial findings. Genet. Med. 2014, 16, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urv, T.K.; Parisi, M.A. Newborn Screening: Beyond the Spot. Rare Diseases Epidemiology: Update Overview; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 323–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, S.; Rink, B.; Biggio, J., Jr. Carrier screening in the age of genomic medicine: ACOG committee opinion, number 690. Obs. Gynecol. 2017, 129, e35–e40. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shachar, R.; Svenson, A.; Goldberg, J.D.; Muzzey, D. A data-driven evaluation of the size and content of expanded carrier screening panels. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotoski, D.; Namaste, S.; Raouf, R.K.; El Nekhely, I.; Hindi-Alexander, M.; Engelson, G.; Hanson, J.W.; Howell, R.R.; Committee, M.N.S. Conference report: Second conference of the Middle East and North Africa newborn screening initiative: Partnerships for sustainable newborn screening infrastructure and research opportunities. Genet. Med. 2009, 11, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teebi, A.S.; El-Shanti, H.I. Consanguinity: Implications for practice, research, and policy. J. Lancet 2006, 367, 970–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsairi, M.; Mehdi, F.; Bellaaj, R.; Kassis, M.J.L.T. Health screening strategies in Maghreb countries: Situation Analysis and perspectives. Tunis. Med. 2018, 96, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.; Elsheikh, W.; Al-Aqeel, A.I.; Alhashem, A.M.; Alodaib, A.; Alahaideb, L.; Almashary, M.; Alharbi, F.; AlMalawi, H.; Ammari, A.; et al. Incidence of newborn screening disorders among 56632 infants in Central Saudi Arabia. A 6-year study. Saudi Med. J. 2020, 41, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmoktader, A.M. Risk factors for congenital hypothyroidism in Egypt: Results of a population case-control study (2003–2010). Ann. Saudi Med. 2013, 33, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadek, A.A.; Hassan, M.H.; Mohammed, N.A. Clinical and neuropsychological outcomes for children with phenylketonuria in Upper Egypt; a single-center study over 5 years. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sirdah, M.M.; Al-Kahlout, M.S.; Reading, N.S. National G6PD neonatal screening program in Gaza Strip of Palestine: Rationale, challenges and recommendations. Clin. Genet. 2016, 90, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouaili, E.B.H.; Chaouachi, S.; Bezine, A.; Hamadi, M.; Mbarek, C. Dépistage Systématique de la Surdité en Maternité par Oto-Emissions Acoustiques Provoquées (OTEAP): Etude Pilote. Tunis. Méd. 2010, 88, 482–485. [Google Scholar]
- Raz, A.E.; Atar, M. Cousin marriage and premarital carrier matching in a Bedouin community in Israel: Attitudes, service development and educational intervention. BMJ. Sex. Reprod. Health 2004, 30, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiloh, S.; Reznik, H.; Bat-Miriam-Katznelson, M.; Goldman, B. Pre-marital genetic counselling to consanguineous couples: Attitudes, beliefs and decisions among counselled, noncounselled and unrelated couples in Israel. Soc. Sci. Med. 1995, 41, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Arrayed, S. Campaign to control genetic blood diseases in Bahrain. Public Health Genom. 2005, 8, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Arrayed, S.; Al Hajeri, A. Public awareness of sickle cell disease in Bahrain. Ann. Saudi Med. 2010, 30, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitouna, N.; Zekri, L.A.; Wardi, N.; Marrakchi, J.; Bouattour, Y.; Ben Hassine, H. Setting-up of a Science Shop project on the early detection of hearing impairment among preschool and school children. In Proceedings of the Inaugural Meeting of the Hearing Institute, Collège de France, Paris, France, 16–17 September 2019. [Google Scholar]


| Disease Name | OMIM | Inheritance | Gene (OMIM) | Genetic Variant(s) | ICD-10 Classification | Approach Used for Molecular Diagnosis | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adrenal Hyperplasia, Congenital, due to 11-β-Hydroxylase Deficiency | 202010 | AR | CYP11B1 (610613) | c.1066C > T (p.Gln356Ter) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [24] |
| c.1136G > T (p.Gly379Val) | |||||||
| Adrenoleukodystrophy | 300100 | XL | ABCD1 (300371) | c.284C > A (p.Ala95Asp) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [25] |
| Alstrom syndrome | 203800 | AR | ALMS 1 (606844) | c.10388-2A > G | Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities | Targeted Gene sequencing | [26] |
| Bloom syndrome | 210900 | AR | BLM (604610) | c.1980-1982delAA (p.Lys662fsX5) | Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities | Sanger sequencing | Ezzine et al., Unpublished [27] |
| FVII deficiency | 227500 | AR | F7 (613878) | c.90-91insA (p.12LeufsX11) | Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | Sanger sequencing | [28] |
| c.592 T > C (p.Cys198Arg) | |||||||
| c.1615 G > C (p.Gly539Arg) | |||||||
| c.2409 T > C (p.Asn784Asn) | |||||||
| c.2167 G > A (p.Ala704Thr) | |||||||
| c.3870-3871insA (p.1271LysfsX29) | |||||||
| c.1696 C > T (p.Leu547Phe) | |||||||
| c.1492 G > A (p.Gly479Arg) | |||||||
| c.77 T > C (p.Leu7Pro) | |||||||
| c.5071-5075delATGAA (p.1671-3fsX) | |||||||
| c.3637-3638delA (p.1191IlefsX5) | |||||||
| c.6873-6876delTC (p.2272ThrfsX) | |||||||
| c.4379-4380insA (p.1441LysfsX2) | |||||||
| c.3637-3638insA (p.1191LeufsX29) | |||||||
| c.2236-2237insT (p.727SerfsTer) | |||||||
| Gaucher disease type III A | 231000 | AR | GBA (606463) | c.1109T > C (p.Phe370Ser) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [29] |
| c.1330_1331delGAinsCC (p.Asp444Pro) | |||||||
| Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (JEB) Herlitz type | 226700 | AR | LAMA3 (600805) | c.2865C > G (p.His955Gln) | Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities | Sanger sequencing | [30] |
| Lafora disease | 254780 | AR | EPM2A (607566) | c.659 T > A (p.Leu220Gln) | Diseases of the nervous system | Sanger sequencing | [31] |
| Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency | 278000 | AR | LIPA (613497) | c.153 C > A (p.Tyr51Ter) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [32] |
| Maple syrup urine disease, type Ib | 248600 | AR | BCKDHB (248611) | c.716A > G (p.Glu239Gly) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [33] |
| Meckel syndrome type 2 | 603194 | AR | TMEM216(613277) | c.341T > G (p.Leu114Arg) | Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities | Exome sequencing | [34] |
| MELAS syndrome | 540000 | Mitochondrial | MT-TV (590105) | m.1640A > G | Diseases of the nervous system | Sanger sequencing | [35] |
| Microphthalmia isolated, 6 | 613517 | AR | PRSS56 (613858) | c.1059_1066insC (p.Gln356ProfsTer152) | Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities | Sanger sequencing | [36] |
| Miyoshi muscular dystrophy 1 | 254130 | AR | DYSF (603009) | c.4597-2A > G | Diseases of the nervous system | Targeted Gene Sequencing | [37] |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type II | 309900 | XL | IDS (300823) | c.240 + 1 G > A | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [38] |
| c.263G > A (p.Arg88Pro) | |||||||
| c.610C > T (p.Gln204Ter) | |||||||
| c.1348G > A (Asp450Asn) | |||||||
| c.281G > A (p.Gly94Asp) | |||||||
| c.1186C > T (p.Gln396Ter) | |||||||
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA | 252900 | AR | SGSH (605270) | c.2t > C (p.Met1Thr) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [39] |
| c.1129C > T (p.Arg377Cys) | |||||||
| g.75802301_75809393del | |||||||
| c.1093C > T (p.Gln365Ter) | |||||||
| c.29dup (p.Leu11AlafsTer22) | |||||||
| c.197C > G (p.Ser66Trp) | |||||||
| c.1080del (p.Val361SerfsTer52) | |||||||
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB | 252920 | AR | NAGLU (60970) | c.1674C > G (p.Tyr558X) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [39] |
| c.1811C > T (p.Pro604Leu) | |||||||
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIC | 252930 | AR | HGSNAT (610453) | c.1209G > A (p.Trp403X) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [39] |
| c.1880A > G (p.Tyr627Cys) | |||||||
| Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora | 254780 | AR | EPM2A (607566) | c.659 T > A (p.Leu220Gln) | Diseases of the nervous System | Sanger sequencing | [31] |
| Nephropathic cystinosis | 219800 | AR | CTNS (606272) | c.1515G > A (p.Gly308Arg) | Endocrine, nutritional, and metabolic diseases | Sanger sequencing | [40] |
| c.771_793del (p.Gly258SerfsTer30) | |||||||
| Punctate palmoplantar keratoderma type 1 | 148600 | AD | AAGAB (614888) | c.481C > T (p.Arg161Ter) | Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities | Whole exome sequencing | [41] |
| Associations | Familial/Individual | Inheritance | Consanguinity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allgrove syndrome—Hearing loss | Familial | AR—AR | Yes | Mkaouar et al., unpublished |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—Behcet’s disease | Individual | AD, AR—Unknown | NA | [43] |
| Autism—Hearing loss | Familial | Complex heredity—AR | Yes | Lahbib et al., unpublished |
| Cutis laxa—Pulmonary disease | Familial | Unknown-Unknown | NA | Tinsa et al., unpublished |
| Growth hormone deficiency—Immunodeficiency | Individual | Unknown-Unknown | NA | Tinsa et al., unpublished |
| Ichthyosis congenital autosomal recessive 1—Erythrokeratodermia variabilis | Familial | AR—AD | No | Laroussi et al., Unpublished |
| Ichthyosis congenital autosomal recessive 5—hearing loss | Individual | AR—AR | Yes | [44] |
| Ichthyosis congenital autosomal recessive 1-Muscular dystrophy limb girdle type 2A | Individual | AR-AR | Yes | Mezzi et al., Unpublished |
| Incontinentia pigmenti—Noonan syndrome | Individual | XLD—AD | No | [45] |
| Maternally inherited diabetes—deafness-Retinopathy | Individual | Mitochondrial—Unknown | No | [46] |
| Niemann-Pick disease type B—Systemic lupus erythematous | Familial | AR—AD | No | [47] |
| Pernicious anemia—Pseudohypoparathyroidism | Individual | Unknown-Unknown | NA | Tinsa et al., unpublished |
| Xeroderma pigmentosum group A—Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome I | Individual | AR—AR, AD | Yes | Messaoud et al., Unpublished |
| Xeroderma pigmentosum group C—Rothmund Thomson syndrome | Familial | AR—AR | Yes | Ezzine et al., Unpublished |
| Diseases | Unusual Clinical Findings | Case count | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chanarin-Dorfman syndrome | Thyroid function impairment | 7 | [48] |
| Palmoplantar keratoderma | Abnormal cornification and a diffuse yellowish keratoderma with the characteristic skin thickening | 1 | [49] |
| Juvenile Parkinson disease | No evidence of sleep or autonomic dysfunctions and psychiatric disorders in both patients | 1 | [50] |
| Genetic Disease (MIM) | Frequency | References | Measure of Estimation | State/Region/Group | Prevalence in Orphanet ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anemia, Nonspherocytic hemolytic, due to G6PD deficiency (ANH- G6PD) (300908) | 18,400/million/year | [51] | Incidence | All across Tunisia | <1/1,000,000 |
| β thalassemia ( β -thal) (613985) | 44.2/2000 | [52] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1–9/1,000,000 |
| Creutzleldt-Jakob Disease (CJD*) (123400) | 2.3/million/year | [53] | Incidence | Among Tunisian Jews | <1/1,000,000 |
| Cystic fibrosis (CF*) (219700) | 1.5 new cases/year 0.4/1000 | [54] | Incidence Prevalence | In the Pediatric department B of the Children’s Hospital Béchir Hamza de Tunis (among patients’ series) Most from the north and the south of Tunisia | NA |
| 0.4/1000 Its prevalence was 0.4 per 1000 hospitalizations. | 1–9/100,000 | ||||
| Dermatitis, Atopic (ATOD) (603165) | 451 cases during a 7 years period | [55] | Incidence | All across Tunisia | NA |
| Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica Hallopeau-Simens type 1 (RDEB*) (226600) | 2.3/2000 | Cherif et al., 2005 unpublished | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | <1/1,000,000 |
| 0.1/2000 | [56] | In the governorate of Sfax | |||
| Exfoliation syndrome (XFS) (177650) | 220/2000 | [57] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | NA |
| Familial Adenomatous polyposis of the colon (FAP1) (MIM: 175100) | 74/million/year | [58] | Incidence | All across Tunisia | 1–9/100,000 |
| Fanconi anemia (FA) (227650) | 1.4/million/year | [59] | Incidence | All across Tunisia | 1/160,000 |
| Familial hypercholesterolemia, (FHCL*) | 12.12/2000 | [60] | Prevalence | In central and southern Tunisia | 1–9/1,000,000 |
| Gaucher disease, type I (GD1) (230800) | 0.0096/2000 | [61] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1/100,000 |
| Glycine encephalopathy (GCE*) (605899) | 1/9322 | [62] | Incidence | In the governorate of Kairouan | 1–9/1,000,000 |
| Glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD1A*) (232200) | 0.02/2000 | [63] | Prevalence | In the north of Tunisia | NA |
| 7.93/million/year | Incidence | 1/100,000 (Incidence) | |||
| Hemoglobinopathies | 89.6/2000 | [52] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | NA |
| Hurler syndrome (HS*) (607014) | 0.064/2000 | [64] | Prevalence | In Tunisian Jews | 1/200,000 |
| Limb-girdle Muscular dystrophytype 2C (LGMD2C) (253700) | 0.6/2000 | [65] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1–9/1,000,000 |
| Lynch syndrome 1 (LS1) (120435) | 70/million/year | [66] | Incidence | All across Tunisia | NA |
| Megaloblastic anemia 1 (MGA1*) (261100) | 2/2000 | [67] | Prevalence | In Tunisian Jews | NA |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis I (MPS1-S) (607016) | 0.0126/2000 | [59] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1/100,000 |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIA (MPS 3A) (252900) | 0.007/2000 | [59] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1–9/100,000 |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA (MPS4A) (253000) | 0.025/2000 | [68] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1–5/10,000 |
| Mucopolysaccharidosis type VI (MPS 6) (253200) | 0.013/2000 | [62] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1–9/1,000,000 |
| Niemann Pick disease B (607616) | 0.1/2000 | [66] | Prevalence | 1–9/1,000,000 | |
| Phenylketonuria (PKU) (261600) | Varies between 0.29/2000 and 0.6/2000 | [67] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1–5/10,000 |
| Sickle Cell Anemia (SCA) (603903) | 37.8/2000 | [52] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1/150 |
| Xeroderma pigmentosum , complementation group A (XPA) (278700) | 0.2/2000 | [69] | Prevalence | All across Tunisia | 1/1,000,000 |
| Diseases (MIM) | Screening Type | Screening Techniques | Country Coverage | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-thalassemia | Prenatal screening | DNA analysis from amniotic fluid | Biochemistry and molecular biology department in children’s hospital of Tunis (pilot study) | [70] |
| β-thalassemia | Prenatal screening Carrier screening | DNA analysis from amniotic fluid Screening for mutations described in Tunisians | Biochemistry and molecular biology department in children’s hospital of Tunis (pilot study) | [70] |
| Congenital hypothyroidism | Newborn screening | TSH and T4 radioimmunoassay on drops of blood | Maternity and Neonatal Centre in Tunis (pilot study) | Elkadri et al. * |
| Cystic fibrosis | Prenatal screening | Genetic analysis by denaturant gradient gel electrophoresis and denaturing high-pressure liquid phase chromatography | Biochemistry Laboratory, Bechir Hamza Children’s hospital in Tunis Center of maternity and neonatology, in Tunis (pilot study) | [71] |
| Hearing impairment | Newborn screening | Evoked otoacoustic emissions (EOAE) and auditory brain stem response (ABR) | Charles Nicolle hospital of Tunis ((pilot study) Regional hospital in Nabeul (pilot study) Regional hospital in Sfax (systematic) | [72] Feedback from collaborating clinician |
| G6PD deficiency | Newborn screening | Dosage of the enzymatic activity using spectrophotometric method | Maternity and Neonatal Centre in Tunis (pilot study) | [73] |
| Phenylketonuria | Newborn screening | Dosage of phenylalanine in dried blood spots | Hospital of La Rabta in Tunis (pilot study) | [68] |
| Sickle cell disease | Newborn screening | Isoelectrofocusing | Maternity Centre of Aziza Othmana Hospital and Neonatal and Maternity Centre—La Rabta in Tunis (pilot study) | [74] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mezzi, N.; Messaoud, O.; Mkaouar, R.; Zitouna, N.; Romdhane, S.; Abdessalem, G.; Charfeddine, C.; Maazoul, F.; Ouerteni, I.; Hamdi, Y.; et al. Spectrum of Genetic Diseases in Tunisia: Current Situation and Main Milestones Achieved. Genes 2021, 12, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111820
Mezzi N, Messaoud O, Mkaouar R, Zitouna N, Romdhane S, Abdessalem G, Charfeddine C, Maazoul F, Ouerteni I, Hamdi Y, et al. Spectrum of Genetic Diseases in Tunisia: Current Situation and Main Milestones Achieved. Genes. 2021; 12(11):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111820
Chicago/Turabian StyleMezzi, Nessrine, Olfa Messaoud, Rahma Mkaouar, Nadia Zitouna, Safa Romdhane, Ghaith Abdessalem, Cherine Charfeddine, Faouzi Maazoul, Ines Ouerteni, Yosr Hamdi, and et al. 2021. "Spectrum of Genetic Diseases in Tunisia: Current Situation and Main Milestones Achieved" Genes 12, no. 11: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111820
APA StyleMezzi, N., Messaoud, O., Mkaouar, R., Zitouna, N., Romdhane, S., Abdessalem, G., Charfeddine, C., Maazoul, F., Ouerteni, I., Hamdi, Y., Zaouak, A., Mrad, R., Abdelhak, S., & Romdhane, L. (2021). Spectrum of Genetic Diseases in Tunisia: Current Situation and Main Milestones Achieved. Genes, 12(11), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12111820






