Transcriptomic Profiling of Fe-Responsive lncRNAs and Their Regulatory Mechanism in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
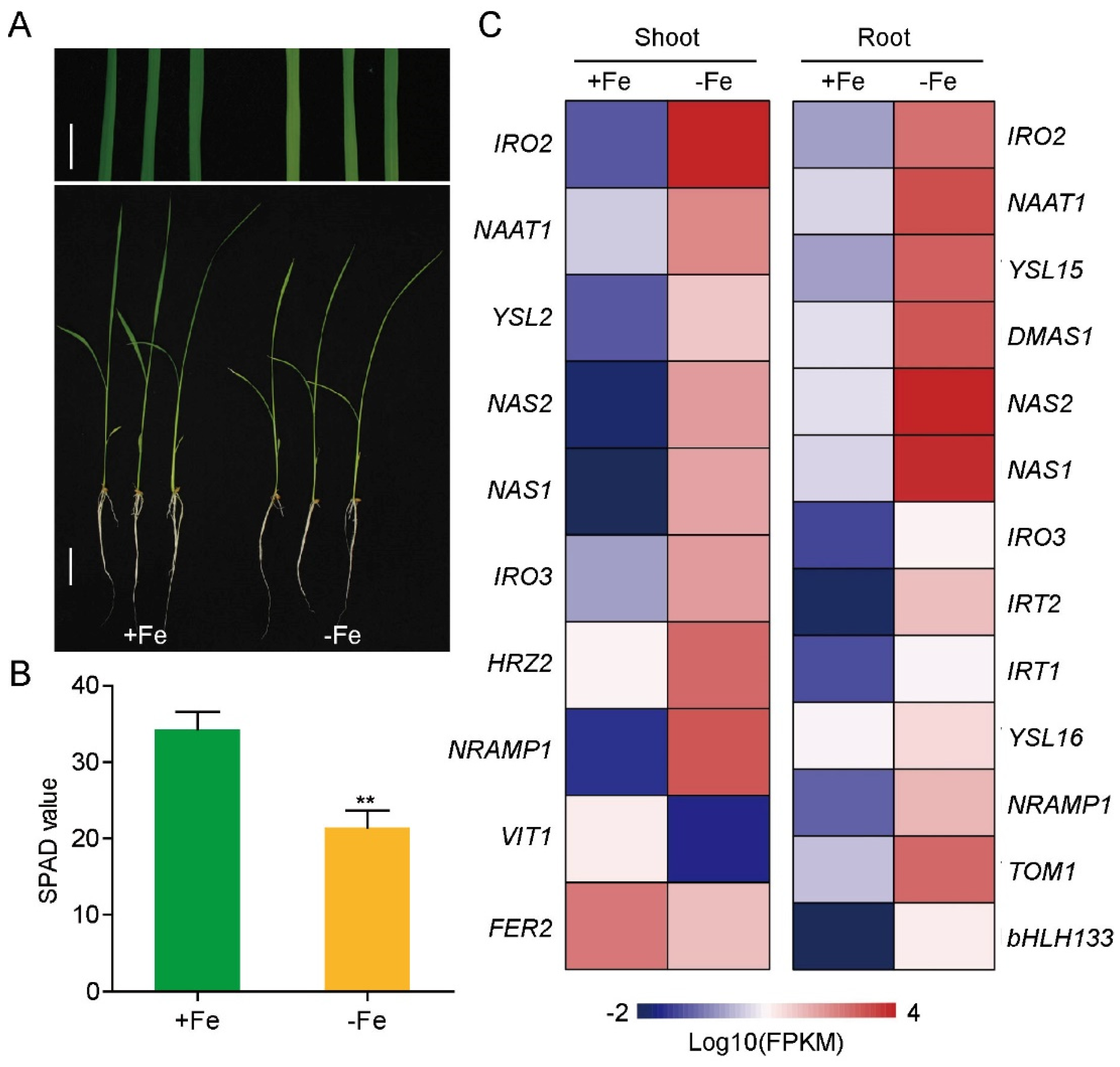
2.1. Plant Growth Condition
2.2. Strand-Specific RNA Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3. Identification and Characterization Pipeline of LncRNAs
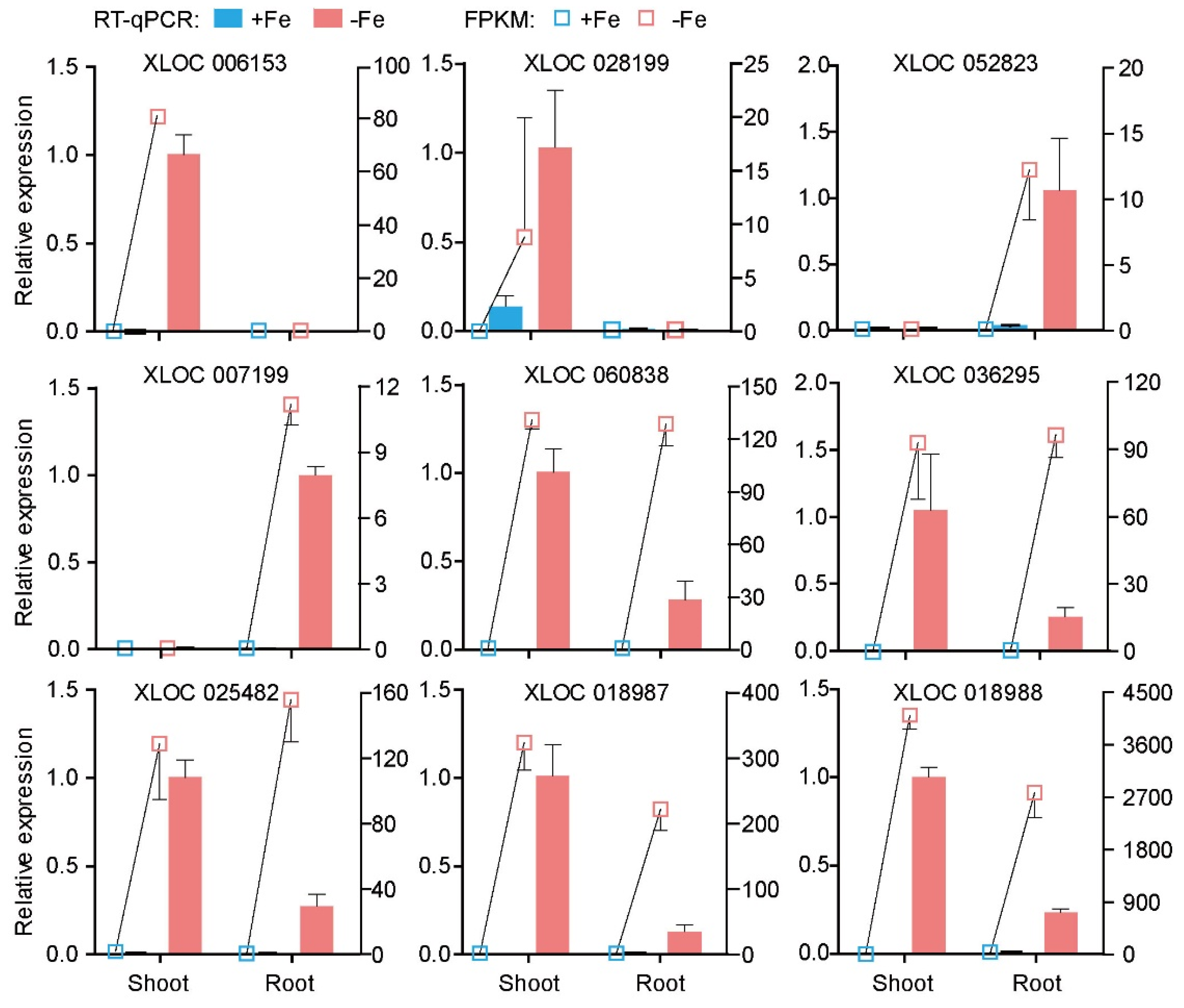
2.4. Validation of Several LncRNAs Using RT-qPCR
2.5. Prediction of the LncRNA-Derived miRNAs and Target Genes
2.6. Prediction and Annotation of DE-LncRNA Targets
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Iidentification of LncRNAs
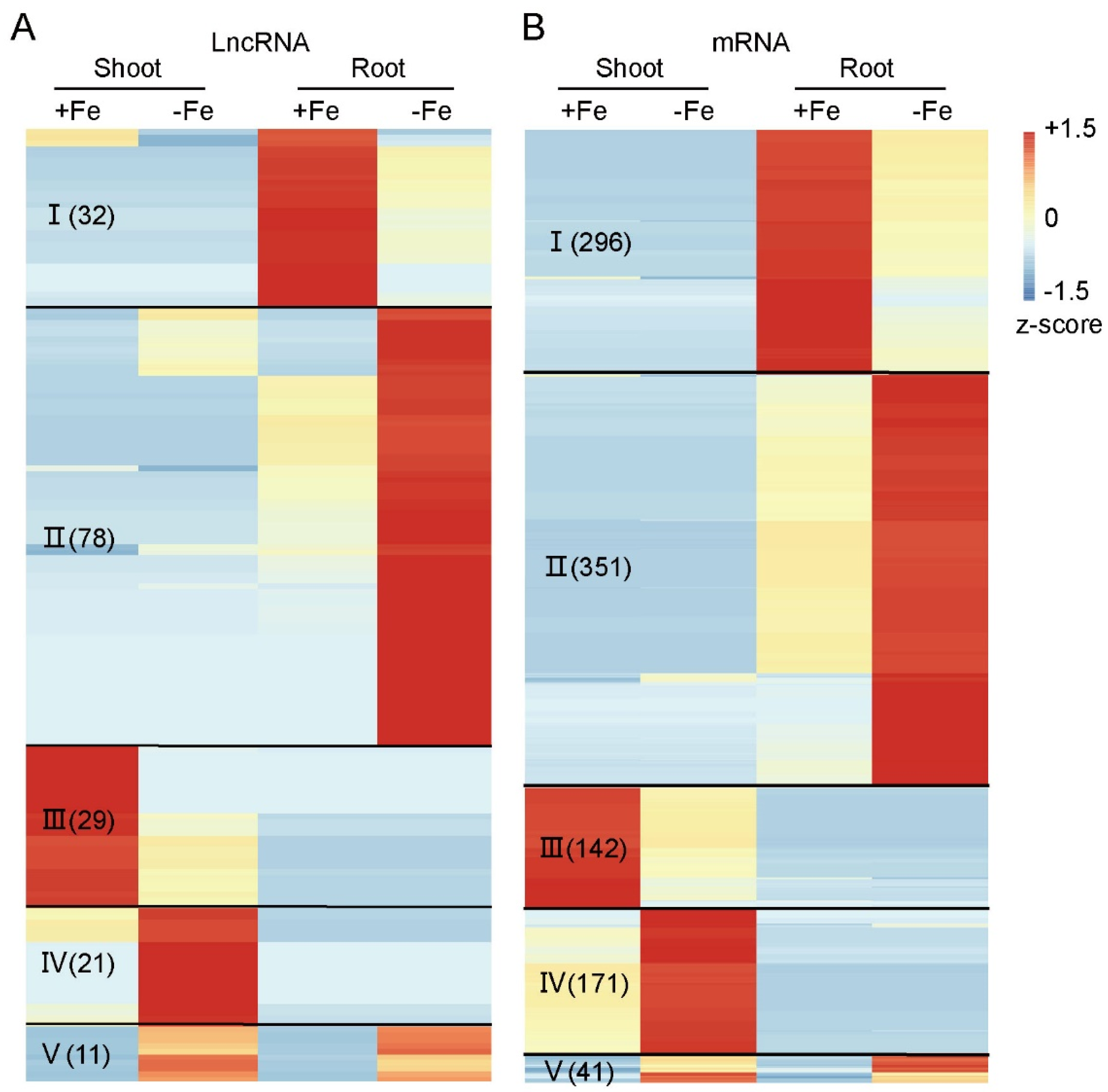
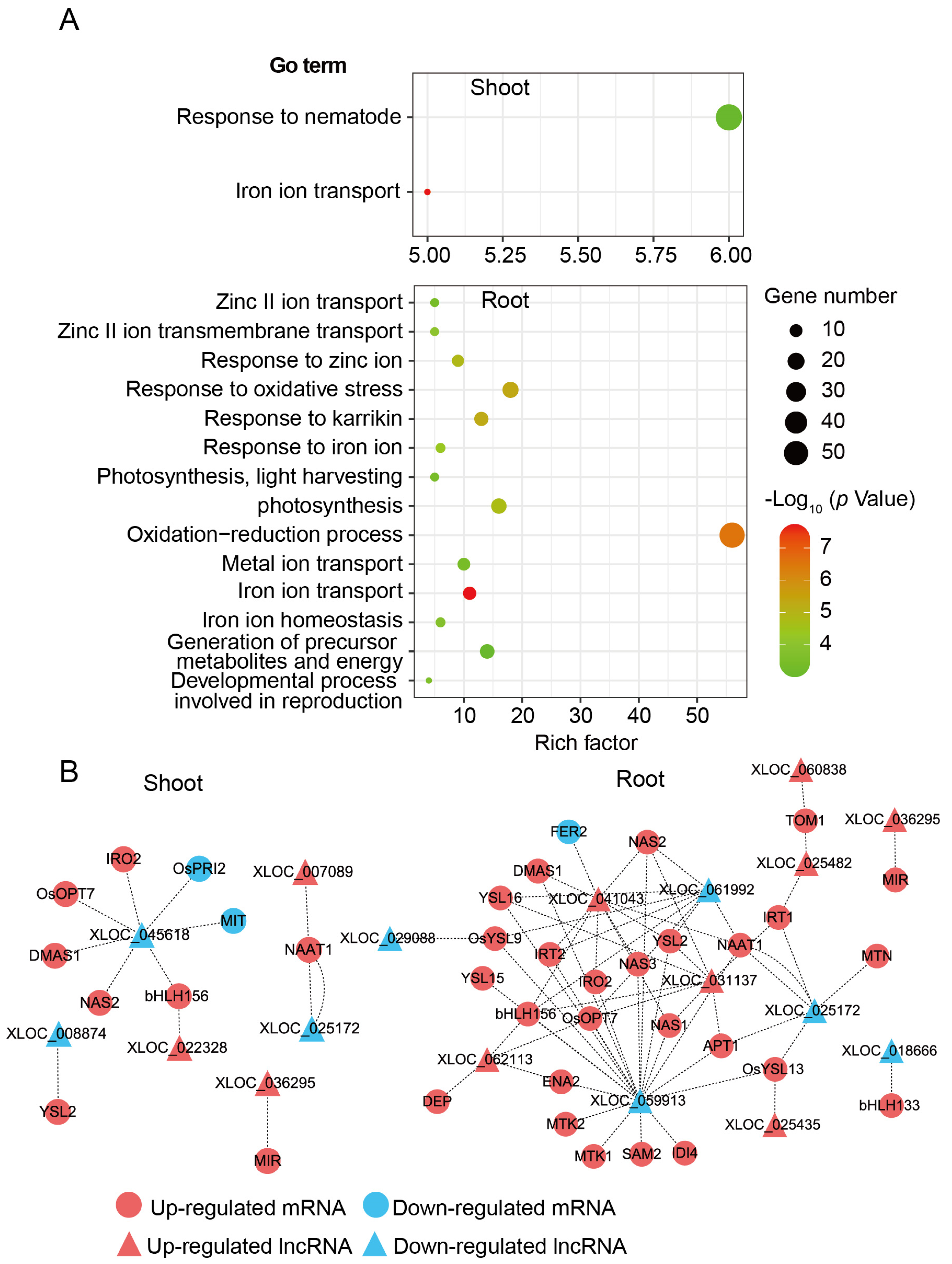
3.2. Fe-Deficiency Responsive LncRNAs and mRNAs in Rice Shoot and Root
3.3. Verification of LncRNAs Responding to Fe Deficiency Using RT-qPCR
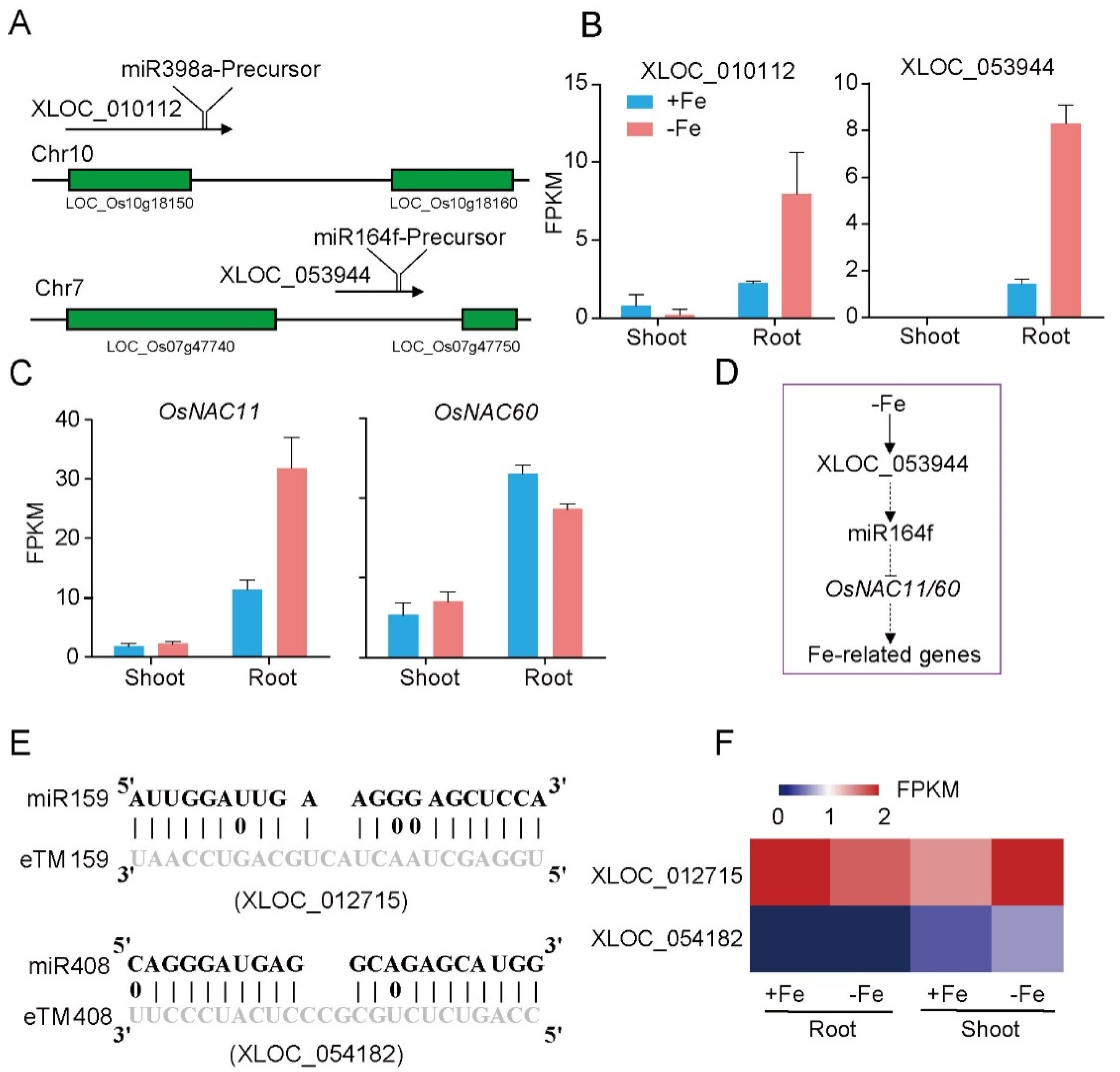
3.4. Identification of LncRNAs as Potential miRNA Precursors and miRNA Target Mimics
3.5. Interactions of DE-LncRNAs with mRNAs
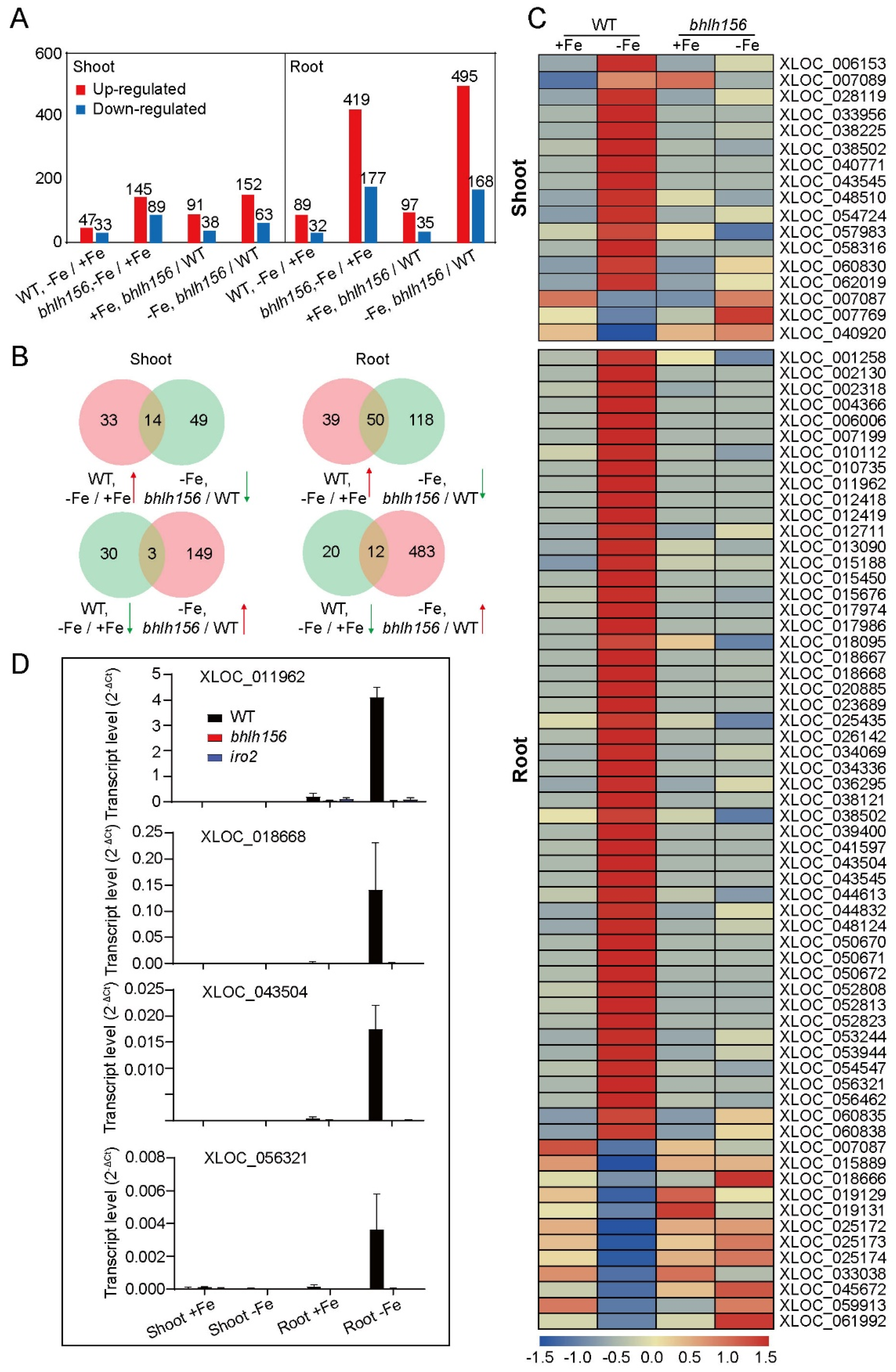
3.6. DE-LncRNAs Regulated by Transcription Factors bHLH156 and IRO2 at the Transcriptional Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guerinot, M.L.; Yi, Y. Iron: Nutritious, noxious, and not readily available. Plant Physiol. 1994, 104, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron uptake, translocation, and regulation in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2012, 63, 131–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Itai, N.R.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron deficiency responses in rice roots. Rice 2014, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughio, N.; Yamaguchi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K.; Nakanishi, H.; Mori, S. Cloning an iron-regulated metal transporter from rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, F.; Shou, H.; Huang, F.; Zheng, L.; He, F.; Li, J.; Zhao, F.-J.; Ueno, D.; Ma, J.F.; et al. Mutation in nicotianamine aminotransferase stimulated the Fe(II) acquisition system and led to iron accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Tsukamoto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Nakazono, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Wada, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Matsuhashi, S.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Rice plants take up iron as an Fe3+-phytosiderophore and as Fe2+. Plant J. 2006, 45, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, H.; Higuchi, K.; Takahashi, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. Three rice nicotianamine synthase genes, OsNAS1, OsNAS2, and OsNAS3 are expressed in cells involved in long-distance transport of iron and differentially regulated by iron. Plant. J. 2003, 36, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogo, Y.; Itai, R.N.; Nakanishi, H.; Inoue, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Takahashi, M.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. Isolation and characterization of IRO2, a novel iron-regulated bHLH transcription factor in graminaceous plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ogo, Y.; Itai, R.N.; Nakanishi, H.; Takahashi, M.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. The transcription factor IDEF1 regulates the re-sponse to and tolerance of iron deficiency in plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19150–19155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogo, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Itai, R.N.; Nakanishi, H.; Kakei, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Toki, S.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. A Novel NAC Transcription factor, IDEF2, that recognizes the iron deficiency-responsive element 2 regulates the genes involved in iron homeostasis in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13407–13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Nozoye, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kakei, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Nakazono, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Mori, S.; Nishizawa, N.K. Rice OsYSL15 is an iron-regulated iron (III)-deoxymugineic acid transporter expressed in the roots and is essential for iron uptake in early growth of the seedlings. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3470–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Ying, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Whelan, J.; Shou, H. Identification of a novel iron regulated basic helix-loop-helix protein involved in Fe homeostasis in Oryza sativa. BMC Plant. Biol. 2010, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ying, Y.; Narsai, R.; Ye, L.; Zheng, L.; Tian, J.; Whelan, J.; Shou, H. Identification of OsbHLH133 as a regulator of iron distribution between roots and shoots in Oryza sativa. Plant. Cell Environ. 2012, 36, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Ying, Y.; Wang, J.; Shao, J.F.; Yamaji, N.; Whelan, J.; Ma, J.F.; Shou, H. A transcription factor OsbHLH156 regulates Strategy II iron acquisition through localising IRO2 to the nucleus in rice. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1247–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinley, E.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.A.; Dutta, A.; Guigo, R.; Gingeras, T.R.; Marguiles, E.H. Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 2007, 447, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Xia, X.; Jiang, B.; Ma, K.; Zhu, L.; Wang, L.; Jin, B. Identification and characterization of novel lncRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 488, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Yin, K.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, T.; Han, B.; Liu, X.; et al. Long non-coding and coding RNA profiling using strand-specific RNA-seq in human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, I.M.; Emanueli, C. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekanova, A.J. Long non-coding RNAs and their functions in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 2015, 27, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M. Functions of long intergenic non-coding (linc) RNAs in plants. J. Plant. Res. 2017, 130, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiezewski, S.; Liu, F.; Magusin, A.; Dean, C. Cold-induced silencing by long antisense transcripts of an Arabidopsis Polycomb target. Nature 2009, 462, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.B.; Sung, S. Vernalization-mediated epigenetic silencing by a long intronic noncoding RNA. Science 2010, 331, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Csorba, T.; Skourti-Stathaki, K.; Proudfoot, N.J.; Dean, C. R-loop stabilization represses antisense transcription at the Arabidopsis FLC locus. Science 2013, 340, 619–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Lu, Q.; Ouyang, Y.; Mao, H.; Zhang, P.; Yao, J.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q. A long noncoding RNA regulates photoperiod-sensitive male sterility, an essential component of hybrid rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2654–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Valli, A.; Todesco, M.; Mateos, I.; Puga, M.I.; Rubio-Somoza, I.; Leyva, A.; Weigel, D.; García, J.A.; Paz-Ares, J. Target mimicry provides a new mechanism for regulation of microRNA activity. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabnoune, M.; Secco, D.; Lecampion, C.; Robaglia, C.; Shu, Q.; Poirier, Y. A rice cis-natural antisense RNA acts as a trans-lational enhancer for its cognate mRNA and contributes to phosphate homeostasis and plant fitness. Plant. Cell 2013, 25, 4166–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Wittmann, S.; Kilchert, C.; Vasiljeva, L. lncRNA recruits RNAi and the exosome to dynamically regulate pho1 expression in response to phosphate levels in fission yeast. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Huang, F.; Narsai, R.; Wu, J.; Giraud, E.; He, F.; Cheng, L.; Wang, F.; Wu, P.; Whelan, J.; et al. Physiological and Transcriptome Analysis of Iron and Phosphorus Interaction in Rice Seedlings. Plant. Physiol. 2009, 151, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Lam, T.-W.; Yiu, S.-M.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP2: An improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; Van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.-Q.; Liu, X.-Q.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Kuang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Hao, C.; Wang, T.; et al. PmiREN: A comprehensive encyclopedia of plant miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, P.X. psRNATarget: A plant small RNA target analysis server (2017 release). Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, W.; Zeng, P.; Wang, J.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.; Cui, Q. LncTar: A tool for predicting the RNA targets of long noncoding RNAs. Briefings Bioinform. 2015, 16, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2013, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hao, L.; Li, D.; Zhu, L.; Hu, S. Long Non-coding RNAs and their biological roles in plants. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, B.M.; McInturf, S.A.; Stein, R.J. Rosette iron deficiency transcript and microRNA profiling reveals links between copper and iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5903–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Datta, S.K.; Datta, K. miRNA regulation of nutrient homeostasis in plants. Front. Plant. Sci. 2015, 6, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkouris, M.; Kouroupi, G.; Vourvoukelis, A.; Papagiannakis, N.; Kaltezioti, V.; Matsas, R.; Stefanis, L.; Xilouri, M.; Politis, P.K. Long non-coding RNAs associated with neurodegeneration-linked genes are reduced in parkinson’s disease patients. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Nagasaka, S.; Senoura, T.; Itai, R.N.; Nakanishi, H.; Nishizawa, N.K. Iron-binding haemerythrin RING ubiquitin ligases regulate plant iron responses and accumulation. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Xie, K.; Xiong, L. Conserved miR164-targeted NAC genes negatively regulate drought resistance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2119–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borah, P.; Das, A.; Milner, M.J.; Ali, A.; Bentley, A.R.; Pandey, R. Long non-coding RNAs as endogenous target mimics and exploration of their role in low nutrient stress tolerance in plants. Genes 2018, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørom, U.A.; Derrien, T.; Beringer, M.; Gumireddy, K.; Gardini, A.; Bussotti, G.; Lai, F.; Zytnicki, M.; Notredame, C.; Huang, Q.; et al. Long Noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells. Cell 2010, 143, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Haines, J.E.; Perez, E.M.; Munson, G.; Chen, J.; Kane, M.; McDonel, P.E.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 539, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, M.A.; Wahlestedt, C. Regulatory roles of natural antisense transcripts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsani, O.; Zhu, J.; Verslues, P.E.; Sunkar, R.; Zhu, J.-K. Endogenous siRNAs Derived from a pair of natural cis-antisense transcripts regulate salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Cell 2005, 123, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, M.A.; Modarresi, F.; Khalil, A.M.; Wood, D.E.; Sahagan, B.G.; Morgan, T.E.; Finch, C.E.; Laurent, G.S., III; Kenny, P.J.; Wahlestedt, C. Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in Alzheimer’s disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of β-secretase. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| miRNA | Target | Description | miRNA and Target Aligned_Fragment |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR164f | LOC_Os06g23650 | No apical meristem protein | 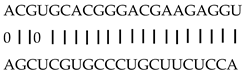 |
| miR164f | LOC_Os06g46270 | OsNAC11; OsY37; OsMTN4 | 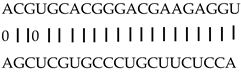 |
| miR164f | LOC_Os12g41680 | OsMTN3, OsNAC60 | 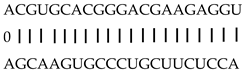 |
| miR159a | LOC_Os10g05230 | Zinc finger, C3HC4 type domain containing protein | 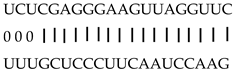 |
| miR159a/b | LOC_Os01g59660 | OsGAMYB |  |
| miR159a/b/c/d/e | LOC_Os01g12700 | MYB transcription factor |  |
| miR159a/b/c/d/e | LOC_Os05g41166 | MYB transcription factor | 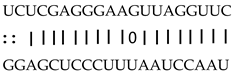 |
| miR159a/b/c/d/e | LOC_Os09g36650 | Expressed protein | 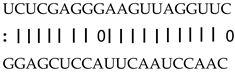 |
| miR159b | LOC_Os03g21380 | OsCML27, calmodulin-like protein | 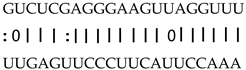 |
| miR159c/d/e | LOC_Os06g40330 | OsGAMYBL1 |  |
| miR408 | LOC_Os07g43540 | ORC6 | 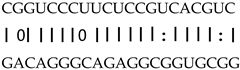 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Sun, S.; Guo, R.; Liao, W.; Shou, H. Transcriptomic Profiling of Fe-Responsive lncRNAs and Their Regulatory Mechanism in Rice. Genes 2021, 12, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040567
Wang S, Sun S, Guo R, Liao W, Shou H. Transcriptomic Profiling of Fe-Responsive lncRNAs and Their Regulatory Mechanism in Rice. Genes. 2021; 12(4):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040567
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shoudong, Shuo Sun, Runze Guo, Wenying Liao, and Huixia Shou. 2021. "Transcriptomic Profiling of Fe-Responsive lncRNAs and Their Regulatory Mechanism in Rice" Genes 12, no. 4: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040567
APA StyleWang, S., Sun, S., Guo, R., Liao, W., & Shou, H. (2021). Transcriptomic Profiling of Fe-Responsive lncRNAs and Their Regulatory Mechanism in Rice. Genes, 12(4), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12040567








