An FGA Frameshift Variant Associated with Afibrinogenemia in Dachshunds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals
2.3. Coagulation Assays
2.4. Genotyping and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Sequencing
2.6. Validation and Effect Prediction
3. Results
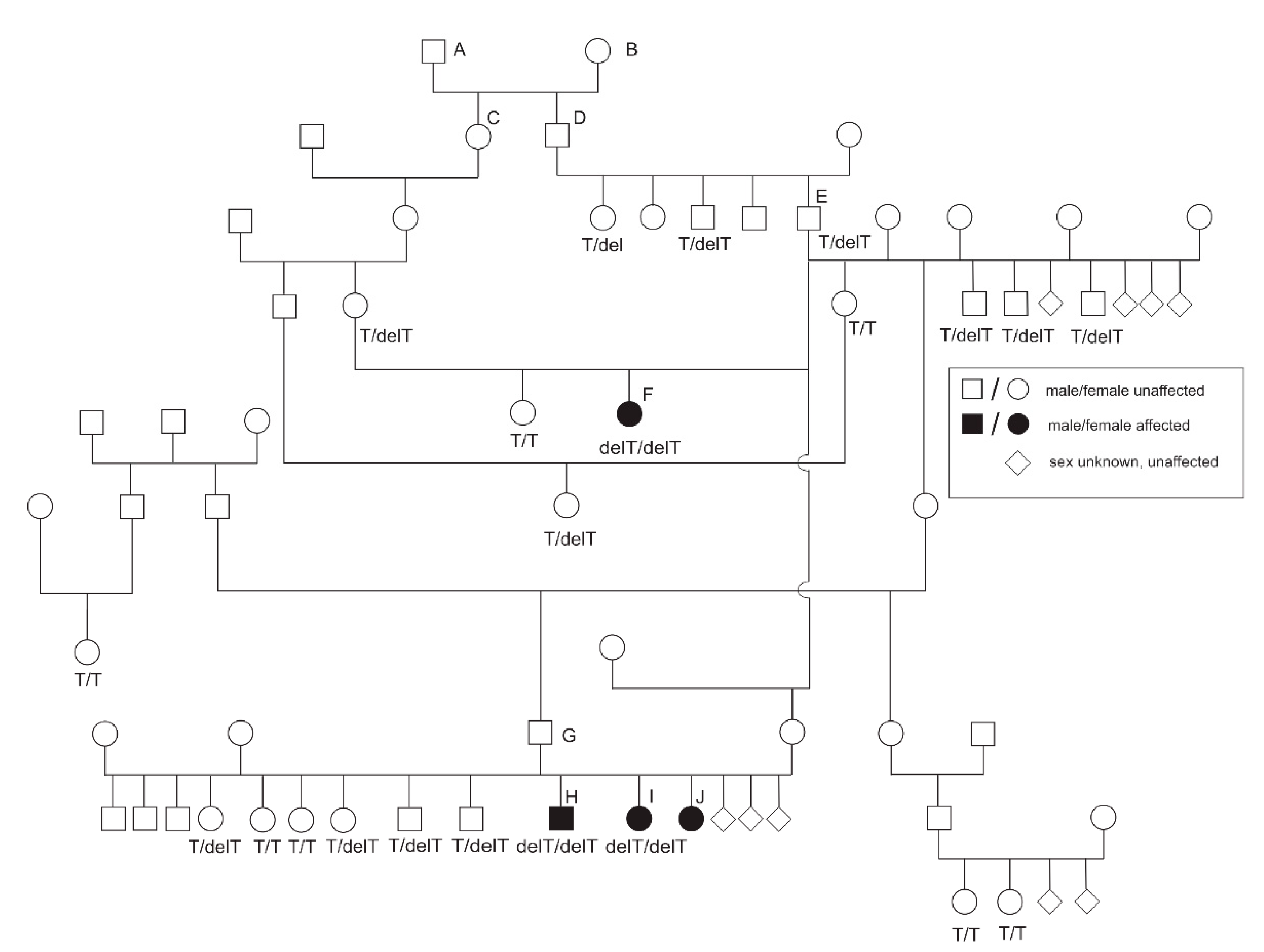
3.1. Phenotype
3.2. Homozygosity Mapping and Genome-Wide Association
3.3. Candidate Gene Sequencing
3.4. Genotyping of the Candidate FGA Variant
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lippi, G.; Franchini, M.; Montagnana, M.; Favaloro, E.J. Inherited disorders of blood coagulation. Ann. Med. 2012, 44, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, A.; Blondon, M.; Tintillier, V.; Goodyer, M.; Sezgin, M.E.; Gunes, A.M.; Hanss, M.; de Moerloose, P.; Neerman-Arbez, M. Mutational Epidemiology of Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Undas, A.; Casini, A. Congenital structural and functional fibrinogen disorders: A primer for internists. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2019, 129, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebreton, A.; Casini, A. Diagnosis of congenital fibrinogen disorders. Ann. Biol. Clin. 2016, 74, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerman-Arbez, M.; de Moerloose, P. Mutations in the fibrinogen gene cluster accounting for congenital afibrinogenemia: An update and report of 10 novel mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moerloose, P.; Casini, A.; Neerman-Arbez, M. Congenital fibrinogen disorders: An update. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2013, 39, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanciakova, L.; Kubisz, P.; Dobrotova, M.; Stasko, J. Congenital afibrinogenemia: From etiopathogenesis to challenging clinical management. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2016, 9, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerman-Arbez, M.; de Moerloose, P.; Casini, A. Laboratory and Genetic Investigation of Mutations Accounting for Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosesson, M.W.; Siebenlist, K.R.; Meh, D.A. The structure and biological features of fibrinogen and fibrin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 936, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolittle, R.F. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Sci. Am. 1981, 245, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virmond, L.A.; Micheletti, C.; Pinto, C.M.S.; Soares, M.F.F.; Milanezi, F.; Nakano, V.; Perrone, E. Congenital afibrinogenemia in a patient with vascular abnormalities and a novel variant: Clinical-molecular description and literature review. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2020, 31, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchini, M.; Marano, G.; Pupella, S.; Vaglio, S.; Masiello, F.; Veropalumbo, E.; Piccinini, V.; Pati, I.; Catalano, L.; Liumbruno, G.M. Rare congenital bleeding disorders. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, W.J. Hemostasis and coagulation. In Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 218–671. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.J. Second international registry of animal models of thrombosis and hemorrhagic diseases. In ILAR News; National Academy Press: London, UK, 1981; p. 24:R16. [Google Scholar]
- Kammermann, B.; Gmür, J.; Stünzi, H. Afibrinogenämie beim Hund. Zent. Vet. A 1971, 18, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, F.; Diquélou, A.; Trumel, C.; Privat, S.; Dossin, O. Fibrinogen deficiency in a dog-a case report. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, M.J.; Johnson, G.S.; Stockham, S.; Riley, L. Afibrinogenemia and a circulating antibody against fibrinogen in a Bichon Frise dog. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 34, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, G. Treatment of afibrinogenemia in a chihuahua. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2013, 49, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M. Hereditary bleeding disorders in dogs and cats. Vet. Med. 1999, 94, 555–565. [Google Scholar]
- Fogh, J.M.; Fogh, I.T. Inherited coagulation disorders. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1988, 18, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.W.; Day, T.K.; Mackin, A. Diagnosing bleeding disorders. Compend. Contin. Educ. Pract. Vet. 2005, 27, 828–843. [Google Scholar]
- Dodds, W.J. Other hereditary coagulopathies. In Schalm’s Veterinary Hematology, 5th ed.; Feldman, B.F., Jain, Z.J., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 1030–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Littlewood, J. Disorders of Secondary Haemostasis; Day, M., Mackin, A., Littlewood, J., Eds.; British Small Animal Veterinary Association: Quedgeley, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sved, J.A. Linkage disequilibrium and homozygosity of chromosome segments in finite populations. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1971, 2, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, W.; Pritchard, B.; Rios, D.; Chen, Y.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. Deriving the consequences of genomic variants with the Ensembl API and SNP Effect Predictor. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2069–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sherry, S.T.; Ward, M.H.; Kholodov, M.; Baker, J.; Phan, L.; Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K. dbSNP: The NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Polymorphism ID | dbSNP-ID | Predicted Effect | Base Change | Genotype Affected Dog 1 | Genotype Affected Dog 2 | Genotype Reference Dog 1 | Genotype Reference Dog 2 | SIFT Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGA:g.2489A>T | rs22378576 | intron variant | - | T/T | T/T | T/T | A/A | - |
| FGA:g.2512C>A | rs22378571 | intron variant | - | A/A | A/A | C/A | C/A | - |
| FGA:g.2706insT | - | intron variant | - | ins/ins | ins/ins | ins/ins | del/ins | - |
| FGA:g.2707A>T | - | intron variant | - | T/T | T/T | T/T | T/T | - |
| FGA:g.2839A>G | rs22378570 | intron variant | - | G/G | G/G | G/A | A/A | - |
| FGA:g.2849insG | - | intron variant | - | ins/ins | ins/ins | ins/ins | ins/ins | - |
| FGA:g.5653insTAGTGCTGGTACTTGGAGCACCAGGCCTGGCAGCACTGGGCCTGG | - | in-frame insertion | - | ins/ins | ins/ins | ins/ins | ins/ins | - |
| FGA:g.5678G>T | rs850697053 | synonymous | - | T/T | T/T | G/T | G/T | - |
| FGA:g.5729T>C | rs851893391 | synonymous | - | C/C | C/C | C/C | C/C | - |
| FGA:g.5749G>A | rs852841801 | missense | S/N | A/A | A/A | G/G | A/A | deleterious low confidence (0.02) |
| FGA:g.5759A>G | rs851142303 | synonymous | - | G/G | G/G | A/A | G/G | - |
| FGA:g.5812T>C | rs851802762 | missense | L/P | C/C | C/C | C/C | C/C | tolerated low confidence (0.63/0.65) |
| FGA:g.5813_5866delGGGCAGTACTGGCACTTGGAGCTCCGGGAGCACCGGGCCTGGCAACACTGGACC | - | in-frame deletion | - | del/del | del/del | del/del | del/del | - |
| FGA:g.6296delT | rs1152388481 | deletion -frameshift | - | del/del | del/del | T/T | T/T | - |
| FGA:g.6299C>T | rs852430931 | synonymous | - | T/T | T/T | C/C | C/C | - |
| FGA:g.7015A>G | - | intron variant | - | G/G | G/G | G/G | G/G | - |
| FGG:g.169T>C | rs8695728 | intron variant | - | C/C | C/C | C/C | T/C | - |
| FGG:g.383insA | - | intron variant | - | ins/ins | ins/ins | ins/ins | ins/ins | - |
| FGG:g.391A>C | - | intron variant | - | A/A | A/A | A/A | A/C | - |
| FGG:g.469T>C | rs8695727 | intron variant | - | C/C | C/C | C/C | C/C | - |
| FGG:g.578T>C | rs8695726 | synonymous | - | C/C | C/C | C/C | T/C | - |
| FGG:g.754T>C | rs22423864 | intron variant | - | C/C | C/C | C/C | C/C | - |
| FGB:g.7827+93C>T | rs22380419 | 3′UTR variant | - | T/T | T/T | T/T | T/T | - |
| Breed | N | T/T | T/delT | delT/delT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Dachshund—smooth-haired | 22 | 22 | 0 | 0 |
| Standard Dachshund—wire-haired | 211 | 209 | 1 | 0 |
| Standard Dachshund—long-haired | 17 | 17 | 0 | 0 |
| Miniature Dachshund—smooth-haired | 11 | 11 | 0 | 0 |
| Miniature Dachshund—wire-haired | 75 | 67 | 2 | 0 |
| Miniature Dachshund—long-haired | 18 | 18 | 0 | 0 |
| Rabbit Dachshund—smooth-haired | 8 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Rabbit Dachshund—wire-haired | 25 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| Rabbit Dachshund—long-haired | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mischke, R.; Metzger, J.; Distl, O. An FGA Frameshift Variant Associated with Afibrinogenemia in Dachshunds. Genes 2021, 12, 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071065
Mischke R, Metzger J, Distl O. An FGA Frameshift Variant Associated with Afibrinogenemia in Dachshunds. Genes. 2021; 12(7):1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071065
Chicago/Turabian StyleMischke, Reinhard, Julia Metzger, and Ottmar Distl. 2021. "An FGA Frameshift Variant Associated with Afibrinogenemia in Dachshunds" Genes 12, no. 7: 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071065
APA StyleMischke, R., Metzger, J., & Distl, O. (2021). An FGA Frameshift Variant Associated with Afibrinogenemia in Dachshunds. Genes, 12(7), 1065. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071065






