Modulation of Cellular MicroRNA by HIV-1 in Burkitt Lymphoma Cells—A Pathway to Promoting Oncogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. miRNA Isolation and PCR Array
2.3. miRNA Target and Pathway Analyses
2.4. RNA Isolation and miRNA Single-Tube TAQMAN® qPCR Assays
2.5. cDNA Synthesis and qPCR for ZEB1 and ZEB2
2.6. Total Protein Isolation and Western Blot Analyses
2.7. Transwell Migration Assay
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Exposure to HIV-1 Leads to Significant Changes in the miRNA Profile of Burkitt Lymphoma Cells
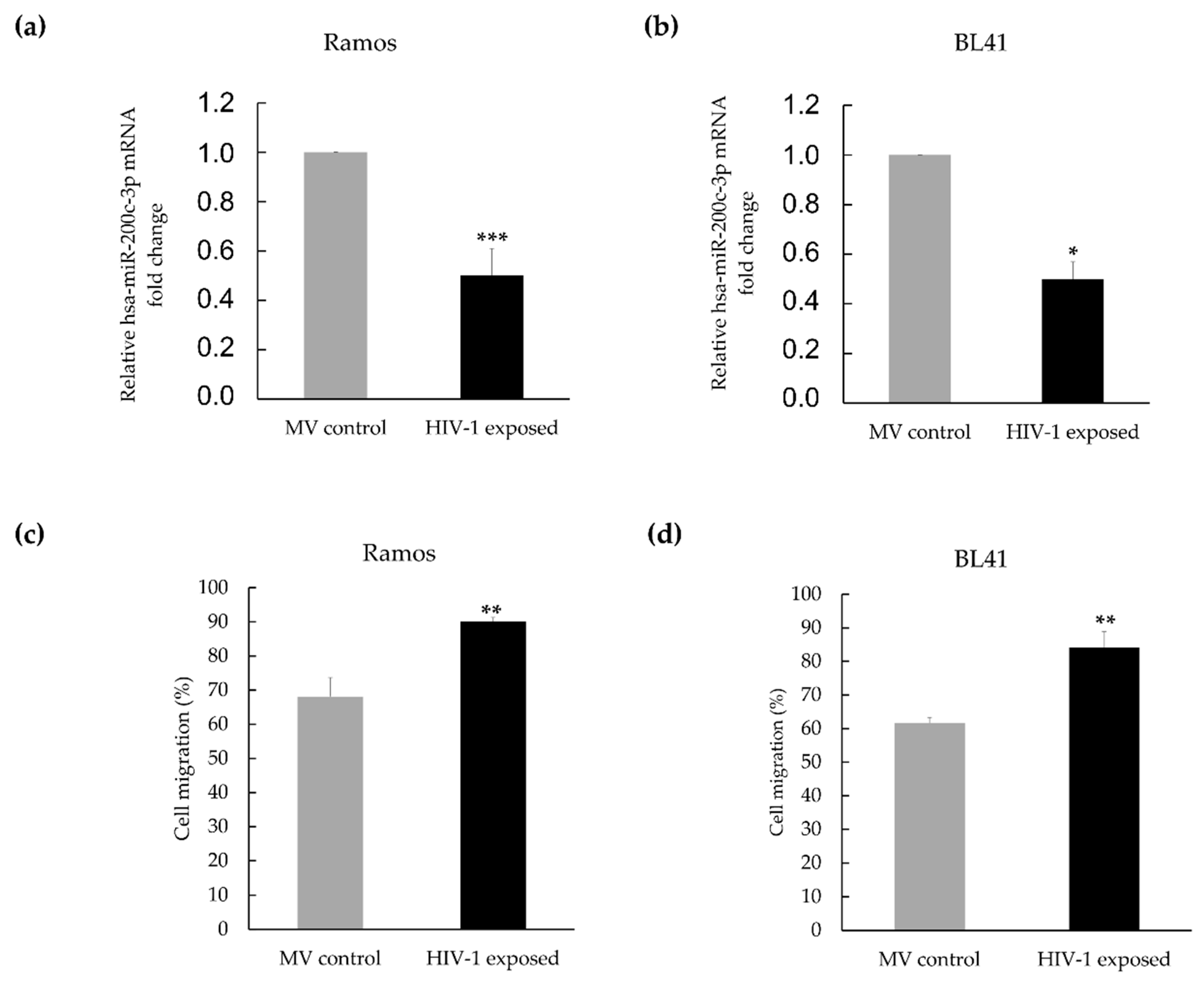
3.2. Hsa-miR-200c-3p Is Significantly Downregulated in HIV-1 Treated Burkitt Lymphoma Cells, and This Is Associated with Enhanced Migration
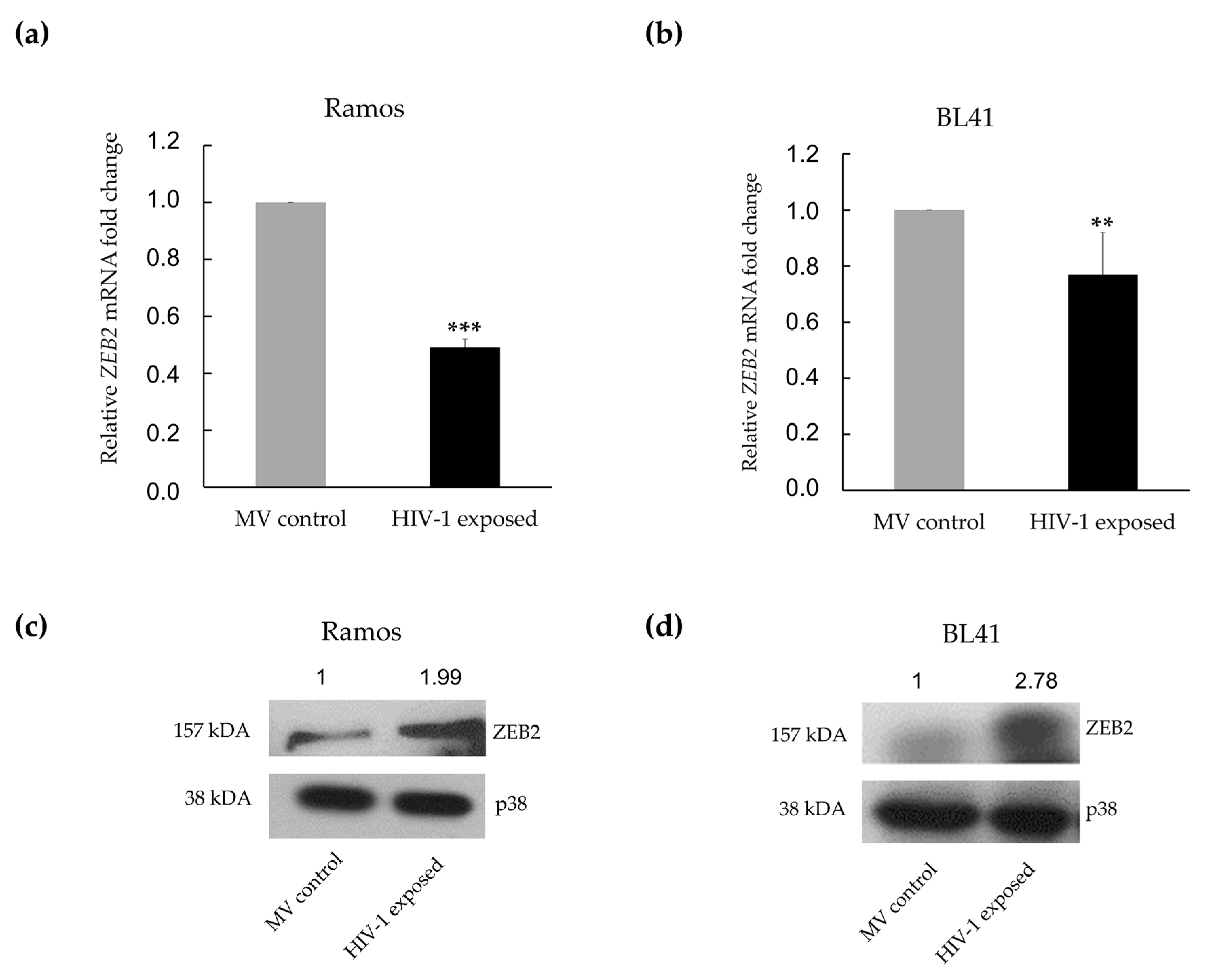
3.3. MiR-200c-3p Downregulation and Enhanced Migration Correlates with Over-Expression of ZEB1 and ZEB2 Proteins in BL Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ambros, V.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Dreyfuss, G.; Eddy, S.R.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Marshall, M.; et al. A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 2003, 9, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Tullio, G.; De Fazio, V.; Sgherza, N.; Minoia, C.; Serratì, S.; Merchionne, F.; Loseto, G.; Iacobazzi, A.; Rana, A.; Petrillo, P.; et al. Challenges and Opportunities of MicroRNAs in Lymphomas. Molecules 2014, 19, 14723–14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacFarlane, L.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Liu, C.G.; Veronese, A.; Spizzo, R.; Sabbioni, S.; Magri, E.; Pedriali, M.; Fabbri, M.; Campiglio, M.; et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7065–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranganathan, K.; Sivasankar, V. MicroRNAs—Biology and clinical applications. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. JOMFP 2014, 18, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.M.; Byrom, M.W.; Shelton, J.; Ford, L.P. Antisense inhibition of human miRNAs and indications for an involvement of miRNA in cell growth and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Re, A.; Cattaneo, C.; Rossi, G. Hiv and Lymphoma: From Epidemiology to Clinical Management. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 11, e2019004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sissolak, G.; Seftel, M.; Uldrick, T.S.; Esterhuizen, T.M.; Mohamed, N.; Kotze, D. Burkitt’s Lymphoma and B-Cell Lymphoma Unclassifiable with Features Intermediate Between Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Burkitt’s Lymphoma in Patients With HIV: Outcomes in a South African Public Hospital. J. Glob. Oncol. 2017, 3, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, G.; Zamparese, R.; Pace, M.; Pedicillo, M.; Cagiano, S.; Somma, P.; Errico, M.; Donofrio, V.; Franco, R.; De Chiara, A.; et al. The role of EBV in the pathogenesis of Burkitt’s Lymphoma: An Italian hospital based survey. Infect. Agents Cancer 2014, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, R.; Ceribelli, M.; Pittaluga, S.; Wright, G.; Staudt, L.M. Oncogenic Mechanisms in Burkitt Lymphoma. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, S.T.; Karim, R.; Nathwani, B.N.; Tulpule, A.; Espina, B.; Levine, A.M. AIDS-Related Burkitt’s Lymphoma Versus Diffuse Large-Cell Lymphoma in the Pre-Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART) and HAART Eras. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4430–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggill, T.M.; Mantina, H.; Willem, P.; Perner, Y.; Stevens, W. Changing Pattern of Lymphoma Subgroups at a Tertiary Academic Complex in a High-Prevalence HIV Setting; A South African Perspective. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2011, 56, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves de Souza Rios, L.; Mapekula, L.; Mdletshe, N.; Chetty, D.; Mowla, S. HIV-1 Transactivator of Transcription (Tat) Co-operates With AP-1 Factors to Enhance c-MYC Transcription. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 693706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mdletshe, N.; Nel, A.; Shires, K.; Mowla, S. HIV Nef enhances the expression of oncogenic c-MYC and activation-induced cytidine deaminase in Burkitt lymphoma cells, promoting genomic instability. Infect. Agents Cancer 2020, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sall, F.B.; El Amine, R.; Markozashvili, D.; Tsfasman, T.; Oksenhendler, E.; Lipinski, M.; Vassetzky, Y.; Germini, D. HIV-1 Tat protein induces aberrant activation of AICDA in human B-lymphocytes from peripheral blood. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 15678–15685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germini, D.; Tsfasman, T.; Klibi, M.; El-Amine, R.; Pichugin, A.; Iarovaia, O.V.; Bilhou-Nabera, C.; Subra, F.; Bou Saada, Y.; Sukhanova, A.; et al. HIV Tat induces a prolonged MYC relocalization next to IGH in circulating B-cells. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolcetti, R.; Giagulli, C.; He, W.; Selleri, M.; Caccuri, F.; Eyzaguirre, L.M.; Mazzuca, P.; Corbellini, S.; Campilongo, F.; Marsico, S.; et al. Role of HIV-1 matrix protein p17 variants in lymphoma pathogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 14331–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mapekula, L.; Ramorola, B.R.; Goolam Hoosen, T.; Mowla, S. The interplay between viruses & host microRNAs in cancer—An emerging role for HIV in oncogenesis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 137, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, S.; Malaspina, A.; Li, Y.; Chun, T.-W.; Lowe, T.; Adelsberger, J.; Baseler, M.; Ehler, L.A.; Liu, S.; Davey, R.T.; et al. B Cells of HIV-1–Infected Patients Bind Virions through Cd21–Complement Interactions and Transmit Infectious Virus to Activated T Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanna, J.; Hossain, G.S.; Kocerha, J. The Potential for microRNA Therapeutics and Clinical Research. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphries, B.; Yang, C. The microRNA-200 family: Small molecules with novel roles in cancer development, progression and therapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6472–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamagawa, S.; Beder, L.B.; Hotomi, M.; Gunduz, M.; Yata, K.; Grenman, R.; Yamanaka, N. Role of miR-200c/miR-141 in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossio, J.L.; Esser, M.T.; Suryanarayana, K.; Schneider, D.K.; Bess, J.W.; Vasquez, G.M.; Wiltrout, T.A.; Chertova, E.; Grimes, M.K.; Sattentau, Q.; et al. Inactivation of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 infectivity with preservation of conformational and functional integrity of virion surface proteins. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7992–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.-W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagkouni, D.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Chatzopoulos, S.; Vlachos, I.S.; Tastsoglou, S.; Kanellos, I.; Papadimitriou, D.; Kavakiotis, I.; Maniou, S.; Skoufos, G.; et al. DIANA-TarBase v8: A decade-long collection of experimentally supported miRNA–gene interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D239–D245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X. Prediction of functional microRNA targets by integrative modeling of microRNA binding and target expression data. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; Da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, G.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvinge, H.; Bertone, P. HTqPCR: High-throughput analysis and visualization of quantitative real-time PCR data in R. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 3325–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mestdagh, P.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; De Weer, A.; Muth, D.; Westermann, F.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. A novel and universal method for microRNA RT-qPCR data normalization. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenze, D.; Leoncini, L.; Hummel, M.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Amato, T.; De Falco, G.; Githanga, J.; Horn, H.; Nyagol, J.; et al. The different epidemiologic subtypes of Burkitt lymphoma share a homogenous micro RNA profile distinct from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Sage, C.; Nagel, R.; Egan, D.A.; Schrier, M.; Mesman, E.; Mangiola, A.; Anile, C.; Maira, G.; Mercatelli, N.; Ciafrè, S.A.; et al. Regulation of the p27Kip1 tumor suppressor by miR-221 and miR-222 promotes cancer cell proliferation. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3699–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, E.L.; Trinh, D.L.; Scott, D.W.; Chu, A.; Krzywinski, M.; Zhao, Y.; Robertson, A.G.; Mungall, A.J.; Schein, J.; Boyle, M.; et al. Comprehensive miRNA sequence analysis reveals survival differences in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berglund, M.; Hedstrom, G.; Amini, R.M.; Enblad, G.; Thunberg, U. High expression of microRNA-200c predicts poor clinical outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, W.; Xie, X.; Jiang, J. Prognostic Significance of MiRNA in Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Shan, B.; Han, J.; Zhu, H.; Lv, Y.; Fan, X.; Sang, M.; Liu, X.-D.; Liu, W. The downregulation of miR-200c/141 promotes ZEB1/2 expression and gastric cancer progression. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, H.; Zhu, D.; Zhi, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, B.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P. miR-200bc/429 cluster modulates multidrug resistance of human cancer cell lines by targeting BCL2 and XIAP. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, D.R.; Howe, E.N.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Richer, J.K. Loss of miR-200c: A Marker of Aggressiveness and Chemoresistance in Female Reproductive Cancers. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 821717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cochrane, D.R.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Howe, E.N.; Nordeen, S.K.; Richer, J.K. MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic agents. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopp, F.; Wagner, E.; Roidl, A. The proto-oncogene KRAS is targeted by miR200c. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Liang, Z.; Chen, L.; Tan, G.; Liu, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Liu, J. MicroRNA-200c suppresses cell growth and metastasis by targeting Bmi-1 and E2F3 in renal cancer cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Cui, R.; Xu, X. miR-200c inhibits melanoma progression and drug resistance through down-regulation of BMI-1. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howe, E.N.; Cochrane, D.R.; Richer, J.K. Targets of miR-200c mediate suppression of cell motility and anoikis resistance. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, D.; Jiang, H. MicroRNA-200c binding to FN1 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, H.; Pelakh, L.; Chuang, T.-D.; Luo, X.; Bukulmez, O.; Chegini, N. Endometrial miR-200c is Altered During Transformation into Cancerous States and Targets the Expression of ZEBs, VEGFA, FLT1, IKKβ, KLF9, and FBLN5. Reprod. Sci. 2012, 19, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Title, A.C.; Hong, S.-J.; Pires, N.D.; Hasenöhrl, L.; Godbersen, S.; Stokar-Regenscheit, N.; Bartel, D.P.; Stoffel, M. Genetic dissection of the miR-200–Zeb1 axis reveals its importance in tumor differentiation and invasion. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, A.; Han, X. The roles of ZEB1 in tumorigenic progression and epigenetic modifications. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 110, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, M.S.; Engels, E.A. Evolving epidemiology of HIV-associated malignancies. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2017, 12, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaguliants, M.; Bayurova, E.; Avdoshina, D.; Kondrashova, A.; Chiodi, F.; Palefsky, J.M. Oncogenic Effects of HIV-1 Proteins, Mechanisms Behind. Cancers 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martorelli, D.; Muraro, E.; Mastorci, K.; Dal Col, J.; Fae, D.A.; Furlan, C.; Giagulli, C.; Caccuri, F.; Rusnati, M.; Fiorentini, S.; et al. A natural HIV p17 protein variant up-regulates the LMP-1 EBV oncoprotein and promotes the growth of EBV-infected B-lymphocytes: Implications for EBV-driven lymphomagenesis in the HIV setting. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modai, S.; Farberov, L.; Herzig, E.; Isakov, O.; Hizi, A.; Shomron, N. HIV-1 infection increases microRNAs that inhibit Dicer1, HRB and HIV-EP2, thereby reducing viral replication. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, S.; Hu, M.; Hao, T.; Li, W.; Xue, X.; Xue, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, F.; Qin, D.; Yan, Q.; et al. MiRNA-891a-5p mediates HIV-1 Tat and KSHV Orf-K1 synergistic induction of angiogenesis by activating NF-κB signaling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 9362–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzzi, A.; Morettini, F.; Gazaneo, S.; Mundo, L.; Onnis, A.; Mannucci, S.; Rogena, E.A.; Bellan, C.; Leoncini, L.; De Falco, G. HIV-1 Tat induces DNMT over-expression through microRNA dysregulation in HIV-related non Hodgkin lymphomas. Infect. Agents Cancer 2014, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manavalan, T.T.; Teng, Y.; Litchfield, L.M.; Muluhngwi, P.; Al-Rayyan, N.; Klinge, C.M. Reduced Expression of miR-200 Family Members Contributes to Antiestrogen Resistance in LY2 Human Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peter, M.E. Let-7 and miR-200 microRNAs: Guardians against pluripotency and cancer progression. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, F.F.; Jamal, R.; Syafruddin, S.E.; Mutalib, N.S.A.; Saidin, S.; MdZin, R.R.; Hossain Mollah, M.M.; Mokhtar, N.M. microRNA-200c and microRNA-31 regulate proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion in serous ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2015, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuang, T.D.; Panda, H.; Luo, X.; Chegini, N. miR-200c is aberrantly expressed in leiomyomas in an ethnic-dependent manner and targets ZEBs, VEGFA, TIMP2, and FBLN5. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valencia-Sanchez, M.A. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caramel, J.; Ligier, M.; Puisieux, A. Pleiotropic roles of ZEB1 in cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brabletz, S.; Brabletz, T. The ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop--a motor of cellular plasticity in development and cancer? EMBO Rep. 2010, 11, 670–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burk, U.; Schubert, J.; Wellner, U.; Schmalhofer, O.; Vincan, E.; Spaderna, S.; Brabletz, T. A reciprocal repression between ZEB1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes EMT and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, L.; Browne, G.; Tulchinsky, E. ZEB/miR-200 feedback loop: At the crossroads of signal transduction in cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtamouni, L.; Ahram, M.; Koblinski, J.; Rolfo, C. Molecular regulaion of cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis. Anal. Cell Pathol. 2019, 2019, 1356508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Shi, J.; Jiang, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Pan, J.; et al. MicroRNA-362-3p Inhibits Migration and Invasion via Targeting BCAP31 in Cervical Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Z.; Lu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, J.; Chai, K.; Chen, W. MicroRNA-145 Inhibits Cell Migration and Invasion in Colorectal Cancer by Targeting TWIST. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 10, 10799–10809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

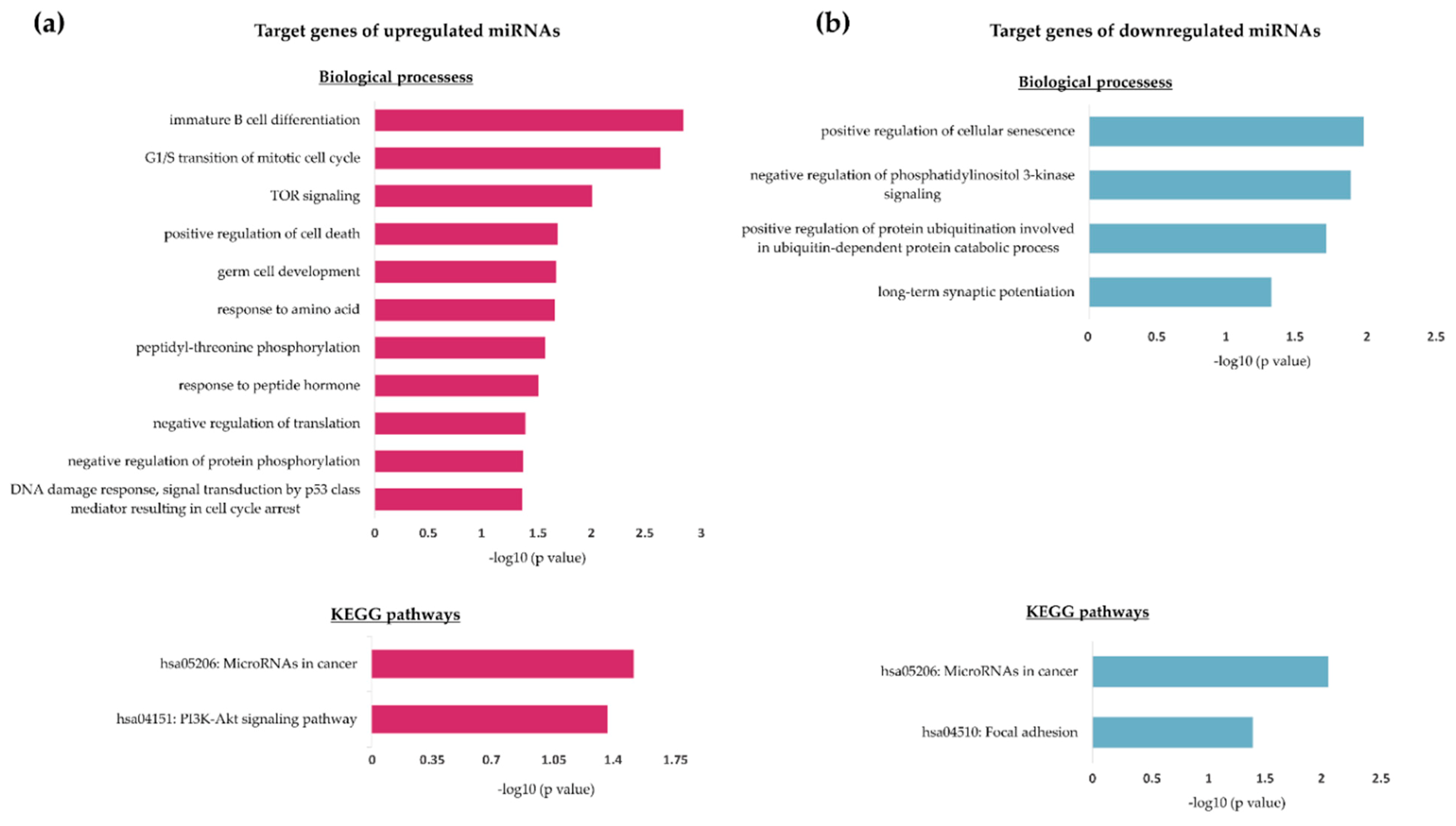

| Predicted Gene Targets of Upregulated miRNAs (13) | Predicted Gene Targets of Downregulated miRNAs (23) |
|---|---|
| CDKN1B, KIT, MIDN, ANKRA2, FNIP1, BTG2, HS3ST2, CTDSPL, SMARCA5, MTOR, TRIM71, MYCN, ACVR1 | NOVA1, FBXW7, ZEB1, GABRA1, POU2F1, MTHFD2, LIN28B, TET1, COL3A1, HMGA2, KLHL3, SERPINE2, PAWR, GNA12, PAK4, BCAR3, CD2AP, FOXN2, ZFP91, SLC22A3, PTEN, C6orf106, SRSF7 |
| Gene Target | Validation Tool | Cancer Type: Process | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc Finger E-box Binding Protein 1 and 2 (ZEB1, ZEB2) | Dual-luciferase reporter assay, Western blotting, qPCR | Gastric, Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration and invasion. | [23,39] |
| X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2) | Dual-luciferase reporter assay, Western blotting | Gastric, Lung: apoptosis | [40] |
| Tubulin β 3 Class III (TUBB3) | Dual-luciferase reporter assay, Western blotting, qPCR | Breast, Ovarian, endometrial: proliferation, drug resistance | [41,42] |
| KRAS proto-oncogene (KRAS) | Dual-luciferase reporter assay, Western blotting | Breast, NSCLC: Proliferation | [43] |
| B-cell-specific Moloney murine leukaemia virus insertion site 1 (BMI1), E2F transcription factor 3 (E2F3) | Reporter assay, Western blotting, qPCR | Renal, Bladder: Proliferation, migration, and invasion | [44,45] |
| Fibronectin 1 (FN1), Moesin (MSN) | Reporter assay, Western blotting, qPCR | Breast, endometrial: Invasion, anoikis resistance | [46,47] |
| Inhibitor of Nuclear Factor Kappa β Kinase Subunit β (IKBKβ), Fms Related Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 1 (FLT1), Kruppel Like Factor 9 (KLF9) | Reporter assay, Western blotting, qPCR | Endometrial: Proliferation, inflammation | [48] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramorola, B.R.; Goolam-Hoosen, T.; Alves de Souza Rios, L.; Mowla, S. Modulation of Cellular MicroRNA by HIV-1 in Burkitt Lymphoma Cells—A Pathway to Promoting Oncogenesis. Genes 2021, 12, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091302
Ramorola BR, Goolam-Hoosen T, Alves de Souza Rios L, Mowla S. Modulation of Cellular MicroRNA by HIV-1 in Burkitt Lymphoma Cells—A Pathway to Promoting Oncogenesis. Genes. 2021; 12(9):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091302
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamorola, Beatrice Relebogile, Taahira Goolam-Hoosen, Leonardo Alves de Souza Rios, and Shaheen Mowla. 2021. "Modulation of Cellular MicroRNA by HIV-1 in Burkitt Lymphoma Cells—A Pathway to Promoting Oncogenesis" Genes 12, no. 9: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091302
APA StyleRamorola, B. R., Goolam-Hoosen, T., Alves de Souza Rios, L., & Mowla, S. (2021). Modulation of Cellular MicroRNA by HIV-1 in Burkitt Lymphoma Cells—A Pathway to Promoting Oncogenesis. Genes, 12(9), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12091302







