Abstract
Pluripotency markers Pou5f1 and Nanog are core transcription factors regulating early embryonic development and maintaining the pluripotency and self-renewal of stem cells. Pou5f1 and Nanog also play important roles in germ cell development and gametogenesis. In this study, Pou5f1 (EcPou5f1) and Nanog (EcNanog) were cloned from orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. The full-length cDNAs of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog were 2790 and 1820 bp, and encoded 475 and 432 amino acids, respectively. EcPou5f1 exhibited a specific expression in gonads, whereas EcNanog was expressed highly in gonads and weakly in some somatic tissues. In situ hybridization analyses showed that the mRNA signals of EcNanog and EcPou5f1 were exclusively restricted to germ cells in gonads. Likewise, immunohistofluorescence staining revealed that EcNanog protein was limited to germ cells. Moreover, both EcPou5f1 and EcNanog mRNAs were discovered to be co-localized with Vasa mRNA, a well-known germ cell maker, in male and female germ cells. These results implied that EcPou5f1 and EcNanog could be also regarded as reliable germ cell marker genes. Therefore, the findings of this study would pave the way for elucidating the mechanism whereby EcPou5f1 and EcNanog regulate germ cell development and gametogenesis in grouper fish, and even in other protogynous hermaphroditic species.
1. Introduction
Germ cell development is indispensable for animal reproduction and fertility. The complex process from the formation of primordial germ cells (PGCs) to the differentiation into gametes is strictly regulated by many factors, such as hormones and reproduction-related genes [1,2,3]. Germ cell marker genes can be used for exploring PGCs formation and migration, germ cell development, and the mechanism behind gametogenesis. In teleost fish, some germ cell-specific genes have been characterized, including PGC-specific gene Nanos3 [4], mitotic germ cell-specific gene Ly75 [5], spermatogonium-specific gene Plzf [6,7], oocyte-specific gene Slbp2 [8], as well as the well-known germline-specific genes Vasa, Dazl and Piwi [9,10].
Pou5f1 (also known as Oct4) and Nanog are closely related to each other and characterized as core transcription factors essential for embryogenesis and the maintenance of cell pluripotency [11,12,13]. Pou5f1 protein is a class V POU domain transcription factor containing a POU domain that consists of POU specific domain (POUs), POU homeodomain (POUhD), and a linker between them [14]. The POU domain of Pou5f1 can regulate the transcription of its target genes possessing an octamer sequence motif of ATGC(A/T)AAT [15]. Most interestingly, the combined actions of Pou5f1, Sox2, Klf4, and C-myc are capable of reprogramming somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (IPSCs) [16]. Nanog protein is a DNA binding homeobox transcription factor with a homeodomain (HD) [12,17]. The existence of OCT-SOX enhancer in Nanog promoter indicates that Pou5f1 and Sox2 are direct modulators of Nanog transcript [18]. Moreover, the protein complex formed by Nanog and Pou5f1 can influence the activity of at least 300 target genes [19]. In human (Homo sapiens) and mouse (Mus musculus), Pou5f1 and Nanog are mainly expressed in multipotent stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells (ESCs), IPSCs, PGCs, spermatogonial stem cells, and oogonial stem cells [16,20,21]. In fish, such as zebrafish (Danio rerio), medaka (Oryzias latipes), and Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus), Pou5f1 and Nanog are also detected in the above-mentioned stem cells [22,23,24,25]. Additionally, Pou5f1 and Nanog participate in the differentiation and development of germ cells [20,21]. In mouse, Nanog serves as an epigenetic modifier involved in the maturation of haploid male germ cells [26], and the downregulation of Pou5f1 results in the developmental arrest of oocytes [27]. Intriguingly, Nanog and Pou5f1 are significantly expressed in spermatocytes and spermatids, rather than spermatogonia in pig (Sus scrofa) testis [28]. In medaka, Nanog can regulate the expression level of Cxcr4b which is the guider of PGCs migration [29]. In gonads of medaka, zebrafish, and Japanese flounder, Pou5f1 and Nanog are restricted to oogonia, oocytes, and spermatogonia [24,25,30,31]. Nevertheless, in large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea), Pou5f1 is expressed in spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes, as well as all female germ cells [32]. In blunt-snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala), Nanog is detected in all male germ cells and most female germ cells [33]. In goldfish (Carassius auratus), the Nanog promoter is in a state of hypermethylation in oocytes, while hypomethylation in sperm [34]. The expressions of Pou5f1 and Nanog in germ cells indicate that they are functionally important in sustaining germ cell development and gametogenesis in mammals and fish.
Orange-spotted grouper (E. coioides) is a protogynous hermaphroditic fish whose gonad first develops as matured ovary and then reverses into testis, and therefore is regarded as an ideal model for studying the mechanism of sex reversal [35]. Pou5f1 and Nanog have been characterized as germ cell-specific genes in some dioecious fish, but their expression patterns present a species difference to a variable extent [24,25,30,31,32,33]. In this study, Pou5f1 (EcPou5f1) and Nanog (EcNanog) were cloned and characterized in orange-spotted grouper, and their expression patterns were analyzed during gametogenesis. These results would contribute to further studies on the mechanisms underlying PGCs formation and migration, germ cell development, and sex reversal in hermaphroditic fish.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Ethics
Animal experiments in this study were performed under the guidelines and approval of the Institutional Animal Care and use Committee of Sun Yat-Sen University. Female orange-spotted groupers with 25–35 cm in body length and 0.5–1 kg in body weight were bought from Huangsha Fisheries Trading Market, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. Male orange-spotted groupers with 60–70 cm in body length and 5 kg in body weight were bought from Marine Fisheries Development Center of Guangdong Province, Huizhou, Guangdong, China. Groupers were anesthetized euthanized with 30 mg/L eugenol (Solarbio, Beijing, China) before being sacrificed. Tissue samples were as follows: brain, pituitary, gill filament, heart, head kidney, kidney, muscle, liver, stomach, intestine, spleen, testis, and ovary. These tissues were collected from groupers for the subsequent experiments, including RNA extraction, protein extraction, and frozen section.
2.2. Cloning of Full-Length cDNA Sequences
Full-length cDNA sequences of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog were cloned from testis using SMARTer RACE cDNA Amplification Kit (Clontech Laboratories Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA). Based on the cDNA fragments of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog in E. coioides genome data (unpublished data), specific primers were designed and listed in Table 1. Two rounds of PCR were carried out for amplifying the 5′ and 3′ cDNA ends. Pou5f1-F1 and UPM comprising UPM long and UPM short were mixed for the first round 3′ RACE amplification, while Pou5f1-R1 and UPM were employed for the first round 5′ RACE amplification. Pou5f1-R2 and NUP, as well as Pou5f1-F2 and NUP, were used for the second round 5′ and 3′ RACE amplification, respectively. The 5′ and 3′ cDNA end sequences of EcNanog were obtained via the same method. PCR procedure was as follows: denaturation at 95 °C for 1 min, followed by 35 cycles at 95 °C for 10 s, 58 °C for 10 s, 72 °C for 1 min, and a final extension of 5 min at 72 °C After agarose gel electrophoresis, the desired bands were purified by Gel Extraction Kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Norcross, GA, USA) and then sequenced by Sangon Biotech Company (Shanghai, China). According to sequencing data of purified DNA products, the 3′ and 5′ cDNA sequences of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog were spliced into full-length cDNA sequences. Amino acid sequences of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog were predicted and performed for multiple sequence alignments using DNAMAN version 7.0 (Lynnon Biosoft, Quebec, QC, Canada). Phylogenetic trees were generated with MEGA version 5.0 (Biodesign Institute, Tempe, AZ, USA).

Table 1.
Primers for synthesizing RNA probes, cloning the full-length cDNAs, and analyzing gene expression levels.
2.3. Total RNA Extraction and PCR
Total RNA of tissue was extracted with TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). RNA quality was evaluated by agarose gel electrophoresis. The cDNA was synthesized with 1 µg total RNA using ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Master Mix with gDNA Remover (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan). Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was performed on a Roche LightCycler 480 System (Roche Diagnostics, San Francisco, CA, USA) with SYBR Green Realtime PCR Master Mix (Toyobo). Produce was as follows: 30 s at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles of 5 s at 95 °C, 5 s at 58 °C, and 15 s at 72 °C, with final step for 15 s at 95 °C and 30 s at 60 °C. Semi-quantitative PCRs for about 240 bp DNA fragments were performed with Taq PCR StarMix (Genstar, Shanghai, China), and PCR procedure was as follows: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 2 min, followed by 35 cycles of 30 s at 94 °C, 30 s at 58 °C, and 15 s at 72 °C, finally 72 °C for 5 min. Semi-quantitative PCR for the 1299 bp open reading frame (ORF) of EcNanog was performed with KOD One PCR Master Mix-Blue (Toyobo), and PCR procedure was as follows: initial denaturation at 94 °C for 2 min, followed by 35 cycles of 5 s at 98 °C, 5 s at 60 °C, and 5 s at 68 °C, finally 68 °C for 5 min. After gel electrophoresis, bands were photographed with a Tanon 1600 image system (Tanon, Shanghai, China). The β-Actin was used as an internal control. Genetic expression quantifications were normalized to β-Actin. Primers were listed in Table 1.
2.4. Western Blotting
The monoclonal anti-Nanog antibody from medaka was provided by Professor Hongyan Xu [36]. The total protein of tissues was extracted with RIPA Lysis Buffer (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) and mixed with SDS-PAGE Sample Loading Buffer (Beyotime). After being boiled for 5 min, 10 µL protein buffer was loaded into a lane, electrophoresed through 10% SDS-PAGE gels, and electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) by an electroblotter (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA). The membrane was blocked with 5% BSA (Solarbio) for 1 h. After being washed with TBS (Solarbio), the membrane was incubated with anti-β-Actin antibody (Bioss, Beijing, China) or anti-Nanog antibody (1:1000 dilution in TBS) at 4 °C overnight. Then, the membrane was washed with TBS and incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Bioss) (1:2000 dilution in TBS) for 2 h. Finally, protein blots were colored with Chemiluminescent Substrate for Western blotting Kit (Cyanagen, Bologna, Italy) and imaged by an Alliance MINI HD9 system (Uvitec, Cambridge, UK). The β-Actin was used as an internal control.
2.5. In Situ Hybridization (ISH)
ISH protocol was described in our previous study [37]. Briefly, after being fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (Sangon, Shanghai, China) at 4 °C overnight, gonads were dehydrated with gradient methanol/PBS from 20% to 100% methanol, and then stored at −20 °C until further use. Gonads were rehydrated with gradient methanol/PBS up to 100% PBS, immersed in 30% (w/v) sucrose at 4 °C overnight, and embedded in OCT compound (SAKURA Tissue-Tek, Atlanta, GA, USA). These gonad samples were cryosectioned at 4 µm using a Leica RM2135 Microtome (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Probes were synthesized using DIG RNA labeling kit (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). Lengths of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog probes were 1037 bp and 1299 bp, respectively. Ingredients of hybridization buffer were as follows: 50% deionized formamide, 5 × saline sodium citrate (SSC), 0.5 mg/mL salmon sperm RNA, 1 × Denhart’s solution, and 5% dextran sulphate. Gonadal sections were pre-hybridized with hybridization buffer for 2 h and then hybridized with 1 µg/mL DIG probes at 65 °C for 15 h. Subsequently, sections were washed with SSC and blocked with Blocking Reagent (Roche) for at least 1 h. Sections were incubated with anti-Digoxigenin-AP (Roche), then colored with NBT/BCIP (Roche). Photographs were imaged by a Leica DMI8 microscope (Leica).
2.6. Dual-Label ISH
Dual-label ISH protocol referred to our previous study [38]. The Vasa probe was 1040 bp and synthesized using Fluorescein RNA labeling kit (Roche). Gonadal sections were pre-hybridized for 2 h, then hybridized by 1 µg/mL Vasa probe and one of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog probes at the same time at 65 °C for 15 h. Subsequently, sections were washed with SSC and blocked with Blocking Reagent for at least 1 h. The Vasa probe was incubated with anti-Fluorescein-POD (Roche), then stained red fluorescence for 10 min with TSATM PLUS Fluorescein system (PerkinElmer, Shelton, USA). After being washed, the EcPou5f1 or EcNanog probes were incubated with anti-Digoxigenin-POD (Roche) and were stained green fluorescence for 10 min. Finally, gonadal sections were counterstained by DAPI (Solarbio) for cell nuclei staining. Sections were imaged with a Zeiss LSM 800 microscope (Zeiss, Jena, Germany) or a Leica TCS SP5 microscope (Leica).
2.7. Fluorescent Immunostaining
Gonadal sections were dried in a drying oven and washed with PBS. After being blocked with 5% goat serum (Sangon) for 1 h, sections were incubated with the anti-Nanog antibody for 2 h (1:200 dilution in PBS containing 2% goat serum). After being washed with PBS, sections were incubated with HRP-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (1:3000 dilution in PBS) for 1 h. Signals were developed using the TSATM Plus Fluorescence System. The nucleus was colored by PI (Solarbio). Photographs were imaged by a Leica DMI8 microscope.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
All data were shown as the mean values ± SEM. Statistical analysis was implemented by one-way ANOVA and Student’s t-test. A probability level less than 0.05 (p < 0.05) was considered statistically significant. All statistics were carried out using GraphPad Prism version 5.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Identifications of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog
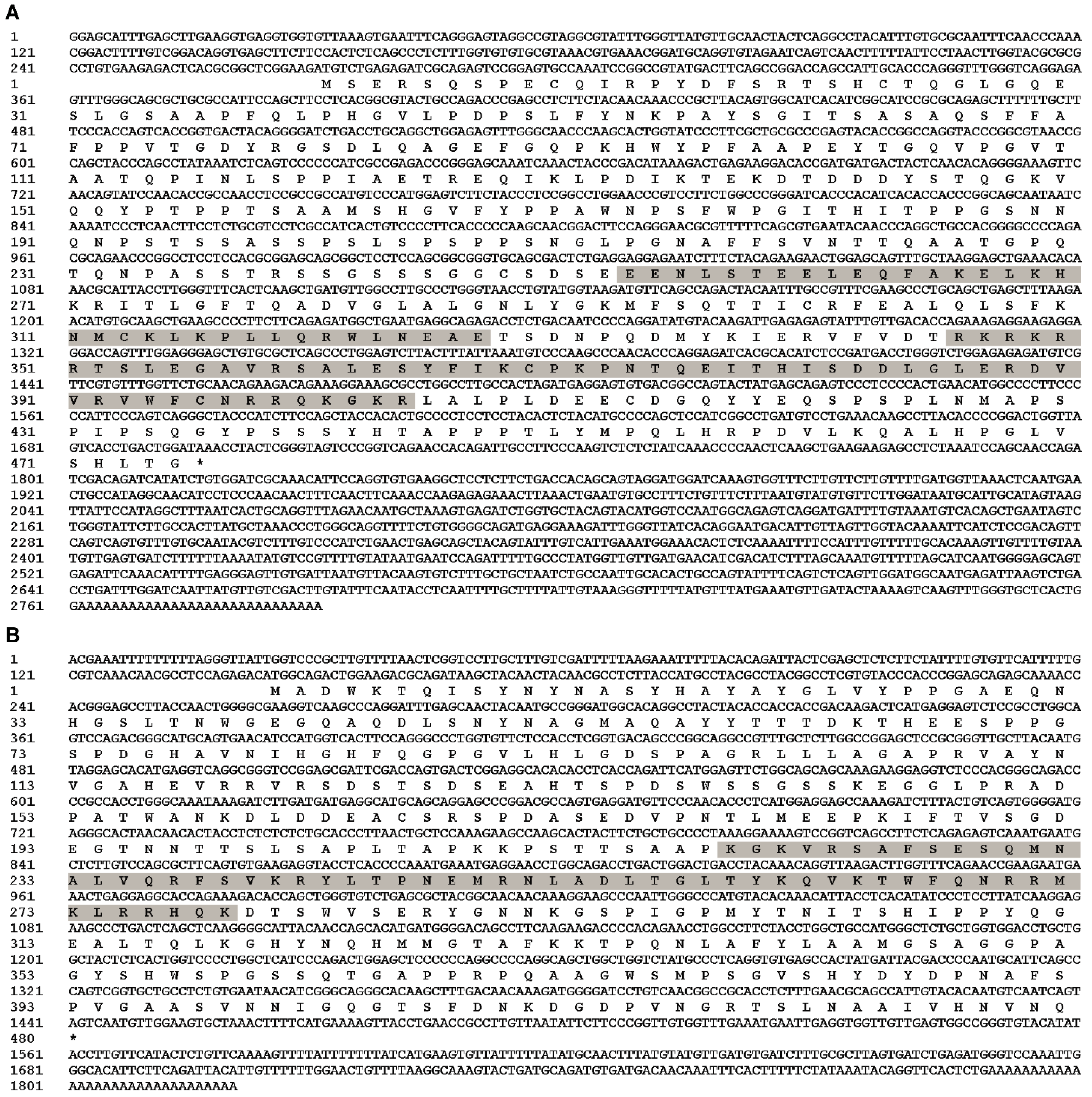
Full-length cDNA of EcPou5f1 was 2790 bp with a 1428 bp ORF, a 269 bp 5′-untranslated region (UTR), and a 1093 bp 3′-UTR, as well as encoded a predicted protein of 475 amino acids containing POUs and POUhD (Figure 1A). Full-length cDNA of EcNanog was 1820 bp with a 1299 bp ORF encoding a 432 amino acid peptide with an HD domain, a 143 bp 5′-UTR, and a 378 bp 3′-UTR (Figure 1B). Sequences of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog were deposited in GenBank with accession numbers OL439940 and OK415852, respectively.
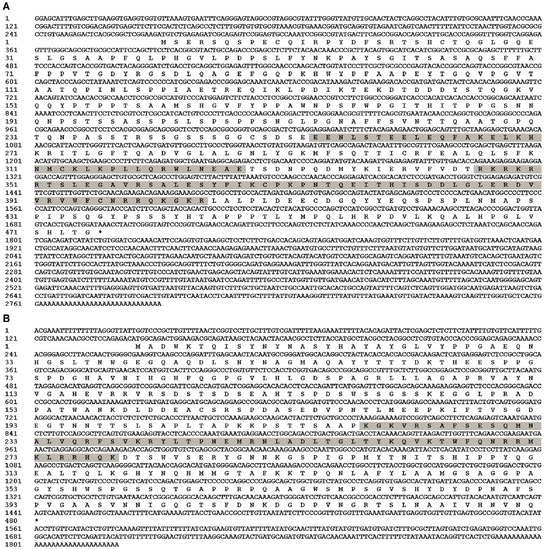
Figure 1.
Full-length cDNA sequences and predicted polypeptides of (A) EcPou5f1 and (B) EcNanog. Gray shadow: POUs and POUhD in (A), and HD in (B). Stop codon is labeled with an asterisk (*).
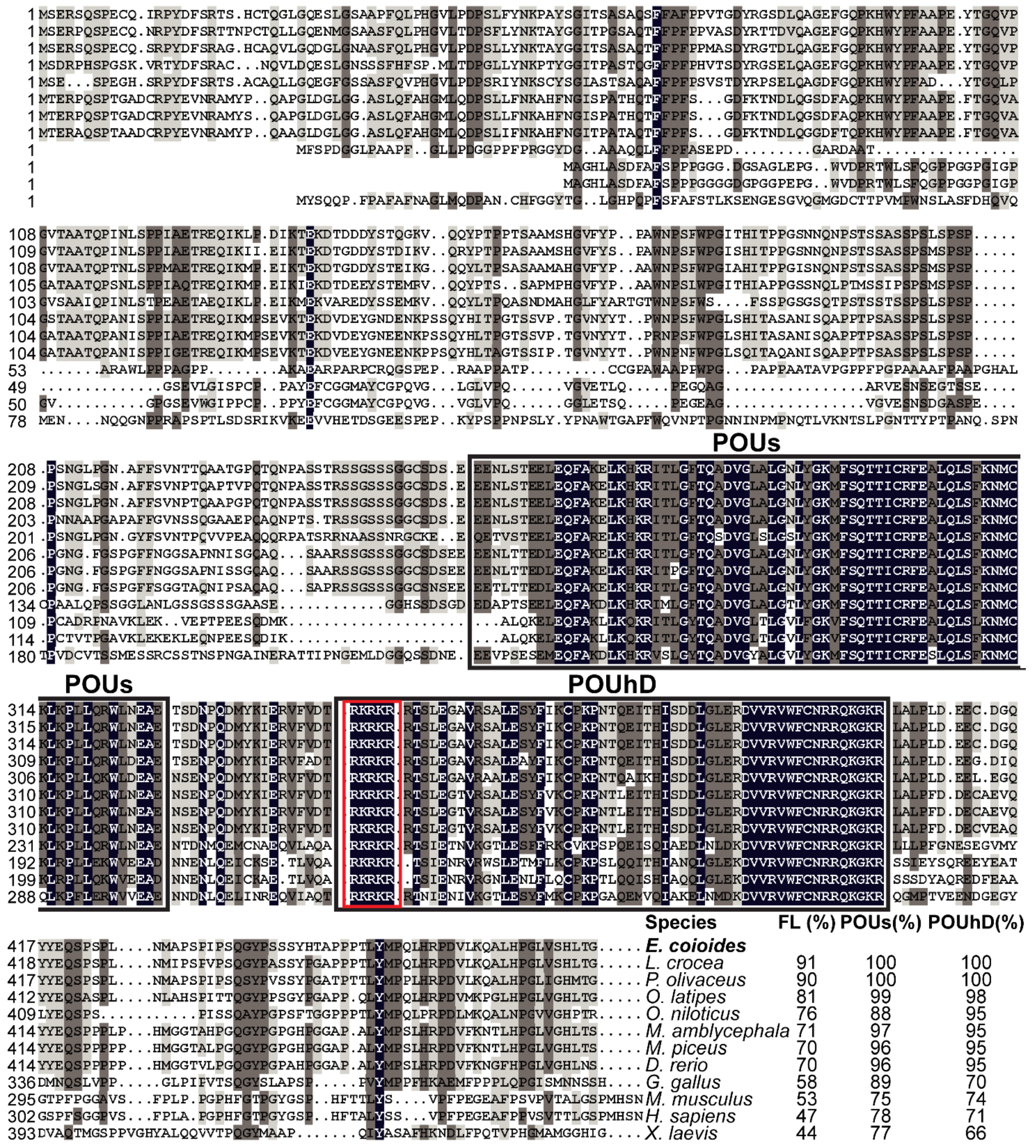
Multiple sequence alignments showed that EcPou5f1 protein had the conserved POUs and POUhD, as well as a nuclear localization motif of RKRKR (Figure 2). Full-length polypeptide of EcPou5f1 showed very high homology to fish Pou5f1 homologs from 70% to 91%, while low similar to tetrapod Pou5f1 homologs from 44% to 58% (Figure 2). In addition, POU domains showed a conserved feature in diverse vertebrates, with an identity ranging from 66% to 100% (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignment and comparison of EcPou5f1 with the homologs from other vertebrates. Black shadow: 100% identity; Brown shadow: 75% ≤ identity < 100%; Light brown shadow: 50% ≤ identity < 75%. Large black box: POUs and POUhD domains; Red box: a nuclear localization motif of RKRKR. The percent identity among EcPou5f1 and other Pou5f1 homologs in full-length (FL) and POU domains is displayed at the end of the alignment. The species’ name with a bold font indicates the EcPou5f1 protein of orange-spotted grouper. GenBank accession numbers for Pou5f1 are as follows: E. coioides, OL439940; L. crocea, NP_001290294; P. olivaceus, ALA23412; O. latipes, NP_001098339; Oreochromis niloticus, XP_003444455; M. amblycephala, AVV48156; Mylopharyngodon piceus, ATP62009; D. rerio, NP_571187; Gallus gallus, NP_001296301; M. musculus, NP_038661; H. sapiens, NP_002692; and Xenopus laevis, NP_001079832.
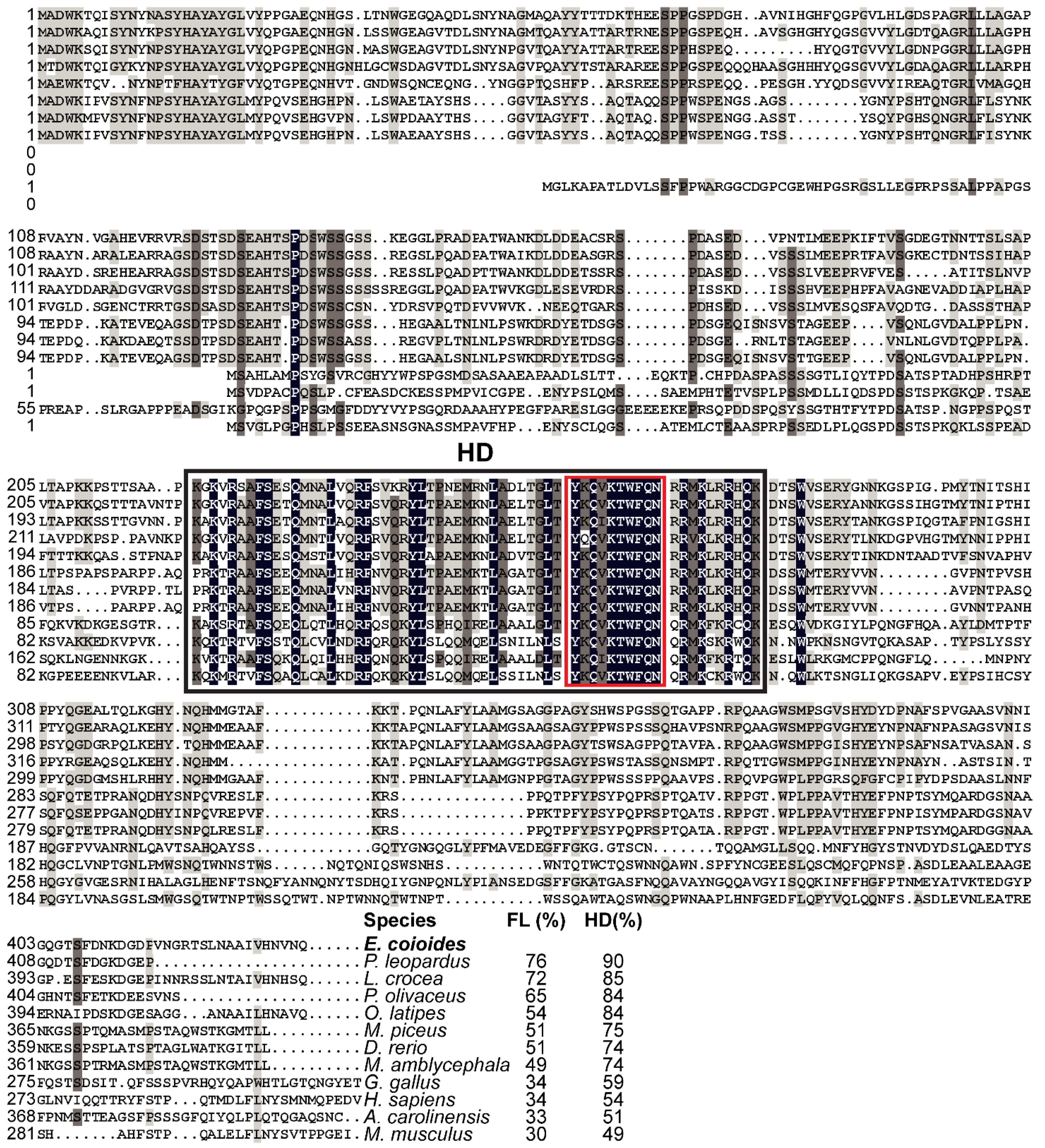
EcNanog protein had a conserved HD domain with a nuclear localization motif of YKQVKTWFQN (Figure 3). EcNanog shared a low identity with tetrapod Nanog homologs, ranging from 30% to 34%, while a high identity with fish Nanog homologs ranging from 49% to 76% (Figure 3). Likewise, the greatest similarity appeared on the most important functional domains, i.e., HD domain, ranging from 49% to 90% (Figure 3).
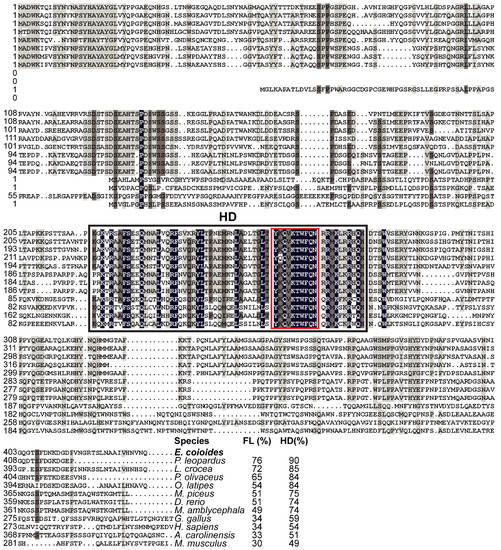
Figure 3.
Multiple sequence alignment and comparison of EcNanog with the homologs from other vertebrates. Black shadow: 100% identity; Brown shadow: 75% ≤ identity < 100%; Light brown shadow: 50% ≤ identity < 75%. Large black box: HD domain; Red box: a nuclear localization motif of YKQVKTWFQN. The percent identity among EcNanog and its homologs in full-length (FL) and HD domain is displayed at the end of the alignment. The species name with a bold font indicates the EcNanog protein of orange-spotted grouper. GenBank accession numbers for Nanog are as follow: E. coioides, OK415852; Plectropomus leopardus, XP_042366645; L. crocea, XP_010739920; P. olivaceus, AGX84982; O. latipes, NP_001153902; M. piceus, ATP62010; D. rerio, NP_001091862; M. amblycephala, AMY98422; G. gallus, NP_001139614; H. sapiens, NP_079141; M. musculus, NP_082292; and Anolis carolinensis, XP_003216891.
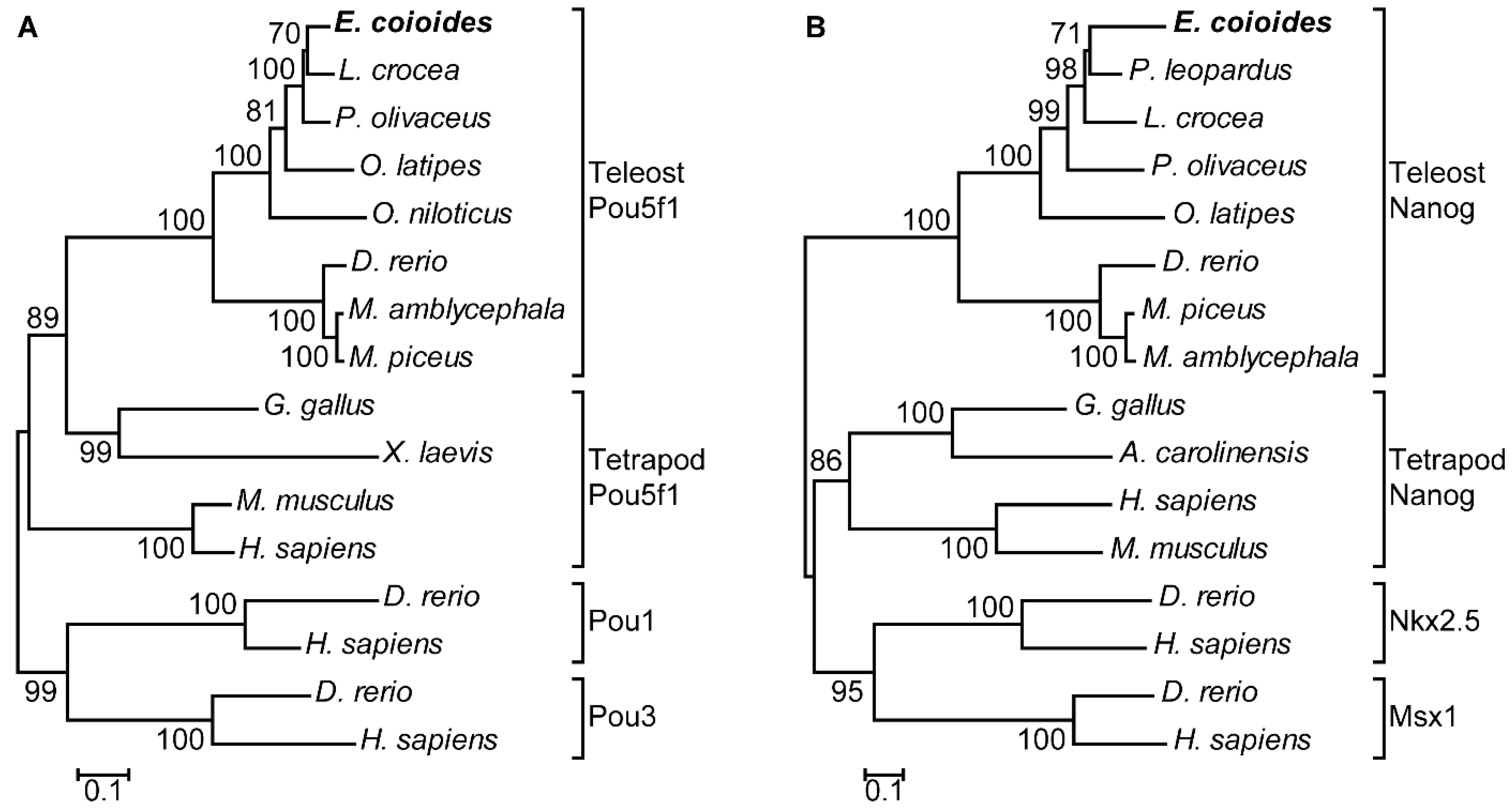
In phylogenetic tree analysis, EcPou5f1 and EcNanog were respectively clustered into a single clade with fish homologs and separated from other POU and HD proteins, including Pou1, Pou3, Nkx2.5, and Msx1 (Figure 4A,B).
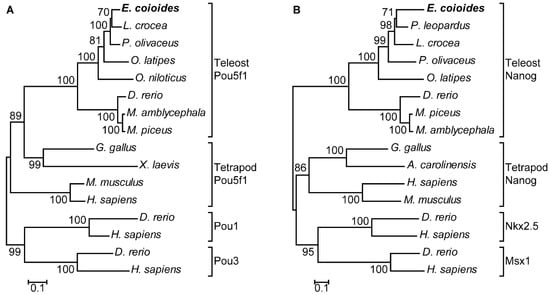
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic trees of (A) EcPou5f1 and (B) EcNanog. Phylogenetic trees were deduced by MEGA version 5.0 using the neighbor-joining method with 1500 bootstrap replicates. Numerals at bifurcation points of phylogenetic tree are bootstrap values. The species names in the first line indicate the EcPou5f1 and EcNanog proteins of orange-spotted grouper. GenBank accession numbers for Pou5f1 are as follows: E. coioides, OL439940; L. crocea, NP_001290294; P. olivaceus, ALA23412; O. latipes, NP_001098339; O. niloticus, XP_003444455; M. amblycephala, AVV48156; M. piceus, ATP62009; D. rerio, NP_571187; G. gallus, NP_001296301; M. musculus, NP_038661; H. sapiens, NP_002692; and X. laevis, NP_001079832. GenBank accession numbers for Pou1 and Pou3 are as follows: D. rerio, NP_998016, NP_571236; H. sapiens, NP_000297, NP_002690. GenBank accession numbers for Nanog are as follows: E. coioides, OK415852; P. leopardus, XP_042366645; L. crocea, XP_010739920; P. olivaceus, AGX84982; O. latipes, NP_001153902; M. piceus, ATP62010; D. rerio, NP_001091862; M. amblycephala, AMY98422; G. gallus, NP_001139614; H. sapiens, NP_079141; M. musculus, NP_082292; A. carolinensis, XP_003216891. GenBank accession numbers for Nkx2.5 and Msx1 are as follow: D. rerio, NP_571496, NP_571348; and H. sapiens, NP_004378, NP_002439.
3.2. Tissue Distributions of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog
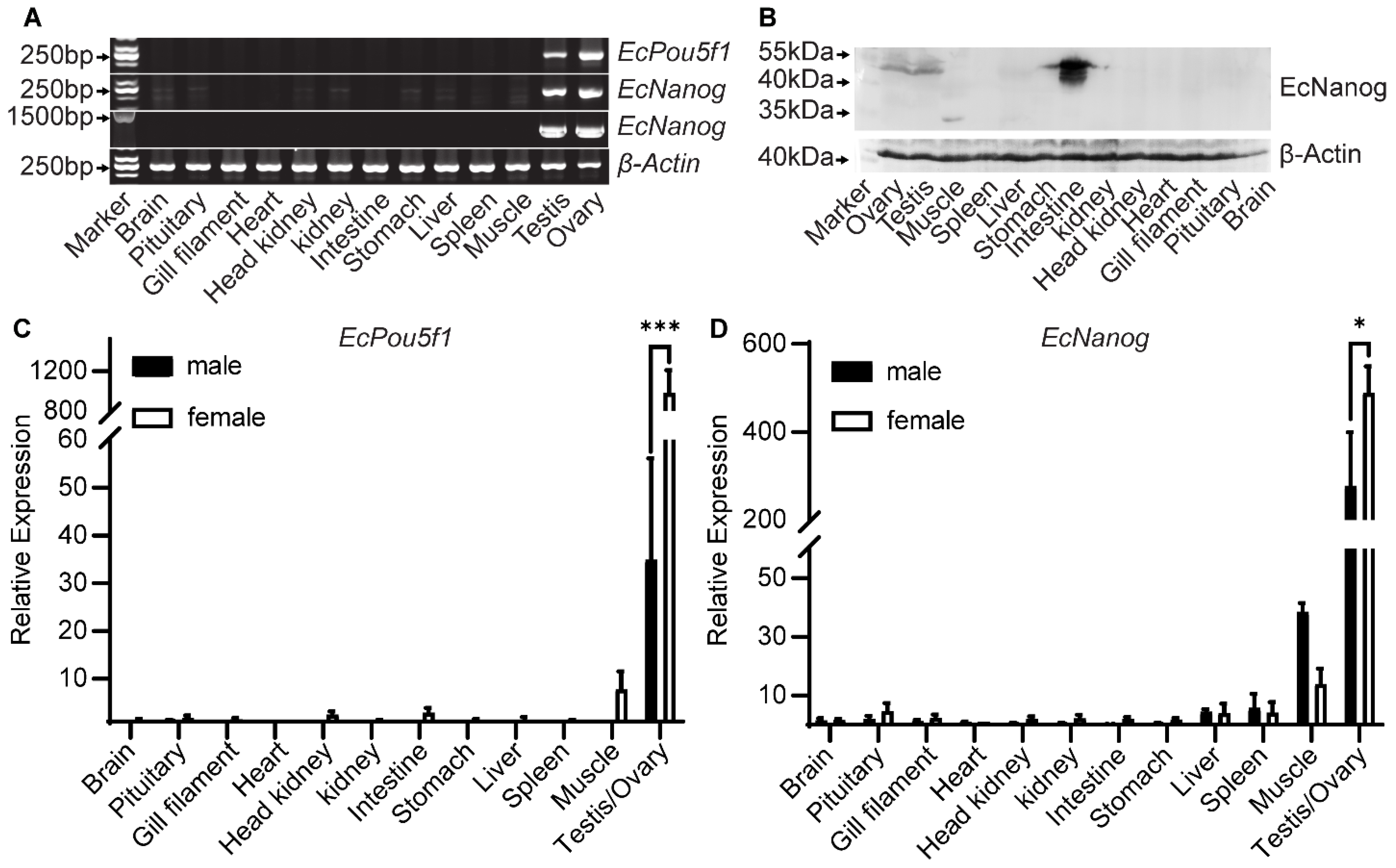
Semi-quantitative PCR results showed that a 245 bp fragment of EcPou5f1 was limited to gonads, whereas a 240 bp fragment of EcNanog was highly detected in gonads and weakly in other tissues, including brain, pituitary, head kidney, kidney, stomach, liver, and muscle (Figure 5A). However, the 1299 bp ORF of EcNanog was only amplified in gonads (Figure 5A). In Western blotting, EcNanog signals were detected as three strong bands between 40 and 55 kDa in intestine, a distinct band between 40 and 55 kDa in gonads and stomach, a single band about 35 kDa in muscle, a weak band between 40 and 55 kDa in kidney, as wells as no bands in other somatic tissues (Figure 5B). In RT-qPCR analyses, EcPou5f1 and EcNanog were extremely expressed in gonads with a higher level in ovary than in testis (Figure 5C,D).
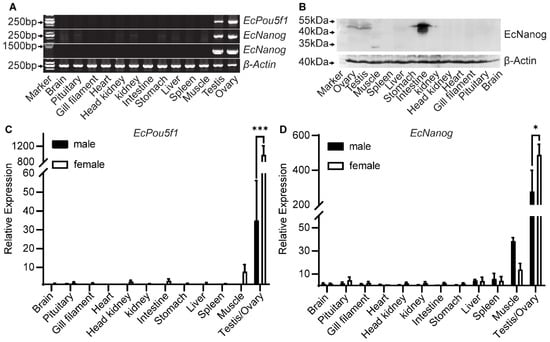
Figure 5.
Expression pattern analyses of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog. (A) Semi-quantitative PCR analyses of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog in 13 tissues. The sizes of DNA fragments: EcPou5f1, 245 bp; EcNanog, 240 bp, 1299 bp; β-Actin, 235 bp. (B) Western blotting analysis of EcNanog protein in 13 tissues. (C,D) RT-qPCR analyses of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog in 13 tissues. The data in C and D are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). The values with asterisks are significantly different with p < 0.05 (*) or p < 0.001 (***). The β-Actin was used as an internal control.
3.3. Chemical ISH of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog in Gonads
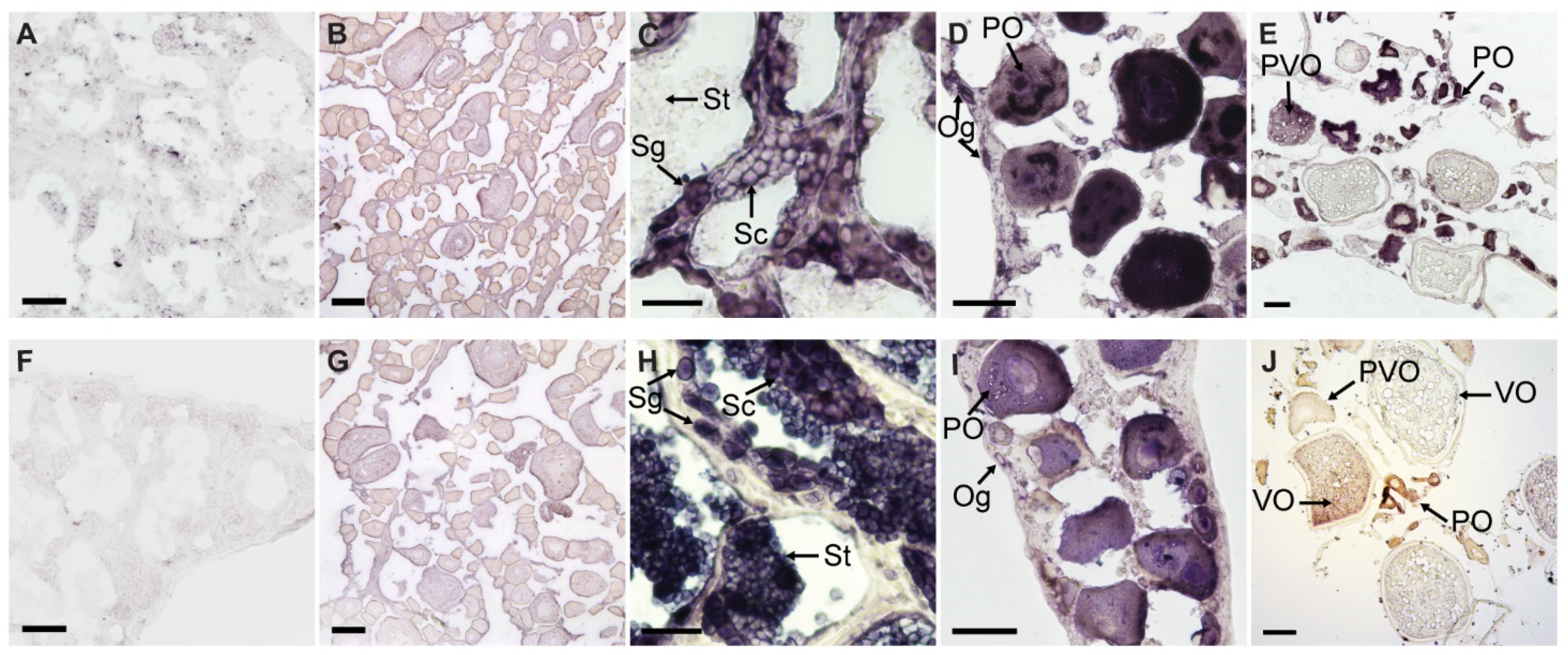
The sense riboprobes of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog showed no specific signal in ovary and testis (Figure 6A,B,F,G). In testis, the antisense probe signal of EcPou5f1 was intense in spermatogonia, moderate in spermatocytes, and no signal could be detected in spermatids (Figure 6C). In ovary, the antisense probe signal of EcPou5f1 was obviously observed in oogonia, primary growth stage oocytes, and cortical-alveolus stage oocytes, but scarcely detected in vitellogenic stage oocytes (Figure 6D,E). In some primary growth stage oocytes, EcPou5f1 mRNA signals were unevenly distributed in perinuclear speckles and nuclei (Figure 6D). The distribution of EcNanog mRNA in gonads had some differences from EcPou5f1 mRNA. In testis, EcNanog mRNA signal was observed in the spermatogenic cells from spermatogonium to spermatid (Figure 6H). In ovary, EcNanog mRNA signal was detected in oogonia, primary growth stage oocytes, cortical-alveolus stage oocytes, and early vitellogenic stage oocytes, but scarcely in late vitellogenic stage oocytes (Figure 6I,J). In addition, it was observed that a few small oval cells, possibly oogonia or oogonial stem cells, were EcPou5f1 or EcNanog-positive (Figure 6D,I).
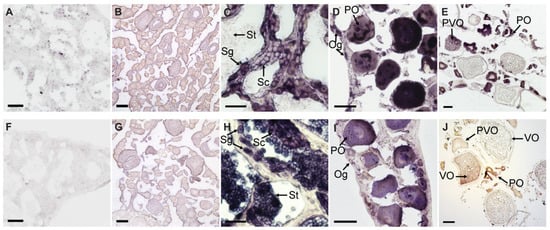
Figure 6.
Chemical ISH of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog in gonads of orange-spotted grouper. (A,B) Sense probe signal of EcPou5f1 in testis and ovary. (C–E) Antisense probe signal of EcPou5f1 in testis and ovaries. (F,G) Sense probe signal of EcNanog in testis and ovary. (H–J) Antisense probe signal of EcNanog in testis and ovaries. Sg, Spermatogonium; Sc, Spermatocyte; St, spermatid; Og, oogonium; PO, primary growth stage oocyte; PVO, cortical-alveolus stage oocyte; VO, vitellogenic stage oocyte. Scale bars: 50 µm in (A,D,F,I); 100 µm in (B,E,G,J); 20 µm in (C,H).
3.4. Dual-Label ISH for EcPou5f1 or EcNanog with Vasa in Gonads
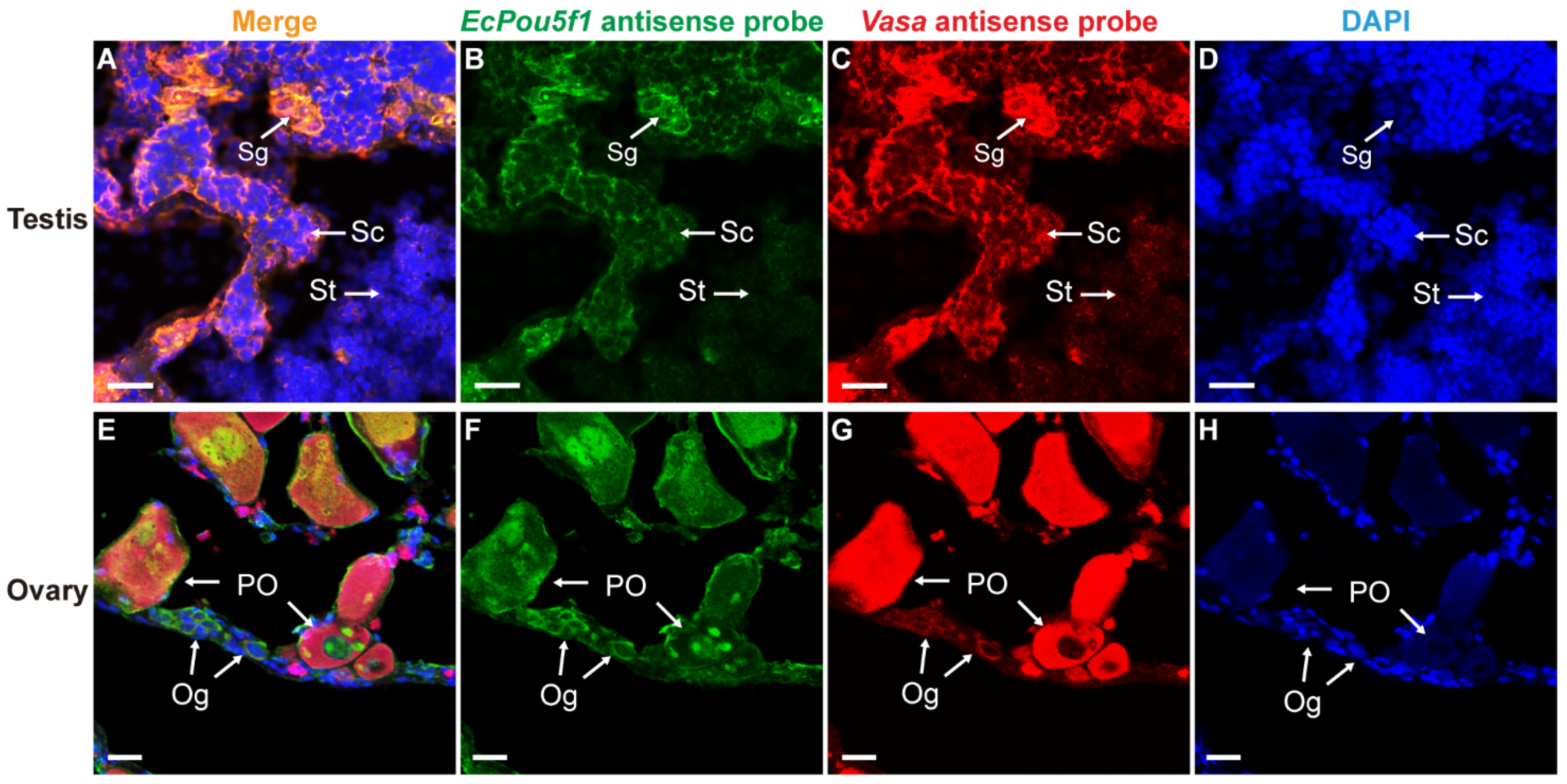
In order to further verify the reliability of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog as germ cell-specific genes, we adopted Vasa, a well-known germ cell-specific gene [9], as a positive control in dual-label ISH. In testis and ovary, the mRNA signal of EcPou5f1 had an identical localization with Vasa mRNA signal in male and female germ cells (Figure 7). It was worth mentioning that the very faInt. fluorescence of EcPou5f1 mRNA could be observed in spermatids by Tyramide Signal Amplification system (Figure 7B). Similar to the chemical ISH result of EcPou5f1 mRNA in ovary, the fluorescent signal of EcPou5f1 mRNA was obviously observed in the cytoplasm of oogonia, and the perinuclear speckles and nuclei of some primary growth stage oocytes (Figure 7F). In ovary, the small oval cells, possibly oogonia or oogonial stem cells, with EcPou5f1 signal would be marked by Vasa signal (Figure 7E–G).
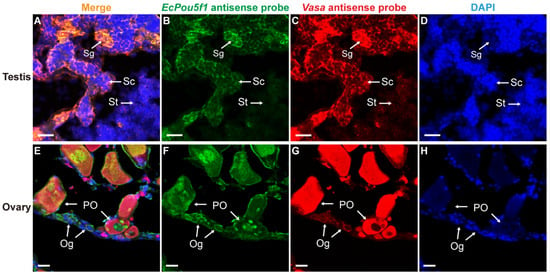
Figure 7.
Co-localizations of EcPou5f1 and Vasa in gonads of orange-spotted grouper. (A,E) Merged images. (B,F) Fluorescent signal of EcPou5f1 antisense probe in testis and ovary. (C,G) Fluorescent signal of Vasa antisense probe in testis and ovary. (D,H) Nucleus was counterstained with DAPI. Sg, Spermatogonium; Sc, Spermatocyte; St, spermatid; Og, oogonium; PO, primary growth stage oocyte. Scale bars: 20 µm.
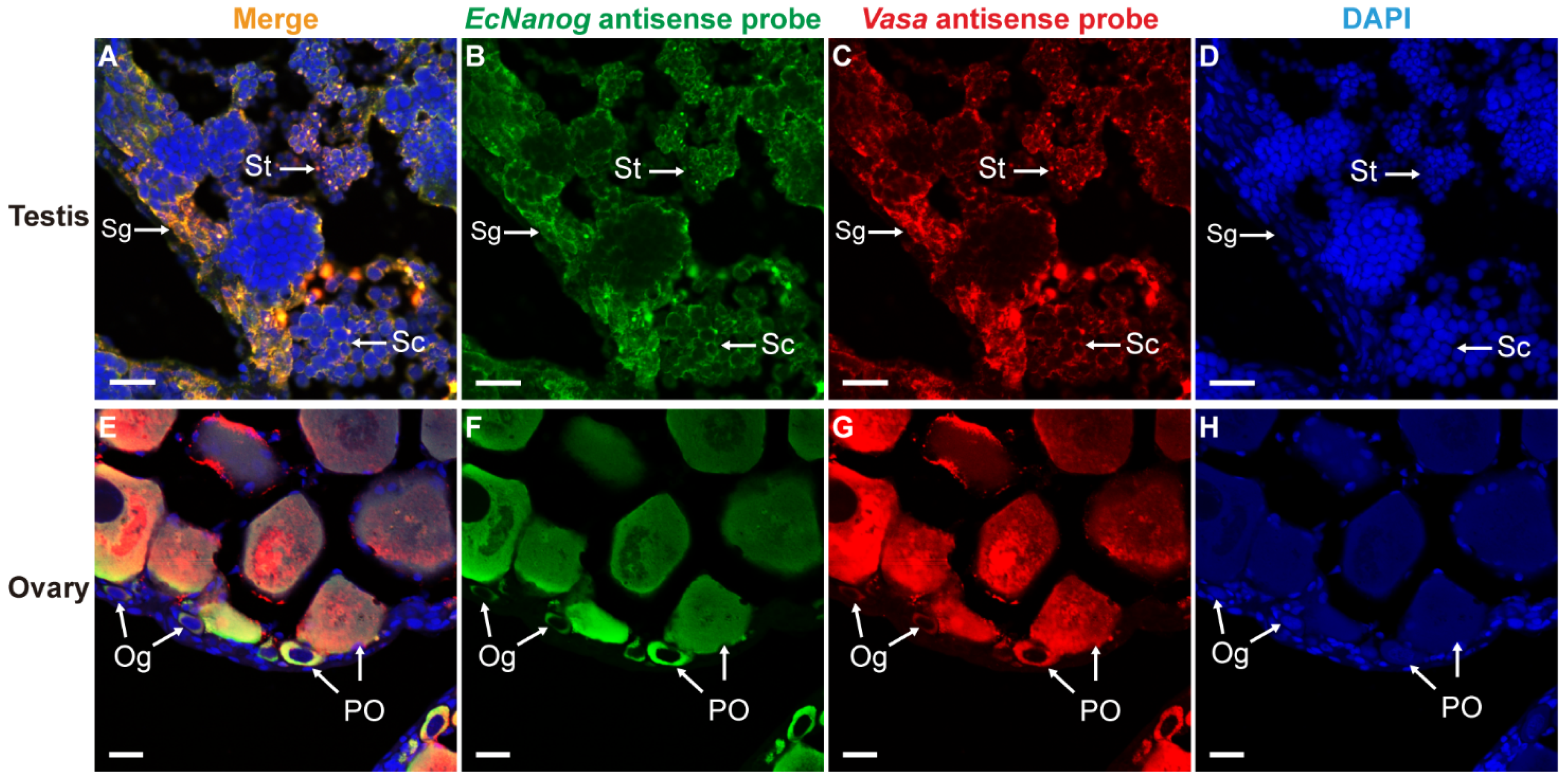
Likewise, EcNanog signal had an identical localization with Vasa signal in male and female germ cells (Figure 8). In testis, the EcNanog and Vasa signals were detected in different spermatogenic cells (Figure 8B,C). The fluorescent signals of EcNanog and Vasa were distributed in the whole cytoplasm of female germ cells (Figure 8F,G). In ovary, the small oval cells, possibly oogonia or oogonial stem cells, showed the EcNanog and Vasa-positive signals at the same time (Figure 8E–G).
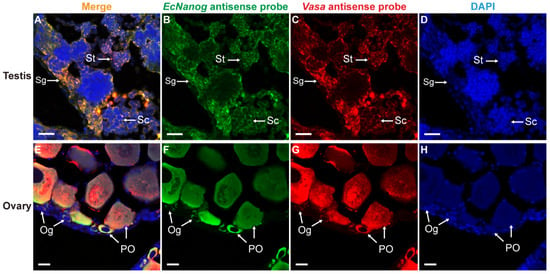
Figure 8.
Co-localizations of EcNanog and Vasa in gonads of orange-spotted grouper. (A,E) Merged images. (B,F) Fluorescent signal of EcNanog antisense probe in testis and ovary. (C,G) Fluorescent signal of Vasa antisense probe in testis and ovary. (D,H) Nucleus was counterstained with DAPI. Sg, Spermatogonium; Sc, Spermatocyte; St, spermatid; Og, oogonium; PO, primary growth stage oocyte. Scale bars: 20 µm.
3.5. Immunohistofluorescence of Anti-Nanog Antibody in Gonads
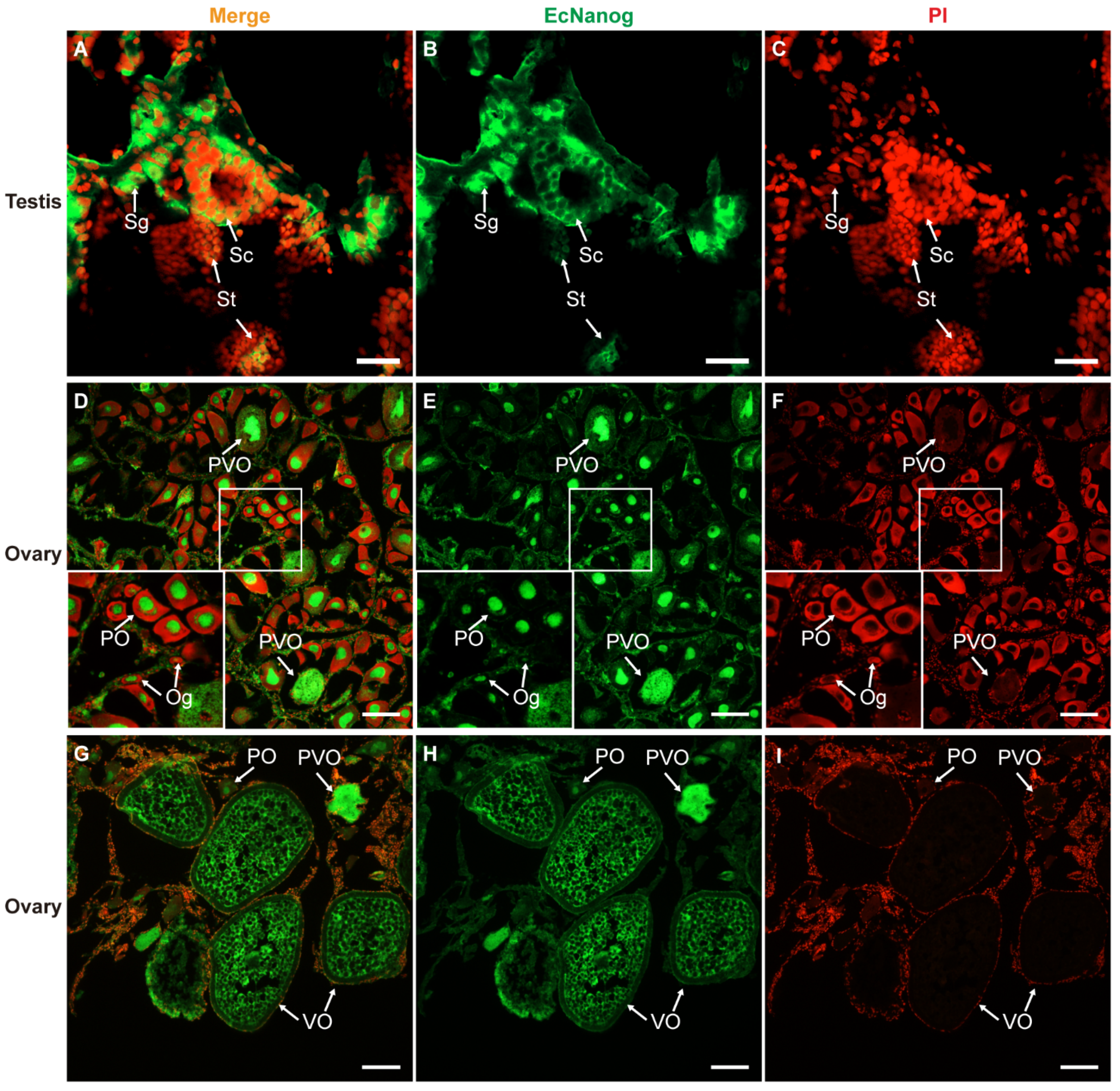
Immunohistofluorescence was carried out for examining the localization of EcNanog protein in gonads of orange-spotted grouper. In testis, the signal of anti-Nanog antibody was mainly detected in the nucleus and cytoplasm of spermatogonia and the cytoplasm of spermatocytes, while slight in spermatids (Figure 9A–C). In ovary, the signal of anti-Nanog antibody was predominantly detected in the nuclei of oogonia and primary growth stage oocytes, and then gradually spread in the cytoplasm of cortical alveolus stage oocytes, up to a homogeneous distribution in the whole vitellogenic stage oocytes (Figure 9D–I).
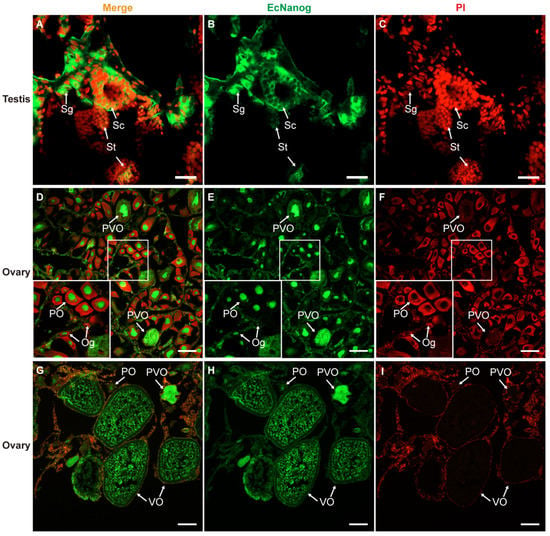
Figure 9.
Immunohistofluorescence staining for anti-Nanog antibody in gonads of orange-spotted grouper. (A,D,G) Merged images. (B,E,H) Fluorescent signal of anti-Nanog antibody in testis and ovaries. (C,F,I) Nucleus was counterstained with PI. Sg, Spermatogonium; Sc, Spermatocyte; St, spermatid; Og, oogonium; PO, primary growth stage oocyte; PVO, the cortical-alveolus stage oocyte; VO, vitellogenic stage oocyte. Scale bars: 20 µm in (A–C); 100 µm in (D–I).
4. Discussion
Pluripotency markers Pou5f1 and Nanog are generally regarded as core transcription factors sustaining stem cell pluripotency and embryogenesis [11,12,13]. However, their roles are unclear in germ cell development and gametogenesis in teleost fish. In this study, the cDNA sequences and expression patterns of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog were characterized and analyzed in a protogynous hermaphroditic fish, orange-spotted grouper. Sequence analysis showed that EcPou5f1 protein possessed a conserved POU domain, and EcNanog protein had a conserved HD domain. The similarity of POU domain and HD domain is much higher than the full-length sequences in various species. This situation reflects the conserved nature of Pou5f1 and Nanog in the process of evolution to a certain extent. For instance, the Nanog required for inducing mouse IPSCs can be replaced with chicken or zebrafish Nanog [39], and other tetrapod Pou5f1 can maintain the pluripotency and self-renewal of mouse ESCs [40,41]. Additionally, sequence alignments revealed that EcPou5f1 and EcNanog shared the highest homology with the orthologs in fish, in agreement with phylogenetic tree analysis. The greatest homology among fish implies that the functions of EcPou5f1 and EcNanog in orange-spotted grouper would be very similar to other fish homologs.
EcPou5f1 and EcNanog show two discrepant tissue distribution patterns. The protein and short DNA fragment of EcNanog were detected in gonads and some nongonadal tissues, e.g., stomach and muscle, whereas the ORF region of EcNanog was only detected in gonads. This is consistent with the PCR result of Nanog in blunt-snout bream, the short fragment is detected in gonads and nongonadal tissues, but the long fragment just exists in gonads [33]. In zebrafish, the transcript and protein of Nanog are distinctly detected in gonads, liver, and heart [42]. On the contrary, in adult Japanese flounder, Nanog is restrictively expressed in ovary and testis [25]. We deduce that the alternative splicing of EcNanog lead to the inconsistent PCR amplification between the short and long fragments, and the appearance of protein bands in some somatic tissues that may possess Nanog-positive stem cells [33,43,44]. Similar to the tissue distribution pattern of Japanese flounder Pou5f1 [30], EcPou5f1 was restrictively expressed in gonads. Nonetheless, some somatic tissues of medaka and Chinese sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis), for example, brain, can also express Pou5f1 [22,45]. Pou5f1 protein is a direct regulator of Nanog transcript [18]. Intriguingly, EcPou5f1 was not detected in those nongonadal tissues expressing the short DNA fragment or protein of EcNanog. We guess that other regulators, such as Sox2 and Klf4, and the auto-regulatory of Nanog might account for the absence of EcPou5f1 in nongonadal tissues [46,47]. In short, the tissue distributions of Pou5f1 and Nanog show species differences to a variable extent in diverse fish, and suggest that they play multifunctional roles in gonads and somatic tissues.
EcPou5f1 and EcNanog are dependable germ cell-specific genes in orange-spotted grouper. EcPou5f1 was restricted to germ cells, but scarce in vitellogenic stage oocytes. Using Tyramide Signal Amplification system, EcPou5f1 signal was faintly observed in spermatids, suggesting that a few EcPou5f1 transcripts existed in spermatids. These ISH results indicate that EcPou5f1 exists exclusively in germ cells of gonads and would downregulate dramatically from spermatocyte to spermatid. In medaka and Japanese flounder, Pou5f1 is limited to spermatogonia, oogonia, and most oocytes, but absent in spermatocytes and spermatids [22,30]. In testis of Nile tilapia, Pou5f1 protein shows a specific localization in undifferentiated spermatogonia [48,49]. However, in large yellow croaker, Pou5f1 is detected in spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes [32]. EcNanog was detected in all male germ cells and the female germ cells from oogonia to early vitellogenic stage oocytes. A similar expression pattern is also observed for Nanog in gonads of blunt-snout bream [33]. However, in testes of zebrafish, medaka, and Japanese flounder, Nanog is only expressed in spermatogonia [25,31,42]. The differential expression in differentiated male germ cells implies that EcPou5f1 and EcNanog may participate in spermatogenesis, whereas the Pou5f1 and/or Nanog of medaka, zebrafish, Japanese flounder, and Nile tilapia is mainly responsible for the pluripotency and self-renewal of spermatogonia. In accordance with the EcNanog ISH, EcNanog protein specifically existed in all male and female germ cells, including vitellogenic stage oocyte in which EcNanog mRNA was difficultly detected. EcNanog contained a motif of YKQVKTWFQN that had been identified as a nuclear localization motif in human Nanog [50]. As expected, fluorescent immunostaining revealed the nuclear localization of EcNanog in spermatogonia, oogonia, and primary growth stage oocytes. This is also supported by the nuclear localization of Nanog in zebrafish and blunt-snout bream [33,42]. Interestingly, we observed that EcNanog also existed in the cytoplasm of spermatocytes and spermatids. A similar localization of Nanog is observed in the spermatocytes and spermatids of pig testis [28]. The translocation of Nanog from nucleus to cytoplasm may imply the loss of function sustaining the pluripotency characteristics of spermatogonia. Although the subcellular localization of EcPou5f1 protein was not tested in this study, we speculated that EcPou5f1 might also locate in the nuclei of germ stem cells, on account of the nuclear localization signal RKRKR [50]. Vasa is a widely accepted germline-specific marker [51,52], and shows a specific expression in the germ cell lineage in many animals, e.g., medaka [53] and mouse [54]. Our previous study has demonstrated that Vasa is exclusively expressed in germ cells in gonads of orange-spotted grouper [9]. In adult testis of rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta), Nanog is restrictively expressed in all spermatogenic cells, most of which are Vasa-positive [55]. In human fetal testis and ovary, Pou5f1 is limited to some fetal germ cells, whereas only a part of the cell shows the low intensity immunofluorescences of Pou5f1 and Vasa [20]. In this study, dual-label ISH analysis revealed that Vasa was co-localized with EcPou5f1 and EcNanog in gonads. Furthermore, in ovary, the small oval cells expressing EcPou5f1 or EcNanog would be marked by Vasa signal, suggesting that these cells exactly were oogonia or oogonial stem cells. On the basis of these results, we conclude that EcPou5f1 and EcNanog are reliable germ cell-specific markers in orange-spotted grouper.
Although there have been a few studies about the functions of Pou5f1 and Nanog in differentiated germ cells in mammals [26,27,28], it is widely accepted that Pou5f1 and Nanog are mainly responsible for the pluripotency of germline stem cells [20,21,56,57]. Conversely, the teleost Nanog and Pou5f1 are expressed in spermatogonia, oogonia, and a large proportion of oocytes, as well as have different expression patterns in the differentiated male germ cells in diverse fish [22,25,30,31,33,42,49]. Likewise, EcPou5f1 and EcNanog can be detected in all spermatogonia and oogonia, most oocytes, spermatocytes, and spermatid. The high expressions of teleost Nanog and Pou5f1 during oocyte development may be related to maternal inheritance, i.e., mRNA or protein delivery to the next generation [24,25,33]. The comparisons in differentiated male germ cells indicate that Pou5f1 and Nanog may have some differences in promoting spermatogenesis in different fish. Moreover, the differentials among diverse fish would provide a new perspective for understanding the evolution and conserved nature of teleost Pou5f1 and Nanog.
5. Conclusions
In summary, EcPou5f1 and EcNanog are germ cell-specific marker genes and play important roles in gametogenesis in a protogynous hermaphroditic fish, orange-spotted grouper. Our findings would contribute to further studies on the molecular mechanism underlying germ cell development, gametogenesis, and sex reversal in hermaphroditic fish.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and H.X.; methodology, C.Z. and M.L.; validation, X.W., T.W., and Y.Y.; formal Analysis, C.Z. and Y.T.; investigation, C.Z., Y.T., and M.L.; data curation, C.Z., Z.M., and Y.T.; writing—original draft preparation, C.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.L., H.X., and X.W.; supervision, X.L. and H.X.; project administration, X.L.; funding acquisition, X.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Project of Hainan Academician Team Innovation Center (grant number YSPTZX202122); National Key Research and Development Program (grant number 2018YFD0900203); China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (grant number CARS-47); Yang Fan Innovative & Entrepreneurial Research Team Project (grant number 201312H10); Huizhou Swan Project (grant number 20170214023102296); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou (grant number 201804020013); National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 31872572).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and use Committee of Sun Yat-Sen University (Approval Number SYSU-IACUC-2021-B0494 and approval date 20 February 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The study did not report any other data.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to Ling Qu and Xiaoli Liu for their assistance in sample collection and experiment materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Williamson, A.; Lehmann, R. Germ cell development in Drosophila. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996, 12, 365–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, A.E.; Kennedy, S. Phase Separation in Germ Cells and Development. Dev. Cell 2020, 55, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, V.; Riesco, M.F.; Psenicka, M.; Saito, T.; Valcarce, D.G.; Cabrita, E.; Herraez, P. Biology of teleost primordial germ cells (PGCs) and spermatogonia: Biotechnological applications. Aquaculture 2017, 472, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, W.J.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.C.; Li, S.S.; Zhou, L.; Gui, J.F. Divergent Expression Patterns and Function Implications of Four nanos Genes in a Hermaphroditic Fish, Epinephelus coioides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.H.; Ma, D.Y.; Song, Z.C.; Li, J. A potential germ cell-specific marker in Japanese flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus: Identification and characterization of lymphocyte antigen 75 (Ly75/CD205). J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, C.; Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Lin, H.; Liu, X. Transcriptome profiling of laser-captured germ cells and functional characterization of zbtb40 during 17alpha-methyltestosterone-induced spermatogenesis in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozaki, Y.; Saito, K.; Shinya, M.; Kawasaki, T.; Sakai, N. Evaluation of Sycp3, Plzf and Cyclin B3 expression and suitability as spermatogonia and spermatocyte markers in zebrafish. Gene Expr. Patterns 2011, 11, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Qu, L.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.; He, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Lin, H. Molecular characterization and expression patterns of stem-loop binding protein (SLBP) genes in protogynous hermaphroditic grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Gene 2019, 700, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, M.; Zhong, C.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Lin, H.; Liu, X. Identification and characterization of germ cell genes vasa and dazl in a protogynous hermaphrodite fish, orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Gene Expr. Patterns 2020, 35, 119095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Duan, J.; Cheng, N.; Nagahama, Y. Specific expression of Olpiwi1 and Olpiwi2 in medaka (Oryzias latipes) germ cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 418, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, M.; Scholer, H.R. Oct-4: Gatekeeper in the beginnings of mammalian development. Stem Cells 2001, 19, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, I.; Colby, D.; Robertson, M.; Nichols, J.; Lee, S.; Tweedie, S.; Smith, A. Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell 2003, 113, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh, Y.H.; Wu, Q.; Chew, J.L.; Vega, V.B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Bourque, G.; George, J.; Leong, B.; Liu, J.; et al. The Oct4 and Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse embryonic stem cells. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholer, H.R.; Balling, R.; Hatzopoulos, A.K.; Suzuki, N.; Gruss, P. Octamer binding proteins confer transcriptional activity in early mouse embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jerabek, S.; Merino, F.; Scholer, H.R.; Cojocaru, V. OCT4: Dynamic DNA binding pioneers stem cell pluripotency. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitsui, K.; Tokuzawa, Y.; Itoh, H.; Segawa, K.; Murakami, M.; Takahashi, K.; Maruyama, M.; Maeda, M.; Yamanaka, S. The homeoprotein Nanog is required for maintenance of pluripotency in mouse epiblast and ES cells. Cell 2003, 113, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodda, D.J.; Chew, J.L.; Lim, L.H.; Loh, Y.H.; Wang, B.; Ng, H.H.; Robson, P. Transcriptional regulation of nanog by OCT4 and SOX2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24731–24737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Rayner, S.; Katoku-Kikyo, N.; Romanova, L.; Kikyo, N. Successful co-immunoprecipitation of Oct4 and Nanog using cross-linking. BioChem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 361, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, R.A.; Fulton, N.; Cowan, G.; Coutts, S.; Saunders, P.T. Conserved and divergent patterns of expression of DAZL, VASA and OCT4 in the germ cells of the human fetal ovary and testis. BMC Dev. Biol. 2007, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Deng, B.; Geng, L.; Li, L.; Wu, X. Pluripotency factor NANOG promotes germ cell maintenance in vitro without triggering dedifferentiation of spermatogonial stem cells. Theriogenology 2020, 148, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Hong, N.; Xu, H.; Hong, Y. Medaka Oct4 is essential for pluripotency in blastula formation and ES cell derivation. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2015, 11, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Jiang, M.; Li, H.; Long, M.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, Y. Generation of Stable Induced Pluripotent Stem-like Cells from Adult Zebra Fish Fibroblasts. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2340–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, A.V.; Camp, E.; Garcia-Espana, A.; Leal-Tassias, A.; Mullor, J.L. Medaka Oct4 is expressed during early embryo development, and in primordial germ cells and adult gonads. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, J.; Fan, L.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Identification and characterization of a nanog homolog in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Gene 2013, 531, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijk, E.W.; de Gier, J.; Lopes, S.M.; Chambers, I.; van Pelt, A.M.; Colenbrander, B.; Roelen, B.A. A distinct expression pattern in mammalian testes indicates a conserved role for NANOG in spermatogenesis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccotti, M.; Merico, V.; Sacchi, L.; Bellone, M.; Brink, T.C.; Bellazzi, R.; Stefanelli, M.; Redi, C.A.; Garagna, S.; Adjaye, J. Maternal Oct-4 is a potential key regulator of the developmental competence of mouse oocytes. BMC Dev. Biol. 2008, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goel, S.; Fujihara, M.; Minami, N.; Yamada, M.; Imai, H. Expression of NANOG, but not POU5F1, points to the stem cell potential of primitive germ cells in neonatal pig testis. Reproduction 2008, 135, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, A.V.; Camp, E.; Leal-Tassias, A.; Atkinson, S.P.; Armstrong, L.; Diaz-Llopis, M.; Mullor, J.L. Nanog regulates primordial germ cell migration through Cxcr4b. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Evolutionary Conservation of pou5f3 Genomic Organization and Its Dynamic Distribution during Embryogenesis and in Adult Gonads in Japanese Flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Manali, D.; Wang, T.; Bhat, N.; Hong, N.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, R.; Hong, Y. Identification of pluripotency genes in the fish medaka. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Han, K.; Chen, S.; Cai, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. Molecular cloning and expression of Octamer-binding transcription factor (Oct4) in the large yellow croaker, Larimichthys crocea. Gene Expr. Patterns 2018, 27, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xue, T.; Chen, T.; Fang, J.; Pan, Q.; Deng, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, K.; Wang, Y. Maternal inheritance of Nanog ortholog in blunt-snout bream. J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2017, 328, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marandel, L.; Labbe, C.; Bobe, J.; Le Bail, P.Y. nanog 5′-upstream sequence, DNA methylation, and expression in gametes and early embryo reveal striking differences between teleosts and mammals. Gene 2012, 492, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; de Mitcheson, Y.S. Gonad development during sexual differentiation in hatchery-produced orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) and humpback grouper (Cromileptes altivelis) (Pisces: Serranidae, Epinephelinae). Aquaculture 2009, 287, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, X.; Li, W.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X. Isolation and in vitro culture of ovarian stem cells in Chinese soft-shell turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). J. Cell BioChem. 2018, 119, 7667–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, C.; Guo, Y.; Wei, T.; Li, S.; Lin, H.; Liu, X. Integration of ATAC-seq and RNA-seq Unravels Chromatin Accessibility during Sex Reversal in Orange-Spotted Grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; He, M.; Tang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Lin, H. Molecular mechanism of feedback regulation of 17beta-estradiol on two kiss genes in the protogynous orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 84, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theunissen, T.W.; Costa, Y.; Radzisheuskaya, A.; van Oosten, A.L.; Lavial, F.; Pain, B.; Castro, L.F.; Silva, J.C. Reprogramming capacity of Nanog is functionally conserved in vertebrates and resides in a unique homeodomain. Development 2011, 138, 4853–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niwa, H.; Sekita, Y.; Tsend-Ayush, E.; Grutzner, F. Platypus Pou5f1 reveals the first steps in the evolution of trophectoderm differentiation and pluripotency in mammals. Evol. Dev. 2008, 10, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, G.M.; Brickman, J.M. Conserved roles for Oct4 homologues in maintaining multipotency during early vertebrate development. Development 2006, 133, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ye, D.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Deng, F. Knockdown of zebrafish Nanog increases primordial germ cells during early embryonic development. Dev. Growth Differ. 2016, 58, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Sharma, R.; George, A.; Singla, S.K.; Palta, P.; Manik, R.; Chauhan, M.S.; Singh, D. Cloning and characterization of buffalo NANOG gene: Alternative transcription start sites, splicing, and polyadenylation in embryonic stem cell-like cells. DNA Cell Biol. 2012, 31, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Jena, S.; Levasseur, D.N. Alternative splicing produces Nanog protein variants with different capacities for self-renewal and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42690–42703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, H.; Du, H.; Chen, X.H.; Cao, H.; Liu, T.; Li, C.J. Identification of a pou2 ortholog in Chinese sturgeon, Acipenser sinensis and its expression patterns in tissues, immature individuals and during embryogenesis. Fish. Physiol. BioChem. 2012, 38, 929–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.K.; Zhang, J.; Chia, N.Y.; Chan, Y.S.; Sim, H.S.; Tan, K.S.; Oh, S.K.; Ng, H.H.; Choo, A.B. KLF4 and PBX1 directly regulate NANOG expression in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanak, S.; Helms, V. DNA methylation and the core pluripotency network. Dev. Biol. 2020, 464, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos Nassif Lacerda, S.M.; Costa, G.M.; da Silva Mde, A.; Campos-Junior, P.H.; Segatelli, T.M.; Peixoto, M.T.; Resende, R.R.; de Franca, L.R. Phenotypic characterization and in vitro propagation and transplantation of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) spermatogonial stem cells. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiaohuan, H.; Yang, Z.; Linyan, L.; Zhenhua, F.; Linyan, Z.; Zhijian, W.; Ling, W.; Deshou, W.; Jing, W. Characterization of the POU5F1 Homologue in Nile Tilapia: From Expression Pattern to Biological Activity. Stem Cells Dev. 2016, 25, 1386–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Qin, B.; Liu, N.; Scholer, H.R.; Pei, D. Identification of a nuclear localization signal in OCT4 and generation of a dominant negative mutant by its ablation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37013–37020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noce, T.; Okamoto-Ito, S.; Tsunekawa, N. Vasa homolog genes in mammalian germ cell development. Cell Struct. Funct. 2001, 26, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raz, E. The function and regulation of vasa-like genes in germ-cell development. Genome Biol. 2000, 1, REVIEWS1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinomiya, A.; Tanaka, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nagahama, Y.; Hamaguchi, S. The vasa-like gene, olvas, identifies the migration path of primordial germ cells during embryonic body formation stage in the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Dev. Growth Differ. 2000, 42, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyooka, Y.; Tsunekawa, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Matsui, Y.; Satoh, M.; Noce, T. Expression and intracellular localization of mouse Vasa-homologue protein during germ cell development. Mech Dev. 2000, 93, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, C.B.; Pacchiarotti, J.; Ramos, T.; Pascual, M.; Pham, J.; Kinjo, J.; Anorve, S.; Izadyar, F. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of spermatogonial stem cells in adult primate testes. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 24, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventela, S.; Makela, J.A.; Kulmala, J.; Westermarck, J.; Toppari, J. Identification and regulation of a stage-specific stem cell niche enriched by Nanog-positive spermatogonial stem cells in the mouse testis. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi-Farsani, S.; Amidi, F.; Habibi Roudkenar, M.; Sobhani, A. Isolation and enrichment of mouse female germ line stem cells. Cell J. 2015, 16, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).