Epigenetic and Epitranscriptomic Gene Regulation in Plasmodium falciparum and How We Can Use It against Malaria
Abstract
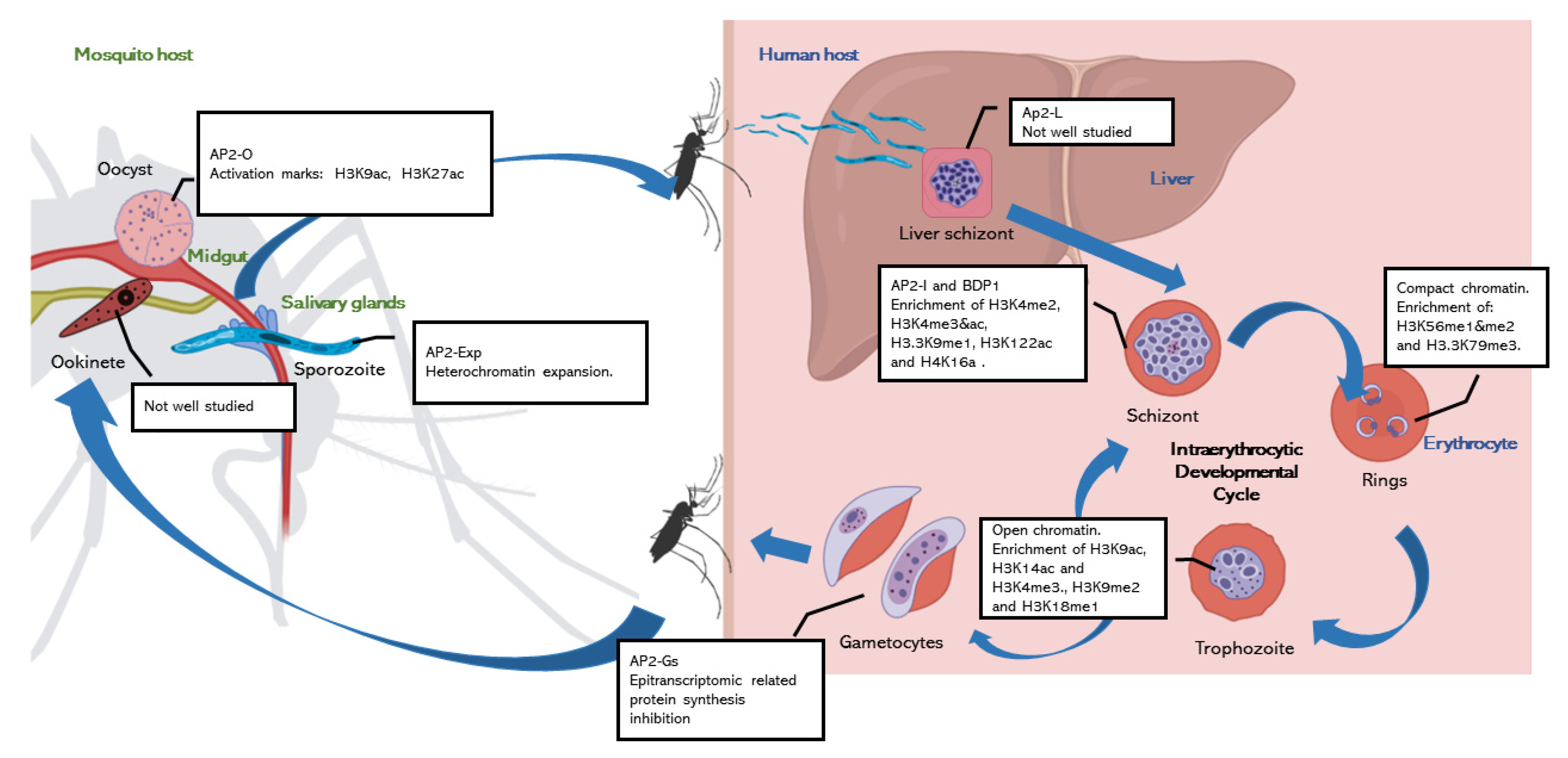
:1. Introduction
2. Chromatin Regulation of Parasite Development
2.1. Chromatin Regulation during Intraerythocytic Development
2.2. The Knowns and the Unknowns about Chromatin Regulation in the Mosquito
3. Epigenetic Mechanisms Controlling Parasite Adaptation
3.1. Antigenic Variation and Immune Evasion
3.2. Sexual Differentiation Regulation
3.3. Erythrocyte Invasion
3.4. Cellular Transport, Nutrients and Drug Resistance
3.5. Heat Shock Response to Febrile Temperatures
4. Epitranscriptomics a New Layer in the Malaria Parasite Gene Expression Regulation
5. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cox, F.E.G. History of Human Parasitology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 595–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Malaria Programme. World Malaria Report 2021; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Josling, G.A.; Williamson, K.C.; Llinás, M. Regulation of Sexual Commitment and Gametocytogenesis in Malaria Parasites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehn, A.; Pradel, G. The Coming-out of Malaria Gametocytes. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 976827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, S.; Madan Babu, M.; Iyer, L.M.; Aravind, L. Discovery of the Principal Specific Transcription Factors of Apicomplexa and Their Implication for the Evolution of the AP2-Integrase DNA Binding Domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 3994–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.L.; de Silva, E.K.; Olszewski, K.L.; Elemento, O.; Llinás, M. Identification and Genome-Wide Prediction of DNA Binding Specificities for the ApiAP2 Family of Regulators from the Malaria Parasite. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Shen, S.; Tang, J.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; He, X.; Guo, G.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; et al. A Cascade of Transcriptional Repression Determines Sexual Commitment and Development in Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9264–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, F.; Bunnik, E.M.; Varoquaux, N.; Bol, S.M.; Prudhomme, J.; Vert, J.P.; Noble, W.S.; le Roch, K.G. Three-Dimensional Modeling of the P. falciparum Genome during the Erythrocytic Cycle Reveals a Strong Connection between Genome Architecture and Gene Expression. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnik, E.M.; Polishko, A.; Prudhomme, J.; Ponts, N.; Gill, S.S.; Lonardi, S.; le Roch, K.G. DNA-Encoded Nucleosome Occupancy Is Associated with Transcription Levels in the Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorà-Batlle, O.; Tintó-Font, E.; Cortés, A. Transcriptional Variation in Malaria Parasites: Why and How. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2019, 18, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, A.; Cervantes, S.; Bunnik, E.M.; Ponts, N.; Sardiu, M.E.; Chung, D.W.D.; Prudhomme, J.; Varberg, J.M.; Wen, Z.; Washburn, M.P.; et al. Dynamic and Combinatorial Landscape of Histone Modifications during the Intraerythrocytic Developmental Cycle of the Malaria Parasite. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 2787–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, J.; Fan, Q.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Cui, L. The Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum Histones: Organization, Expression, and Acetylation. Gene 2006, 369, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, N.; Sidoli, S.; van Biljon, R.; Painter, H.; Llinás, M.; Garcia, B.A.; Birkholtz, L.M. Quantitative Chromatin Proteomics Reveals a Dynamic Histone Post-Translational Modification Landscape That Defines Asexual and Sexual Plasmodium falciparum Parasites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batugedara, G.; Lu, X.M.; Bunnik, E.M.; le Roch, K.G. The Role of Chromatin Structure in Gene Regulation of the Human Malaria Parasite. Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeijmakers, W.A.M.; Salcedo-Amaya, A.M.; Smits, A.H.; Françoijs, K.J.; Treeck, M.; Gilberger, T.W.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; Bártfai, R. H2A.Z/H2B.Z Double-Variant Nucleosomes Inhabit the AT-Rich Promoter Regions of the Plasmodium falciparum Genome. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 87, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, V.M.; Rovira-Graells, N.; de Pouplana, L.R.; Cortés, A. Heterochromatin Formation in Bistable Chromatin Domains Controls the Epigenetic Repression of Clonally Variant Plasmodium falciparum Genes Linked to Erythrocyte Invasion. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozdech, Z.; Llinás, M.; Pulliam, B.L.; Wong, E.D.; Zhu, J.; DeRisi, J.L. The Transcriptome of the Intraerythrocytic Developmental Cycle of Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Roch, K.G.; Zhou, Y.; Blair, P.L.; Grainger, M.; Moch, J.K.; Haynes, J.D.; de la Vega, P.; Holder, A.A.; Batalov, S.; Carucci, D.J.; et al. Discovery of Gene Function by Expression Profiling of the Malaria Parasite Life Cycle. Science 2003, 301, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeton, T.J.; Iyer, L.M.; Anantharaman, V.; Enomoto, S.; Abrahante, J.E.; Subramanian, G.M.; Hoffman, S.L.; Abrahamsen, M.S.; Aravind, L. Comparative Analysis of Apicomplexa and Genomic Diversity in Eukaryotes. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1686–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, A.; Hughes, K.R.; Modrzynska, K.K.; Otto, T.D.; Pfander, C.; Dickens, N.J.; Religa, A.A.; Bushell, E.; Graham, A.L.; Cameron, R.; et al. A Cascade of DNA-Binding Proteins for Sexual Commitment and Development in Plasmodium. Nature 2014, 507, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poran, A.; Nötzel, C.; Aly, O.; Mencia-Trinchant, N.; Harris, C.T.; Guzman, M.L.; Hassane, D.C.; Elemento, O.; Kafsack, B.F.C. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals a Signature of Sexual Commitment in Malaria Parasites. Nature 2017, 551, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Díaz, E.; Yerbanga, R.S.; Lefèvre, T.; Cohuet, A.; Rowley, M.J.; Ouedraogo, J.B.; Corces, V.G. Epigenetic Regulation of Plasmodium falciparum Clonally Variant Gene Expression during Development in Anopheles Gambiae. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filarsky, M.; Fraschka, S.A.; Niederwieser, I.; Brancucci, N.M.B.; Carrington, E.; Carrió, E.; Moes, S.; Jenoe, P.; Bártfai, R.; Voss, T.S. GDV1 Induces Sexual Commitment of Malaria Parasites by Antagonizing HP1-Dependent Gene Silencing. Science 2018, 359, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollin, T.; le Roch, K.G. From Genes to Transcripts, a Tightly Regulated Journey in Plasmodium. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuda, M.; Iwanaga, S.; Kaneko, I.; Kato, T. Global Transcriptional Repression: An Initial and Essential Step for Plasmodium Sexual Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12824–12829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuda, M.; Iwanaga, S.; Shigenobu, S.; Mair, G.R.; Janse, C.J.; Waters, A.P.; Kato, T.; Kaneko, I. Identification of a Transcription Factor in the Mosquito-Invasive Stage of Malaria Parasites. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 71, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuda, M.; Iwanaga, S.; Shigenobu, S.; Kato, T.; Kaneko, I. Transcription Factor AP2-Sp and Its Target Genes in Malarial Sporozoites. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 854–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanaga, S.; Kaneko, I.; Kato, T.; Yuda, M. Identification of an AP2-Family Protein That Is Critical for Malaria Liver Stage Development. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chisholm, S.A.; Yeoh, L.M.; Gilson, P.R.; Papenfuss, A.T.; Day, K.P.; Petter, M.; Duffy, M.F. Histone Modifications Associated with Gene Expression and Genome Accessibility Are Dynamically Enriched at Plasmodium falciparum Regulatory Sequences. Epigenet. Chromatin 2020, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponts, N.; Harris, E.Y.; Prudhomme, J.; Wick, I.; Eckhardt-Ludka, C.; Hicks, G.R.; Hardiman, G.; Lonardi, S.; le Roch, K.G. Nucleosome Landscape and Control of Transcription in the Human Malaria Parasite. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.; Dahan-Pasternak, N.; Shimoni, E.; Shinder, V.; von Huth, P.; Elbaum, M.; Dzikowski, R. 3D Nuclear Architecture Reveals Coupled Cell Cycle Dynamics of Chromatin and Nuclear Pores in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Cell Microbiol. 2011, 13, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.P.; Chin, W.H.; Zhu, L.; Mok, S.; Luah, Y.H.; Lim, E.H.; Bozdech, Z. Dynamic Epigenetic Regulation of Gene Expression during the Life Cycle of Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kensche, P.R.; Hoeijmakers, W.A.M.; Toenhake, C.G.; Bras, M.; Chappell, L.; Berriman, M.; Bártfai, R. The Nucleosome Landscape of Plasmodium falciparum Reveals Chromatin Architecture and Dynamics of Regulatory Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, 2110–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Fan, Q.; Cui, L.; Miao, J. Histone Lysine Methyltransferases and Demethylases in Plasmodium falciparum. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártfai, R.; Hoeijmakers, W.A.M.; Salcedo-Amaya, A.M.; Smits, A.H.; Janssen-Megens, E.; Kaan, A.; Treeck, M.; Gilberger, T.W.; Francoijs, K.J.; Stunnenberg, H.G. H2A.Z Demarcates Intergenic Regions of the Plasmodium falciparum Epigenome That Are Dynamically Marked by H3K9ac and H3K4me3. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.L.; Tena, J.J.; Bancells, C.; Cortés, A.; Gómez-Skarmeta, J.L.; Gomez-Díaz, E. Characterization of the Accessible Genome in the Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 9414–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancucci, N.M.B.; Bertschi, N.L.; Zhu, L.; Niederwieser, I.; Chin, W.H.; Wampfler, R.; Freymond, C.; Rottmann, M.; Felger, I.; Bozdech, Z.; et al. Heterochromatin Protein 1 Secures Survival and Transmission of Malaria Parasites. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan-Pasternak, N.; Nasereddin, A.; Kolevzon, N.; Pe’er, M.; Wong, W.; Shinder, V.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Elbaum, M.; Gilberger, T.W.; et al. Pfsec13 Is an Unusual Chromatin-Associated Nucleoporin of Plasmodium falciparum That Is Essential for Parasite Proliferation in Human Erythrocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 3055–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.M.; Batugedara, G.; Lee, M.; Prudhomme, J.; Bunnik, E.M.; le Roch, K.G. Nascent RNA Sequencing Reveals Mechanisms of Gene Regulation in the Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 7825–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Josling, G.; Ross, P.; Joshi, P.; Orchard, L.; Campbell, T.; Schieler, A.; Cristea, I.M.; Llinás, M. Red Blood Cell Invasion by the Malaria Parasite Is Coordinated by the PfAP2-I Transcription Factor. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 731–741.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josling, G.A.; Petter, M.; Oehring, S.C.; Gupta, A.P.; Dietz, O.; Wilson, D.W.; Schubert, T.; Längst, G.; Gilson, P.R.; Crabb, B.S.; et al. A Plasmodium falciparum Bromodomain Protein Regulates Invasion Gene Expression. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muller, I.; Jex, A.R.; Kappe, S.H.I.; Mikolajczak, S.A.; Sattabongkot, J.; Patrapuvich, R.; Lindner, S.; Flannery, E.L.; Koepfli, C.; Ansell, B.; et al. Transcriptome and Histone Epigenome of Plasmodium Vivax Salivary-Gland Sporozoites Point to Tight Regulatory Control and Mechanisms for Liver-Stage Differentiation in Relapsing Malaria. Int. J. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witmer, K.; Fraschka, S.A.; Vlachou, D.; Bártfai, R.; Christophides, G.K. An Epigenetic Map of Malaria Parasite Development from Host to Vector. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, E.; Martienssen, R.A. Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance: Myths and Mechanisms. Cell 2014, 157, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlambo, G.; Coppens, I.; Kumar, N. Aberrant Sporogonic Development of Dmc1 (a Meiotic Recombinase) Deficient Plasmodium Berghei Parasites. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, P.J.; Brugat, T.; Langhorne, J. Mosquitoes Reset Malaria Parasites. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, I.; Iwanaga, S.; Kato, T.; Kobayashi, I.; Yuda, M. Genome-Wide Identification of the Target Genes of AP2-O, a Plasmodium AP2-Family Transcription Factor. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrzynska, K.; Pfander, C.; Chappell, L.; Yu, L.; Suarez, C.; Dundas, K.; Gomes, A.R.; Goulding, D.; Rayner, J.C.; Choudhary, J.; et al. A Knockout Screen of ApiAP2 Genes Reveals Networks of Interacting Transcriptional Regulators Controlling the Plasmodium Life Cycle. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Cui, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Su, X.Z.; et al. Systematic CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated Modifications of Plasmodium Yoelii ApiAP2 Genes Reveal Functional Insights into Parasite Development. mBio 2017, 8, e01986-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanghì, G.; Vembar, S.S.; Baumgarten, S.; Ding, S.; Guizetti, J.; Bryant, J.M.; Mattei, D.; Jensen, A.T.R.; Rénia, L.; Goh, Y.S.; et al. A Specific PfEMP1 Is Expressed in P. falciparum Sporozoites and Plays a Role in Hepatocyte Infection. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talman, A.M.; Lacroix, C.; Marques, S.R.; Blagborough, A.M.; Carzaniga, R.; Ménard, R.; Sinden, R.E. PbGEST Mediates Malaria Transmission to Both Mosquito and Vertebrate Host. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 82, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Tolia, N.H. Getting in: The Structural Biology of Malaria Invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, S.E.; Swearingen, K.E.; Shears, M.J.; Walker, M.P.; Vrana, E.N.; Hart, K.J.; Minns, A.M.; Sinnis, P.; Moritz, R.L.; Kappe, S.H.I. Transcriptomics and Proteomics Reveal Two Waves of Translational Repression during the Maturation of Malaria Parasite Sporozoites. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvie, O.; Briquet, S.; Müller, K.; Manzoni, G.; Matuschewski, K. Post-Transcriptional Silencing of UIS4 in Plasmodium Berghei Sporozoites Is Important for Host Switch. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 91, 1200–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Fennell, C.; Ranford-Cartwright, L.; Sakthivel, R.; Gueirard, P.; Meister, S.; Caspi, A.; Doerig, C.; Nussenzweig, R.S.; Tuteja, R.; et al. The Plasmodium Eukaryotic Initiation Factor-2alpha Kinase IK2 Controls the Latency of Sporozoites in the Mosquito Salivary Glands. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, H.J.; Carrasquilla, M.; Llinás, M. Capturing in Vivo RNA Transcriptional Dynamics from the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasonder, E.; Rijpma, S.R.; van Schaijk, B.C.L.; Hoeijmakers, W.A.M.; Kensche, P.R.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Italiaander, A.; Vos, M.W.; Woestenenk, R.; Bousema, T.; et al. Integrated Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses of P. falciparum Gametocytes: Molecular Insight into Sex-Specific Processes and Translational Repression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6087–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Guo, G.; Qian, P.; Mu, J.; Lu, B.; He, X.; Fan, Y.; Shang, X.; Yang, G.; Shen, S.; et al. 5-Methylcytosine Modification by Plasmodium NSUN2 Stabilizes MRNA and Mediates the Development of Gametocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2110713119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira-Graells, N.; Gupta, A.P.; Planet, E.; Crowley, V.M.; Mok, S.; de Pouplana, L.R.; Preiser, P.R.; Bozdech, Z.; Cortés, A. Transcriptional Variation in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deitsch, K.W.; Dzikowski, R. Variant Gene Expression and Antigenic Variation by Malaria Parasites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mira-Martínez, S.; Rovira-Graells, N.; Crowley, V.M.; Altenhofen, L.M.; Llinás, M.; Cortés, A. Epigenetic Switches in Clag3 Genes Mediate Blasticidin S Resistance in Malaria Parasites. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mira-Martínez, S.; van Schuppen, E.; Amambua-Ngwa, A.; Bottieau, E.; Affara, M.; van Esbroeck, M.; Vlieghe, E.; Guetens, P.; Rovira-Graells, N.; Gómez-Pérez, G.P.; et al. Expression of the Plasmodium falciparum Clonally Variant Clag3 Genes in Human Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billker, O.; Lindo, V.; Panico, M.; Etienne, A.E.; Paxton, T.; Dell, A.; Rogers, M.; Sinden, R.E.; Morris, H.R. Identification of Xanthurenic Acid as the Putative Inducer of Malaria Development in the Mosquito. Nature 1998, 392, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billker, O.; Dechamps, S.; Tewari, R.; Wenig, G.; Franke-Fayard, B.; Brinkmann, V. Calcium and a Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase Regulate Gamete Formation and Mosquito Transmission in a Malaria Parasite. Cell 2004, 117, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancucci, N.M.B.; Gerdt, J.P.; Wang, C.Q.; de Niz, M.; Philip, N.; Adapa, S.R.; Zhang, M.; Hitz, E.; Niederwieser, I.; Boltryk, S.D.; et al. Lysophosphatidylcholine Regulates Sexual Stage Differentiation in the Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Cell 2017, 171, 1532–1544.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancio-Silva, L.; Slavic, K.; Grilo Ruivo, M.T.; Grosso, A.R.; Modrzynska, K.K.; Vera, I.M.; Sales-Dias, J.; Gomes, A.R.; Macpherson, C.R.; Crozet, P.; et al. Nutrient Sensing Modulates Malaria Parasite Virulence. Nature 2017, 547, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, K.; Ponmee, N.; Jiang, L.; Fowble, J.W.; White, J.; Kamchonwongpaisan, S.; Yuthavong, Y.; Wilairat, P.; Rathod, P.K. A Genetically Hard-Wired Metabolic Transcriptome in Plasmodium falciparum Fails to Mount Protective Responses to Lethal Antifolates. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Roch, K.G.; Johnson, J.R.; Ahiboh, H.; Chung, D.W.D.; Prudhomme, J.; Plouffe, D.; Henson, K.; Zhou, Y.; Witola, W.; Yates, J.R.; et al. A Systematic Approach to Understand the Mechanism of Action of the Bisthiazolium Compound T4 on the Human Malaria Parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, A.; Crowley, V.M.; Vaquero, A.; Voss, T.S. A View on the Role of Epigenetics in the Biology of Malaria Parasites. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizetti, J.; Scherf, A. Silence, Activate, Poise and Switch! Mechanisms of Antigenic Variation in Plasmodium falciparum. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, A.; Carret, C.; Kaneko, O.; Yim Lim, B.Y.S.; Ivens, A.; Holder, A.A. Epigenetic Silencing of Plasmodium falciparum Genes Linked to Erythrocyte Invasion. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Rubio, J.J.; Gontijo, A.M.; Nunes, M.C.; Issar, N.; Hernandez Rivas, R.; Scherf, A. 5′ Flanking Region of Var Genes Nucleate Histone Modification Patterns Linked to Phenotypic Inheritance of Virulence Traits in Malaria Parasites. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; López-Barragán, M.J.; Jiang, H.; Mu, J.; Gaur, D.; Zhao, K.; Felsenfeld, G.; Miller, L.H. Epigenetic Control of the Variable Expression of a Plasmodium falciparum Receptor Protein for Erythrocyte Invasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2224–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chookajorn, T.; Dzikowski, R.; Frank, M.; Li, F.; Jiwani, A.Z.; Hartl, D.L.; Deitsch, K.W. Epigenetic Memory at Malaria Virulence Genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeaux, C.A.; Coleman, B.I.; Bei, A.K.; Whitehurst, N.; Duraisingh, M.T. Functional Analysis of Epigenetic Regulation of Tandem RhopH1/Clag Genes Reveals a Role in Plasmodium falciparum Growth. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rubio, J.J.; Mancio-Silva, L.; Scherf, A. Genome-Wide Analysis of Heterochromatin Associates Clonally Variant Gene Regulation with Perinuclear Repressive Centers in Malaria Parasites. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafsack, B.F.C.; Rovira-Graells, N.; Clark, T.G.; Bancells, C.; Crowley, V.M.; Campino, S.G.; Williams, A.E.; Drought, L.G.; Kwiatkowski, D.P.; Baker, D.A.; et al. A Transcriptional Switch Underlies Commitment to Sexual Development in Malaria Parasites. Nature 2014, 507, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, B.I.; Ribacke, U.; Manary, M.; Bei, A.K.; Winzeler, E.A.; Wirth, D.F.; Duraisingh, M.T. Nuclear Repositioning Precedes Promoter Accessibility and Is Linked to the Switching Frequency of a Plasmodium falciparum Invasion Gene. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, S.A.; Scheidig-Benatar, C.; Scherf, A. Antigenic Variation in Plasmodium falciparum Is Associated with Movement of Var Loci between Subnuclear Locations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5414–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisingh, M.T.; Voss, T.S.; Marty, A.J.; Duffy, M.F.; Good, R.T.; Thompson, J.K.; Freitas, L.H.; Scherf, A.; Crabb, B.S.; Cowman, A.F. Heterochromatin Silencing and Locus Repositioning Linked to Regulation of Virulence Genes in Plasmodium falciparum. Cell 2005, 121, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikowski, R.; Li, F.; Amulic, B.; Eisberg, A.; Frank, M.; Patel, S.; Wellems, T.E.; Deitsch, K.W. Mechanisms Underlying Mutually Exclusive Expression of Virulence Genes by Malaria Parasites. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Toledo, K.; Rojas-Meza, A.P.; Mancio-Silva, L.; Hernández-Cuevas, N.A.; Delgadillo, D.M.; Vargas, M.; Martínez-Calvillo, S.; Scherf, A.; Hernandez-Rivas, R. Plasmodium falciparum Heterochromatin Protein 1 Binds to Tri-Methylated Histone 3 Lysine 9 and Is Linked to Mutually Exclusive Expression of Var Genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 2596–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flueck, C.; Bartfai, R.; Volz, J.; Niederwieser, I.; Salcedo-Amaya, A.M.; Alako, B.T.F.; Ehlgen, F.; Ralph, S.A.; Cowman, A.F.; Bozdech, Z.; et al. Plasmodium falciparum Heterochromatin Protein 1 Marks Genomic Loci Linked to Phenotypic Variation of Exported Virulence Factors. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés, A.; Deitsch, K.W. Malaria Epigenetics. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, J.; Mphande, F.A.; Berriman, M.; Pain, A.; Rogerson, S.J.; Taylor, T.E.; Molyneux, M.E.; Craig, A. Differential Var Gene Expression in the Organs of Patients Dying of Falciparum Malaria. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 65, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Fernandez, V.; Sundström, A.; Schlichtherle, M.; Datta, S.; Hagblom, P.; Wahlgren, M. Developmental Selection of Var Gene Expression in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 1998, 394, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherf, A.; Hernandez-Rivas, R.; Buffet, P.; Bottius, E.; Benatar, C.; Pouvelle, B.; Gysin, J.; Lanzer, M. Antigenic Variation in Malaria: In Situ Switching, Relaxed and Mutually Exclusive Transcription of Var Genes during Intra-Erythrocytic Development in Plasmodium falciparum. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 5418–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Mu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ni, T.; Srinivasan, P.; Rayavara, K.; Yang, W.; Turner, L.; Lavstsen, T.; Theander, T.G.; et al. PfSETvs Methylation of Histone H3K36 Represses Virulence Genes in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 2013, 499, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, L.H.; Hernandez-Rivas, R.; Ralph, S.A.; Montiel-Condado, D.; Ruvalcaba-Salazar, O.K.; Rojas-Meza, A.P.; Mâncio-Silva, L.; Leal-Silvestre, R.J.; Gontijo, A.M.; Shorte, S.; et al. Telomeric Heterochromatin Propagation and Histone Acetylation Control Mutually Exclusive Expression of Antigenic Variation Genes in Malaria Parasites. Cell 2005, 121, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, J.E.; Kyes, S.A.; Otto, T.D.; Feller, A.I.; Eastman, R.T.; Pinches, R.A.; Berriman, M.; Su, X.Z.; Newbold, C.I. Genome-Wide Profiling of Chromosome Interactions in Plasmodium falciparum Characterizes Nuclear Architecture and Reconfigurations Associated with Antigenic Variation. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 90, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnik, E.M.; Venkat, A.; Shao, J.; McGovern, K.E.; Batugedara, G.; Worth, D.; Prudhomme, J.; Lapp, S.A.; Andolina, C.; Ross, L.S.; et al. Comparative 3D Genome Organization in Apicomplexan Parasites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petter, M.; Selvarajah, S.A.; Lee, C.C.; Chin, W.H.; Gupta, A.P.; Bozdech, Z.; Brown, G.V.; Duffy, M.F. H2A.Z and H2B.Z Double-Variant Nucleosomes Define Intergenic Regions and Dynamically Occupy Var Gene Promoters in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 87, 1167–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petter, M.; Lee, C.C.; Byrne, T.J.; Boysen, K.E.; Volz, J.; Ralph, S.A.; Cowman, A.F.; Brown, G.V.; Duffy, M.F. Expression of P. falciparum Var Genes Involves Exchange of the Histone Variant H2A.Z at the Promoter. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraschka, S.A.K.; Henderson, R.W.M.; Bártfai, R. H3.3 Demarcates GC-Rich Coding and Subtelomeric Regions and Serves as Potential Memory Mark for Virulence Gene Expression in Plasmodium falciparum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volz, J.C.; Bártfai, R.; Petter, M.; Langer, C.; Josling, G.A.; Tsuboi, T.; Schwach, F.; Baum, J.; Rayner, J.C.; Stunnenberg, H.G.; et al. PfSET10, a Plasmodium falciparum Methyltransferase, Maintains the Active Var Gene in a Poised State during Parasite Division. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 11, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyes, S.; Christodoulou, Z.; Pinches, R.; Kriek, N.; Horrocks, P.; Newbold, C. Plasmodium falciparum Var Gene Expression Is Developmentally Controlled at the Level of RNA Polymerase II-Mediated Transcription Initiation. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 63, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit-Avraham, I.; Pozner, G.; Eshar, S.; Fastman, Y.; Kolevzon, N.; Yavin, E.; Dzikowski, R. Antisense Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate Var Gene Activation in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E982–E991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, K.; Pearson, M.; Grate, L.; Sterne-Weiler, T.; Deans, J.; Donohue, J.P.; Ares, M. Structural RNAs of Known and Unknown Function Identified in Malaria Parasites by Comparative Genomics and RNA Analysis. RNA 2007, 13, 1923–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizetti, J.; Barcons-Simon, A.; Scherf, A. Trans-Acting GC-Rich Non-Coding RNA at Var Expression Site Modulates Gene Counting in Malaria Parasite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 9710–9718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.G.; Walliker, D.; Ranford-Cartwright, L.C. Sexual Differentiation and Sex Determination in the Apicomplexa. Trends Parasitol. 2002, 18, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksi, S.; Morahan, B.J.; Haile, Y.; Furuya, T.; Jiang, H.; Ali, O.; Xu, H.; Kiattibutr, K.; Suri, A.; Czesny, B.; et al. Plasmodium falciparum Gametocyte Development 1 (Pfgdv1) and Gametocytogenesis Early Gene Identification and Commitment to Sexual Development. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trager, W.; Gill, G.S. Enhanced Gametocyte Formation in Young Erythrocytes by Plasmodium falciparum In Vitro. J. Protozool. 1992, 39, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckling, A.; Ranford-Cartwright, L.C.; Miles, A.; Read, A.F. Chloroquine Increases Plasmodium falciparum Gametocytogenesis in Vitro. Parasitology 1999, 118 Pt 4, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent, R.S.; Modrzynska, K.K.; Cameron, R.; Philip, N.; Billker, O.; Waters, A.P. Inducible Developmental Reprogramming Redefines Commitment to Sexual Development in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium berghei. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, B.I.; Skillman, K.M.; Jiang, R.H.Y.; Childs, L.M.; Altenhofen, L.M.; Ganter, M.; Leung, Y.; Goldowitz, I.; Kafsack, B.F.C.; Marti, M.; et al. A Plasmodium falciparum Histone Deacetylase Regulates Antigenic Variation and Gametocyte Conversion. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadbent, K.M.; Broadbent, J.C.; Ribacke, U.; Wirth, D.; Rinn, J.L.; Sabeti, P.C. Strand-Specific RNA Sequencing in Plasmodium falciparum Malaria Identifies Developmentally Regulated Long Non-Coding RNA and Circular RNA. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancells, C.; Llorà-Batlle, O.; Poran, A.; Nötzel, C.; Rovira-Graells, N.; Elemento, O.; Kafsack, B.F.C.; Cortés, A. Revisiting the Initial Steps of Sexual Development in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 4, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraschka, S.A.; Filarsky, M.; Hoo, R.; Niederwieser, I.; Yam, X.Y.; Brancucci, N.M.B.; Mohring, F.; Mushunje, A.T.; Huang, X.; Christensen, P.R.; et al. Comparative Heterochromatin Profiling Reveals Conserved and Unique Epigenome Signatures Linked to Adaptation and Development of Malaria Parasites. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 407–420.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnik, E.M.; Cook, K.B.; Varoquaux, N.; Batugedara, G.; Prudhomme, J.; Cort, A.; Shi, L.; Andolina, C.; Ross, L.S.; Brady, D.; et al. Changes in Genome Organization of Parasite-Specific Gene Families during the Plasmodium Transmission Stages. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Santos, J.M.; Orchard, L.M.; Yamada, N.; van Biljon, R.; Painter, H.J.; Mahony, S.; Llinás, M. The PfAP2-G2 Transcription Factor Is a Critical Regulator of Gametocyte Maturation. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 1005–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, J.; Simpson, K.M.; Triglia, T.; Plouffe, D.; Tonkin, C.J.; Duraisingh, M.T.; Maier, A.C.; Winzeler, E.A.; Cowman, A.F. Molecular Mechanism for Switching of P. falciparum Invasion Pathways into Human Erythrocytes. Science 2005, 309, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maier, A.G.; Duraisingh, M.T.; Reeder, J.C.; Patel, S.S.; Kazura, J.W.; Zimmerman, P.A.; Cowman, A.F. Plasmodium falciparum Erythrocyte Invasion through Glycophorin C and Selection for Gerbich Negativity in Human Populations. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisingh, M.T.; Triglia, T.; Ralph, S.A.; Rayner, J.C.; Barnwell, J.W.; McFadden, G.I.; Cowman, A.F. Phenotypic Variation of Plasmodium falciparum Merozoite Proteins Directs Receptor Targeting for Invasion of Human Erythrocytes. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, M.B.; Caruana, S.R.; Batchelor, A.H.; Thompson, J.K.; Crabb, B.S.; Cowman, A.F. Targeted Disruption of an Erythrocyte Binding Antigen in Plasmodium falciparum Is Associated with a Switch toward a Sialic Acid-Independent Pathway of Invasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7509–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.M.; Grainger, M.; Holder, A.A. Variation in the Expression of a Plasmodium falciparum Protein Family Implicated in Erythrocyte Invasion. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5779–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadafora, C.; Awandare, G.A.; Kopydlowski, K.M.; Czege, J.; Moch, J.K.; Finberg, R.W.; Tsokos, G.C.; Stoute, J.A. Complement Receptor 1 Is a Sialic Acid-Independent Erythrocyte Receptor of Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, W.H.; Schmidt, C.Q.; Hauhart, R.E.; Guariento, M.; Tetteh-Quarcoo, P.B.; Lopaticki, S.; Atkinson, J.P.; Barlow, P.N.; Cowman, A.F. Plasmodium falciparum Uses a Key Functional Site in Complement Receptor Type-1 for Invasion of Human Erythrocytes. Blood 2011, 118, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, D.; Furuya, T.; Mu, J.; Jiang, L.B.; Su, X.Z.; Miller, L.H. Upregulation of Expression of the Reticulocyte Homology Gene 4 in the Plasmodium falciparum Clone Dd2 Is Associated with a Switch in the Erythrocyte Invasion Pathway. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 145, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraisingh, M.T.; Maier, A.G.; Triglia, T.; Cowman, A.F. Erythrocyte-Binding Antigen 175 Mediates Invasion in Plasmodium falciparum Utilizing Sialic Acid-Dependent and -Independent Pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4796–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguitragool, W.; Bokhari, A.A.B.; Pillai, A.D.; Rayavara, K.; Sharma, P.; Turpin, B.; Aravind, L.; Desai, S.A. Malaria Parasite Clag3 Genes Determine Channel-Mediated Nutrient Uptake by Infected Red Blood Cells. Cell 2011, 145, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.D.; Nguitragool, W.; Lyko, B.; Dolinta, K.; Butler, M.M.; Nguyen, S.T.; Peet, N.P.; Bowlin, T.L.; Desai, S.A. Solute Restriction Reveals an Essential Role for Clag3-Associated Channels in Malaria Parasite Nutrient Acquisition. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovira-Graells, N.; Crowley, V.M.; Bancells, C.; Mira-Martínez, S.; de Pouplana, L.R.; Cortés, A. Deciphering the Principles That Govern Mutually Exclusive Expression of Plasmodium falciparum Clag3 Genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 8243–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Wollenberg, K.; Sellers, M.; Zainabadi, K.; Galinsky, K.; Moss, E.; Nguitragool, W.; Neafsey, D.; Desai, S.A. An Epigenetic Antimalarial Resistance Mechanism Involving Parasite Genes Linked to Nutrient Uptake. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19429–19440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraisingh, M.T.; Skillman, K.M. Epigenetic Variation and Regulation in Malaria Parasites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintó-Font, E.; Cortés, A. Malaria Parasites Do Respond to Heat. Trends Parasitol. 2022, 38, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintó-Font, E.; Michel-Todó, L.; Russell, T.J.; Casas-Vila, N.; Conway, D.J.; Bozdech, Z.; Llinás, M.; Cortés, A. A Heat-Shock Response Regulated by the PfAP2-HS Transcription Factor Protects Human Malaria Parasites from Febrile Temperatures. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.Y.; Lell, B.; Dietz, K.; Kremsner, P.G. Plasmodium falciparum: In Vitro Growth Inhibition by Febrile Temperatures. Parasitol. Res. 2001, 87, 553–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, M.; Srivastava, A.; Johri, S.; Gupta, I.; Karmodiya, K. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Cellular Heterogeneity and Stage Transition under Temperature Stress in Synchronized Plasmodium falciparum Cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0000821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugaliza, H.P.; Miyazaki, S.; Geurten, F.J.A.; Pell, C.; Rosanas-Urgell, A.; Janse, C.J.; Cortés, A. Artemisinin Exposure at the Ring or Trophozoite Stage Impacts Plasmodium falciparum Sexual Conversion Differently. Elife 2020, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, M.S.M.; Kumar, S.; Anantharaman, V.; Zheng, H.; Mahajan, B.; Haynes, J.D.; Moch, J.K.; Fairhurst, R.; McCutchan, T.F.; Aravind, L. Molecular Factors and Biochemical Pathways Induced by Febrile Temperature in Intraerythrocytic Plasmodium falciparum Parasites. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 2012–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solís, E.J.; Pandey, J.P.; Zheng, X.; Jin, D.X.; Gupta, P.B.; Airoldi, E.M.; Pincus, D.; Denic, V. Defining the Essential Function of Yeast Hsf1 Reveals a Compact Transcriptional Program for Maintaining Eukaryotic Proteostasis. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nonaka, G.; Blankschien, M.; Herman, C.; Gross, C.A.; Rhodius, V.A. Regulon and Promoter Analysis of the E. Coli Heat-Shock Factor, Sigma32, Reveals a Multifaceted Cellular Response to Heat Stress. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1776–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Varunan, S.M.; Bhattacharyya, M.K. Febrile Temperature Causes Transcriptional Downregulation of Plasmodium falciparum Sirtuins through Hsp90-Dependent Epigenetic Modification. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, J.A.; Norris, E.L.; Gilson, P.; Przyborski, J.; Shonhai, A.; Blatch, G.L.; Skinner-Adams, T.S.; Gorman, J.; Headlam, M.; Andrews, K.T. Proteomic Analysis of Plasmodium falciparum Histone Deacetylase 1 Complex Proteins. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 198, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammam, E.; Sinha, A.; Baumgarten, S.; Nardella, F.; Liang, J.; Miled, S.; Bonhomme, F.; Erdmann, D.; Arcangioli, B.; Arimondo, P.B.; et al. Malaria Parasite Stress Tolerance Is Regulated by DNMT2-Mediated TRNA Cytosine Methylation. mBio 2021, 12, e0255821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, M. RNA Modification and the Epitranscriptome; the next Frontier. RNA 2015, 21, 703–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.D.; Jaffrey, S.R. The Dynamic Epitranscriptome: N6-Methyladenosine and Gene Expression Control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.S.; Sinha, A.; Aniweh, Y.; Nah, Q.; Babu, I.R.; Gu, C.; Chionh, Y.H.; Dedon, P.C.; Preiser, P.R. TRNA Epitranscriptomics and Biased Codon Are Linked to Proteome Expression in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2018, 14, e8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgarten, S.; Bryant, J.M.; Sinha, A.; Reyser, T.; Preiser, P.R.; Dedon, P.C.; Scherf, A. Transcriptome-Wide Dynamics of Extensive M6A MRNA Methylation during Plasmodium falciparum Blood-Stage Development. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2246–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Padgett, L.R.; Bastos, M.S.; Sullivan, W.J. M6A RNA Methylation Facilitates Pre-MRNA 3′-End Formation and Is Essential for Viability of Toxoplasma Gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, D.C.; Bowler, M.W.; Communie, G.; Pontier, D.; Belmudes, L.; Mas, C.; Corrao, C.; Couté, Y.; Bougdour, A.; Lagrange, T.; et al. A Plant-like Mechanism Coupling M6A Reading to Polyadenylation Safeguards Transcriptome Integrity and Developmental Gene Partitioning in Toxoplasma. Elife 2021, 10, e68312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaal, B.K.; Gupta, A.P.; Wastuwidyaningtyas, B.D.; Luah, Y.H.; Bozdech, Z. Histone Deacetylases Play a Major Role in the Transcriptional Regulation of the Plasmodium falciparum Life Cycle. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmquist, N.A.; Sundriyal, S.; Caron, J.; Chen, P.; Witkowski, B.; Menard, D.; Suwanarusk, R.; Renia, L.; Nosten, F.; Jiménez-Díaz, M.B.; et al. Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors Are Orally Bioavailable, Fast-Acting Molecules with Activity against Different Species Causing Malaria in Humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmquist, N.A.; Moss, T.A.; Mecheri, S.; Scherf, A.; Fuchter, M.J. Small-Molecule Histone Methyltransferase Inhibitors Display Rapid Antimalarial Activity against All Blood Stage Forms in Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16708–16713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The malERA Consultative Group on Drugs A Research Agenda for Malaria Eradication: Drugs. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1000402. [CrossRef]
- Paton, D.G.; Probst, A.S.; Ma, E.; Adams, K.L.; Shaw, W.R.; Singh, N.; Bopp, S.; Volkman, S.K.; Hien, D.F.S.; Paré, P.S.L.; et al. Using an Antimalarial in Mosquitoes Overcomes Anopheles and Plasmodium Resistance to Malaria Control Strategies. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.C.; Vega-Rodríguez, J.; Jacobs-Lorena, M. The Plasmodium Bottleneck: Malaria Parasite Losses in the Mosquito Vector. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2014, 109, 644–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.A. Population Dynamics of Plasmodium Sporogony. Trends Parasitol. 2007, 23, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.L.; Gómez-Díaz, E. The Second Life of Plasmodium in the Mosquito Host: Gene Regulation on the Move. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2019, 18, 313–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano-Durán, R.; López-Farfán, D.; Gómez-Díaz, E. Epigenetic and Epitranscriptomic Gene Regulation in Plasmodium falciparum and How We Can Use It against Malaria. Genes 2022, 13, 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101734
Serrano-Durán R, López-Farfán D, Gómez-Díaz E. Epigenetic and Epitranscriptomic Gene Regulation in Plasmodium falciparum and How We Can Use It against Malaria. Genes. 2022; 13(10):1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101734
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano-Durán, Rafael, Diana López-Farfán, and Elena Gómez-Díaz. 2022. "Epigenetic and Epitranscriptomic Gene Regulation in Plasmodium falciparum and How We Can Use It against Malaria" Genes 13, no. 10: 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101734
APA StyleSerrano-Durán, R., López-Farfán, D., & Gómez-Díaz, E. (2022). Epigenetic and Epitranscriptomic Gene Regulation in Plasmodium falciparum and How We Can Use It against Malaria. Genes, 13(10), 1734. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101734





