A Genome-Wide Scan Divulges Key Loci Involved in Resistance to Aphids (Aphis craccivora) in Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Aphid Culturing
2.3. Experimental Layout
2.4. Aphid Infestation and Damage Severity Score
2.5. Phenotypic Data Analysis
2.6. SNP Genotype Data Acquisition
2.7. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
2.8. Candidate Gene Prediction
3. Results
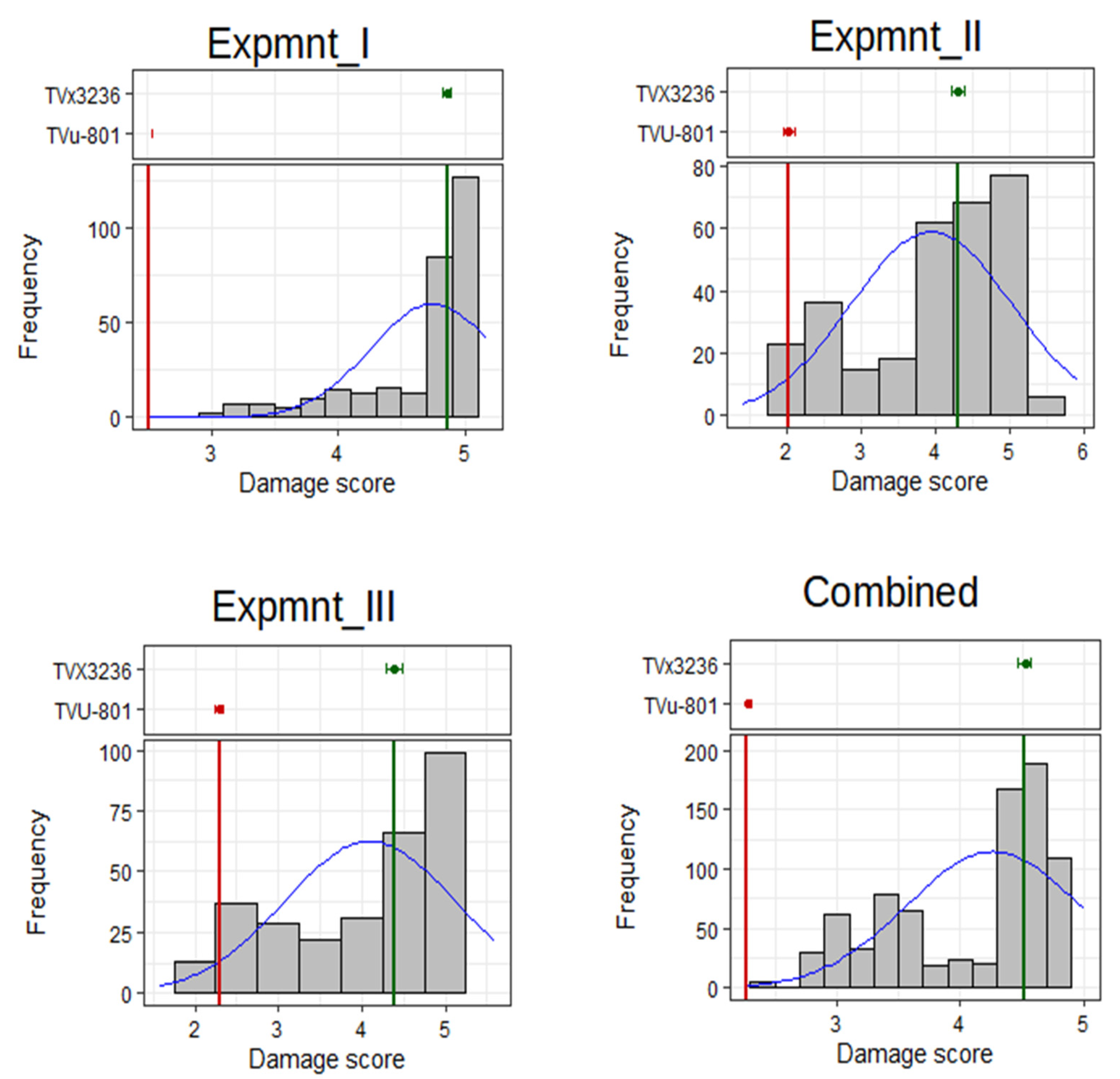
3.1. Phenotypic Assessments
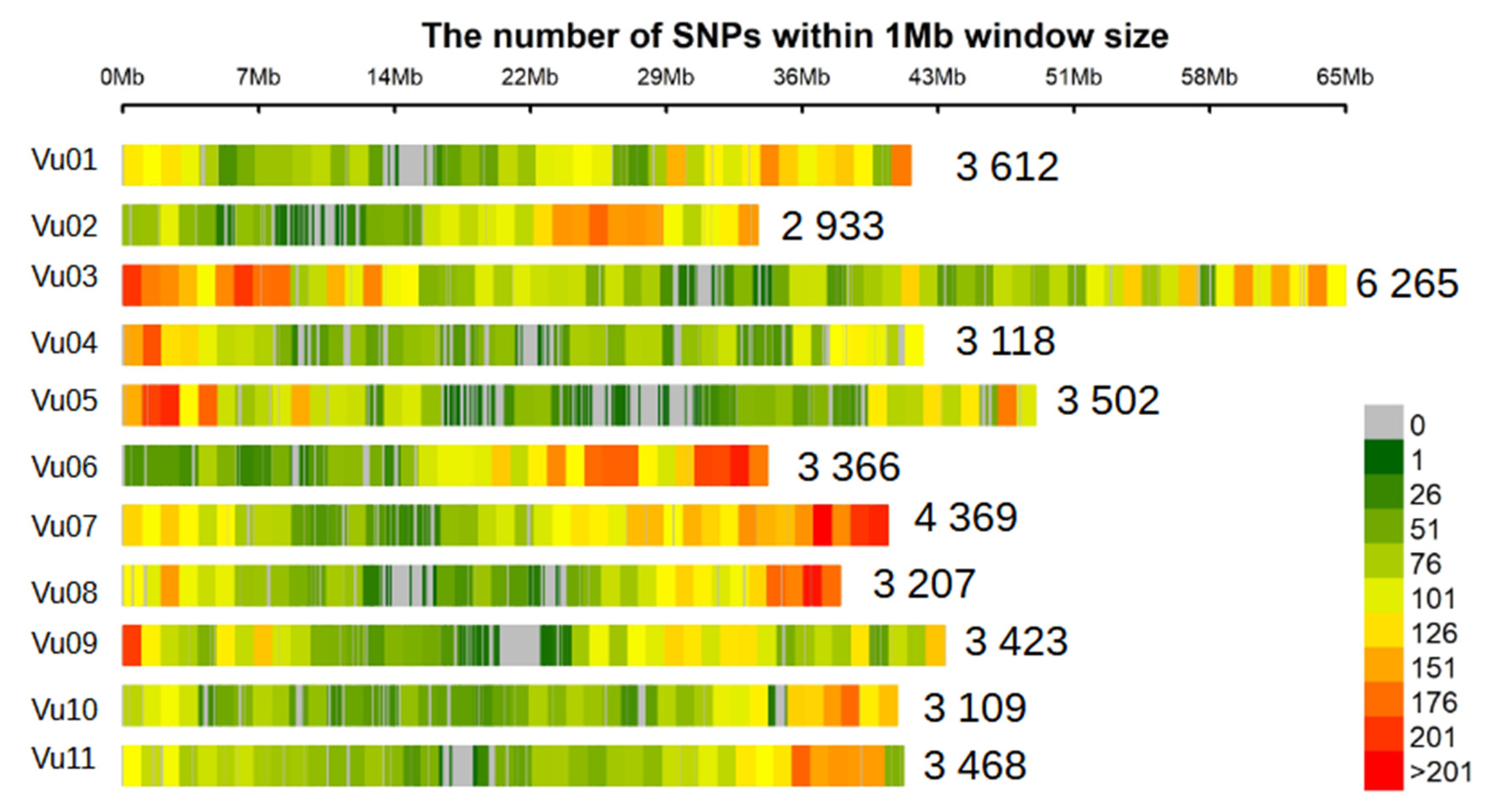
3.2. SNP Density and Linkage Disequilibrium
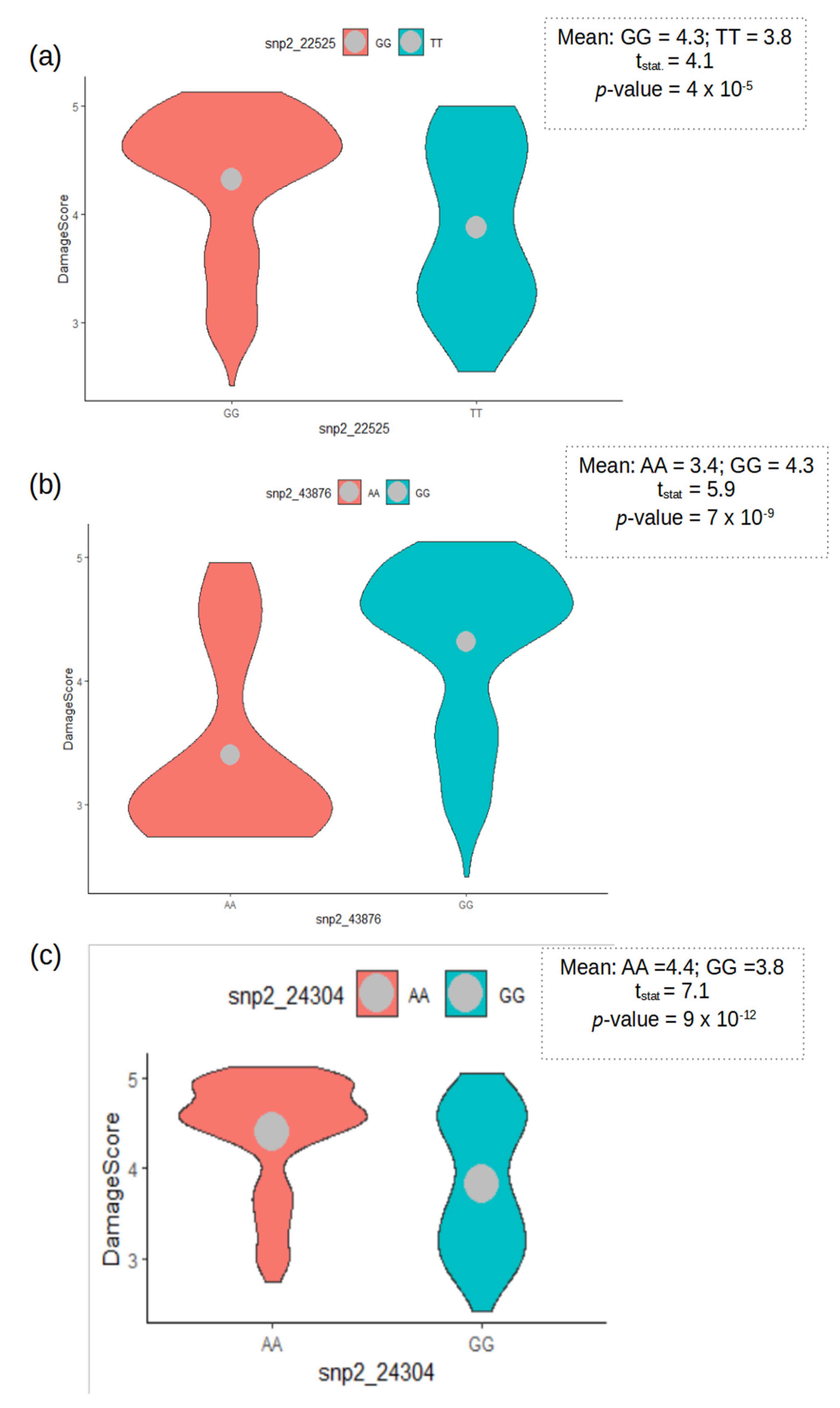
3.3. Genome-Wide Association Signals
3.4. Gene Predictions and Functions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lonardi, S.; Muñoz-Amatriaín, M.; Liang, Q.; Shu, S.; Wanamaker, S.I.; Lo, S.; Tanskanen, J.; Schulman, A.H.; Zhu, T.; Luo, M.C.; et al. The Genome of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata [L.] Walp.). Plant J. 2019, 98, 767–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukar, O.; Belko, N.; Chamarthi, S.; Togola, A.; Batieno, J.; Owusu, E.; Haruna, M.; Diallo, S.; Umar, M.L.; Olufajo, O.; et al. Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata): Genetics, Genomics and Breeding. Plant Breed. 2018, 138, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCLM (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Annan, I.B.; Tingey, W.M.; Schaefers, G.A.; Tjallingii, W.F.; Backus, E.A.; Saxena, K.N. Stylet Penetration Activities by Aphis caccivora (Homoptera: Aphididae) on Plants and Excised Plant Parts of Resistant and Susceptible Cultivars of Cowpea (Leguminosae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2006, 93, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusi, F.; Padi, F.K.; Obeng-Ofori, D.; Asante, S.K.; Agyare, R.Y.; Sugri, I.; Timko, M.P.; Koebner, R.; Huynh, B.L.; Santos, J.R.P.; et al. A Novel Aphid Resistance Locus in Cowpea Identified by Combining SSR and SNP Markers. Plant Breed. 2018, 137, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphuis, L.G.; Gao, L.; Singh, K.B. Identification and Characterization of Resistance to Cowpea Aphid (Aphis caccivora Koch) in Medicago Truncatula. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togola, A.; Boukar, O.; Sergvent, A.; Chamarthi, S.; Tamò, M.; Fatokun, C. Identification of Sources of Resistance in Cowpea Mini Core Accessions to Aphis caccivora Koch (Homoptera: Aphididae) and Their Biochemical Characterization. Euphytica 2020, 216, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops. An Information and Identification Guide, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.R. Cowpea Cultivars Resistant to Insect Pests in World Germplasm Collection. Trop. Grain Legume Bull. 1977, 9, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Omoigui, L.O.; Ekeuro, G.C.; Kamara, A.Y.; Bello, L.L.; Timko, M.P.; Ogunwolu, G.O. New Sources of Aphids [Aphis caccivora (Koch)] Resistance in Cowpea Germplasm Using Phenotypic and Molecular Marker Approaches. Euphytica 2017, 213, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofuya, T.I. Control of the Cowpea Aphid, Aphis caccivora Koch (Homoptera: Aphididae), in Cowpea, Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. Integr. Pest Manag. Rev. 1997, 2, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souleymane, A.; Aken’Ova, M.; Fatokun, C.A.; Alabi, O.Y. Screening for Resistance to Cowpea Aphid (Aphis caccivora Koch) in Wild and Cultivated Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) Accessions. Int. J. Sci. Environ. 2013, 2, 611–621. [Google Scholar]
- Aliyu, H.; Ishiyaku, M.F. Identification of Novel Resistance Gene Sources to Cowpea Aphid (Aphis caccivora Koch) in Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.). Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 16, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Githiri, S.M.; Ampong-Nyarko, K.; Osir, E.O.; Kimani, P.M. Genetics of Resistance to Aphis caccivora in Cowpea. Euphytica 1996, 28, 474–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombakho, G.A.; Tyagi, A.P.; Pathak, R.S. Inheritance of Resistance to the Cowpea Aphid in Cowpea. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1987, 74, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, B.L.; Ehlers, J.D.; Ndeve, A.; Wanamaker, S.; Lucas, M.R.; Close, T.J.; Roberts, P.A. Genetic Mapping and Legume Synteny of Aphid Resistance in African Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) Grown in California. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.B. Recent Genetic Studies in Cowpea. In Challenges and Opportunities for Enhancing Sustainable Cowpea Production, Proceedings of the World Cowpea Conference III, Ibadan, Nigeria, 4–8 September 2002; Fatokun, C.A., Tarawali, S.A., Kormawa, P.M., Tamò, M., Eds.; IITA: Ibadan, Nigeria, 2002; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Boukar, O.; Fatokun, C.A.; Huynh, B.L.; Roberts, P.A.; Close, T.J. Genomic Tools in Cowpea Breeding Programs: Status and Perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K.; Rustgi, S.; Kulwal, P.L. Linkage Disequilibrium and Association Studies in Higher Plants: Present Status and Future Prospects. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 57, 461–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obopile, M.; Ositile, B. Life Table and Population Parameters of Cowpea Aphid, Aphis caccivora Koch (Homoptera: Aphididae) on Five Cowpea Vigna unguiculata (L. Walp.) Varieties. J. Pest Sci. 2010, 83, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givovich, A.; Weibull, J.; Pettersson, J. Cowpea Aphid Performance and Behaviour on Two Resistant Cowpea Lines. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1988, 49, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couldridge, C.; Newbury, H.J.; Ford-Lloyd, B.; Bale, J.; Pritchard, J. Exploring Plant Responses to Aphid Feeding Using a Full Arabidopsis Microarray Reveals a Small Number of Genes with Significantly Altered Expression. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2007, 97, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez De Ilarduya, O.; Xie, Q.G.; Kaloshian, I. Aphid-Induced Defense Responses in Mi-1-Mediated Compatible and Incompatible Tomato Interactions. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 2003, 16, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Li, M.; Bilgin, D.D.; Vodkin, L.O.; Hartman, G.L.; Clough, S.J. Soybean Defense Responses to the Soybean Aphid. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingler, J.; Creasy, R.; Gao, L.; Nair, R.M.; Calix, A.S.; Jacob, H.S.; Edwards, O.R.; Singh, K.B. Aphid Resistance in Medicago Truncatula Involves Antixenosis and Phloem-Specific, Inducible Antibiosis, and Maps to a Single Locus Flanked by NBS-LRR Resistance Gene Analogs. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bata, H.D.; Singh, B.B.; Singh, S.R.; Ladeinde, T.O. Inheritance of Resistance to Aphid in Cowpea. Crop Sci. 1987, 27, 892–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, G.O.; Fatokun, C.A.; Young, N.D. RFLP Mapping of an Aphid Resistance Gene in Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp). Euphytica 1996, 91, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Shi, A.; Mou, B.; Bhattarai, G.; Yang, W.; Weng, Y.; Motes, D. Association Mapping of Aphid Resistance in USDA Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) Core Collection Using SNPs. Euphytica 2017, 213, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Amatriaín, M.; Lo, S.; Herniter, I.A.; Boukar, O.; Fatokun, C.; Carvalho, M.; Castro, I.; Guo, Y.N.; Huynh, B.L.; Roberts, P.A.; et al. The UCR Minicore: A Resource for Cowpea Research and Breeding. Legume Sci. 2021, 3, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatokun, C.; Girma, G.; Abberton, M.; Gedil, M.; Unachukwu, N.; Oyatomi, O.; Yusuf, M.; Rabbi, I.; Boukar, O. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of a Mini-Core Subset from the World Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) Germplasm Collection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.C.; Barrion, A.A. Biotypes of Insect Pests of Agricultural Crops. Int. J. Trop Insect. Sci. 1987, 8, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusi, F.; Obeng-Ofori, D.; Asante, S.; Padi, F. New Sources of Resistance in Cowpea to the Cowpea Aphid (Aphis caccivora Koch) (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Ghana Sci. Assoc. 2010, 12, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.; Muñoz-Amatriaín, M.; Hokin, S.A.; Cisse, N.; Roberts, P.A.; Farmer, A.D.; Xu, S.; Close, T.J. A Genome-Wide Association and Meta-Analysis Reveal Regions Associated with Seed Size in Cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp]. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 3079–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, B.-L.; Close, T.J.; Roberts, P.A.; Hu, Z.; Wanamaker, S.; Lucas, M.R.; Chiulele, R.; Cissé, N.; David, A.; Hearne, S.; et al. Gene Pools and the Genetic Architecture of Domesticated Cowpea. Plant Genome 2013, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Amatriain, M.; Lo, S.; Herniter, I.; Guo, Y.-N.; Roberts, P.A.; Close, T.J. Development and Characterization of a Mini-Core Collection of Cowpea. In Proceedings of the Resilience Emerging from Scarcity and Abundance, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 6–9 November 2016; American Society of Agronomy; Crop Science Society of America; Soil Science Society of America: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Aravind, J.; Mukesh Sankar, S.; Wankhede, D.P.; Kaur, V. Data Analysis with AugmentedRCBD. Available online: https://aravind-j.github.io/augmentedRCBD/articles/Data_Analysis_with_augmentedRCBD.html (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Federer, W.T.; Searle, S.R. Model Considerations and Variance Vomponent Estimation in Augmented Completely Randomized and Randomized Complete Blocks Designs; Cornell University: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Amatriaín, M.; Mirebrahim, H.; Xu, P.; Wanamaker, S.I.; Luo, M.C.; Alhakami, H.; Alpert, M.; Atokple, I.; Batieno, B.J.; Boukar, O.; et al. Genome Resources for Climate-Resilient Cowpea, an Essential Crop for Food Security. Plant J. 2017, 89, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for Association Mapping of Complex Traits in Diverse Samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Xu, J.; Yin, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; et al. RMVP: A Memory-Efficient, Visualization-Enhanced, and Parallel-Accelerated Tool for Genome-Wide Association Study. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.; Patterson, N.J.; Plenge, R.M.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A.; Reich, D. Principal Components Analysis Corrects for Stratification in Genome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ersoz, E.; Lai, C.-Q.; Todhunter, R.J.; Tiwari, H.K.; Gore, M.A.; Bradbury, P.J.; Yu, J.; Arnett, D.K.; Ordovas, J.M.; et al. Mixed Linear Model Approach Adapted for Genome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, M.; Fan, B.; Buckler, E.S.; Zhang, Z. Iterative Usage of Fixed and Random Effect Models for Powerful and Efficient Genome-Wide Association Studies. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, K.J.F.; Simonsen, K.L.; McIntyre, L.M. Implementing False Discovery Rate Control: Increasing Your Power. Oikos 2005, 108, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glickman, M.E.; Rao, S.R.; Schultz, M.R. False Discovery Rate Control Is a Recommended Alternative to Bonferroni-Type Adjustments in Health Studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Jiang, C.; Huang, Z.; Torres-Jerez, I.; Chang, J.; Zhang, H.; Udvardi, M.; Liu, R.; Verdier, J. The Vigna unguiculata Gene Expression Atlas (VuGEA) from de Novo Assembly and Quantification of RNA-Seq Data Provides Insights into Seed Maturation Mechanisms. Plant J. 2016, 88, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnott, E.W. The Relation of Gene to Character in Quantitative Inheritance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1937, 23, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, B.V.; Williams, H.T.; Mar, J.C. Investigating Skewness to Understand Gene Expression Heterogeneity in Large Patient Cohorts. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togola, A.; Boukar, O.; Belko, N.; Chamarthi, S.K.; Fatokun, C.; Tamo, M.; Oigiangbe, N. Host Plant Resistance to Insect Pests of Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.): Achievements and Future Prospects. Euphytica 2017, 213, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.B.; Chambliss, O.L.; Sharma, B. Recent Advances in Cowpea Breeding. In Advances in Cowpea Research; International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA): Ibadan, Nigeria, 1997; pp. 30–49. [Google Scholar]
- Ansari, A.K.; van Emden, H.F.; Singh, S.R. Differential Reaction of Two Biotypes of Cowpea Aphid, Aphis caccivora (Koch) to Cowpea, Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp. UNISWA Res. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 1996, 1, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Close, T.J.; Wanamaker, S.; Roose, M.L.; Lyon, M. HarvEST: An EST Database and Viewing Software. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Edwards, D., Ed.; Human Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 161–177. ISBN 9781597455350. [Google Scholar]
- Pommerrenig, B.; Papini-Terzi, F.S.; Sauer, N. Differential Regulation of Sorbitol and Sucrose Loading into the Phloem of Plantago Major in Response to Salt Stress. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinders, A.; Panshyshyn, J.A.; Ward, J.M. Analysis of Transport Activity of Arabidopsis Sugar Alcohol Permease Homolog AtPLT5. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, G.K. β-Catenin in Plants and Animals: Common Players but Different Pathways. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.M.; Boyko, E.V. The Molecular Bases of Plant Resistance and Defense Responses to Aphid Feeding: Current Status. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2007, 122, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, D.C.; Drurey, C.; Zipfel, C.; Hogenhout, S.A. The Leucine-Rich Repeat Receptor-like Kinase BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE1-ASSOCIATED KINASE1 and the Cytochrome P450 PHYTOALEXIN DEFICIENT3 Contribute to Innate Immunity to Aphids in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, P.; Pandey, A.; Tiwari, M.; Chandrashekar, K.; Sidhu, O.P.; Asif, M.H.; Chakrabarty, D.; Singh, P.K.; Trivedi, P.K.; Nath, P.; et al. Modulation of Transcriptome and Metabolome of Tobacco by Arabidopsis Transcription Factor, AtMYB12, Leads to Insect Resistance. Plant Physiol. 2010, 152, 2258–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoala, T.; Edwards, M.G.; Knight, M.R.; Gatehouse, A.M.R. OXI1 Kinase Plays a Key Role in Resistance of Arabidopsis towards Aphids (Myzus Persicae). Transgenic Res. 2018, 27, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Aphid Damage Severity Experiment I | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F-value |
| Treatment | 358 | 250.46 | 0.70 | 17.90 *** |
| Check entry | 1 | 101.72 | 101.72 | 2602.31 *** |
| Test entry | 356 | 78.24 | 0.22 | 5.62 *** |
| Test vs. Check | 1 | 70.50 | 70.50 | 1803.66 *** |
| Block | 35 | 0.91 | 0.03 | 0.66 ns |
| Residuals | 37 | 1.45 | 0.04 | |
| Aphid Damage Severity Experiment II | ||||
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F-value |
| Treatment | 319 | 475.60 | 1.49 | 5.91 *** |
| Check entry | 1 | 91.40 | 91.43 | 362.67 *** |
| Test entry | 317 | 349.00 | 1.10 | 4.37 *** |
| Test vs. Check | 1 | 35.10 | 35.14 | 139.40 *** |
| Block | 34 | 6.90 | 0.20 | 0.81 ns |
| Residuals | 34 | 8.60 | 0.25 | |
| Aphid Damage Severity Experiment III | ||||
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F-value |
| Treatment | 319 | 420.20 | 1.32 | 5.50 *** |
| Check entry | 1 | 76.80 | 76.76 | 320.62 *** |
| Test entry | 317 | 310.70 | 0.98 | 4.09 *** |
| Test vs. Check | 1 | 32.80 | 32.77 | 136.89 *** |
| Block | 34 | 5.00 | 0.15 | 0.61 ns |
| Residuals | 34 | 8.10 | 0.24 | |
| Aphid Damage Severity Combined | ||||
| Source | DF | SS | MS | F-value |
| Treatment | 366 | 906.60 | 2.48 | 7.16 *** |
| Check entry | 1 | 269.30 | 269.29 | 778.07 *** |
| Test entry | 364 | 492.10 | 1.35 | 3.90 *** |
| Test vs. Check | 1 | 145.20 | 145.20 | 419.45 *** |
| Experiment | 2 | 116.60 | 58.28 | 168.39 *** |
| Residuals | 838 | 290.00 | 0.35 | |
| Statistics * | Experiment I | Experiment II | Experiment III | Combined |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 4.75 | 3.95 | 4.10 | 4.27 |
| Min | 2.51 | 1.42 | 1.42 | 2.27 |
| Max | 5.17 | 5.92 | 5.92 | 5.00 |
| SE | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| CD(α=0.05) | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.98 |
| CV (%) | 4.32 | 13.17 | 12.36 | 14.23 |
| GCV (%) | 8.94 | 23.31 | 21.01 | 23.49 |
| PCV (%) | 9.86 | 26.55 | 24.17 | 27.23 |
| H2BS (%) | 82.22 | 77.10 | 75.57 | 74.40 |
| GA | 0.80 | 1.67 | 1.54 | 1.78 |
| GAM (%) | 16.73 | 42.23 | 37.68 | 41.80 |
| Experiment | SNP Name | Chromosome | Position(bp) | Allele | −Log10(p) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2_43876 e | Vu10 | 4,096,878 | G/A | 13.19 | 8.02 | |
| 2_22525 d | Vu08 | 27,780,564 | G/T | 10.37 | 4.34 | |
| Combined | 2_24304 b | Vu02 | 24,348,915 | A/G | 6.19 | 6.06 |
| 2_28582 a | Vu01 | 40,503,572 | G/A | 4.90 | 3.84 | |
| 2_30711 c | Vu06 | 33,320,998 | G/A | 4.10 | 5.43 | |
| Experiment I | 2_43876 e | Vu10 | 4,096,878 | G/A | 6.02 | 5.49 |
| 2_16937 | Vu02 | 28,397,818 | C/T | 5.13 | 4.00 | |
| 2_37658 | Vu02 | 26,139,374 | T/C | 5.21 | 5.00 | |
| 2_30970 | Vu02 | 28,402,526 | G/A | 4.47 | 3.70 | |
| Experiment II | 2_43876 e | Vu10 | 4,096,878 | G/A | 5.09 | 5.40 |
| 2_03743 g | Vu10 | 4,104,605 | T/C | 5.47 | 5.70 | |
| 2_13144 | Vu10 | 4,058,697 | G/A | 4.43 | 4.10 | |
| 2_38695 f | Vu08 | 27,786,635 | T/C | 4.80 | 4.30 | |
| 2_22525 d | Vu08 | 27,780,564 | G/T | 4.80 | 4.34 | |
| 2_22524 | Vu08 | 27,782,280 | T/G | 4.80 | 4.30 | |
| 2_24304 b | Vu02 | 24,348,915 | A/G | 4.96 | 5.54 | |
| 2_24860 | Vu02 | 25,636,527 | T/C | 4.82 | 3.60 | |
| 2_47978 | Vu02 | 24,342,315 | A/T | 4.35 | 5.00 | |
| 2_30711 c | Vu06 | 33,320,998 | G/A | 5.41 | 5.43 | |
| 2_34496 | Vu06 | 33,320,879 | T/A | 4.60 | 4.30 | |
| 2_54768 | Vu06 | 33,347,257 | C/T | 4.62 | 4.70 | |
| Experiment III | 2_43876 e | Vu10 | 4,096,878 | G/A | 4.32 | 4.60 |
| 2_03743 g | Vu10 | 4,104,605 | T/C | 5.01 | 5.40 | |
| 2_28582 a | Vu01 | 40,503,572 | G/A | 4.56 | 4.47 | |
| 2_22525 d | Vu08 | 27,780,564 | G/T | 4.39 | 4.21 | |
| 2_38695 f | Vu08 | 27,786,635 | T/C | 4.39 | 4.20 | |
| 2_22524 | Vu08 | 27,782,280 | T/G | 4.39 | 4.20 | |
| 2_55335 | Vu08 | 35,392,403 | C/T | 4.27 | 3.40 | |
| 2_24304 b | Vu02 | 24,348,915 | A/G | 4.82 | 5.76 | |
| 2_30711 c | Vu06 | 33,320,998 | G/A | 4.17 | 4.33 |
| SNP | Chr a | Pos(Bp) b | Gene | GPos(Bp) c | GDist (Bp) d | Gene Functional Annotation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2_43876 | Vu10 | 4,096,878 | Vigun10g031100.1 | 4,094,239 | −2639 | Leucine-Rich Repeat-containing Protein |
| 2_22525 | Vu08 | 27,780,564 | Vigun08g030200.1 | 27,780,218 | −346 | Solute carrier family 45 |
| 2_24304 | Vu02 | 24,348,915 | Vigun02g088900.1 | 24,352,038 | 3123 | Cysteine-rich TM module stress tolerance (CYSTM) |
| 2_28582 | Vu01 | 40,503,572 | Vigun01g233100.1 | 40,501,388 | −2184 | PROTEIN NRT1/PTR FAMILY 5.1 |
| 2_30711 | Vu06 | 33,320,998 | Vigun06g224900.1 | 33,321,105 | 107 | DNAJ HOMOLOG SUBFAMILY C MEMBER |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ongom, P.O.; Togola, A.; Fatokun, C.; Boukar, O. A Genome-Wide Scan Divulges Key Loci Involved in Resistance to Aphids (Aphis craccivora) in Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Genes 2022, 13, 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112002
Ongom PO, Togola A, Fatokun C, Boukar O. A Genome-Wide Scan Divulges Key Loci Involved in Resistance to Aphids (Aphis craccivora) in Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Genes. 2022; 13(11):2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112002
Chicago/Turabian StyleOngom, Patrick Obia, Abou Togola, Christian Fatokun, and Ousmane Boukar. 2022. "A Genome-Wide Scan Divulges Key Loci Involved in Resistance to Aphids (Aphis craccivora) in Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata)" Genes 13, no. 11: 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112002
APA StyleOngom, P. O., Togola, A., Fatokun, C., & Boukar, O. (2022). A Genome-Wide Scan Divulges Key Loci Involved in Resistance to Aphids (Aphis craccivora) in Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata). Genes, 13(11), 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112002