Environmental Influences on the Relation between the 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome and Mental Health: A Literature Review
Abstract
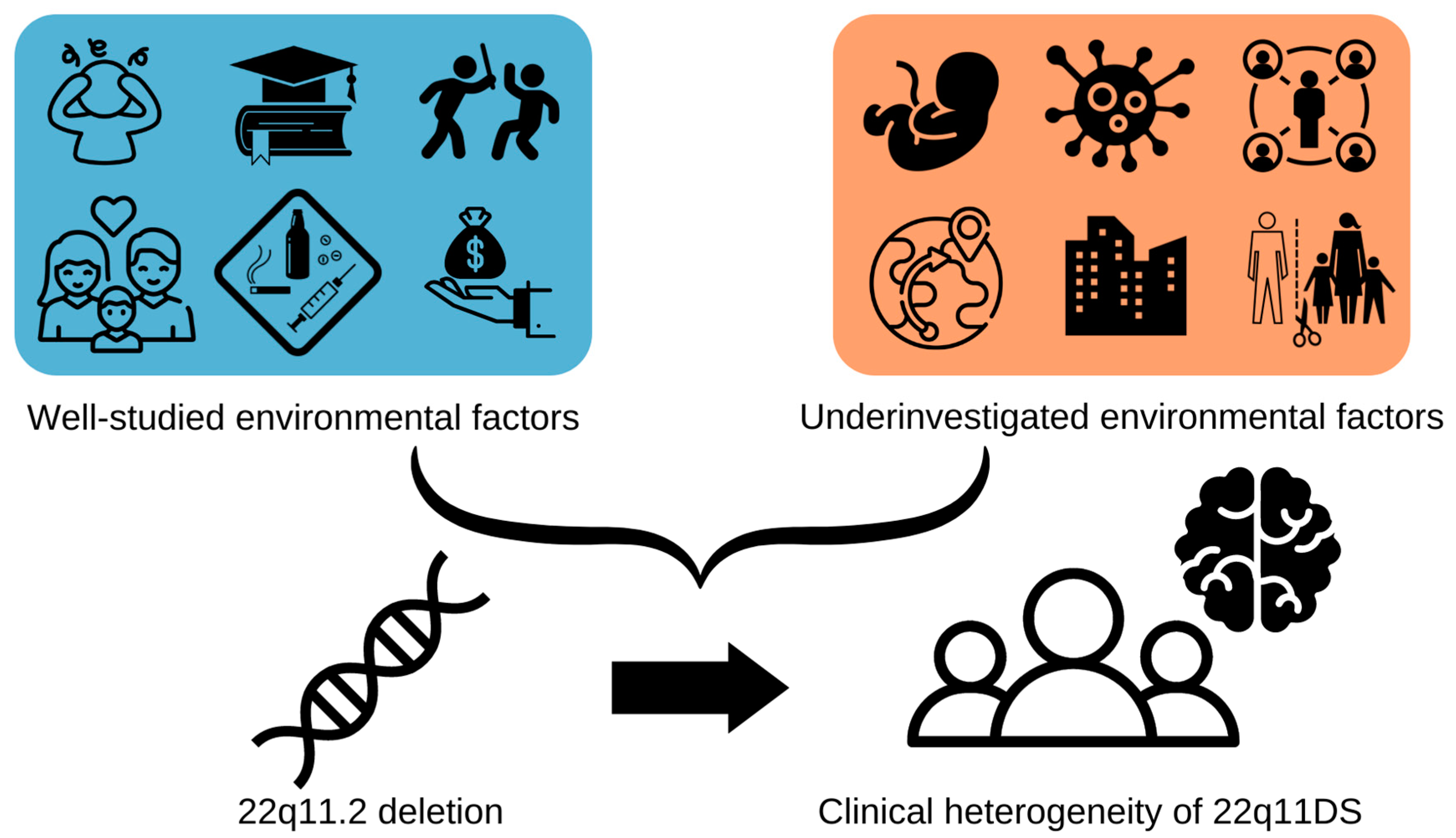
:1. Introduction
2. Within-Group Studies
3. Between-Group Studies
4. Biological Mechanisms
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Sullivan, K.E.; Marino, B.; Philip, N.; Swillen, A.; Vorstman, J.A.S.; Zackai, E.H.; Emanuel, B.S.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Morrow, B.E.; et al. 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voll, S.L.; Boot, E.; Butcher, N.J.; Cooper, S.; Heung, T.; Chow, E.W.; Silversides, C.K.; Bassett, A.S. Obesity in adults with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cirillo, A.; Lioncino, M.; Maratea, A.; Passariello, A.; Fusco, A.; Fratta, F.; Monda, E.; Caiazza, M.; Signore, G.; Esposito, A.; et al. Clinical Manifestations of 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Heart Fail. Clin. 2022, 18, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, A.S.; Chow, E.W.; AbdelMalik, P.; Gheorghiu, M.; Husted, J.; Weksberg, R. The Schizophrenia Phenotype in 22q11 Deletion Syndrome. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassett, A.S.; Chow, E.W.C. Schizophrenia and 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2008, 10, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleynen, I.; Engchuan, W.; Hestand, M.S.; Heung, T.; Holleman, A.M.; Johnston, H.R.; Monfeuga, T.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Gur, R.E.; Morrow, B.E.; et al. Genetic contributors to risk of schizophrenia in the presence of a 22q11.2 deletion. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 4496–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, M.; Debbané, M.; Bassett, A.S.; Chow, E.W.; Fung, W.L.A.; Bree, M.B.V.D.; Owen, M.; Murphy, K.C.; Niarchou, M.; Kates, W.R.; et al. Psychiatric Disorders From Childhood to Adulthood in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome: Results From the International Consortium on Brain and Behavior in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroi, N.; Takahashi, T.; Hishimoto, A.; Izumi, T.; Boku, S.; Hiramoto, T. Copy number variation at 22q11.2: From rare variants to common mechanisms of developmental neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 18, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wenger, T.L.; Miller, J.S.; DePolo, L.M.; de Marchena, A.B.; Clements, C.C.; Emanuel, B.S.; Zackai, E.H.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Schultz, R.T. 22q11.2 duplication syndrome: Elevated rate of autism spectrum disorder and need for medical screening. Mol. Autism 2016, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swillen, A.; Moss, E.; Duijff, S. Neurodevelopmental outcome in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome and management. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2018, 176, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niarchou, M.; Martin, J.; Thapar, A.; Owen, M.J.; Bree, M.B.M.V.D. The clinical presentation of attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2015, 168, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boot, E.; Bassett, A.S.; Marras, C. 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome-Associated Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 6, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stephenson, D.D.; Beaton, E.A.; Weems, C.F.; Angkustsiri, K.; Simon, T.J. Identifying patterns of anxiety and depression in children with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: Comorbidity predicts behavioral difficulties and impaired functional communications. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 276, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norkett, E.M.; Lincoln, S.H.; Gonzalez-Heydrich, J.; D’Angelo, E.J. Social cognitive impairment in 22q11 deletion syndrome: A review. Psychiatry Res. 2017, 253, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solot, C.B.; Moore, T.M.; Crowley, T.B.; Gerdes, M.; Moss, E.; McGinn, D.E.; Emanuel, B.S.; Zackai, E.H.; Gallagher, S.; Calkins, M.E.; et al. Early language measures associated with later psychosis features in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2020, 183, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milic, B.; Feller, C.; Schneider, M.; Debbané, M.; Loeffler-Stastka, H. Social cognition in individuals with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome and its link with psychopathology and social outcomes: A review. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, D.; Bolden, K.A.; Simon, T.J.; Niendam, T.A. Bullying and psychosis: The impact of chronic traumatic stress on psychosis risk in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome-a uniquely vulnerable population. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 114, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Vaessen, T.; Van Duin, E.D.A.; Kasanova, Z.; Viechtbauer, W.; Reininghaus, U.; Vingerhoets, C.; Booij, J.; Swillen, A.; Vorstman, J.A.S.; et al. Affective and psychotic reactivity to daily-life stress in adults with 22q11DS: A study using the experience sampling method. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, A.F.P.; Hobbs, D.A.; Stephenson, D.D.; Laird, R.D.; Beaton, E.A. Working Memory Impairments in Chromosome 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome: The Roles of Anxiety and Stress Physiology. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uher, R. Gene–Environment Interactions in Severe Mental Illness. Front. Psychiatry 2014, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, R.K.; Montojo, C.A.; Bearden, C.E. The 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome as a Window into Complex Neuropsychiatric Disorders Over the Lifespan. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olsen, L.; Sparsø, T.; Weinsheimer, S.M.; Dos Santos, M.B.Q.; Mazin, W.; Rosengren, A.; Sanchez, X.C.; Hoeffding, L.K.; Schmock, H.; Baekvad-Hansen, M.; et al. Prevalence of rearrangements in the 22q11.2 region and population-based risk of neuropsychiatric and developmental disorders in a Danish population: A case-cohort study. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Agrawal, A.; Bulik, C.; Andreassen, O.A.; Børglum, A.; Breen, G.; Cichon, S.; Edenberg, H.J.; Faraone, S.V.; Gelernter, J.; et al. Psychiatric Genomics: An Update and an Agenda. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sønderby, I.E.; Ching, C.R.K.; Thomopoulos, S.I.; van der Meer, D.; Sun, D.; Villalon-Reina, J.E.; Agartz, I.; Amunts, K.; Arango, C.; Armstrong, N.J.; et al. Effects of copy number variations on brain structure and risk for psychiatric illness: Large-scale studies from the ENIGMA working groups on CNVs. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 300–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, R.E.; Bassett, A.S.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Bearden, C.E.; Chow, E.; Emanuel, B.S.; Owen, M.; Swillen, A.; Van den Bree, M.; Vermeesch, J.; et al. A neurogenetic model for the study of schizophrenia spectrum disorders: The International 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome Brain Behavior Consortium. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemont, S.; Huguet, G.; Klein, M.; Chawner, S.J.; Donald, K.A.; Bree, M.B.V.D.; Sebat, J.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Constantino, J.N.; Earl, R.K.; et al. Genes To Mental Health (G2MH): A Framework to Map the Combined Effects of Rare and Common Variants on Dimensions of Cognition and Psychopathology. Am. J. Psychiatry 2022, 179, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandini, C.; Schneider, M.; Eliez, S.; Armando, M. Association Between Parental Anxiety and Depression Level and Psychopathological Symptoms in Offspring With 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briegel, W.; Andritschky, C. Psychological Adjustment of Children and Adolescents with 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome and Their Mothers’ Stress and Coping—A Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, T.M.; Hersh, J.; Schoch, K.; Curtiss, K.; Hooper, S.R.; Shashi, V. Association of the family environment with behavioural and cognitive outcomes in children with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2014, 58, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klaassen, P.; Duijff, S.; de Veye, H.S.; Beemer, F.; Sinnema, G.; Breetvelt, E.; Schappin, R.; Vorstman, J. Explaining the variable penetrance of CNVs: Parental intelligence modulates expression of intellectual impairment caused by the 22q11.2 deletion. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2016, 171, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewski, A.K.; Radoeva, P.D.; Fremont, W.; Kates, W.R.; Antshel, K.M. Is child intelligence associated with parent and sibling intelligence in individuals with developmental disorders? An investigation in youth with 22q11.2 deletion (velo-cardio-facial) syndrome. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 3582–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shashi, V.; Veerapandiyan, A.; Schoch, K.; Kwapil, T.; Keshavan, M.; Ip, E.; Hooper, S. Social skills and associated psychopathology in children with chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: Implications for interventions. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2012, 56, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gur, R.E.; White, L.K.; Shani, S.; Barzilay, R.; Moore, T.M.; Emanuel, B.S.; Zackai, E.H.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Matalon, N.; Weinberger, R.; et al. A binational study assessing risk and resilience factors in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 138, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armando, M.; Sandini, C.; Chambaz, M.; Schaer, M.; Schneider, M.; Eliez, S. Coping Strategies Mediate the Effect of Stressful Life Events on Schizotypal Traits and Psychotic Symptoms in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, S525–S535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingerhoets, C.; Van Oudenaren, M.J.; Bloemen, O.J.; Boot, E.; Van Duin, E.D.; Evers, L.J.; Fiksinski, A.M.; Breetvelt, E.J.; Palmer, L.D.; Vergaelen, E.; et al. Low prevalence of substance use in people with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Br. J. Psychiatry 2019, 215, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serur, Y.; Sher-Censor, E.; Sofrin-Frumer, D.; Daon, K.; Sobol-Havia, D.; Weinberger, R.; Shulman, C.; Gothelf, D. Parental Expressed Emotion, Parenting Stress, and Behavioral Problems of Young Children with 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome and Idiopathic Autism Spectrum Disorder. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashi, V.; Keshavan, M.; Kaczorowski, J.; Schoch, K.; Lewandowski, K.E.; McConkie-Rosell, A.; Hooper, S.R.; Kwapil, T.R. Socioeconomic Status and Psychological Function in Children with Chromosome 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome: Implications for Genetic Counseling. J. Genet. Couns. 2010, 19, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Duin, E.D.; Vaessen, T.; Kasanova, Z.; Viechtbauer, W.; Reininghaus, U.; Saalbrink, P.; Vingerhoets, C.; Hernaus, D.; Booij, J.; Swillen, A.; et al. Lower cortisol levels and attenuated cortisol reactivity to daily-life stressors in adults with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 106, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Scheibler, E.N.M.M.; van Amelsvoort, T.A.M.J.; Vingerhoets, C.; van Eeghen, A.M.; Boot, E. Post-traumatic stress in adults with 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. BJPsych Open 2022, 8, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor-Graae, E.; Selten, J.-P. Schizophrenia and Migration: A Meta-Analysis and Review. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibber, M.S.; Walji, F.; Kirkbride, J.B.; Huddy, V. The association between income inequality and adult mental health at the subnational level—A systematic review. Soc. Psychiatry 2022, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samele, C.; Patel, M.; Boydell, J.; Leese, M.; Wessely, S.; Murray, R. Physical illness and lifestyle risk factors in people with their first presentation of psychosis. Soc. Psychiatry 2007, 42, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayatbakhsh, R.; Clavarino, A.M.; Williams, G.M.; Bor, W.; O’Callaghan, M.J.; Najman, J.M. Family structure, marital discord and offspring’s psychopathology in early adulthood: A prospective study. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2013, 22, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, C.; Kirkbride, J.; Hutchinson, G.; Craig, T.; Morgan, K.; Dazzan, P.; Boydell, J.; Doody, G.A.; Jones, P.B.; Murray, R.M.; et al. Cumulative social disadvantage, ethnicity and first-episode psychosis: A case-control study. Psychol. Med. 2008, 38, 1701–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pinto, A.; Vega, P.; Ibáñez, B.; Mosquera, F.; Barbeito, S.; Gutiérrez, M.; De Azúa, S.R.; Ruiz, I.; Vieta, E. Impact of cannabis and other drugs on age at onset of psychosis. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2008, 69, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.X.; Yi, J.J.; Calkins, M.E.; Whinna, D.A.; Kohler, C.G.; Souders, M.C.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Zackai, E.H.; Emanuel, B.S.; Gur, R.C. Psychiatric disorders in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome are prevalent but undertreated. Psychol. Med. 2014, 44, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clayton, D.G. Prediction and Interaction in Complex Disease Genetics: Experience in Type 1 Diabetes. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shieh, G. Detecting Interaction Effects in Moderated Multiple Regression With Continuous Variables Power and Sample Size Considerations. Organ. Res. Methods 2009, 12, 510–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Ching, C.R.K.; Lin, A.; Forsyth, J.K.; Kushan, L.; Vajdi, A.; Jalbrzikowski, M.; Hansen, L.; Villalon-Reina, J.E.; Qu, X.; et al. Large-scale mapping of cortical alterations in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome: Convergence with idiopathic psychosis and effects of deletion size. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1822–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schreiner, M.J.; Karlsgodt, K.H.; Uddin, L.Q.; Chow, C.; Congdon, E.; Jalbrzikowski, M.; Bearden, C.E. Default mode network connectivity and reciprocal social behavior in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 2014, 9, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkstok, J.R.; Boot, E.; Bassett, A.S.; Hiroi, N.; Butcher, N.J.; Vingerhoets, C.; Vorstman, J.A.S.; van Amelsvoort, T.A.M.J. Neurobiological perspective of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Lancet Psychiatry 2019, 6, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayiorgou, M.; Gogos, J.A. The molecular genetics of the 22q11-associated schizophrenia. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 132, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fénelon, K.; Mukai, J.; Xu, B.; Hsu, P.-K.; Drew, L.J.; Karayiorgou, M.; Fischbach, G.D.; MacDermott, A.B.; Gogos, J.A. Deficiency of Dgcr8, a gene disrupted by the 22q11.2 microdeletion, results in altered short-term plasticity in the prefrontal cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4447–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armando, M.; Papaleo, F.; Vicari, S. COMT Implication in Cognitive and Psychiatric Symptoms in Chromosome 22q11 Microdeletion Syndrome: A Selective Review. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 11, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Li, X.; Amendt, B.A. Understanding the Role of Tbx1 as a Candidate Gene for 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2013, 13, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, G.; Harper, K.M.; Hiramoto, T.; Sawamura, T.; Lee, M.; Kang, G.; Tanigaki, K.; Buell, M.; Geyer, M.A.; Trimble, W.S.; et al. Sept5 deficiency exerts pleiotropic influence on affective behaviors and cognitive functions in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natarajan, S.K.; Zhu, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Demers, A.J.; Zimmerman, M.C.; Simpson, M.A.; Becker, D.F. Proline dehydrogenase is essential for proline protection against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Biochemistry of Oxidative Stress. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1986, 25, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Shin, C. Emerging roles of DROSHA beyond primary microRNA processing. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Janicki-Deverts, D.; Miller, G.E. Psychological Stress and Disease. JAMA 2007, 298, 1685–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.; Doyle, W.J.; Turner, R.B.; Alper, C.M.; Skoner, D.P. Childhood Socioeconomic Status and Host Resistance to Infectious Illness in Adulthood. Psychosom. Med. 2004, 66, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissinen, E.; Männistö, P.T. Biochemistry and Pharmacology of Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Inhibitors. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2010, 95, 73–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craddock, N.; Owen, M.J.; O’Donovan, M.C. The catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT) gene as a candidate for psychiatric phenotypes: Evidence and lessons. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voelker, P.; Sheese, B.; Rothbart, M.; Posner, M. Variations in catechol-O-methyltransferase gene interact with parenting to influence attention in early development. Neuroscience 2009, 164, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collip, D.; Van Winkel, R.; Peerbooms, O.; Lataster, T.; Thewissen, V.; Lardinois, M.; Drukker, M.; Rutten, B.P.; Van Os, J.; Myin-Germeys, I. COMT Val158Met-Stress Interaction in Psychosis: Role of Background Psychosis Risk. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2010, 17, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolassa, I.-T.; Kolassa, S.; Ertl, V.; Papassotiropoulos, A.; De Quervain, D.J.-F. The Risk of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder After Trauma Depends on Traumatic Load and the Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Val158Met Polymorphism. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, N.; Bergen, S.E. Environmental Risk Factors for Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder and Their Relationship to Genetic Risk: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 686666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramoto, T.; Sumiyoshi, A.; Yamauchi, T.; Tanigaki, K.; Shi, Q.; Kang, G.; Ryoke, R.; Nonaka, H.; Enomoto, S.; Izumi, T.; et al. Tbx1, a gene encoded in 22q11.2 copy number variant, is a link between alterations in fimbria myelination and cognitive speed in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Wang, H. A study of the relationship between adverse childhood experiences, life events, and executive function among college students in China. Psicol. Reflex. Crit. 2018, 31, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodeo, D.A.; Lai, C.-Y.; Hassan, O.; Mukamel, E.A.; Behrens, M.M.; Powell, S.B. Maternal immune activation impairs cognitive flexibility and alters transcription in frontal cortex. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 125, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olver, J.S.; Pinney, M.; Maruff, P.; Norman, T.R. Impairments of Spatial Working Memory and Attention Following Acute Psychosocial Stress. Stress Health 2015, 31, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, J.H.; Kawamata, H.; Yoo, M.S.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, S.; Dawson, T.M.; Zhang, H.; Sulzer, D.; Yang, L.; et al. Neurotoxicity and behavioral deficits associated with Septin 5 accumulation in dopaminergic neurons. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2021, 397, 2284–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, S.M. Environmental Toxins and Parkinson’s Disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2014, 54, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiu, E.; Arru, G.; Hosseiniporgham, S.; Niegowska, M.; Sechi, G.; Zarbo, I.R.; Sechi, L.A. Inflammation, Infectious Triggers, and Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kruszka, P.; Addissie, Y.A.; McGinn, D.E.; Porras, A.R.; Biggs, E.; Share, M.; Crowley, T.B.; Chung, B.H.Y.; Mok, G.T.K.; Mak, C.C.Y.; et al. 22q11.2 deletion syndrome in diverse populations. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2017, 173, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botto, L.D.; May, K.; Fernhoff, P.M.; Correa, A.; Coleman, K.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Merritt, R.K.; O’Leary, L.A.; Wong, L.-Y.; Elixson, E.M.; et al. A Population-Based Study of the 22q11.2 Deletion: Phenotype, Incidence, and Contribution to Major Birth Defects in the Population. Pediatrics 2003, 112, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiksinski, A.M.; Schneider, M.; Zinkstok, J.; Baribeau, D.; Chawner, S.J.R.A.; Vorstman, J.A.S. Neurodevelopmental Trajectories and Psychiatric Morbidity: Lessons Learned From the 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2021, 23, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, A.; Jain, M.; Kalsi, A.K. Mosaicism in 22q11.2 microdeletion syndrome. J. Clin. Diagnostic Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, A.S.; Lowther, C.; Merico, D.; Costain, G.; Chow, E.W.C.; Van Amelsvoort, T.; McDonald-McGinn, D.; Gur, R.E.; Swillen, A.; Bree, M.V.D.; et al. Rare Genome-Wide Copy Number Variation and Expression of Schizophrenia in 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrow, B.E.; McDonald-McGinn, D.M.; Emanuel, B.S.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Scambler, P.J. Molecular genetics of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2018, 176, 2070–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Age Range | Sample Size | Environmental Factor | Outcome Measure | Significance * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within 22q11DS | |||||
| Parental influence | |||||
| Sandini et al., 2020 [27] | Patients > 11 years old | 103 patients in a total sample | Parental anxiety and depression | Children’s psychopathology | + |
| Briegel and Andritschky 2021 [28] | 4–14 years old and their mothers | 41 children for the analysis | Maternal stress | Children’s behaviour problems | - |
| Allen et al., 2014 [29] | 9–18 years old | 48 children and adolescents | Parenting style | Children’s behaviour problems | + |
| Klaassen et al., 2016 [30] | 5.2–15.9 years old | 171 children | Parental Intelligence | The intelligence of the offspring | + |
| Socio-economic status (SES) | |||||
| Olszewski et al., 2014 [31] | 11.8 ± 2.0 years old | 73 children | Parental education | The intelligence of the offspring | + |
| Shashi et al., 2012 [32] | 10.5 ± 2.6 years old | 66 children | Parental SES | Social competency | + |
| Stress | |||||
| Gur et al., 2021 [33] | 24.6 ± 9.3 years old | 80 patients | Peer victimisation | Reports of anxiety/depression | + |
| Armando et al., 2018 [34] | 12 to 25 years old | 59 patients | Past stress load | Dysfunctional coping strategies | + |
| Substances | |||||
| Vingerhoets et al., 2019 [35] | 30.91 ± 12.65 years old | 434 adults | Substance use | Psychosis | - |
| Between-groups | |||||
| Parental influence | |||||
| Serur et al., 2022 [36] | 3–8 years old | 24 children with 22q11DS, 28 children with idiopathic ASD and 23 typically developed children | Parental expressed emotions | Children’s behavioural problems | - |
| Socio-economic status (SES) | |||||
| Shashi et al., 2010 [37] | 10.2 ± 2.6 years old for patients | 65 children with 22q11DS and 52 controls | SES | Cognition | - |
| Stress | |||||
| van Duin et al., 2019 [38] | 34.11 ± 9.81 years old for patients | 27 adults with 22q11DS and 24 age/sex-matched healthy controls | Activity-related stress | Cortisol reactivity | + |
| Schneider et al., 2020 [18] | 34.11 ± 9.81 years old for patients | 27 adults with 22q11DS and 24 matched controls | Daily-life stressors | Affective and psychotic reactivity | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Snihirova, Y.; Linden, D.E.J.; van Amelsvoort, T.; van der Meer, D. Environmental Influences on the Relation between the 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome and Mental Health: A Literature Review. Genes 2022, 13, 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112003
Snihirova Y, Linden DEJ, van Amelsvoort T, van der Meer D. Environmental Influences on the Relation between the 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome and Mental Health: A Literature Review. Genes. 2022; 13(11):2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112003
Chicago/Turabian StyleSnihirova, Yelyzaveta, David E. J. Linden, Therese van Amelsvoort, and Dennis van der Meer. 2022. "Environmental Influences on the Relation between the 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome and Mental Health: A Literature Review" Genes 13, no. 11: 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112003
APA StyleSnihirova, Y., Linden, D. E. J., van Amelsvoort, T., & van der Meer, D. (2022). Environmental Influences on the Relation between the 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome and Mental Health: A Literature Review. Genes, 13(11), 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112003





