Differential Expression Profiles and Bioinformatics Analysis of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in a Chinese Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
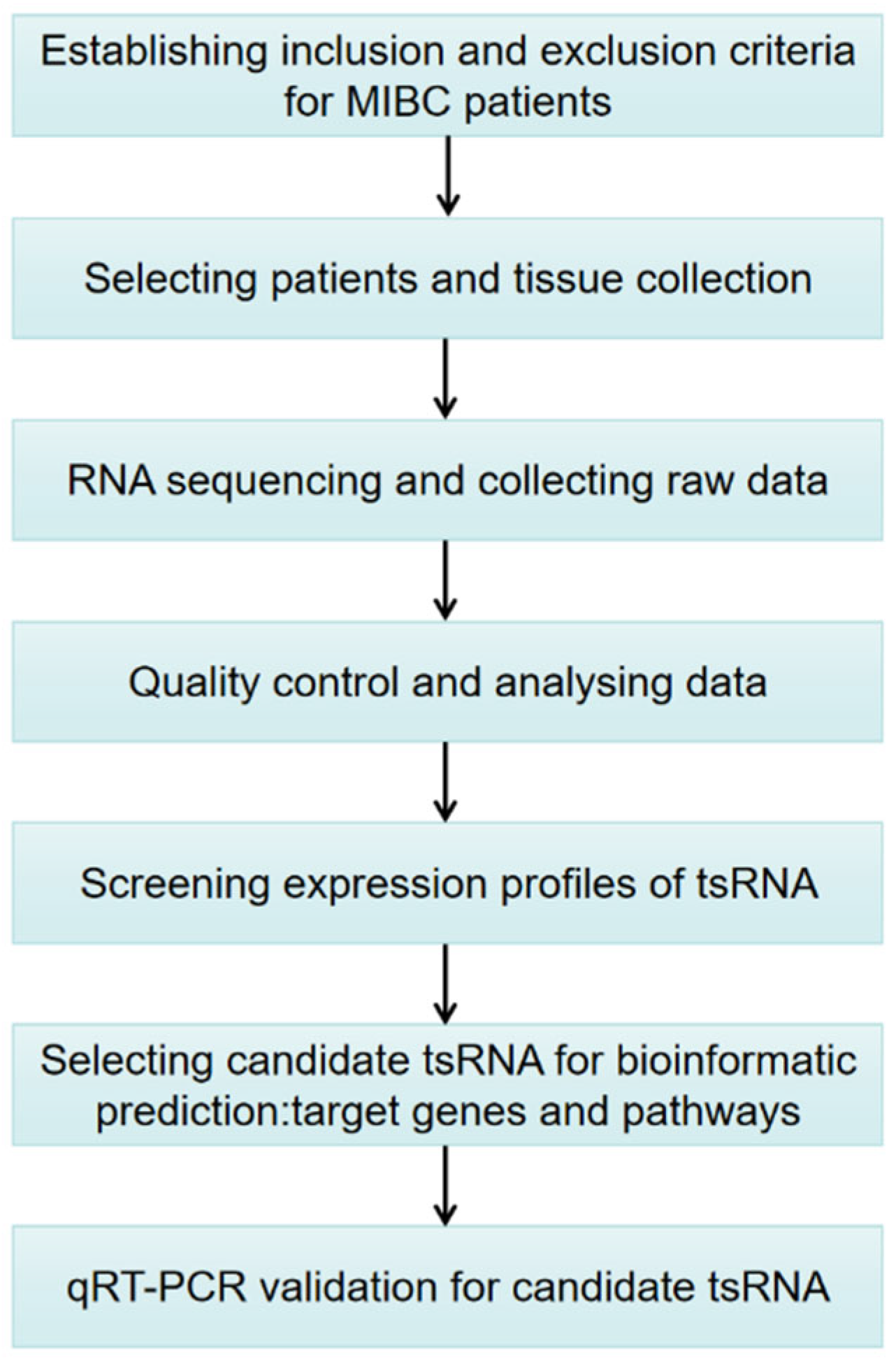
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MIBC Patients and Sample Collection
2.2. Pre-Sequencing Preparation
2.3. Pretreatment of tsRNA and Library Preparation
2.4. Libraries Denaturation and tsRNA Sequencing
2.5. Data Collection and Analysis
2.6. Bioinformatic Prediction
2.7. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Database and Accession Numbers
3. Results
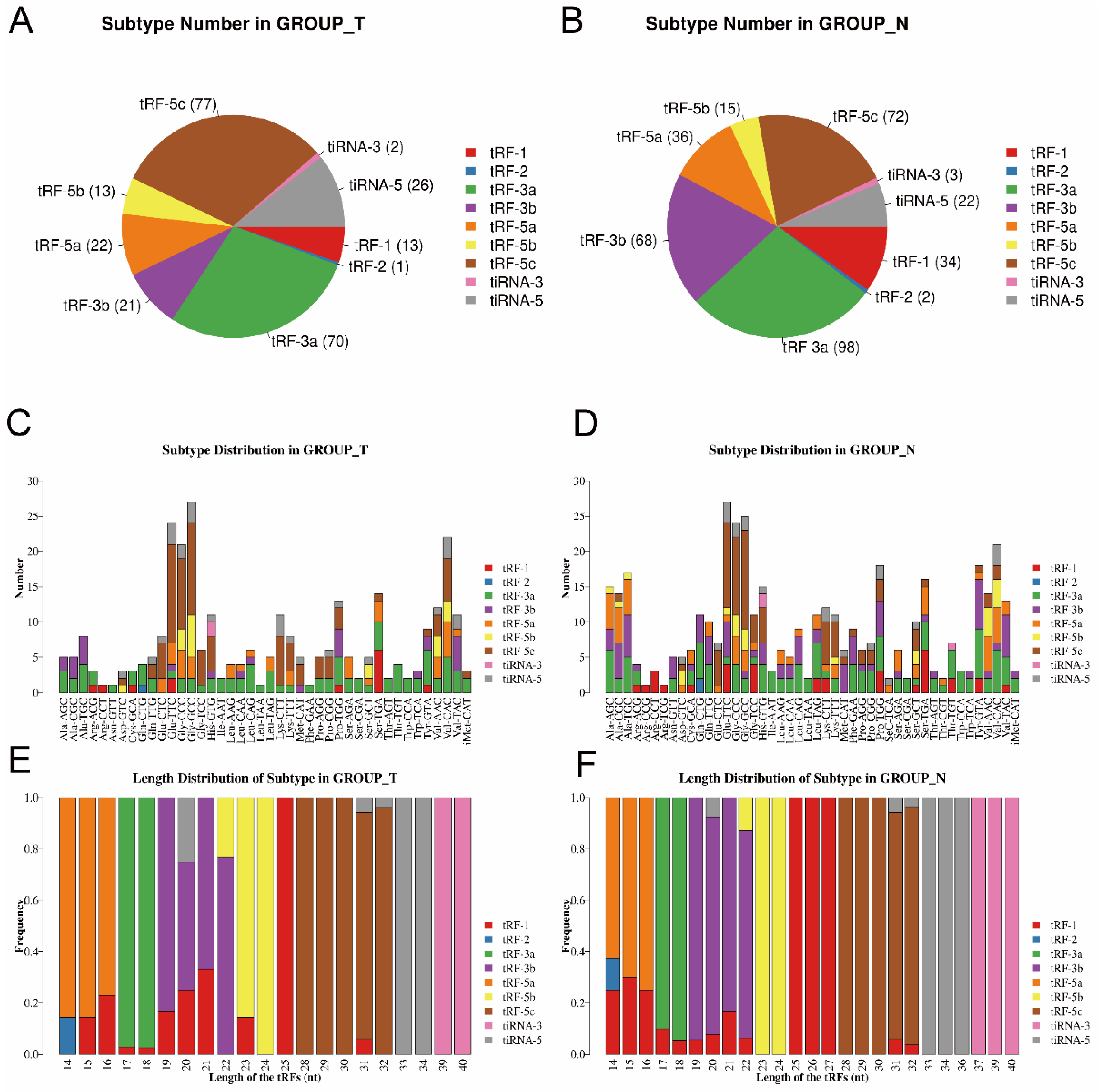
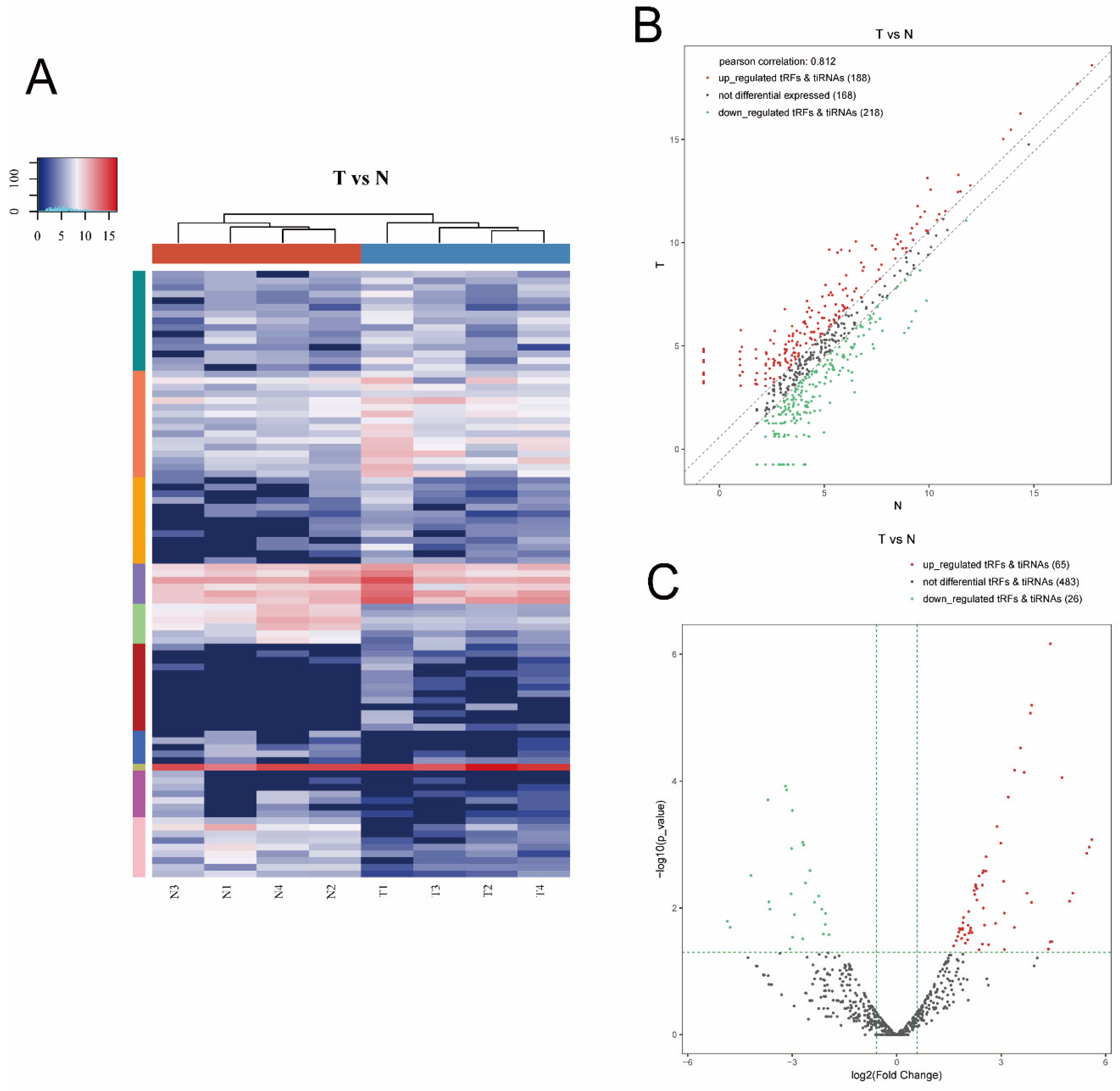
3.1. Altered Expression Profiles of tsRNAs in MIBC Tissues
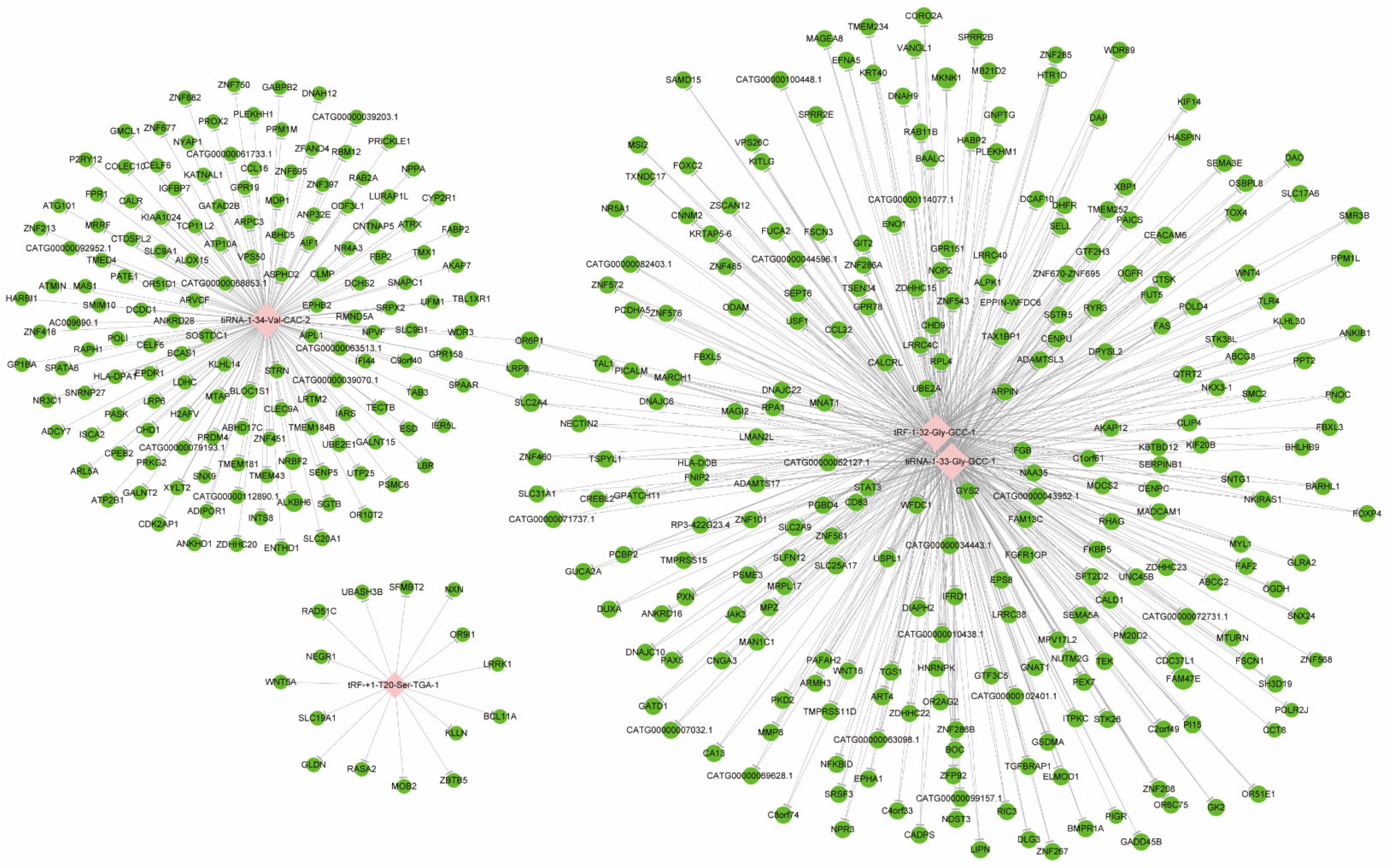
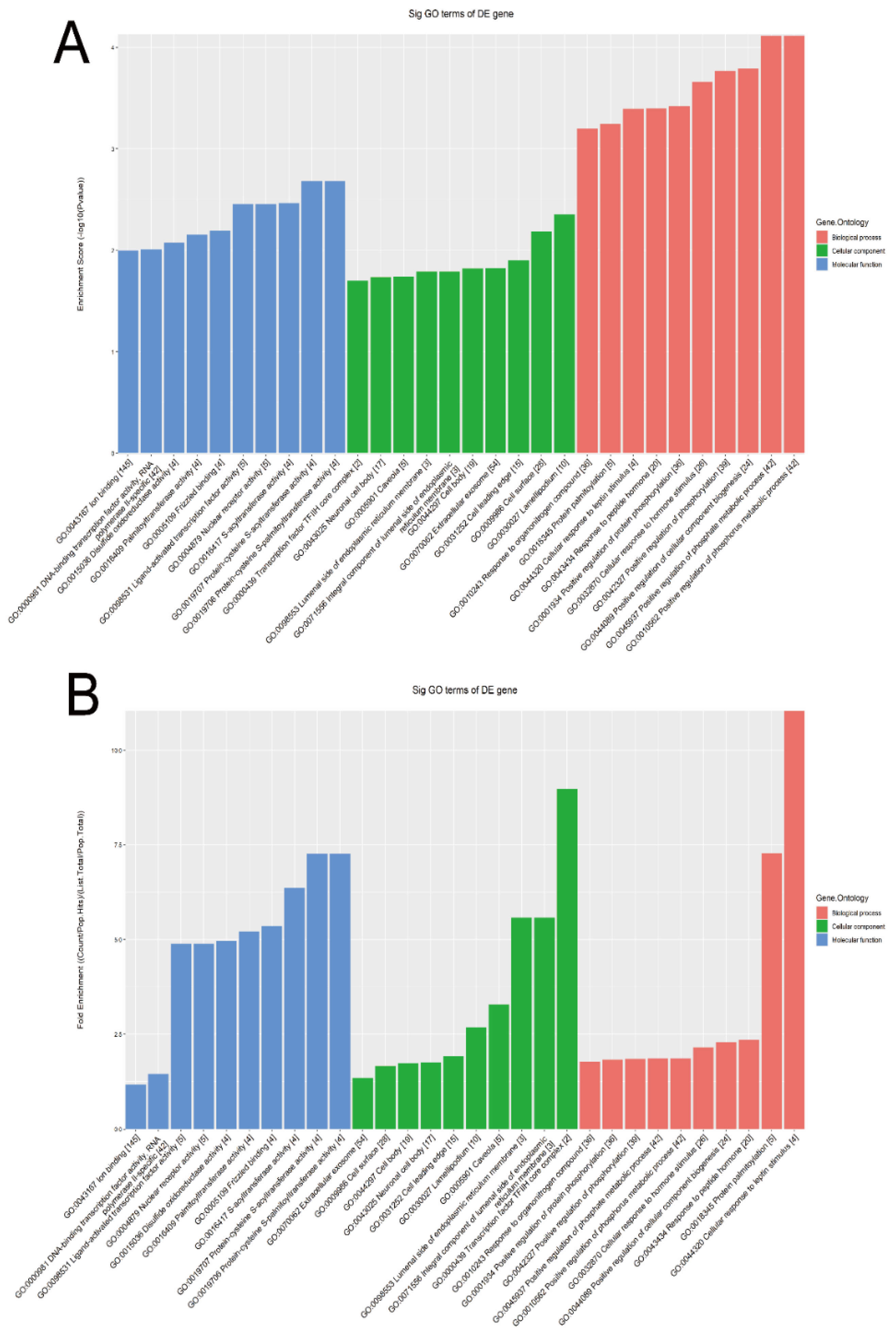
3.2. Target Gene Prediction
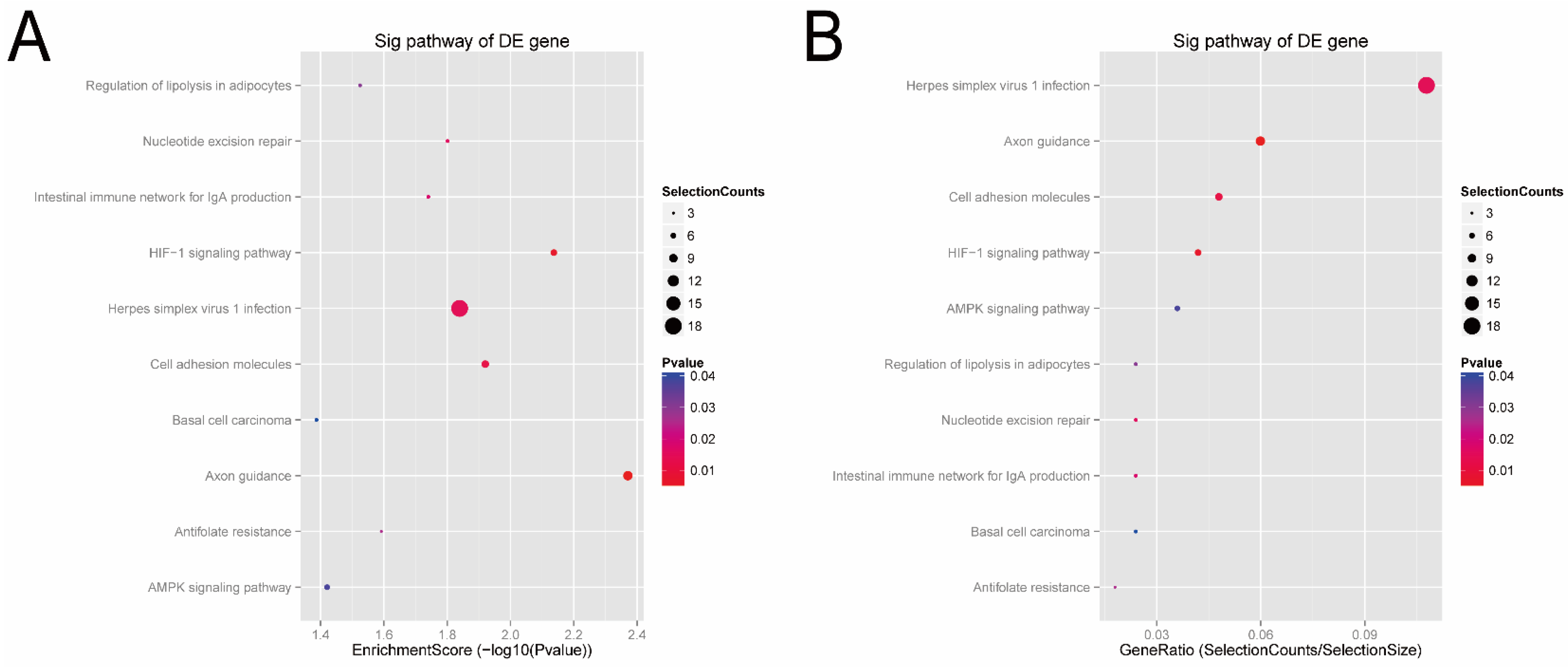
3.3. Signal Pathways Analysis
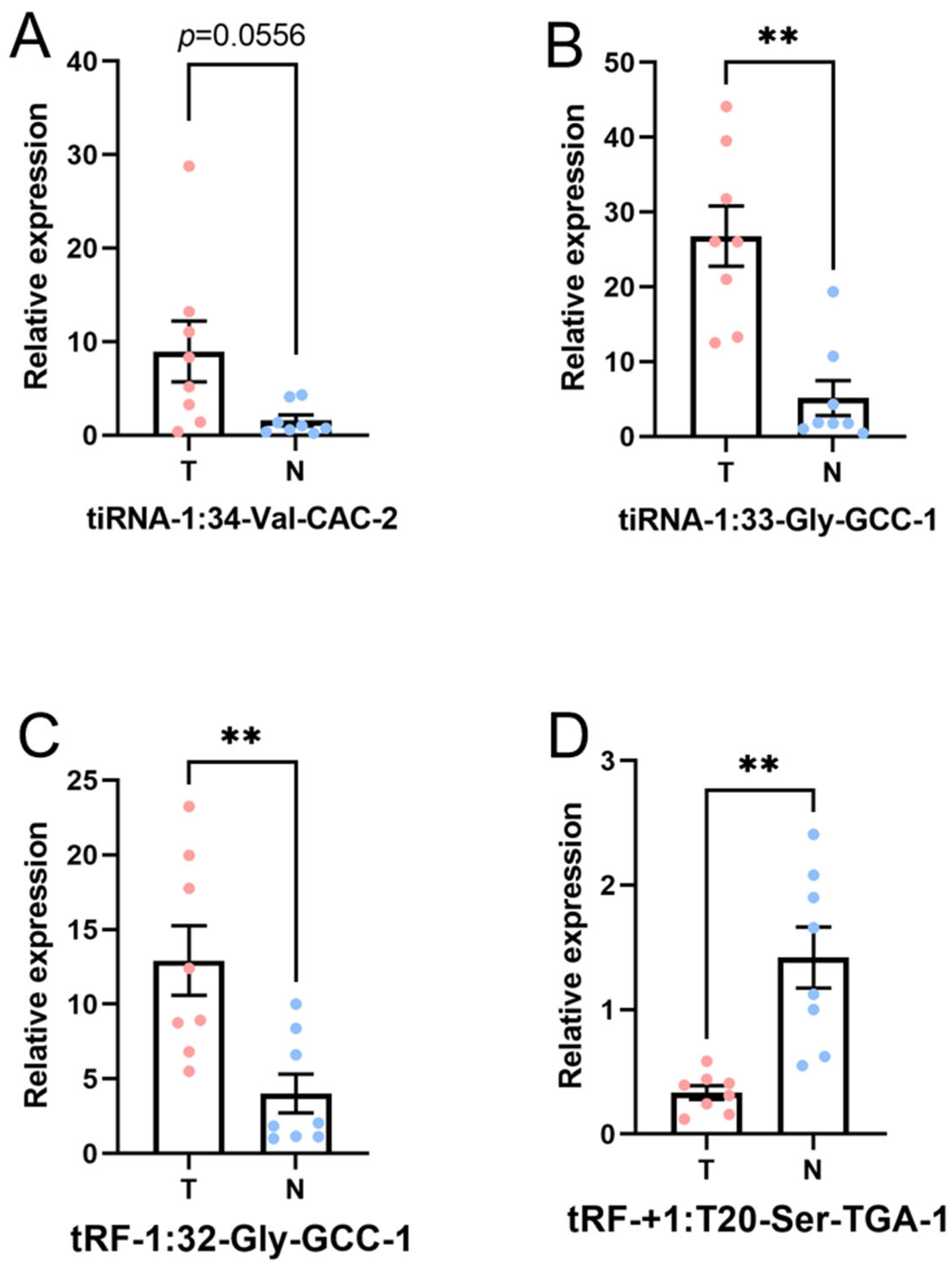
3.4. Verification by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenis, A.T.; Lec, P.M.; Chamie, K.; Mshs, M.D. Bladder Cancer. JAMA 2020, 324, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.D.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanli, O.; Dobruch, J.; Knowles, M.A.; Burger, M.; Alemozaffar, M.; Nielsen, M.E.; Lotan, Y. Bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Packiam, V.; Nottingham, C.; Steinberg, G.; Smith, N.D.; Patel, S. Upstaging of nonurothelial histology in bladder cancer at the time of surgical treatment in the National Cancer Data Base. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2017, 35, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yafi, F.A.; Aprikian, A.G.; Chin, J.L.; Fradet, Y.; Izawa, J.; Estey, E.; Fairey, A.; Rendon, R.; Cagiannos, I.; Lacombe, L.; et al. Contemporary outcomes of 2287 patients with bladder cancer who were treated with radical cystectomy: A Canadian multicentre experience. BJU Int. 2011, 108, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woldu, S.L.; Bagrodia, A.; Lotan, Y. Guideline of guidelines: Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2017, 119, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faiena, I.; Rosser, C.J.; Chamie, K.; Furuya, H. Diagnostic biomarkers in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhanvadia, S.K. Bladder Cancer Survivorship. Curr. Urol. Rep. 2018, 19, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.G.; Kim, J.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Bellmunt, J.; Guo, G.; Cherniack, A.D.; Hinoue, T.; Laird, P.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Akbani, R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cell 2018, 174, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siracusano, S.; Rizzetto, R.; Porcaro, A.B. Bladder cancer genomics. Urol. J. 2020, 87, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Guo, B.; Wei, Y.; Lan, T.; Wen, S.; Li, G. Impact of Long Non-coding RNAs Associated with Microenvironment on Survival for Bladder Cancer Patients. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 567200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Bu, Q.; Zeng, M.; Xia, D.; Wu, A. MicroRNA-93 promotes bladder cancer proliferation and invasion by targeting PEDF. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xia, S.; Lin, D.; Xiao, B.; Xiu, Y. Novel circRNA_0071196/miRNA-19b-3p/CIT axis is associated with proliferation and migration of bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, F.J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Oncology. Cell 2019, 179, 1033–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, M.B.; Stephenson, M.L.; Scott, J.F.; Hecht, L.I.; Zamecnik, P.C. A soluble ribonucleic acid intermediate in protein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1958, 231, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ling, Z.; Winnicki, A.; Xu, L.; Xu, S.; Gong, T.; Jiang, B.; Huang, G.; Deng, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of a tRNA-Derived Small RNA in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 701440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G.; Choudury, S.G.; Slotkin, R.K. tRNA-derived small RNAs target transposable element transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 5142–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Tolkach, Y.; Schmidt, D.; Kristiansen, G.; Müller, S.C.; Ellinger, J. 5′-tRNA Halves are Dysregulated in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Urol. 2018, 199, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Tolkach, Y.; Schmidt, D.; Muders, M.; Kristiansen, G.; Müller, S.C.; Ellinger, J. tRNA-halves are prognostic biomarkers for patients with prostate cancer. In Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 36, pp. 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, X. A tRNA-derived fragment (tRF-3001b) aggravates the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting autophagy. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yan, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Feng, G.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Sperm tsRNAs contribute to intergenerational inheritance of an acquired metabolic disorder. Science 2016, 351, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; He, W.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, Z.; Cao, Y. tRNA-derived fragment tRF-03357 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 6371–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mo, D.; He, F.; Zheng, J.; Chen, H.; Tang, L.; Yan, F. tRNA-Derived Fragment tRF-17-79MP9PP Attenuates Cell Invasion and Migration via THBS1/TGF-β1/Smad3 Axis in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, M.A.; Avgeris, M.; Levis, P.; Papasotiriou, E.C.; Kotronopoulos, G.; Stravodimos, K.; Scorilas, A. tRNA-Derived Fragments (tRFs) in Bladder Cancer: Increased 5’-tRF-LysCTT Results in Disease Early Progression and Patients’ Poor Treatment Outcome. Cancers 2020, 12, 3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magers, M.J.; Lopez Beltran, A.; Montironi, R.; Williamson, S.R.; Kaimakliotis, H.Z.; Cheng, L. Staging of bladder cancer. Histopathology 2019, 74, 112–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopezbeltran, A. Non-Invasive Urothelial Neoplasms: According to the Most Recent WHO Classification. Eur. Urol. 2004, 46, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C. A comprehensive expression profile of tRNA-derived fragments in papillary thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Peng, C.; Chen, X.; et al. Differential Expression Profiles and Function Predictions for tRFs & tiRNAs in Skin Injury Induced by Ultraviolet Irradiation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 707572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Feng, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Du, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, M.; Gao, F.; et al. Differential Expression Profiles and Functional Prediction of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs in Rats After Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Mccarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.K.; Fuchs, G.; Wang, S.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Park, H.; Roy-Chaudhuri, B.; Li, P.; Xu, J.; Chu, K.; et al. A transfer-RNA-derived small RNA regulates ribosome biogenesis. Nature 2017, 552, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Anaya, J.; Mudunuri, S.B.; Dutta, A. Meta-analysis of tRNA derived RNA fragments reveals that they are evolutionarily conserved and associate with AGO proteins to recognize specific RNA targets. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Mei, J.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ma, B.; Li, W. A novel tsRNA-16902 regulating the adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.F.; Guo, S.C.; Liu, T.; Cui, H.; Feng, D.; Yang, A.; Cheng, Z.; Luo, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y. Integrative analysis of transcriptomes highlights potential functions of transfer-RNA-derived small RNAs in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Aging 2020, 12, 22794–22813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borek, E.; Baliga, B.S.; Gehrke, C.W.; Kuo, C.W.; Belman, S.; Troll, W.; Waalkes, T.P. High turnover rate of transfer RNA in tumor tissue. Cancer Res. 1977, 37, 3362–3366. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Gao, F.; Yang, M.; Du, L.; Li, J. Pathological significance of tRNA-derived small RNAs in neurological disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Gao, P.; Zhang, W.; Qu, B.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z. A 3′-tRNA-derived fragment enhances cell proliferation, migration and invasion in gastric cancer by targeting FBXO47. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 690, 108467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, M.; Xia, Y.; Fu, Z.; Ge, H.; Wang, S.; Xie, H. Hypoxia-induced tRNA-derived fragments, novel regulatory factor for doxorubicin resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8740–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Shi, M.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Deng, X.; Peng, C.; Shen, B.; Xu, H.; Chen, H. Serum tRNA-derived small RNAs as potential novel diagnostic biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goodarzi, H.; Liu, X.; Nguyen, H.C.B.; Zhang, S.; Fish, L.; Tavazoie, S.F. Endogenous tRNA-Derived Fragments Suppress Breast Cancer Progression via YBX1 Displacement. Cell 2015, 161, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sobala, A.; Hutvagner, G. Small RNAs derived from the 5’ end of tRNA can inhibit protein translation in human cells. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loras, A.; Segovia, C.; Ruiz-Cerdá, J.L. Epigenomic and Metabolomic Integration Reveals Dynamic Metabolic Regulation in Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Qu, G.Y.; Wu, Y.P.; Lin, Y.Z.; Chen, D.N.; Li, X.D.; Chen, S.H.; Huang, J.B.; Zheng, Q.S.; Xue, X.Y.; et al. ARPC4 promotes bladder cancer cell invasion and is associated with lymph node metastasis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vantaku, V.; Dong, J.; Ambati, C.R.; Perera, D.; Donepudi, S.R.; Amara, C.S.; Putluri, V.; Ravi, S.S.; Robertson, M.J.; Piyarathna, D.W.B.; et al. Multi-omics Integration Analysis Robustly Predicts High-Grade Patient Survival and Identifies CPT1B Effect on Fatty Acid Metabolism in Bladder Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3689–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Ryu, D.; Kim, W.; Kim, S. Aberrantly expressed microRNAs in the context of bladder tumorigenesis. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2016, 57, S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortada, W.I.; Awadalla, A.; Khater, S.; Ahmed, A.; Hamam, E.T.; El-Zayat, M.; Shokeir, A.A. Copper and zinc levels in plasma and cancerous tissues and their relation with expression of VEGF and HIF-1 in the pathogenesis of muscle invasive urothelial bladder cancer: A case-controlled clinical study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2020, 27, 15835–15841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Wen, X.; Zhang, S. Identification of key candidate genes and biological pathways in bladder cancer. PeerJ 2018, 6, e6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, G.R.; Horvath, A.; Annels, N.E.; Pencavel, T.; Metcalf, S.; Seth, R.; Peschard, P.; Price, T.; Coffin, R.S.; Mostafid, H.; et al. Combination of a fusogenic glycoprotein, pro-drug activation and oncolytic HSV as an intravesical therapy for superficial bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Number | Age (Year) | Sex | TNM Stage and Grade | Tumor Size and Pathological Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 65 | Female | T3aN2M0 High grade | Multifocal tumor with the biggest size of 3.0 cm × 2.5 cm located in the left front bladder wall; urothelium carcinoma with necrosis and 3/4 lymph node metastasis beside the left iliac blood vessels |
| 2 | 64 | Male | T3bN1M0 High grade | Multifocal tumor with the biggest size of 8.0 cm × 4.3 cm located in the posterior bladder wall; urothelium carcinoma with neurovascular invasion and 1/3 lymph node metastasis beside the right iliac blood vessels |
| 3 | 80 | Male | T3aN0M0 High grade | Multifocal tumor with the biggest size of 4.0 cm × 3.3 cm located in the right bladder wall; urothelium carcinoma without neurovascular invasion and node metastasis |
| 4 | 63 | Male | T3aN0Mx High grade | Multifocal tumor with the biggest size of 3.4 cm × 2.7 cm located in the left bladder wall; urothelium carcinoma with blood vessel invasion and without node metastasis |
| 5 | 78 | Male | T2aN2Mx High grade | Unifocal tumor with the size of 3.8 cm × 2.6 cm located in the left front bladder wall; urothelium carcinoma with lymphatic vessel invasion and with 2/3 lymph node metastasis beside the left iliac blood vessels |
| 6 | 77 | Male | T2aN0Mx High grade | Unifocal tumor with the size of 3.0 cm × 1.8 cm located in the right bladder wall; urothelium carcinoma with vascular tumor thrombus and without lymph node metastasis |
| 7 | 65 | Male | T3aN0Mx High grade | Multifocal tumor with the biggest size of 1.8 cm × 1.6 cm located in the posterior wall; urothelium carcinoma with vascular tumor thrombus and without lymph node metastasis |
| 8 | 61 | Male | T2aN0Mx High grade | Multifocal tumor with the biggest size of 1.3 cm × 1.2 cm located in the right wall; urothelium carcinoma with vascular tumor thrombus and without lymph node metastasis |
| Gene Name | Type | Length | Fold Change | p-Value | q-Value | Regulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tRF-+1:T23-chrM.Glu-TTC | tRF-1 | 23 | 48.724 | 8.305 × 10−4 | 0.034 | Up |
| tRF-1:29-Gln-TTG-1-M3 | tRF-5c | 29 | 46.138 | 1.093 × 10−3 | 0.035 | Up |
| tRF-1:28-Pro-AGG-1-M6 | tRF-5c | 28 | 44.035 | 1.372 × 10−3 | 0.039 | Up |
| tRF-+1:T33-chrM.Phe-GAA-M1-31:C>T | tRF-1 | 33 | 33.304 | 5.826 × 10−3 | 0.090 | Up |
| tRF-1:24-His-GTG-1 | tRF-5b | 24 | 31.182 | 7.829 × 10−3 | 0.104 | Up |
| tiRNA-1:34-Val-AAC-1-M3 | tiRNA-5 | 34 | 26.866 | 8.724 × 10−5 | 0.007 | Up |
| tRF-1:24-Val-CAC-2 | tRF-5b | 24 | 21.919 | 3.389 × 10−2 | 0.240 | Up |
| tRF-1:29-Glu-TTC-1 | tRF-5c | 29 | 21.344 | 6.822 × 10−7 | 0.000 | Up |
| tiRNA-1:34-Val-AAC-2 | tiRNA-5 | 34 | 21.203 | 3.434 × 10−2 | 0.240 | Up |
| tRF-1:28-Val-CAC-2 | tRF-5c | 28 | 20.604 | 4.441 × 10−2 | 0.287 | Up |
| tRF-+1:T23-Thr-AGT-2-2 | tRF-1 | 23 | 0.034 | 1.627 × 10−2 | 0.173 | Down |
| tRF-+1:T21-Leu-TAG-3 | tRF-1 | 21 | 0.036 | 2.019 × 10−2 | 0.186 | Down |
| tRF-+1:T15-Gly-TCC-1 | tRF-1 | 15 | 0.055 | 3.062 × 10−3 | 0.066 | Down |
| tRF-1:15-Thr-CGT-5 | tRF-5a | 15 | 0.077 | 1.966 × 10−4 | 0.010 | Down |
| tRF-1:14-Asp-GTC-1-M3 | tRF-5a | 14 | 0.079 | 8.031 × 10−3 | 0.104 | Down |
| tRF-+1:T18-Ile-AAT-2 | tRF-1 | 18 | 0.080 | 1.040 × 10−2 | 0.125 | Down |
| tRF-54:75-His-GTG-1-M2 | tRF-3b | 22 | 0.109 | 1.190 × 10−4 | 0.009 | Down |
| tRF-+1:T17-Ser-TGA-1 | tRF-1 | 17 | 0.112 | 1.371 × 10−4 | 0.009 | Down |
| tRF-52:69-chrM.Tyr-GTA | tRF-3a | 18 | 0.119 | 4.422 × 10−2 | 0.287 | Down |
| tRF-+1:T15-Lys-CTT-2-2 | tRF-1 | 15 | 0.123 | 5.960 × 10−3 | 0.090 | Down |
| The candidate tsRNAs selected for bioinformatics and PCR | ||||||
| tiRNA-1:34-Val-CAC-2 | tiRNA-5 | 34 | 14.342 | 8.535 × 10−6 | 0.002 | Up |
| tiRNA-1:33-Gly-GCC-1 | tiRNA-5 | 33 | 9.222 | 1.774 × 10−4 | 0.010 | Up |
| tRF-1:32-Gly-GCC-1 | tRF-5c | 32 | 3.703 | 2.204 × 10−2 | 0.189 | Up |
| tRF-+1:T20-Ser-TGA-1 | tRF-1 | 20 | 0.154 | 9.193 × 10−4 | 0.034 | Down |
| Gene Name | Sequencing | PCR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | p-Value | Regulation | FC | p-Value | Regulation | |
| tiRNA-1:34-Val-CAC-2 | 14.342 | 8.535 × 10−6 | Up | 7.925 | 0.0556 | Up |
| tRF-1:32-Gly-GCC-1 | 3.703 | 2.204 × 10−2 | Up | 4.349 | 0.0082 | Up |
| tRF-+1:T20-Ser-TGA-1 | 0.154 | 9.193 × 10−4 | Down | 0.231 | 0.0014 | Down |
| tiRNA-1:33-Gly-GCC-1 | 9.222 | 1.774 × 10−6 | Up | 5.869 | 0.0028 | Up |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, C.; Chen, Z.-H.; Cao, R.; Shi, M.-J.; Tian, Y. Differential Expression Profiles and Bioinformatics Analysis of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in a Chinese Population. Genes 2022, 13, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040601
Qin C, Chen Z-H, Cao R, Shi M-J, Tian Y. Differential Expression Profiles and Bioinformatics Analysis of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in a Chinese Population. Genes. 2022; 13(4):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040601
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Chuan, Zheng-Hao Chen, Rui Cao, Ming-Jun Shi, and Ye Tian. 2022. "Differential Expression Profiles and Bioinformatics Analysis of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in a Chinese Population" Genes 13, no. 4: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040601
APA StyleQin, C., Chen, Z.-H., Cao, R., Shi, M.-J., & Tian, Y. (2022). Differential Expression Profiles and Bioinformatics Analysis of tRNA-Derived Small RNAs in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer in a Chinese Population. Genes, 13(4), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040601





