The Role of SLC22A1 and Genomic Ancestry on Toxicity during Treatment in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia of the Amazon Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Ethical Aspects
2.2. Study Populations
2.3. Induction Therapy Protocol for ALL
2.4. Assessment and Classification of Toxicity
2.5. DNA Extraction and Quantification
2.6. Selection of Polymorphisms
2.7. Genotyping of Polymorphisms
2.8. Genomic Ancestry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pui, C.H.; Cheng, C.; Leung, W.; Rai, S.N.; Rivera, G.K.; Sandlund, J.T.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Relling, M.V.; Kun, L.E.; Evans, W.E.; et al. Extended follow-up of long-term survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Bishop, K.; Kosary, C.L.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; et al. (Eds.) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2014; National Cancer Institute, Bethesda: Rockville, MD, USA. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/archive/csr/1975_2014/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Ministério da Saúde; Instituto Nacional de Câncer José Alencar Gomes da Silva. Estimativa 2020: Incidência de Câncer No Brasil.; INCA: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2019. Available online: https://www.inca.gov.br/sites/ufu.sti.inca.local/files//media/document//estimativa-2020-incidencia-de-cancer-no-brasil.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Kishi, S.; Cheng, C.; French, D.; Pei, D.; Das, S.; Cook, E.H.; Hijiya, N.; Rizzari, C.; Rosner, G.L.; Frudakis, T.; et al. Ancestry and pharmacogenetics of antileukemic drug toxicity. Blood 2007, 109, 4151–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meadows, A.T.; Robison, L.L.; Neglia, J.P.; Sather, H.; Hammond, D. Potential long-term toxic effects in children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 1830–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, D.C.; Wanderley, A.V.; Amador, M.A.; Fernandes, M.R.; Cavalcante, G.C.; Pantoja, K.B.; Mello, F.A.; de Assumpção, P.P.; Khayat, A.S.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, Â.; et al. Amerindian genetic ancestry and INDEL polymorphisms associated with susceptibility of childhood B-cell Leukemia in an admixed population from the Brazilian Amazon. Leuk. Res. 2015, 39, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stary, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Campbell, M.; Castillo, L.; Dibar, E.; Donska, S.; Gonzalez, A.; Izraeli, S.; Janic, D.; Jazbec, J.; et al. Intensive chemotherapy for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Results of the randomized intercontinental trial ALL IC-BFM 2002. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.J.; Cheng, C.; Devidas, M.; Cao, X.; Fan, Y.; Campana, D.; Yang, W.; Neale, G.; Cox, N.J.; Scheet, P.; et al. Ancestry and pharmacogenomics of relapse in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Lou, H.; Yang, X.; Lu, D.; Li, S.; Jin, L.; Pan, X.; Yang, W.; Song, M.; Mamatyusupu, D.; et al. Genetic architectures of ADME genes in five Eurasian admixed populations and implications for drug safety and efficacy. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hareedy, M.S.; El Desoky, E.S.; Woillard, J.B.; Thabet, R.H.; Ali, A.M.; Marquet, P.; Picard, N. Genetic variants in 6-mercaptopurine pathway as potential factors of hematological toxicity in acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, D.C.; Wanderley, A.V.; Dos Santos, A.M.R.; Moreira, F.C.; de Sá, R.B.A.; Fernandes, M.R.; Modesto, A.A.C.; de Souza, T.P.; Cohen-Paes, A.; Leitão, L.P.C.; et al. Characterization of pharmacogenetic markers related to Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia toxicity in Amazonian native Americans population. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, B.J.; Bostrom, B.C.; Cherlow, J.M.; Sensel, M.G.; La, M.K.; Rackoff, W.; Heerema, N.A.; Wimmer, R.S.; Trigg, M.E.; Sather, H.N.; et al. Double-delayed intensification improves event-free survival for children with intermediate-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A report from the Children’s Cancer Group. Blood 2002, 99, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.H.; Robison, L.L.; Look, A.T. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet 2008, 371, 1030–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Lopez, E.; Gutierrez-Camino, A.; Bilbao-Aldaiturriaga, N.; Pombar-Gomez, M.; Martin-Guerrero, I.; Garcia-Orad, A. Pharmacogenetics of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, J.C.G.; Souza, T.P.; Pastana, L.F.; Ribeiro Dos Santos, A.M.; Fernandes, M.R.; Pinto, P.; Wanderley, A.V.; Souza, S.J.; Kroll, J.E.; Pereira, A.L.; et al. Identification of NUDT15 gene variants in Amazonian Amerindians and admixed individuals from northern Brazil. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goswami, S.; Gong, L.; Giacomini, K.; Altman, R.B. PharmGKB summary: Very important pharmacogene information for SLC22A1. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2014, 24, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ALL IC-BFM 2009 A Randomized Trial of the I-BFM-SG for the Management of Childhood Non-B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Final Version of Therapy Protocol from August-14-2009. Available online: https://www.bialaczka.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/ALLIC_BFM_2009.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Saad, E.D.; Hoff, P.M.; Carnelós, R.P.; Katz, A.; Novis, Y.A.S.; Pietrocola, M.; Hamerschlak, N.; Tabacof, J.; Gansl, R.C.; Simon, S.D. Critérios comuns de toxicidade do Instituto Nacional de Câncer dos Estados Unidos. Rev. Bras. Cancerol. 2002, 48, 63–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, B.R.D.A.; D’Elia, M.P.B.; Amador, M.A.T.; Santos, N.P.C.; Santos, S.E.B.; Castelli, E.D.C.; Witkin, S.S.; Miot, H.A.; Miot, L.D.B.; da Silva, M.G. Neither self-reported ethnicity nor declared family origin are reliable indicators of genomic ancestry. Genetica 2016, 144, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmiegelow, K.; Attarbaschi, A.; Barzilai, S.; Escherich, G.; Frandsen, T.L.; Halsey, C.; Hough, R.; Jeha, S.; Kato, M.; Liang, D.C.; et al. Consensus definitions of 14 severe acute toxic effects for childhood lymphoblastic leukaemia treatment: A Delphi consensus. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e231–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Z.; Kar, Y.; Turhan, A.; Bör, Ö. Assessment of Hematological Toxicity in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Receiving Treatment with ALL IC-BFM 2009 Protocol. OALib J. 2017, 4, 78829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez-Kurtz, G.; Brisson, G.D.; Hutz, M.H.; Petzl-Erler, M.L.; Salzano, F.M. NUDT15 Polymorphism in Native American Populations of Brazil. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 105, 1321–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, D.C.; Wanderley, A.V.; dos Santos, A.M.R.; Fernandes, M.R.; Cohen Lima de Castro, A.N.; Leitão, L.P.C.; de Carvalho, J.A.N.; de Souza, T.P.; Khayat, A.S.; dos Santos, S.E.B.; et al. Pharmacogenomics and variations in the risk of toxicity during the consolidation/maintenance phases of the treatment of pediatric B-cell leukemia patients from an admixed population in the Brazilian Amazon. Leuk. Res. 2018, 74, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradveisi, B.; Muwakkit, S.; Zamani, F.; Ghaderi, E.; Mohammadi, E.; Zgheib, N.K. ITPA, TPMT, and NUDT15 Genetic Polymorphisms Predict 6-Mercaptopurine Toxicity in Middle Eastern Children With Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wahlund, M.; Nilsson, A.; Kahlin, A.Z.; Broliden, K.; Myrberg, I.H.; Appell, M.L.; Berggren, A. The Role of TPMT, ITPA, and NUDT15 Variants during Mercaptopurine Treatment of Swedish Pediatric Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Pediatr. 2020, 216, 150–157.e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buaboonnam, J.; Sripatanatadasakul, P.; Treesucon, A.; Glomglao, W.; Siraprapapat, P.; Narkbunnam, N.; Vathana, N.; Takpradit, C.; Phuakpet, K.; Pongtanakul, B.; et al. Effect of NUDT15 on incidence of neutropenia in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Int. 2019, 61, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relling, M.V.; Schwab, M.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Suarez-Kurtz, G.; Pui, C.H.; Stein, C.M.; Moyer, A.M.; Evans, W.E.; Klein, T.E.; Antillon-Klussmann, F.G.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Thiopurine Dosing Based on TPMT and NUDT15 Genotypes: 2018 Update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 105, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arimany-Nardi, C.; Koepsell, H.; Pastor-Anglada, M. Role of SLC22A1 polymorphic variants in drug disposition, therapeutic responses, and drug-drug interactions. Pharm. J. 2015, 15, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yee, S.W.; Brackman, D.J.; Ennis, E.A.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kamdem, L.K.; Blanchard, R.; Galetin, A.; Zhang, L.; Giacomini, K.M. Influence of Transporter Polymorphisms on Drug Disposition and Response: A Perspective From the International Transporter Consortium. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 104, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerb, R.; Brinkmann, U.; Chatskaia, N.; Gorbunov, D.; Gorboulev, V.; Mornhinweg, E.; Keil, A.; Eichelbaum, M.; Koepsell, H. Identification of genetic variations of the human organic cation transporter hOCT1 and their functional consequences. Pharmacogenetics 2002, 12, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Leabman, M.K.; Feng, B.; Mangravite, L.M.; Huang, C.C.; Stryke, D.; Kawamoto, M.; Johns, S.J.; DeYoung, J.; Carlson, E.; et al. Evolutionary conservation predicts function of variants of the human organic cation transporter, OCT1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5902–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzvetkov, M.V.; Matthaei, J.; Pojar, S.; Faltraco, F.; Vogler, S.; Prukop, T.; Seitz, T.; Brockmöller, J. Increased Systemic Exposure and Stronger Cardiovascular and Metabolic Adverse Reactions to Fenoterol in Individuals with Heritable OCT1 Deficiency. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 103, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnin, S.; Ravegnini, G.; Soverini, S.; Angelini, S.; Terrazzino, S. Impact of SLC22A1 and CYP3A5 genotypes on imatinib response in chronic myeloid leukemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 131, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhu, Q.; Cole, P.D.; Stevenson, K.; Harris, M.H.; Schultz, E.; Kahn, J.M.; Ladas, E.J.; Athale, U.H.; Clavell, L.A.; et al. Genetic ancestry and skeletal toxicities among childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients in the DFCI 05-001 cohort. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | General Toxicity | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n. 27) | No (n. 24) | ||
| Gender | |||
| Female | 9 (33.3%) | 13 (54.2%) | 0.134 a |
| Male | 18 (66.7%) | 11 (45.8%) | |
| Age (years) | |||
| Average (±SD) | 7.19 (±4.34) | 6.96 (±4.43) | 0.776 b |
| ALL Sub-type | |||
| ALL B | 23 (37.0%) | 19 (16.7%) | 0.804 a |
| ALL T | 4 (14.8%) | 5 (20.8%) | |
| Ancestry | |||
| European | 0.494 (±0.520) | 0.496 (±0.120) | 0.439 b |
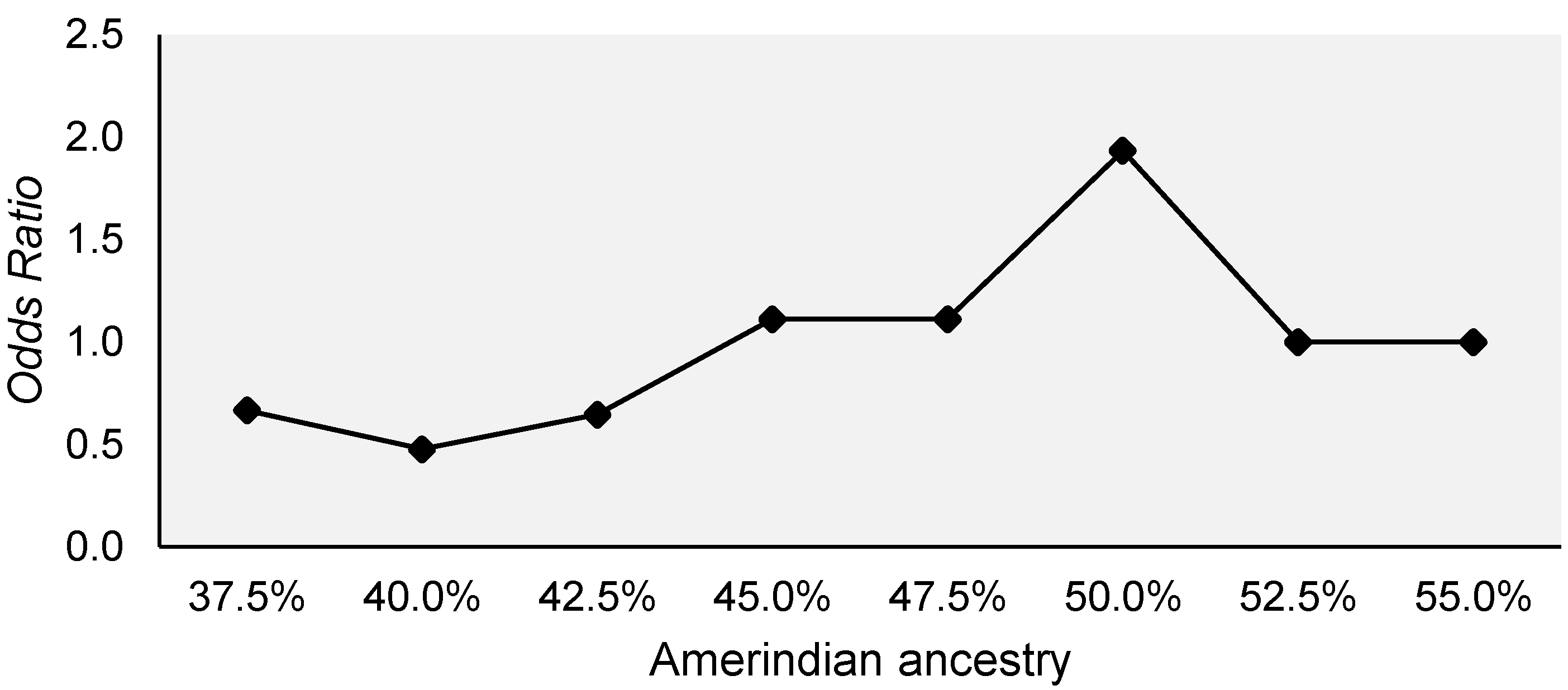
| Amerindian | 0.342 (±0.149) | 0.324 (±0.123) | 0.970 b |
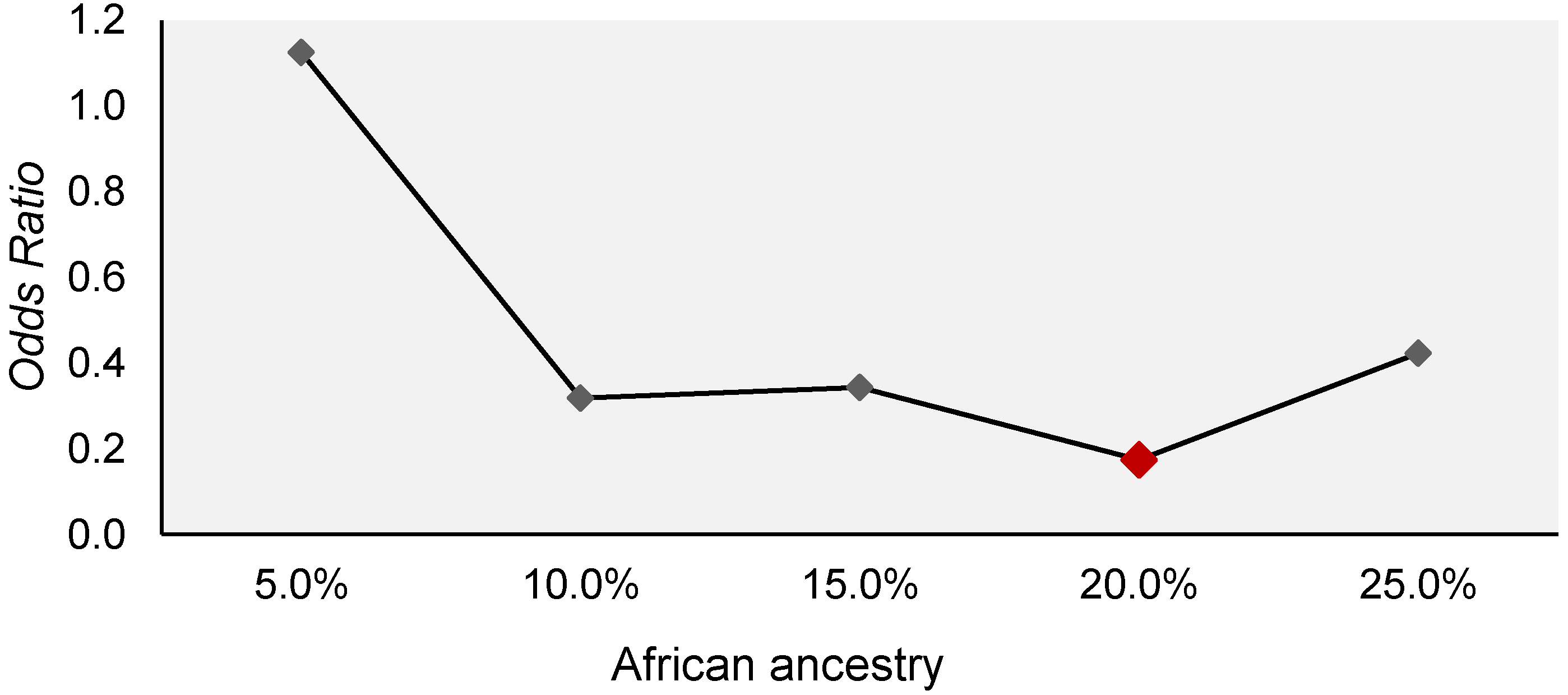
| African | 0.143 (±0.060) | 0.179 (±0.057) | 0.029 b,* |
| Toxicity type | |||
| Gastrointestinal | |||
| Low | 9 (33.3%) | NA | NA |
| Moderate | 8 (29.6%) | NA | |
| High | 0 (0.0%) | NA | |
| Hepatic | |||
| Low | 2 (7.4%) | NA | NA |
| Moderate | 21 (77.7%) | NA | |
| High | 3 (11.1%) | NA | |
| Infectious | |||
| Low | 0 (0.0%) | NA | NA |
| Moderate | 11 (40.7%) | NA | |
| High | 14 (51.8%) | NA | |
| Mortality | |||
| Yes | 6 (22.2%) | 9 (37.5%) | 0.375 a |
| No | 21 (77.8%) | 15 (62.5%) | |
| Polymorphisms | General Toxicity | p Value a | p Value b | OR (95%IC) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n. 27) | No (n. 24) | ||||
| SLC22A1 | |||||
| n-n | 5 (18.5%) | 9 (37.5%) | 0.112 | 0.230 | 0.43 (0.11–1.69) |
| n-ins | 6 (22.2%) | 2 (8.3%) | 0.209 | 3.64 (0.51–20.63) | |
| n-del | 9 (33.3%) | 6 (25.0%) | 0.435 | 1.70 (0.45–6.51) | |
| del-ins | 1 (3.7%) | 5 (20.8%) | 0.072 | 0.12 (0.01–1.20) | |
| del-del | 5 (18.5%) | 1 (4.2%) | 0.196 | 4.68 (0.45–48.62) | |
| ins-ins | 1 (3.7%) | 1 (4.2%) | 0.635 | 0.50 (0.03–8.77) | |
| Allele n | 25 (46.3%) | 26 (54.2%) | 0.578 | 0.737 | 0.86 (0.37–2.01) |
| Allele ins | 9 (16.7%) | 9 (18.8%) | 0.502 | 0.68 (2.31–2.05) | |
| Allele del | 20 (37.0%) | 13 (27.1%) | 0.366 | 1.52 (0.61–3.77) | |
| NUDT15 | |||||
| Del-Del | 20 (76.9%) | 22 (91.7%) | 0.155 | 0.321 | 0.39 (0.06–2.64) |
| Ins-Del | 6 (23.1%) | 2 (8.3%) | |||
| Allele Del | 46 (88.5%) | 46 (95.8%) | 0.175 | 0.347 | 2.32 (0.40–13.55) |
| Allele Ins | 6 (11.5%) | 2 (4.2%) | |||
| Polymorphisms | Severe Infectious Toxicity | p Value a | p Value b | OR (95%IC) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes (n. 14) | No (n. 37) | ||||
| SLC22A1 | |||||
| n-n | 3 (21.4%) | 11 (29.7%) | 0.304 | 0.597 | 0.66 (0.15–3.02) |
| n-ins | 2 (14.3%) | 6 (16.2%) | 0.216 | 0.27 (0.03–2.13) | |
| n-del | 6 (42.9%) | 9 (24.3%) | 0.194 | 2.80 (0.69–11.32) | |
| del-ins | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (16.2%) | 0.999 | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | |
| del-del | 3 (21.4%) | 3 (8.1%) | 0.085 | 6.17 (0.78–49.11) | |
| ins-ins | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (5.4%) | 0.999 | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | |
| Allele n | 14 (50.0%) | 37 (50.0%) | 0.155 | 0.715 | 1.19 (1.06–1.33) |
| Allele ins | 2 (7.1%) | 16 (21.6%) | 0.049* | 0.19 (0.04–0.99) | |
| Allele del | 12 (42.9%) | 21 (28.4%) | 0.031* | 3.18 (1.11–9.11) | |
| NUDT15 | |||||
| Del-Del | 10 (76.9%) | 32 (86.5%) | 0.418 | 0.333 | 0.43 (0.08–2.33) |
| Ins-Del | 3 (23.1%) | 5 (13.5%) | |||
| Allele Del | 23 (88.5%) | 69 (93.2%) | 0.432 | 0.356 | 2.11 (0.43–10.35) |
| Allele Ins | 3 (11.5%) | 5 (6.8%) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, S.d.S.M.; Leitão, L.P.C.; Cohen-Paes, A.d.N.; Gellen, L.P.A.; Pastana, L.F.; de Carvalho, D.C.; Modesto, A.A.C.; da Costa, A.C.A.; Wanderley, A.V.; Lima, C.H.V.d.; et al. The Role of SLC22A1 and Genomic Ancestry on Toxicity during Treatment in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia of the Amazon Region. Genes 2022, 13, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040610
Fernandes SdSM, Leitão LPC, Cohen-Paes AdN, Gellen LPA, Pastana LF, de Carvalho DC, Modesto AAC, da Costa ACA, Wanderley AV, Lima CHVd, et al. The Role of SLC22A1 and Genomic Ancestry on Toxicity during Treatment in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia of the Amazon Region. Genes. 2022; 13(4):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040610
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Sweny de S. M., Luciana P. C. Leitão, Amanda de N. Cohen-Paes, Laura P. A. Gellen, Lucas F. Pastana, Darlen C. de Carvalho, Antônio A. C. Modesto, Ana C. A. da Costa, Alayde V. Wanderley, Carlos H. V. de Lima, and et al. 2022. "The Role of SLC22A1 and Genomic Ancestry on Toxicity during Treatment in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia of the Amazon Region" Genes 13, no. 4: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040610
APA StyleFernandes, S. d. S. M., Leitão, L. P. C., Cohen-Paes, A. d. N., Gellen, L. P. A., Pastana, L. F., de Carvalho, D. C., Modesto, A. A. C., da Costa, A. C. A., Wanderley, A. V., Lima, C. H. V. d., Pereira, E. E. B., Fernandes, M. R., Burbano, R. M. R., de Assumpção, P. P., Santos, S. E. B. d., & Santos, N. P. C. d. (2022). The Role of SLC22A1 and Genomic Ancestry on Toxicity during Treatment in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia of the Amazon Region. Genes, 13(4), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13040610








