Gene Expression Meta-Analysis of Potential Shared and Unique Pathways between Autoimmune Diseases under Anti-TNFα Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
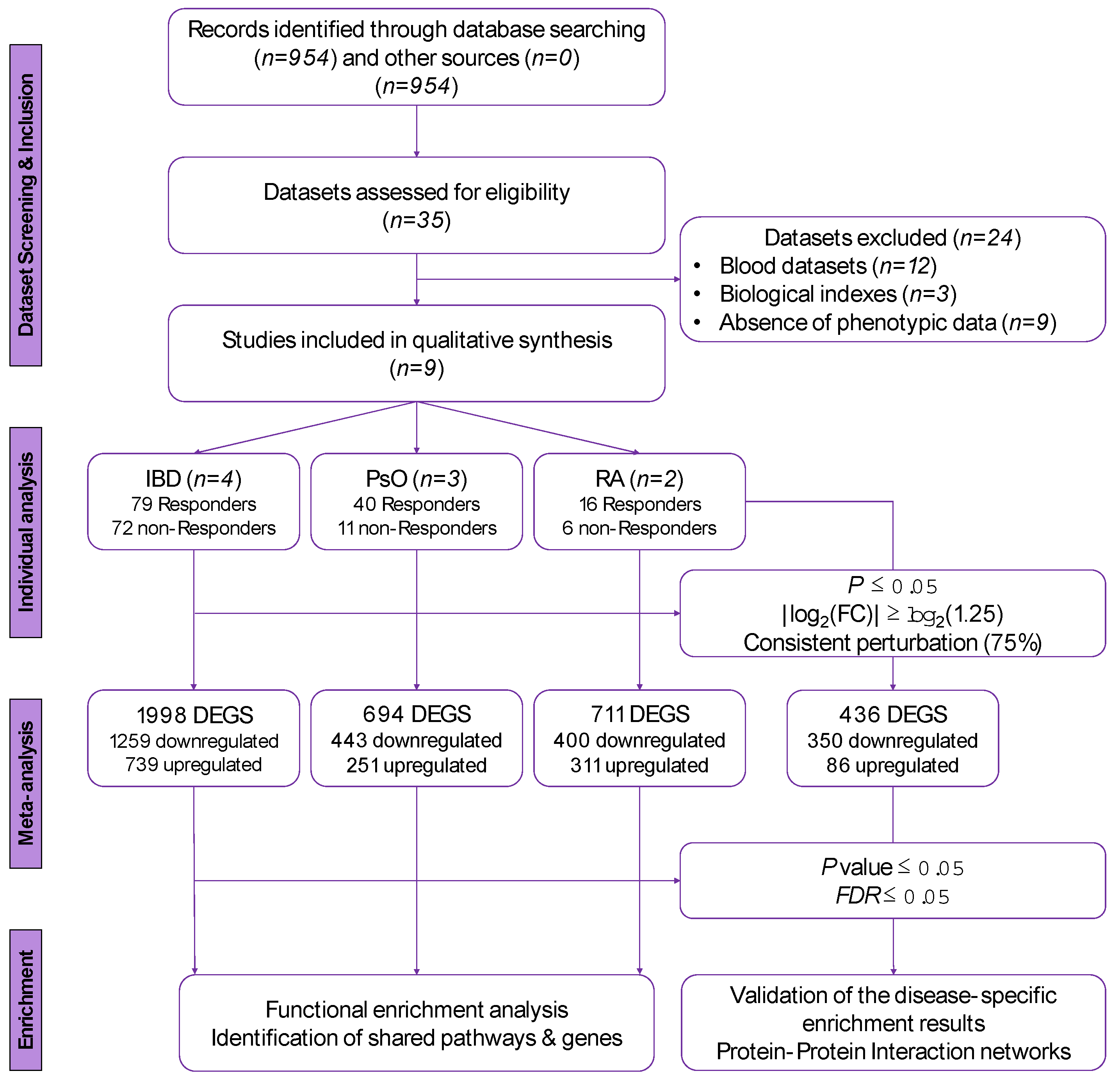
2.1. Identification of Eligible Datasets and Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Dataset Pre-Processing
2.3. Disease-Specific and Combined Meta-Analyses
2.4. Over-Representation Analysis
2.5. Construction of Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Networks
3. Results
3.1. Included Datasets
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes in the Disease-Specific Meta-Analyses
3.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis of the Disease-Specific DEGs
3.4. Differentially Expressed Genes in the Combined Meta-Analyses
3.5. Functional Enrichment in the Combined Meta-Analysis
3.6. Protein–Protein Interaction Network
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Wang, F.S.; Gershwin, M.E. Human autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive update. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 278, 369–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakolpour, S.; Darvishi, M.; Ghasemiadl, M.; Diseases, I. Pharmacogenetics: A strategy for personalized medicine for autoimmune diseases. Clin. Genet. 2018, 98, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenblum, M.D.; Gratz, I.K.; Paw, J.S.; Abbas, A.K. Treating human autoimmunity: Current practice and future prospects. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 125sr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosman, Z.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Zandman-Goddard, G. Biologic therapy for autoimmune diseases: An update. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.J.; Perez-Chada, L.M.; Merola, J.F. TNF inhibitor-induced psoriasis: Proposed algorithm for treatment and management. J. Psoriasis Psoriatic Arthritis 2019, 4, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, D.; Lassen, K.G.; Xavier, R.J. Advances in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: Linking host genetics and the microbiome. Gut 2013, 62, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkacz, A.; Olczyk, P.; Olczyk, K.; Komosinska-Vassev, K. The role of extracellular matrix components in inflammatory bowel diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, F. The genetic basis of psoriasis. IJMS 2017, 18, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Cui, L.; Shi, Y.; Guo, C. Advances in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: From keratinocyte perspective. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; Barton, A.; Burmester, G.R.; Emery, P.; Firestein, G.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Solomon, D.H.; Strand, V.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottini, N.; Firestein, G.S. Duality of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tracey, D.; Klareskog, L.; Sasso, E.H.; Salfeld, J.G.; Tak, P.P. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 117, 244–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, G.; Jharap, B.; Neeraj, N.; Colombel, J.F. Loss of Response to Anti-TNFs: Definition, epidemiology, and management. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Rutgeerts, P.; Enns, R.; Hanauer, S.B.; Colombel, J.-F.; Panaccione, R.; D’Haens, G.; Li, J.; Rosenfeld, M.R.; Kent, J.D.; et al. Adalimumab induction therapy for Crohn disease previously treated with infliximab a randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2007, 146, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, G.E.; Yajnik, V.; Khalili, H.; Giallourakis, C.; Garber, J.; Xavier, R.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Genetic markers predict primary non-response and durable response to anti-TNF biologic therapies in Crohn’s disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caputo, V.; Strafella, C.; Cosio, T.; Lanna, C.; Campione, E.; Novelli, G.; Giardina, E.; Cascella, R. Pharmacogenomics: An update on biologics and small-molecule drugs in the treatment of psoriasis. Genes 2021, 12, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rodriguez, R.; Perez-Pampin, E.; Marquez, A.; Blanco, F.J.; Joven, B.; Carreira, P.; Ferrer, M.A.; Caliz, R.; Valor, L.; Narvaez, J.; et al. Validation study of genetic biomarkers of response to TNF inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bank, S.; Julsgaard, M.; Abed, O.K.; Burisch, J.; Broder Brodersen, J.; Pedersen, N.K.; Gouliaev, A.; Ajan, R.; Nytoft Rasmussen, D.; HonoreGrauslund, C.; et al. Polymorphisms in the NFkB, TNF-Alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-18 Pathways Are Associated with Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Danish Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonatos, C.; Stavrou, E.F.; Evangelou, E.; Vasilopoulos, Y. Exploring pharmacogenetic variants for predicting response to Anti-TNF therapy in autoimmune diseases: A meta-analysis. Pharmacogenomics 2021, 22, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightbody, G.; Haberland, V.; Browne, F.; Taggart, L.; Zheng, H.; Parkes, E.; Blayney, J.K. Review of applications of high-throughput sequencing in personalized medicine: Barriers and facilitators of future progress in research and clinical application. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1795–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.S.; Van Vleet, T.R.; Ciurlionis, R.; Buck, W.R.; Mittelstadt, S.W.; Blomme, E.A.G.; Liguori, M.J. Comparison of RNA-Seq and microarray gene expression platforms for the toxicogenomic evaluation of liver from short-term rat toxicity studies. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leal, R.F.; Planell, N.; Kajekar, R.; Lozano, J.J.; Ordás, I.; Dotti, I.; Esteller, M.; Masamunt, M.C.; Parmar, H.; Ricart, E.; et al. Identification of inflammatory mediators in patients with Crohn’s disease unresponsive to Anti-TNFα therapy. Gut 2015, 64, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arijs, I.; De Hertogh, G.; Lemaire, K.; Quintens, R.; Van Lommel, L.; Van Steen, K.; Leemans, P.; Cleynen, I.; Van Assche, G.; Vermeire, S.; et al. Mucosal Gene Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides in Inflammatory Bowel Disease before and after First Infliximab Treatment. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toedter, G.; Li, K.; Marano, C.; Ma, K.; Sague, S.; Huang, C.C.; Song, X.Y.; Rutgeerts, P.; Baribaud, F. Gene expression profiling and response signatures associated with differential responses to infliximab treatment in ulcerative colitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodmerkel, C.; Li, K.; Garcet, S.; Hayden, K.; Chiricozzi, A.; Novitskaya, I.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Campbell, K.; Krueger, J.G. Modulation of inflammatory gene transcripts in psoriasis vulgaris: Differences between Ustekinumab and Etanercept. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1965–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaba, L.C.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Nograles, K.E.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Cardinale, I.; Lowes, M.A.; Krueger, J.G. Effective Treatment of Psoriasis with Etanercept Is Linked to Suppression of IL-17 Signaling, Not Immediate Response TNF Genes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Correa da Rosa, J.; Kim, J.; Tian, S.; Tomalin, L.E.; Krueger, J.G.; Suárez-Fariñas, M. Shrinking the psoriasis assessment gap: Early gene-expression profiling accurately predicts response to long-term treatment. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Julià, A.; Ávila, G.; Celis, R.; Sanmartí, R.; Ramírez, J.; Marsal, S.; Cañete, J. Lower peripheral helper T cells in the synovium are associated with a better response to Anti-TNF therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badot, V.; Galant, C.; Toukap, A.N.; Theate, I.; Maudoux, A.L.; Van den Eynde, B.J.; Durez, P.; Houssiau, F.A.; Lauwerys, B.R. Gene expression profiling in the synovium identifies a predictive signature of absence of response to adalimumab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramasamy, A.; Mondry, A.; Holmes, C.C.; Altman, D.G. Key Issues in Conducting a Meta-Analysis of Gene Expression Microarray Datasets. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, 1320–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell-Marugán, J.; López-Domínguez, R.; García-Moreno, A.; Toro-Domínguez, D.; Villatoro-García, J.A.; Barturen, G.; Martín-Gómez, A.; Troule, K.; Gómez-López, G.; Al-Shahrour, F.; et al. A Comprehensive Database for Integrated Analysis of Omics Data in Autoimmune Diseases. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for Functional Genomics Data Sets-Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sean, D.; Meltzer, P.S. GEOquery: A Bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1846–1847. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: Open Software Development for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gentleman, R. Annotate: Annotation for Microarrays. R Package Version 1.72.0. Available online: https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/annotate.html (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Limma Powers Differential Expression Analyses for RNA-Sequencing and Microarray Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prada, C.; Lima, D.; Nakaya, H. MetaVolcanoR: Gene Expression Meta-Analysis Visualization Tool. Available online: https://github.com/csbl-usp/MetaVolcanoR (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Harrison, P.F.; Pattison, A.D.; Powell, D.R.; Beilharz, T.H. Topconfects: A package for confident effect sizes in differential expression analysis provides improved usability ranking genes of interest. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 343145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blighe, K.; Rana, S.; Lewis, M. EnhancedVolcano: Publication-Ready Volcano Plots with Enhanced Colouring and Labeling. Available online: https://github.com/kevinblighe/EnhancedVolcano (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Harris, M.A.; Clark, J.; Ireland, A.; Lomax, J.; Ashburner, M.; Foulger, R.; Eilbeck, K.; Lewis, S.; Marshall, B.; Mungall, C.; et al. The Gene Oncology (GO) Database and Informatics Resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 258–261. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; He, Q.-Y. ReactomePA: An R/Bioconductor Package for Reactome Pathway Analysis and Visualization. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. ClusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z.; Du, Z.; Payattakool, R.; Yu, P.S.; Chen, C.-F. A new method to measure the semantic similarity of GO terms. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING Database in 2021: Customizable Protein-Protein Networks, and Functional Characterization of User-Uploaded Gene/Measurement Sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransen, J.; van Riel, P.L.C.M. The disease activity score and the EULAR response criteria. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 35, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Haens, G.R.; Geboes, K.; Peeters, M.; Baert, F.; Penninckx, F.; Rutgeerts, P. Early lesions of recurrent Crohn’s disease caused by infusion of intestinal contents in excluded ileum. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro-Domínguez, D.; Villatoro-Garciá, J.A.; Martorell-Marugán, J.; Román-Montoya, Y.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Carmona-Saéz, P. A survey of gene expression meta-analysis: Methods and applications. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Musco, H.; Simpson-Yap, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.; Taylor, B.; Gratten, J.; Zhou, Y. Investigating the shared genetic architecture between multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel diseases. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A Systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-Y.; Chang, W.-C.; Wang, J.-M. Biological roles of CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding protein delta during inflammation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litvak, V.; Ramsey, S.A.; Rust, A.G.; Zak, D.E.; Kennedy, K.A.; Lampano, A.E.; Nykter, M.; Shmulevich, I.; Aderem, A. Function of C/EBPδ in a Regulatory Circuit That Discriminates between Transient and Persistent TLR4-Induced Signals. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, S.; Akira, S.; Kishimoto, T. A member of the C/EBP family, NF-IL6,f, forms a heterodimer and transcriptionally synergizes with NF-IL6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1473–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedrich, M.; Diegelmann, J.; Schauber, J.; Auernhammer, C.J.; Brand, S. Intestinal neuroendocrine cells and goblet cells are mediators of IL-17A-Amplified Epithelial IL-17C production in human inflammatory bowel disease. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 943–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.-H.; Huang, H.-S.; Wu, P.-T.; Jou, I.-M.; Pan, M.-H.; Chang, W.-C.; Wang, D.D.H.; Wang, J.-M. Role of macrophage CCAAT/Enhancer binding protein delta in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis in collagen-induced arthritic mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jozawa, H.; Inoue-Yamauchi, A.; Arimura, S.; Yamanashi, Y. Loss of C/EBPδ enhances apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells and exacerbates experimental colitis in mice. Genes Cells 2019, 24, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.-S.; Vancamelbeke, M.; Verstockt, S.; Wilms, T.; Verstockt, B.; Sabino, J.; Ferrante, M.; Vermeire, S.; Cleynen, I. Molecular changes in the non-inflamed terminal ileum of patients with ulcerative colitis. Cells 2020, 9, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Wang, H.; Qi, R.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guo, H.; Gao, X.; Geng, L. Shikonin Inhibits CEBPD Downregulation in IL-17-treated HaCaT Cells and in an Imiquimod-induced psoriasis model. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rørvig, S.; Honore, C.; Larsson, L.-I.; Ohlsson, S.; Pedersen, C.C.; Jacobsen, L.C.; Cowland, J.B.; Garred, P.; Borregaard, N. Ficolin-1 is present in a highly mobilizable subset of human neutrophil granules and associates with the cell surface after stimulation with FMLP. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 86, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandahl, T.D.; Kelsen, J.; Dige, A.; Dahlerup, J.F.; Agnholt, J.; Hvas, C.L.; Thiel, S. The lectin pathway of the complement system is downregulated in Crohn’s disease patients who respond to Anti-TNF-α therapy. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2014, 8, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eshelman, M.A.; Harris, L.; Deiling, S.; Koltun, W.A.; Jeganathan, N.A.; Yochum, G.S. Transcriptomic Analysis of Ileal Tissue from Crohn’s disease patients identifies extracellular matrix genes that distinguish individuals by age at diagnosis. Physiol. Genom. 2020, 52, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniers, A.; Goll, R.; Pasing, Y.; Sørbye, S.W.; Florholmen, J.; Hansen, T. Ulcerative Colitis: Functional Analysis of the in-Depth Proteome. Clin. Proteom. 2019, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katayama, M.; Ota, K.; Nagi-Miura, N.; Ohno, N.; Yabuta, N.; Nojima, H.; Kumanogoh, A.; Hirano, T. Ficolin-1 is a promising therapeutic target for autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.; Ma, F.; Chen, L. Gene regulatory networks by transcription factors and MicroRNAs in breast cancer. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ingegnoli, F.; Coletto, L.A.; Scotti, I.; Compagnoni, R.; Randelli, P.S.; Caporali, R. The crucial questions on synovial biopsy: When, Why, Who, What, Where, and How? Front. Med. 2021, 8, 705382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| GSE Series Accession Number | Array Platform | Biopsy | Clinical Assessment | Patients (R/NR) | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inflammatory Bowel Disease | |||||
| GSE52746 [22] | GPL17996 | Intestinal Mucosa | CDEIS | 12 (7/5) | ADA, IFX |
| GSE16879 [23] | GPL570 | Intestinal Mucosa | Mayo scores/ Endoscopic healing | 60 (27/33) | IFX |
| GSE92415 | GPL13158 | Intestinal Mucosa | Mayo scores | 50 (29/21) | GOL |
| GSE23597 [24] | GPL570 | Intestinal Mucosa | Mayo scores | 29 (16/13) | IFX |
| Psoriasis | |||||
| GSE106992 [25] | GPL570 | Skin | PASI | 21 (19/2) | ETA |
| GSE11903 [26] | GPL571 | Skin | PASI | 15 (11/4) | ETA, ADA |
| GSE85034 [27] | GPL10558 | Skin | PASI | 15 (10/5) | ETA, ADA |
| Rheumatoid Arthritis | |||||
| GSE140036 [28] | GPL8234 | Synovial | EULAR | 11 (8/3) | ADA, IFX, ETA |
| GSE15602 [29] | GPL570 | Synovial | EULAR | 11 (8/3) | ADA |
| Disease | Symbol | log2(FC) | p Value | Disease | Symbol | log2(FC) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Down-regulated | Up-regulated | ||||||
| IBD | PROK2 | −2.36027 | 2.93 × 10−20 | IBD | PCK1 | 2.129965 | 1.13 × 10−10 |
| CHI3L1 | −2.78866 | 2.05 × 10−12 | HMGCS2 | 1.998756 | 2.42 × 10−11 | ||
| FCGR3B | −2.54556 | 7.94 × 10−12 | GUCA2B | 1.778594 | 1.07 × 10−12 | ||
| S100A12 | −1.94699 | 6.70 × 10−16 | GUCA1B | 1.683352 | 3.74 × 10−13 | ||
| FPR1 | −1.80196 | 7.42 × 10−17 | TRPM6 | 1.657438 | 1.36 × 10−12 | ||
| Psoriasis | PRDM1 | −0.62185 | 7.66 × 10−7 | Psoriasis | PHF1 | 0.501467 | 4.43 × 10−7 |
| ABHD17C | −0.54337 | 5.58 × 10−6 | C1orf115 | 0.646972 | 1.61 × 10−6 | ||
| SERPINB13 | −0.8009 | 8.94 × 10−6 | DEPP1 | 0.720268 | 1.87 × 10−5 | ||
| THBD | −0.51355 | 6.97 × 10−6 | MIR7114 | 0.48793 | 1.45 × 10−5 | ||
| DNAJB6 | −0.39466 | 4.72 × 10−6 | ASMTL | 0.420074 | 2.19 × 10−5 | ||
| RA | C1QTNF6 | −1.14956 | 6.59 × 10−7 | RA | AK1 | 1.206349 | 2.48 × 10−6 |
| FMO1 | −1.93396 | 4.47 × 10−6 | NAV1 | 0.68339 | 2.54 × 10−7 | ||
| IL2RA | −1.16699 | 3.35 × 10−6 | PLAC9 | 0.886543 | 2.40 × 10−6 | ||
| IL12RB2 | −0.50277 | 7.88 × 10−8 | SOX8 | 1.324758 | 1.90 × 10−5 | ||
| SIGLEC7 | −0.56548 | 1.73 × 10−6 | GPSM2 | 0.908652 | 2.87 × 10−5 | ||
| Combined | S100A9 | −1.7893 | 1.88 × 10−10 | Combined | ZNF91 | 0.670157 | 1.13 × 10−13 |
| GNA15 | −0.64899 | 6.11 × 10−14 | TRIM2 | 0.518893 | 2.70 × 10−12 | ||
| NOD2 | −0.63377 | 1.29 × 10−13 | NR3C2 | 0.515162 | 1.80 × 10−11 | ||
| PRDM1 | −0.60289 | 5.49 × 10−12 | TCEA3 | 0.549032 | 6.47 × 10−09 | ||
| LYN | −0.54475 | 2.33 × 10−13 | PHYH | 0.410147 | 2.68 × 10−10 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antonatos, C.; Panoutsopoulou, M.; Georgakilas, G.K.; Evangelou, E.; Vasilopoulos, Y. Gene Expression Meta-Analysis of Potential Shared and Unique Pathways between Autoimmune Diseases under Anti-TNFα Therapy. Genes 2022, 13, 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050776
Antonatos C, Panoutsopoulou M, Georgakilas GK, Evangelou E, Vasilopoulos Y. Gene Expression Meta-Analysis of Potential Shared and Unique Pathways between Autoimmune Diseases under Anti-TNFα Therapy. Genes. 2022; 13(5):776. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050776
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntonatos, Charalabos, Mariza Panoutsopoulou, Georgios K. Georgakilas, Evangelos Evangelou, and Yiannis Vasilopoulos. 2022. "Gene Expression Meta-Analysis of Potential Shared and Unique Pathways between Autoimmune Diseases under Anti-TNFα Therapy" Genes 13, no. 5: 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050776
APA StyleAntonatos, C., Panoutsopoulou, M., Georgakilas, G. K., Evangelou, E., & Vasilopoulos, Y. (2022). Gene Expression Meta-Analysis of Potential Shared and Unique Pathways between Autoimmune Diseases under Anti-TNFα Therapy. Genes, 13(5), 776. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050776







