The Yin-Yang Pharmacomicrobiomics on Treatment Response in Inflammatory Arthritides: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
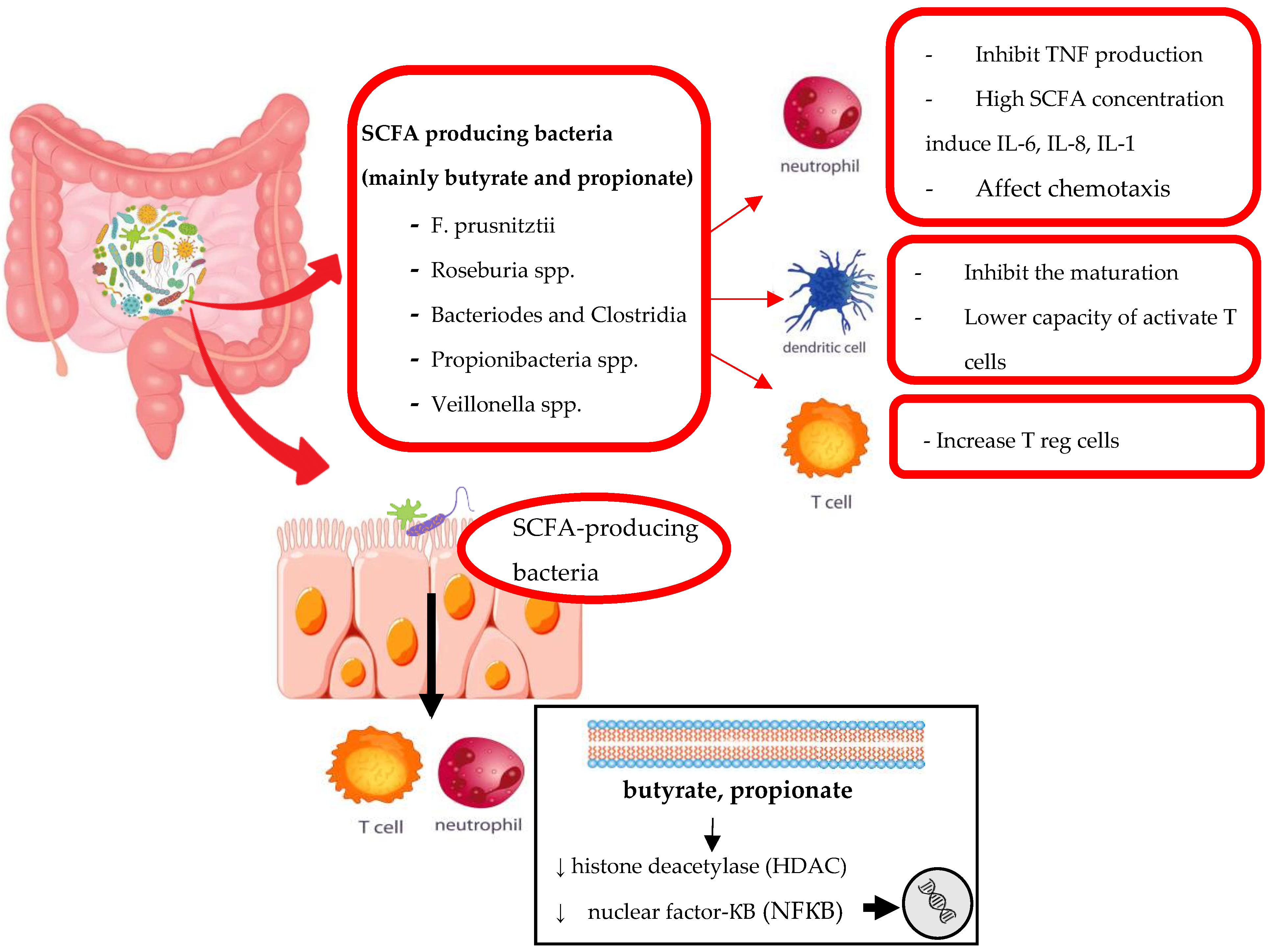
3.1. Interaction of Methotrexate with Microbiome
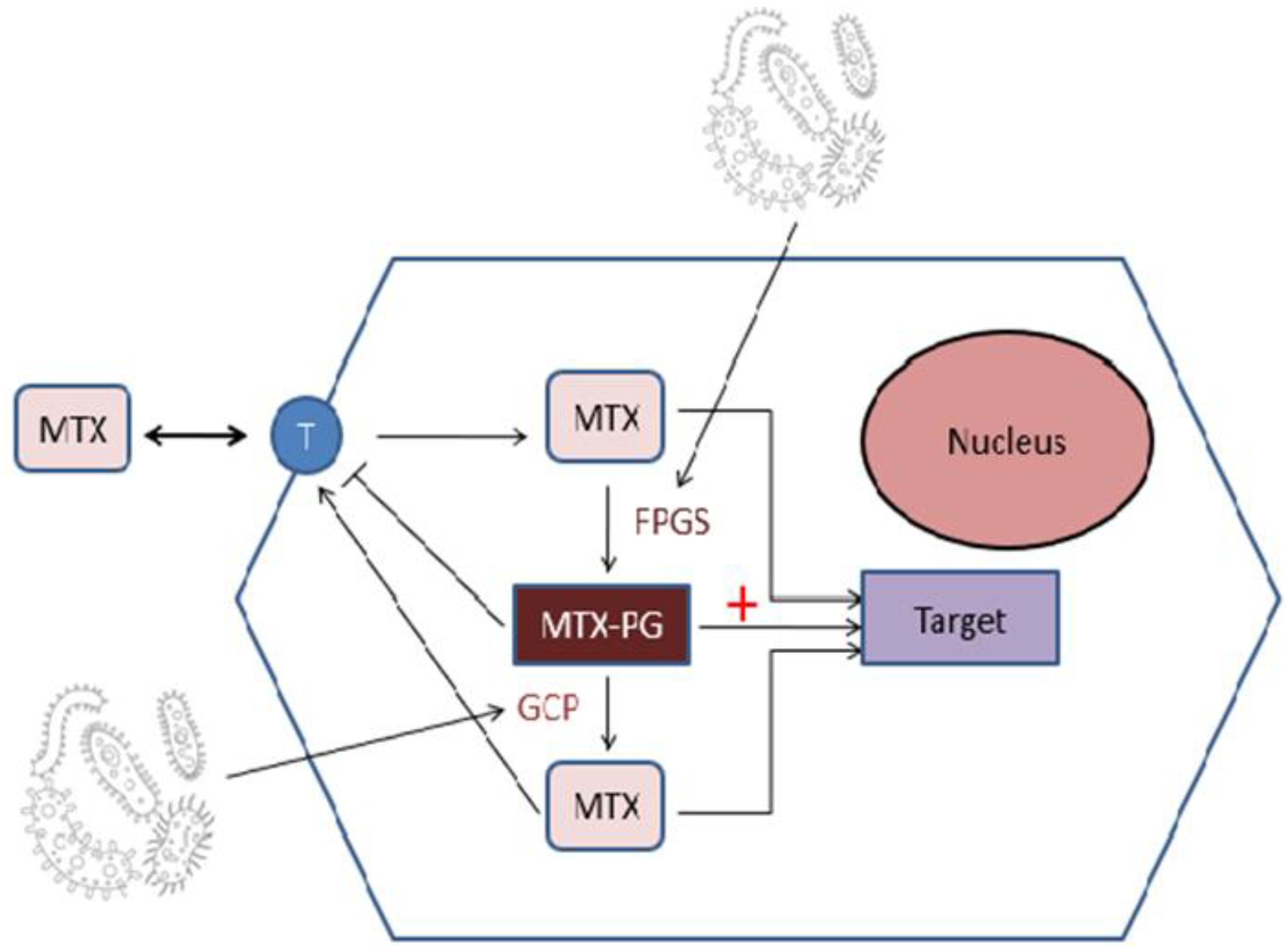
3.1.1. The Influence of Microbiota on MTX Response
3.1.2. The Influence of MTX on Microbiota Structure
3.2. Interaction of TNF-α Inhibitors with Microbiome
3.2.1. The Influence of Microbiota on TNF-α Inhibitors (TNFi) Response
3.2.2. The Influence of TNFi on Microbiota Structure
3.3. Interaction of IL-17 Inhibitors with Microbiome
The Influence of IL-17 Inhibitors on Microbiota Structure
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Abramson, S.B.; Scher, J.U. The metabolic role of the gut microbiota in health and rheumatic disease: Mechanisms and interventions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, M.F. The microbiome in autoimmune rheumatic disease. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 34, 101473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perricone, C.; Ceccarelli, F.; Saccucci, M.; Di Carlo, G.; Bogdanos, D.P.; Lucchetti, R.; Pilloni, A.; Valesini, G.; Polimeni, A.; Conti, F. Porphyromonasgingivalis and rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Zou, F.; Cheng, X.; Huang, Y.; Zou, H.; Niu, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Shan, F.; Luo, A.; Teng, W.; et al. Porphyromonasgingivalis induces periodontitis, causes immune imbalance, and promotes rheumatoid arthritis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 110, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, R.; Oduro, P.K.; Sun, T.; Chen, H.; Yi, Y.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Q.; Leng, L.; Yang, L.; et al. The Relationship Between Porphyromonas Gingivalis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022, 12, 956417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimenti, M.S.; Perricone, C.; Novelli, L.; Caso, F.; Costa, L.; Bogdanos, D.; Conigliaro, P.; Triggianese, P.; Ciccacci, C.; Borgiani, P.; et al. Interaction between microbiome and host genetics in psoriatic arthritis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, N.; Wait, R.; Sroka, A.; Eick, S.; Nguyen, K.A.; Lundberg, K.; Kinloch, A.; Culshaw, S.; Potempa, J.; Venables, P.J. Peptidylarginine deiminase from Porphyromonas gingivalis citrullinates human fibrinogen and α-enolase: Implications for autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2662–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, F.P.J.; Sprenger, N.; Yap, I.K.S.; Wang, Y.; Bibiloni, R.; Rochat, F.; Rezzi, S.; Cherbut, C.; Kochhar, S.; Lindon, J.C.; et al. Panorganismal gut microbiome-host metabolic crosstalk. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 2090–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mowat, A.M. To respond or not to respond–A personal perspective of intestinal tolerance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulthess, J.; Pandey, S.; Capitani, M.; Rue-Albrecht, K.C.; Arnold, I.; Franchini, F.; Chomka, A.; Ilott, N.E.; Johnston, D.G.W.; Pires, E.; et al. The Short Chain Fatty Acid Butyrate Imprints an Antimicrobial Program in Macrophages. Immunity 2019, 50, 432–445.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Constantinides, M.G.; McDonald, B.D.; Verhoef, P.A.; Bendelac, A. A committed precursor to innate lymphoid cells. Nature 2014, 508, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Courtemanche, C.; Elson-Schwab, I.; Mashiyama, S.T.; Kerry, N.; Ames, B.N. Folate deficiency inhibits the proliferation of primary human CD8+ T lymphocytes in vitro. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3186–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peterson, D.A.; McNulty, N.P.; Guruge, J.L.; Gordon, J.I. IgA response to symbiotic bacteria as a mediator of gut homeostasis. Cell. Host Microbe 2007, 2, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gil-Cruz, C.; Perez-Shibayama, C.; De Martin, A.; Ronchi, F.; Van Der Borght, K.; Niederer, R.; Onder, L.; Lütge, M.; Novkovic, M.; Nindl, V.; et al. Microbiota-derived peptide mimics drive lethal inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Science 2019, 366, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, S.; Maruya, M.; Kato, L.M.; Suda, W.; Atarashi, K.; Doi, Y.; Tsutsui, Y.; Qin, H.; Honda, K.; Okada, T.; et al. Foxp3(+) T cells regulate immunoglobulin a selection and facilitate diversification of bacterial species responsible for immune homeostasis. Immunity 2014, 41, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enright, E.F.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Joyce, S.A.; Griffin, B.T. The Impact of the Gut Microbiota on Drug Metabolism and Clinical Outcome. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2016, 89, 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Quirke, A.M.; Lugli, E.B.; Wegner, N.; Hamilton, B.C.; Charles, P.; Chowdhury, M.; Ytterberg, A.J.; Zubarev, R.A.; Potempa, J.; Culshaw, S.; et al. Heightened immune response to autocitrullinatedPorphyromonasgingivalispeptidylarginine deiminase: A potential mechanism for breaching immunologic tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scher, J.U.; Abramson, S.B. The microbiome and rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Koenders, M.I.; Devesa, I.; Roelofs, M.F.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Heuvelmans-Jacobs, M.; Akira, S.; Nicklin, M.J.H.; Ribeiro-Dias, F.; et al. Stimulation of TLR2 and TLR4 differentially skews the balance of T cells in a mouse model of arthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.J.; Ivanov, I.I.; Darce, J.; Hattori, K.; Shima, T.; Umesaki, Y.; Littman, D.R.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Gut-residing segmented filamentous bacteria drive autoimmune arthritis via T helper 17 cells. Immunity 2010, 32, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.M.; Hazen, S.L. The gut microbial endocrine organ: Bacterially derived signals driving cardiometabolic diseases. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kriegel, M.A.; Sefik, E.; Hill, J.A.; Wu, H.J.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Naturally transmitted segmented filamentous bacteria segregate with diabetes protection in nonobese diabetic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11548–11553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochoa-Repáraz, J.; Mielcarz, D.W.; Ditrio, L.E.; Burroughs, A.R.; Foureau, D.M.; Haque-Begum, S.; Kasper, L.H. Role of gut commensal microflora in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6041–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greiling, T.M.; Dehner, C.; Chen, X.; Hughes, K.; Iñiguez, A.J.; Boccitto, m.; Zegarra Ruiz, D.; Renfroe, S.C.; Vieira, S.M.; Ruff, W.E.; et al. Commensal orthologs of the human autoantigen Ro60 as triggers of autoimmunity in lupus. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaan2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horai, R.; Zárate-Bladés, C.R.; Dillenburg-Pilla, P.; Chen, J.; Kielczewski, J.L.; Silver, P.B.; Jittayasothorn, Y.; Chan, C.C.; Yamane, H.; Honda, K.; et al. Microbiota-Dependent Activation of an Autoreactive T Cell Receptor Provokes Autoimmunity in an Immunologically Privileged Site. Immunity 2015, 43, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tai, N.; Peng, J.; Liu, F.; Gulden, E.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Wong, F.S.; Wen, L. Microbial antigen mimics activate diabetogenic CD8 T cells in NOD mice. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2129–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hebbandi Nanjundappa, R.; Ronchi, F.; Wang, J.; Clemente-Casares, X.; Yamanouchi, J.; Sokke Umeshappa, C.; Yang, Y.; Blanco, J.; Bassolas-Molina, H.; Salas, A.; et al. A Gut Microbial Mimic that Hijacks Diabetogenic Autoreactivity to Suppress Colitis. Cell 2017, 171, 655–667.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruff, W.E.; Dehner, C.; Kim, W.J.; Pagovich, O.; Aguiar, C.L.; Yu, A.T.; Roth, A.S.; Vieira, S.M.; Kriegel, C.; Adeniyi, O.; et al. Pathogenic Autoreactive T and B Cells Cross-React with Mimotopes Expressed by a Common Human Gut Commensal to Trigger Autoimmunity. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 100–113.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amedei, A.; Boem, F. I’ve Gut A Feeling: Microbiota Impacting the Conceptual and Experimental Perspectives of Personalized Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, E3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baraliakos, X.; Listing, J.; Fritz, C.; Haibel, H.; Alten, R.; Burmester, G.R.; Krause, A.; Schewe, S.; Schneider, M.; Sörensen, H.; et al. Persistent clinical efficacy and safety of infliximab in ankylosing spondylitis after 8 years--early clinical response predicts long-term outcome. Rheumatol. Oxf. Engl. 2011, 50, 1690–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedger, L.M.; McDermott, M.F. TNF and TNF-receptors: From mediators of cell death and inflammation to therapeutic giants—past, present and future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 453–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sfikakis, P.P. The first decade of biologic TNF antagonists in clinical practice: Lessons learned, unresolved issues and future directions. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2010, 11, 180–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.M.; Deodhar, A.; Akl, E.A.; Lui, A.; Ermann, J.; Gensler, L.S.; Smith, J.A.; Borenstein, D.; Hiratzka, J.; Weiss, P.F.; et al. American College of Rheumatology/Spondylitis Association of America/Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network 2015 Recommendations for the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 282–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizkallah, M.R.; Saad, R.; Aziz, R.K. The Human Microbiome Project, Personalized Medicine and the Birth of Pharmacomicrobiomics. Curr. Pharm. Pers Med. 2010, 8, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smolen, J.S.; Landewé, R.B.M.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Kerschbaumer, A.; McInnes, I.B.; Sepriano, A.; Van Vollenhoven, R.; De Wit, M.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gossec, L.; Baraliakos, X.; Kerschbaumer, A.; De Wit, M.; McInnes, I.; Dougados, M.; Primdahl, J.; McGonagle, D.G.; Aletaha, D.; Balanescu, A.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of psoriatic arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2019 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijde, D.; Ramiro, S.; Landewé, R.; Baraliakos, X.; Van Den Bosch, F.; Sepriano, A.; Regel, A.; Ciurea, A.; Dagfinrud, H.; Dougados, M.; et al. 2016 update of the ASAS-EULAR management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artacho, A.; Isaac, S.; Nayak, R.; Flor-Duro, A.; Alexander, M.; Koo, I.; Manasson, J.; Smith, P.B.; Rosenthal, P.; Homsi, Y.; et al. The Pretreatment Gut Microbiome Is Associated with Lack of Response to Methotrexate in New-Onset Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, H.; Feng, H.; Wang, D.; Liang, D.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, R.S.; Becker, M.L. Metabolomic Profiling Identifies Exogenous and Microbiota-Derived Metabolites as Markers of Methotrexate Efficacy in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2021.768599 (accessed on 24 September 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öman, A.; Dicksved, J.; Engstrand, L.; Berntson, L. Fecal microbiota in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis treated with methotrexate or etanercept. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2021, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazin, T.; Hooks, K.B.; Barnetche, T.; Truchetet, M.E.; Enaud, R.; Richez, C.; Dougados, M.; Hubert, C.; Barrè, A.; Nikolski, M.; et al. Microbiota Composition May Predict Anti-Tnf α Response in Spondyloarthritis Patients: An Exploratory Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, X.; Fang, l.; Jin, O.; Gu, J. Adalimumab Therapy Restores the Gut Microbiota in Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 700570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Sternes, P.R.; Wang, M.; Song, J.; Morrison, M.; Li, T.; Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; He, F.; Zhu, J.; et al. Shotgun metagenomics reveals an enrichment of potentially cross-reactive bacterial epitopes in ankylosing spondylitis patients, as well as the effects of TNFi therapy upon microbiome composition. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Xia, X.; He, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Q.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Association of anti-TNF-α treatment with gut microbiota of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2022, 32, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Ma, C.; Zhang, B. Dynamic Variations in Gut Microbiota in Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Treated with Anti-TNF-α for Six Months. Ann. Clin. Lab Sci. 2020, 50, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Manasson, J.; Wallach, D.S.; Guggino, G.; Stapylon, M.; Badri, M.H.; Solomon, G.; Reddy, S.M.; Coras, R.; Aksenov, A.A.; Jones, D.R.; et al. Interleukin-17 Inhibition in Spondyloarthritis Is Associated With Subclinical Gut Microbiome Perturbations and a Distinctive Interleukin-25-Driven Intestinal Inflammation. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronstein, B.N.; Aune, T.M. Methotrexate and its mechanisms of action in inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinblatt, M.E. Methotrexate: Who would have predicted its importance in rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Detert, J.; Bastian, H.; Listing, J.; Weiß, A.; Wassenberg, S.; Liebhaber, A.; Rockwitz, K.; Alten, R.; Krüger, K.; Rau, R.; et al. Induction therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate for 24 weeks followed by methotrexate monotherapy up to week 48 versus methotrexate therapy alone for DMARD-naive patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: HIT HARD, an investigator-initiated study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijbrandts, C.A.; Tak, P.P. Prediction of Response to Targeted Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letertre, M.P.M.; Munjoma, N.; Wolfer, K.; Pechlivanis, A.; McDonald, J.A.K.; Hardwick, R.N.; Cherrington, N.J.; Coen, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Hoyles, L.; et al. A Two-Way Interaction between Methotrexate and the Gut Microbiota of Male Sprague–Dawley Rats. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 3326–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Xia, X.; Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Yu, C.; Huang, R.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuan, F.; et al. Induction and Amelioration of Methotrexate-Induced Gastrointestinal Toxicity are Related to Immune Response and Gut Microbiota. EBioMedicine 2018, 33, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webb, M. Inactivation of analogues of folic acid by certain non-exacting bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1955, 17, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, R.R.; Alexander, M.; Deshpande, I.; Stapleton-Gray, K.; Rimal, B.; Patterson, A.D.; Ubeda, C.; Scher, J.U.; Turnbaugh, P.J. Methotrexate impacts conserved pathways in diverse human gut bacteria leading to decreased host immune activation. Cell Host. Microbe 2021, 29, 362–377.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.M. Toward a better understanding of methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelatos, G.; Bamias, G.; Kitas, G.D.; Kollias, G.; Sfikakis, P.P. The second decade of anti-TNF-a therapy in clinical practice:New lessons and future directions in the COVID-19 era. Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 1493–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolge, S.C.; Goren, A.; Tandon, N. Reasons for discontinuation of subcutaneous biologic therapy in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A patient perspective. Patient. Prefer Adherence 2015, 9, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cong, J.; Zhang, X. Roles of intestinal microbiota in response to cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Spencer, C.N.; Nezi, L.; Reuben, A.; Andrews, M.C.; Karpinets, T.V.; Prieto, P.A.; Vicente, D.; Hoffman, K.; Wei, S.C.; et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalyana Chakravarthy, S.; Jayasudha, R.; Sai Prashanthi, G.; Hasnat Ali, M.; Sharma, S.; Tyagi, M.; Shivaji, S. Dysbiosis in the Gut Bacterial Microbiome of Patients with Uveitis, an Inflammatory Disease of the Eye. Indian J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, N.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Tsai, T.F.; Chiu, H.Y. Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis is Perturbed Differently During Secukinumab and Ustekinumab Therapy and Associated with Response to Treatment. Clin. Drug Investig. 2019, 39, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditto, M.C.; Parisi, S.; Landolfi, G.; Borrelli, R.; Realmuto, C.; Finucci, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Astegiano, M.; Zanetti, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota changes induced by TNF-inhibitors in IBD-related spondyloarthritis. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets, D.; Mas-de-Xaxars, T.; López-Siles, M.; Martínez-Medina, M.; Bahì, A.; Sàbat, M.; Louvriex, R.; Miquel-Cusachs, J.O.; Garcia-Gil, J.L.; Aldeguer, X. Anti-tumour Necrosis Factor Treatment with Adalimumab Induces Changes in the Microbiota of Crohn’s Disease. J. Crohns Colitis 2015, 9, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Fan, Q.; Li, Z.; Goll, R.; Florholmen, J. Evaluation of anti-TNF therapeutic response in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: Current and novel biomarkers. EBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Geng, S.; Guo, K. Effectiveness and safety of Adalimumab in psoriasis and its influence on gut microbiome. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 162, 105308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vétizou, M.; Pitt, J.M.; Daillère, R.; Lepage, P.; Waldschmitt, N.; Flament, C.; Rusakiewicz, S.; Routy, B.; Roberti, M.P.; Duong, C.P.M.; et al. Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on the gut microbiota. Science 2015, 350, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Fukui, H.; Ran, Y.; Xu, X.; Ebisutani, N.; Nakanishi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Maeda, A.; Makizaki, Y.; Tomita, T.; et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 Has a Preventive Effect on the Acceleration of Colonic Permeability and M1 Macrophage Population in Maternally Separated Rats. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wiesnoski, D.H.; Helmink, B.A.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Choi, K.; Dupont, H.L.; Jiang, Z.D.; Abu-Sbeih, H.; Sanchez, C.A.; Chang, C.C.; et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation for refractory immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated colitis. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | N° PT | N° HC | Disease | Therapy | Sample | Results |
| Artacho, 2021 [39] | 26 | 21 | RA | MTX | Stool |
|
| Zhang X., 2015 [40] | 77 | 80 | RA | MTX | Stool |
|
| Funk and Becker, 2021 [41] | 30 | 0 | JIA | MTX | Plasma |
|
| Öman, 2021 [42] | 41 | 45 | JIA | 29 MTX 12 ETN | Stool |
|
| Bazin, 2018 [43] | 18 | 0 | AS | 15 ETN 2 ADA 1 INF | Stool |
|
| Chen, 2021 [44] | 30 | 24 | AS | ADA | Stool |
|
| Yin, 2020 [45] | 127 | 123 | AS | TNFi | Stool |
|
| Dai, 2022 [46] | 24 | 11 | AS | TNFi | Stool |
|
| Zhang, 2020 [47] | 20 | 19 | SpA (both AS and PsA) | ADA | Stool |
|
| Manasson, 2020 [48] | 29 | 0 | PsA/AS | 15 TNFi 14 IL-17i | Stool (n = 29), Ileal biopsy (n = 5) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peretti, S.; Torracchi, S.; Russo, E.; Bonomi, F.; Fiorentini, E.; Aoufy, K.E.; Bruni, C.; Lepri, G.; Orlandi, M.; Chimenti, M.S.; et al. The Yin-Yang Pharmacomicrobiomics on Treatment Response in Inflammatory Arthritides: A Narrative Review. Genes 2023, 14, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010089
Peretti S, Torracchi S, Russo E, Bonomi F, Fiorentini E, Aoufy KE, Bruni C, Lepri G, Orlandi M, Chimenti MS, et al. The Yin-Yang Pharmacomicrobiomics on Treatment Response in Inflammatory Arthritides: A Narrative Review. Genes. 2023; 14(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010089
Chicago/Turabian StylePeretti, Silvia, Sara Torracchi, Edda Russo, Francesco Bonomi, Elisa Fiorentini, Khadija El Aoufy, Cosimo Bruni, Gemma Lepri, Martina Orlandi, Maria Sole Chimenti, and et al. 2023. "The Yin-Yang Pharmacomicrobiomics on Treatment Response in Inflammatory Arthritides: A Narrative Review" Genes 14, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010089
APA StylePeretti, S., Torracchi, S., Russo, E., Bonomi, F., Fiorentini, E., Aoufy, K. E., Bruni, C., Lepri, G., Orlandi, M., Chimenti, M. S., Guiducci, S., Amedei, A., Matucci-Cerinic, M., & Bellando Randone, S. (2023). The Yin-Yang Pharmacomicrobiomics on Treatment Response in Inflammatory Arthritides: A Narrative Review. Genes, 14(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010089








