Identification of CmbHLH Transcription Factor Family and Excavation of CmbHLHs Resistant to Necrotrophic Fungus Alternaria in Chrysanthemum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Pathogenic Strains
2.2. Screening and Physicochemical Properties Analysis of the CmbHLH TF Family
2.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment, Phylogenetic, and Conserved Motifs Analysis of CmbHLH Family Proteins
2.4. Excavation of Candidate CmbHLHs Resistant to Necrotrophic Fungi and Their Cis-Element Analysis
2.5. Isolation and Arabidopsis Transformation of CmbHLH18
2.6. Inoculation of Necrotrophic Fungi and Sampling
2.7. Morphology and Disease Severity Index (DSI) after Inoculation with A. brassicicola in CmbHLH18 Transgenic Arabidopsis Lines
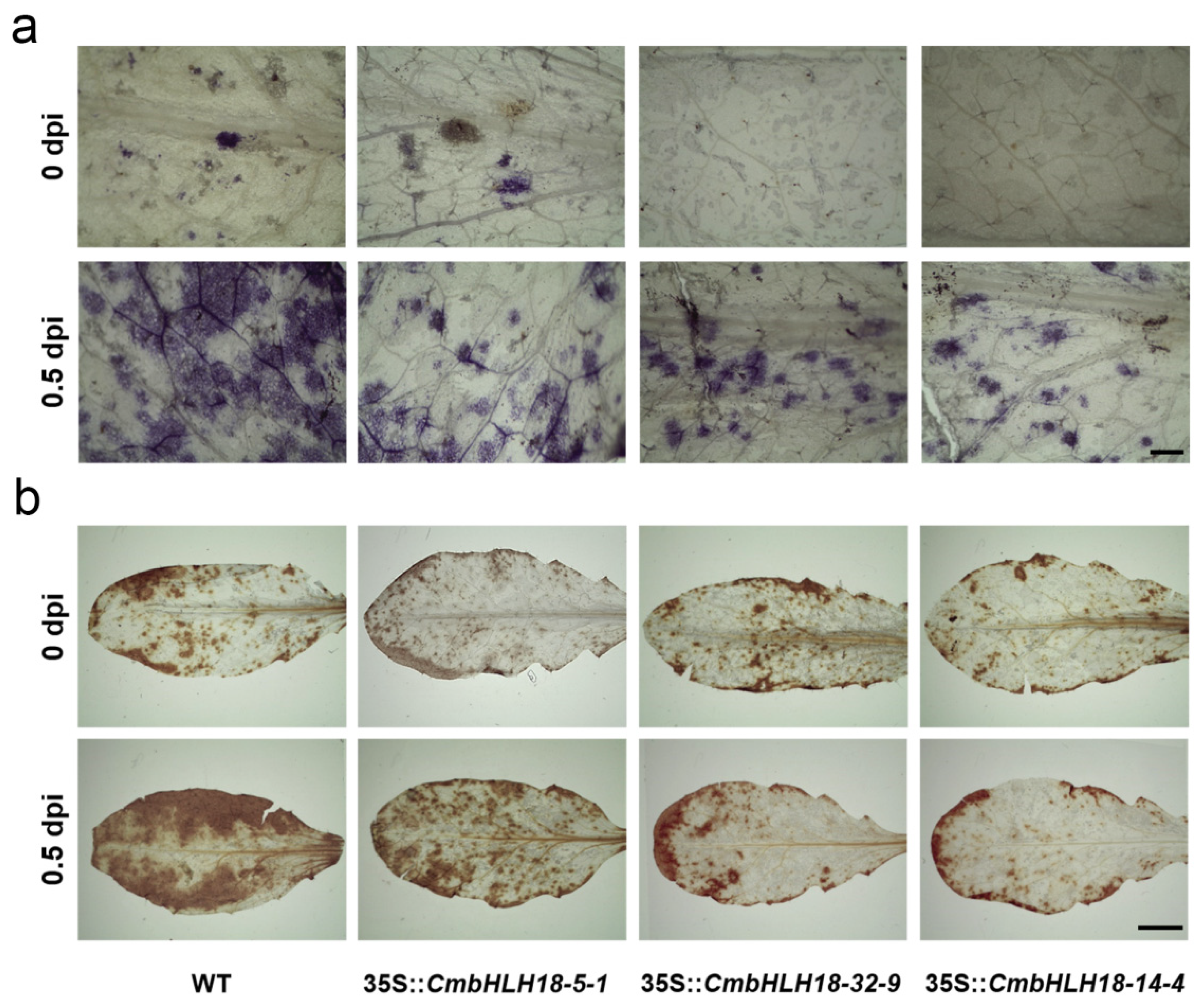
2.8. Histochemical Staining and Microscopic Analysis after Inoculation with A. brassicicola in Arabidopsis and CmbHLH18 Transgenic Arabidopsis Lines
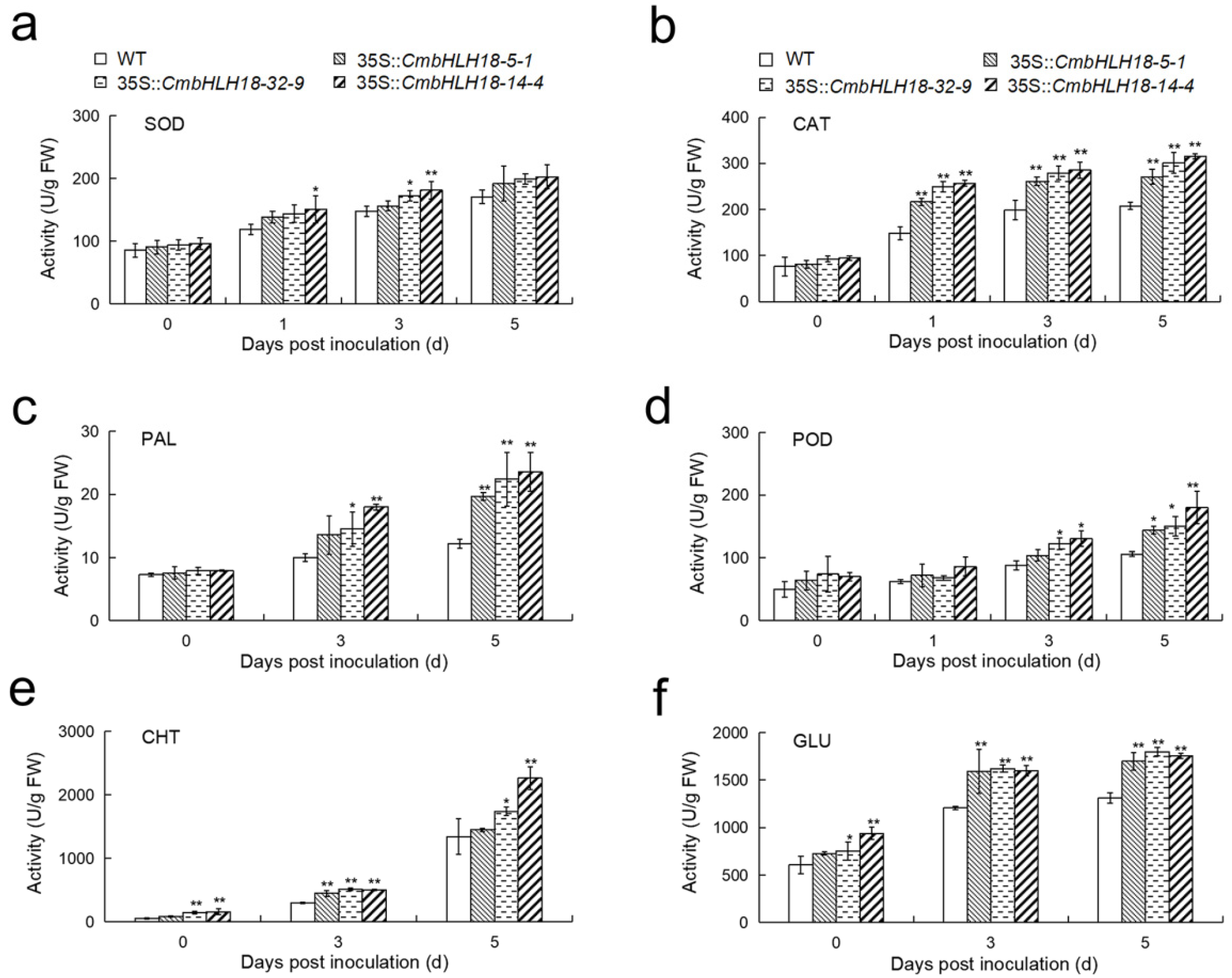
2.9. Determination of Enzyme Activity and Gene Expression Analysis of Arabidopsis Lines
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the CmbHLH Transcription Factor Family
3.1.1. Hydrophilicity and High Aliphatic Amino Acid Content in 71 CmbHLH TFs Identified in Chrysanthemum
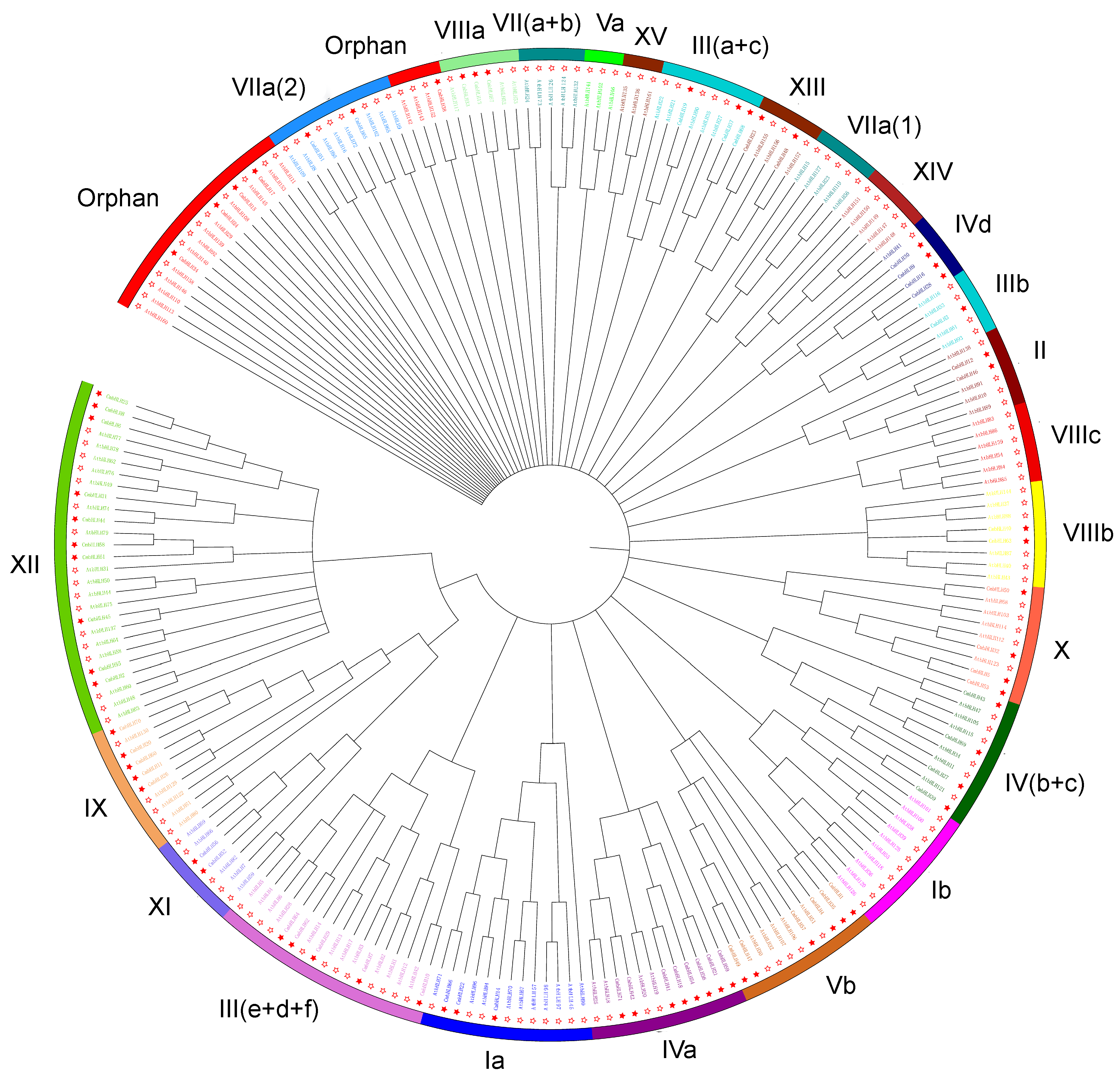
3.1.2. Phylogenetic Differences between Groups of bHLHs from Chrysanthemum and Arabidopsis
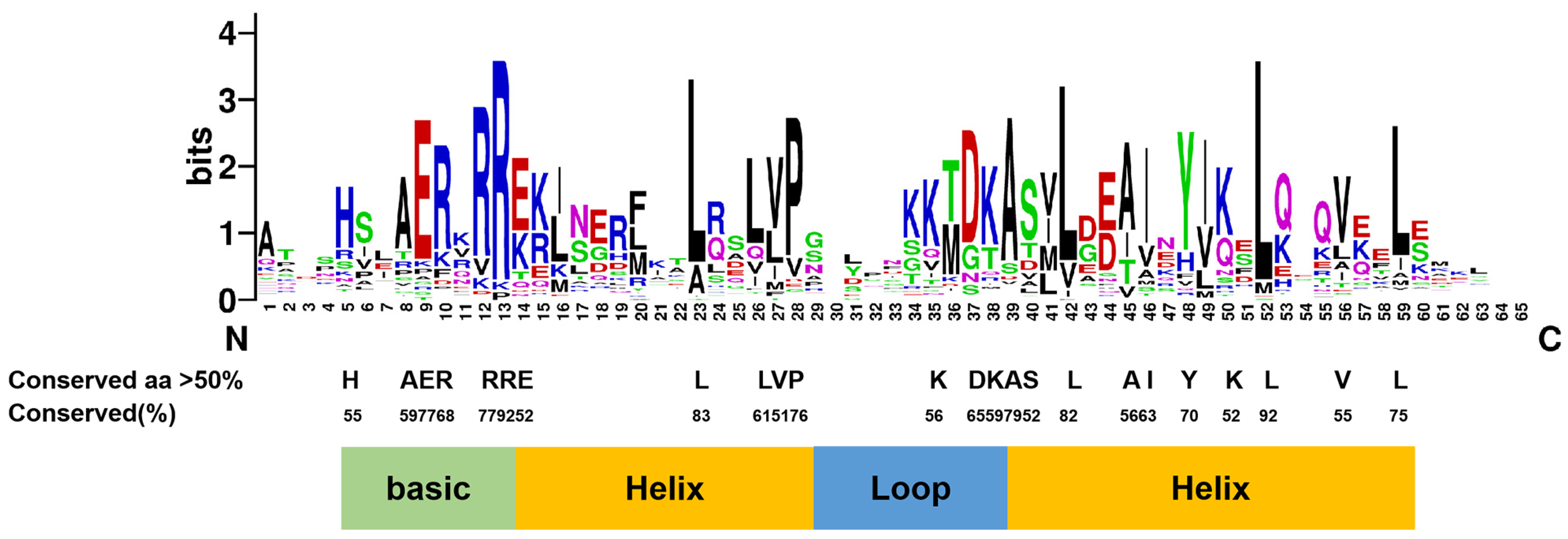
3.1.3. Domains of CmbHLHs Identified by Variation-Conserved Residues
3.2. Excavation of Candidate CmbHLHs’ Resistance to Necrotrophic Fungus Alternaria
3.2.1. Analysis of Promoters of the Five Candidate CmbHLHs
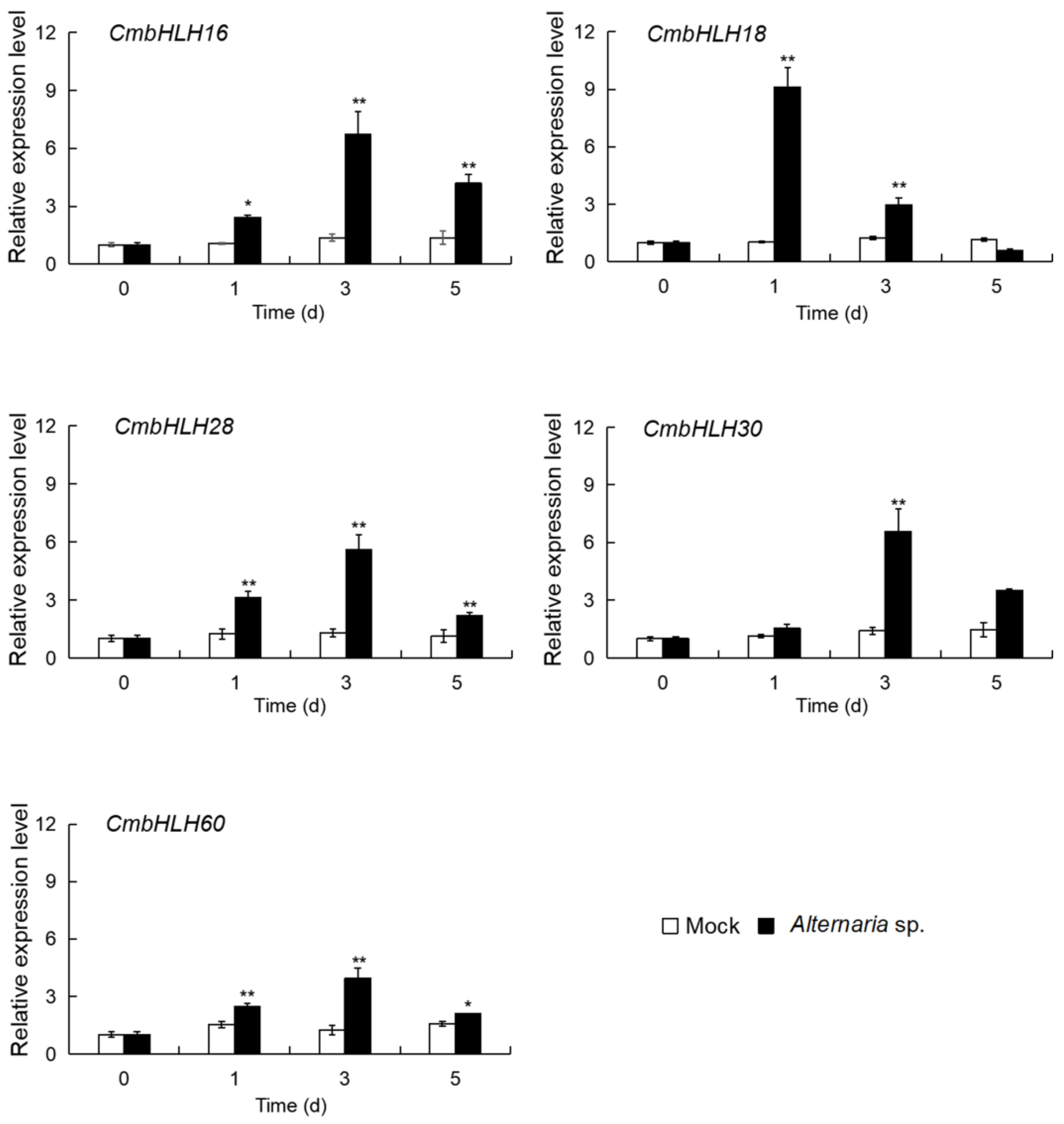
3.2.2. Expression Analysis of the Five up CmbHLHs in Response to Necrotrophic Fungus Alternaria
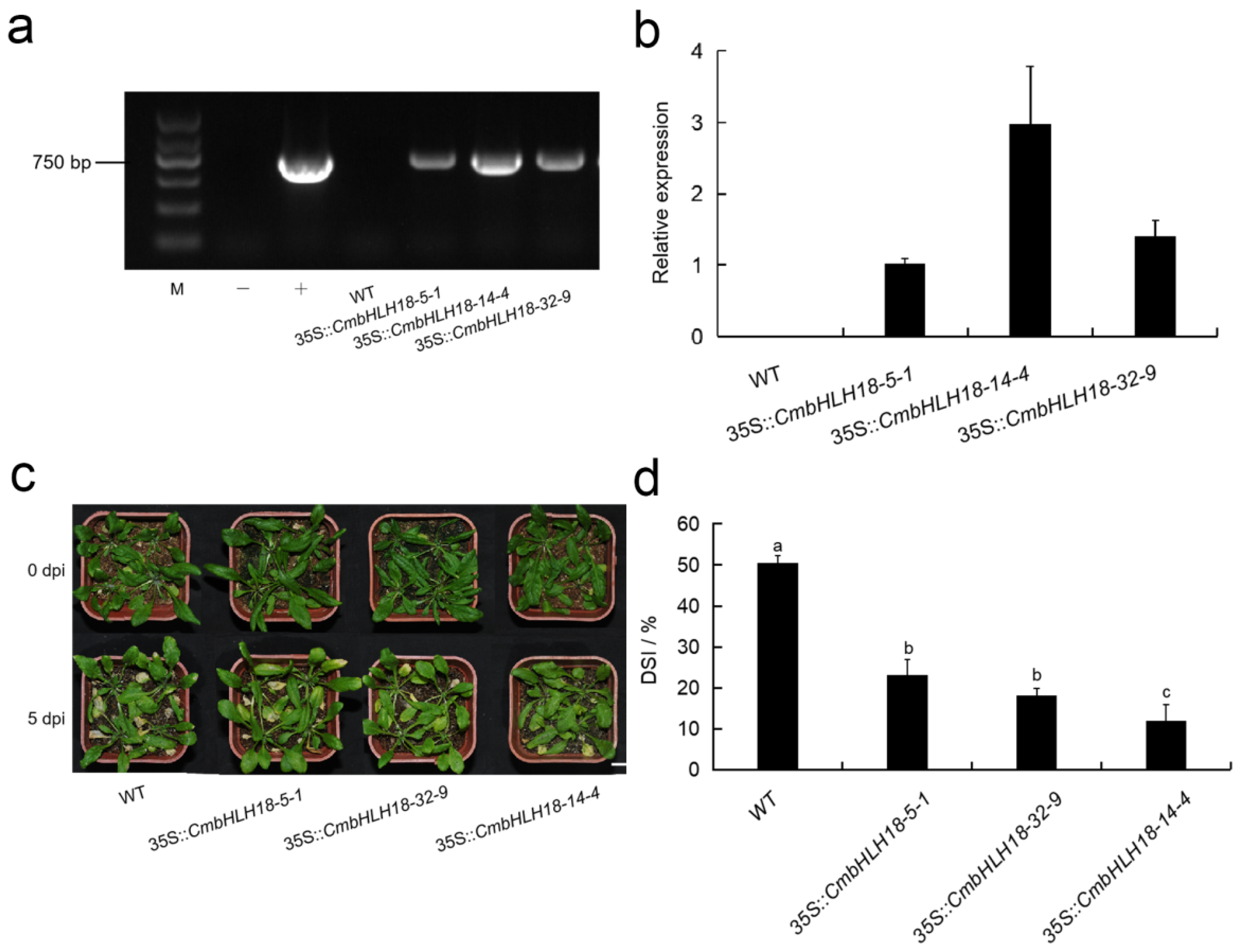
3.2.3. CmbHLH18 Enhances Resistance against Necrotrophic Fungus Alternaria in Arabidopsis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yasemin, S.; Köksal, N.; Özkaya, A.; Yener, M. Growth and physiological responses of “Chrysanthemum paludosum” under salinity stress. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 11, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Li, H.Q.; Hu, S.X. Investigation on the present situation of commodity types of Chrysanthemum. China Mod. Med. 2016, 23, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.T.; Song, L.Y.; Jiang, L.W.; Zhu, Y.T.; Gao, Q.H.; Wang, D.D.; Xie, J.; Lv, M.; Liu, P.; Li, M.J. The integration of transcriptomic and transgenic analyses reveals the involvement of the SA response pathway in the defense of Chrysanthemum against the necrotrophic fungus Alternaria sp. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.T.; Wang, M.; Wang, T.L.; Li, M.J. Isolation and identification of the pathogen of black spot disease of Chrysanthemum huai. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2015, 42, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.M.; Yang, Y.C.; Zhang, H.H. A preliminary report on the occurrence and prevention of Chrysanthemum black spot in some areas of Shandong province. Guangdong Landsc. Archit. 2005, 6, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Sui, N. Transcriptional regulation of bHLH during plant response to stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferre-D’amare, A.R.; Pognonec, P.; Roeder, R.G.; Burley, S.K. Structure and function of the b/HLH/Z domain of USF. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D. Identification of bHLH Transcription Factor Family and Heterologous Disease Resistance Function of CmbHLH18 Gene in Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. Master’s Thesis, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang, China, May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.N.; Guo, H.Y.; Dai, X.M.; Cheng, Y.X.; Zheng, K.J.; Wang, X.P.; Wang, S.C. An ABA down-regulated bHLH transcription repressor gene, bHLH129 regulates root elongation and ABA response when overexpressed in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Lv, W.; Zhang, H.S.; Ma, L.; Li, P.H.; Ge, L.; Li, G. Genome-wide analysis of the basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factor family in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, H.; Tan, L.; Htet, N.N.W. Genome-wide identification, characterization of bHLH transcription factors in Mango. Trop. Plant Biol. 2021, 14, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichsen, D.M.; Nemhauser, J.; Muramitsu, T.; Maloof, J.N.; Alonso, J.; Ecker, J.R.; Furuya, M.; Chory, J. Three redundant brassinosteroid early response genes encode putative bHLH transcription factors required for normal growth. Genetics 2002, 162, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Qu, Y.X.; Wang, H.B.; Wang, J.J.; Song, A.P.; Hu, Y.H.; Chen, S.M.; Jiang, J.F.; Chen, F.D. The heterologous expression of a Chrysanthemum TCP-P transcription factor CmTCP14 suppresses organ size and delays senescence in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.S.; Joo, J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Nahm, B.H.; Song, S.L.; Cheong, J.J.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.K.; Choi, Y.D. OsbHLH148, a basic helix-loop-helix protein, interacts with OsJAZ proteins in a jasmonate signaling pathway leading to drought tolerance in rice. Plant J. 2011, 65, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Xiang, X.H.; Liu, D.; Yang, A.G.; Wang, Y.Y. Tobacco transcription factor NtbHLH123 confers tolerance to cold stress by regulating the NtCBF pathway and reactive oxygen species homeostasis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Li, S.X.; Yao, W.J.; Zhou, B.R.; Li, R.H.; Jiang, T.B. Characterization of the basic helix-loop-helix gene family and its tissue-differential expression in response to salt stress in poplar. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Song, A.P.; Li, P.L.; Chen, S.M.; Jiang, J.F.; Chen, F.D. A bHLH transcription factor regulates iron intake under Fe deficiency in Chrysanthemum. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.H.; Liu, T.X.; Nan, W.Z.; Jeewani, D.C.; Niu, Y.L.; Li, C.L.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Two transcription factors TaPpm1 and TaPpb1 co-regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple pericarps of wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, V.M.; Cavaçana, N.; Dantas, L.L.D.B.; Lee, N.; Hotta, C.T.; Imaizumi, T.; Menossi, M. The FBH family of bHLH transcription factors controls ACC synthase expression in sugarcane. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 2511–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Fujiwara, S.; Mitsuda, N.; Ohme-Takagi, M. A triantagonistic basic helix-loop-helix system regulates cell elongation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4483–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljegren, S.J.; Roeder, A.H.K.; Kempin, S.A.; Gremski, K.; Østergaard, L.; Guimil, S.; Reyes, D.K.; Yanofsky, A.M.F. Control of fruit patterning in Arabidopsis by INDEHISCENT. Cell 2004, 116, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szecsi, J.; Joly, C.; Bordji, K.; Varaud, E.; Cock, J.M.; Dumas, C.; Bendahmane, M. BIGPETALp, a bHLH transcription factor is involved in the Control of Arabidopsis petal size. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3912–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, B.; Amyot, L.; Johansen, C.; Sato, S.; Tabata, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Szczyglowski, K. Conservation of Lotus and Arabidopsis basic helix-loop-helix proteins reveals new players in root hair development. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaoka, M.M.; Pillitteri, L.J.; Fujii, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Bogenschutz, N.L.; Takabayashi, J.; Zhu, J.K.; Torii, K.U. SCREAM/ICE1 and SCREAM2 specify three cell-state transitional steps leading to Arabidopsis stomatal differentiation. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1775–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.T.; Lin, R.M.; Feng, J.; Qiu, D.W.; Chen, W.Q.; Xu, S.C. Wheat bHLH transcription factor gene, TabHLH060, enhances susceptibility of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana to Pseudomonas syringae. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 90, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ai, G.; Shen, D.; Chai, C.; Jia, Y.; Liu, W.; Dou, D. Bioinformatical analysis and prediction of Nicotiana benthamiana bHLH transcription factors in Phytophthora parasitica resistance. Genomics 2018, 111, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhu, L.F.; Wassan, G.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Miao, Y.H.; Shaban, M.; Hu, H.Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.L. GhJAZ2 attenuates cotton resistance to biotic stresses via the inhibition of the transcriptional activity of GhbHLH171. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Niu, B.F.; Gao, Y.; Fu, L.M.; Li, W.Z. CD-HIT Suite: A web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Z.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Yamashita, R.A.; Marchler-Bauer, A. NCBI’s conserved domain database and tools for protein domain analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 69, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acid. Res. 2018, 46, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; Castro, E.D.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASY: SIB bioinformatics resource portal. Nucleic Acid. Res. 2012, 40, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Gao, W.L.; Xue, C.L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.W.; Liu, M.J.; Zhao, J. Genome-wide analysis of the bHLH gene family in Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) and wild jujube. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamesch, P.; Berardini, T.Z.; Li, D.H.; Swarbreck, D.; Wilks, C.; Sasidharan, R.; Muller, R.; Dreher, K.; Alexander, D.L.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): Improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acid. Res. 2012, 40, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL): An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Fehling, H.; Matthiesen, J.; Lorenzen, S.; Schuldt, K.; Bernin, H.; Mareen, Z.; Lender, C.; Ernst, T.; Ittrich, H.; et al. Overexpression of differentially expressed genes identified in non-pathogenic and pathogenic entamoeba histolytica clones allow identification of new pathogenicity factors involved in amoebic liver abscess formation. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Peer, Y.V.; Rouzéet, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acid. Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghedira, R.; Buck, S.D.; Ex, F.V.; Angenon, G.; Depicker, A. T-DNA transfer and T-DNA integration efficiencies upon Arabidopsis thaliana root explant cocultivation and floral dip transformation. Planta 2013, 238, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.K.; Newman, T.K.; Gultzow, D.L.; Parfitt, S.C.; Drenth, A.; Smith, M.W. Commercial-scale Alternaria brown spot resistance screening as the first step in breeding new mandarins for Australia. Acta Hortic. 2015, 1065, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.J. Studies on Seedling’s Resistance of Related Species of Chrysanthemum to Alternaria Leaf Spot and Genetic Transformation of Chrysanthemum with hrfA gene. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Lin, Z.F. Use of evans blue for testing cell viability of intact leaves of plant. J. Plant Physiol. 2011, 47, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuritatashiro, A.; Hayashi, N.; Oyanagi, T.; Sasamoto, H. New factors for protoplast-callose-fiber formation in salt-tolerant mangrove plants, Avicennia alba and Bruguiera sexangula and analysis of fiber substructures. J. Plant Stud. 2021, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Fu, X.Z.; Peng, T.; Huang, X.S.; Fan, Q.J.; Liu, J.H. Spermine pretreatment confers dehydration tolerance of citrus in vitro plants via modulation of antioxidative capacity and stomatal response. Tree Physiol. 2010, 30, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Jiang, W.B.; Bi, Y.; Luo, Y.B. Postharvest BTH treatment induces resistance of peach (Prunus persica L. cv. Jiubao) fruit to infection by Penicillium expansum and enhances activity of fruit defense mechanisms. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2005, 35, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−△△CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Guan, Y.X.; Chen, S.K.; Li, H.F. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Duan, X.P.; Jiang, H.X.; Sun, Y.J.; Tang, Y.P.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J.K.; Liang, W.Q.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.Y.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of basic/helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, K.A.; Hudson, M.E. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in the sacred lotus, Nelumbo Nucifera. Trop. Plant Biol. 2014, 7, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gu, X.R.; Wei, C.H.; Yang, X.Z.; Zhang, X. Identification and expression analysis under abiotic stresses of the bHLH transcription factor gene family in Watermelon. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2016, 43, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Z.Q.; Li, R.H.; Xu, Y.; Kong, Y.Z.; Zhou, G.K.; Meng, C.X.; Hu, R.B. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of HD-ZIP gene family in Medicago truncatula. Genomics 2020, 112, 3624–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesi, N.; Debeaujon, I.; Jond, C.; Pelletier, G.; Caboche, M.; Lepiniec, L. The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis Siliques. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, T.C.; Wang, J.J.; Huang, H.; Liu, B.; Gao, H.; Liu, Y.L.; Song, S.S.; Xie, D.X. Regulation of jasmonate-induced leaf senescence by antagonism between bHLH subgroup IIIe and IIId factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 1634–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.L.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.W.; Yan, F.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.Y. Jasmonic acid-induced inhibition of root growth and leaf senescence is reduced by GmbHLH3, a soybean bHLH transcription factor. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 100, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Xin, R.J.; Kim, D.H.; Sung, S.; Lange, T.; Hu, E. NO FLOWERING IN SHORT DAY (NFL) is a bHLH transcription factor that promotes flowering specifically under short-day conditions in Arabidopsis. Development 2016, 143, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Yang, D.Y.; Ma, F.L.; Zhu, M.L.; Shi, Z.Y.; Miao, X.X. OsHLH61-OsbHLH96 influences rice defense to brown planthopper through regulating the pathogen-related genes. Rice 2019, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, C.; Lee, M.M.; Gonzalez, A.; Zhang, F.; Lloyd, A.; Schiefelbein, J. The bHLH genes GLABRA3 (GL3) and ENHANCER OF GLABRA3 (EGL3) specify epidermal cell fate in the Arabidopsis root. Development 2003, 130, 6431–6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, C.L.; Cui, M.; Zhou, W.J.; Wu, H.L.; Ling, H.Q. Four IVa bHLH transcription factors are novel interactors of FIT and mediate JA inhibition of iron uptake in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 1166–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.; Lamb, C. Systemic immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, R.; Jones, J.D.G. Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flors, V.; Ton, J.; Jakab, G.; Mauch-Mani, B. Abscisic acid and callose: Team players in defence against pathogens? J. Phytopathol. 2005, 153, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzeslowska, M. The cell wall in plant cell response to trace metals: Polysaccharide remodeling and its role in defense strategy. Acta Physiol. Plant 2011, 33, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, E.; Pastor, V.; Robert, J.; Flors, V.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Ton, J. Callose deposition: A multifaceted plant defense response. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, K.; Kimura, S.; Rokka, A.; Tran, H.C.; Toyota, M.; Kukkonen, J.P.; Wrzaczek, M. CRK2 enhances salt tolerance by regulating callose deposition in connection with PLDα1. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Andargie, M.; Fang, R. The function and biosynthesis of callose in high plants. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.F.; Sun, Z.X.; Li, C.L.; Zhao, X.R.; Li, M.F.; Deng, R.Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Zhao, H.X.; Chen, H.; Wu, Q. Overexpression of Fagopyrum tataricum FtbHLH2 enhances tolerance to cold stress in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.Q.; Xu, H.R.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, G.Q.; Bai, Y.J.; Wei, Y.X.; Shi, H.T. LSD3 mediates the oxidative stress response through fine-tuning APX2 activity and the NF-YC15-GSTs module in cassava. Plant J. 2022, 110, 1447–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.B.; Zhu, H.; Chen, D.H.; Li, Z.J.; Peng, R.H.; Yao, Q.H. A grape bHLH transcription factor gene, VvbHLH1, increases the accumulation of flavonoids and enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2016, 125, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayoso, C.; Pomar, F.; Novo-Uzal, E.; Merino, F.; de Ilárduya, Ó.M. The Ve-mediated resistance response of the tomato to Verticillium dahliae involves H2O2, peroxidase and lignins and drives PAL gene expression. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.J.; Zhou, J.X.; Zhang, J.R.; Zhang, S.Y. Chitosan combined with sodium silicate treatment induces resistance against rot caused by Alternaria alternata in postharvest jujube fruit. J. Phytopathol. 2019, 167, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Iwai, T.; Hiraga, S.; Kuroda, K.; Seo, S.; Mitsuhara, I.; Miyasaka, A.; Iwano, M.; Ito, H.; Matsui, H.; et al. Ten rice peroxidases redundantly respond to multiple stresses including infection with rice blast fungus. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | ID | aa | MW (×104) | pI | II | AI | GRAVY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CmbHLH1 | CHR00023546-RA | 272 | 3.062 | 7.79 | 49.89 | 81.36 | −0.436 |
| CmbHLH2 | CHR00043772-RA | 307 | 3.483 | 6.41 | 52.99 | 73.65 | −0.578 |
| CmbHLH3 | CHR00034167-RA | 328 | 3.700 | 4.8 | 62.02 | 74.85 | −0.588 |
| CmbHLH4 | CHR00082406-RA | 244 | 2.729 | 5.99 | 28.9 | 80.7 | −0.441 |
| CmbHLH5 | CHR00073020-RA | 417 | 4.630 | 5.59 | 59.66 | 54.68 | −0.792 |
| CmbHLH6 | CHR00087928-RA | 411 | 4.581 | 6.82 | 57.63 | 61.39 | −0.763 |
| CmbHLH7 | CHR00079719-RA | 468 | 5.246 | 6.35 | 45.31 | 75.79 | −0.551 |
| CmbHLH8 | CHR00010518-RA | 480 | 5.293 | 6.09 | 47.99 | 58.06 | -0.739 |
| CmbHLH9 | CHR00002838-RA | 398 | 4.480 | 8.64 | 60.66 | 76.68 | −0.589 |
| CmbHLH10 | CHR00029628-RA | 609 | 6.830 | 4.92 | 47.81 | 87.87 | −0.329 |
| CmbHLH11 | CHR00053551-RA | 361 | 4.081 | 6.08 | 61.37 | 54.88 | −0.923 |
| CmbHLH12 | CHR00027604-RA | 278 | 3.093 | 8.41 | 29.44 | 80.22 | −0.53 |
| CmbHLH13 | CHR00020071-RA | 410 | 4.558 | 9.29 | 47.53 | 76.56 | −0.437 |
| CmbHLH14 | CHR00001268-RA | 306 | 3.452 | 5.73 | 61.53 | 78.73 | −0.423 |
| CmbHLH15 | CHR00066657-RA | 453 | 5.049 | 6.33 | 32.95 | 63.07 | −0.728 |
| CmbHLH16 | CHR00085490-RA | 937 | 10.349 | 5.36 | 51.72 | 70.52 | −0.551 |
| CmbHLH17 | CHR00014650-RA | 350 | 3.838 | 6.19 | 50.86 | 61.57 | −0.693 |
| CmbHLH18 | CHR00061827-RA | 280 | 3.096 | 5.07 | 52.56 | 74.18 | −0.44 |
| CmbHLH19 | CHR00004349-RA | 427 | 4.836 | 5.51 | 51.06 | 77.07 | −0.594 |
| CmbHLH20 | CHR00030629-RA | 291 | 3.261 | 9.08 | 60.77 | 56.98 | −0.832 |
| CmbHLH21 | CHR00050993-RA | 310 | 3.481 | 6.76 | 46.73 | 84.00 | −0.414 |
| CmbHLH22 | CHR00078227-RA | 201 | 2.288 | 6.3 | 48.15 | 109.6 | −0.098 |
| CmbHLH23 | CHR00016706-RA | 534 | 6.031 | 5.9 | 38.2 | 80.24 | −0.398 |
| CmbHLH24 | CHR00089135-RA | 376 | 4.183 | 4.87 | 52.25 | 66.68 | −0.716 |
| CmbHLH25 | CHR00058509-RA | 262 | 2.931 | 6.62 | 46.86 | 59.12 | −0.844 |
| CmbHLH26 | CHR00075848-RA | 169 | 1.871 | 8.3 | 54.21 | 76.21 | −0.576 |
| CmbHLH27 | CHR00021504-RA | 294 | 3.272 | 7.01 | 48.12 | 66.33 | −0.805 |
| CmbHLH28 | CHR00085488-RA | 567 | 6.347 | 5.99 | 59.9 | 85.31 | −0.386 |
| CmbHLH29 | CHR00066393-RA | 592 | 6.578 | 6.42 | 41.98 | 79.34 | −0.503 |
| CmbHLH30 | CHR00049557-RA | 191 | 2.134 | 6.2 | 45.33 | 90.79 | −0.458 |
| CmbHLH31 | CHR00020620-RA | 501 | 5.364 | 5.56 | 58.67 | 57.84 | −0.734 |
| CmbHLH32 | CHR00040132-RA | 399 | 4.398 | 5.3 | 55.48 | 59.65 | −0.624 |
| CmbHLH33 | CHR00025933-RA | 251 | 2.872 | 8.31 | 43.43 | 67.17 | −0.74 |
| CmbHLH34 | CHR00067596-RA | 319 | 3.529 | 6.32 | 39.39 | 87.12 | −0.37 |
| CmbHLH35 | CHR00085567-RA | 249 | 2.785 | 7.65 | 37.57 | 90.44 | −0.363 |
| CmbHLH36 | CHR00032751-RA | 326 | 3.705 | 6.47 | 51.81 | 80.77 | −0.557 |
| CmbHLH37 | CHR00051320-RA | 200 | 2.273 | 6 | 58.68 | 83.3 | −0.385 |
| CmbHLH38 | CHR00052362-RA | 277 | 3.206 | 6.51 | 48.97 | 86.86 | −0.588 |
| CmbHLH39 | CHR00032387-RA | 309 | 3.414 | 6.26 | 62 | 54.56 | −0.984 |
| CmbHLH40 | CHR00068388-RA | 211 | 2.379 | 4.75 | 55.92 | 42.99 | −1.068 |
| CmbHLH41 | CHR00062368-RA | 280 | 3.096 | 5.07 | 52.56 | 74.18 | −0.44 |
| CmbHLH42 | CHR00005466-RA | 319 | 3.574 | 6.77 | 46.83 | 78.84 | −0.399 |
| CmbHLH43 | CHR00028154-RA | 215 | 2.422 | 6.46 | 49.22 | 86.56 | −0.66 |
| CmbHLH44 | CHR00041708-RA | 322 | 3.517 | 5.84 | 44.78 | 58.73 | −0.793 |
| CmbHLH45 | CHR00076371-RA | 310 | 3.501 | 7.29 | 43.91 | 70.81 | −0.701 |
| CmbHLH46 | CHR00027603-RA | 368 | 4.127 | 6.07 | 29.5 | 78.59 | −0.551 |
| CmbHLH47 | CHR00053214-RA | 318 | 3.554 | 6.98 | 55.24 | 84.37 | −0.614 |
| CmbHLH48 | CHR00031690-RA | 572 | 6.428 | 5.22 | 43.38 | 83.50 | −0.306 |
| CmbHLH49 | CHR00022486-RA | 354 | 3.957 | 5.81 | 61.58 | 79.35 | −0.638 |
| CmbHLH50 | CHR00077133-RA | 398 | 4.381 | 6.1 | 58.84 | 71.28 | −0.572 |
| CmbHLH51 | CHR00002812-RA | 323 | 3.562 | 6.33 | 49.77 | 67.28 | −0.541 |
| CmbHLH52 | CHR00091912-RA | 360 | 3.774 | 5.98 | 48.34 | 64.28 | −0.498 |
| CmbHLH53 | CHR00040106-RA | 445 | 4.818 | 5.44 | 61.72 | 56.36 | −0.612 |
| CmbHLH54 | CHR00053312-RA | 240 | 2.746 | 7.01 | 35.36 | 71.88 | −0.659 |
| CmbHLH55 | CHR00073646-RA | 293 | 3.244 | 6.26 | 35.57 | 65.87 | −0.744 |
| CmbHLH56 | CHR00078290-RA | 391 | 4.097 | 5.98 | 50.74 | 69.44 | −0.423 |
| CmbHLH57 | CHR00063973-RA | 238 | 2.673 | 8.49 | 51.21 | 92.69 | −0.329 |
| CmbHLH58 | CHR00023344-RA | 255 | 2.752 | 5.28 | 56.8 | 69.65 | −0.636 |
| CmbHLH59 | CHR00015822-RA | 172 | 1.906 | 4.89 | 44.96 | 80.41 | −0.412 |
| CmbHLH60 | CHR00050362-RA | 517 | 5.822 | 9.16 | 49.15 | 56.44 | −0.992 |
| CmbHLH61 | CHR00025279-RA | 268 | 2.892 | 5.77 | 60.24 | 54.55 | −0.83 |
| CmbHLH62 | CHR00061024-RA | 418 | 4.680 | 5.69 | 51.93 | 85.50 | −0.364 |
| CmbHLH63 | CHR00086566-RA | 158 | 1.767 | 5.86 | 55.74 | 78.92 | −0.717 |
| CmbHLH64 | CHR00076271-RA | 240 | 2.699 | 9.2 | 33.72 | 85.21 | −0.556 |
| CmbHLH65 | CHR00065282-RA | 185 | 2.105 | 8.52 | 37.98 | 90.11 | −0.437 |
| CmbHLH66 | CHR00005538-RA | 317 | 3.586 | 8.59 | 59.45 | 85.52 | −0.466 |
| CmbHLH67 | CHR00079802-RA | 392 | 4.363 | 7.15 | 57.19 | 62.45 | −0.627 |
| CmbHLH68 | CHR00060897-RA | 244 | 2.806 | 5.07 | 61.31 | 85.08 | −0.498 |
| CmbHLH69 | CHR00064856-RA | 229 | 2.593 | 5.31 | 57.55 | 70.83 | −0.717 |
| CmbHLH70 | CHR00031761-RA | 327 | 3.679 | 8.15 | 51.81 | 64.71 | −0.779 |
| CmbHLH71 | CHR00029899-RA | 311 | 3.510 | 8.28 | 61.74 | 77.78 | −0.446 |
| Items | Name of cis-Element | Sequence | Position from Translation Start Site | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hormone response | ABRE | ACGTG/CACGTG /GACACGTGGC | +477 | Cis-acting element involved in the ABA responsiveness |
| CGTCA-motif | CGTCA | −1760 | Cis-acting element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | |
| P-box | CCTTTTG | +1172 | GA-responsive element | |
| TCA-element | CCATCTTTTT | −905 | Cis-acting element involved in SA responsiveness | |
| TGACG-motif | TGACG | +1760 | Cis-acting element involved in the MeJA-responsiveness | |
| AuxRR-core | TGTCTCAATAAG | −287 | Cis-acting element involved in auxin responsiveness | |
| Defense and stress response | TC-rich repeats | GTTTTCTTAC | −515 | Cis-acting element involved in defense and stress responsiveness |
| ARE | AAACCA | −1728 − 1711 − 1162 +338 | Cis-acting element essential for the anaerobic induction | |
| LTR | CCGAAA | +1616 + 1963 | Cis-acting element involved in low-temperature responsiveness | |
| MBS | CAACTG | −1234 | MYB binding site involved in drought-inducibility | |
| Growth and development | GCN4-motif | TGAGTCA | +1694 | Cis-regulatory element involved in endosperm expression |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L.; Xie, J.; Wang, T.; Song, L.; Zhao, X. Identification of CmbHLH Transcription Factor Family and Excavation of CmbHLHs Resistant to Necrotrophic Fungus Alternaria in Chrysanthemum. Genes 2023, 14, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020275
Ding Y, Wang X, Wang D, Jiang L, Xie J, Wang T, Song L, Zhao X. Identification of CmbHLH Transcription Factor Family and Excavation of CmbHLHs Resistant to Necrotrophic Fungus Alternaria in Chrysanthemum. Genes. 2023; 14(2):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020275
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yifeng, Xiaomeng Wang, Dandan Wang, Liwei Jiang, Jing Xie, Tianle Wang, Lingyu Song, and Xiting Zhao. 2023. "Identification of CmbHLH Transcription Factor Family and Excavation of CmbHLHs Resistant to Necrotrophic Fungus Alternaria in Chrysanthemum" Genes 14, no. 2: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020275
APA StyleDing, Y., Wang, X., Wang, D., Jiang, L., Xie, J., Wang, T., Song, L., & Zhao, X. (2023). Identification of CmbHLH Transcription Factor Family and Excavation of CmbHLHs Resistant to Necrotrophic Fungus Alternaria in Chrysanthemum. Genes, 14(2), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020275







