Stage-Specific Transcriptomes of the Mussel Mytilus coruscus Reveals the Developmental Program for the Planktonic to Benthic Transition
Abstract
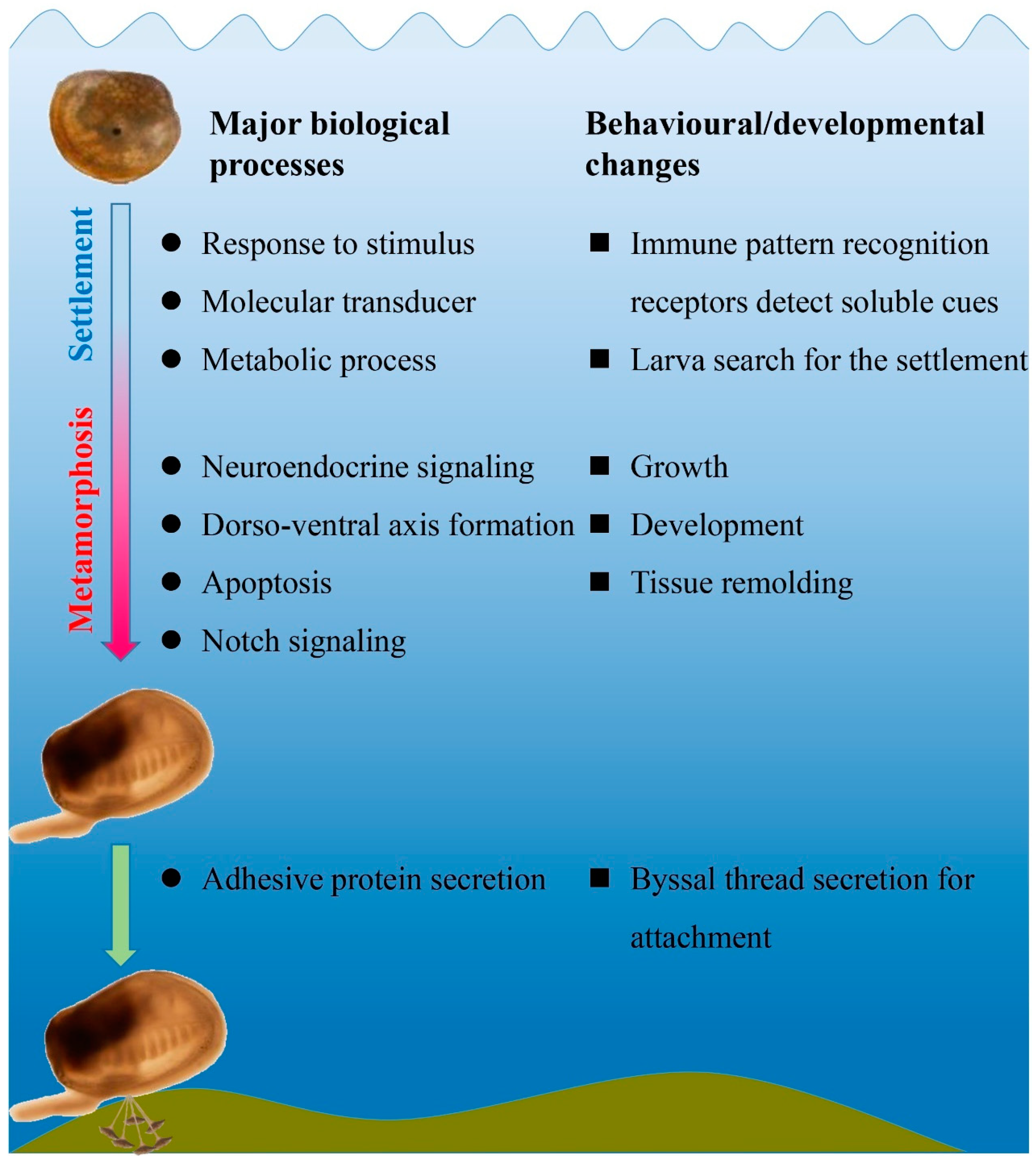
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
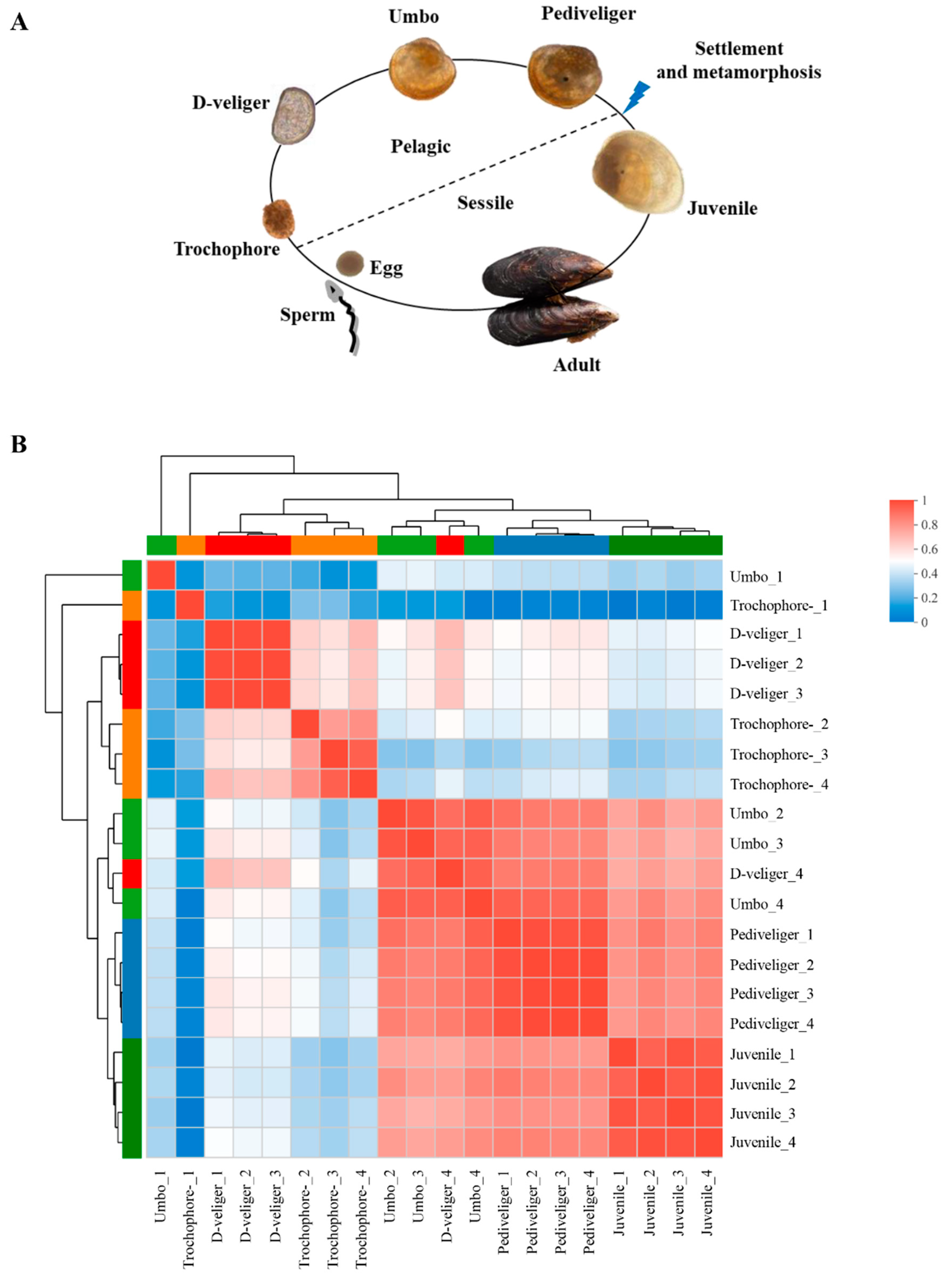
2.1. Sample Acquisition
2.2. RNA Extraction, cDNA Library Construction, and Illumina Sequencing
2.3. Transcriptome Analysis
2.4. qPCR Analysis
3. Results
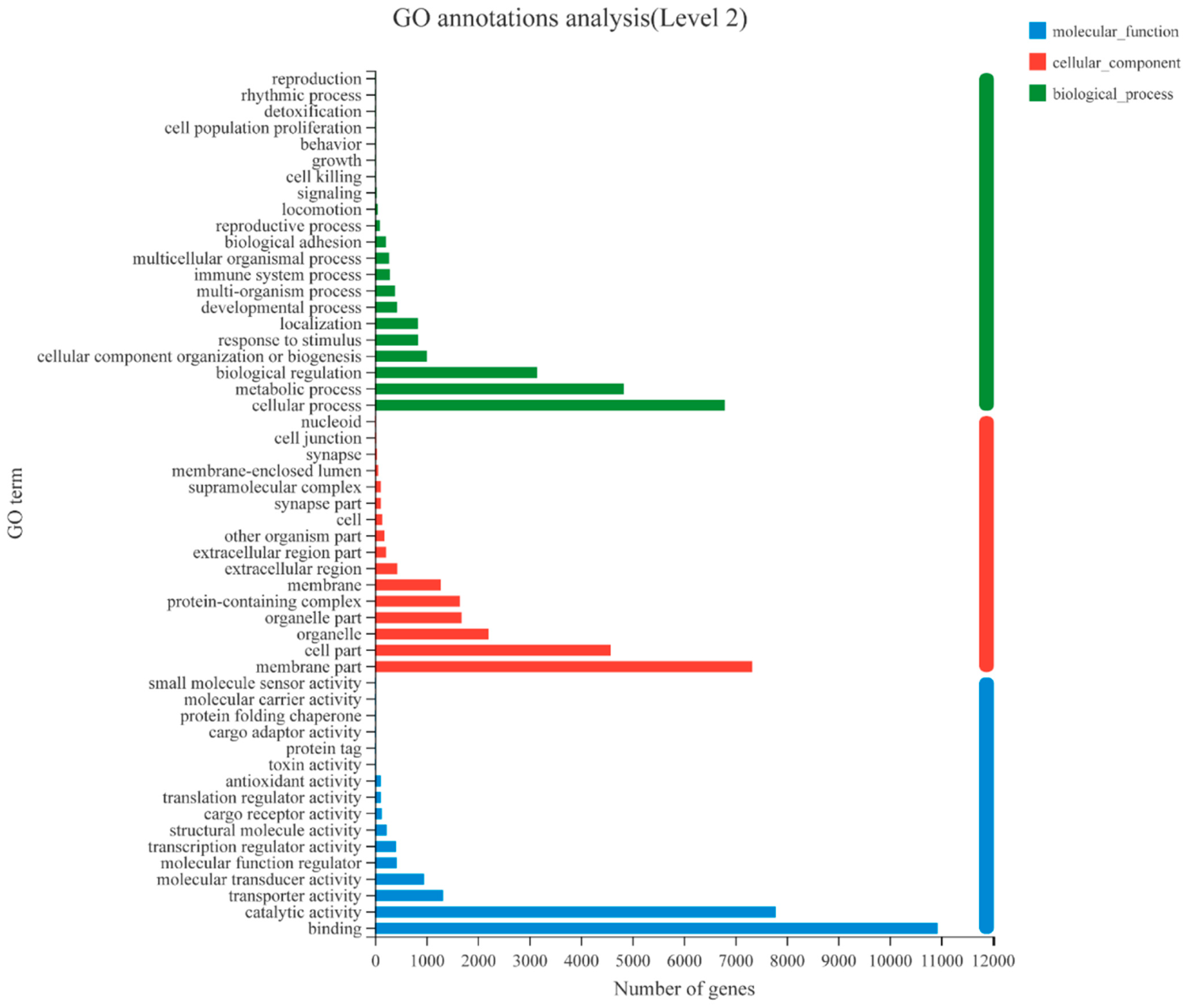
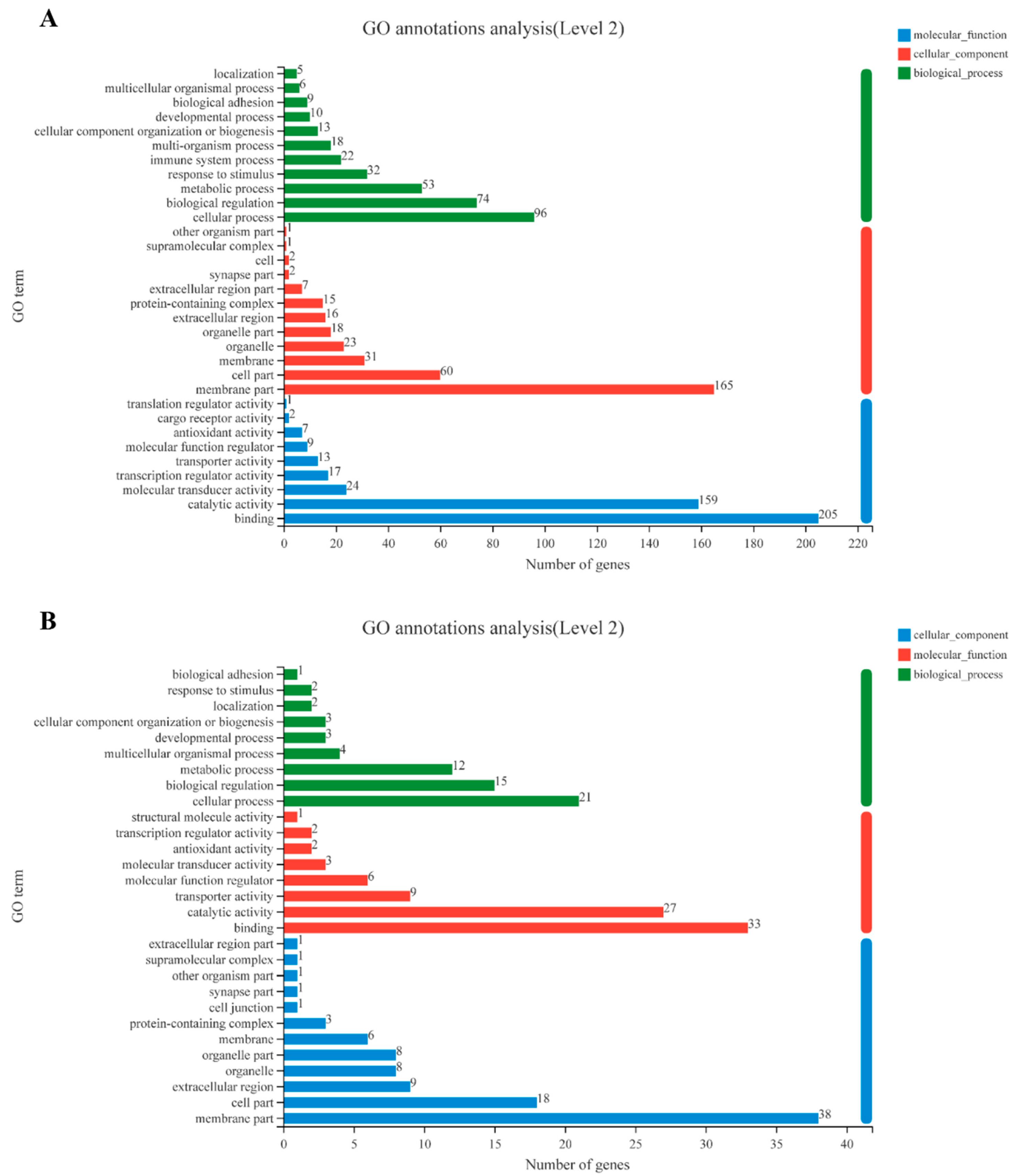
3.1. Transcriptome Analysis
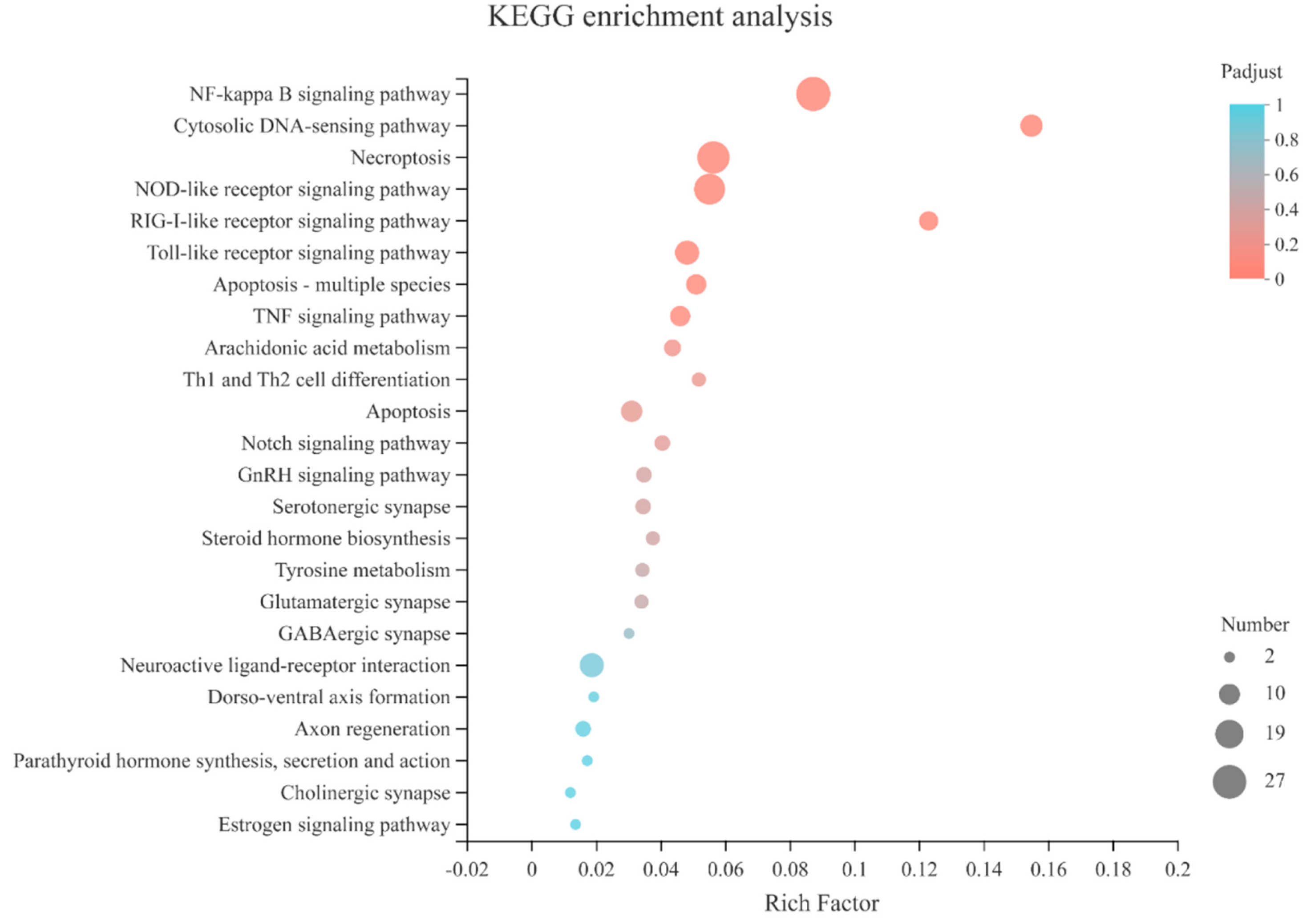
3.2. Differential Gene Expression between Five Developmental Stages of Mussel
3.3. qPCR Analysis of Differential Gene Expression during Development of Mussel
4. Discussion
4.1. Immune-Related Genes Involved in Larval Metamorphosis
4.2. Neuroendocrine Signaling in Metamorphosis
4.3. Genes Involved in Development and Apoptosis
4.4. Adhesive Protein Genes in Metamorphosis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bureau of Fisheries of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (BFMOA). In China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2022; p. 43. (In Chinese)
- Qian, P.Y.; Lau SC, K.; Dahms, H.U.; Dobretsov, S.; Harder, T. Marine biofilms as mediators of colonization by marine macroorganisms: Implications for antifouling and aquaculture. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrington, E.; Waite, J.H.; Sarà, G.; Sebens, K.P. Mussels as a model system for integrative ecomechanics. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 443–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Cheng, Y.L.; Chen, K.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Zhu, X.; Cardoso, J.C.R.; Liang, X.; Zhu, Y.T.; Power, D.M.; Yang, J.L. Thyroid hormone receptor: A new player in epinephrine-induced larval metamorphosis of the hard-shelled mussel. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 287, 113347–113355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, M.G. Why and how marine-invertebrate larvae metamorphose so fast. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 116, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, M.G. Biofilms and marine invertebrate larvae: What bacteria produce that larvae use to choose settlement sites. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, A.; Vogeler, S. Molluscan bivalve settlement and metamorphosis: Neuroendocrine inducers and morphogenetic responses. Aquaculture 2018, 487, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Shen, P.J.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.F.; Bao, W.Y.; Li, J.L. Larval settlement and metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus coruscus in response to monospecific bacterial biofilms. Biofouling 2013, 29, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonar, D.B.; Coon, S.L.; Walch, M.; Weiner, R.M.; Fitt, W. Control of oyster settlement and metamorphosis by endogenous and exogenous chemical cues. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1990, 46, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.F.; Bao, W.Y.; Yoshida, A.; Osatomi, K.; Yang, J.L. An α2-adrenergic receptor is involved in larval metamorphosis in the mussel Mytilus coruscus. Biofouling 2019, 35, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Qin, J.; Shi, B.; Han, G.D.; Chen, J.; Huang, H.Q.; Ke, C.H. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of adrenergic like receptor during larval metamorphosis in Crassostrea angulata. Aquaculture 2012, 366, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogeler, S.; Carboni, S.; Li, X.; Nevejan, N.; Monaghan, S.; Ireland, J.; Joyce, A.L. Bivalves are NO different: Nitric oxide as negative regulator of metamorphosis in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas. BMC Dev. Biol. 2020, 20, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.X.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, Y.H.; Qian, P.Y. HSP90 regulates larval settlement of the bryozoan Bugula neritina through NO pathway. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb167478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Li, Y.F.; Yoshida, A.; Osatomi, K.; Yang, J.L.; Liang, X. Nitric oxide negatively regulates larval metamorphosis in hard-shelled mussel (Mytilus coruscus). Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.L.; Xiao, X.H.; Tong, M.H.; Chen, X.H.; Li, L.; Huang, M.Q.; Zhou, L.; Ke, C.H. Proteome of larval metamorphosis induced by epinephrine in the Fujian oyster Crassostrea angulata. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 675–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.H.; Wang, F.; Xie, S.M.; Sun, F.Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, M.X.; Li, J.L. Developmental transcriptome analysis and identification of genes involved in larval metamorphosis of the razor clam, Sinonovacula constricta. Mar. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.A.; Degnan, S.M. Carry-over effect of larval settlement cue on postlarval gene expression in the marine gastropod Haliotis asinina. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4434–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Feng, D.D.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.K.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.F.; Zhu, Y.T.; Liang, X.; Lu, Y. Chromosome-level genome assembly of the hard-shelled mussel Mytilus coruscus, a widely distributed species from the temperate areas of East Asia. Gigascience 2021, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Res. 2014, 15, 550–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Mao, X.Z.; Huang, J.J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.M.; Dong, S.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Li, C.Y.; Wei, L.P. KOBAS 2.0: A web server for annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W316–W322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Gotz, S.; Garcia-Gomez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.L.; Zhu, X.; Yang, J.L.; Liang, X. Larval metamorphosis is inhibited by methimazole and propylthiouracil that reveals possible hormonal action in the mussel Mytilus coruscus. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yang, Y.M.; Li, Y.F. Knockdown of two iodothyronine deiodinase genes inhibits epinephrine-induced larval metamorphosis of the hard-shelled mussel Mytilus coruscus. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 914283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Satuitob, C.G.; Bao, W.Y.; Kitamura, H. Induction of metamorphosis of pediveliger larvae of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819 using neuroactive compounds, KCl, NH4Cl and organic solvents. Biofouling 2008, 24, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Li, Y.F.; Bao, W.Y.; Satuito, C.G.; Kitamura, H. Larval metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819 in response to neurotransmitter blockers and tetraethylammonium. Biofouling 2011, 27, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Li, S.H.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, Z.W.; Liang, X.; Bao, W.Y.; Li, J.L. Effects of neuroactive compounds, ions and organic solvents on larval metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus coruscus. Aquaculture 2013, 396–399, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.L.; Li, W.S.; Liang, X.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, Y.R.; Bao, W.Y.; Li, J.L. Effects of adrenoceptor compounds on larval metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus coruscus. Aquaculture 2014, 426–427, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balseiro, P.; Moreira, R.; Chamorro, R.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Immune responses during the larval stages of Mytilus galloprovincialis: Metamorphosis alters immunocompetence, body shape and behavior. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 35, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.J.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Du, S.J. Developmental dynamics of myogenesis in Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 227, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachère, E. Anti-infectious immune effectors in marine invertebrates: Potential tools for disease control in larviculture. Aquaculture 2003, 227, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.L.; Jenkins, C.; Seymour, J.R.; Labbate, M. Oyster disease in a changing environment: Decrypting the link between pathogen, microbiome and environment. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 143, 124–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, B.; Swalla, B.J. A molecular analysis of ascidian metamorphosis reveals activation of an innate immune response. Development 2002, 129, 4739–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobretsov, S.; Rittschof, D. Love atfirst taste: Induction of larval settlement by marine microbes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.Y.; Yang, J.L.; Satuito, C.G.; Kitamura, H. Larval metamorphosis of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in response to Alteromonas sp. 1: Evidence for two chemical cues? Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Hadfield, M.G. Composition and density of bacterial biofilms determine larval settlement of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 260, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggett, M.J.; Williamson, J.E.; Nys, R.D.; Kjelleberg, S.; Steinberg, P.D. Larval settlement of the common Australian sea urchin Heliocidaris erythrogramma in response to bacteria from the surface of coralline algae. Oecologia 2006, 149, 604–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Hadfield, M.G. Larvae of Pocillopora damicornis (Anthozoa) settle and metamorphose in response to surface-biofilm bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 433, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.H.; Liang, X.; Xu, J.K.; Dobretsov, S.; Yang, J.L. Monospecifc bioflms of Pseudoalteromonas promote larval settlement and metamorphosis of Mytilus coruscus. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirapé, A.; Bacque, C.; Brizard, R.; Vandenbulcke, F.; Boulo, V. Expression of immune-related genes in the oyster Crassostrea gigas during ontogenesis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2007, 31, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puill-Stephan, E.; Seneca, F.O.; Miller, D.J.; van Oppen, M.J.H.; Willis, B.L. Expression of putative immune response genes during early ontogeny in the coral Acropora millepora. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coon, S.L.; Bonar, D.B.; Weiner, R.M. Induction of settlement and metamorphosis of the pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg), by L-DOPA and catecholamines. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1985, 94, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobretsov, S.V.; Qian, P.Y. Pharmacological induction of larval settlement and metamorphosis in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. Biofouling 2003, 19, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Qian, P.Y. Larval settlement of the silver- or goldlip pearl oyster Pinctada maxima (Jameson) in response to natural biofilms and chemical cues. Aquaculture 2003, 220, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; He, L.S.; Wong, Y.H.; Yu, L.; Qian, P.Y. siRNA transfection in larvae of the barnacle Amphibalanus amphitrite. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 2505–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, A.M.; Janes, T.A.; Visser, F.; Zaidi, W.; Syed, N.I. Neurotrophic factors and target-specifc retrograde signaling interactions define the specificity of classical and neuropeptide cotransmitter release at identified Lymnaea synapses. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.P. Do mollusks use vertebrate sex steroids as reproductive hormones? Part I: Critical appraisal of the evidence for the presence, biosynthesis and uptake of steroids. Steroids 2012, 77, 1450–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.P. Do mollusks use vertebrate sex steroids as reproductive hormones? II. Critical review of the evidence that steroids have biological effects. Steroids 2013, 78, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudet, V. The origins and evolution of vertebrate metamorphosis. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R726–R737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, D.M.; Llewellyn, L.; Faustino, M.; Nowell, M.A.; Björnsson, B.T.; Einarsdottir, I.E.; Canario, A.V.M.; Sweeney, G.E. Thyroid hormones in growth and development of fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 130, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, M.; Escriva, H.; Schubert, M.; Brunet, F.; Brtko, J.; Ciesielski, F.; Roecklin, D.; Vivat-Hannah, V.; Jamin, E.L.; Cravedi, J.P.; et al. Amphioxus postembryonic development reveals the homology of chordate metamorphosis. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patricolo, E.; Cammarata, M.; D'Agati, P. Presence of thyroid hormones in ascidian larvae and their involvement in metamorphosis. J. Exp. Zool. 2001, 290, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukazawa, H.; Hirai, H.; Hori, H.; Roberts, R.D.; Nukaya, H.; Ishida, H.; Tsuji, K. Induction of abalone larval metamorphosis by thyroid hormones. Fish. Sci. 2001, 67, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xu, F.; Li, L.; Que, H.Y.; Zhang, G.F. The transcription of iodothyronine deiodinase genes is regulated by thyroid hormone receptor in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.D.; Zhang, L.L.; Xu, J.B.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Z.P.; Wang, Y.L. The roles of thyroid hormone receptor and T3 in metamorphosis of Haliotis diversicolor. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2019, 37, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.T.; Shi, X.W.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.L.; Wang, M.Q.; Wang, L.L.; Huang, M.M.; Yang, C.Y.; Song, L.S. An iodothyronine deiodinase from Chlamys farreri and its induced mRNA expression after LPS stimulation. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, G.; Roux, N.; Laudet, V. Evolution of ligands, receptors and metabolizing enzymes of thyroid signaling. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2017, 459, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, M. An overview of the Notch signalling pathway. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2003, 14, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazave, E.; Lapébie, P.; Richards, G.S.; Brunet, F.; Ereskovsky, A.V.; Degnan, B.M.; Borchiellini, C.; Vervoort, M.; Renard, E. Origin and evolution of the Notch signalling pathway: An overview from eukaryotic genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S.; Rand, M.D.; Lake, R.J. Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 1999, 284, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazave, E.; Lemaıtre, Q.I.B.; Balavoine, G. The Notch pathway in the annelid Platynereis: Insights into chaetogenesis and neurogenesis processes. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 160242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, A.S.; Gonsalves, F.C.; Song, M.H.; Norris, B.J.; Weisblat, D.A. Characterization of Notch-class gene expression in segmentation stem cells and segment founder cells in Helobdella robusta (Lophotrochozoa; Annelida; Clitellata; Hirudinida; Glossiphoniidae). Evol. Dev. 2005, 7, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.H.; Ryu, T.; Seridi, L.; Ghosheh, Y.; Bougouffa, S.; Qian, P.Y.; Ravasi, T. Transcriptome analysis elucidates key developmental components of bryozoan lophophore development. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.D.; Li, Q.; Yu, H.; Zhao, X.L.; Kong, L.F. Comparative transcriptome analysis of the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas characterized by shell colors: Identification of genetic bases potentially involved in pigmentation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, eo145257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Nie, Q.; Xiao, G.Q.; Liu, B.Z. Transcriptome analysis of shell color-related genes in the clam Meretrix meretrix. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.D.; Weil, M.; Raff, M.C. Programmed Cell Death in Animal Development. Cell 1997, 88, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Y.; Li, L.L.; Pu, F.; You, W.W.; Huang, H.Q.; Ke, C.H. Molecular cloning of two molluscan caspases and gene functional analysis during Crassostrea angulata (Fujian oyster) larval metamorphosis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 42, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qian, P.Y. Involvement of a novel p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in larval metamorphosis of the polychaete Hydroides elegans (Haswell). J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol. 2010, 314, 390–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambon, J.P.; Soule, J.; Pomies, P.; Fort, P.; Sahuquet, A.; Alexandre, D.; Mangeat, P.H.; Baghdiguian, S. Tail regression in Ciona intestinalis (Prochordate) involves a Caspase-dependent apoptosis event associated with ERK activation. Development 2002, 129, 3105–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutek, K.; Dhaliwal, R.S.; Raay, T.J.V.; Heyland, A. Sea urchin histamine receptor 1 regulates programmed cell death in larval Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4002–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, H.G.; Roberto, F.F. Understanding marine mussel adhesion. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Gourdon, D.; Sun, C.J.; Holten-Andersen, N.; Anderson, T.H.; Waite, J.H.; Israelachvili, J.N. Adhesion mechanisms of the mussel foot proteins mfp-1 and mfp-3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007, 104, 3782–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; George, M.N.; Carrington, E. Mussel byssus attachment weakened by ocean acidification. Nature Clim. Change 2013, 3, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.R.; de Araújo, J.L.F.; Filho, A.N.; Guañabens, A.C.P.; Carvalho, M.D.; Cardoso, A.V. Functional Surface of the golden mussel’s foot: Morphology, structures and the role of cilia on underwater adhesion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 54, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulon, V.; Boudry, P.; Artigaud, S.; Guérard, F.; Hellio, C. In silico analysis of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) transcriptome over developmental stages reveals candidate genes for larval settlement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, S.G.; Huang, J.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Jia, G.C.; Xie, L.P.; Zhang, R.Q. Extensible byssus of Pinctada fucata: Ca2+-stabilized nanocavities and a thrombospondin-1 protein. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.-M.; Shi, X.; Power, D.M.; Li, Y.-F. Stage-Specific Transcriptomes of the Mussel Mytilus coruscus Reveals the Developmental Program for the Planktonic to Benthic Transition. Genes 2023, 14, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020287
Wang Y-Q, Liu Q, Zhou Y, Chen L, Yang Y-M, Shi X, Power DM, Li Y-F. Stage-Specific Transcriptomes of the Mussel Mytilus coruscus Reveals the Developmental Program for the Planktonic to Benthic Transition. Genes. 2023; 14(2):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020287
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu-Qing, Qi Liu, Yan Zhou, Lizhi Chen, Yue-Ming Yang, Xue Shi, Deborah M. Power, and Yi-Feng Li. 2023. "Stage-Specific Transcriptomes of the Mussel Mytilus coruscus Reveals the Developmental Program for the Planktonic to Benthic Transition" Genes 14, no. 2: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020287
APA StyleWang, Y.-Q., Liu, Q., Zhou, Y., Chen, L., Yang, Y.-M., Shi, X., Power, D. M., & Li, Y.-F. (2023). Stage-Specific Transcriptomes of the Mussel Mytilus coruscus Reveals the Developmental Program for the Planktonic to Benthic Transition. Genes, 14(2), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020287




