FRMD7 Gene Alterations in a Pakistani Family Associated with Congenital Idiopathic Nystagmus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
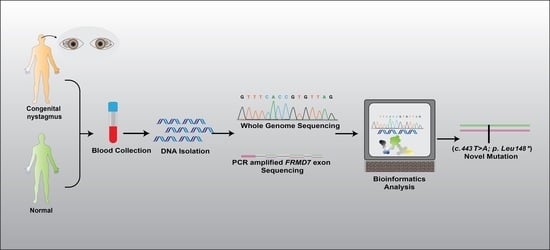
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Genetic Studies
2.3. Clinical Examination
2.4. Bioinformatics’ Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Findings
3.2. Clinical Evaluation
3.3. In-Silico Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghannam, A.S.B.; Yassine, S. Pediatric Nystagmus. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2018, 58, 23–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, D.R. Eye Movement Disorders: Nystagmus and nystagmoid eye movements. In Liu Volpe Galetta’s Neuro-Ophthalmology; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 585–610. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, C.; Vieregge, P.; Heide, W.; Kemper, B.; Hagedorn-Greiwe, M. Exclusion of chromosome regions 6p12 and 15q11, but not chromosome region 7p11, in a German family with autosomal dominant congenital nystagmus. Genomics 1998, 54, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, M.; Jeffery, S.; Lee, N.; Hogg, C. Congenital nystagmus cosegregating with a balanced 7; 15 translocation. J. Med. Genet. 1993, 30, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerrison, J.B.; Vagefi, M.R.; Barmada, M.M.; Maumenee, I.H. Congenital motor nystagmus linked to Xq26-q27. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 64, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q.; Jia, X.; Li, S.; Guo, X. Novel mutations of FRMD7 in Chinese patients with congenital motor nystagmus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabot, A.; Rozet, J.-M.; Gerber, S.; Perrault, I.; Ducroq, D.; Smahi, A.; Souied, E.; Munnich, A.; Kaplan, J. A gene for X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus (NYS1) maps to chromosome Xp11. 4-p11. 3. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 64, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bassi, M.T.; Schiaffino, M.V.; Renieri, A.; Nigris, F.D.; Galli, L.; Bruttini, M.; Gebbia, M.; Bergen, A.A.; Lewis, R.A.; Ballabio, A. Cloning of the gene for ocular albinism type 1 from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Ren, X.; Yang, X.; Guo, T.; Yao, Q.; Li, L.; Dai, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, M. Identification of a novel GPR143 mutation in a large Chinese family with congenital nystagmus as the most prominent and consistent manifestation. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 52, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hu, L.; Kong, X. Identification of a novel GPR143 deletion in a Chinese family with X-linked congenital nystagmus. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 1015. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, R.J.; Thomas, M.G.; Talbot, C.J.; Gottlob, I.; Shackleton, S. The role of FRMD7 in idiopathic infantile nystagmus. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schorderet, D.F.; Tiab, L.; Gaillard, M.C.; Lorenz, B.; Klainguti, G.; Kerrison, J.B.; Traboulsi, E.I.; Munier, F.L. Novel mutations in FRMD7 in X-linked congenital nystagmus. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, J.E.; Shawkat, F.; Malpas, C.T.; Thomas, N.S.; Harris, C.M.; Hodgkins, P.R.; Chen, X.; Trump, D.; Lotery, A.J. Allelic variation of the FRMD7 gene in congenital idiopathic nystagmus. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2007, 125, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.G.; Maconachie, G.; Hisaund, M.; Gottlob, I. FRMD7-Related Infantile Nystagmus; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chishti, A.H.; Kim, A.C.; Marfatia, S.M.; Lutchman, M.; Hanspal, M.; Jindal, H.; Liu, S.C.; Low, P.S.; Rouleau, G.A.; Mohandas, N. The FERM domain: A unique module involved in the linkage of cytoplasmic proteins to the membrane. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1998, 23, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, A.J. A FERM-adjacent (FA) region defines a subset of the 4.1 superfamily and is a potential regulator of FERM domain function. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aychoua, N.; Schiff, E.; Malka, S.; Tailor, V.K.; Chan, H.W.; Oluonye, N.; Theodorou, M.; Moosajee, M. Prospective study of pediatric patients presenting with idiopathic infantile nystagmus—Management and molecular diagnostics. Front. Genet. 2022, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-F.; Chen, H.; Huang, P.-J.; Feng, Z.-K.; Hua, Z.-Q.; Feng, X.; Han, F.; Xu, X.-T.; Shen, R.-J.; Li, Y. Genotype-Phenotype Analysis and Mutation Spectrum in a Cohort of Chinese Patients with Congenital Nystagmus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 627295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarpey, P.; Thomas, S.; Sarvananthan, N.; Mallya, U.; Lisgo, S.; Talbot, C.J.; Roberts, E.O.; Awan, M.; Surendran, M.; McLean, R.J. Mutations in FRMD7, a newly identified member of the FERM family, cause X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1242–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Tian, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, B. Expression and localization of FRMD7 in human fetal brain, and a role for F-actin. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 591. [Google Scholar]
- Betts-Henderson, J.; Bartesaghi, S.; Crosier, M.; Lindsay, S.; Chen, H.-L.; Salomoni, P.; Gottlob, I.; Nicotera, P. The nystagmus-associated FRMD7 gene regulates neuronal outgrowth and development. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimberg, J.; Nawoschik, S.; Belluscio, L.; McKee, R.; Turck, A.; Eisenberg, A. A simple and efficient non-organic procedure for the isolation of genomic DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plagnol, V.; Curtis, J.; Epstein, M.; Mok, K.Y.; Stebbings, E.; Grigoriadou, S.; Wood, N.W.; Hambleton, S.; Burns, S.O.; Thrasher, A.J. A robust model for read count data in exome sequencing experiments and implications for copy number variant calling. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, T.W.; De Franco, E.; Johnson, M.B.; Patel, K.; Ellard, S.; Weedon, M.N.; Flanagan, S.E.; Wakeling, M.N. SavvyCNV: Genome-wide CNV calling from off-target reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 18, e1009940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.W.; Harlalka, G.V.; Lin, S.; D’Atri, I.; Mehmood, S.; Shakil, M.; Hassan, M.J.; Chioza, B.A.; Self, J.E.; Ennis, S. Mutations in TYR and OCA2 associated with oculocutaneous albinism in Pakistani families. Meta Gene 2018, 17, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.W.; Lee, Y.; Malik, M.A.; Khan, J.; Khan, A.; Kareem, A.; Kang, C.; Shabbir, M.I. Identification of Novel Mutation in CNGA3 gene by Whole-Exome Sequencing and In-Silico Analyses for Genotype-Phenotype Assessment with Autosomal Recessive Achromatopsia in Pakistani families. JPMA 2019, 69, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, Y.; Vargel, I.; Kansu, T.; Akin, B.; Rohmann, E.; Kamaci, S.; Uz, E.; Ozcelik, T.; Wollnik, B.; Akarsu, N.A. Skewed X inactivation in an X linked nystagmus family resulted from a novel, p. R229G, missense mutation in the FRMD7 gene. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 92, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, W.; Lin, P.; Xie, Y.; He, K.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, N. Correlations of FRMD7 gene mutations with ocular oscillations. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.G.; Crosier, M.; Lindsay, S.; Kumar, A.; Araki, M.; Leroy, B.P.; McLean, R.J.; Sheth, V.; Maconachie, G.; Thomas, S. Abnormal retinal development associated with FRMD7 mutations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 4086–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salman, A.; Hutton, S.B.; Newall, T.; Scott, J.A.; Griffiths, H.L.; Lee, H.; Gomez-Nicola, D.; Lotery, A.J.; Self, J.E. Characterization of the Frmd7 Knock-Out Mice Generated by the EUCOMM/COMP Repository as a Model for Idiopathic Infantile Nystagmus (IIN). Genes 2020, 11, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R.J.; Patil, R.; Goult, B.T.; Thomas, M.G.; Gottlob, I.; Shackleton, S. A novel interaction between FRMD7 and CASK: Evidence for a causal role in idiopathic infantile nystagmus. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2105–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, X.; Mao, J.; Gao, Y.; Yi, P.; Wang, L. FRMD7 Mutations Disrupt the Interaction with GABRA2 and may result in infantile nystagmus syndrome. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Gu, F.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, S.; Ma, X. A novel mutation in FRMD7 causing X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus in a large family. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, M. The role of Rho GTPases and associated kinases in regulating neurite outgrowth. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahirovic, S.; Hellal, F.; Neukirchen, D.; Hindges, R.; Garvalov, B.K.; Flynn, K.C.; Stradal, T.E.; Chrostek-Grashoff, A.; Brakebusch, C.; Bradke, F. Rac1 regulates neuronal polarization through the WAVE complex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 6930–6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Sasaki, T.; Mammoto, A.; Hotta, I.; Takaishi, K.; Imamura, H.; Nakano, K.; Kodama, A.; Takai, Y. Interaction of radixin with Rho small G protein GDP/GTP exchange protein Dbl. Oncogene 1998, 16, 3279–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeboom, R.G.; Supek, F.; Lehner, B. The rules and impact of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human cancers. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurosaki, T.; Maquat, L.E. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in humans at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsukita, S.; Yonemura, S. Cortical actin organization: Lessons from ERM (ezrin/radixin/moesin) proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 34507–34510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubo, T.; Yamashita, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Sumimoto, H.; Hosokawa, K.; Tohyama, M. A novel FERM domain including guanine nucleotide exchange factor is involved in Rac signaling and regulates neurite remodeling. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8504–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toyofuku, T.; Yoshida, J.; Sugimoto, T.; Zhang, H.; Kumanogoh, A.; Hori, M.; Kikutani, H. FARP2 triggers signals for Sema3A-mediated axonal repulsion. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrison, J.B.; Arnould, V.J.; Barmada, M.M.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Schmeckpeper, B.J.; Maumenee, I.H. A gene for autosomal dominant congenital nystagmus localizes to 6p12. Genomics 1996, 33, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragge, N.; Hartley, C.; Dearlove, A.; Walker, J.; Russell-Eggitt, I.; Harris, C. Familial vestibulocerebellar disorder maps to chromosome 13q31-q33: A new nystagmus locus. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Q. A novel locus for autosomal dominant congenital motor nystagmus mapped to 1q31-q32. 2 between D1S2816 and D1S2692. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Shin, J.-H.; Seo, J.H.; Jung, J.-H.; Choi, K.-D. A start codon mutation of the FRMD7 gene in two Korean families with idiopathic infantile nystagmus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Angalena, R.; Naushad, S.; Devi, A.R.R.; Dalal, B.A. Single gene disorders. Genom. Med. 2008, 2, 241–252. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, H.Y.; Alipanahi, B.; Lee, L.J.; Bretschneider, H.; Merico, D.; Yuen, R.K.; Hua, Y.; Gueroussov, S.; Najafabadi, H.S.; Hughes, T.R. The human splicing code reveals new insights into the genetic determinants of disease. Science 2015, 347, 1254806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AlMoallem, B.; Bauwens, M.; Walraedt, S.; Delbeke, P.; De Zaeytijd, J.; Kestelyn, P.; Meire, F.; Janssens, S.; Van Cauwenbergh, C.; Verdin, H. Novel FRMD7 mutations and genomic rearrangement expand the molecular pathogenesis of X-linked idiopathic infantile nystagmus. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Wang, L.; Cui, L.; Zhang, L.; Dai, S.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Hejtmancik, J.F.; Zhao, K. Five novel mutations of the FRMD7 gene in Chinese families with X-linked infantile nystagmus. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 733. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Guo, X. FRMD7 mutations in Chinese families with X-linked congenital motor nystagmus. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 1375–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Pathak, E.; Chaudhry, V.N.; Chaudhry, P.; Mishra, R.; Chandra, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Mutsuddi, M. A novel mutation in FRMD7 causes X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus in a North Indian family. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 597, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Jung, J.-H.; Oh, E.H.; Shin, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Seo, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, C. Genotype and phenotype spectrum of FRMD7-associated infantile nystagmus syndrome. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 3181–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Ying, M.; Han, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, K. Investigation of the gene mutations in two Chinese families with X-linked infantile nystagmus. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, S.; Pu, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ding, M. A novel missense mutation in the FERM domain containing 7 (FRMD7) gene causing X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus in a Chinese family. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 1834. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Ge, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Yang, J.; Gu, F. Identifcation of a novel mutation p. I240T in the FRMD7 gene in a family with congenital nystagmus. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Ge, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Luan, Y.; Sun, J.; Qu, J.; Jin, Z.-B.; Gu, F. Identification of three novel mutations in the FRMD7 gene for X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, F.-W.; Chen, B.-B.; Sun, Z.-H.; Wu, L.-P.; Zhao, S.-J.; Miao, Q.; Tang, X.-J. Novel mutation c. 980_983delATTA compound with c. 986C> A mutation of the FRMD7 gene in a Chinese family with X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus. J. Zhejiang Univ. Science B 2013, 14, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Lu, B. Identification and functional characterization of a novel missense mutation in FRMD7 responsible for idiopathic congenital nystagmus. Acta Biochim. Et Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.G.; Crosier, M.; Lindsay, S.; Kumar, A.; Thomas, S.; Araki, M.; Talbot, C.J.; McLean, R.J.; Surendran, M.; Taylor, K. The clinical and molecular genetic features of idiopathic infantile periodic alternating nystagmus. Brain 2011, 134, 892–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, T.; Pan, M.; Yang, H.; Fang, W.; Gu, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y. Identification of a novel idiopathic congenital nystagmus-causing missense mutation, p. G296C, in the FRMD7 gene. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2816–2822. [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishna, U.; Ratnamala, U.; Deutsch, S.; Bartoloni, L.; Kuracha, M.R.; Singh, R.; Banwait, J.; Bastola, D.K.; Johar, K.; Nath, S.K. Novel homozygous, heterozygous and hemizygous FRMD7 gene mutations segregated in the same consanguineous family with congenital X-linked nystagmus. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, Z.; Xu, H.; Yi, J.; Zheng, W.; Xiang, H.; Deng, X.; Lv, H.; Gao, K.; Qi, Y. Heterogeneous phenotype in a family with the FERM domain-containing 7 gene R335X mutation. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 49, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Huang, X.-F.; Zheng, Z.-L.; Deng, W.-L.; Lei, X.-L.; Xing, D.-J.; Ye, L.; Xu, S.-Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. Molecular genetic analysis of patients with sporadic and X-linked infantile nystagmus. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, T.; Huang, S.; Yuan, H. A novel splicing mutation of the FRMD7 gene in a Chinese family with X-linked congenital nystagmus. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.O.; Shinwari, J.; Al-Sharif, L.; Khalil, D.S.; Al Tassan, N. Prolonged pursuit by optokinetic drum testing in asymptomatic female carriers of novel FRMD7 splice mutation c. 1050+ 5 G> A. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011, 129, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wei, Y.; Tian, L.; Kang, X. A novel frameshift mutation in FRMD7 causes X-linked infantile nystagmus in a Chinese family. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.; Bu, J.; Dong, J.; Jia, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, C.; Si, S.; Wang, L. A novel frame-shift mutation in FRMD7 causes X-linked idiopathic congenital nystagmus in a Chinese family. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 2765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reynaert, N.; Braat, E.; de Zegher, F. Congenital nystagmus and central hypothyroidism. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fingert, J.H.; Roos, B.; Eyestone, M.E.; Pham, J.D.; Mellot, M.L.; Stone, E. Novel intragenic FRMD7 deletion in a pedigree with congenital X-linked nystagmus. Ophthalmic Genet. 2010, 31, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guan, H.; Liu, W.; Zhao, G.; Liu, S. Next-generation sequencing identifies a novel frameshift variant in FRMD7 in a Chinese family with idiopathic infantile nystagmus. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| ID | III: 1 | III: 2 | IV: 1 | IV: 2 | IV: 3 | IV: 5 | IV: 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Years) | 37 | 55 | 25 | 23 | 21 | 18 | 15 | |
| Gender | Female | Male | Male | Male | Male | Male | Female | |
| Province | KPK * | KPK * | KPK * | KPK * | KPK * | KPK * | KPK * | |
| Hair colour | Black | Black | Black | Black | Black | Black | Black | |
| Skin colour | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | |
| Visual acuity (logMAR) | Right Eye | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.70 | 0.0 | 0.0 | Not available | 0.0 |
| Left Eye | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.60 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Iris colour | De-pigmented | De-pigmented | De-pigmented | De-pigmented | De-pigmented | De-pigmented | De-pigmented | |
| Photophobia | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | |
| Head nodding | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Colour blindness | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
| Nystagmus | Present | Absent | Present | Present | Present | Absent | Absent | |
| Waveform | Horizontal | N/A | Horizontal | Horizontal | Horizontal | N/A | N/A | |
| Convergence | No change | No change | No change | No change | No change | No change | No change | |
| Head dyskinesia | Not found | Not found | Present | Present | Present | Not found | Not found | |
| Age of onset | Early infancy | N/A | Early infancy | Early infancy | Early infancy | N/A | N/A | |
| Fundus | Normal | N/A | Normal | Normal | Normal | N/A | N/A | |
| Family | PKNYS07 |
|---|---|
| Nucleotide Variant | c.443T>A |
| Protein Variant | p. Leu148 * |
| Status | Heterozygous (Affected Mother) Hemizygous (Affected Sons) |
| Type of Mutation | Nonsense |
| Previously reported | Novel (This study) |
| ACMG classification | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2,PP1) |
| Mutation taster | Disease causing (1.000) |
| CADD score | 37 |
| SIFT | - |
| Polyphen-2 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arshad, M.W.; Shabbir, M.I.; Asif, S.; Shahzad, M.; Leydier, L.; Rai, S.K. FRMD7 Gene Alterations in a Pakistani Family Associated with Congenital Idiopathic Nystagmus. Genes 2023, 14, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020346
Arshad MW, Shabbir MI, Asif S, Shahzad M, Leydier L, Rai SK. FRMD7 Gene Alterations in a Pakistani Family Associated with Congenital Idiopathic Nystagmus. Genes. 2023; 14(2):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020346
Chicago/Turabian StyleArshad, Muhammad Waqar, Muhammad Imran Shabbir, Saaim Asif, Mohsin Shahzad, Larissa Leydier, and Sunil Kumar Rai. 2023. "FRMD7 Gene Alterations in a Pakistani Family Associated with Congenital Idiopathic Nystagmus" Genes 14, no. 2: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020346
APA StyleArshad, M. W., Shabbir, M. I., Asif, S., Shahzad, M., Leydier, L., & Rai, S. K. (2023). FRMD7 Gene Alterations in a Pakistani Family Associated with Congenital Idiopathic Nystagmus. Genes, 14(2), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14020346