Gene Losses and Homology of the Chloroplast Genomes of Taxillus and Phacellaria Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Total DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Assembly and Annotation of Chloroplast Genomes
2.4. Structural Analysis
2.5. Genome Comparison and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
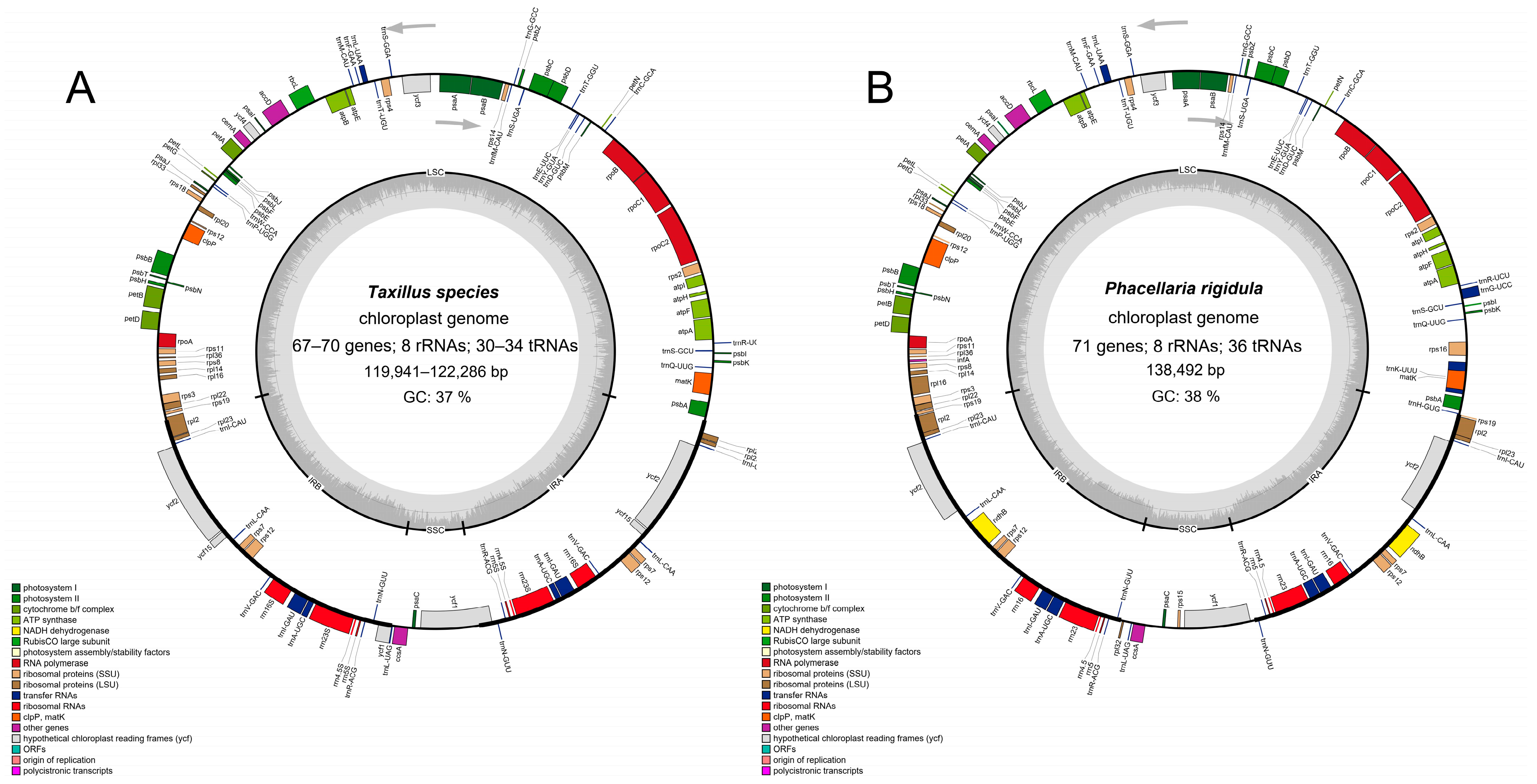
3.1. Basic Characteristics of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Three Taxillus Species and P. rigidula
3.2. Gene Losses in the Chloroplast Genomes of Taxillus and Phacellaria Species
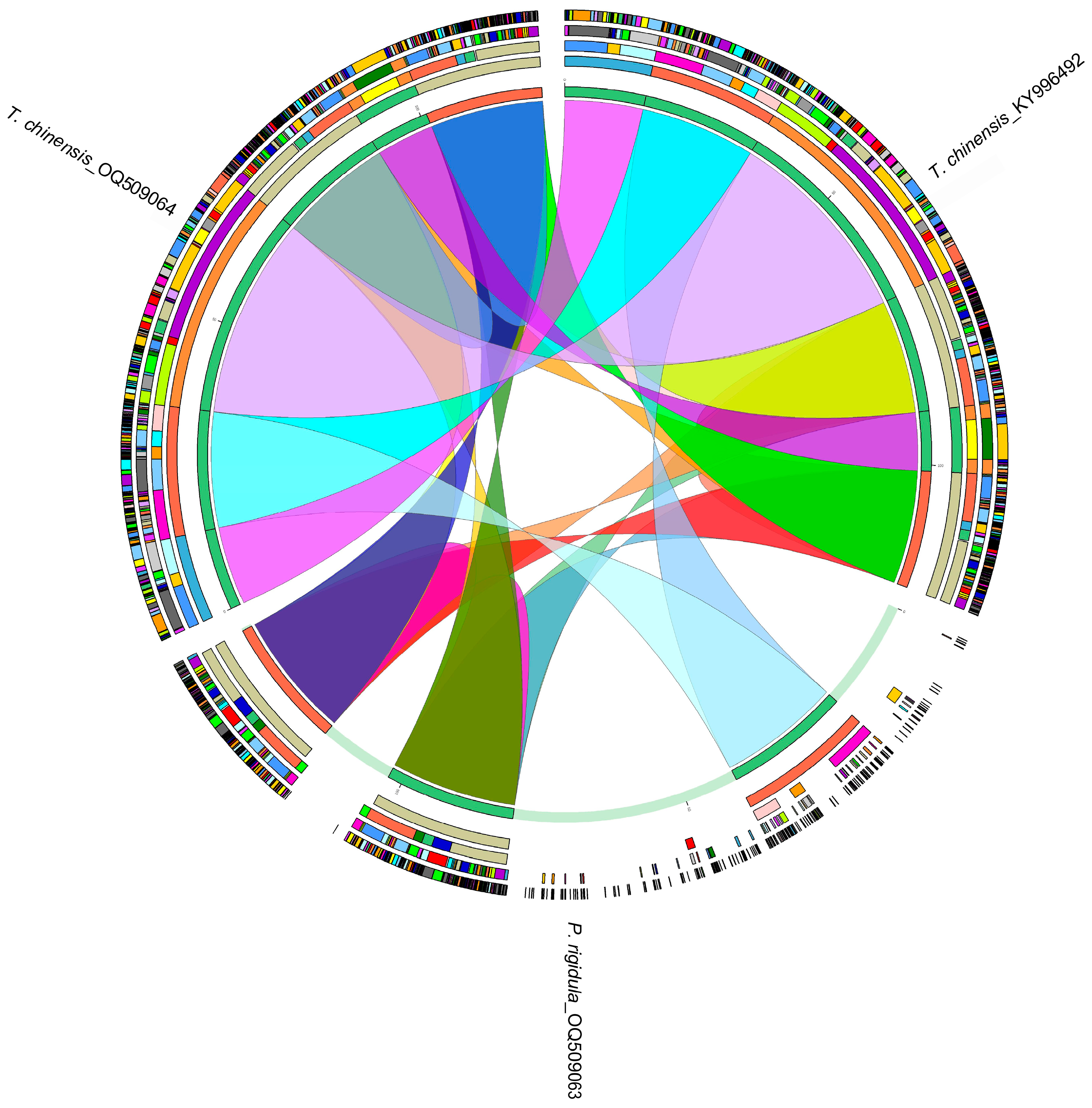
3.3. Homology Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes of P. rigidula and T. chinensis
3.4. Codon Usage Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Taxillus and Phacellaria Species
3.5. Long Repeat Sequences and SSRs
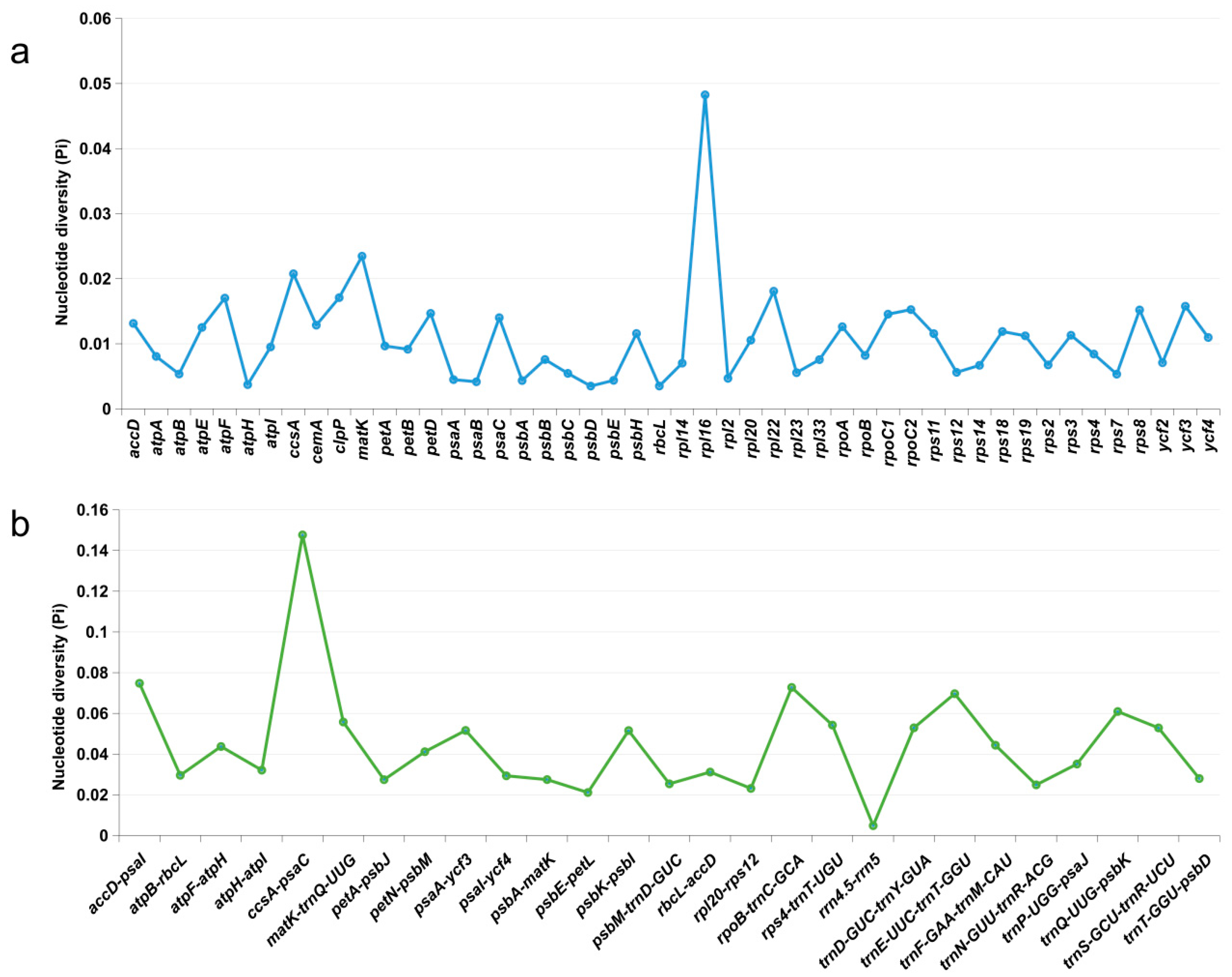
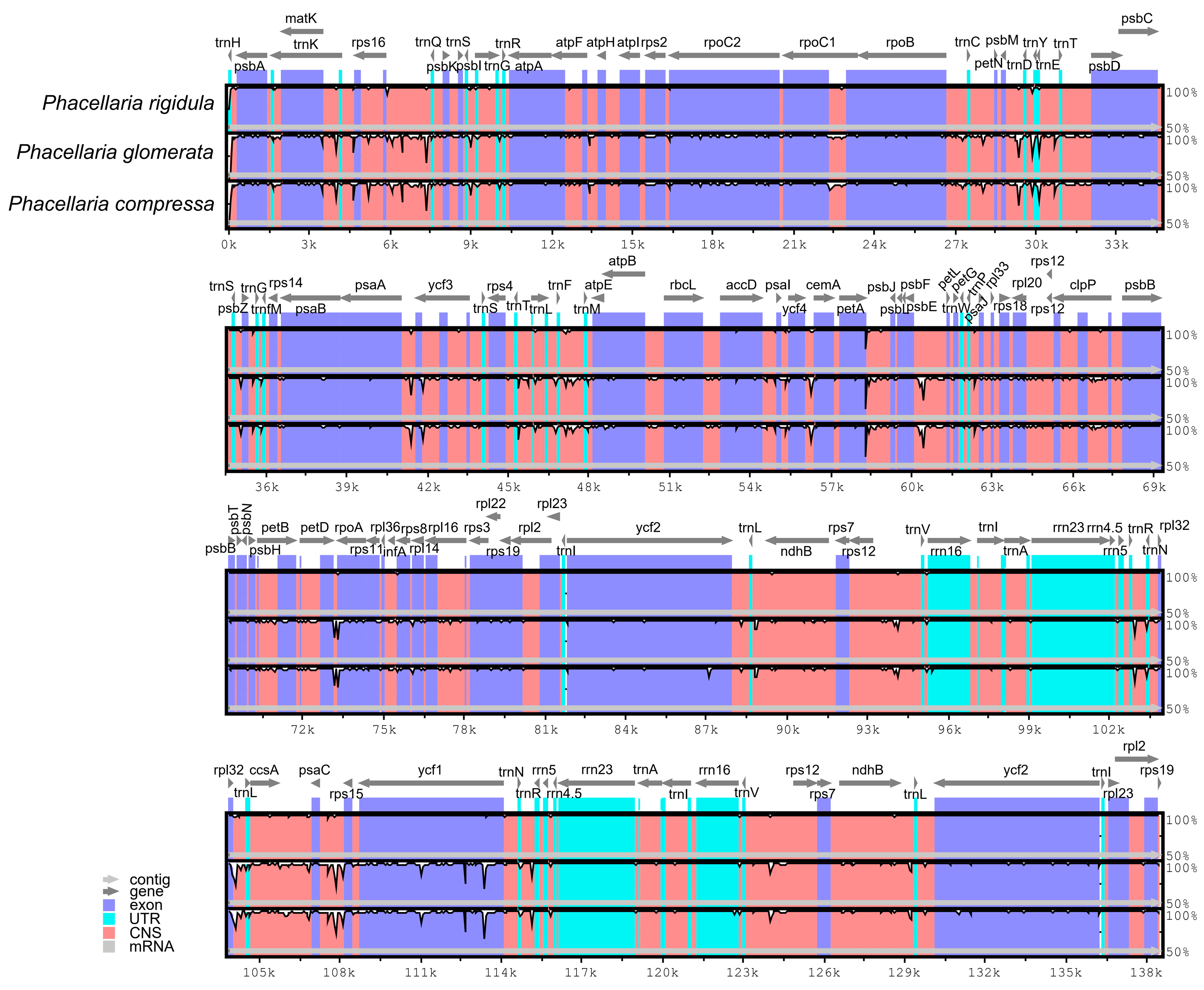
3.6. Comparative Analysis of Chloroplast Genomes
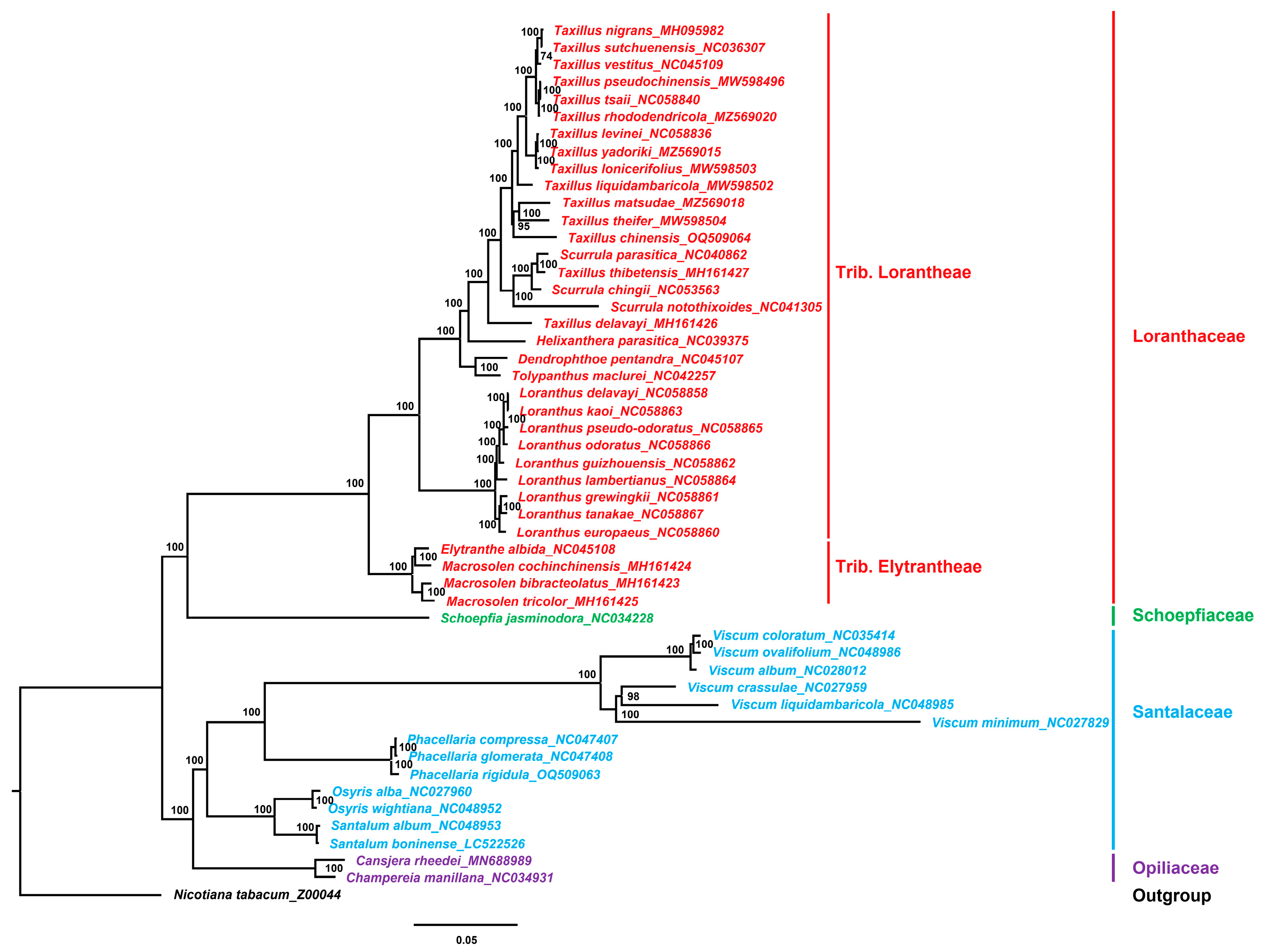
3.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dyall, S.D.; Brown, M.T.; Johnson, P.J. Ancient invasions: From endosymbionts to organelles. Science 2004, 304, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, M.T.; Gaut, B.S.; Learn, G.H.; Morton, B.R. Rates and patterns of chloroplast DNA evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6795–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Plant DNA barcoding: From gene to genome. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2015, 90, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y. Chloroplast genome evolution and species identification of Styrax (Styracaceae). BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5364094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonti-Filippini, J.; Nevill, P.G.; Dixon, K.; Small, I. What can we do with 1000 plastid genomes? Plant J. 2017, 90, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Qiao, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Wu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, G.; Qin, M. An integrated study of Violae Herba (Viola philippica) and five adulterants by morphology, chemical compositions and chloroplast genomes: Insights into its certified plant origin. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.L.; Wu, L.W.; Wang, Q.; Pan, Y.J.; Li, B.L.; Lin, Y.L.; Yao, H. Comparison analysis based on complete chloroplast genomes and insights into plastid phylogenomic of four Iris species. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 2194021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.P.; Bi, Y.; Yang, F.P.; Zhang, M.F.; Chen, X.Q.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X.H. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Lilium: Insights into evolutionary dynamics and phylogenetic analyses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, H.E.; Emes, M.J. Nonphotosynthetic metabolism in plastids. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 51, 111–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heide-Jørgensen, H.S. Parasitic Flowering Plants; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 1–438. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, G.; Cuenca, A.; Seberg, O. Plastome evolution in hemiparasitic mistletoes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2520–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Cui, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yao, H. Gene losses and variations in chloroplast genome of parasitic plant macrosolen and phylogenetic relationships within Santalales. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Arnold, B.J.; Xi, Z.; Khost, D.E.; Patel, N.; Hartmann, C.B.; Manickam, S.; Sasirat, S.; Nikolov, L.A.; Mathews, S.; et al. Deeply altered genome architecture in the endoparasitic flowering plant Sapria himalayana Griff. (Rafflesiaceae). Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Ruan, J.L.; Chen, S.L.; Lv, D.; Zhu, K.X.; Zhao, M.H.; Pei, H.H. Study on Medicinal Plants of Loranthaceae Resources in China. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Med. World Sci. Technol. 2009, 11, 665–669. [Google Scholar]
- The Editorial Committee of Flora of China. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China; Missouri Botanical Garden Press: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2003; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X. Research on Chinese Herbs which Have Diuresis Effect in Chinese Materia Medic. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M. The Research on Cognition and Development of the Efficacy of Water-Disinhibiting Damp-Percolating Medicine on the Basis of Ancient and Modern Literature. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mathiasen, R.L.; Nickrent, D.L.; Shaw, D.C.; Watson, D.M. Mistletoes: Pathology, systematics, ecology, and management. Plant Dis. 2008, 92, 988–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasylenko, Y.; Tesitel, J.; Ceccantini, G.; Oliveira-da-Silva, M.; Dvorak, V.; Steele, D.; Sosnovsky, Y.; Piwowarczyk, R.; Watson, D.M.; Teixeira-Costa, L. Parasites on parasites: Hyper-, epi-, and autoparasitism among flowering plants. Am. J. Bot. 2021, 108, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.A.; Calvin, C.L. Metadata provide insights on patterns of epiparasitism in mistletoes (Santalales), an overlooked topic in forest biology. Botany 2017, 95, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ding, Y. Geographical distribution of Phacellaria Benth. (Santalaceae) and its hosts. Front. Biol. China 2006, 1, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Chen, X.L.; Cui, Y.X.; Xu, Z.C.; Li, Y.H.; Song, J.Y.; Duan, B.Z.; Yao, H. Gene losses and partial deletion of small single-copy regions of the chloroplast genomes of two hemiparasitic Taxillus species. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.J.; Liang, S.L.; Nickrent, D.L. Plastome variation and phylogeny of Taxillus (Loranthaceae). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Yan, H.; Jin, L.; Su, W.; Ji, Y. The complete plastomes of two flowering epiparasites (Phacellaria glomerata and P. compressa): Gene content, organization, and plastome degradation. Genomics 2021, 113, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, W.; Yuan, J.; He, G.; Chen, Y.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; et al. SOAPdenovo2: An empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 2012, 1, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, C. CPGAVAS2, an integrated plastome sequence annotator and analyzer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W65–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schattner, P.; Brooks, A.N.; Lowe, T.M. The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W686–W689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ni, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, C. CPGView: A package for visualizing detailed chloroplast genome structures. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2023, 23, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW): A tool for the easy generation of high-quality custom graphical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Curr. Genet. 2007, 52, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.H. The codon Adaptation Index—A measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Song, J.; Yao, H. Identification and phylogenetic analysis of five Crataegus species (Rosaceae) based on complete chloroplast genomes. Planta 2021, 254, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkin, I.; Patel, A.; Kolmogorov, M.; Vyahhi, N.; Pham, S. Sibelia: A Scalable and Comprehensive Synteny Block Generation Tool for Closely Related Microbial Genomes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 215–229. [Google Scholar]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, T.C.; Qiao, Q.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yonezawa, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Crabbe, M.J.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of holoparasite Cistanche deserticola (Orobanchaceae) reveals gene loss and horizontal gene transfer from its host Haloxylon ammodendron (Chenopodiaceae). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Feng, D.; Song, G.; Wei, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z. The first intron of rice EPSP synthase enhances expression of foreign gene. Sci. China. Ser. C Life Sci. 2003, 46, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Lee, H.L. Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants. DNA Res. 2004, 11, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samigullin, T.H.; Logacheva, M.D.; Penin, A.A.; Vallejo-Roman, C.M. Complete plastid genome of the recent holoparasite Lathraea squamaria reveals earliest stages of plastome reduction in Orobanchaceae. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Lin, X.; Li, Q.; Gao, H.; Luo, G.; Chen, S. High-throughput pyrosequencing of the complete chloroplast genome of Magnolia officinalis and its application in species identification. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2012, 47, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Bergthorsson, U.; Adams, K.L.; Thomason, B.; Palmer, J.D. Widespread horizontal transfer of mitochondrial genes in flowering plants. Nature 2003, 424, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.C.; Wurdack, K.J. Host-to-parasite gene transfer in flowering plants: Phylogenetic evidence from Malpighiales. Science 2004, 305, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.C.; Anderson, W.R.; Wurdack, K.J. Gene transfer from a parasitic flowering plant to a fern. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2005, 272, 2237–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mower, J.P.; Stefanović, S.; Young, G.J.; Palmer, J.D. Plant genetics: Gene transfer from parasitic to host plants. Nature 2004, 432, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Manen, J.F.; Schneeweiss, G.M. Horizontal gene transfer of a plastid gene in the non-photosynthetic flowering plants Orobanche and Phelipanche (Orobanchaceae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2007, 43, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Xue, Q. Codon usage biases of transposable elements and host nuclear genes in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2009, 7, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.; Malakar, A.K.; Chakraborty, S. Codon usage and amino acid usage influence genes expression level. Genetica 2018, 146, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberg, R.; Petrov, D.A. Selection on codon bias. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffler, E.M.; Bullaughey, K.; Matute, D.R.; Meyer, W.K.; Ségurel, L.; Venkat, A.; Andolfatto, P.; Przeworski, M. Revisiting an old riddle: What determines genetic diversity levels within species? PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhan, D.F.; Jia, X.; Mei, W.L.; Dai, H.F.; Chen, X.T.; Peng, S.Q. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) gilg and evolution analysis within the Malvales order. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.H.; Shang, A.Q.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X.Y.; Ren, Y.C.; Yang, M.S.; Wang, J.M. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences of Ulmus species by de novo sequencing: Genome comparative and taxonomic position analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, P.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Y. Codon bias analysis method and research progress on codon bias in Camellia sinensis. J. Tea Commun. 2016, 43, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, M.; Liu, F.; Hua, J.; Wang, K. Analysis on codon usage of chloroplast genome of Gossypium hirsutum. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2011, 44, 245–253. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.; Yang, S.; Choi, G.; Kim, W.J.; Moon, B.C. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of Aconitum pseudolaeve and Aconitum longecassidatum, and development of molecular markers for distinguishing species in the Aconitum Subgenus Lycoctonum. Molecules 2017, 22, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, W.; Morgante, M.; McDevitt, R.; Vendramin, G.G.; Rafalski, J.A. Polymorphic simple sequence repeat regions in chloroplast genomes: Applications to the population genetics of pines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7759–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Yao, X.H.; Huang, H.W. Chloroplast microsatellite markers in Liriodendron tulipifera (Magnoliaceae) and cross-species amplification in L. chinense. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, e123–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Jia, H.M.; Li, X.W.; Chai, M.L.; Jia, H.J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.Y.; Chai, C.Y.; van de Weg, E.; Gao, Z.S. Development of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers from a genome survey of Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra). BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.L. Polymorphic chloroplast microsatellite loci in Nelumbo (Nelumbonaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, e240–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, D.Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.L.; Gao, L.M.; Zhang, S.Z.; Lu, L. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Magnolia kwangsiensis (Magnoliaceae): Implication for DNA barcoding and population genetics. Genome 2011, 54, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.R.; Timko, M.P.; Yoder, J.I.; Axtell, M.J.; Westwood, J.H. Molecular Dialog Between Parasitic Plants and Their Hosts. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2019, 57, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Highly variable chloroplast markers for evaluating plant phylogeny at low taxonomic levels and for DNA barcoding. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D. Advances in phylogenomics based on complete chloroplast genomes. Plant Divers. Resour. 2011, 33, 365–375. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Qiu, H. Pollen morphology of Loranthaceae in China. Guihaia 1993, 133, 235–245. [Google Scholar]
- The Editorial Committee of Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae. Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1988; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xu, L.; Xu, G. A chemotaxonomic study of 27 species of the Loranthaceae plant from China. Guihaia 2004, 24, 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Hao, G.; Zhang, D. Interfamilial relationships of Santalales as revealed by chloroplast trnL intron sequences. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2004, 12, 393–398. [Google Scholar]


| Species | GC3s | GC | CAI | ENc | Fop | Gravy | Aromo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. chinensis | 0.268 | 0.37 | 0.165 | 49.75 | 0.351 | −0.152821 | 0.116124 |
| T. delavayi | 0.27 | 0.372 | 0.166 | 49.89 | 0.354 | −0.155567 | 0.114421 |
| T. levinei | 0.268 | 0.371 | 0.165 | 49.7 | 0.351 | −0.151184 | 0.114695 |
| T. liquidambaricola | 0.269 | 0.37 | 0.165 | 49.75 | 0.351 | −0.152355 | 0.114921 |
| T. lonicerifolius | 0.268 | 0.371 | 0.165 | 49.72 | 0.351 | −0.151446 | 0.114566 |
| T. matsudae | 0.268 | 0.37 | 0.165 | 49.72 | 0.352 | −0.153982 | 0.114106 |
| T. nigrans | 0.276 | 0.379 | 0.166 | 50.10 | 0.354 | −0.133505 | 0.113285 |
| T. pseudochinensis | 0.269 | 0.37 | 0.165 | 49.80 | 0.351 | −0.151886 | 0.115412 |
| T. rhododendricola | 0.269 | 0.37 | 0.166 | 49.78 | 0.351 | −0.15293 | 0.115557 |
| T. sutchuenensis | 0.275 | 0.379 | 0.166 | 50.13 | 0.354 | −0.128203 | 0.113377 |
| T. theifer | 0.267 | 0.37 | 0.166 | 49.65 | 0.351 | −0.161496 | 0.115448 |
| T. thibetensis | 0.266 | 0.368 | 0.166 | 49.57 | 0.352 | −0.153661 | 0.115179 |
| T. tsaii | 0.269 | 0.37 | 0.165 | 49.79 | 0.351 | −0.150685 | 0.115575 |
| T. vestitus | 0.269 | 0.371 | 0.166 | 49.84 | 0.352 | −0.158731 | 0.114805 |
| T. yadoriki | 0.268 | 0.37 | 0.165 | 49.66 | 0.351 | −0.151572 | 0.114484 |
| P. compressa | 0.272 | 0.381 | 0.169 | 50.00 | 0.356 | −0.190492 | 0.109123 |
| P. glomerata | 0.273 | 0.381 | 0.169 | 50.02 | 0.356 | −0.192315 | 0.108927 |
| P. rigidula | 0.272 | 0.381 | 0.169 | 50.01 | 0.356 | −0.202924 | 0.108829 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Fan, P.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Yao, H. Gene Losses and Homology of the Chloroplast Genomes of Taxillus and Phacellaria Species. Genes 2023, 14, 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040943
Wu L, Fan P, Zhou J, Li Y, Xu Z, Lin Y, Wang Y, Song J, Yao H. Gene Losses and Homology of the Chloroplast Genomes of Taxillus and Phacellaria Species. Genes. 2023; 14(4):943. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040943
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Liwei, Panhui Fan, Jianguo Zhou, Yonghua Li, Zhichao Xu, Yulin Lin, Yu Wang, Jingyuan Song, and Hui Yao. 2023. "Gene Losses and Homology of the Chloroplast Genomes of Taxillus and Phacellaria Species" Genes 14, no. 4: 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040943
APA StyleWu, L., Fan, P., Zhou, J., Li, Y., Xu, Z., Lin, Y., Wang, Y., Song, J., & Yao, H. (2023). Gene Losses and Homology of the Chloroplast Genomes of Taxillus and Phacellaria Species. Genes, 14(4), 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040943






