The Transmission Patterns of the Endosymbiont Wolbachia within the Hawaiian Drosophilidae Adaptive Radiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Biological Specimens Screened for Wolbachia Endosymbionts
2.2. Wolbachia Gene Sequencing
2.2.1. Amplicon Sequencing and Primer Redesign
2.2.2. Wolbachia Sequence Datasets
2.2.3. Wolbachia Supergroup Designation
2.2.4. Wolbachia Strain Typing
2.2.5. Phylogenetic Reconstructions
2.2.6. Wolbachia Phylogenetic Signals
2.2.7. Host Sequence Data Set
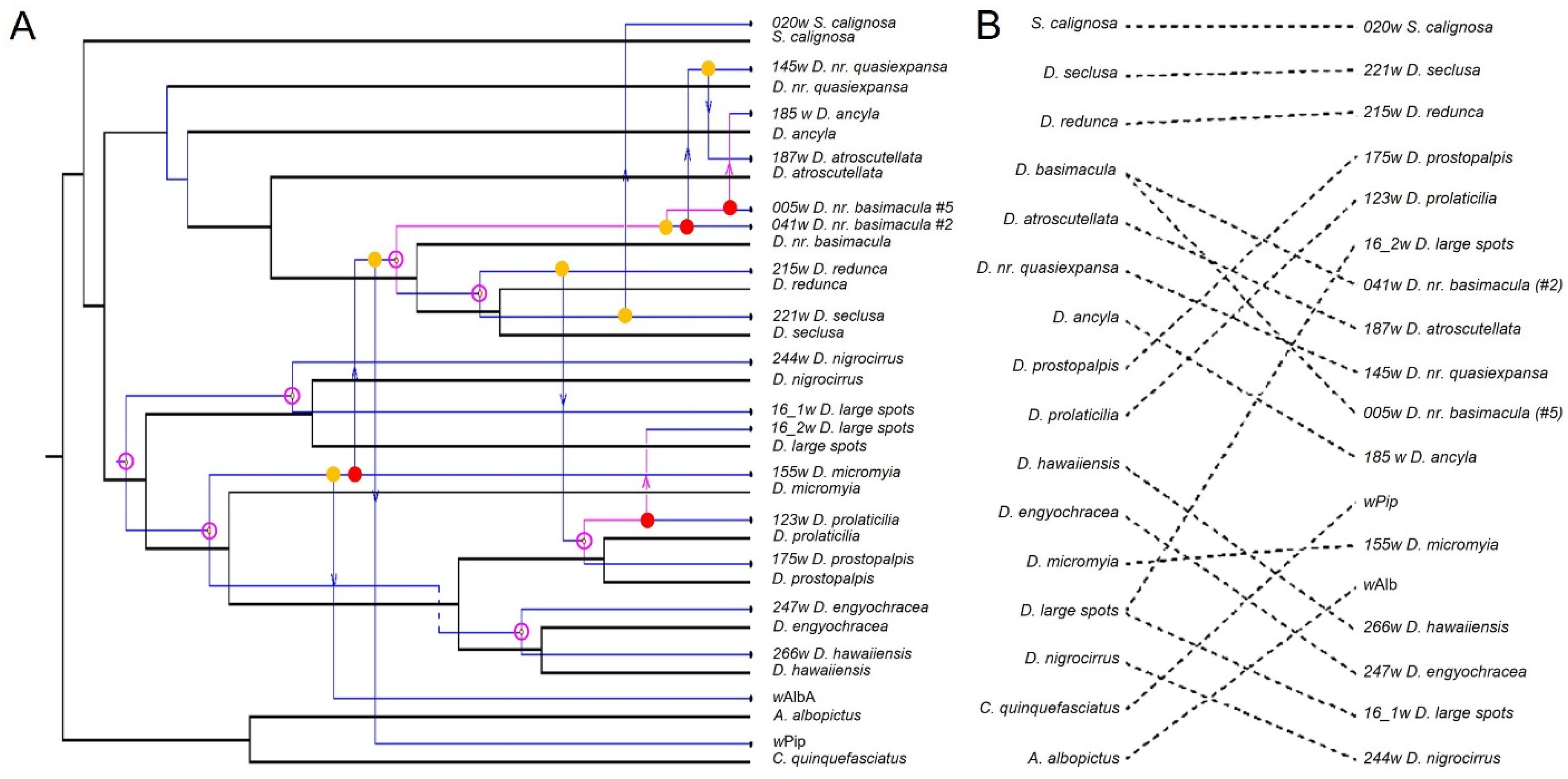
2.2.8. Co-phylogenetic Assessment of Host Species and Wolbachia Strains
2.2.9. Stochastic Character Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Incidence of Wolbachia Infection
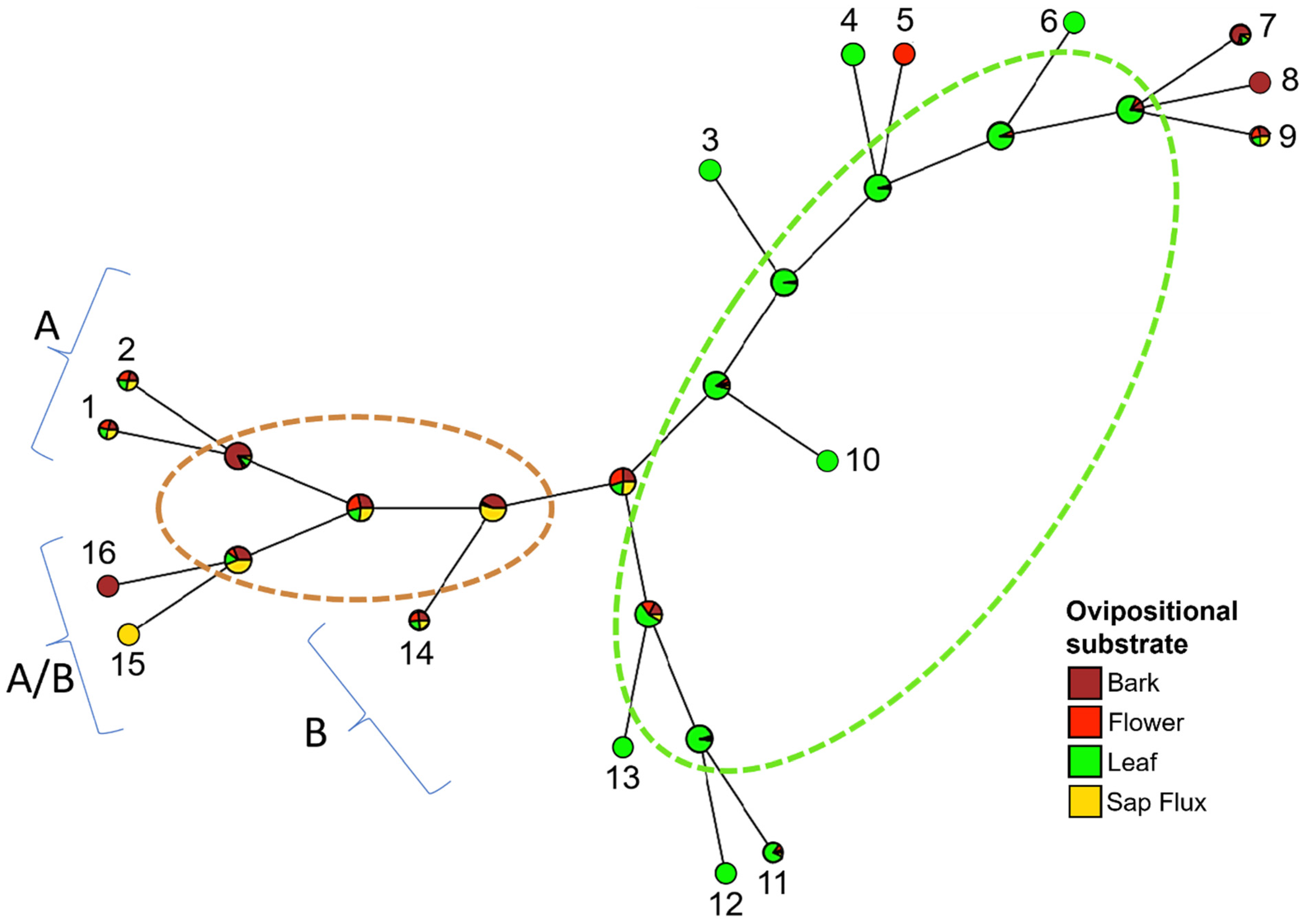
3.2. Wolbachia Strain Typing and Supergroup Designations
3.3. Strain Typing
3.4. Phylogenetic Reconstruction Analysis
3.5. Co-Phylogenetic Reconciliation
3.6. Stochastic Character Trait Mapping
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanisms of Wolbachia Transmission
4.2. Discrepancy in Supergroup Designation of Loci
4.3. Conservation Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kambysellis, M.P.; Ho, K.; Craddock, E.M.; Piano, F.; Parisi, M.; Cohen, J. Pattern of ecological shifts in the diversification of Hawaiian Drosophila inferred from a molecular phylogeny. Curr. Biol. 1995, 5, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, G.M.; Pantoja, N.A.; O’Grady, P.M. Diversity and phylogenetic relationships of Wolbachia in Drosophila and other native Hawaiian insects. Fly 2012, 6, 273–283. [Google Scholar]
- Magnacca, K.N.; Price, D.K. Rapid adaptive radiation and host plant conservation in the Hawaiian picture wing Drosophila (Diptera: Drosophilidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 92, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Grady, P.M.; DeSalle, R. Phylogeny of the genus Drosoph. Genet. 2018, 209, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, E.C. Insects of Hawaii: Volume 1; University of Hawaii Press: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1948; 222p. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneshiro, K.Y. Speciation in the Hawaiian “Drosophila”: Sexual selection sppears to play an important role. BioScience 1988, 38, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karvonen, A.; Seehausen, O. The role of parasitism in adaptive radiations-When might parasites promote and when might they constrain ecological speciation? Int. J. Ecol. 2012, 2012, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werren, J.H.; Windsor, D.; Guo, L. Distribution of Wolbachia among neotropical arthropods. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1995, 262, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer, R.; Breeuwer, J.A.J.; Hurst, G.D.D. Wolbachia pipientis: Microbial manipulator of arthropod reproduction. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1999, 53, 71–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordenstein, S.R.; O’hara, F.P.; Werren, J.H. Wolbachia-induced incompatibility precedes other hybrid incompatibilities in Nasonia. Nature 2001, 409, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenike, J.; Dyer, K.A.; Cornish, C.; Minhas, M.S. Asymmetrical reinforcement and Wolbachia infection in Drosophila. Public Libr. Sci. (PLOS) Biol. 2006, 4, 1852–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Werren, J.H.; Baldo, L.; Clark, M.E. Wolbachia: Master manipulators of invertebrate biology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zug, R.; Hammerstein, P. Still a host of hosts for Wolbachia: Analysis of recent data suggests that 40% of terrestrial arthropod species are infected. Public Libr. Sci. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Werren, J.H. Biology of Wolbachia. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 587–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourtzis, K.; O’Neill, S. Wolbachia infections and arthropod reproduction. BioScience 1998, 48, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Telschow, A.; Hammerstein, P.; Werren, J.H. Effects of Wolbachia on genetic divergence between populations: Mainland-island model. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Telschow, A.; Hammerstein, P.; Werren, J.H. The effect of Wolbachia versus genetic incompatibilities on reinforcement and speciation. Evolution 2005, 59, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halfner, M.S.; Page, R.D.M. Molecular phylogenies and host-parasite cospeciation: Gophers and lice as a model system. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 1995, 349, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Ridland, P.M.; Umina, P.A.; Gill, A.; Ross, P.A.; Pirtle, E.; Hoffmann, A.A. High incidence of related Wolbachia across unrelated leaf-mining Diptera. Insects 2021, 12, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegler, M.; Sidhu, M.; Miller, W.J.; O’Neill, S.L. Evidence for a global Wolbachia replacement in Drosophila melanogaster. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turelli, M.; Cooper, B.S.; Richardson, K.M.; Ginsberg, P.S.; Peckenpaugh, B.; Antelope, C.X.; Kim, K.J.; May, M.R.; Abrieux, A.; Wilson, D.A.; et al. Rapid global spread of wRi-like Wolbachia across multiple Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, M.; Anderson, T.J.C.; Bandi, C.; Bazzacchi, C.; Genchi, C. A phylogenetic analysis of filarial nematodes: Comparison with the phylogeny of Wolbachia endosymbionts. Parasitology 2001, 122, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lefoulon, E.; Bain, O.; Makepeace, B.L.; d’Haese, C.; Uni, S.; Martin, C.; Gavotte, L. Breakdown of coevolution between symbiotic bacteria Wolbachia and their filarial hosts. PeerJ 2016, 4, e18401-30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, M.Z.; Li, S.; Xue, X.; Yin, X.; Ren, S.; Jiggins, F.M.; Greeff, J.M.; Qiu, B. The intracellular bacterium Wolbachia uses parasitoid wasps as phoretic vectors for efficient horizontal Transmission. Public Libr. Sci. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Lv, N.; Shi, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Qiu, B. Plant-mediated horizontal transmission of Wolbachia between whiteflies. Int. Soc. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 11, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Laidoudi, Y.; Levasseur, A.; Medkour, H.; Maaloum, M.; Ben Khedher, M.; Sambou, M.; Bassene, H.; Davoust, B.; Fenollar, F.; Raoult, D.; et al. An earliest endosymbiont, Wolbachia massiliensis sp. nov., strain PL13 from the bed bug (Cimex hemipterus), type strain of a new supergroup T. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Shropshire, J.D.; Cross, K.L.; Leigh, B.; Mansueto, A.J.; Stewart, V.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Bordenstein, S.R. Living in the endosymbiotic world of Wolbachia: A centennial review. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerth, M.; Gansauge, M.T.; Weigert, A.; Bleidorn, C. Phylogenomic analyses uncover origin and spread of the Wolbachia pandemic. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeyaprakash, A.; Hoy, M.A. Long PCR improves Wolbachia DNA amplification: Wsp sequences found in 76% of sixty-three arthropod species. Insect Mol. Biol. 2000, 9, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenboecker, K.; Hammerstein, P.; Schlattmann, P.; Telschow, A.; Werren, J.H. How many species are infected with Wolbachia?—A statistical analysis of current data. Fed. Eur. Microbiol. Soc. (FEMS) Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 281, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magnacca, K.N.; Foote, D.; O’Grady, P.M. A review of the endemic Hawaiian Drosophilidae and their host plants. Zootaxa 2008, 1782, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.B.; Dupuis, J.R.; Jardeleza, M.K.; Ouedraogo, N.; Geib, S.M.; Follett, P.A.; Price, D.K. Population genomic and phenotype diversity of invasive Drosophila suzukii in Hawai‘i. Biol. Invasions 2020, 22, 1753–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.T.; Watcher-Weatherwax, W.; LaPointe, D.A. Genetic Diversity of Wolbachia endosymbionts in Culex quinquefasciatus from Hawaii, Midway Atoll and American Samoa; Technical Report HCSU-074; Hawaii Cooperative Studies Unit, University of Hawai‘i at Hilo: Hilo, HI, USA, 2016; 33p. [Google Scholar]
- Baldo, L.; Dunning Hotopp, J.C.; Jolley, K.A.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Biber, S.A.; Choudhury, R.R.; Hayashi, C.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Tettelin, H.; Werren, J.H. Multilocus sequence typing system for the endosymbiont Wolbachia pipientis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 7098–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Sun, L.V.; Vamathevan, J.; Riegler, M.; Deboy, R.; Brownlie, J.C.; McGraw, E.A.; Martin, W.; Esser, C.; Ahmadinejad, N.; et al. Phylogenomics of the reproductive parasite Wolbachia pipientis wMel: A streamlined genome overrun by mobile genetic elements. Public Libr. Sci. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metcalf, J.A.; Jo, M.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Jaenike, J.; Bordenstein, S.R. Recent genome reduction of Wolbachia in Drosophila recens targets phage WO and narrows candidates for reproductive parasitism. PeerJ 2014, 2, e529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellegaard, K.M.; Klasson, L.; Naslund, K.; Bourtzis, K.; Andersson, S.G.E. Comparative genomics of Wolbachia and the bacterial species concept. Public Libr. Sci. (PLOS) Genet. 2013, 9, e1003381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salzberg, S.L.; Dunning Hotopp, J.C.; Delcher, A.L.; Pop, M.; Smith, D.R.; Eisen, M.B.; Nelson, W.C. Serendipitous discovery of Wolbachia genomes in multiple Drosophila species. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, R23.1–R23.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siozios, S.; Cestaro, A.; Kaur, R.; Pertot, I.; Rota-Stabelli, O.; Anfora, G. Draft genome sequence of the Wolbachia endosymbiont of Drosophila suzukii. Genome Announc. 2013, 1, e00032-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klasson, L.; Walker, T.; Sebaihia, M.; Sanders, M.J.; Quail, M.A.; Lord, A.; Sanders, S.; Earl, J.; O’Neill, S.L.; Thomson, N.; et al. Genome Evolution of Wolbachia strain wPip from the Culex pipiens Group. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salzberg, S.L.; Puiu, D.; Sommer, D.D.; Nene, V.; Lee, N.H. Genome announcement: Genome sequence of the Wolbachia endosymbiont of Culex quinquefasciatus JHB. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foster, J.; Ganatra, M.; Kamal, I.; Ware, J.; Makarova, K.; Ivanova, N.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Kapatral, V.; Kumar, S.; Posfai, J.; et al. The Wolbachia genome of Brugia malayi endosymbiont evolution within a human pathogenic nematode. Public Libr. Sci. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoh, N.; Hosokawa, T.; Moriyama, M.; Oshima, K.; Hattori, M.; Fukatsu, T. Evolutionary origin of insect-Wolbachia nutritional mutualism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10257–10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, L.; Werren, J.H. Revisiting Wolbachia supergroup typing based on wsp: Spurious lineages and discordance with MLST. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinform. Appl. Note 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1. 3.1. 2009. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 1 January 2018).
- Conow, C.; Fielder, D.; Ovadia, Y.; Libeskind-Hadas, R. Jane: A new tool for the cophylogeny reconstruction problem. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2010, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viale, E.; Martinez-Sanudo, I.; Brown, J.M.; Simonato, M.; Girolami, V.; Squartini, A.; Bressan, A.; Faccoli, M.; Mazzon, L. Pattern of association between endemic Hawaiian fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) and their symbiotic bacteria: Evidence of cospeciation events and proposal of “Candidatus Stammerula trupaneae”. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 90, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revell, L.J. Phytools: An R package for phylogenetic comparative biology (and other things). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Nielsen, R.; Bollback, J.P. Stochastic mapping of morphological characters. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 131–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneshiro, K.Y. Dynamics of sexual selection in the Hawaiian Drosophilidae: A paradigm for evolutionary change. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 2006, 38, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sintupachee, S.; Milne, J.R.; Poonchaisri, S.; Baimai, V.; Kittayapong, P. Closely related Wolbachia strains within the pumpkin arthropod community and the potential for horizontal transmission via the plant. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, S.L.; Bourtzis, K.; Braig, H.R.; Jones, B.F.; Zhou, W.; Rousset, F.; O’Neill, S.L. Wolbachia infections are distributed throughout insect stomatic and germline tissues. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrostek, E.; Pelz-Stelinski, K.; Hurst, G.D.D.; Hughes, G.L. Horizontal transmission of intracellular insect symbionts via Plants. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kriesner, P.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Lee, S.F.; Turelli, M.; Weeks, A.R. Rapid sequential spread of two Wolbachia variants in Drosophila simulans. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanaei, E.; Charlat, S.; Engelstädter, J. Wolbachia host shifts: Routes, mechanisms, constraints and evolutionary consequences. Biol. Rev. 2021, 96, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xiong, X.; Cao, W.; Zhang, C.; Werren, J.H.; Wang, X. Phylogenomic analysis of Wolbachia strains reveals patterns of genome evolution and recombination. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 2508–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, L.; Bordenstein, S.; Wernegreen, J.J.; Werren, J.H. Widespread recombination throughout Wolbachia genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ilinsky, Y.; Kosterin, O.E. Molecular diversity of Wolbachia in Lepidoptera: Prevalent allelic content and high recombination of MLST genes. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2017, 109, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, K.L.; LeDuc, R.; Ganote, C.; Price, D.K. Physiological effects of heat stress on Hawaiian picture-wing Drosophila: Genome-wide expression patterns and stress-related traits. Conserv. Physiol. 2015, 3, cou062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldon, J.; Bellinger, M.R.; Price, D.K. Hawaiian picture-winged Drosophila exhibit adaptive population divergence along a narrow climatic gradient on Hawaii Island. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hague, M.T.; Caldwell, C.N.; Cooper, B.S. Pervasive effects of Wolbachia on host temperature preference. MBio 2020, 11, e01768-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Song, Z.R.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Hong, X.Y. Spider mites singly infected with either Wolbachia or Spiroplasma have reduced thermal tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 706321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ometto, L.; Cestaro, A.; Ramasamy, S.; Grassi, A.; Revadi, S.; Siozios, S.; Moretto, M.; Fontana, P.; Varotto, C.; Pisani, D.; et al. Linking genomics and ecology to investigate the complex evolution of an invasive Drosophila pest. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- dos Santos, G.; Schroeder, A.J.; Goodman, J.L.; Strelets, V.B.; Crosby, M.A.; Thurmond, J.; Emmeret, D.B.; Gelbart, W.M.; FlyBase Consortium. FlyBase: Introduction of the Drosophila melanogaster Release 6 reference genome assembly and large-scale migration of genome annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D690–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, T.T.; Eisen, M.B.; Thornton, K.R.; Andolfatto, P. A second-generation assembly of the Drosophila simulans genome provides new insights into patterns of lineage-specific divergence. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arensburger, P.; Megy, K.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Abrudan, J.; Amedeo, P.; Antelo, B.; Bartholomay, L.; Bidwell, S.; Caler, E.; Atkinson, P.W.; et al. Sequencing of Culex quinquefasciatus establishes a platform for mosquito comparative genomics. Science 2010, 330, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, J.R.; Koren, S.; Dilley, K.A.; Puri, V.; Brown, D.M.; Harkins, D.M.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Rosen, B.; Chen, X.G.; Shabman, R.S.; et al. Analysis of the Aedes albopictus C6/36 genome provides insight into cell line utility for viral propagation. Gigascience 2018, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Deans, A.R. Bayesian phylogenetics and its influence on insect systematics. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 189–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Lewis, P.O.; Fan, Y.; Kuo, L.; Chen, M.-H. Improving marginal likelihood estimation for Bayesian phylogenetic model selection. Syst. Biol. 2011, 60, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.; Teslenko, M. Draft MrBayes Version 3.2 Manual: Tutorials and Model Summaries. 2011. Available online: https://pbil.univ-lyon1.fr/members/perriere/pdf/mb3.2_manual.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2018).
- Kass, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayes factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.; Rannala, B. Frequentist properties of Bayesian posterior probabilities of phylogenetic trees under simple and complex substitution models. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53, 53904–53913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Wolbachia Host | Wolbachia Strain | Host Collect Location | Genome Accession | Citation | Supergroup | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drosophila recens | wRec | Rochester, New York, USA | GCF_000742435.1 | [37] | A | PR |
| D. melanogaster | wMel | Stock Center D. melanogaster strain yw67c23 | GCF_000008025.1 | [35] | A | PR, A/P |
| D. simulans | wNo | Noumea, New Caledonia | GCF_000376585.1 | [38] | B | PR, A/P |
| D. simulans | wHa | Hawai’i, USA | GCF_000376605.1 | [38] | A | A/P |
| D. ananassae | wAna | Tucson Strain Center [strain 14024-0371.13] | GCF_000167475.1 | [39] | A | PR |
| D. suzukii | wSuzi, strain valsugana | Trentino Alto Adige, Italy | GCF_000333795.1 | [40] | A | PR, A/P |
| Culex quinquefasciatus | wPip strain Pel | Sri Lanka | AM999887.1 | [41] | B | A/P |
| C. quinquefasciatus | wPip strain JHB | Johannesburg, Africa | ABZA0100000 | [42] | B | A/P |
| Aedes albopictus | wAlbA | Unknown | 1 | [34] | A | A/P |
| Brugia malayi | wBm | TRS Lab colony (Athens, GA, USA) | NC_006833.1 | [43] | D | A/P |
| Cimex lectularius strain JESC | wCle | Japan | AP013028.1 | [44] | F | A/P |
| Species | Screened | Confirmed Infected | PCR Product Only | Zero Amplifications | Proportion Infected |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. ciliaticrus | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0.00 |
| D. engyochracea | 7 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0.29 |
| D. hawaiiensis | 15 | 2 | 0 | 13 | 0.13 |
| D. heteroneura | 5 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0.40 |
| D. murphyi | 5 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0.40 |
| D. ochracea | 11 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 0.09 |
| D. odontophallus | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0.00 |
| D. orphnopeza | 7 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 0.00 |
| D. primaeva | 11 | 0 | 1 | 10 | 0.00 |
| D. silvestris | 6 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0.00 |
| D. sproati | 114 | 0 | 5 | 109 | 0.00 |
| D. tanythrix | 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0.00 |
| D. yooni | 10 | 2 | 1 | 7 | 0.20 |
| totals | 219 | 17 | 11 | 191 | n/a |
| Wolbachia Sample Name | Host Species Name | Island of Collection | coxA | fbpA | hcpA | ftsZ | gatB | Strain Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native Hawaiian Drosophilidae | 247w | Drosophila engyochracea | Hawai‘i | 2 (A) | --- | 11 (B) | 2 (A) | --- | A/B |
| 250_1w | D. engyochracea | Hawai‘i | 2 | --- | --- | 2 | --- | A | |
| 250_2w | D. engyochracea | Hawai‘i | 5 | --- | --- | 10 | --- | A | |
| 264w | D. hawaiiensis | Hawai‘i | 2 | --- | --- | --- | --- | A | |
| 266w | D. hawaiiensis | Hawai‘i | 2 (A) | --- | 11 (B) | 2 (A) | --- | A/B | |
| 252w | D. heteroneura | Hawai‘i | 2 (A) | --- | 11 (B) | --- | --- | A/B | |
| 253w | D. heteroneura | Hawai‘i | 6 (A) | --- | 11 (B) | --- | --- | A/B | |
| 16_1w | D. large spots | Hawai‘i | 2 | 7 | 6 | 2 | --- | A | |
| 16_2w | D. large spots | Hawai‘i | 4 | 8 | 2 | 1 | --- | B | |
| 171w | D. murphyi | Hawai‘i | --- | 4 (A) | 3 (?) | 4 (B) | --- | A/?/B | |
| MLL6w (415) | D. murphyi | Hawai‘i | 13 | --- | 1 | --- | --- | B | |
| 244w | D. nigrocirrus | Hawai‘i | 2 | 6 | 5 | 11 | --- | A | |
| 256w | D. ochracea | Hawai‘i | 2 (A) | 3 | 11 (B) | --- | --- | A/B | |
| 123w | D. prolaticilia | Hawai‘i | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | B | |
| 197w | D. prolaticilia | Hawai‘i | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | --- | B | |
| 221w | D. seclusa | Hawai‘i | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | B | |
| 291w | D. yooni | Hawai‘i | 13 | --- | --- | --- | --- | B | |
| 292w | D. yooni | Hawai‘i | 13 | --- | --- | --- | --- | B | |
| 20w | Scaptomyza caliginosa | Hawai‘i | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | B | |
| 152w | S. cyrtandrae | Hawai‘i | 2 (A) | --- | 11 (B) | --- | --- | A/B | |
| 204w | S. reducta | Hawai‘i | --- | --- | 11 | --- | --- | B | |
| 205w | S. reducta | Hawai‘i | 3 | 2 | 11 | --- | --- | B | |
| 206w | S. undulata | Hawai‘i | 1 | --- | 14 | --- | --- | B | |
| 185w | D. ancyla | Maui | 13 | 12 | 1 | 7 | 1 | B | |
| 175w | D. prostopalpis | Maui | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 4 | B | |
| 145w | D. quasiexpansa | Maui | 1 | --- | 4 | 4 | --- | B | |
| 216w | D. nr. redunca | Hawai‘i | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | --- | B | |
| 200w | S. crassifemur | Maui | 1 | --- | 1 | --- | --- | B | |
| 201w | S. crassifemur | Maui | 9 | 10 | 11 | --- | --- | B | |
| 202w | S. nasalis | Maui | 1 | --- | --- | --- | --- | B | |
| 203w | S. nasalis | Maui | 1 | 3 | 1 | --- | --- | B | |
| 208_1w | D. apodasta | Kaua‘i | 8 (A) | --- | 11 (B) | --- | --- | A/B | |
| 208_2w | D. apodasta | Kaua‘i | 3 | --- | 11 | --- | --- | B | |
| 187w | D. atroscutellata | Kaua‘i | 13 | 13 | 1 | 4 | --- | B | |
| 41w | D. nr. basimacula #2 | Kaua‘i | 13 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | B | |
| 59w | D. nr. basimacula #1 | Kaua‘i | 13 | 1 | 1 | 3 | --- | B | |
| 209w | D. basimacula | Kaua‘i | 1 | --- | 11 | --- | --- | B | |
| 212w | D. nr. basimacula #1 | Kaua‘i | 13 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | B | |
| 213w | D. nr. basimacula #2 | Kaua‘i | 13 | 1 | 1 | 5 | --- | B | |
| 5w | D. nr. basimacula #5 | Kaua‘i | 13 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | B | |
| 127w | D. kikiko | Kaua‘i | 7 | --- | 8 | --- | --- | B | |
| 155w | D. micromyia | Kaua‘i | 10 | 11 | 7 | 8 | 2 | B | |
| 215_1w | D. nr. perissopoda #1 | Kaua‘i | 1 (B) | 5 (A) | --- | --- | --- | A/B | |
| 215_2w | D. nr. perissopoda #1 | Kaua‘i | 13 | 9 | --- | --- | --- | B | |
| Non-native Drosophila and mosquitoes collected in Hawaii | 3_A12w | D. suzukii | Kaua‘i | --- | --- | 12 | --- | --- | A |
| 3_B11w | D. suzukii | Kaua‘i | --- | --- | 14 | --- | --- | B | |
| 3_C2w | D. suzukii | O‘ahu | 15 | 17 | 14 | --- | --- | B | |
| 3_C3w | D. suzukii | Kaua‘i | 16 | --- | 13 | --- | --- | A | |
| 3_D5w | D. suzukii | Kaua‘i | --- | --- | 13 | --- | --- | A | |
| 3_E3w | D. suzukii | Kaua‘i | --- | --- | 13 | --- | --- | A | |
| 3_F6w | D. suzukii | Kaua‘i | --- | --- | 14 | --- | --- | B | |
| 3_H4w | D. suzukii | Kaua‘i | --- | --- | 13 | --- | --- | A | |
| wHa 6 | D. simulans wHa | Hawai‘i | 16 | 20 | 13 | 15 | --- | A | |
| wAlb | Aedes albopictus | Hawai‘i | 11 (A) | 14 (B) | 9 (B) | 12 (B) | --- | A/B | |
| 6771w | Culex quinquefasciatus | Hawai‘i | 13 | 16 | 11 | 14 | --- | B | |
| Other Drosophila and Mosquitoes | wAlbA 1 | A. albopictus | Unknown | 12 | 15 | 10 | 13 | --- | A |
| wPip 2 | C. quinquefasciatus Pel | Sri Lanka | 13 | 16 | 11 | 14 | --- | B | |
| wPip 3 | C. quinquefasciatus JHB | Johannesburg | 13 | 16 | 11 | 14 | --- | B | |
| wDmel 4 | D. melanogaster | Laboratory Stock | 17 | 19 | 15 | 16 | --- | A | |
| wDsuzi 5 | D. suzukii | Italy | 14 | 18 | 12 | 15 | --- | A | |
| wNo 6 | D. simulans | New Caledonia | 18 | 21 | 16 | 17 | --- | B | |
| O G | wBm 7 | Brugia malayi | Unknown | 19 | 22 | 17 | 18 | 5 | D |
| wCle 8 | Cimex lectularius | Unknown | 20 | 23 | 18 | 19 | 6 | F |
| Drosophila and Wolbachia | Invasive Mosquitoes, Drosophila, and Wolbachia | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost 0 | Cost 1 | Cost 0 | Cost 1 | |
| Co-speciation | 8 | 8 | 9 | 7 |
| Duplication | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Duplication and host switches | 7 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Loss | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corpuz, R.L.; Bellinger, M.R.; Veillet, A.; Magnacca, K.N.; Price, D.K. The Transmission Patterns of the Endosymbiont Wolbachia within the Hawaiian Drosophilidae Adaptive Radiation. Genes 2023, 14, 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081545
Corpuz RL, Bellinger MR, Veillet A, Magnacca KN, Price DK. The Transmission Patterns of the Endosymbiont Wolbachia within the Hawaiian Drosophilidae Adaptive Radiation. Genes. 2023; 14(8):1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081545
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorpuz, Renée L., M. Renee Bellinger, Anne Veillet, Karl N. Magnacca, and Donald K. Price. 2023. "The Transmission Patterns of the Endosymbiont Wolbachia within the Hawaiian Drosophilidae Adaptive Radiation" Genes 14, no. 8: 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081545
APA StyleCorpuz, R. L., Bellinger, M. R., Veillet, A., Magnacca, K. N., & Price, D. K. (2023). The Transmission Patterns of the Endosymbiont Wolbachia within the Hawaiian Drosophilidae Adaptive Radiation. Genes, 14(8), 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14081545






