Vitamin D: An Overview of Gene Regulation, Ranging from Metabolism to Genomic Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
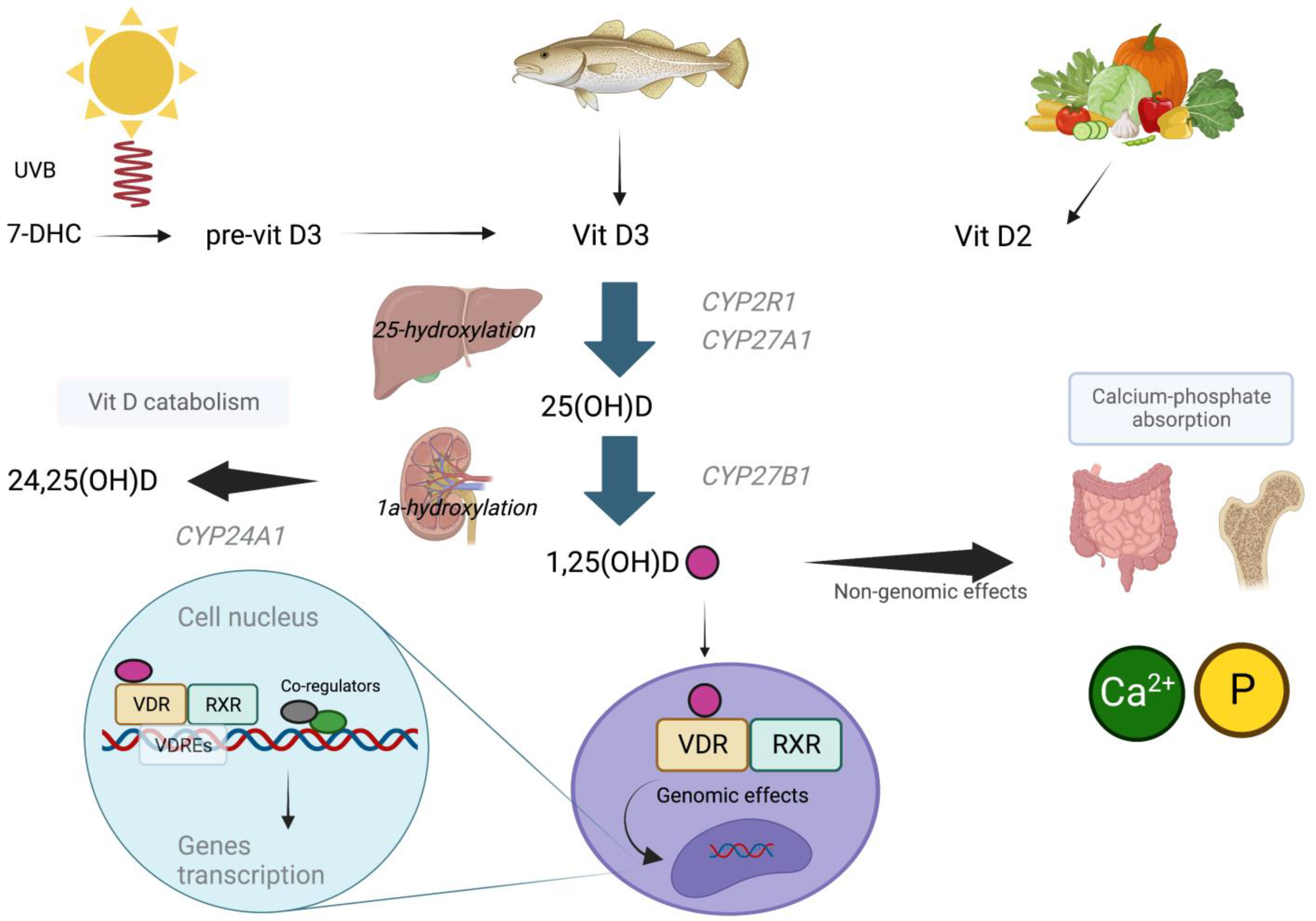
2. Vitamin D Metabolism and Homeostasis
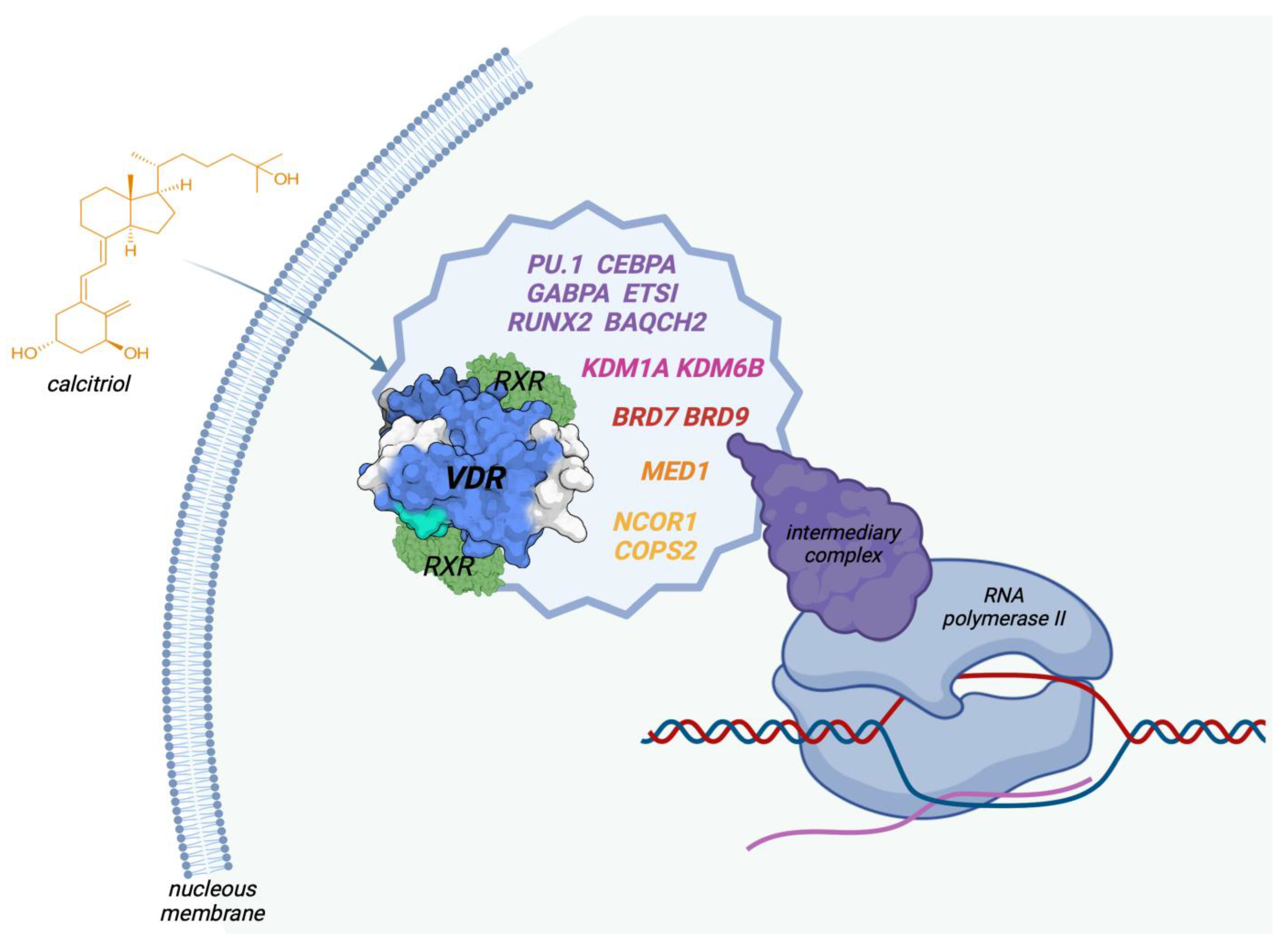
3. Genomic and Non-Genomic Effects of Vitamin D
4. Genetic Factors Influencing Vitamin D Status
4.1. DHCR7 (7-Dehydrocholesterol Reductase)
4.2. CYP2R1 (Vitamin D 25-Hydroxylase)
4.3. CYP27B1 (25(OH)D-1-α Hydroxylase)
4.4. CYP24A1 (Vitamin D 24-Hydroxylase)
4.5. GC (Vitamin D Binding Protein)
4.6. VDR (Vitamin D Receptor)
4.7. Epigenetic Factors Influencing Vitamin D Status
5. Genetic Effects of Vitamin D
5.1. Genomic Action
5.2. Immune System Regulation
5.3. Focus on Clinical Outcomes
5.4. Viral Infections and COVID-19
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reijven, P.; Soeters, P. Vitamin D: A magic bullet or a myth? Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2663–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, H.F. Vitamin D. Vitam. Horm. 2016, 100, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistini, C.; Ballan, R.; Herkenhoff, M.E.; Saad, S.M.I.; Sun, J. Vitamin D Modulates Intestinal Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Marcocci, C.; Carmeliet, G.; Bikle, D.; White, J.H.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Lips, P.; Munns, C.F.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; Giustina, A.; et al. Skeletal and Extraskeletal Actions of Vitamin D: Current Evidence and Outstanding Questions. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1109–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Carmeliet, G.; Verlinden, L.; van Etten, E.; Verstuyf, A.; Luderer, H.F.; Lieben, L.; Mathieu, C.; Demay, M. Vitamin D and Human Health: Lessons from Vitamin D Receptor Null Mice. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 726–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitterlinden, A.G.; Fang, Y.; van Meurs, J.B.; Pols, H.A.; van Leeuwen, J.P. Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene 2004, 338, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berretta, M.; Quagliariello, V.; Bignucolo, A.; Facchini, S.; Maurea, N.; Di Francia, R.; Fiorica, F.; Sharifi, S.; Bressan, S.; Richter, S.N.; et al. The Multiple Effects of Vitamin D against Chronic Diseases: From Reduction of Lipid Peroxidation to Updated Evidence from Clinical Studies. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holick, M.F.; Uskokovic, M.; Henley, J.W.; MacLaughlin, J.; Holick, S.A.; Potts, J.T. The Photoproduction of 1α,25–Dihydroxyvitamin D3in Skin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1980, 303, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberg-Allardt, C. Vitamin D in foods and as supplements. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2006, 92, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G.L.; Chen, T.C.; Holick, M.F.; Langman, C.B.; Price, H.; Celis, M.M.; Herndon, D.N. Synthesis of vitamin D in skin after burns. Lancet 2004, 363, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Nezhad, A.; Holick, M.F. Vitamin D for Health: A Global Perspective. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 720–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D Deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.G.; Ochalek, J.T.; Kaufmann, M.; Jones, G.; DeLuca, H.F. CYP2R1 is a major, but not exclusive, contributor to 25-hydroxyvitamin D production in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 15650–15655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollis, B.W. Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels Indicative of Vitamin D Sufficiency: Implications for Establishing a New Effective Dietary Intake Recommendation for Vitamin D. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazahery, H.; Von Hurst, P.R. Factors Affecting 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration in Response to Vitamin D Supplementation. Nutrients 2015, 7, 5111–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffels, K.; Overbergh, L.; Bouillon, R.; Mathieu, C. Immune regulation of 1α-hydroxylase in murine peritoneal macrophages: Unravelling the IFNγ pathway. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 103, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christakos, S.; Ajibade, D.V.; Dhawan, P.; Fechner, A.J.; Mady, L.J. Vitamin D: Metabolism. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, H.S. Extrarenal Vitamin D Hydroxylase Expression and Activity in Normal and Malignant Cells: Modification of Expression by Epigenetic Mechanisms and Dietary Substances. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, S108–S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitanaka, S.; Takeyama, K.-I.; Murayama, A.; Kato, S. The Molecular Basis of Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type I. Endocr. J. 2001, 48, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permana, D.; Kitaoka, T.; Ichinose, H. Conversion and synthesis of chemicals catalyzed by fungal cytochrome P450 monooxygenases: A review. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2023, 120, 1725–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, A.; Takeyama, K.-I.; Kitanaka, S.; Kodera, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Hosoya, T.; Kato, S. Positive and Negative Regulations of the Renal 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 1α-Hydroxylase Gene by Parathyroid Hormone, Calcitonin, and 1α,25(OH)2D3 in Intact Animals. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 2224–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omdahl, J.L.; Morris, H.A.; May, B.K. Hydroxylaseenzymes of thevitamind pathway: Expression, Function, and Regulation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 139–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tang, W.; Zhou, J.; Stubbs, J.R.; Luo, Q.; Pi, M.; Quarles, L.D. Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Is a Counter-Regulatory Phosphaturic Hormone for Vitamin D. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Kakitani, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Fujita, T.; Fukumoto, S.; Tomizuka, K.; Yamashita, T. Targeted ablation of Fgf23 demonstrates an essential physiological role of FGF23 in phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thacher, T.D.; Fischer, P.R.; Singh, R.J.; Roizen, J.; Levine, M.A. CYP2R1 Mutations Impair Generation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and Cause an Atypical Form of Vitamin D Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1005–E1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.B.; Levine, M.A.; Bell, N.H.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Russell, D.W. Genetic evidence that the human CYP2R1 enzyme is a key vitamin D 25-hydroxylase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7711–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Yu, K.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Simon, K.C.; McCullough, M.L.; Gallicchio, L.; Jacobs, E.J.; Ascherio, A.; Helzlsouer, K.; Jacobs, K.B.; et al. Genome-wide association study of circulating vitamin D levels. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 2739–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, F.-X.; Armas, L.; Lappe, J.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, G.; Wang, H.-W.; Recker, R.; Zhao, L.-J. Comprehensive association analysis of nine candidate genes with serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels among healthy Caucasian subjects. Hum. Genet. 2010, 128, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltzman, D. Functions of vitamin D in bone. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 149, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goltzman, D.; Mannstadt, M.; Marcocci, C. Physiology of the Calcium-Parathyroid Hormone-Vitamin D Axis. Front. Horm. Res. 2018, 50, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śledzińska, K.; Landowski, P.; Żmijewski, M.A.; Kamińska, B.; Kowalski, K.; Liberek, A. Diet, Sun, Physical Activity and Vitamin D Status in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, H.F. The Metabolism and Functions of Vitamin D. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1986, 196, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirajudeen, S.; Shah, I.; Menhali, A. A Narrative Role of Vitamin D and Its Receptor: With Current Evidence on the Gastric Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenngam, N.; Shirvani, A.; Kalajian, T.A.; Song, A.; Holick, M.F. The Effect of Various Doses of Oral Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Gut Microbiota in Healthy Adults: A Randomized, Double-blinded, Dose-response Study. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zella, L.A.; Meyer, M.B.; Nerenz, R.D.; Lee, S.M.; Martowicz, M.L.; Pike, J.W. Multifunctional Enhancers Regulate Mouse and Human Vitamin D Receptor Gene Transcription. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 128–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.W.; Okamura, W.H.; Hammond, M.W.; Bishop, J.E.; Dormanen, M.C.; Bouillon, R.; van Baelen, H.; Ridall, A.L.; Daane, E.; Khoury, R.; et al. Comparison of 6-s-cis- and 6-s-trans-Locked Analogs of 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Indicates That the 6-s-cis Conformation Is Preferred for Rapid Nongenomic Biological Responses and That Neither 6-s-cis- nor 6-s-trans-Locked Analogs Are Preferred for Genomic Biological Responses. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 1518–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legarth, C.; Grimm, D.; Wehland, M.; Bauer, J.; Krüger, M. The Impact of Vitamin D in the Treatment of Essential Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, A.; Mazloum, S.R.; Maghsoudi, S.; Soleimani, D.; Khayyatzadeh, S.S.; Arekhi, S.; Arya, A.; Mirmoosavi, S.J.; Ferns, G.A.; Bahrami-Taghanaki, H.; et al. High Dose Vitamin D Supplementation Is Associated with a Reduction in Depression Score Among Adolescent Girls: A Nine-Week Follow-Up Study. J. Diet. Suppl. 2018, 15, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, M.L.; Bostick, R.M.; Mayo, T.L. Vitamin D Gene Pathway Polymorphisms and Risk of Colorectal, Breast, and Prostate Cancer. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2009, 29, 111–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaeizadeh, S.; Avan, A.; Bahrami, A.; Khodashenas, E.; Esmaeili, H.; Ferns, G.A.; Abdizadeh, M.F.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M. High Dose Supplementation of Vitamin D Affects Measures of Systemic Inflammation: Reductions in High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein Level and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio (NLR) Distribution. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 4317–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, M.K.; Benjamin, E.J.; Dupuis, J.; Massaro, J.M.; Jacques, P.F.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Ordovas, J.M.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Vasan, R.S.; et al. Genetic and non-genetic correlates of vitamins K and D. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orton, S.-M.; Morris, A.P.; Herrera, B.M.; Ramagopalan, S.V.; Lincoln, M.R.; Chao, M.J.; Vieth, R.; Sadovnick, A.D.; Ebers, G.C. Evidence for genetic regulation of vitamin D status in twins with multiple sclerosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 88, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, A.; Sadeghnia, H.R.; Tabatabaeizadeh, S.; Bahrami-Taghanaki, H.; Behboodi, N.; Esmaeili, H.; Ferns, G.A.; Mobarhan, M.G.; Avan, A. Genetic and epigenetic factors influencing vitamin D status. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 4033–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; He, J.-W.; Fu, W.-Z.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-L. An analysis of the association between the vitamin D pathway and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in a healthy Chinese population. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, E.L.; Rees, J.R.; Peacock, J.L.; Mott, L.A.; Amos, C.I.; Bostick, R.M.; Figueiredo, J.C.; Ahnen, D.J.; Bresalier, R.S.; Burke, C.A.; et al. Genetic Variants in CYP2R1, CYP24A1, and VDR Modify the Efficacy of Vitamin D3Supplementation for Increasing Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2133–E2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Holt, B.J.; Pennell, C.E.; Holt, P.G.; Hart, P.H.; Blackwell, J.M. Genome-wide association study of vitamin D levels in children: Replication in the Western Australian Pregnancy Cohort (Raine) study. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyppönen, E.; Berry, D.J.; Wjst, M.; Power, C. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and IgE—A significant but nonlinear relationship. Allergy 2009, 64, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, P. Relative Value of 25(OH)D and 1,25(OH)2D Measurements. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1668–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, K.; Kattan, W.E.; Zou, M.; Durmaz, E.; BinEssa, H.; Nalbantoğlu, Ö.; Al-Rijjal, R.A.; Meyer, B.; Özkan, B.; Shi, Y. Novel CYP27B1 Gene Mutations in Patients with Vitamin D-Dependent Rickets Type 1A. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malloy, P.J.; Hochberg, Z.; Tiosano, D.; Pike, J.W.; Hughes, M.R.; Feldman, D. The molecular basis of hereditary 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 resistant rickets in seven related families. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, P.; Philipsen, P.A.; Olsen, P.; Bogh, M.K.; Johansen, P.; Schmedes, A.V.; Morling, N.; Wulf, H.C. The half-life of 25(OH)D after UVB exposure depends on gender and vitamin D receptor polymorphism but mainly on the start level. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2017, 16, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wjst, M.; Altmüller, J.; Faus-Kessler, T.; Braig, C.; Bahnweg, M.; André, E. Asthma families show transmission disequilibrium of gene variants in the vitamin D metabolism and signalling pathway. Respir. Res. 2006, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurylowicz, A.; Ramos-Lopez, E.; Bednarczuk, T.; Badenhoop, K. Vitamin D-Binding Protein (DBP) Gene Polymorphism is Associated with Graves’ Disease and the Vitamin D Status in a Polish Population Study. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2006, 114, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, C.D.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Langefeld, C.D.; Hicks, P.J.; Rich, S.S.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Bowden, D.W.; Norris, J.M. Genetic and Environmental Determinants of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D Levels in Hispanic and African Americans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3381–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, J.; Rasmussen, L.B.; Ravn-Haren, G.; Andersen, E.W.; Hansen, B.; Andersen, R.; Mejborn, H.; Madsen, K.H.; Vogel, U. Common Variants in CYP2R1 and GC Genes Predict Vitamin D Concentrations in Healthy Danish Children and Adults. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibler, E.A.; Hu, C.; Jurutka, P.W.; Martinez, M.E.; Jacobs, E.T. Polymorphic Variation in the GC and CASR Genes and Associations with Vitamin D Metabolite Concentration and Metachronous Colorectal Neoplasia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usategui-Martín, R.; De Luis-Román, D.-A.; Fernández-Gómez, J.M.; Ruiz-Mambrilla, M.; Pérez-Castrillón, J.-L. Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) Gene Polymorphisms Modify the Response to Vitamin D Supplementation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shree, T.; Banerjee, P.; Senapati, S. A meta-analysis suggests the association of reduced serum level of vitamin D and T-allele of Fok1 (rs2228570) polymorphism in the vitamin D receptor gene with celiac disease. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 996450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, G.P.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; de Boer, I.H.; Houston, D.K.; Lohman, K.; Liu, Y.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Cauley, J.A.; Tanaka, T.; Ferrucci, L.; et al. Genetic Variants and Associations of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations with Major Clinical Outcomes. JAMA 2012, 308, 1898–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, H.; Miyamoto, K.-I.; Yoshida, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Taketani, Y.; Morita, K.; Kubota, M.; Yoshida, S.; Ikeda, M.; Watabe, F.; et al. The Polymorphism in the Caudal-Related Homeodomain Protein Cdx-2 Binding Element in the Human Vitamin D Receptor Gene. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2001, 16, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alésio, A.; Garabédian, M.; Sabatier, J.P.; Guaydier-Souquières, G.; Marcelli, C.; Lemaçon, A.; Walrant-Debray, O.; Jehan, F. Two single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the human vitamin D receptor promoter change protein–DNA complex formation and are associated with height and vitamin D status in adolescent girls. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 3539–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorieux, F.H. Calcitriol treatment in vitamin D-dependent and vitamin D-resistant rickets. Metabolism 1990, 39, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, J.P.; Williams, J.S.; Fisher, N.D. Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Regulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Humans. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, A.; Forman, J.P.; Hopkins, P.N.; Seely, E.W.; Williams, J.S. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D is associated with plasma renin activity and the pressor response to dietary sodium intake in Caucasians. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2011, 12, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrara, D.; Bernini, M.; Bacca, A.; Rugani, I.; Duranti, E.; Virdis, A.; Ghiadoni, L.; Taddei, S.; Bernini, G. Cholecalciferol administration blunts the systemic renin–angiotensin system in essential hypertensives with hypovitaminosis D. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2014, 15, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Pan, W.; Kong, J.; Zheng, W.; Szeto, F.L.; Wong, K.E.; Cohen, R.; Klopot, A.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.C. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Suppresses Renin Gene Transcription by Blocking the Activity of the Cyclic AMP Response Element in the Renin Gene Promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29821–29830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, E.D.; Hawkins, R.G.; Watanabe, M. Interaction of 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D and Plasma Renin Activity in High Renin Essential Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 1990, 3, 903–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, I.F.O.C.; Cavalcante, A.A.C.M.; Alencar, M.V.O.B.; Carvalho, M.D.F.; Sarmento, J.L.R.; Teixeira, N.S.C.C.A.; Paiva, A.A.; Carvalho, L.R.; Nascimento, L.F.M.; Cruz, M.S.P.; et al. Meta-Analysis of the Association Between the rs228570 Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphism and Arterial Hypertension Risk. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2020, 11, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurutka, P.W.; Remus, L.S.; Whitfield, G.K.; Thompson, P.D.; Hsieh, J.-C.; Zitzer, H.; Tavakkoli, P.; Galligan, M.A.; Dang, H.T.L.; Haussler, C.A.; et al. The Polymorphic N Terminus in Human Vitamin D Receptor Isoforms Influences Transcriptional Activity by Modulating Interaction with Transcription Factor IIB. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padma, T.; Vamsi, U.; Swapna, N.; Usha, G. Risk conferred by FokI polymorphism of vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene for essential hypertension. Indian J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 17, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muray, S.; Parisi, E.; Cardús, A.; Craver, L.; Fernández, E. Influence of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and 25-hydroxyvitamin D on blood pressure in apparently healthy subjects. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.K.; Lee, G.S.; Stewart, W.F.; Ahn, K.D.; Simon, D.; Kelsey, K.T.; Todd, A.C.; Schwartz, B.S. Associations of blood pressure and hypertension with lead dose measures and polymorphisms in the vitamin D receptor and delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase genes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Manson, J.E.; Buring, J.E.; Gaziano, J.M.; Sesso, H.D. A prospective study of plasma vitamin D metabolites, vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms, and risk of hypertension in men. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tourkochristou, E.; Mouzaki, A.; Triantos, C. Gene Polymorphisms and Biological Effects of Vitamin D Receptor on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Development and Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, B.; Curley, A.J.; Hannan, F.M.; Christie, P.T.; Bowl, M.R.; Turner, J.J.O.; Barber, M.; Gillham-Nasenya, I.; Hampson, G.; Spector, T.D.; et al. Functional characterization of calcium sensing receptor polymorphisms and absence of association with indices of calcium homeostasis and bone mineral density. Clin. Endocrinol. 2006, 65, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekkinen, M.; Laine, C.M.; Mäkitie, R.; Leinonen, E.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Viljakainen, H.; Mäkitie, O. FGF23 gene variation and its association with phosphate homeostasis and bone mineral density in Finnish children and adolescents. Bone 2015, 71, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibler, E.; Jurutka, P.; Egan, J.; Hu, C.; LeRoy, E.; Martinez, M.; Thompson, P.; Jacobs, E. Association between polymorphic variation in VDR and RXRA and circulating levels of vitamin D metabolites. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 438–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henikoff, S.; Greally, J.M. Epigenetics, cellular memory and gene regulation. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R644–R648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlberg, C. Nutrigenomics of Vitamin D. Nutrients 2019, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, L.-J.; Xu, X.; Ye, A.; Travers-Gustafson, D.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.-W.; Zhang, W.; Hamm, L.L.; Deng, H.-W.; et al. DNA methylation levels of CYP2R1 and CYP24A1 predict vitamin D response variation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wang, X.; Shi, H.; Su, S.; Harshfield, G.A.; Gutin, B.; Snieder, H.; Dong, Y. A Genome-Wide Methylation Study of Severe Vitamin D Deficiency in African American Adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 1004–1009.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.B.; Zella, L.A.; Nerenz, R.D.; Pike, J.W. Characterizing Early Events Associated with the Activation of Target Genes by 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 in Mouse Kidney and Intestine In Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22344–22352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Kong, W.; He, B.; Li, Z.; Song, H.; Shi, P.; Wang, J. Vitamin D and the promoter methylation of its metabolic pathway genes in association with the risk and prognosis of tuberculosis. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wjst, M.; Heimbeck, I.; Kutschke, D.; Pukelsheim, K. Epigenetic regulation of vitamin D converting enzymes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, E.L.; Duesing, K.; Martin, C.; Jones, P.; Furst, J.; King, K.; Niblett, S.; Yates, Z.; Veysey, M.; Lucock, M. Relationship between methylation status of vitamin D-related genes, vitamin D levels, and methyl-donor biochemistry. J. Nutr. Intermed. Metab. 2016, 6, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D: A millenium perspective. J. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 88, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D: Importance in the prevention of cancers, type 1 diabetes, heart disease, and osteoporosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 79, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangpricha, V.; Flanagan, J.N.; Whitlatch, L.W.; Tseng, C.C.; Chen, T.C.; Holt, P.R.; Lipkin, M.S.; Holick, M.F. 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1α-hydroxylase in normal and malignant colon tissue. Lancet 2001, 357, 1673–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gombart, A.F.; Borregaard, N.; Koeffler, H.P. Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussler, M.R.; Jurutka, P.W.; Mizwicki, M.; Norman, A.W. Vitamin D receptor (VDR)-mediated actions of 1α,25(OH)2vitamin D3: Genomic and non-genomic mechanisms. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, J.W.; Meyer, M.B. The Vitamin D Receptor: New Paradigms for the Regulation of Gene Expression by 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Abe, E.; Miyaura, C.; Kuribayashi, T.; Konno, K.; Nishii, Y.; Suda, T. 1α,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol and a human myeloid leukaemia cell line (HL-60). Biochem. J. 1982, 204, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, F.; Peräkylä, M.; Carlberg, C. Vitamin D Receptor Agonists Specifically Modulate the Volume of the Ligand-binding Pocket. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10516–10526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, C. Genome-wide (over)view on the actions of vitamin D. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, C. Vitamin D and Its Target Genes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquerizas, J.M.; Kummerfeld, S.K.; Teichmann, S.A.; Luscombe, N.M. A census of human transcription factors: Function, expression and evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuoresmäki, P.; Väisänen, S.; Neme, A.; Heikkinen, S.; Carlberg, C. Patterns of Genome-Wide VDR Locations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurminen, V.; Neme, A.; Seuter, S.; Carlberg, C. The impact of the vitamin D-modulated epigenome on VDR target gene regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2018, 1861, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurminen, V.; Neme, A.; Seuter, S.; Carlberg, C. Modulation of vitamin D signaling by the pioneer factor CEBPA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neme, A.; Seuter, S.; Carlberg, C. Vitamin D-dependent chromatin association of CTCF in human monocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, H.S.; Bareis, P.; Hofer, H.; Bischof, M.G.; Bajna, E.; Kriwanek, S.; Bonner, E.; Peterlik, M. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3-1α-hydroxylase and vitamin D receptor gene expression in human colonic mucosa is elevated during early cancerogenesis. Steroids 2001, 66, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, A.; Carlberg, C. Time-Resolved Gene Expression Analysis Monitors the Regulation of Inflammatory Mediators and Attenuation of Adaptive Immune Response by Vitamin D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, J.; Wang, J.; Weaver, V.; Zhang, Y.; Cantorna, M.T. Novel insight into the role of the vitamin D receptor in the development and function of the immune system. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2022, 219, 106084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D regulation of immune function during COVID-19. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Ferro, M.; Romero-Bueno, F.I.; del Castillo, C.S.; Mahillo, I.; Alvear, A.; Largo, R.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Sánchez-Pernaute, O. A subgroup of lupus patients with nephritis, innate T cell activation and low vitamin D is identified by the enhancement of circulating MHC class I-related chain A. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 196, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komisarenko, Y.I.; Bobryk, M.I. Vitamin D Deficiency and Immune Disorders in Combined Endocrine Pathology. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Chun, S.; Hwang, S.; Kim, J.; Cho, Y.; Lee, J.; Kwack, K.; Choi, S.-W. Vitamin D and Exercise Are Major Determinants of Natural Killer Cell Activity, Which Is Age- and Gender-Specific. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 594356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlberg, C.; Velleuer, E. Vitamin D and the risk for cancer: A molecular analysis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 196, 114735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, S.; Boniol, M.; Haukka, J.; Byrnes, G.; Cox, B.; Sneyd, M.J.; Mullie, P.; Autier, P. Meta-analysis of observational studies of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and colorectal, breast and prostate cancer and colorectal adenoma. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, A.K.; Hodge, A.M.; Ebeling, P.R.; Eyles, D.W.; Kvaskoff, D.; Buchanan, D.D.; Giles, G.G.; Williamson, E.J.; English, D.R. Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentration and Risk of Breast, Prostate, and Colorectal Cancers: The Melbourne Collaborative Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulou, V.I.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Haycock, P.C.; Dimou, N.L.; Al-Dabhani, K.; Martin, R.; Lewis, S.J.; Gunter, M.J.; Mondul, A.; Shui, I.M.; et al. Circulating vitamin D concentration and risk of seven cancers: Mendelian randomisation study. BMJ 2017, 359, j4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Knuiman, M.; Divitini, M.; Hung, J.; Lim, E.M.; Cooke, B.R.; Walsh, J.P. Lower serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with colorectal and breast cancer, but not overall cancer risk: A 20-year cohort study. Nutr. Res. 2019, 67, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Lee, I.M.; Christen, W.; Bassuk, S.S.; Mora, S.; Gibson, H.; Gordon, D.; Copeland, T.; D’Agostino, D.; et al. Vitamin D Supplements and Prevention of Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, J.E.; Bassuk, S.S.; Buring, J.E. Principal results of the VITamin D and OmegA-3 TriaL (VITAL) and updated meta-analyses of relevant Vitamin D trials. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 198, 105522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feige, J.; Moser, T.; Bieler, L.; Schwenker, K.; Hauer, L.; Sellner, J. Vitamin D Supplementation in Multiple Sclerosis: A Critical Analysis of Potentials and Threats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubatan, J.; Moss, A.C. Vitamin D in inflammatory bowel disease: More than just a supplement. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 34, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousaki, D.; Harroud, A.; Mitchell, R.E.; Ross, S.; Forgetta, V.; Timpson, N.J.; Smith, G.D.; Polychronakos, C.; Richards, J.B. Vitamin D levels and risk of type 1 diabetes: A Mendelian randomization study. PLOS Med. 2021, 18, e1003536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A.T.; Veesler, D. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell 2020, 181, 281–292.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, A.R.; Jolliffe, D.A.; Hooper, R.L.; Greenberg, L.; Aloia, J.F.; Bergman, P.; Dubnov-Raz, G.; Esposito, S.; Ganmaa, D.; Ginde, A.A.; et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ 2017, 356, i6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radujkovic, A.; Hippchen, T.; Tiwari-Heckler, S.; Dreher, S.; Boxberger, M.; Merle, U. Vitamin D Deficiency and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, D.; Locatelli, M.; Faraldi, M.; Lombardi, G. Changes in 25-(OH) Vitamin D Levels during the SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak: Lockdown-Related Effects and First-to-Second Wave Difference—An Observational Study from Northern Italy. Biology 2021, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, I.H.; Fernandes, A.L.; Antonangelo, L.; Gualano, B.; Pereira, R.M.R. Effect of a Single High-Dose Vitamin D3 on the Length of Hospital Stay of Severely 25-Hydroxyvitamin D-Deficient Patients with COVID-19. Clinics 2021, 76, e3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Oldani, S.; Borgonovo, K.; Cabiddu, M.; Dognini, G.; Ghilardi, M.; Parati, M.C.; Petro’, D.; Dottorini, L.; Rea, C.; et al. Vitamin D3 and COVID-19 Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivieri, F.M.; Banfi, G.; Camozzi, V.; Colao, A.; Formenti, A.M.; Frara, S.; Lombardi, G.; Napoli, N.; Giustina, A. Vitamin D in the COVID-19 era: A review with recommendations from a G.I.O.S.E.G. expert panel. Endocrine 2021, 72, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voltan, G.; Cannito, M.; Ferrarese, M.; Ceccato, F.; Camozzi, V. Vitamin D: An Overview of Gene Regulation, Ranging from Metabolism to Genomic Effects. Genes 2023, 14, 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091691
Voltan G, Cannito M, Ferrarese M, Ceccato F, Camozzi V. Vitamin D: An Overview of Gene Regulation, Ranging from Metabolism to Genomic Effects. Genes. 2023; 14(9):1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091691
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoltan, Giacomo, Michele Cannito, Michela Ferrarese, Filippo Ceccato, and Valentina Camozzi. 2023. "Vitamin D: An Overview of Gene Regulation, Ranging from Metabolism to Genomic Effects" Genes 14, no. 9: 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091691
APA StyleVoltan, G., Cannito, M., Ferrarese, M., Ceccato, F., & Camozzi, V. (2023). Vitamin D: An Overview of Gene Regulation, Ranging from Metabolism to Genomic Effects. Genes, 14(9), 1691. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091691






