Hotspot Regions of Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes for Ear-Related Traits in Maize: A Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. QTLs for Eight Ear-Related Traits in Maize
3.1. QTLs for Ear Length
3.2. QTLs for Ear Diameter
3.3. QTLs for Kernel Row Number
3.4. QTLs for Kernel Number per Row
3.5. QTL for Four Kernel Traits
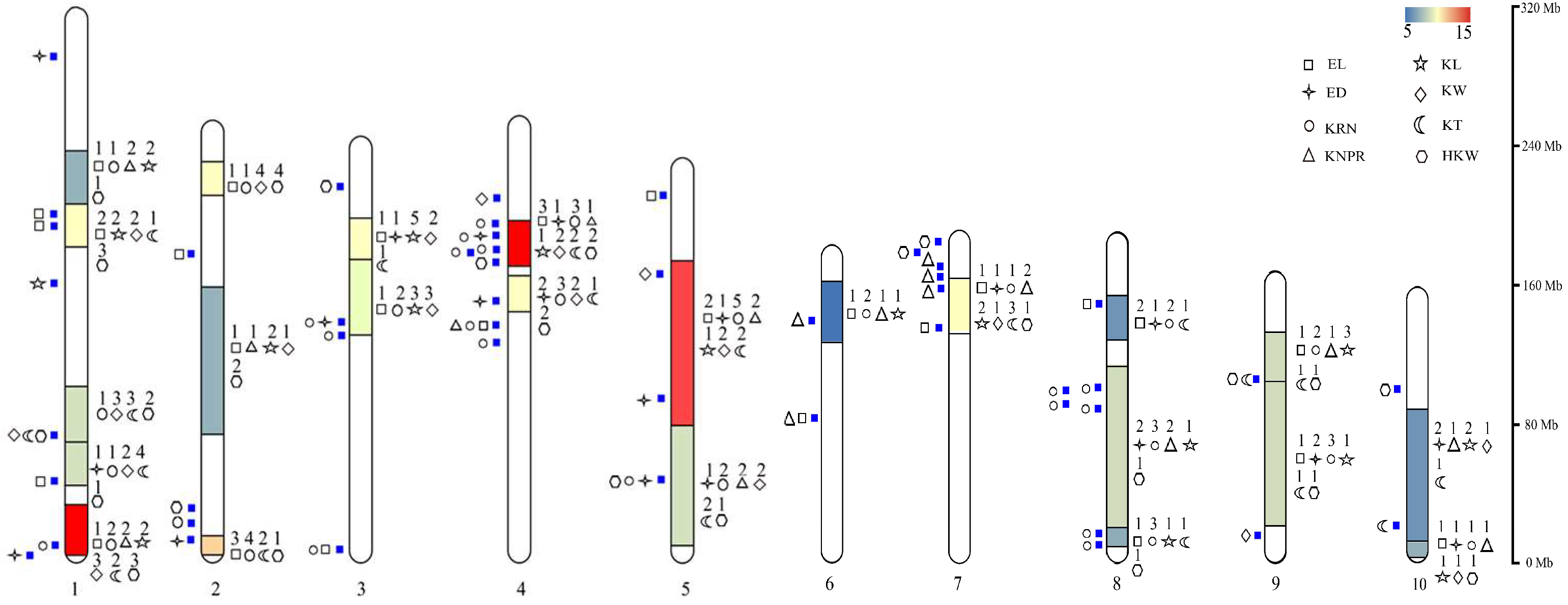
4. Hotspot Bin Regions and Distributional Characteristics of QTLs for Ear-Related Traits on Chromosomes
4.1. Hotspot Bin Regions on Chromosomes Associated with Ear-Related Trait QTLs
4.2. Distributional Characteristics of QTLs for Ear-Related Traits on Maize Chromosomes
5. Candidate Genes for Ear-Related Traits
| Gene (Chromosome) | Predicted Feature | Bin Interval | Physical Interval | Traits Involved | Validation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zm00001eb123060 (Chr 3) | RA2 LOB domain protein | 3.02 | 12,830,057–12,832,763 | EL, KNPR | Cloned | [84] |
| Zm00001eb184050 (Chr 4) | Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein | 4.05 | 138,680,814–138,683,429 | EL, KRN, KNPR | Cloned | [78] |
| GRMZM5G803935 (Chr 3) * | Encode mir172 microRNA | 3.05 | 144,918,011–144,918,720 | ED, KRN | Implication | [38] |
| Zm00001d027412 (Chr 1) * | Dicer-like 101 (dcl101) protein | 1.01–1.02 | 4,722,956–4,738,332 | ED | Implication | [20] |
| Zm00001d016656 (Chr 5) * | Serine/threonine protein kinase | 5.04 | 171,563,168–171,566,437 | ED, KRN, HKW | Implication | |
| Zm00001d052191 (Chr 4) * | Cupredoxin superfamily protein | 4.08 | 182,743,279–182,744,379 | HKW | Implication | |
| Zm00001d015650 (Chr 5) * | Lycopene β-cyclase andchloroplast-specific lycopene β-cyclase | 5.04 | 103,228,157–103,232,629 | ED | Implication | [41] |
| Zm00001d052442 (Chr 4) * | Auxin effluxcarrier component protein | 4.08 | 190,119,181–190,122,383 | ED, KRN | Implication | [85] |
| Zm00001d034629 (Chr 1) | AP2/EREBP protein | 1.12 | 298,422,859–298,427,050 | KRN | Cloned | [79] |
| Zm00001d038022 (Chr 6) * | Chloroplastic pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein | 6.05 | 145,415,188–145,419,374 | KNPR | Implication | [77] |
| Zm00001d041584 (Chr 3) * | NB-ARC domain-containing protein | 3.05 | 128,389,890–128,392,834 | KRN | Implication | [86] |
| Zm00001d002737 (Chr 2) | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit C | 2.03 | 20,918,928–20,924,673 | ED | Implication | [80] |
| Zm00001d051328 (Chr 4) * | WRKY transcription factor 12 | 4.06 | 154,581,235–154,589,610 | ED | Implication | [87] |
| Zm00001d053080 (Chr 4) | Receptor protein kinase | 4.09 | 212,685,412–212,689,787 | KW | Implication | [88] |
| Zm00001d011060 (Chr 8) * | No annotation | 8.05 | 137,865,777–137,865,788 | EL | Implication | |
| Zm00001d010004 (Chr 8) * | F-box protein At-B | 8.03 | 94,660,952–94,661,221 | KRN | Implication | [49] |
| Zm00001d010007 (Chr 8) * | START domain-containing protein | 8.03 | 94,844,625–94,845,188 | KRN | Implication | |
| Zm00001d010008 (Chr 8) * | Haloacid dehalogenase (HAD)-like hydrolase superfamily protein | 8.03 | 94,945,161–94,946,129 | KRN | Implication | |
| Zm00001d010009 (Chr 8) * | 60S ribosomal protein L17 | 8.03 | 94,987,331–94,992,881 | KRN | Implication | |
| Zm00001eb199880 (Chr 4) * | SBP-box transcription factor | 4.08 | 205,124,194–205,128,840 | KRN | Implication | [89] |
| Zm00001eb336530 (Chr 8) * | Grass-specific tryptophan aminotransferase | 8.02 | 17,391,163–17,395,311 | KRN | Implication | [47] |
| Zm00001eb336930 (Chr 8) * | Serine/threonine protein kinase | 8.02 | 18,928,567–18,930,699 | KRN | Implication | |
| Zm00001d031906 (Chr 1) * | Dilated protein A24 | 1.06 | 206,261,034–206,261,843 | EL | Implication | [50] |
| Zm00001d027721 (Chr 1) * | High-affinity nickel transporter | 1.01–1.02 | 12,140,948–12,146,615 | KRN | Implication | |
| Zm00001eb314610 (Chr 7) * | 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase2 | 7.03 | 129,695,760–129,697,548 | EL | Cloned | [22] |
| Zm00001d022202 (Chr 7) | Protein phosphatase homolog2 | 7.05 | 172,755,383–172,761,407 | KNPR | Implication | [56] |
| Zm00001d022168 (Chr 7) | AT hook-containing MAR binding 1-like protein | 7.05 | 171,565,347–171,605,347 | KNPR | Implication | |
| Zm00001d022169 (Chr 7) | RNA polymerase T phage-like 1 | 7.05 | 171,565,347–171,605,347 | KNPR | Implication | |
| Zm00001eb019600 (Chr 1) * | GS3-like protein | 1.04 | 71,243,947–71,252,899 | KW, KT, HKW | Implication | [57] |
| Zm00001eb376630 (Chr 9) | RING-type protein with E3 ubiquitin ligase activity | 9.02 | 20,581,735–20,585,861 | KW | Cloned | [58] |
| Zm00001d030895 (Chr 1) | Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 chloroplastic | 1.05 | 166,287,332–166,290,184 | KL | Implication | [60] |
| Zm00001d014530 (Chr 5) * | Phenolic glucoside malonyl transferase | 5.03 | 51,914,095–51,915,783 | KW | Implication | |
| Zm00001d025152 (Chr 10) | Pentatricopeptide repeat-containing protein/PPR | 10.04 | 106,764,011–106,766,200 | KT | Implication | |
| Zm00001d044081 (Chr 3) | Homeobox-leucine zipper protein (ATHB-4) | 3.09 | 218,481,322–218,485,402 | HKW | Implication | [81] |
| Zm00001eb079220 (Chr 2) | Auxin-binding protein | 2.04 | 37,967,776–37,976,021 | HKW | Implication | [82] |
| Zm00001eb410780 (Chr 10) * | Auxin-binding protein homolog4 | 10.03 | 27,107,964–27,113,709 | HKW | Implication | [83] |
| Zm00001eb014970 (Chr 1) * | No annotation | 1.03 | 50,584,192–50,589,950 | EL | Implication | [90] |
| Zm00001d046723 (Chr 9) * | EXPANSIN protein family | 9.04 | 103,579,654–103,582,402 | KL, HKW | Implication | [91] |
| GRMZM2G16129 (Chr 2) | 7-TM protein | 2.06 | 184,753,214–184,756,735 | EL | Implication | [92] |
| GRMZM2G38381 (Chr 1) * | Protein with an NDR domain | 1.06 | 193,519,623–193,521,732 | EL | Implication | |
| GRMZM2G168371 (Chr 5) | Protein with the Duf640 domain | 5.08 | 214,951,997–214,955,917 | EL | Implication | |
| Zm00001eb331370 (Chr 7) | E3 ubiquitin/ISG15 ligase TRIM25 | 7.06 | 174,554,103–174,559,004 | HKW | Implication | [40] |
| Zm00001d022578 (Chr 7) | Ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 3 | 7.06 | 174,785,186–174,790,941 | HKW | Implication | |
| Zm00001d052909 (Chr 4) * | No annotation | 4.08 | 204,448,863–204,453,294 | KRN | Implication | [48] |
| Zm00001d052910 (Chr 4) * | No annotation | 4.08 | 204,476,980–204,480,339 | KRN | Implication | |
| Zm00001d051012 (Chr 4) | Leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein | 4.05 | 136,764,371–136,769,212 | KRN | Cloned | [93] |
| Zm00001d002641 (Chr 2) | WD40 protein | 2.03 | 17,742,986–17,750,216 | KRN | Implication | [23] |
| Zm00001d036602 (Chr 6) | Serine/threonine protein kinase | 6.02 | 94,190,254–94,199,686 | EL, KNPR | Implication | [94] |
6. Discussion
6.1. Consistency of QTLs for Ear-Related Traits
6.2. The Advantages of Screening Candidate Genes in Hotspot Regions and the Application of Hotspot Regions in Gene Cloning and Maize Breeding in the Future
6.3. The Trend of the QTL for Ear-Related Traits in Maize
6.4. Using of QTLs for Ear-Related Traits in Maize Breeding
7. Future Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- da Fonseca, R.R.; Smith, B.D.; Wales, N.; Cappellini, E.; Skoglund, P.; Fumagalli, M.; Samaniego, J.A.; Carøe, C.; Ávila-Arcos, M.C.; Hufnagel, D.E.; et al. The origin and evolution of maize in the Southwestern United States. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wang, Y.B.; Liu, X.G.; Jin, M.L.; Vallebueno-Estrada, M.; Calfee, E.; Chen, L.; Dilkes, B.P.; Gui, S.T.; Fan, X.M.; et al. Two teosintes made modern maize. Science 2023, 382, eadg8940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, D.; Ning, Q.; Shen, X.M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.X. QTL mapping of kernel number-related traits and validation of one major QTL for ear length in maize. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Z. Identification and Mapping of Quantitative Trait Lociconferring Cold Tolerance at the Early Seedlingstage in Maize (Zea mays L.). Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University, Liaoning, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Huo, C.; Peng, C.Y.; Huo, S.P. QTL of kernel yield of maize and its Components’ traits: Research Progress. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2022, 38, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L. QTL Mapping of Ear-Kernel Related Traits in Maize (Zea mays L.). Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, Chongqing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Upadyayula, N.; Wassom, J.; Bohn, M.O.; Rocheford, T.R. Genetic and QTL analysis of maize tassel and ear inflorescence architecture. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abler, B.S.B.; Edwards, M.D.; Stuber, C.W. Isoenzymatic identification of quantitative trait loci in crosses of elite maize inbreds. Crop Sci. 1991, 31, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Botstein, D. Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 1989, 121, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.B. Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 1994, 136, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Ye, G.Y.; Wang, J.K. A modified algorithm for the improvement of composite interval mapping. Genetics 2007, 175, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikha, K.; Shahi, J.P.; Vinayan, M.T.; Zaidi, P.H.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, B. Genome-wide association mapping in maize: Status and prospects. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.B.; Zhou, Z.J.; Dong, C.P.; Chen, J.F.; Ding, J.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Mu, C.; Chen, Y.N.; Li, X.P.; Li, H.M.; et al. Linkage mapping and genome-wide association study reveals conservative QTL and candidate genes for Fusarium rot resistance in maize. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqudah, A.M.; Sallam, A.; Baenziger, P.S.; Börner, A. GWAS: Fast-forwarding gene identification and characterization in temperate Cereals: Lessons from Barley-A review. J. Adv. Res. 2019, 22, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Q.; Xu, Y.H. Bulk segregation analysis in the NGS era: A review of its teenage years. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2022, 109, 1355–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zegeye, W.A.; Zhang, Y.X.; Cao, L.Y.; Cheng, S.H. Whole genome resequencing from bulked populations as a rapid QTL and gene identification method in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Z. Map-Based Cloning and Functional Analysis of Multiple Disease Resistance Locus qLMchr7 in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agriculture University, Hubei, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Coulson, A.; Sulston, J.; Brenner, S.; Karn, J. Toward a physical map of the genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 7821–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.Y.; Lu, X.M.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, M.M.; Mao, K.J.; Li, Q.H.; Wei, F.; Sun, P.; Tang, J.H. Genetic analysis of heterosis for maize grain yield and its components in a set of SSSL testcross populations. Euphytica 2016, 210, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ren, Z.Y.; Luo, B.W.; Zhong, H.X.; Ma, P.; Zhang, H.K.; Hu, H.M.; Wang, Y.K.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, D.; et al. Genetic architecture of maize yield traits dissected by QTL mapping and GWAS in maize. Crop J. 2022, 10, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamlom, S.F.; Zhang, Y.; Su, B.; Wu, H.T.; Zhang, X.; Fu, J.D.; Zhang, B.; Qiu, L.J. Map-based cloning of a novel QTL qBN-1 influencing branch number in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.]. Crop J. 2020, 8, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Q.; Jian, Y.N.; Du, Y.F.; Li, Y.F.; Shen, X.M.; Jia, H.T.; Zhao, R.; Zhan, J.M.; Yang, F.; Jackson, D.; et al. An ethylene biosynthesis enzyme controls quantitative variation in maize ear length and kernel yield. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.K.; Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, N.; Guo, J.H.; Wang, M.; Ji, S.H.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yin, P.F.; Cai, L.C.; et al. Convergent selection of a WD40 protein that enhances grain yield in maize and rice. Science 2022, 375, eabg7985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.B.; Lu, J.Y.; Jiang, Q.P.; Liu, Z.B.; Yao, D.; Qu, J.; Liu, S.Y.; Guan, S.Y.; Ma, Y.Y. Maize plant architecture trait QTL mapping and candidate gene identification based on multiple environments and double populations. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.H.; Zhang, Y.K.; Ren, W.; Chen, P.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Mi, G.H.; Chen, F.J.; Pan, Q.C. QTL mapping and transcriptome analysis identify candidate genes influencing water-nitrogen interaction in maize. Crop J. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Bao, J.X.; Li, Y.N.; Yin, Z.C.; Long, Y.; Wan, X.Y. The genetic structures and molecular mechanisms underlying ear traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Cells 2023, 12, 1900. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.M. Cloning and Functional Analysis of QTL qKRN5 for Kernel Row Number in Maize. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Hubei, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, H.; Kim, S.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Suh, J.P.; Park, H.M.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Misra, G.; Kim, S.M.; Hechanova, S.L.; Kim, H.; et al. Map-based cloning and characterization of the BPH18 gene from wild rice conferring resistance to brown planthopper (BPH) insect pest. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, D.F.; Lee, M. Comparative mapping in F2:3 and F6:7 generations of quantitative trait loci for grain yield and yield components in maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1996, 92, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.P.; Rong, T.Z.; Xiang, D.Q.; Tang, H.T.; Huang, L.J.; Dai, J.R. QTL mapping of quantitative traits in maize. J. Crop Sci. 2005, 2, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.Y.; Su, S.Z.; Zhang, S.Z.; Liu, H.L.; Luo, B.W.; Liu, D.; Wu, L.; Rong, T.Z.; Gao, S.B. Characterization and QTL mapping of yield trait under two phosphorus regimes in Maize. Acta Agric. Boreal Sin. 2015, 30, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Hou, X.B.; Zhang, X.G.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.J.; Liu, H.M.; Hu, Y.F.; Yu, G.W.; Li, Y.P.; et al. Genetic dissection of yield-related traits and mid-parent heterosis for those traits in maize (Zea mays L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.P.; Dong, E.F.; Liang, Q.Y.; Bai, Y.; Nan, J.; Yang, Y.; Cai, Y.L. Identification of QTL for fasciated ear related traits in maize. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, K.J.; Choi, I.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, J.K.; Ryu, S.H.; Lee, J.K. Mapping of QTL for agronomic traits using high-density SNPs with an RIL population in maize. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldboom, L.R.; Lee, M. Molecular-marker-facilitated studies of morphological traits in maize. II: Determination of QTLs for grain yield and yield components. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1994, 89, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Niu, S.Z.; Dong, Y.B.; Cui, D.Q.; Wang, Y.Z.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wei, M.G. Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci for grain yield components from a dent corn inbred line in an advanced backcross BC2F2 population and comparison with its F2:3 population in popcorn. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 115, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.M.; Zheng, Z.P.; Liu, X.H.; Li, Z.; He, C.; Liu, D.H.; Luo, Y.C.; Zhang, G.Q.; Tan, Z.B.; Li, R.Z. QTL mapping for ear length and ear diameter under different nitrogen regimes in maize. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 626–630. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes-Moreira, P.; Alves, M.L.; Satovic, Z.; Dos Santos, J.P.; Santos, J.N.; Souza, J.C.; Pêgo, S.E.; Hallauer, A.R.; Vaz Patto, M.C. Genetic architecture of ear fasciation in maize (Zea mays) under QTL scrutiny. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.F.; Wang, W.; Gong, S.L.; Zuo, J.H.; Li, S.J.; Xu, S.Z. High density linkage map construction and mapping of yield trait QTLs in maize (Zea mays) using the genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) technology. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Su, C.F. Mapping quantitative trait loci for yield-related traits and predicting candidate genes for grain weight in maize. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.W.; Bi, Y.Q.; Yin, X.F.; Guo, R.J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Shaw, R.K.; Fan, X.F. Identification of candidate QTLs and genes for ear diameter by multi-parent population in maize. Genes 2023, 14, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavis, W.D.; Smith, O.S.; Grant, D.M.; Fincher, R.R. Identification of quantitative trait loci using a small sample of topcrossed and F4 progeny from maize. Crop Sci. 1994, 34, 882–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.B.; Tang, H.; Huang, Y.Q.; Zheng, Y.L.; Subhash, C.; Li, J.S. A genome scan for quantitative trait loci affecting grain yield and its components of maize both in single-and two-locus levels. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karen Sabadin, P.; Lopes de Souza Júnior, C.; Pereira de Souza, A.; Augusto Franco Garcia, A. QTL mapping for yield components in a tropical maize population using microsatellite markers. Hereditas 2008, 145, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Rong, T.Z. Detection of quantitative trait loci for ear row number in F2 populations of maize. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 14229–14238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Liu, S.T.; Li, Z.M.; Huang, R.R.; Li, Y.M.; Cheng, H.L.; Li, X.T.; Zhou, B.; Wu, S.W.; et al. The genetic basis of natural variation in kernel size and related traits using a four-way cross population in maize. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.S.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Yong, H.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Hao, Z.F.; Zhang, F.J.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, D.G.; Li, X.H.; Wang, Z.H.; et al. Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize ear and grain morphological traits by combined linkage and association mapping. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 1011–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, N.N.; Ding, X.Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.; An, Y.X.; Li, C.H.; Song, Y.C.; Zhang, D.F.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, T.Y.; et al. Characterization and fine mapping of qkrnw4, a major QTL controlling kernel row number in maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 3321–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.S.; Qin, Y.; Sandrine, A.M.N.; Qiu, F.Z. Fine mapping of qKRN8, a QTL for maize kernel row number, and prediction of the candidate gene. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 3139–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, R.Q.; Wang, A.G.; Guo, X.Y.; Liu, P.F.; Zhu, Y.F.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.H. QTL mapping and candidate gene analysis about ear-related traits in maize based on high density SNP markers. J. Maize Sci. 2021, 29, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.B.; Tang, H.; Huang, Y.Q.; Zheng, Y.L.; Li, J.S. Quantitative trait loci mapping and epistatic analysis for grain yield and yield components using molecular markers with an elite maize hybrid. Euphytica 2006, 149, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.L.; Cai, Y.L.; Xu, D.L.; Lv, X.G.; Wang, G.Q.; Wang, J.G.; Sun, H.Y. QTL mapping for ear traits in maize (Zea mays L.). J. Southwest Norm. Univ. Sci. Ed. 2009, 34, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M. The Genetic Analysis of Maize Yield Related Traits. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Hubei, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, F.F.; Cai, X.Y.; Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Huang, X.Q. Detection of quantitative trait loci for maize grain yield and kernel-related traits. J. Fudan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2017, 56, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liao, C.J.; Wang, X.J.; Yang, R.C.; Zhai, L.H.; Huang, J. Construction of maize-teosinte introgression line population and identification of major quantitative trait loci. Euphytica 2021, 217, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Bi, Y.Q.; Jiang, F.Y.; Shaw, R.K.; Sun, J.C.; Hu, C.; Guo, R.J.; Fan, X.M. Mapping and functional analysis of QTL for kernel number per row in tropical and temperate-tropical introgression lines of maize (Zea mays L.). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 4416–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.W.; Sun, C.L.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zheng, Y.L.; Qiu, F.Z. Genetic analysis and major QTL detection for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1019–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raihan, M.S.; Liu, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, H.; Pan, Q.C.; Yan, J.B. Multi-environment QTL analysis of grain morphology traits and fine mapping of a kernel-width QTL in Zheng58 × SK maize population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.R.; He, K.H.; Chang, L.G.; Cui, T.T.; Zhao, Z.X.; Xue, J.Q.; Liu, J.C. QTL mapping and genetic analysis for maize kernel size and weight in multi-environments. Euphytica 2018, 214, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tan, X.L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Ma, L.L.; Li, Z.L.; et al. Analysis of the genetic architecture of maize kernel size traits by combined linkage and association mapping. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, X.H.; Li, L.L.; Schnable, J.; Gu, R.L.; Wang, J.H. QTL identification and epistatic effect analysis of seed size- and weight-related traits in Zea mays L. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Yi, Q.; Hou, X.B.; Hu, Y.F.; Li, Y.P.; Yu, G.W.; Liu, H.M.; Zhang, J.J.; Huang, Y.B. Identification of quantitative trait loci for kernel-related traits and the heterosis for these traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2020, 295, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Zhao, Y.M.; Mao, W.B.; Ma, X.J.; Su, C.F. QTL Analysis and fine mapping of a major QTL conferring kernel size in maize (Zea mays). Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 603920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, Z.; Wen, M.; Qiu, H.B. QTL mapping of maize (Zea mays L.) kernel traits under low-phosphorus stress. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2023, 29, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.S.; Zhang, H.X.; Lv, X.L.; Hao, Z.F.; Li, B.; Li, M.S.; Wang, H.W.; Ci, X.K.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, X.H.; et al. Analysis of meta-QTL and candidate genes related to yield components in maize. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 39, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. QTL Mapping and Analysis on Plant Architectures and Yield Related Traits in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Henan Agricultural University, Henan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ragot, M.; Sisco, P.H.; Hoisington, D.A.; Stuber, C.W. Molecular-Marker-Mediated characterization of favorable exotic alleles at quantitative trait loci in maize. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J.H.; Song, X.Y.; Xie, C.X.; Li, M.S.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, X.H. QTL analysis of seven main ear traits in three environments in an elite cross of maize (Zea mays L.). J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2012, 20, 756–765. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. QTL Mapping and Genentic Analysis of Kernel Size Yield Components in Maize. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Hubei, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.Z.; Wang, D.; Tan, W.W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B.C.; Shi, Y.S.; et al. QTL Analysis for yield components and kernel-related traits in Maize under different water regimes. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 36, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Feltus, F.A.; Waghmare, V.N.; Pierce, G.J.; Chee, P.W.; Draye, X.; Saranga, Y.; Wright, R.J.; Wilkins, T.A.; May, O.L.; et al. Meta-analysis of polyploid cotton QTL shows unequal contributions of subgenomes to a complex network of genes and gene clusters implicated in lint fiber development. Genetics 2007, 176, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Xie, C.X.; Li, X.H.; Hao, Z.F.; Li, M.S.; Weng, J.F.; Zhang, D.G.; Bai, L.; Zhang, S.H. Mapping of quantitative trait loci for kernel row number in maize across seven environments. Mol. Breed. 2011, 28, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y. QTL Mapping, Cloning and Functional Analysis of Ear Length in Maize. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Hubei, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Salvi, S.; Tuberosa, R. To clone or not to clone plant QTLs: Present and future challenges. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collard, B.C.Y.; Jahufer, M.Z.Z.; Brouwer, J.B.; Pang, E.C.K. An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: The basic concepts. Euphytica 2005, 142, 169–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuberosa, R.; Salvi, S.; Sanguineti, M.C.; Landi, P.; Maccaferri, M.; Conti, S. Mapping QTLs regulating morpho-physiological traits and yield: Case studies, shortcomings and perspectives in drought-stressed maize. Ann. Bot. 2002, 89, 941–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.J.; Upadyayula, N.; Mahone, G.S.; Tian, F.; Bradbury, P.J.; Myles, S.; Holland, J.B.; Flint-Garcia, S.; McMullen, M.D.; Buckler, E.S.; et al. Distinct genetic architectures for male and female inflorescence traits of maize. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommert, P.; Nagasawa, N.S.; Jackson, D. Quantitative variation in maize kernel row number is controlled by the FASCIATED EAR2 locus. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Z.L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.Q.; Zhou, L.N.; Zhong, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Lin, Z.W. krn1, a major quantitative trait locus for kernel row number in maize. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 1634–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, T.; Tian, X.K.; Yang, B.P.; Lao, Y.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, X.H.; Xue, J.Q.; Xu, S.T. Genome-wide association study (GWAS) reveals genetic basis of ear-related traits in maize. Euphytica 2020, 216, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, A.Q.; Mu, L.Y.; Zhao, H.L.; Qin, Y.; Gong, D.M.; Qiu, F.Z. Identification of a candidate gene underlying qHKW3, a QTL for hundred-kernel weight in maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.H.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, Q.L.; Zhou, Y.G.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, B.T.; Zhang, F.F.; Liang, X.J. Detection and integration of quantitative trait loci for grain yield components and oil content in two connected recombinant inbred line populations of high-oil maize. Mol. Breed. 2012, 29, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurišić-Knežev, D.; Čudejková, M.; Zalabak, D.; Hlobilova, M.; Rolčík, J.; Pěnčík, A.; Bergougnoux, V.; Fellner, M. Maize auxin-binding protein 1 and auxin-binding protein 4 impact on leaf growth, elongation, and seedling responsiveness to auxin an lingt. Botany 2012, 90, 990–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortiri, E.; Chuck, G.; Vollbrecht, E.; Rocheford, T.; Martienssen, R.; Hake, S. ramosa2 encodes a LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARY domain protein that determines the fate of stem cells in branch meristems of maize. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestan, C.; Farinati, S.; Varotto, S. The maize PIN gene family of auxin transporters. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.X.; Shi, Y.S.; Song, Y.C.; Zhang, D.F.; Li, C.H.; Buckler, E.S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.W.; Wang, T.Y. Joint-linkage mapping and GWAS reveal extensive genetic loci that regulate male inflorescence size in maize. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.J.; Ren, Q.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Xu, G.L.; Qian, Y.X. Genome-wide identification and analysis of WRKY gene family in maize provide insights into regulatory network in response to abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Zhao, S.H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.J.; Du, J.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Wen, W.W.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhao, C.J. Investigating the genetic basis of maize ear characteristics: A comprehensive genome-wide study utilizing high-throughput phenotypic measurement method and system. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1248446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuck, G.S.; Brown, P.J.; Meeley, R.; Hake, S. Maize SBP-box transcription factors unbranched2 and unbranched3 affect yield traits by regulating the rate of lateral primordia initiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18775–18780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.Q.; Chen, G.S.; Peng, Y.; Jin, M.; Wei, W.J.; Jian, L.M.; et al. Genetic variation in YIGE1 contributes to ear length and grain yield in maize. New Phytol. 2022, 234, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, D.M.; Tan, Z.D.; Zhao, H.L.; Pan, Z.Y.; Sun, Q.; Qiu, F.Z. Fine mapping of a kernel length-related gene with potential value for Maize breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Zhou, Z.J.; Ding, J.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Mu, C.; Wu, Y.B.; Gao, J.Y.; Song, Y.X.; Wang, S.W.; Ma, J.L.; et al. Combining three mapping strategies to reveal quantitative trait loci and candidate genes for maize ear length. Plant Genome 2018, 11, 170107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung, K.H.; Tran, Q.H.; Bui, N.H.; Tran, T.T.; Luu, K.Q.; Tran, N.T.T.; Nguyen, L.T.; Nguyen, D.T.N.; Vu, B.D.; Quan, D.T.T.; et al. A weak allele of FASCIATED EAR 2 (FEA2) increases maize kernel row number (KRN) and yield in elite maize hybrids. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.T.; Li, M.F.; Li, W.Y.; Liu, L.; Jian, Y.N.; Yang, Z.X.; Shen, X.M.; Ning, Q.; Du, Y.F.; Zhao, R.; et al. A serine/threonine protein kinase encoding gene kernel number per row6 regulates maize grain yield. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Guo, X.H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, G.D.; Tian, Y.C.; Wang, Z.L. Mapping QTLs for grain yield and yield components under high and low phosphorus treatments in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci. 2010, 178, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.F.; Zhu, Q.L.; Yang, G.L.; Huang, J.; Cheng, S.Y.; Yue, B.; Zhang, Z.X. qEL7.2 is a pleiotropic QTL for kernel number per row, ear length and ear weight in maize (Zea mays L.). Euphytica 2015, 203, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-González, J. Efficiency of generations for estimating marker-associated QTL effects by multiple regression. Genetics 1993, 135, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Joshi, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, N.K.; Jaiswal, J.P.; Jeena, A.S.; Pant, U.S. Identification of QTLs for yield and contributing traits in maize-teosinte derived bils under diseased-stressed and control conditions. Genetika 2022, 53, 951–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.Z.; Tan, W.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Shi, Y.S.; Sun, B.C.; et al. QTL analysis for yield components and kernel-related traits in maize across multi-environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Chen, Q.; Qu, Y.Z.; Tang, J.H.; Lübberstedt, T.; Li, H.C. Mapping of QTL for grain yield components based on a DH population in maize. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, P.X.; Chen, B.J.; Zhu, S.W.; Xie, C.X. Meta-analysis of QTL for ear row number in maize. J. Maize Sci. 2014, 22, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Liu, H.; Hong, Y.B.; Li, H.F.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Wen, S.J.; Zhou, G.Y.; Li, S.X.; Chen, X.P.; et al. Consensus map integration and QTL meta-analysis narrowed a locus for yield traits to 0.7 cM and refined a region for late leaf spot resistance traits to 0.38 cM on linkage group A05 in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.H.; Qu, P.P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, H.B.; Liu, Y.N.; Zhang, M.M.; Zhanh, L.P.; Zhao, C.P.; Zhang, S.Q.; Pang, B.S. Consensus linkage map construction and QTL mapping for eight yield-related traits in wheat using BAAFS 90K SNP array. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L. Fine Mapping of Major QTL qEL1.01 Controlling Maize Ear Length and Candidate Gene Function Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Guizhou University, Guizhou, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, N.; Choudhary, S.; Naaz, N.; Sharma, N.; Laskar, R.A. Recent advancements in molecular marker-assisted selection and applications in plant breeding programmes. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Tu, L.; Wang, A.G.; Guo, X.Y.; Liu, P.F.; Zhu, Y.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Wu, X. Research progress on tassel differentiation and related QTL in maize. Agrotech. Serv. 2020, 37, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Sandhu, N.; Singh, V.K.; Catolos, M.; Kumar, A. Genotyping-by-sequencing based QTL mapping for rice grain yield under reproductive stage drought stress tolerance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.J.; Wu, W.R.; Tang, J.L. DNA Marker-Assisted Crop Breeding; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2001; pp. 64–79. [Google Scholar]
- Melchinger, A.E.; Utz, H.F.; Schön, C.C. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping using different testers and independent population samples in maize reveals low power of QTL detection and large bias in estimates of QTL effects. Genetics 1998, 149, 383–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Shimizu, A.; Sato, K.; Takeda, K.; Kawasaki, S. Efficient construction of high-density linkage map and its application to QTL analysis in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Rakshit, S.; Choudhary, M.; Das, A.K.; Kumar, R.R. Meta-analysis of QTLs associated with popping traits in maize (Zea mays L.). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, K.; McHale, L.K. Meta-Analyses of QTLs associated with protein and oil contents and compositions in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] seed. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
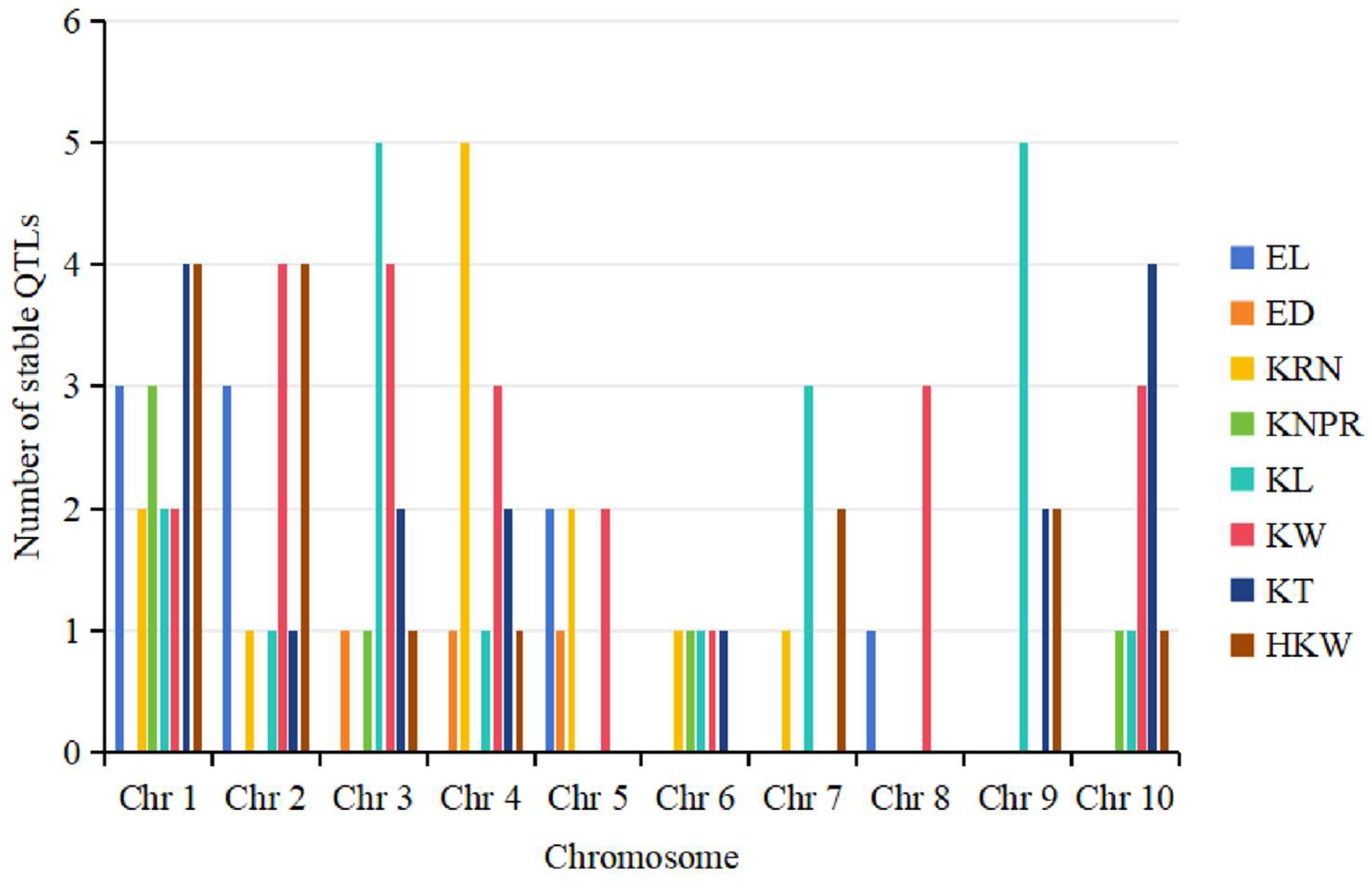



| Trait | Chr 1 | Chr 2 | Chr 3 | Chr 4 | Chr 5 | Chr6 | Chr 7 | Chr 8 | Chr 9 | Chr 10 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EL | 10 | 11 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 62 |
| ED | 11 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 47 |
| KRN | 7 | 8 | 3 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 64 |
| KPRN | 16 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 50 |
| KL | 14 | 16 | 15 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 20 | 4 | 98 |
| KW | 22 | 18 | 18 | 13 | 8 | 5 | 9 | 13 | 8 | 9 | 123 |
| KT | 19 | 6 | 14 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 12 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 87 |
| HKW | 14 | 10 | 14 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 13 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 79 |
| Total | 113 | 75 | 79 | 55 | 47 | 27 | 64 | 53 | 55 | 42 | 610 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Wang, T.; Shaw, R.K.; Jiang, F.; et al. Hotspot Regions of Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes for Ear-Related Traits in Maize: A Literature Review. Genes 2024, 15, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010015
Zhang X, Sun J, Zhang Y, Li J, Liu M, Li L, Li S, Wang T, Shaw RK, Jiang F, et al. Hotspot Regions of Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes for Ear-Related Traits in Maize: A Literature Review. Genes. 2024; 15(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xingjie, Jiachen Sun, Yudong Zhang, Jinfeng Li, Meichen Liu, Linzhuo Li, Shaoxiong Li, Tingzhao Wang, Ranjan Kumar Shaw, Fuyan Jiang, and et al. 2024. "Hotspot Regions of Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes for Ear-Related Traits in Maize: A Literature Review" Genes 15, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010015
APA StyleZhang, X., Sun, J., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Liu, M., Li, L., Li, S., Wang, T., Shaw, R. K., Jiang, F., & Fan, X. (2024). Hotspot Regions of Quantitative Trait Loci and Candidate Genes for Ear-Related Traits in Maize: A Literature Review. Genes, 15(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15010015






