A Comprehensive View on the Protein Functions of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
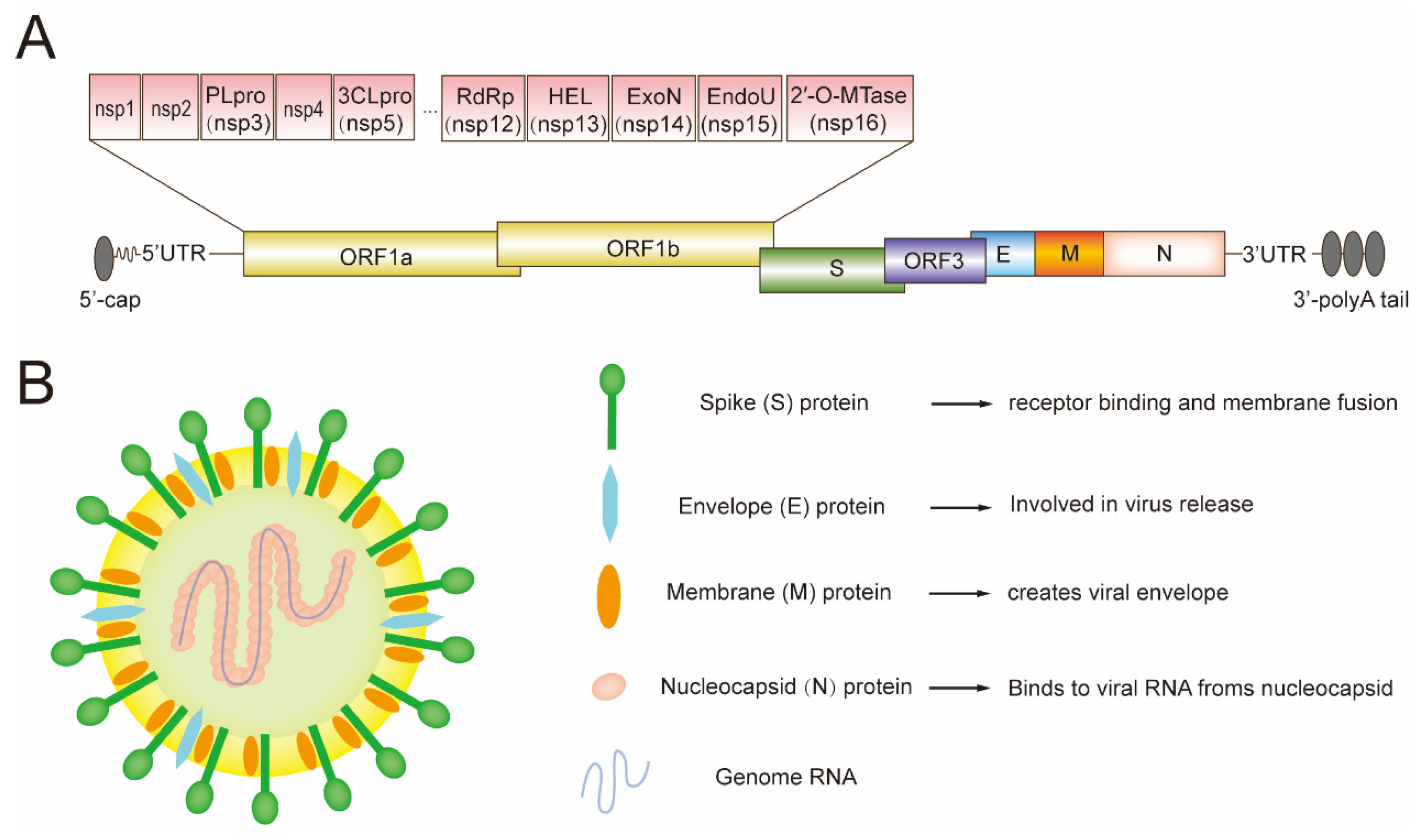
2. The Genome of PEDV and Its Encoded Proteins
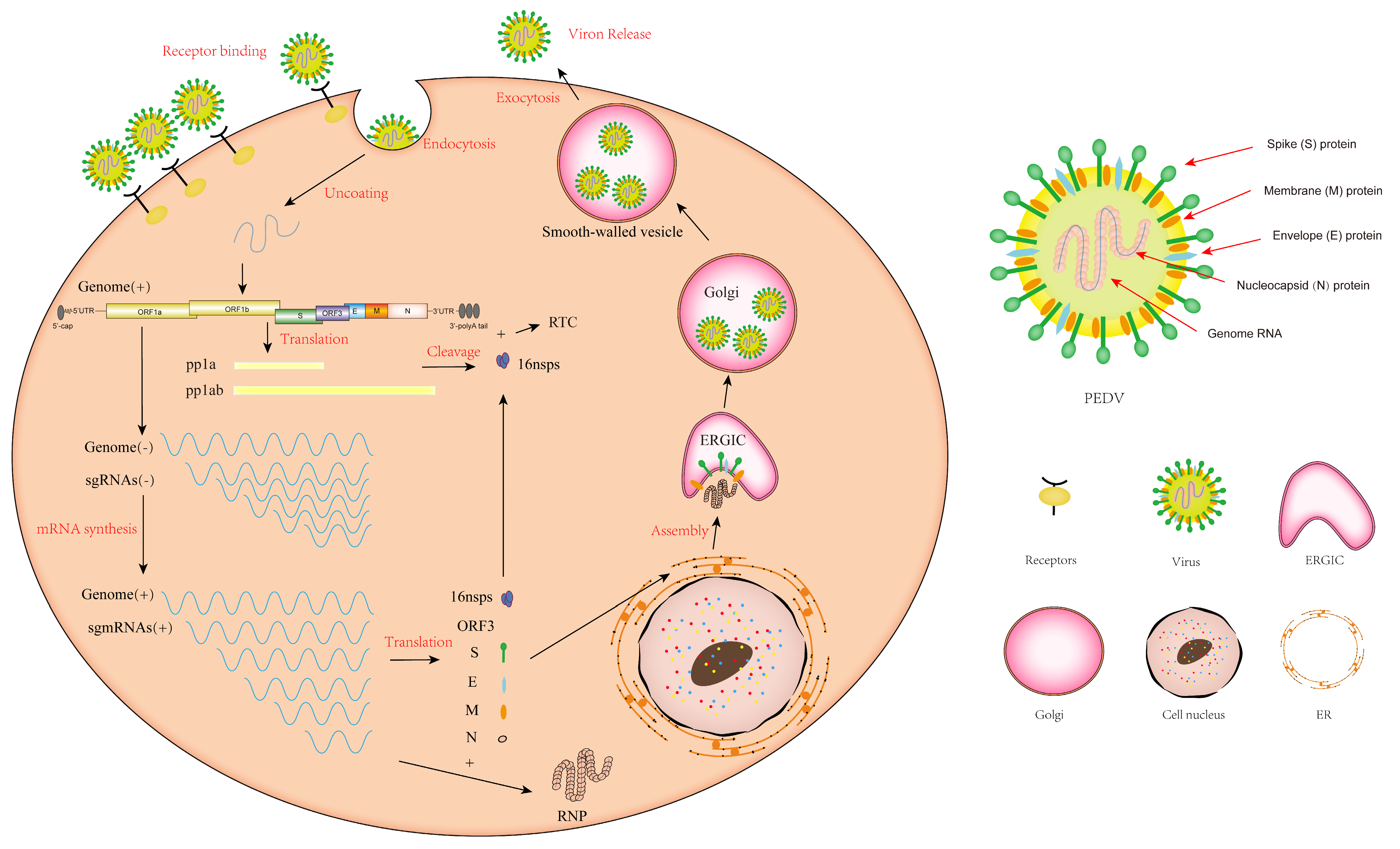
3. The Replication Cycle of PEDV
4. The Structural Proteins of PEDV
4.1. The Function of PEDV S Protein
4.2. The Function of PEDV E Protein
4.3. The Function of PEDV M Protein
4.4. The Function of PEDV N Protein
5. The Accessory Protein of PEDV
6. The Nonstructural Proteins of PEDV
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pensaert, M.B.; de Bouck, P. A new coronavirus-like particle associated with diarrhea in swine. Arch. Virol. 1978, 58, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavanagh, D. Nidovirales: A new order comprising Coronaviridae and Arteriviridae. Arch. Virol. 1997, 142, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.L.; Yu, L.Y.; Liu, J. Development and evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on recombinant nucleocapsid protein for detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea (PEDV) antibodies. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 123, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, E. An apparently new syndrome of porcine epidemic diarrhoea. Vet. Rec. 1977, 100, 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.-Q.; Cai, R.-J.; Chen, Y.-Q.; Liang, P.-S.; Chen, D.-K.; Song, C.-X. Outbreak of porcine epidemic diarrhea in suckling piglets, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: An emerging and re-emerging epizootic swine virus. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, G.W.; Hoang, H.; Schwartz, K.J.; Burrough, E.R.; Sun, D.; Madson, D.; Cooper, V.L.; Pillatzki, A.; Gauger, P.; Schmitt, B.J.; et al. Emergence of Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in the United States: Clinical signs, lesions, and viral genomic sequences. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, H.-Y. Porcine enteric coronaviruses: An updated overview of the pathogenesis, prevalence, and diagnosis. Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.-X.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Meng, X.-Z.; Ma, J.; Ni, H.-B.; Zhang, X.; Qi, Y.; et al. Epidemiology of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus among Chinese pig populations: A meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 129, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Qiao, W.-T.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Lu, W.-H.; Wang, Z.-W.; Li, H.-X.; Li, J.-L. A new PEDV strain CH/HLJJS/2022 can challenge current detection methods and vaccines. Virol. J. 2023, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, V.D.; Kim, Y.; Yang, M.; Vannucci, F.; Molitor, T.; Torremorell, M.; Cheeran, M.C. Immune responses to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) in swine and protection against subse-quent infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Yuan, H.; Pang, D.; Ouyang, H. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus: An Updated Overview of Virus Epidemiology, Virulence Variation Patterns and Virus–Host Interactions. Viruses 2022, 14, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Xie, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, A. A Comprehensive View on the Host Factors and Viral Proteins Associated with Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 762358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, B.J.; van der Zee, R.; de Haan, C.A.; Rottier, P.J.M. The coronavirus spike protein is a class i virus fusion protein: Structural and functional characterization of the fusion core complex. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 8801–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Bidon, M.; Jaimes, J.A.; Whittaker, G.R.; Daniel, S. Coronavirus membrane fusion mechanism offers a potential target for antiviral development. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178, 104792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, W.; De Esesarte, E.L.; Guo, H.; van den Elzen, P.; van den Born, A.E.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Bosch, B.J. Cell Attachment Domains of the Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Spike Protein Are Key Targets of Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Virol. 2017, 91, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.-J.; Deng, M.-C.; Wang, F.-I.; Tsai, S.-H.; Chang, C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-L. Deletion in the S1 Region of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Reduces the Virulence and Influences the Virus-Neutralizing Activity of the Antibody Induced. Viruses 2020, 12, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, J.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.-J.; Tong, D. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus E protein causes endoplasmic reticulum stress and up-regulates interleukin-8 expression. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, D.; Cao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, X.; Zou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus E protein suppresses RIG-I signaling-mediated interferon-beta production. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 254, 108994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Han, W.; Chang, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y.; Xu, L.; Zheng, H.; et al. Deletion of a 7-amino-acid region in the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus envelope protein induces higher type I and III interferon responses and results in attenuation in vivo. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0084723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.G.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, J.; Huang, Y.; Tong, D.W. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus M protein blocks cell cycle progression at S-phase and its subcellular localization in the porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Acta Virol. 2015, 59, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Shi, K.; Yoo, D. Suppression of type I interferon production by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and degradation of CREB-binding protein by nsp1. Virology 2016, 489, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, K.R.; Koetzner, C.A.; Masters, P.S. Characterization of a critical interaction between the coronavirus nucleocapsid protein and nonstructural protein 3 of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 9159–9172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Shi, D.; Xing, X.; Qi, S.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; et al. Coronavirus Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Nucleocapsid Protein Interacts with p53 To Induce Cell Cycle Arrest in S-Phase and Promotes Viral Replication. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0018721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Liu, Z.Q.; Li, G.W.; Chen, C.; Luo, H.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhuo, X.H.; Shi, X.F.; Fang, W.H.; Li, X.L. Nucleocapsid protein from porcine epidemic diarrhea virus isolates can antagonize interferon-lambda production by blocking the nuclear factor-κB nuclear translocation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2018, 19, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Dong, J.; Liang, Y.; Liu, H.-J.; Tong, D. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus N protein prolongs S-phase cell cycle, induces endoplasmic reticulum stress, and up-regulates interleukin-8 expression. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Fang, L.; Jing, H.; Zeng, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Luo, R.; Chen, H.; Xiao, S. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nucleocapsid protein antagonizes beta interferon production by sequestering the interaction between IRF3 and TBK. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8936–8945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Cao, L.; Ge, X.; Gao, Y.; Herrler, G.; Ren, Y.; Ren, X.; Li, G. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus inhibits dsRNA-induced interferon-beta production in porcine intestinal epithelial cells by blockade of the RIG-I-mediated pathway. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Li, W.; Guo, X.; Hu, H.; He, Q. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus ORF3 gene prolongs S-phase, facilitates formation of vesicles and promotes the proliferation of attenuated PEDV. Virus Genes. 2015, 51, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Xu, J.; Duan, X.; Xu, X.; Li, P.; Cheng, L.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus ORF3 protein causes endoplasmic reticulum stress to facilitate autophagy. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 235, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Xu, J.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Zou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Shen, Y.; et al. The accessory protein ORF3 of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus inhibits cellular interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 productions by blocking the nuclear factor-κB p65 activation. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 251, 108892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewborisuth, C.; Koonpaew, S.; Srisutthisamphan, K.; Viriyakitkosol, R.; Jaru-Ampornpan, P.; Jongkaewwattana, A. PEDV ORF3 Independently Regulates IκB Kinase beta-Mediated NF-κB and IFN-beta Promoter Activities. Pathogens 2020, 9, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, S.; Fu, Z.F.; Peng, G. Structural and Biological Basis of Alphacoronavirus nsp1 Associated with Host Proliferation and Immune Evasion. Viruses 2020, 12, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ke, H.; Blikslager, A.; Fujita, T.; Yoo, D. Type III Interferon Restriction by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and the Role of Viral Protein nsp1 in IRF1 Signaling. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, J.; Yoo, D. Inhibition of NF-κB activity by the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nonstructural protein 1 for innate immune evasion. Virology 2017, 510, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Innate Immune Evasion of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus through Degradation of the FBXW7 Protein via the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0088921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Chen, J.; Tu, J.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Shi, H.; Baker, S.C.; Feng, L.; Chen, Z. The papain-like protease of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus negatively regulates type I interferon pathway by acting as a viral deubiquitinase. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94 Pt 7, 1554–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xing, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Nichols, D.B.; Clementz, M.A.; Banach, B.S.; Li, K.; Baker, S.C.; et al. Coronavirus Papain-like proteases negatively regulate antiviral innate immune response through disruption of STING-mediated signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liang, P.; Wang, L.; Song, C. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nsp4 induces pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression inhibiting viral replication in vitro. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, S.; Johnston, M.L.; St. John, S.E.; Osswald, H.L.; Nyalapatla, P.R.; Paul, L.N.; Ghosh, A.K.; Denison, M.R.; Mesecar, A.D. Ligand-induced Dimerization of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus nsp5 Protease (3CLpro): Implications for nsp5 regulation and the development of antivirals. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 19403–19422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Wang, X.; Tong, X.; Shi, Y.; Fu, Z.F.; Peng, G. Structural Basis for Inhibiting Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication with the 3C-Like Protease Inhibitor GC. Viruses 2020, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, S.; Peng, Q.; Ding, Z.; Hao, W.; Peng, G.; Xiao, S.; Fang, L. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp7 Inhibits Interferon-Induced JAK-STAT Signaling through Sequestering the Interaction between KPNA1 and STAT1. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0040022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, P.; Ren, J.; Xia, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, X.; Ding, T.; Xiao, S.; Fang, L. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp7 Inhibits MDA5 Dephosphorylation to Antagonize Type I Interferon Production. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0501722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ma, M.; Shi, X.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. The novel Nsp9-interacting host factor H2BE promotes PEDV replication by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis. Vet. Res. 2023, 54, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, M.; Imbert, I.; Subissi, L.; Gluais, L.; Canard, B.; Decroly, E. RNA 3′-end mismatch excision by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nonstructural protein nsp10/nsp14 exoribonuclease complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9372–9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhuo, Z.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; Wang, T. Expression and immunogenicity of nsp10 protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 144, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, N.R.; Smith, E.C.; Blanc, H.; Vignuzzi, M.; Peersen, O.B.; Denison, M.R. Homology-Based Identification of a Mutation in the Coronavirus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase That Confers Resistance to Multiple Mutagens. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 7415–7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Jia, X.; Chen, J.; Qiao, C.; Li, C.; Yang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp13 Protein Downregulates Neonatal Fc Receptor Expression by Causing Promoter Hypermethylation through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J. Immunol. 2023, 210, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Ren, J.; Yang, G.; Jiang, C.; Dong, L.; Sun, Q.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; He, Q. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and Its nsp14 Suppress ER Stress Induced GRP78. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, F.; Ma, C.; Cao, W.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, H. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nsp14 inhibits NF-κB pathway activation by targeting the IKK complex and p65. Anim. Dis. 2021, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Shi, H.; Shi, D.; Guo, L.; Feng, L. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp15 Antagonizes Interferon Signaling by RNA Degradation of TBK1 and IRF3. Viruses 2020, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, T.; Yang, Z.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, L.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Transcriptome analysis of host response to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nsp15 in IPEC-J2 cells. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 162, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Ke, H.; Kim, J.; Yoo, D.; Su, Y.; Boley, P.; Chepngeno, J.; Vlasova, A.N.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Engineering a Live Attenuated Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Vaccine Candidate via Inactivation of the Viral 2′-O-Methyltransferase and the Endocytosis Signal of the Spike Protein. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00406-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV): An update on etiology, transmission, pathogenesis, and prevention and control. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocherhans, R.; Bridgen, A.; Ackermann, M.; Tobler, K. Completion of the porcine epidemic diarrhoea coronavirus (PEDV) genome sequence. Virus Genes 2001, 23, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, D.A.; Baric, R.S. Coronavirus genome structure and replication. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 287, 75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Su, W.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shang, K.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, S.; Wu, H. Genome-wide analysis of differentially expressed genes and the modulation of PEDV infection in Vero E6 cells. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 117, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, R.; Dong, S.; Yu, R.; Li, Z. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) ORF3 Enhances Viral Proliferation by Inhibiting Apoptosis of Infected Cells. Viruses 2020, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Cruz, D.J.M.; Shin, H.-J. Clathrin- and serine proteases-dependent uptake of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus into Vero cells. Virus Res. 2014, 191, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snijder, E.J.; Decroly, E.; Ziebuhr, J. The Nonstructural Proteins Directing Coronavirus RNA Synthesis and Processing. Adv. Virus Res. 2016, 96, 59–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses post-SARS: Update on replication and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; He, Q.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Bosch, B.-J. Cellular entry of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, Y.; Peng, G.; Qi, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Du, L.; et al. Receptor Usage and Cell Entry of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6121–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Shi, D.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Chi, Y.; Feng, L. Detection and molecular diversity of spike gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in China. Viruses 2013, 5, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Guo, J.; Fang, L.; Ye, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, S.; Zhu, X.; Miao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xiao, S. Evolutionary and genotypic analyses of global porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Wang, K.; Hou, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, F.; Tong, W.; Yu, H.; et al. Genetic evolution analysis and pathogenicity assessment of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus strains circulating in part of China during 2011—2017. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 69, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, F.C.; Lin, C.N.; Chiou, H.-Y.; Chia, M.Y.; Chiou, M.T.; Haga, T.; Kao, C.F.; Chang, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Jeng, C.R.; et al. Updated phylogenetic analysis of the spike gene and identification of a novel recombinant porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus strain in Taiwan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Lian, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, Z.; Dai, Y.; Liu, M.; Fan, H.; Shi, Y.; Cong, F. Molecular Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of a Variant Recombinant Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Strain in China. Animals 2022, 12, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Deng, G.; Yue, H.; Tang, C.; Wu, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of recombinant adenovirus expressing a novel genotype G2b PEDV spike protein in protecting newborn piglets against PEDV. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 12, e0240323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicht, O.; Li, W.; Willems, L.; Meuleman, T.J.; Wubbolts, R.W.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Rottier, P.J.M.; Bosch, B.J. Proteolytic activation of the porcine epidemic diarrhea coronavirus spike fusion protein by trypsin in cell culture. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7952–7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Bhandari, M.; Martini, O.; Sewall, L.M.; Bangaru, S.; Yoon, K.-J.; Ward, A.B. Structure and immune recognition of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus spike protein. Structure 2021, 29, 385–392.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Li, R.; Xie, S.; Qiao, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.X.; Deng, R.; Zhang, G. Identification of a novel linear B-cell epitope within the collagenase equivalent domain of porcine epi-demic diarrhea virus spike glycoprotein. Virus Res. 2019, 266, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makadiya, N.; Brownlie, R.; Hurk, J.V.D.; Berube, N.; Allan, B.; Gerdts, V.; Zakhartchouk, A. S1 domain of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus spike protein as a vaccine antigen. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ge, J.; Li, Y. Porcine aminopeptidase N is a functional receptor for the PEDV coronavirus. Virology 2007, 365, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, E.; Lee, C. Contribution of the porcine aminopeptidase N (CD13) receptor density to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 144, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Yang, H. Aminopeptidase N Knockout Pigs Are Not Resistant to Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Fan, B.; Liu, T.; Wang, L.; Zhao, P.; Dang, Y.; Sun, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Aminopeptidase N-null neonatal piglets are protected from transmissible gastroenteritis virus but not porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.M.; Wang, B.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.W. Aminopeptidase-N-independent entry of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus into Vero or porcine small intestine epithelial cells. Virology 2018, 517, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirato, K.; Maejima, M.; Islam, M.T.; Miyazaki, A.; Kawase, M.; Matsuyama, S.; Taguchi, F. Porcine aminopeptidase N is not a cellular receptor of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, but promotes its infectivity via aminopeptidase activity. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2528–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, R.; He, Q.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.; Rottier, P.J.; Bosch, B.-J. Aminopeptidase N is not required for porcine epidemic diarrhea virus cell entry. Virus Res. 2017, 235, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwegmann-Wessels, C.; Bauer, S.; Winter, C.; Enjuanes, L.; Laude, H.; Herrler, G. The sialic acid binding activity of the S protein facilitates infection by porcine transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmarets, L.M.B.; Theuns, S.; Roukaerts, I.D.M.; Acar, D.D.; Nauwynck, H.J. Role of sialic acids in feline enteric coronavirus infections. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95 Pt 9, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, M.; Liu, X.; Liang, T.; Ban, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; Song, C. The Alpha-1 Subunit of the Na+/K+-ATPase (ATP1A1) Is a Host Factor Involved in the Attachment of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Han, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus S1 protein is the critical inducer of apoptosis. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F. Structure, Function, and Evolution of Coronavirus Spike Proteins. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 237–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Ma, Z.; Li, Y.; Gao, S.; Xiao, S. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus: Molecular mechanisms of attenuation and vaccines. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Ji, Z.; Jing, Z.; Feng, L. A New Neutralization Epitope in the Spike Protein of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Dong, S.; Yu, L.; Si, F.; Li, C.; Xie, C.; Yu, R.; Li, Z. Three Amino Acid Substitutions in the Spike Protein Enable the Coronavirus Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus to Infect Vero Cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0387222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, G.; Shi, Y.; Dong, W.; Fu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Chen, H.; Peng, G. Trypsin-enhanced infection with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus is determined by the S2 subunit of the spike glycoprotein. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02453-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Cheng, A.; Zhang, G. HSPA5 Promotes Attachment and Internalization of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus through Interaction with the Spike Protein and the Endo-/Lysosomal Pathway. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0054923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Montalto-Morrison, C.; Masters, P.S. Genetic analysis of determinants for spike glycoprotein assembly into murine coronavirus virions: Distinct roles for charge-rich and cysteine-rich regions of the endodomain. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9904–9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cong, Y.; Veenendaal, T.; Klumperman, J.; Shi, D.; Mari, M.; Reggiori, F. Ultrastructural Characterization of Membrane Rearrangements Induced by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection. Viruses 2017, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, C.; Schwegmann-Wessels, C.; Neumann, U.; Herrler, G. The spike protein of infectious bronchitis virus is retained intracellularly by a tyrosine motif. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Meulia, T.; Gao, X.; Saif, L.J.; Wang, Q. Deletion of both the Tyrosine-Based Endocytosis Signal and the Endoplasmic Reticulum Retrieval Signal in the Cytoplasmic Tail of Spike Protein Attenuates Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus in Pigs. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01758-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Maheswari, U.; Parthasarathy, K.; Ng, L.; Liu, D.X.; Gong, X. Conductance and amantadine binding of a pore formed by a lysine-flanked transmembrane domain of SARS coronavirus envelope protein. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, Z.; Kay, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Han, H.; Xia, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus E protein inhibits type I interferon production through endoplasmic reticulum stress response (ERS)-mediated suppression of antiviral proteins translation. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 152, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Nan, Y.; Wu, C. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Envelope Protein Blocks SLA-DR Expression in Barrow-Derived Dendritic Cells by Inhibiting Promoters Activation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 741425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, M.M.; Costa, P.A.C.; Diniz, S.Q.; Henriques, P.M.; Kano, F.S.; Tada, M.S.; Pereira, D.B.; Soares, I.S.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Jankovic, D.; et al. T follicular helper cells regulate the activation of B lymphocytes and antibody production during Plasmodium vivax infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Weng, Z.; Feng, Y.; Gong, T.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, G.; Gong, L. KPNA2 suppresses porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication by targeting and degrading virus envelope protein through selective autophagy. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0011523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.-M.; Yang, Y.-L.; He, Y.-Q.; Peng, L.; Zhao, P.; Xu, S.-Y.; Cao, H.; Fang, P.; Qiu, W.; Qin, P.; et al. Specific recombinant proteins of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus are immunogenic, revealing their potential use as diagnostic markers. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 236, 108387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, A.L.; Larson, B.J.; Hogue, B.G. A conserved domain in the coronavirus membrane protein tail is important for virus assembly. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11418–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, J.; Niemann, H.; Smeekens, S.; Rottier, P.; Warren, G. Sequence and topology of a model intracellular membrane protein, E1 glycoprotein, from a coronavirus. Nature 1984, 308, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.H.; Zuo, Y.Z.; Shen, X.Q.; Gu, W.Y.; Di, J.M. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the monitoring and surveillance of anti-bodies to porcine epidemic diarrhea virus based on a recombinant membrane protein. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 225, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, T.; Song, D.; Huang, T.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Q.; Ye, Y.; et al. Comparison and evaluation of conventional RT-PCR, SYBR green I and TaqMan real-time RT-PCR assays for the detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Mol. Cell Probes 2017, 33, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Suo, S.; Jang, Y.S. Development of a porcine epidemic diarrhea virus M protein-based ELISA for virus detection. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, X.; Shi, D.; Feng, L.; Yang, B. Identification of a conserved linear B-cell epitope in the M protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Enríquez, A.; Herrera-Camacho, I.; Millán-Pérez-Peña, L.; Reyes-Leyva, J.; Santos-López, G.; Rivera-Benítez, J.F.; Rosas-Murrieta, N.H. Predicted 3D model of the M protein of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and analysis of its immunogenic potential. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, F.; Cao, W.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.; Zhao, Z.; Tian, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, J.; et al. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Membrane Protein Interacted with IRF7 to Inhibit Type I IFN Production during Viral Infection. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 2909–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yu, R.; Chen, B.; Si, F.; Wang, J.; Xie, C.; Men, C.; Dong, S.; Li, Z. Identification of host cell proteins that interact with the M protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 246, 108729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.Y.; Ryu, J.; Park, J.E.; Hong, E.J.; Shin, H.J. Heat shock protein 70 could enhance porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus replication by interacting with membrane proteins. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gill, A.; Dove, B.K.; Emmett, S.R.; Kemp, C.F.; Ritchie, M.A.; Dee, M.; Hiscox, J.A. Mass spectroscopic characterization of the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus nucleoprotein and elucidation of the role of phosphorylation in RNA binding by using surface plasmon resonance. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.W.; Fang, S.; Fan, H.; Lescar, J.; Liu, D. Amino acid residues critical for RNA-binding in the N-terminal domain of the nucleocapsid protein are essential determinants for the infectivity of coronavirus in cultured cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4816–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Ooi, A.; Tan, Y.W.; Wang, S.; Fang, S.; Liu, D.X.; Lescar, J. The nucleocapsid protein of coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus: Crystal structure of its N-terminal domain and multimerization properties. Structure 2005, 13, 1859–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-W.; Wang, M.; Zhan, J.; Liu, Q.-Y.; Fang, L.-L.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.-F.; Bai, J. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of a new strain of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus containing a novel deletion in the N gene. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, K.; Maeda, A.; Maeda, J.; Makino, S. Characterization of the coronavirus M protein and nucleocapsid interaction in infected cells. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8127–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-K.; Yeo, S.-G. Cloning and sequence analysis of the nucleocapsid gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus Chinju99. Virus Genes 2003, 26, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junwei, G.; Baoxian, L.; Lijie, T.; Yijing, L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the N. gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus LJB/03. Virus Genes 2006, 33, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Lv, M.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, L. Molecular characterizations of subcellular localization signals in the nucleocapsid protein of porcine epi-demic diarrhea virus. Viruses 2014, 6, 1253–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Shi, H.; Sun, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Z.; Liu, J.; Cao, L.; et al. Nucleocapsid Interacts with NPM1 and Protects it from Proteolytic Cleavage, Enhancing Cell Survival, and is Involved in PEDV Growth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, H.; Qin, W.; Dong, S.; Yang, X.; Zhai, X.; Tong, W.; Liu, C.; Zheng, H.; Yu, H.; Kong, N.; et al. PEDV N protein capture protein translation element PABPC1 and eIF4F to promote viral replication. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 284, 109844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, Z.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.; Luo, J.; Guo, X. TRIM28 promotes porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication by mitophagy-mediated inhibition of the JAK-STAT1 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 254 Pt 1, 127722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kong, N.; Jiao, Y.; Dong, S.; Sun, D.; Chen, X.; Zheng, H.; Tong, W.; Yu, H.; Yu, L.; et al. EGR1 Suppresses Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication by Regulating IRAV To Degrade Viral Nucleocapsid Protein. J. Virol. 2021, 95, JVI0064521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Kong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, S.; Zhai, H.; Zhai, X.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; Ye, M.; et al. PTBP1 suppresses porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication via inducing protein degradation and IFN production. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Kong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Qin, W.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; Ye, M.; Tong, W.; Liu, C.; et al. N protein of PEDV plays chess game with host proteins by selective autophagy. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2338–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Kong, N.; Wang, C.; Qin, W.; Dong, S.; Zhai, H.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; Ye, M.; Li, G.; et al. PRPF19 Limits Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication through Targeting and Degrading Viral Capsid Protein. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0161422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Kong, N.; Wang, C.; Dong, S.; Zhai, H.; Zhai, X.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; Ye, M.; Tong, W.; et al. hnRNP K Degrades Viral Nucleocapsid Protein and Induces Type I IFN Production to Inhibit Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0155522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, W.; Kong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhai, H.; Zhai, X.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; Ye, M.; Liu, C.; et al. Nuclear ribonucleoprotein RALY targets virus nucleocapsid protein and induces autophagy to restrict porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Kong, N.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Qin, W.; Zhai, H.; Zhai, X.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; et al. FUBP3 Degrades the Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Nucleocapsid Protein and Induces the Production of Type I Interferon. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0061822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Kong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Qin, W.; Zhai, H.; Zhai, X.; Yang, X.; Ye, C.; et al. TARDBP Inhibits Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication through Degrading Viral Nucleocapsid Protein and Activating Type I Interferon Signaling. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0007022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Shan, T.; Wang, H.; Jiao, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Li, L.; Tong, W.; Yu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. BST2 suppresses porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication by targeting and degrading virus nucleocapsid protein with selective autophagy. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1737–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Kong, N.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, D.; Dong, S.; Qin, W.; Zhai, H.; Yu, L.; Zheng, H.; et al. TRIM21 inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus proliferation by proteasomal degradation of the nucleocapsid protein. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liwnaree, B.; Narkpuk, J.; Sungsuwan, S.; Jongkaewwattana, A.; Jaru-Ampornpan, P. Growth enhancement of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) in Vero E6 cells expressing PEDV nucleocapsid protein. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Lu, W.; Chen, J.; Xie, S.; Shi, H.; Hsu, H.; Yu, W.; Xu, K.; Bian, C.; Fischer, W.B.; et al. PEDV ORF3 encodes an ion channel protein and regulates virus production. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.S.; Yang, J.S.; Oh, J.S.; Han, J.H.; Park, B.K. Differentiation of a Vero cell adapted porcine epidemic diarrhea virus from Korean field strains by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of ORF3. Vaccine 2003, 21, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongthida, P.; Liwnaree, B.; Wanasen, N.; Narkpuk, J.; Jongkaewwattana, A. The role of ORF3 accessory protein in replication of cell-adapted porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV). Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2553–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beall, A.; Yount, B.; Lin, C.-M.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.; Baric, R. Characterization of a Pathogenic Full-Length cDNA Clone and Transmission Model for Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Strain PC22A. mBio 2016, 7, e01451-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Son, K.Y.; Noh, Y.H.; Lee, S.C.; Choi, H.W.; Yoon, I.J.; Lee, C. Genetic characteristics, pathogenicity, and immunogenicity associated with cell adaptation of a virulent genotype 2b porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Ji, P.; Xing, G.; Jiang, D.; Liu, C.; Song, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Detection and phylogenetic analysis of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in central China based on the ORF3 gene and the S1 gene. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Qiu, H.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, L. Molecular epidemiology of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in China. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-J.; Moon, H.-J.; Luo, Y.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, E.-M.; Yang, J.-S.; Song, D.-S.; Kang, B.-K.; Lee, C.-S.; Park, B.-K. Cloning and further sequence analysis of the ORF3 gene of wild- and attenuated-type porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses. Virus Genes 2008, 36, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Li, H.X.; Chen, X.M.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Luo, A.F.; Yang, Y.R.; Zheng, L.L.; Chen, H.Y. Genetic Characteristics and Pathogenicity of a Novel Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus with a Naturally Occurring Truncated ORF3 Gene. Viruses 2022, 14, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhong, L.; Qin, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, R.; Su, X.; Du, C.; Mi, X.; et al. Comparative Characterization and Pathogenicity of a Novel Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) with a Naturally Occurring Truncated ORF3 Gene Coinfected with PEDVs Possessing an Intact ORF3 Gene in Piglets. Viruses 2021, 13, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.; Lee, D.; Lee, C. Development of a Next-Generation Vaccine Platform for Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Using a Reverse Genetics System. Viruses 2022, 14, 2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristen-Burmann, C.; Rogger, P.; Veiga, I.B.; Riebesehl, S.; Rappe, J.; Ebert, N.; Sautter, C.A.; Kelly, J.N.; Stalder, H.; Ehmann, R.; et al. Reverse Genetic Assessment of the Roles Played by the Spike Protein and ORF3 in Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Pathogenicity. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0196422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewborisuth, C.; He, Q.; Jongkaewwattana, A. The Accessory Protein ORF3 Contributes to Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication by Direct Binding to the Spike Protein. Viruses 2018, 10, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewborisuth, C.; Yingchutrakul, Y.; Roytrakul, S.; Jongkaewwattana, A. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDV) ORF3 Interactome Reveals Inhibition of Virus Replication by Cellular VPS36 Protein. Viruses 2019, 11, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, E.J.; Bredenbeek, P.J.; Dobbe, J.C.; Thiel, V.; Ziebuhr, J.; Poon, L.L.M.; Guan, Y.; Rozanov, M.; Spaan, W.J.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Unique and conserved features of genome and proteome of sars-coronavirus, an early split-off from the coronavirus group 2 lineage. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 331, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiel, V.; Ivanov, K.A.; Putics, A.; Hertzig, T.; Schelle, B.; Bayer, S.; Weißbrich, B.; Snijder, E.J.; Rabenau, H.; Doerr, H.W.; et al. Mechanisms and enzymes involved in SARS coronavirus genome expression. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2305–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Kong, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q. Mutations in Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp1 Cause Increased Viral Sensitivity to Host Interferon Responses and Attenuation In Vivo. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0046922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, B.; Peng, Q.; Song, S.; Shi, D.; Zhang, X.; Guo, W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Nonstructural Protein 1 of Variant PEDV Plays a Key Role in Escaping Replication Restriction by Complement C3. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0102422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Ye, G.; Deng, F.; Wang, G.; Cui, M.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S.; Fu, Z.F.; Peng, G. Structural Basis for the Inhibition of Host Gene Expression by Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus nsp1. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01896-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, G.; Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Fang, L.; Li, F.; Xiao, S.; Fu, Z.F.; Peng, G. A conserved region of nonstructural protein 1 from alphacoronaviruses inhibits host gene expression and is critical for viral virulence. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 13606–13618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.H.; Zhu, J.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Ni, R.Z.; Mu, D. Papain-like protease of SARS-CoV-2 inhibits RLR signaling in a deubiquitination-dependent and deubiquitination-independent manner. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 947272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fang, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, L.; Peng, G.; Chen, H.; Li, K.; Xiao, S. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus 3C-Like Protease Regulates Its Interferon Antagonism by Cleaving NEMO. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2090–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ye, X.; Foda, M.F.; Xiao, S. Porcine deltacoronavirus nsp5 inhibits interferon-beta production through the cleavage of NEMO. Virology 2017, 502, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Lv, M.; Ye, X.; Peng, G.; Fang, L.; et al. Porcine Deltacoronavirus nsp5 Antagonizes Type I Interferon Signaling by Cleaving STAT2. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00003-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Li, B.; Liu, M.; Zhou, H.; He, K.; Fan, H. Nonstructural protein 6 of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus induces autophagy to promote viral replication via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peti, W.; Johnson, M.A.; Herrmann, T.; Neuman, B.W.; Buchmeier, M.J.; Nelson, M.; Joseph, J.; Page, R.; Stevens, R.C.; Kuhn, P.; et al. Structural genomics of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus: Nuclear magnetic resonance structure of the protein nsP7. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12905–12913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Sun, F.; Li, X.; Pang, H.; Xu, X.; Bartlam, M.; Rao, Z. Insights into SARS-CoV transcription and replication from the structure of the nsp7-nsp8 hexadecamer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, G.; Fry, E.; Carter, L.; Sainsbury, S.; Walter, T.; Nettleship, J.; Berrow, N.; Owens, R.; Gilbert, R.; Davidson, A.; et al. The nsp9 replicase protein of SARS-coronavirus, structure and functional insights. Structure 2004, 12, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Deng, F.; Shi, K.; Ye, G.; Wang, G.; Fang, L.; Xiao, S.; Fu, Z.; Peng, G. Dimerization of Coronavirus nsp9 with Diverse Modes Enhances Its Nucleic Acid Binding Affinity. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00692-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yu, Q.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Wang, Q.; Tu, Z.; Tao, F.; Yang, P.; Kong, L.; et al. Expression and immunogenicity of recombinant porcine epidemic diarrhea virus Nsp9. Virology 2023, 587, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet, M.; Debarnot, C.; Imbert, I.; Selisko, B.; Snijder, E.J.; Canard, B.; Decroly, E. In vitro reconstitution of SARS-coronavirus mRNA cap methylation. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Huang, M.; Wu, D.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Mu, J.; Wang, R.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, D.-Y.; et al. SARS-Coronavirus-2 Nsp13 Possesses NTPase and RNA Helicase Activities That Can Be Inhibited by Bismuth Salts. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denison, M.R.; Graham, R.L.; Donaldson, E.F.; Eckerle, L.D.; Baric, R.S. Coronaviruses: An RNA proofreading machine regulates replication fidelity and diversity. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, H.; Pan, J.; Xiang, N.; Tien, P.; Ahola, T.; Guo, D. Functional screen reveals SARS coronavirus nonstructural protein nsp14 as a novel cap N7 methyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3484–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Kong, F.; Hou, Y.J.; Wang, Q. Crucial mutation in the exoribonuclease domain of nsp14 of PEDV leads to high genetic instability during viral replication. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Cai, H.; Lu, M.; Ma, Y.; Li, A.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gu, H.; Li, J.; Gu, J. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Deficient in RNA Cap Guanine-N-7 Methylation Is Attenuated and Induces Higher Type I and III Interferon Responses. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00447-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindler, E.; Gil-Cruz, C.; Spanier, J.; Li, Y.; Wilhelm, J.; Rabouw, H.H.; Züst, R.; Hwang, M.; V’Kovski, P.; Stalder, H.; et al. Early endonuclease-mediated evasion of RNA sensing ensures efficient coronavirus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Gong, X.; Fang, S.; Weng, W.; Wang, H.; Chu, H.; Sun, Y.; Meng, C.; Tan, L.; Song, C.; et al. Inhibition of anti-viral stress granule formation by coronavirus endoribonuclease nsp15 ensures efficient virus replication. PLOS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1008690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroly, E.; Imbert, I.; Coutard, B.; Bouvet, M.; Selisko, B.; Alvarez, K.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Snijder, E.J.; Canard, B. Coronavirus nonstructural protein 16 is a cap-0 binding enzyme possessing (nucleo-side-2′O)-methyltransferase activity. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8071–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Su, Y.; Li, R.; Liang, Z.; Dong, S.; Huang, J. PEDV nsp16 negatively regulates innate immunity to promote viral proliferation. Virus Res. 2019, 265, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, K.A.; Ziebuhr, J. Human coronavirus 229E nonstructural protein 13: Characterization of duplex-unwinding, nucleoside triphosphatase, and RNA 5’-triphosphatase activities. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7833–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroly, E.; Debarnot, C.; Ferron, F.; Bouvet, M.; Coutard, B.; Imbert, I.; Gluais, L.; Papageorgiou, N.; Sharff, A.; Bricogne, G.; et al. Crystal structure and functional analysis of the SARS-coronavirus RNA cap 2’-O-methyltransferase nsp10/nsp16 complex. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Su, C.; Ke, M.; Jin, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, A.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tien, P.; et al. Biochemical and structural insights into the mechanisms of SARS coronavirus RNA ribose 2’-O-methylation by nsp16/nsp10 protein complex. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.Y.; Wu, L.J.; Shaw, N.; Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.N.; Lou, Z.Y.; Yan, L.M.; Zhang, R.G.; Rao, Z.H. Structural basis and functional analysis of the SARS coronavirus nsp14–nsp10 complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9436–9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tao, J.; Sun, Y.; Wu, A.; Su, C.; Gao, G.; Cai, H.; Qiu, S.; Wu, Y.; Ahola, T.; et al. Structure-function analysis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus RNA cap gua-nine-N7-methyltransferase. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6296–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Yang, D.-K.; Kim, H.-H.; Cho, I.-S. Efficacy of inactivated variant porcine epidemic diarrhea virus vaccines in growing pigs. Clin. Exp. Vaccine Res. 2018, 7, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Buckley, A.C.; Pillatzki, A.; Lager, K.M.; Faaberg, K.S.; Baker, S.C. Inactivating Three Interferon Antagonists Attenuates Pathogenesis of an Enteric Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00565-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-Y.; Tsai, P.-S.; Chiou, H.-Y.; Jeng, C.-R.; Pang, V.F.; Chang, H.-W. Efficacy of heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit-adjuvanted parenteral porcine epidemic diarrhea virus trimeric spike subunit vaccine in piglets. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7499–7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, B.; Ji, C.-M.; Cong, X.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.-W. Identification of a peptide derived from the heptad repeat 2 region of the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) spike glycoprotein that is capable of suppressing PEDV entry and inducing neutralizing antibodies. Antivir. Res. 2017, 150, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Zhan, J.; Shi, X.; Liu, Q.; Lu, Q.; Bai, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, P. Identification and characterization of linear B cell epitopes on the nucleocapsid protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus using monoclonal antibodies. Virus Res. 2020, 281, 197912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-M.; Ha, T.-K.; Dang, L.-H.; Pham, H.-T.; Tran, V.-O.; Huh, J.; An, J.-P.; Oh, W.-K. Prenylated Phenolic Compounds from the Leaves of Sabia limoniacea and Their Antiviral Activities against Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Yu, R.; Si, F.; Xie, C.; Li, Z.; Dong, S.; Zhang, D. Magnolol, a Neolignan-like Drug, Inhibits Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Replication in Cultured Cells. Pathogens 2023, 12, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Yu, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Si, F.; Zhou, J.; Xie, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D. Bis-Benzylisoquinoline Alkaloids Inhibit Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus In Vitro and In Vivo. Viruses 2022, 14, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Young, B.-E.; Choi, H.-J. Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection: Inhibition by polysaccharide from Ginkgo biloba exocarp and mode of its action. Virus Res. 2014, 195, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Peng, P.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M.; Ma, Y.; Xue, C.; Cao, Y. Aloe extract inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in vitro and in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 249, 108849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, C.-C.; Wang, H.-X.; Sheng, X.-X.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Mao, X. Glycyrrhizin inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection and attenuates the proinflammatory responses by inhibition of high mobility group box-1 protein. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Shim, J.K.; Choi, H.J. Quercetin 7-rhamnoside reduces porcine epidemic diarrhea virus replication via independent pathway of viral induced reactive oxygen species. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Ahn, Y.-J.; Song, J.-H.; Baek, S.-H.; Kwon, D.-H. Antiviral activity of quercetin 7-rhamnoside against porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Antivir. Res. 2009, 81, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Classification | Viral Protein | Role in PEDV Infection | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structural proteins | S | Essential for viral entry, induces neutralizing antibodies, virulence, induces apoptosis | [14,15,16,17] |
| E | Initiates ERS, activates NF-κB, inhibits IFN-β, ISGs, virulence | [18,19,20] | |
| M | Induce cell cycle arrest at the S-phase, acts as IFN antagonist | [21,22] | |
| N | Form ribonucleoprotein complex, induces S-phase arrest, induces ERS, upregulates the expression of IL-8, inhibits IFN-β and IFN-λ production | [23,24,25,26,27,28] | |
| Accessory protein | ORF3 | Arrests cells at the S-phase, triggers ERS, induces autophagy, inhibits IL-6 and IL-8 productions, upregulates IKBKB-meditated NF-κB promoter, downregulates IFN-β promoter | [29,30,31,32] |
| Nonstructural proteins | Nsp1 | Acts as IFN antagonist, induces virulence, inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production, inhibits NF-κB activity | [22,33,34,35] |
| Nsp2 | Promotes the replication of PEDV | [36] | |
| Nsp3 | PLpro, regulates the deubiquitination of RIG-I and STING, inhibits IFN-β and IFN-λ1 | [37,38] | |
| Nsp4 | Upregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines expression (IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF-α, CCL2, CCL5, and CXCL8) | [39] | |
| Nsp5 | 3C-like protease,IFN antagonist | [40,41] | |
| Nsp7 | Inhibits type I IFN | [42,43] | |
| Nsp8 | Inhibits type III IFN | [22] | |
| Nsp9 | Inhibits ERS-mediated apoptosis | [44] | |
| Nsp10 | Essential for viral replication, upregulates IL-2, IL-4, IL-10, TNF-α, and IFN-γ | [45,46] | |
| Nsp12 | RdRp, viral replication | [47] | |
| Nsp13 | HEL, inhibits bidirectional IgG transport by FcRn | [48] | |
| Nsp14 | ExoN, suppresses ER stress-induced GRP78, acts as NF-κB pathway antagonist, downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines | [49,50] | |
| Nsp15 | EndoU, inhibits IFN-β and IRF3, downregulates CCL5, CXCL8, CXCL10, OAS, MXs, STAT1, and IRF9 | [51,52] | |
| Nsp16 | 2′-O-MTase, downregulates the activities of RIG-I/MDA5-mediated IFN-β and ISRE | [53] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Li, G.; Luo, J.; Huang, S.; Guo, X. A Comprehensive View on the Protein Functions of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Genes 2024, 15, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020165
Li X, Wu Y, Yan Z, Li G, Luo J, Huang S, Guo X. A Comprehensive View on the Protein Functions of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Genes. 2024; 15(2):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Yiwan Wu, Zhibin Yan, Gen Li, Jun Luo, Shile Huang, and Xiaofeng Guo. 2024. "A Comprehensive View on the Protein Functions of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus" Genes 15, no. 2: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020165
APA StyleLi, X., Wu, Y., Yan, Z., Li, G., Luo, J., Huang, S., & Guo, X. (2024). A Comprehensive View on the Protein Functions of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Genes, 15(2), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15020165






