The Involvement of the microRNAs miR-466c and miR-340 in the Palmitate-Mediated Dysregulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Gene Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagent Preparation
2.2. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
2.3. MicroRNA Mimic Transfections
2.4. Statistical Analysis
| Gene/microRNA | Treatment | Fold Change | SEM | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Gnrh | − | 1.14 | 0.2396 | ** 0.0028 |
| + | −1.07 | 0.2588 | ** 0.0079 | ||
| Gata4 | − | 0.49 | 0.128 | * 0.0127 | |
| + | −0.52 | 0.1382 | * 0.0143 | ||
| Chop | − | 2.93 | 0.4407 | *** 0.0002 | |
| + | −2.39 | 0.4761 | ** 0.0019 | ||
| Per2 | − | −0.69 | 0.1806 | * 0.0205 | |
| + | 1.15 | 0.1806 | *** 0.0010 | ||
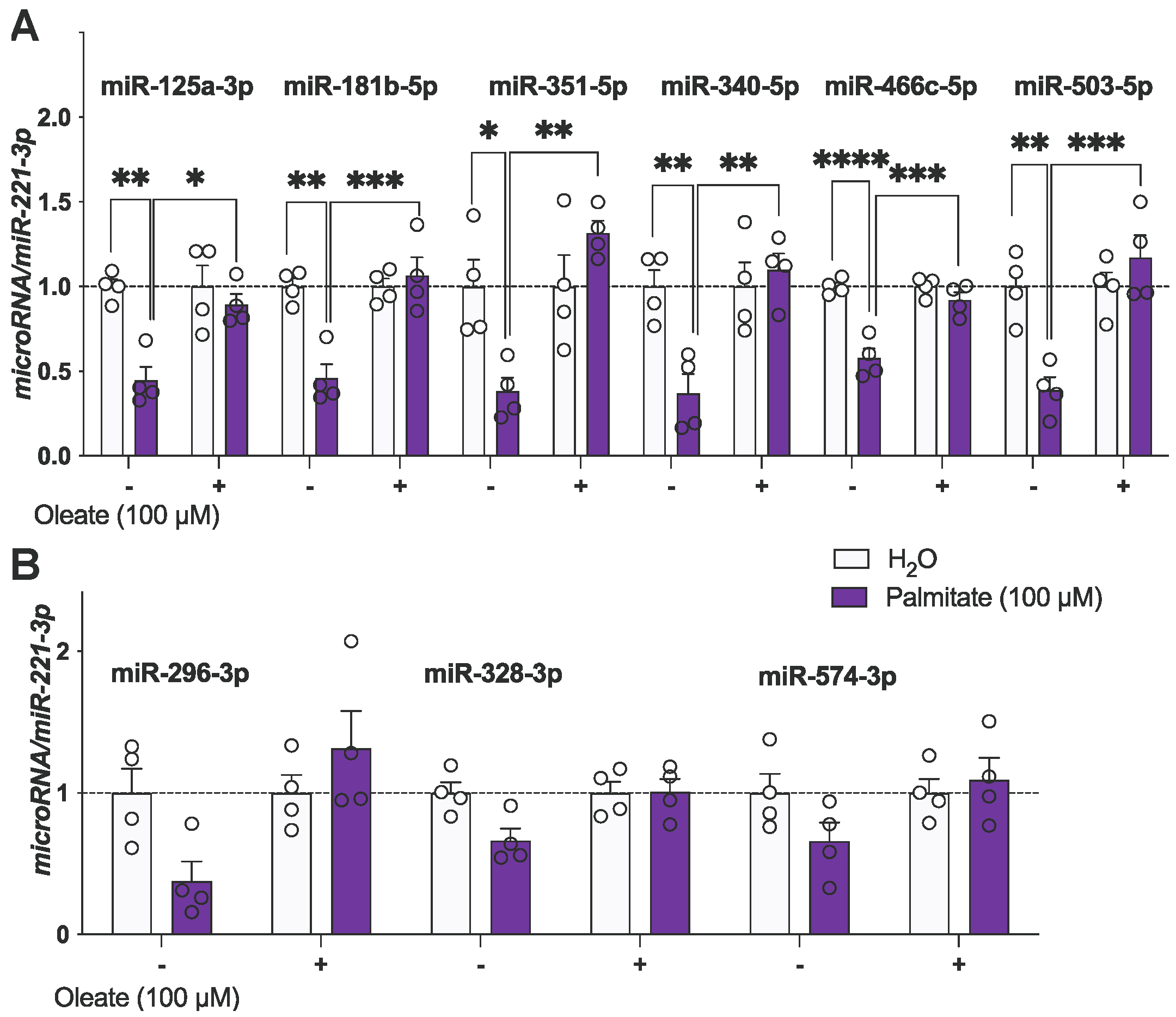
| Figure 2 | miR-125a | − | −0.55 | 0.1176 | ** 0.0025 |
| + | 0.45 | 0.1176 | * 0.0117 | ||
| miR-181b | − | −0.54 | 0.108 | ** 0.0015 | |
| + | 0.61 | 0.108 | *** 0.0006 | ||
| miR-351 | − | −0.62 | 0.1904 | * 0.0307 | |
| + | 0.94 | 0.1904 | ** 0.0018 | ||
| miR-340 | − | −0.63 | 0.161 | ** 0.0097 | |
| + | 0.73 | 0.161 | ** 0.0034 | ||
| miR-466c | − | −0.42 | 0.05808 | **** <0.0001 | |
| + | 0.34 | 0.05808 | *** 0.0004 | ||
| miR-503 | − | −0.61 | 0.1408 | ** 0.0046 | |
| + | 0.78 | 0.1408 | *** 0.0006 | ||
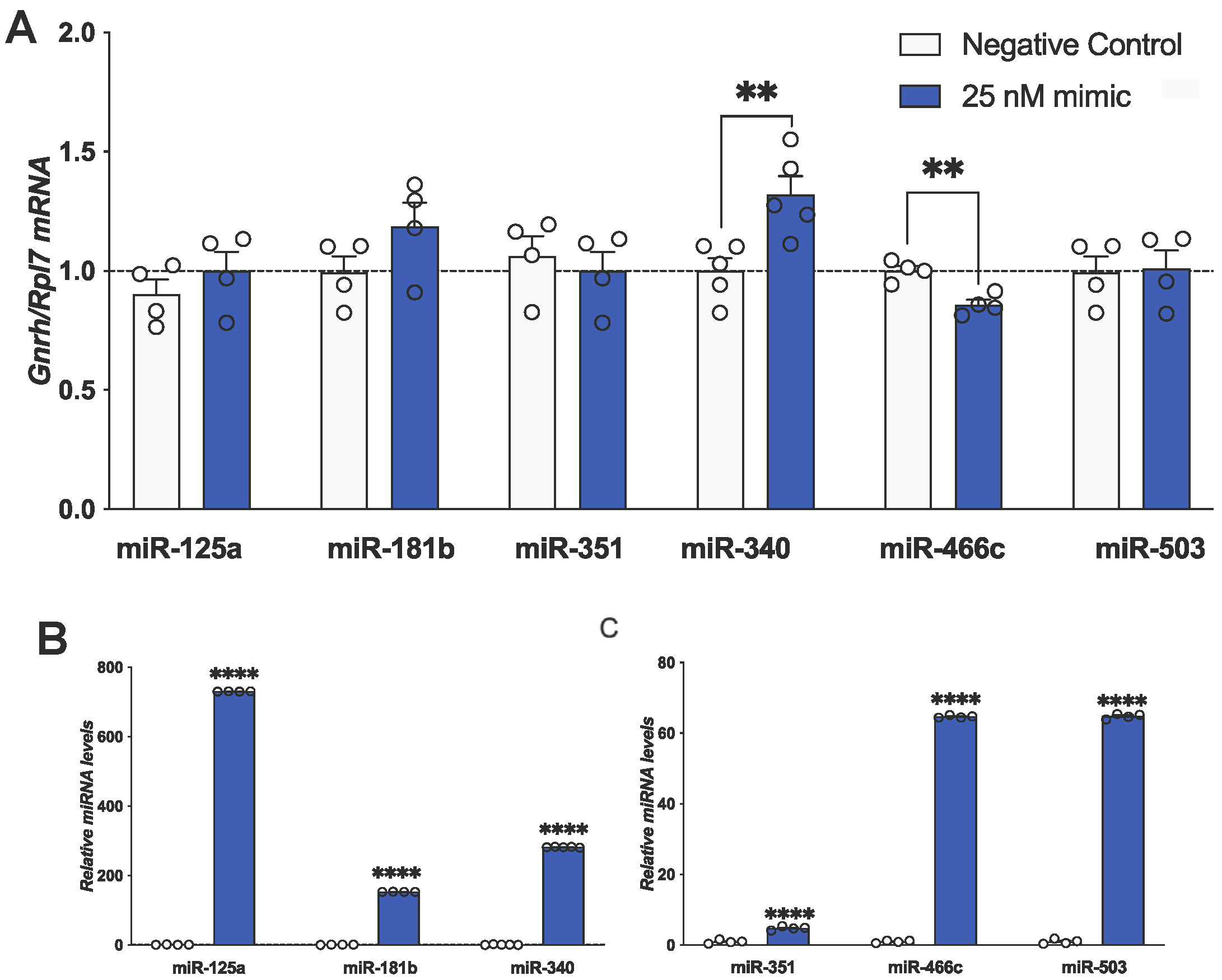
| Figure 3A | Gnrh | 25 nM of miR-466c | −0.14 | 0.03007 | ** 0.0032 |
| 25 nM of miR-340 | 0.32 | 0.09319 | ** 0.0088 | ||
| Figure 4A | Gata4 | 25 nM of miR-466c | −0.34 | 0.1058 | * 0.0179 |
| Chop | −0.2 | 0.01704 | **** <0.0001 | ||
| Per2 | 0.8 | 0.09364 | ** 0.0010 | ||
| Figure 4B | Cebpb | 25 nM of miR-340 | 0.31 | 0.04581 | *** 0.0002 |
| 0ct1 | 0.17 | 0.05706 | * 0.0157 | ||
| Gata4 | 0.25 | 0.08935 | * 0.0225 | ||
| Per2 | 0.46 | 0.02114 | **** <0.0001 | ||
| Figure 5 | Gnrh | 100 µM of palmitate + NC | 0.56 | 0.1526 | * 0.0309 |
| 100 µM of palmitate + 25 nM of miR-340 | 0.69 | 0.1526 | ** 0.0074 |



3. Results
3.1. Oleate Protects against Palmitate-Mediated Upregulation of Gnrh mRNA Expression
3.2. Analysis of miRNAs Expressed in the mHypoA-GnRH/GFP Neurons
3.3. Palmitate Alters miRNA Expression in mHypoA-GnRH/GFP Cells, While Oleate Prevents Palmitate-Induced Dysregulation
3.4. miR-466c Downregulates While miR-340 Upregulates Gnrh mRNA Levels in mHypoA-GnRH/GFP Neurons
3.5. miR-466c and miR-340 Also Alter Transcriptional Regulators of Gnrh in mHypoA-GnRH/GFP Neurons
3.6. miR-466c Blocks the Palmitate-Mediated Upregulation of Gnrh in mHypoA-GnRH/GFP Neurons
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panth, N.; Gavarkovs, A.; Tamez, M.; Mattei, J. The Influence of Diet on Fertility and the Implications for Public Health Nutrition in the United States. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belan, M.; Harnois-Leblanc, S.; Laferrère, B.; Baillargeon, J.-P. Optimizing reproductive health in women with obesity and infertility. CMAJ 2018, 190, E742–E745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belsham, D.D.; Lovejoy, D.A. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone: Gene evolution, expression, and regulation. Vitam. Horm. 2005, 71, 59–94. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.E.; Lawson, M.A.; Belsham, D.D.; Eraly, S.A.; Mellon, P.L. Molecular Aspects of GnRH Gene Expression; JAI Press, Inc.: Greenwich, UK, 1997; Volume 1, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, M.A.; Whyte, D.B.; Mellon, P.L. GATA factors are essential for activity of the neuron-specific enhancer of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 3596–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieu, C.V.; Loganathan, N.; Belsham, D.D. Mechanisms Driving Palmitate-Mediated Neuronal Dysregulation in the Hypothalamus. Cells 2021, 10, 3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blouet, C.; Schwartz, G.J. Hypothalamic nutrient sensing in the control of energy homeostasis. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 209, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migrenne, S.; Cruciani-Guglielmacci, C.; Kang, L.; Wang, R.; Rouch, C.; Lefèvre, A.-L.; Ktorza, A.; Routh, V.H.; Levin, B.E.; Magnan, C. Fatty Acid Signaling in the Hypothalamus and the Neural Control of Insulin Secretion. Diabetes 2006, 55, S139–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.Q.; Ramos, E.H.; Belsham, D.D. Induction of Gnrh mRNA expression by the omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid and the saturated fatty acid palmitate in a GnRH-synthesizing neuronal cell model, mHypoA-GnRH/GFP. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 426, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexheimer, P.J.; Cochella, L. MicroRNAs: From Mechanism to Organism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.J.; Mercader, J.M.; Catalán, V.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Pueyo, N.; Sabater, M.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Anglada, R.; Fernandez-Formoso, J.A.; Ricart, W.; et al. Targeting the circulating microRNA signature of obesity. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomino, G.; Russo, P.; Marena, P.; Lauria, F.; Venezia, A.; Ahrens, W.; De Henauw, S.; De Luca, P.; Foraita, R.; Günther, K.; et al. Circulating microRNAs are associated with early childhood obesity: Results of the I.Family Study. Genes Nutr. 2019, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandao, B.B.; Lino, M.; Kahn, C.R. Extracellular miRNAs as mediators of obesity-associated disease. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzaro, G.; Filardi, T.; Sabato, C.; Vacca, A.; Migliaccio, S.; Morano, S.; Ferretti, E. Tissue and circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of response to obesity treatment strategies. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oses, M.; Margareto Sanchez, J.; Portillo, M.P.; Aguilera, C.M.; Labayen, I. Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers of Obesity and Obesity-Associated Comorbidities in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger, M.; Altirriba, J.; García, A.; Esteban, Y.; Castaño, C.; García-Lavandeira, M.; Alvarez, C.V.; Gomis, R.; Claret, M. Deletion of miRNA processing enzyme Dicer in POMC-expressing cells leads to pituitary dysfunction, neurodegeneration and development of obesity. Mol. Metab. 2012, 2, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, I.A.; Hajdukiewicz, K.; Reymann, J.; Beneke, J.; Czajkowski, R.; Roth, L.C.; Novak, M.; Roller, A.; Dörner, N.; Starkuviene, V.; et al. Hypothalamic miR-103 protects from hyperphagic obesity in mice. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10659–10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhn, S.; Ali, A.; Hossain, M.; Hoelker, M.; Salilew-Wondim, D.; Anthony, R.V.; Tesfaye, D. MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Regulatory Mechanisms in Mammalian Female Reproductive Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Na, H.-M.; Peng, G.; Pu, J.; Liu, P. Alteration of microRNA expression correlates to fatty acid-mediated insulin resistance in mouse myoblasts. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, K.W.Y.; He, W.; Loganathan, N.; Belsham, D.D. Bisphenol A Alters the Levels of miRNAs That Directly and/or Indirectly Target Neuropeptide Y in Murine Hypothalamic Neurons. Genes 2023, 14, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balcells, I.; Cirera, S.; Busk, P.K. Specific and sensitive quantitative RT-PCR of miRNAs with DNA primers. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Ando, H.; Daikoku, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Mieda, M.; Mizumoto, Y.; Iizuka, T.; Kagami, K.; Hosono, T.; Nomura, S.; et al. The Circadian Clock, Nutritional Signals and Reproduction: A Close Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullokandov, G.; Baccarini, A.; Ruzo, A.; Jayaprakash, A.D.; Tung, N.; Israelow, B.; Evans, M.J.; Sachidanandam, R.; Brown, B.D. High-throughput assessment of microRNA activity and function using microRNA sensor and decoy libraries. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataruka, S.; Modrak, M.; Kinterova, V.; Malik, R.; Zeitler, D.M.; Horvat, F.; Kanka, J.; Meister, G.; Svoboda, P. MicroRNA dilution during oocyte growth disables the microRNA pathway in mammalian oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 8050–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlwraith, E.K.; Belsham, D.D. Palmitate alters miR-2137 and miR-503-5p to induce orexigenic Npy in hypothalamic neuronal cell models: Rescue by oleate and docosahexaenoic acid. J. Neuroendocr. 2023, 35, e13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrel, G.; Simon, V.; Denoyelle, C.; Cruciani-Guglielmacci, C.; Migrenne, S.; Counis, R.; Magnan, C.; Cohen-Tannoudji, J. Unsaturated fatty acids stimulate LH secretion via novel PKCε and -θ in gonadotrope cells and inhibit GnRH-induced LH release. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3905–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestris, E.; de Pergola, G.; Rosania, R.; Loverro, G. Obesity as disruptor of the female fertility. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Tamimi, W.; Jones, G.; Jawdat, D.; Tamim, H.; Al-Dorzi, H.M.; Sadat, M.; Afesh, L.; Sakhija, M.; Al-Dawood, A. Free Fatty Acids’ Level and Nutrition in Critically Ill Patients and Association with Outcomes: A Prospective Sub-Study of PermiT Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassilian, S.; Ahmed, S.; Lim, S.K.; Boros, L.G.; Mao, C.S.; Lee, W.-N.P. Loss of regulation of lipogenesis in the Zucker diabetic rat. II. Changes in stearate and oleate synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2002, 282, E507–E513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Koutsari, C.; Ali, A.H.; Mundi, M.S.; Jensen, M.D. Storage of circulating free fatty acid in adipose tissue of postabsorptive humans: Quantitative measures and implications for body fat distribution. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Pillon, N.J.; Sivaloganathan, D.M.; Costford, S.R.; Liu, Z.; Théret, M.; Chazaud, B.; Klip, A. Palmitoleate Reverses High Fat-induced Proinflammatory Macrophage Polarization via AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16979–16988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, B.; Lee, H.-K.; Querfurth, H.W. Oleate prevents palmitate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, insulin resistance and inflammatory signaling in neuronal cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, B.; Querfurth, H.W. Palmitate activates mTOR/p70S6K through AMPK inhibition and hypophosphorylation of raptor in skeletal muscle cells: Reversal by oleate is similar to metformin. Biochimie 2015, 118, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Soibam, B.; Benham, A.; Xu, X.; Chopra, M.; Peng, X.; Yu, W.; Bao, W.; Liang, R.; Azares, A.; et al. miR-322/-503 cluster is expressed in the earliest cardiac progenitor cells and drives cardiomyocyte specification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9551–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Hossain, M.M.; Read, D.E.; Hetz, C.; Samali, A.; Gupta, S. PERK regulated miR-424(322)-503 cluster fine-tunes activation of IRE1 and ATF6 during Unfolded Protein Response. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wan, M.; Zeng, X.; Wu, J. miR-340: A multifunctional role in human malignant diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, P.; Väänänen, M.-A.; Kolari, I.-L.; Mäkinen, P.I.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Weinberg, M.S.; Morris, K.V.; Korhonen, P.; Malm, T.; Ylä-Herttuala, S.; et al. Nuclear microRNA-466c regulates Vegfa expression in response to hypoxia. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colden, M.; Dar, A.A.; Saini, S.; Dahiya, P.V.; Shahryari, V.; Yamamura, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Stein, G.; Dahiya, R.; Majid, S. MicroRNA-466 inhibits tumor growth and bone metastasis in prostate cancer by direct regulation of osteogenic transcription factor RUNX2. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Ling, Z.-M.; Fu, R.; Li, Y.-Q.; Cheng, X.; Song, F.-H.; Luo, H.-X.; Zhou, L.-H. Time-specific microRNA changes during spinal motoneuron degeneration in adult rats following unilateral brachial plexus root avulsion: Ipsilateral vs. contralateral changes. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, C.H.; Friedman, R.C.; Ruby, J.G.; Bartel, D.P. Formation, regulation and evolution of Caenorhabditis elegans 3′UTRs. Nature 2011, 469, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Campbell, S.G.; Engelman, D.M. MicroRNA function can be reversed by altering target gene expression levels. iScience 2021, 24, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.M.A.; Chan, B.P.K.; Roy, D.; Cai, F.; Belsham, D.D. Expression of circadian rhythm genes in gonadotropin-releasing hormone-secreting GT1-7 neurons. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 5285–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reza, A.M.M.T.; Choi, Y.; Han, S.G.; Song, H.; Park, C.; Hong, K.; Kim, J. Roles of microRNAs in mammalian reproduction: From the commitment of germ cells to peri-implantation embryos. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 415–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Zhi, D. The experimental study of miRNA in pituitary adenomas. Turk. Neurosurg. 2013, 23, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, N.; Shareghi-Oskoue, O.; Aghebati-Maleki, L.; Danaii, S.; Heris, J.A.; Soltani-Zangbar, M.S.; Kamrani, A.; Yousefi, M. Role of miRNAs interference on ovarian functions and premature ovarian failure. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothnick, W.B.; Healy, C. Estrogen induces distinct patterns of microRNA expression within the mouse uterus. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 17, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillot, G.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Pierredon, S.; Gratadou, L.; Schmidt, S.; Bénès, V.; Roché, H.; Dalenc, F.; Auboeuf, D.; Millevoi, S.; et al. Widespread estrogen-dependent repression of micrornas involved in breast tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8332–8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Liu, M.; Zhou, C.; You, X.; Su, T.; Yang, Y.; Xu, D. Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in testes of Duroc and Meishan boars. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, H.; Har-Paz, E.; Gindi, N.; Miller, I.; Shalgi, R. Pre-ovulatory intercellular regulation of miR-125a-3p within mouse ovarian follicles. Reproduction 2020, 159, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Rpl7 | F: TCG CAG AGT TGA AGG TGA AG R: GCC TGT ACT CCT TGT GAT AGT G | 114 |
| Gnrh | F: CGT TCA CCC CTC AGG GAT CT R: CTC TTC AAT CAG ACT TTC CAG AGC | 51 |
| Oct-1 | F: AGG AGC GAG TCA AGA TG R: CCA TTG GTT TGT GTG CCT GT | 132 |
| Gata4 | F: AGA CAC CCC AAT CTC GAT ATG TT R: ATT GCA CAG GTA GTG TCC CG | 117 |
| Cebpb | F: CTG AGC GAC GAG TAC AAG ATG R: GAA CAA GTT CCG CAG GGT | 186 |
| Otx2 | F: TGT TAC CAG CCA TCT CAA TC R: AGA GGC AGT TTG GTC CTT AT | 118 |
| Chop | F: TAT GAG GAT CTG CAG GAG R: CAG GGT CAA GAG TAG TGA AG | 109 |
| Per2 | F: TCA TCA TTG GGA GGC ACA AA R: GCA TCA GTA GCC GGT GGA TT | 135 |
| Bmal1 | F: GGG AGG CCC ACA GTC AGA TT R: GTA CCA AAG AAG CCA ATT CAT CAA | 78 |
| microRNA | Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|
| mmu-miR-125a-3p | F: CAG ACA GGT GAG GTT CTT G R: TCC AGT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTG GCT |
| mmu-miR-181b-5p | F: GCA GAA CAT TCA TTG CTG TC R: TCC AGT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTA ACC CA |
| mmu-miR-296-3p | F: GGA GGG TTG GGT GGA G R: GTC CAG TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT GGA GA |
| mmu-miR-328-3p | F: GCC CTC TCT GCC CTT C R: GGT CCA GTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TAC G |
| mmu-miR-340-5p | F: GCG CAG TTA TAA AGC AAT GAG R: GCT CCA GTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TAA TCA GT |
| mmu-miR-351-5p | F: GAG GAG CCC TTT GAG C R: GGT CCA GTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TCA |
| mmu-miR-466c-5p | F: GTG ATG TGT GTG TGC ATG T R: CAG GTC CAG TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT ATA TG |
| mmu-miR-485-5p | F: AGT CAT ACA CGG CTC TCC R: GCT CCA GTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TGA G |
| mmu-miR-503-5p | F: AGC AGC GGG AAC AGT R: CCA GTT TTT TTT TTT TTT TCT GCA GT |
| mmu-miR-574-3p | F: ACG CTC ATG CAC ACA C R: GTC CAG TTT TTT TTT TTT TTT GTG G |
| mmu-let-7k | F: GCA GTG AGG TAG GAG GT R: TCC AGT TTT TTT TTT TTT TTC ACA CA |
| miRNA | Hypothalamus | mHypoE-46 | mHypoA-59 | PA Array Fold Change | Average CT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not Conserved | mmu-miR-125a-3p | 88 | 94 | 93 | −1.56 | 26.5 |
| mmu-miR-181b-5p | 97 | 97 | 97 | −1.25 | 22.6 | |
| mmu-miR-296-3p | 88 | 96 | 93 | −1.3 | 28.5 | |
| mmu-miR-328-3p | 98 | 93 | 94 | −1.4 | 27.2 | |
| mmu-miR-351-5p | 87 | 95 | 96 | −1.64 | 26.9 | |
| mmu-miR-466c-5p | 83 | 77 | 83 | −1.43 | 28.9 | |
| mmu-miR-503-5p, | 72 | 89 | 92 | −2.33 | 28.1 | |
| mmu-miR-574-3p | 89 | 93 | 96 | −1.39 | 25.9 | |
| mmu-let-7k | 95 | 96 | 95 | −1.38 | 35.9 | |
| Highly Conserved | mmu-miR-340-5p | 75 | 48 | 39 | −1.3 * | 26.9 |
| mmu-miR-485-5p | 90 | 83 | 78 | −1.58 | N/D | |
| mmu-mir-539-3p | 36 | 24 | 10 | 1 * | N/D | |
| mmu-miR-876-5p | 2 | 8 | 0 | −1.01 * | N/D | |
| mmu-miR-224-5p | 44 | 65 | 76 | 1.35 | N/D |
| microRNA | Gnrh 3′UTR Binding Site |
|---|---|
| mmu-miR-340-5p | 799–806 |
| mmu-miR-351-5p | 1241–1248 |
| mmu-miR-503-5p | 1918–1924 |
| mmu-miR-125a-3p | 2213–2219 |
| mmu-miR-466c-5p | 2915-2921 |
| mmu-miR-181b-5p | 4235–4242 |
| hsa-miR-340-5p | 65–71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nkechika, V.; Zhang, N.; Belsham, D.D. The Involvement of the microRNAs miR-466c and miR-340 in the Palmitate-Mediated Dysregulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Gene Expression. Genes 2024, 15, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15040397
Nkechika V, Zhang N, Belsham DD. The Involvement of the microRNAs miR-466c and miR-340 in the Palmitate-Mediated Dysregulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Gene Expression. Genes. 2024; 15(4):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15040397
Chicago/Turabian StyleNkechika, Vanessa, Ningtong Zhang, and Denise D. Belsham. 2024. "The Involvement of the microRNAs miR-466c and miR-340 in the Palmitate-Mediated Dysregulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Gene Expression" Genes 15, no. 4: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15040397
APA StyleNkechika, V., Zhang, N., & Belsham, D. D. (2024). The Involvement of the microRNAs miR-466c and miR-340 in the Palmitate-Mediated Dysregulation of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Gene Expression. Genes, 15(4), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15040397





