FOXP3: A Player of Immunogenetic Architecture in Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
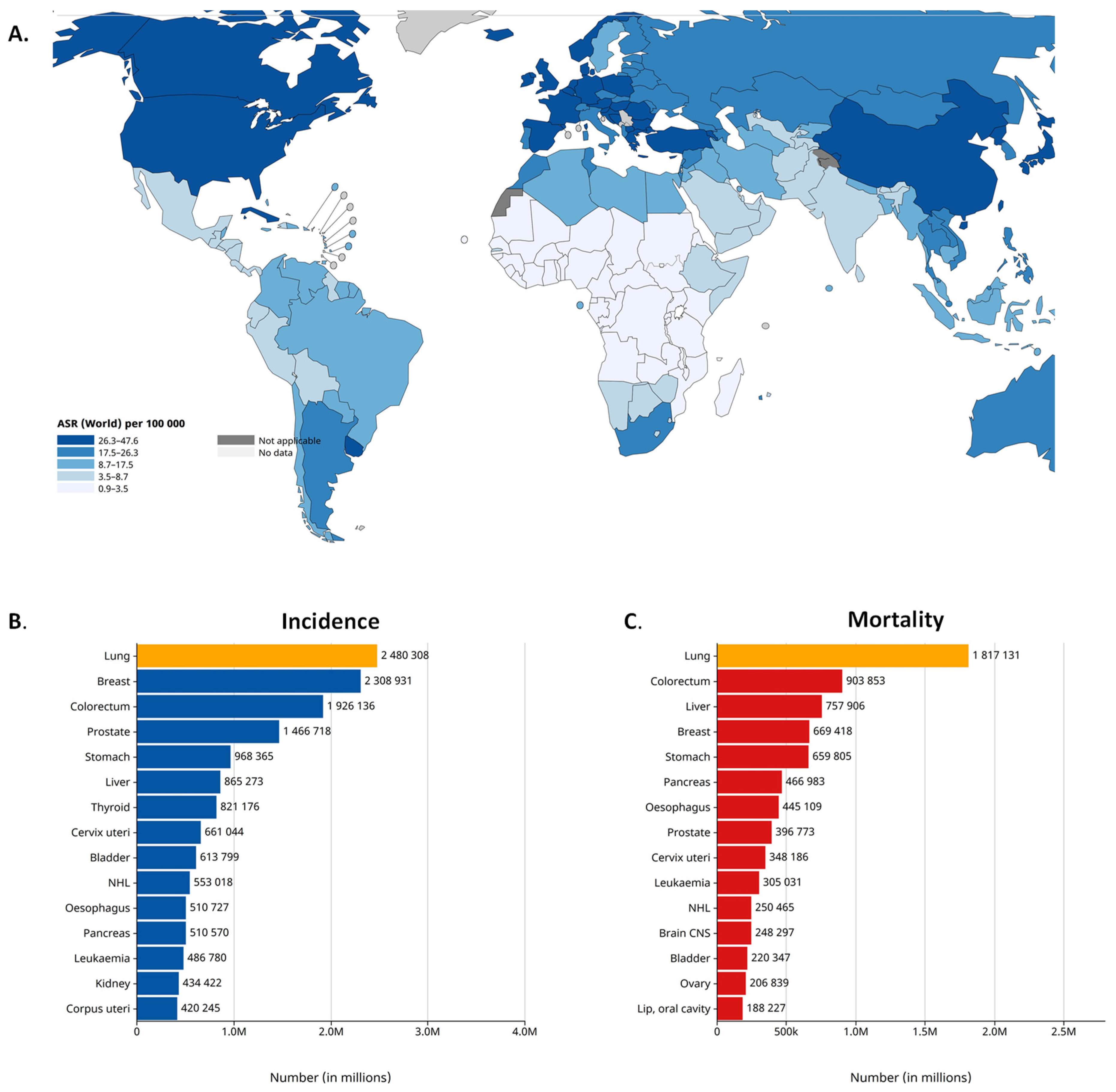
2. Lung Cancer Epidemiology
3. Mutations/Genetic Variants in the FOXP3 Gene in NSCLC
4. FOXP3 Expression in NSCLC
5. Presence of FOXP3 in the TME
6. Spatial Architecture of Tumor-Infiltrating FOXP3+ T Cells in TME
7. FOXP3 Modulates NSCLC Proliferation and Metastatic Potential of NSCLC Cells
8. FOXP3 Impact to NSCLC Cancer Stemness
9. Prognostic Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating FOXP3+ T Lymphocytes
10. Impact of Cancer Therapy on FOXP3+ TILs
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DFS | disease-free survival |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EGFR-TKI | EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| FOXP3 | forkhead box protein 3 |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| ICI | immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| IF | immunofluorescence staining |
| IHC | immunohistochemical staining |
| IL | interleukin |
| IPEX | Immunodysregulation Polyendocrinopathy Enteropathy X-linked |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma virus |
| LNM | lymph node metastases |
| LUAD | lung adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | lung squamous carcinoma |
| Ly-ext | extratumoral lymphatic permeation |
| m6A | N6-methyladenosine |
| NND | nearest neighbour distance |
| NSCLC | non-small-cell lung cancer |
| Nrp-1 | neuropilin-1 |
| PD-1 | programmed death-1 receptor |
| PD-L1 | programmed death-1 receptor ligand |
| r2 | coefficient of determination |
| rho | Spearman’s correlation coefficient |
| SCLC | small-cell lung cancer |
| SNPs | single-nucleotide polymorphisms |
| Tregs | regulatory T cells |
| FoxP3+ Tregs | tumor-infiltrating Tregs |
| TGF | transforming growth factor |
| Th1 | T helper 1 cell |
| Th17 | T helper 17 cell |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TRME2 | triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 |
| YTHDF | YTH domain family protein |
References
- Sakaguchi, S.; Sakaguchi, N.; Asano, M.; Itoh, M.; Toda, M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baecher-Allan, C.; Brown, J.A.; Freeman, G.J.; Hafler, D.A. CD4+CD25high regulatory cells in human peripheral blood. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenot, J.D.; Gavin, M.A.; Rudensky, A.Y. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunkow, M.E.; Jeffery, E.W.; Hjerrild, K.A.; Paeper, B.; Clark, L.B.; Yasayko, S.A.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Galas, D.; Ziegler, S.F.; Ramsdell, F. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.L.; Christie, J.; Ramsdell, F.; Brunkow, M.E.; Ferguson, P.J.; Whitesell, L.; Kelly, T.E.; Saulsbury, F.T.; Chance, P.F.; Ochs, H.D. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat. Genet. 2001, 27, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.M.; Rudensky, A.Y. Maintenance of the Foxp3-dependent developmental program in mature regulatory T cells requires continued expression of Foxp3. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honaker, Y.; Hubbard, N.; Xiang, Y.; Fisher, L.; Hagin, D.; Sommer, K.; Song, Y.; Yang, S.J.; Lopez, C.; Tappen, T.; et al. Gene editing to induce FOXP3 expression in human CD4(+) T cells leads to a stable regulatory phenotype and function. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, T.; Ma, Y. A comprehensive bioinformatics analysis of FOXP3 in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Medicine 2022, 101, e32102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohue, Y.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T (Treg) cells in cancer: Can Treg cells be a new therapeutic target? Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Nakata, M.; Hirami, Y.; Yukawa, T.; Maeda, A.; Tanemoto, K. Tumor-infiltrating Foxp3+ regulatory T cells are correlated with cyclooxygenase-2 expression and are associated with recurrence in resected non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Mimura, Y.; Aoe, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Matsuda, E.; Okabe, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Sugi, K.; Ueoka, H. Prognostic potential of FOXP3 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells combined with tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells. Lung Cancer 2012, 75, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Yang, F.; Yang, D.; Gao, A.; Lin, W.; Ma, X.; et al. B7-H3 in combination with regulatory T cell is associated with tumor progression in primary human non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 13987–13995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Kadota, K.; Sima, C.S.; Nitadori, J.; Rusch, V.W.; Travis, W.D.; Sadelain, M.; Adusumilli, P.S. Clinical impact of immune microenvironment in stage I lung adenocarcinoma: Tumor interleukin-12 receptor beta2 (IL-12Rbeta2), IL-7R, and stromal FoxP3/CD3 ratio are independent predictors of recurrence. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Pineros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Aluru, J.S.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Contemp. Oncol. 2021, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal-Mourino, A.; Ruano-Ravina, A.; Lorenzo-Gonzalez, M.; Rodriguez-Martinez, A.; Giraldo-Osorio, A.; Varela-Lema, L.; Pereiro-Brea, T.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Valdes-Cuadrado, L.; Perez-Rios, M. Epidemiology of stage III lung cancer: Frequency, diagnostic characteristics, and survival. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Vaccarella, S.; Morgan, E.; Li, M.; Etxeberria, J.; Chokunonga, E.; Manraj, S.S.; Kamate, B.; Omonisi, A.; Bray, F. Global variations in lung cancer incidence by histological subtype in 2020: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society: Cancer Facts and Figures 2023. American Cancer Society. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts-figures/2023-cancer-facts-figures.html (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Sereno, M.; Hernandez de Cordoba, I.; Gutierrez-Gutierrez, G.; Casado, E. Brain metastases and lung cancer: Molecular biology, natural history, prediction of response and efficacy of immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1297988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.E.M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France; Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (accessed on 22 February 2024).
- Harrison, P.T.; Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reita, D.; Pabst, L.; Pencreach, E.; Guerin, E.; Dano, L.; Rimelen, V.; Voegeli, A.C.; Vallat, L.; Mascaux, C.; Beau-Faller, M. Direct Targeting KRAS Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Resistance. Cancers 2022, 14, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, M.; Borgeaud, M.; Addeo, A.; Friedlaender, A. Oncogenic driver mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: Past, present and future. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 217–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchetta, R.; Barzaghi, F.; Roncarolo, M.G. From IPEX syndrome to FOXP3 mutation: A lesson on immune dysregulation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1417, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.; Goel, P.N.; Greene, M.I. Regulatory T Cells: Regulation of Identity and Function. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 750542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.M.; Zhang, W.D.; Shi, Z.E.; Zhang, M.Y.; Li, R.; Wang, Q.X.; Ji, X.L.; Qu, Y.Q. FOXP family DNA methylation correlates with immune infiltration and prognostic value in NSCLC. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 937069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazelzadeh Haghighi, M.; Ali Ghayumi, M.; Behzadnia, F.; Erfani, N. Investigation of FOXP3 genetic variations at positions -2383 C/T and IVS9+459 T/C in southern Iranian patients with lung carcinoma. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 465–471. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.Q.; Bo, Q.; Yong, W.; Qiu, Z.X.; Li, Y.L.; Li, W.M. FoxP3 genetic variants and risk of non-small cell lung cancer in the Chinese Han population. Gene 2013, 531, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ming, L. Functional Foxp3 polymorphisms and the susceptibility to cancer: An update meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qi, X.; Bian, C.; Ling, C.; Yi, T.; Mu, X.; Zhao, X. The association of FOXP3 gene polymorphisms with cancer susceptibility: A comprehensive systemic review and meta-analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, P.; Borilova, S.; Fabian, P.; Selingerova, I.; Novak, D.; Muller, P.; Kiss, I.; Vyzula, R. FoxP3 Expression in Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes as Potential Predictor of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Melanoma and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulos, F.I.; Papadaki, H.; Antonacopoulou, A.G.; Kottorou, A.; Gotsis, A.D.; Scopa, C.; Kalofonos, H.P.; Mouzaki, A. Association of FOXP3 expression with non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 1677–1683. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, D.; Yang, W.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Overexpression of the transcription factor FOXP3 in lung adenocarcinoma sustains malignant character by promoting G1/S transition gene CCND1. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 7395–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.Y.; Ng, C.S.H.; Yang, S.L.; Wang, S.; Zou, C.; Dong, Y.; Du, J.; Long, X.; et al. FOXP3 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and EMT in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Dai, L.; Liu, Q.; Jia, L.; Wang, H.; An, L.; Jing, X.; Liu, M.; Li, P.; et al. Foxp3 downregulation in NSCLC mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition via NF-kappaB signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
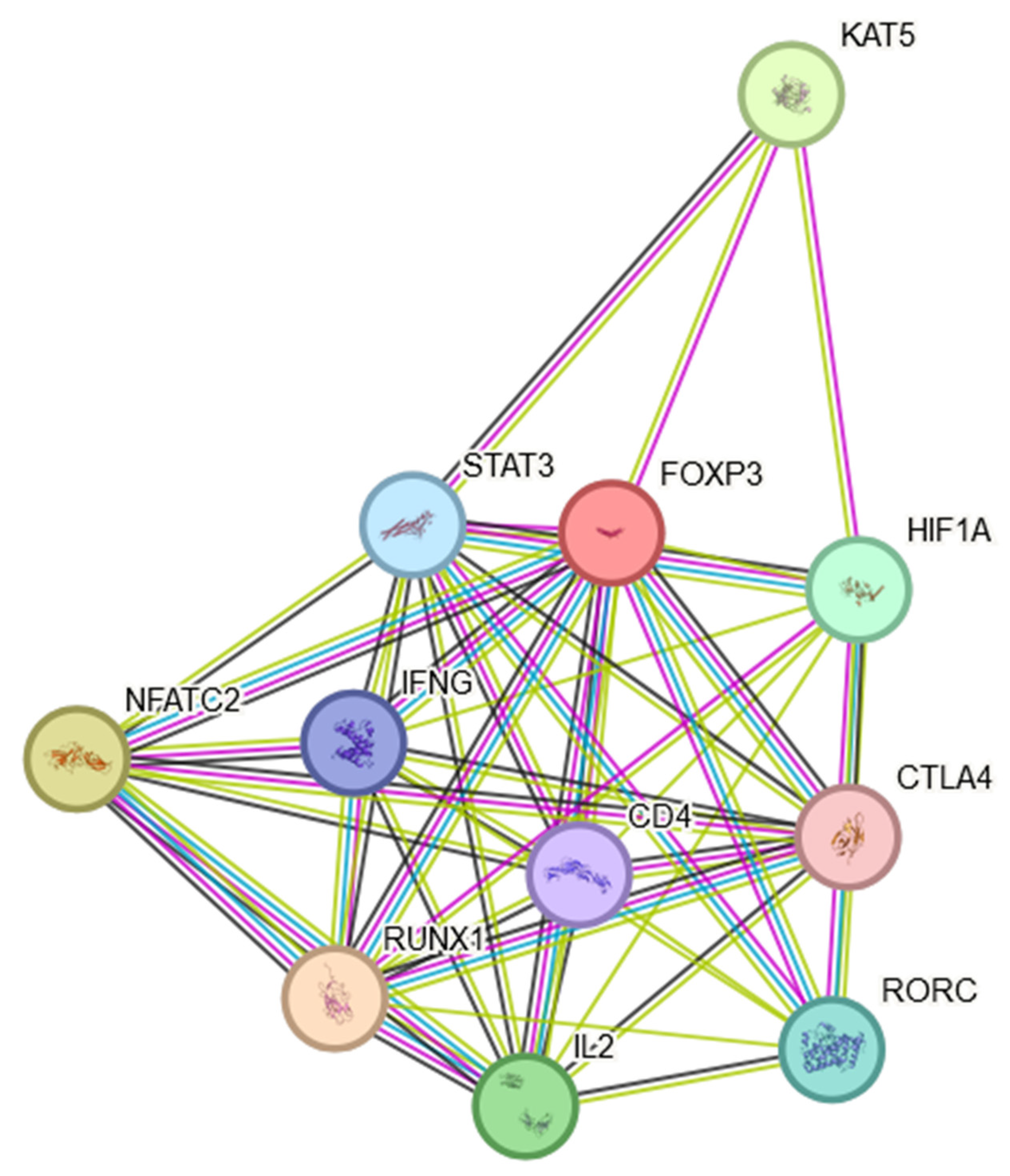
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dees, S.; Ganesan, R.; Singh, S.; Grewal, I.S. Regulatory T cell targeting in cancer: Emerging strategies in immunotherapy. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfani, N.; Mehrabadi, S.M.; Ghayumi, M.A.; Haghshenas, M.R.; Mojtahedi, Z.; Ghaderi, A.; Amani, D. Increase of regulatory T cells in metastatic stage and CTLA-4 over expression in lymphocytes of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, P.; Wei, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: New mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Ke, S.; Chen, J.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhao, G.; Wu, K.; Li, B.; et al. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and the immune escape in solid tumours. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 982986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, D.S.; Rexhepaj, E.; Gately, K.; Coate, L.; Delaney, D.; O’Donnell, D.M.; Kay, E.; O’Connell, F.; Gallagher, W.M.; O’Byrne, K.J. Tumour islet Foxp3+ T-cell infiltration predicts poor outcome in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1762–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekguc, M.; Wing, J.B.; Osaki, M.; Long, J.; Sakaguchi, S. Treg-expressed CTLA-4 depletes CD80/CD86 by trogocytosis, releasing free PD-L1 on antigen-presenting cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2023739118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togashi, Y.; Shitara, K.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunosuppression—Implications for anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.D.; Knab, L.M.; Blatner, N.R.; Haghi, L.; DeCamp, M.M.; Meyerson, S.L.; Heiferman, M.J.; Heiferman, J.R.; Gounari, F.; Bentrem, D.J.; et al. Preferential expansion of pro-inflammatory Tregs in human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzioannou, A.; Boumpas, A.; Papadopoulou, M.; Papafragkos, I.; Varveri, A.; Alissafi, T.; Verginis, P. Regulatory T Cells in Autoimmunity and Cancer: A Duplicitous Lifestyle. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 731947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.A.; Tucker-Heard, G.; Perdue, N.R.; Killebrew, J.R.; Urdahl, K.B.; Campbell, D.J. The transcription factor T-bet controls regulatory T cell homeostasis and function during type 1 inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Cai, S.; Hu, M.; Li, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; Sun, F.; Xing, L.; Sun, X. Functional status and spatial architecture of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells are associated with lymph node metastases in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wu, X.; Zhong, R.; Yu, T.; Cai, X.; Liu, J.; Wen, Y.; Ao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Profiling Tumor Immune Microenvironment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Multiplex Immunofluorescence. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 750046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, D.; Wauters, E.; Boeckx, B.; Aibar, S.; Nittner, D.; Burton, O.; Bassez, A.; Decaluwe, H.; Pircher, A.; Van den Eynde, K.; et al. Phenotype molding of stromal cells in the lung tumor microenvironment. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Park, H.J.; Son, J.; Lee, J.G.; Chung, K.Y.; Cho, N.H.; Shim, H.S.; Park, S.; Kim, G.; In Yoon, H.; et al. Tumor microenvironment dictates regulatory T cell phenotype: Upregulated immune checkpoints reinforce suppressive function. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; He, M.; Xie, C.; Zhong, R.; Liu, J.; Tang, C.; Li, C.; Xiong, S.; et al. Multiplex immunofluorescence and single-cell transcriptomic profiling reveal the spatial cell interaction networks in the non-small cell lung cancer microenvironment. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.Y.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Gai, X.D.; Jia, T.; Lei, Y.M.; Li, Y. FOXP3 and TLR4 protein expression are correlated in non-small cell lung cancer: Implications for tumor progression and escape. Acta Histochem. 2013, 115, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Fang, H.; He, C.; Pei, Y.; Gai, X. FOXP3 facilitates the invasion and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells through regulating VEGF, EMT and the Notch1/Hes1 pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, M.; Hu, C.; Chen, B.; Li, S. MALAT1 modulated FOXP3 ubiquitination then affected GINS1 transcription and drived NSCLC proliferation. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3870–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiri, S.; Shao, C.; Chen, B.; Wilson, A.N.; Yenerall, P.; Timmons, B.C.; Girard, L.; Tian, H.; Behrens, C.; Wistuba, I.I.; et al. GLI1 Blockade Potentiates the Antitumor Activity of PI3K Antagonists in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4448–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Gray, S.; Ng, C.S.H.; Du, J.; Underwood, M.J.; Li, M.Y.; Chen, G.G. EGFR-AS1/HIF2A regulates the expression of FOXP3 to impact the cancer stemness of smoking-related non-small cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919855228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Du, J.; Long, X.; Ng, C.S.; et al. Glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 stimulates FOXP3 to promote non-small cell lung cancer stemness. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 1839–1850. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsakis, A.; Koinis, F.; Katsarou, A.; Gioulbasani, M.; Aggouraki, D.; Kentepozidis, N.; Georgoulias, V.; Vetsika, E.K. Prognostic value of circulating regulatory T cell subsets in untreated non-small cell lung cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, F.; Takada, K.; Yamada, Y.; Oku, Y.; Kosai, K.; Ono, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Wakasu, S.; Oba, T.; Osoegawa, A.; et al. Combined Evaluation of Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ and FoxP3+ Lymphocytes Provides Accurate Prognosis in Stage IA Lung Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimi, T.; Nakai, T.; Aokage, K.; Tane, K.; Miyoshi, T.; Samejima, J.; Miyazaki, S.; Taki, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Sakashita, S.; et al. Prognostic impact of count of extratumoral lymphatic permeation in lung adenocarcinoma and its relation to the immune microenvironment. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Xiang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, A.; Shen, Y.; Li, G. Prognostic value of the common tumour-infiltrating lymphocyte subtypes for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarelli, E.; Lam, V.K.; Parra, E.R.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Behrens, C.; Diao, L.; Wang, J.; Blando, J.; Byers, L.A.; Yanamandra, N.; et al. High OX-40 expression in the tumor immune infiltrate is a favorable prognostic factor of overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, A.; Schilder-Tol, E.J.; Weening, J.J.; Aten, J. Strong expression of CD134 (OX40), a member of the TNF receptor family, in a T helper 2-type cytokine environment. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 64, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Inoue, Y.; Iwashita, Y.; Yamada, H.; Kawase, A.; Watanabe, T.; Tanahashi, M.; Ogawa, H.; Funai, K.; et al. YTHDF1 and YTHDF2 are associated with better patient survival and an inflamed tumor-immune microenvironment in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1962656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; Lu, Z.; Han, D.; Ma, H.; Weng, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, H.; He, C. N(6)-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wu, C.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, W.; Fang, Q.; et al. FOXP3-based immune risk model for recurrence prediction in small-cell lung cancer at stages I-III. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Schulte, A.; Arolt, C.; Tolkach, Y.; Reinhardt, H.C.; Buettner, R.; Quaas, A. Intratumoral Abundance of M2-Macrophages is Associated With Unfavorable Prognosis and Markers of T-Cell Exhaustion in Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crino, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Wen, H.; Guo, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Q.; Yuan, W.; Luo, R.; Lu, C.; Liu, R.; et al. Immunosuppressive TREM2(+) macrophages are associated with undesirable prognosis and responses to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, T.; Tian, X.; Li, W.; Zhao, R.; Yang, W.; Gao, Q.; Li, T.; Shim, J.H.; Zhang, C.; et al. A Small Molecule Antagonist of PD-1/PD-L1 Interactions Acts as an Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor for NSCLC and Melanoma Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 654463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.H.; Yang, J.C.; Mok, T.S.; Loong, H.H. Overview of current systemic management of EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S1), i3–i9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isomoto, K.; Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Shimizu, S.; Tomida, S.; Niwa, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Chiba, Y.; Kato, R.; et al. Impact of EGFR-TKI Treatment on the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2037–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Cao, Z.; Farazuddin, M.; Chen, J.; Janczak, K.W.; Tang, S.; Cannon, J.; Baker, J.R., Jr. A novel intranasal peptide vaccine inhibits non-small cell lung cancer with KRAS mutation. Cancer Gene Ther. 2024, 31, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziółkowska-Suchanek, I.; Żurawek, M. FOXP3: A Player of Immunogenetic Architecture in Lung Cancer. Genes 2024, 15, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15040493
Ziółkowska-Suchanek I, Żurawek M. FOXP3: A Player of Immunogenetic Architecture in Lung Cancer. Genes. 2024; 15(4):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15040493
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiółkowska-Suchanek, Iwona, and Magdalena Żurawek. 2024. "FOXP3: A Player of Immunogenetic Architecture in Lung Cancer" Genes 15, no. 4: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15040493





