Identification of Barley yellow mosaic virus Isolates Breaking rym3 Resistance in Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Phenotypic Observation
2.3. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.4. Analysis of RNA-Seq Data
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of BaYMV Strains
2.6. Correlation Analysis between BaYMV Encoded Protein Residue and the Virus Infection to rym3-Carrying Barley cv. New Sachiho Golden
2.7. Genome-Wide Association Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Barley Yellow Mosaic Virus Isolates on Breaking rym3 Varieties
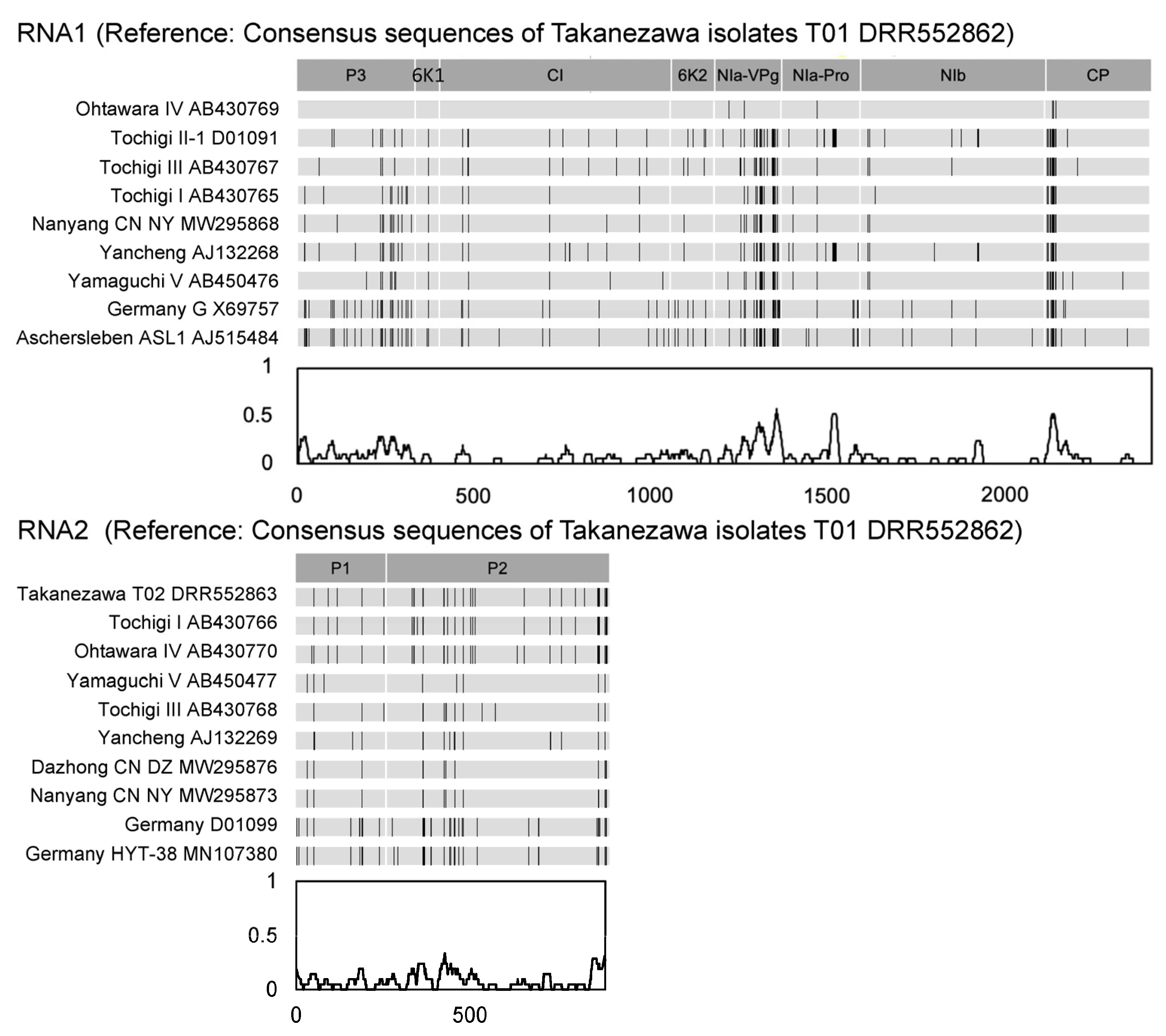
3.2. The Existence of Two Distinct BaYMV Isolates in Takanezawa
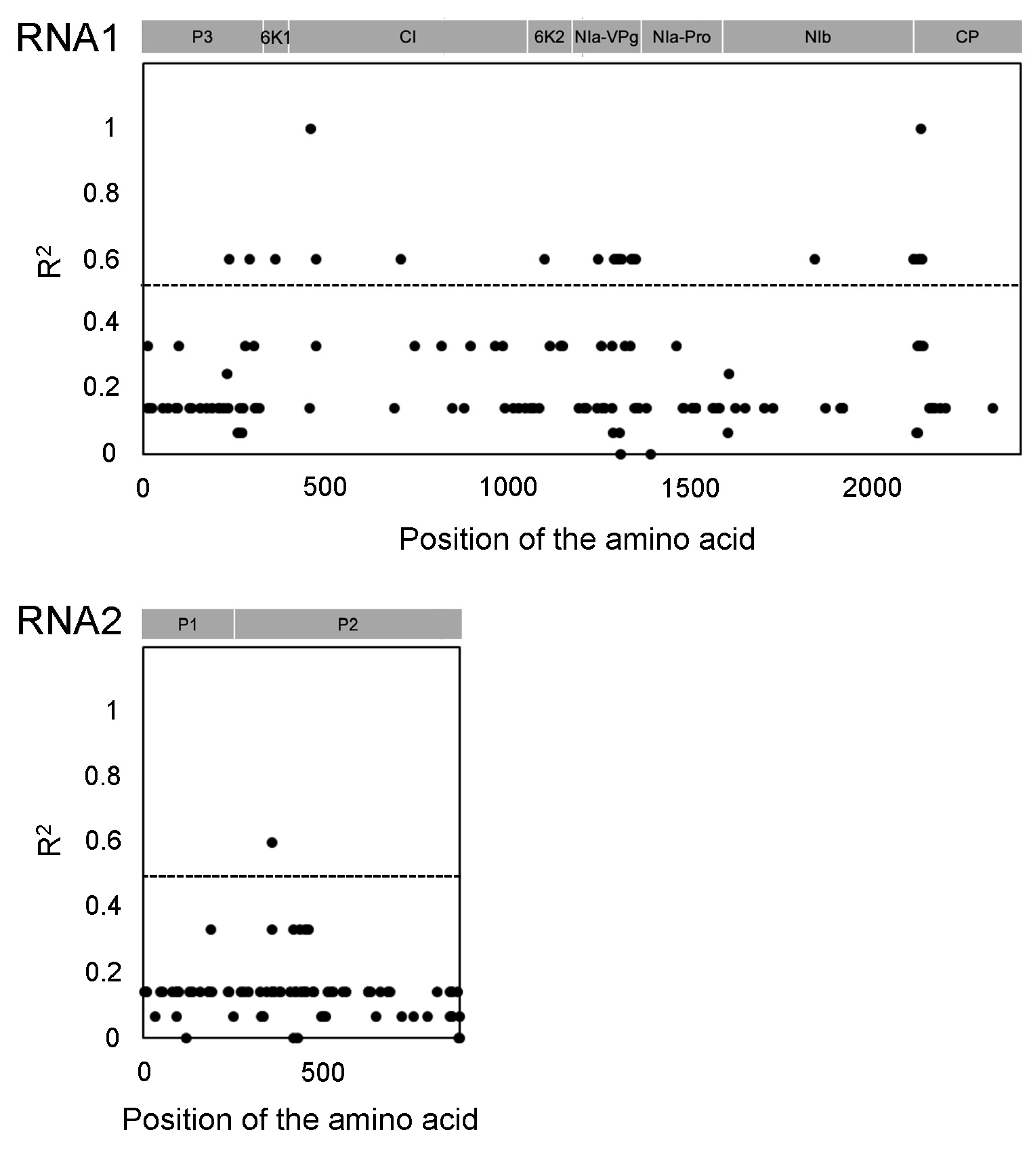
3.3. Variable Sites of Virus Sequence in Amino Acid
3.4. Amino Acid Changes in NIa-VPg Correlated with Pathogenicity
4. Discussion
4.1. rym3 Resistance Breaking in BaYMV-Infected Field
4.2. Co-Existence Isolates of BaYMV Identified in Takanezawa
4.3. The Determinant Protein Responsible for Breaking rym3 Resistance
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanyuka, K.; Ward, E.; Adams, M.J. Polymyxa graminis and the cereal viruses it transmits: A research challenge. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 4, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedt, W.; Kaiser, R.; Götz, R.; Umbach, H. 16. Genetic basis of breeding for resistance to barley yellow mosaic virus (BaYMV). In Proceedings of a Conference at the University of St Andrews; Association of Applied Biologists, AAB Office, c/o Institute of Horticultural Research, Wellesbourne: Warwick, UK, 1987; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.; Yoshida, H.; Sotome, K. Breeding for resistance to yellow mosaic disease in malting barley. Barley Genet. Newsl. 1987, 5, 667–672. [Google Scholar]
- Seko, H. Development of a two-rowed malting barley cultivar resistant to barley yellow mosaic. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 1987, 21, 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sekiwa, T.; Ohtsuka, M.; Sotome, T.; Oda, S. Effects of barley yellow mosaic virus infection on yield and malting quality of barley. Bull. Tochigi Prefect. Agric. Exp. Stn. 2002, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kihara, M. Progress on Malting Barley Breeding-from the Past to the Future. J. Brew. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 106, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedt, W.; Ordon, F. Barley production and breeding in Europe: Modern cultivars combine disease resistance, malting quality and high yield. In Advance in Barley Sciences, Proceedings of 11th International Barley Genetics Symposium, Hangzhou, China, 15–20 April 2012; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 389–400. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Kan, J.; Ordon, F.; Perovic, D.; Yang, P. Bymovirus-induced yellow mosaic diseases in barley and wheat: Viruses, genetic resistances and functional aspects. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inouye, T. Rod-shaped particles found in barley yellow mosaic. Nogaku Kenkyu 1964, 50, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Inouye, T. Rod-shaped particles associated with necrosis mosaic of rice. Jpn. J. Phytopathol. 1968, 34, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.; Zerbini, F.; French, R.; Rabenstein, F.; Stenger, D.; Valkonen, J. Family Potyviridae. In Virus Taxonomy, 9th Report of the International Committee for Taxonomy of Viruses; Elsevier: London, UK; Academic Press: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pasin, F.; Daros, J.A.; Tzanetakis, I.E. Proteome expansion in the Potyviridae evolutionary radiation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuac011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue-Nagata, A.K.; Jordan, R.; Kreuze, J.; Li, F.; López-Moya, J.J.; Mäkinen, K.; Ohshima, K.; Wylie, S.J.; Consortium, I.R. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Potyviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, J.C.; Jensen, P.E.; Schaad, M.C. Genetic evidence for an essential role for potyvirus CI protein in cell-to-cell movement. Plant J. 1998, 14, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochor, J.; Babula, P.; Adam, V.; Krska, B.; Kizek, R. Sharka: The past, the present and the future. Viruses 2012, 4, 2853–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urcuqui-Inchima, S.; Haenni, A.-L.; Bernardi, F. Potyvirus proteins: A wealth of functions. Virus Res. 2001, 74, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.-Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-P. The ‘6K1’protein of a strain of Soybean mosaic virus localizes to the cell periphery. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, B.Y.-W.; Miller, W.A.; Atkins, J.F.; Firth, A.E. An overlapping essential gene in the Potyviridae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5897–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayapalani, P.; Maeshima, M.; Nagasaki-Takekuchi, N.; Miller, W.A. Interaction of the trans-frame potyvirus protein P3N-PIPO with host protein PCaP1 facilitates potyvirus movement. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Zhang, C.; Hong, J.; Xiong, R.; Kasschau, K.D.; Zhou, X.; Carrington, J.C.; Wang, A. Formation of complexes at plasmodesmata for potyvirus intercellular movement is mediated by the viral protein P3N-PIPO. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.-H.; Hajimorad, M. Mutational analysis of the putative pipo of soybean mosaic virus suggests disruption of PIPO protein impedes movement. Virology 2010, 400, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskelin, K.; Hafrén, A.; Rantalainen, K.I.; Mäkinen, K. Potyviral VPg enhances viral RNA translation and inhibits reporter mRNA translation in planta. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9210–9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, N.; Perovic, D.; Kumlehn, J.; Pellio, B.; Stracke, S.; Streng, S.; Ordon, F.; Graner, A. The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E confers multiallelic recessive Bymovirus resistance in Hordeum vulgare (L.). Plant J. 2005, 42, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanyuka, K.; Druka, A.; Caldwell, D.G.; Tymon, A.; McCallum, N.; Waugh, R.; Adams, M.J. Evidence that the recessive bymovirus resistance locus rym4 in barley corresponds to the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E gene. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 6, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robaglia, C.; Caranta, C. Translation initiation factors: A weak link in plant RNA virus infection. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roudet-Tavert, G.; Michon, T.; Walter, J.; Delaunay, T.; Redondo, E.; Le Gall, O. Central domain of a potyvirus VPg is involved in the interaction with the host translation initiation factor eIF4E and the viral protein HcPro. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Shirako, Y. Bymovirus reverse genetics: Requirements for RNA2-encoded proteins in systemic infection. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.J.; Antoniw, J.F.; Beaudoin, F. Overview and analysis of the polyprotein cleavage sites in the family Potyviridae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 6, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwazaki, S.; Hayano, Y.; Minobe, Y.; Omura, T.; Hibino, H.; Tsuchizaki, T. Nucleotide Sequence of the Capsid Protein Gene of Barley Yellow Mosaic Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 1989, 70, 3015–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishigawa, H.; Hagiwara, T.; Yumoto, M.; Sotome, T.; Kato, T.; Natsuaki, T. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of Barley yellow mosaic virus. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotome, T.; Kawada, N.; Kato, T.; Sekiwa, T.; Nishigawa, H.; Natsuaki, T.; Kimura, K.; Maeoka, Y.; Nagamine, T.; Kobayashi, S.-I.; et al. The current and new strains of Barley yellow mosaic virus (BaYMV) in Tochigi prefecture. Jpn. J. Crop Sci. 2010, 79, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Toshima, I.; Ogawa, K. Reaction of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars and lines to barley yellow mosaic virus strains. Jpn. J. Breed. 1992, 42, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanokami, M.; Wang, W.Q.; Yamamoto, M.; Hagiwara, T.; Yumoto, M.; Tomiyama, A.; Mine, S.; Tamura, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Nakazawa, Y.; et al. Utility of a GFP-expressing Barley yellow mosaic virus for analyzing disease resistance genes. Breed. Sci. 2021, 71, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaïanopoulos, C.; Bragard, C.; Moreau, V.; Maraite, H.; Legrève, A. Identification and Quantification of Polymyxa graminis f. sp. temperata and P. graminis f. sp. tepida on Barley and Wheat. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhne, T. Soil-borne viruses affecting cereals: Known for long but still a threat. Virus Res. 2009, 141, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordon, F.; Habekuss, A.; Kastirr, U.; Rabenstein, F.; Kühne, T. Virus resistance in cereals: Sources of resistance, genetics and breeding. J. Phytopathol. 2009, 157, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T.; Ban, T.; Iida, Y.; Yoshimi, R. Genetic analysis of disease resistance to all strains of BaYMV in a Chinese barley landrace, Mokusekko 3. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 94, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oozeki, M.; Sotome, T.; Haruyama, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Watanabe, H.; Okiyama, T.; Kato, T.; Takayama, T.; Oyama, M.; Nagamine, T. The two-row malting barley cultivar ‘New Sachiho Golden’with null lipoxygenase-1 improves flavor stability in beer and was developed by marker-assisted selection. Breed. Sci. 2017, 67, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taketa, S.; Kim, J.-S.; Takahashi, H.; Yajima, S.; Koshiishi, Y.; Sotome, T.; Kato, T.; Mochida, K. Genomic traces of Japanese malting barley breeding in two modern high-quality cultivars,‘Sukai Golden’and ‘Sachiho Golden’. Breed. Sci. 2023, 73, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishina, K.; Suzuki, T.; Oono, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Zhu, H.; Ogawa, T.; Ohta, M.; Doman, K.; Xu, W.; Takahashi, D.; et al. Wheat Ym2 originated from Aegilops sharonensis and confers resistance to soil-borne Wheat yellow mosaic virus infection to the roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2214968120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Mishina, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Tagiri, A.; Kikuchi, S.; Sassa, H.; Oono, Y.; Komatsuda, T. Organ-enriched gene expression during floral morphogenesis in wild barley. Plant J. 2023, 116, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Kondo, H.; Kuhne, T.; Shirako, Y. Barley Yellow Mosaic Virus VPg Is the Determinant Protein for Breaking eIF4E-Mediated Recessive Resistance in Barley Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascher, M.; Wicker, T.; Jenkins, J.; Plott, C.; Lux, T.; Koh, C.S.; Ens, J.; Gundlach, H.; Boston, L.B.; Tulpova, Z.; et al. Long-read sequence assembly: A technical evaluation in barley. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1888–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; Whitwham, A.; Keane, T.; McCarthy, S.A.; Davies, R.M. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. The Clustal Omega Multiple Alignment Package. In Multiple Sequence Alignment; Methods in Molecular Biology; Katoh, K., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Shirako, Y. Evaluation of host resistance to Barley yellow mosaic virus infection at the cellular and whole-plant levels. Plant Pathol. 2013, 62, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endelman, J.B. Ridge Regression and Other Kernels for Genomic Selection with R Package rrBLUP. Plant Genome 2011, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascher, M. Pseudomolecules and annotation of the third version of the reference genome sequence assembly of barley cv. Morex [Morex V3]. 2021, 3, 06466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Oyama, M.; Oozeki, M.; Sekiwa, T.; Sotome, T.; Kato, T. Evaluation of barley cultivars carrying rym1 to rym15 genes against Japanese BaYMV strains, and its utilization for resistant breeding. Bull. Tochigi Agr. Exp. Stn. 2018, 77, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ohki, T.; Sasaya, T.; Maoka, T. Cylindrical inclusion protein of wheat yellow mosaic virus is involved in differential infection of wheat cultivars. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hajimorad, M.R.; Eggenberger, A.L.; Tsang, S.; Whitham, S.A.; Hill, J.H. Cytoplasmic inclusion cistron of Soybean mosaic virus serves as a virulence determinant on Rsv3-genotype soybean and a symptom determinant. Virology 2009, 391, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, K.-H. Strain-specific cylindrical inclusion protein of Soybean mosaic virus elicits extreme resistance and a lethal systemic hypersensitive response in two resistant soybean cultivars. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, R. Chapter 9—Virus–Plant Interactions: RNA Silencing. In Plant Virology, 5th ed.; Hull, R., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 477–530. [Google Scholar]
- Charron, C.; Nicolai, M.; Gallois, J.L.; Robaglia, C.; Moury, B.; Palloix, A.; Caranta, C. Natural variation and functional analyses provide evidence for co-evolution between plant eIF4E and potyviral VPg. Plant J. 2008, 54, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Laliberte, J.F. The genome-linked protein VPg of plant viruses-a protein with many partners. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shirako, Y. Association of VPg and eIF4E in the host tropism at the cellular level of Barley yellow mosaic virus and Wheat yellow mosaic virus in the genus Bymovirus. Virology 2015, 476, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, J.; Kong, D.; Tang, X.; Wen, M.; Wang, G.; Dai, K.; Shi, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Resistance of QYm.nau-2D to wheat yellow mosaic virus was derived from an alien introgression into common wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2023, 136, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Okiyama, T.; Mishina, K.; Kikuchi, S.; Sassa, H.; Komatsuda, T.; Kato, T.; Oono, Y. Identification of Barley yellow mosaic virus Isolates Breaking rym3 Resistance in Japan. Genes 2024, 15, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060697
Zhu H, Okiyama T, Mishina K, Kikuchi S, Sassa H, Komatsuda T, Kato T, Oono Y. Identification of Barley yellow mosaic virus Isolates Breaking rym3 Resistance in Japan. Genes. 2024; 15(6):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060697
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Hongjing, Takeshi Okiyama, Kohei Mishina, Shinji Kikuchi, Hidenori Sassa, Takao Komatsuda, Tsuneo Kato, and Youko Oono. 2024. "Identification of Barley yellow mosaic virus Isolates Breaking rym3 Resistance in Japan" Genes 15, no. 6: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060697
APA StyleZhu, H., Okiyama, T., Mishina, K., Kikuchi, S., Sassa, H., Komatsuda, T., Kato, T., & Oono, Y. (2024). Identification of Barley yellow mosaic virus Isolates Breaking rym3 Resistance in Japan. Genes, 15(6), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060697





