Identification of a Novel Frameshift Variant in MYF5 Leading to External Ophthalmoplegia with Rib and Vertebral Anomalies
Abstract
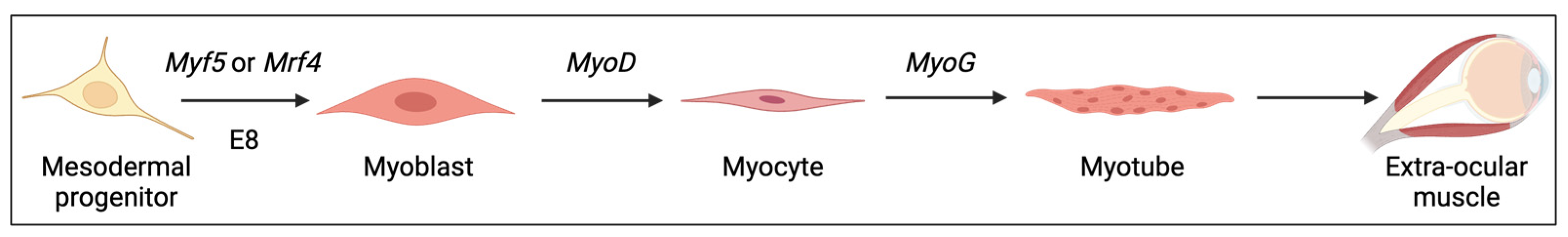
:1. Introduction
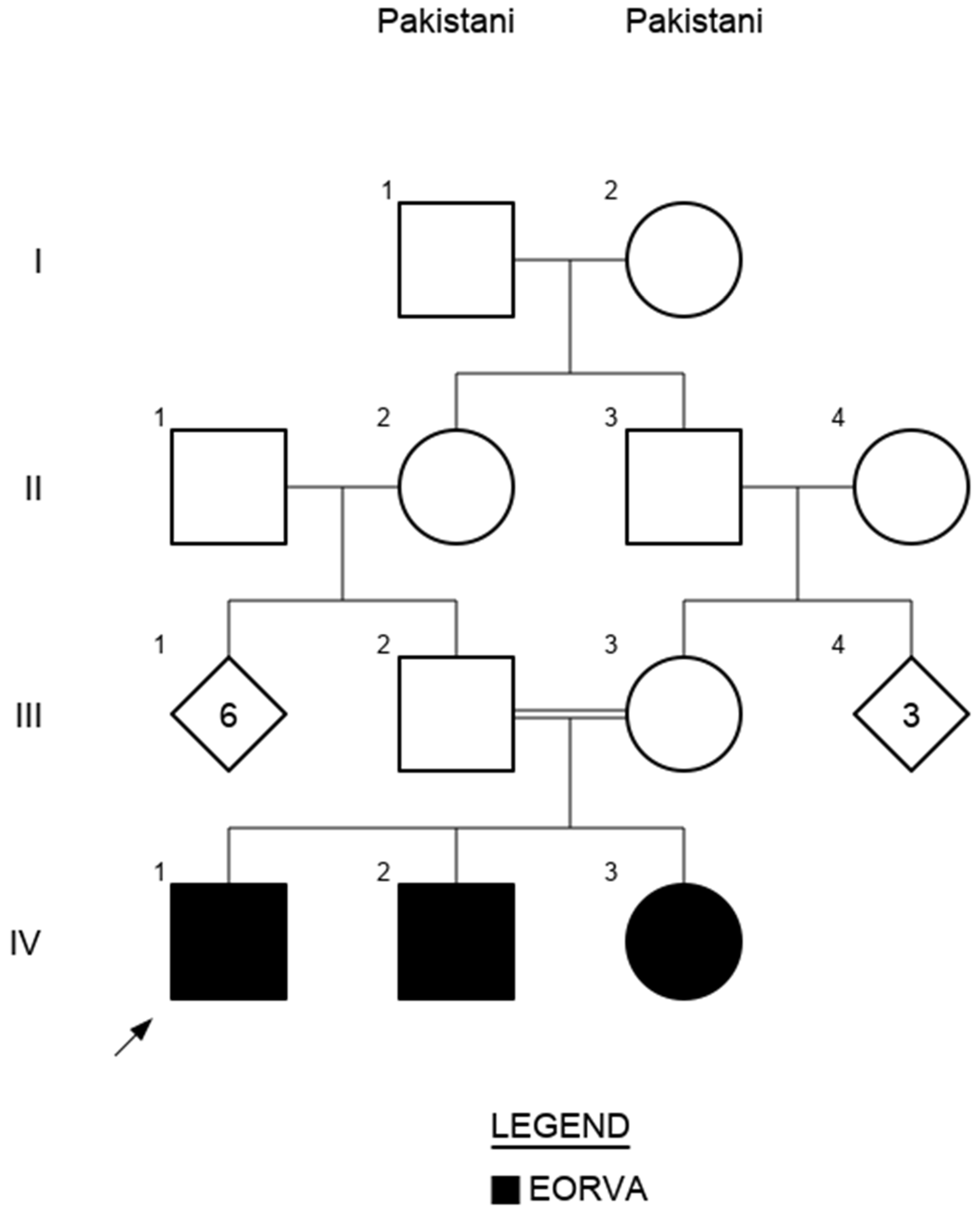
2. Case Description
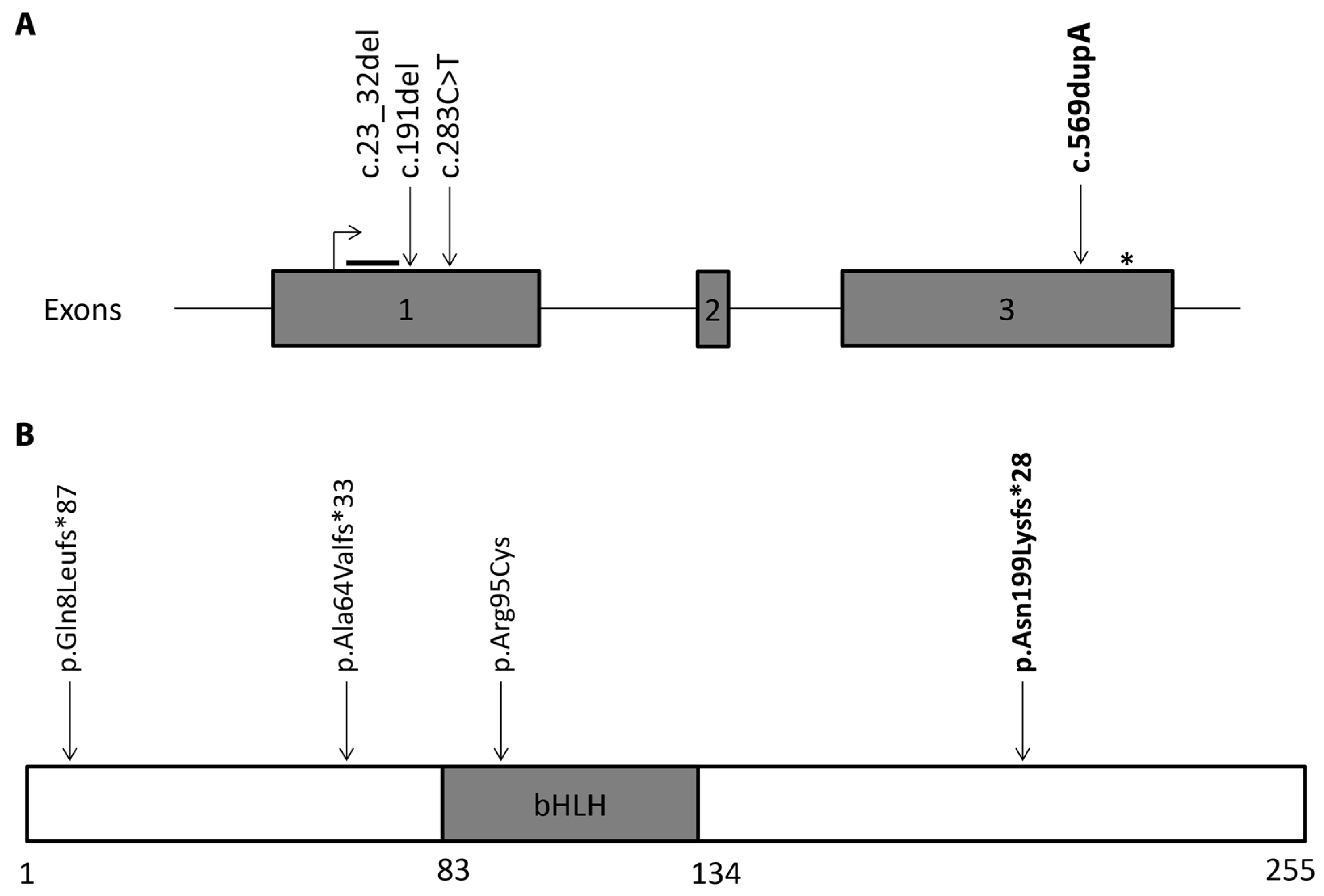
3. Genetic Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Francetic, T.; Li, Q. Skeletal myogenesis and Myf5 activation. Transcription 2011, 2, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.D.; Baker, R.S. Muscles of a different “color”: The unusual properties of the extraocular muscles may predispose or protect them in neurogenic and myogenic disease. Neurology 1996, 46, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Fitzpatrick, K.R.; McLoon, L.K. Extraocular Muscle Repair and Regeneration. Curr. Ophthalmol. Rep. 2017, 5, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellgren, D.; Thornell, L.-E.; Andersen, J.; Pedrosa-Domellöf, F. Myosin Heavy Chain Isoforms in Human Extraocular Muscles. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.D.; Gorospe, J.R.; Felder, E.; Bogdanovich, S.; Pedrosa-Domellöf, F.; Ahima, R.S.; Rubinstein, N.A.; Hoffman, E.P.; Khurana, T.S. Expression profiling reveals metabolic and structural components of extraocular muscles. Physiol. Genomics 2002, 9, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Hernández, J.M.; García-González, E.G.; Brun, C.E.; Rudnicki, M.A. The myogenic regulatory factors, determinants of muscle development, cell identity and regeneration. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, M.A.; Schnegelsberg, P.N.J.; Stead, R.H.; Braun, T.; Arnold, H.-H.; Jaenisch, R. MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell 1993, 75, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassoon, D.; Lyons, G.E.; Wright, W.E.; Lin, V.; Lassar, A.B.; Weintraub, H.; Buckingham, M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoDl during mouse embryogenesis. Nature 1989, 341, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinterberger, T.J.; Sassoon, D.A.; Rhodes, S.J.; Konieczny, S.F. Expression of the muscle regulatory factor MRF4 during somite and skeletal myofiber development. Dev. Biol. 1991, 147, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montarras, D.; Chelly, J.; Bober, E.; Arnold, H.; O Ott, M.; Gros, F.; Pinset, C. Developmental patterns in the expression of Myf5, MyoD, myogenin, and MRF4 during myogenesis. New Biol. 1991, 3, 592–600. [Google Scholar]
- Ott, M.O.; Bober, E.; Lyons, G.; Arnold, H.; Buckingham, M. Early expression of the myogenic regulatory gene, myf-5, in precursor cells of skeletal muscle in the mouse embryo. Development 1991, 111, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambasivan, R.; Gayraud-Morel, B.; Dumas, G.; Cimper, C.; Paisant, S.; Kelly, R.G.; Tajbakhsh, S. Distinct Regulatory Cascades Govern Extraocular and Pharyngeal Arch Muscle Progenitor Cell Fates. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassar-Duchossoy, L.; Gayraud-Morel, B.; Gomès, D.; Rocancourt, D.; Buckingham, M.; Shinin, V.; Tajbakhsh, S. Mrf4 determines skeletal muscle identity in Myf5:Myod double-mutant mice. Nature 2004, 431, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallquist, M.D.; Weismann, K.E.; Hellstrom, M.; Soriano, P. Early myotome specification regulates PDGFA expression and axial skeleton development. Development 2000, 127, 5059–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Arnold, H.-H.; Jaenisch, R. Targeted inactivation of the muscle regulatory gene Myf-5 results in abnormal rib development and perinatal death. Cell 1992, 71, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.; Gautel, M. Transcriptional mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle differentiation, growth and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.K.; Olson, E.N.; Arnold, H.-H.; Wold, B.J. DifferentMRF4Knockout Alleles Differentially Disrupt Myf-5 Expression:cis-Regulatory Interactions at theMRF4/Myf-5Locus. Dev. Biol. 1997, 188, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, E.N.; Arnold, H.-H.; Rigby, P.W.J.; Wold, B.J. Know Your Neighbors: Three Phenotypes in Null Mutants of the Myogenic bHLH Gene MRF4. Cell 1996, 85, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Schnegelsberg, P.N.J.; Dausman, J.; Jaenisch, R. Functional redundancy of the muscle-specific transcription factors Myf5 and myogenin. Nature 1996, 379, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, S.A.; Shaaban, S.; Tüysüz, B.; Elcioglu, N.H.; Chan, W.-M.; Robson, C.D.; Ecklund, K.; Gilette, N.M.; Hamzaoglu, A.; Tayfun, G.A.; et al. Recessive MYF5 Mutations Cause External Ophthalmoplegia, Rib, and Vertebral Anomalies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, C.; Scott, R.H.; Thomas, E.; Jones, L.; Murugaesu, N.; Pretty, F.B.; Halai, D.; Baple, E.; Craig, C.; Hamblin, A.; et al. The 100,000 Genomes Project: Bringing whole genome sequencing to the NHS. BMJ 2018, 361, k1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, E.R.; Tailor, V.K.; Chan, H.W.; Theodorou, M.; Webster, A.R.; Moosajee, M. Novel Biallelic Variants and Phenotypic Features in Patients with SLC38A8-Related Foveal Hypoplasia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Yu, C.; Shang, L.; Li, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Meng, J.; Kong, X. Case Report: A Novel Homozygous Mutation in MYF5 Due to Paternal Uniparental Isodisomy of Chromosome 12 in a Case of External Ophthalmoplegia with Rib and Vertebral Anomalies. Front. Genet. 2022, 12, 780363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traboulsi, E.I.; Lee, B.A.; Mousawi, A.; Khamis, A.R.; Engle, E.C. Evidence of genetic heterogeneity in autosomal recessive congenital fibrosis of the extraocular muscles11Genetic study was performed in the Division of Genetics, Children’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 129, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeboom, R.G.H.; Supek, F.; Lehner, B. The rules and impact of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human cancers. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosaki, T.; Maquat, L.E. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in humans at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, jcs.181008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Stolte, D.; Kurz, H.; Ehehalt, F.; Cann, G.M.; E Stockdale, F.; Patel, K.; Christ, B. Ventral axial organs regulate expression of myotomal Fgf-8 that influences rib development. Dev. Biol. 2003, 255, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinagre, T.; Moncaut, N.; Carapuço, M.; Nóvoa, A.; Bom, J.; Mallo, M. Evidence for a Myotomal HOX/Myf Cascade Governing Nonautonomous Control of Rib Specification within Global Vertebral Domains. Dev. Cell 2010, 18, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, P. The PDGFα receptor is required for neural crest cell development and for normal patterning of the somites. Development 1997, 124, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Bober, E.; Winter, B.; Rosenthal, N.; Arnold, H.H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: Evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patapoutian, A.; Miner, J.H.; Lyons, G.E.; Wold, B. Isolated sequences from the linked Myf-5 and MRF4 genes drive distinct patterns of muscle-specific expression in transgenic mice. Development 1993, 118, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal, J.J.; Cox, D.; Summerbell, D.; Rigby, P.W. A BAC transgenic analysis of the Mrf4/Myf5 locus reveals interdigitated elements that control activation and maintenance of gene expression during muscle development. Development 2001, 128, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Behringer, R.R.; Olson, E.N. Inactivation of the myogenic bHLH gene MRF4 results in up-regulation of myogenin and rib anomalies. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patapoutian, A.; Yoon, J.K.; Miner, J.H.; Wang, S.; Stark, K.; Wold, B. Disruption of the mouse MRF4 gene identifies multiple waves of myogenesis in the myotome. Development 1995, 121, 3347–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Condition | CFEOM | EORVA |
| Pathophysiology | Cranial innervation disorder | Muscle disorder |
| Ocular features | Non-progressive ophthalmoplegia +/− ptosis | Non-progressive ophthalmoplegia +/− ptosis |
| Extra-ocular features | Neurodevelopmental anomalies Brain anomalies Limb anomalies | Rib defects Vertebral defects Scoliosis Torticollis |
| Inheritance | Autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant | Autosomal recessive |
| Causative genes | COL25A1; KIF21A2; PHOX2A; TUBA1A; TUBB2B; TUBB3 | MYF5 |
| ID | Age at Presentation | Age at Last Exam | BC-RVA | BC-LVA | Refractive Error | Strabismus | Torticollis | Ocular Motility | Ptosis | Anterior Segment | Posterior Segment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
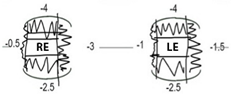
| Pt IV-1 | 6M | 8Y | 0.00 | 0.30 | R: +1.00/−0.50 × 180 L: +1.75/−1.75 × 180 | Constant LXT | Chin elevation | B/L marked r/o elevation B/L small r/o depression R minimal r/o abduction R moderate r/o adduction L minimal r/o adduction L small r/o abduction | Mild B/L | Normal | Normal |
| Pt IV-2 | 23M | 7Y | 0.00 | 0.08 | R: +1.50DS L: +0.75DS | Constant R/AXT | Nil | B/L moderate r/o elevation B/L minimal r/o adduction | Mild B/L | Normal | Normal |
| Pt IV-3 | 4M | 4Y | 0.24 | 0.24 | R: −1.50DS L: −0.50/−1.00 × 170 | Intermittent Distance LXT | Nil | B/L mild r/o elevation B/L slight r/o depression B/L full abduction and adduction | MildR | Normal | Normal |
| Pt IV-1 | Pt IV-2 | Pt IV-3 | |||||||||
 | 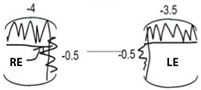 | 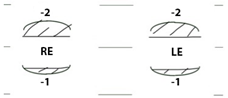 | |||||||||
| Reference | Homozygous MYF5 Variant | MYF5 Protein | Patient ID | External Ophthalmoplegia | Ptosis | Strabismus | Scoliosis | Torticollis | Ribs Anomalies | Vertebral Anomalies |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [20] | c.23_32del | p.Gln8Leufs*86 | I-1 | ✔ | ✔ R>L | XT++, HoT R+ | Cervical scoliosis | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| I-2 | ✔ | ✔ R>L | XT++ | ND | ✔ | ✔ | ND | |||
| I-3 | ✔—EOMs hypoplastic to absent | ✔ R>L | HoT++ | Cervical and thoracic scoliosis | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| [23] | c.191delC | p.Ala64Valfs*33 | II-1 | ND | ✔ | ND | ✔ | ND | ✔ | ✘ |
| [20,24] | c.283C>T | p.Arg95Cys | III-1 | ✔ | ✔ L | XT+++ HoT L+ | ND | possibly | ND | ND |
| III-2 | ✔ | ✘ | XT+ | Lumbar scoliosis | ND | ND | ND | |||
| This study | c.596dup | p.Asn199Lysfs*49 | IV-1 | ✔—EOMs L hypoplastic comparing to R | ✔ | XT L+ | Thoracic scoliosis | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| IV-2 | ✔ | ✔ | XT R+,HT R + | Thoracic and lumbar scoliosis | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ | |||
| IV-3 | ✔ | ✔ R | XT L+ HT L+ | Lumbar scoliosis | ✘ | ✘ | ✘ |
| Genotype Mice Model | Rib Cage Defects | Vertebrae Defects |
|---|---|---|
| Mrf4−/− [34] | Ribs not attached to the sternum Truncation of ribs Bifurcation and fusion of adjacent ribs Irregular sternum ossification | ND |
| Mrf4−/+Myf5−/+ [17] | Ribs not attached to the sternum Truncation of ribs: shorter vs wt/Mrf4-/-; longer vs. Myf5-/- Bifurcation and fusion of adjacent ribs Irregular sternum ossification | ND |
| Myf5−/− [15] | Absence of the distant parts of the ribs Complete ossification of the sternum Lethal immediately postnatally (inability to breath) | ND |
| Pdgfra−/− [29] | Ribs mostly attached to the sternum Bifurcation and fusion of adjacent ribs Irregular and shorter sternum | Structural anomalies of cervical and thoracic vertebrae Spina bifida Anomalies of spinal column curvature |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ocieczek, P.; Oluonye, N.; Méjécase, C.; Schiff, E.; Tailor, V.; Moosajee, M. Identification of a Novel Frameshift Variant in MYF5 Leading to External Ophthalmoplegia with Rib and Vertebral Anomalies. Genes 2024, 15, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060699
Ocieczek P, Oluonye N, Méjécase C, Schiff E, Tailor V, Moosajee M. Identification of a Novel Frameshift Variant in MYF5 Leading to External Ophthalmoplegia with Rib and Vertebral Anomalies. Genes. 2024; 15(6):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060699
Chicago/Turabian StyleOcieczek, Paulina, Ngozi Oluonye, Cécile Méjécase, Elena Schiff, Vijay Tailor, and Mariya Moosajee. 2024. "Identification of a Novel Frameshift Variant in MYF5 Leading to External Ophthalmoplegia with Rib and Vertebral Anomalies" Genes 15, no. 6: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060699
APA StyleOcieczek, P., Oluonye, N., Méjécase, C., Schiff, E., Tailor, V., & Moosajee, M. (2024). Identification of a Novel Frameshift Variant in MYF5 Leading to External Ophthalmoplegia with Rib and Vertebral Anomalies. Genes, 15(6), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060699







